Streptococcus bacteria are spherical, connected in chains and sensitive to environmental influences. Streptococci can stay in the human body for a long time without causing any alarming symptoms or diseases.
Various factors that contribute to a decrease in immunity can activate the growth of bacteria. Medicine identifies several types of streptococci, and the most dangerous is beta hemolytic streptococcus, which performs complete hemolysis of red blood cells.
Classification of streptococci
Streptococcus is divided into several types based on their hemolytic characteristics. Some of the most studied are alpha and beta hemolytic, which pose the greatest danger to the human body.
Alpha hemolytic streptococci
Alpha-hemolytic ones are also called “greening”, since during bacteriological examination they turn green. This type is low-virulent and lives in minimal quantities in the healthy microflora of the oral cavity. With a decrease in immunity, it can cause the development of caries. The following bacteria belong to the alpha type:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae - causes meningitis, sinusitis, otitis media and pneumonia.
- Streptococcus thermophilus is a beneficial bacterium used in the preparation of various fermented milk products.
Alpha-hemolytic streptococci do not cause destruction of red blood cells. The presence of bacteria is determined by examining a smear from the throat, skin inflammation, urine and blood culture, and ultrasound.
Beta-hemolytic streptococci
Beta-hemolytic streptococci are a whole group that includes pathogenic bacteria that can completely destroy red blood cells. The most dangerous is group A beta hemolytic streptococcus, which causes various serious diseases. The beta type includes the following bacteria:
- Streptococcus pyogenes is serogroup A, which causes diseases such as tonsillitis, scarlet fever, tonsillitis, and pharyngitis. In rare cases, pneumonia, fasciitis, and rheumatism may develop.
- Streptococcus agalactiae - serogroup B can be found in 20% of people as part of the healthy microflora of the gastrointestinal tract and urogenital tract. The bacterium often causes serious illness in newborns and mothers.
When immunity decreases, beta bacteria begin to secrete streptolysin, leukocidin, erythrogenin and neurotoxin. These substances destroy blood cells, poison the body, suppress the immune system and consume healthy cells.
Methods of infection with beta-hemolytic streptococcus
The infection is transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse
Infection with beta hemolytic streptococcus is transmitted by various methods. One of the most common is infection from the outside, when infection occurs from a sick carrier:
- Airborne transmission involves the spread of infection through talking, coughing or sneezing. The bacteria spread through the air and are ingested by a healthy person.
- The everyday route is infection through dirty hands and personal belongings, where dried saliva of the patient may be present. Streptococcus bacteria are resistant to cold temperatures and high humidity.
- Sexual transmission involves the transmission of infections through unprotected sexual intercourse.
- The alimentary route is contamination with food products that have not undergone heat treatment: sandwiches, dairy products, cakes and pastries.
- from mother to child in utero or at birth.
There is another way of infection with hemolytic streptococcus - autoinfection.
Streptococci are often located on the human body without causing any pathologies, since their growth is restrained by local immunity.
If the immune system begins to work worse, bacteria penetrate the blood and spread to the internal organs. Infection by an autoinfected method is possible in the following cases:
- Dental treatment.
- Squeezing pimples and boils.
- Removal of adenoids and tonsils.
- Bronchitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis.
The beta hemolytic streptococcus located in the throat begins to actively divide, form chains and secrete toxic poisons.
Symptoms of streptococcal infection
The clinical picture of streptococcal infection is extensive and depends on the organ damage, the patient’s age and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Often, the incubation period is 3-7 days, after which the characteristic symptoms that accompany all streptococcal infections appear.
Fever occurs from the first days of infection
Fever occurs from the first days of infection. This is the body’s protective reaction to the activity of pathogens, and the most alarming signal in which it is necessary to consult a doctor. In patients with strong immunity, the temperature rises slightly, within 37-37.8; in children and the elderly, fever is accompanied by hyperthermia.
Intoxication of the body occurs as a result of the release of toxic poisons by bacteria. Symptoms include nausea, weakness, headache, drowsiness, decreased performance, pain in muscles and joints.
Local inflammation occurs due to the localization of a large colony of bacteria in a specific location. Swelling, suppuration, swelling and itching occur in the area.
Blood pressure during streptococcal infection is always reduced, which indicates unstable heart function.
Allergic reactions accompany streptococcal infections in 50% of cases. The skin rash is localized in various places and has the form of erythematous spots. The cause of this symptom is the destruction of surface capillaries and damage to epithelial cells.
Inflammatory processes in the throat occur due to the development of streptococci on the mucous membrane of the pharynx and tonsils. Symptoms include pain when swallowing, redness and swelling, and the formation of purulent plaque.
Tissue necrosis occurs during severe stages of infection. In the presence of group A beta hemolytic streptococcus, the symptoms are accompanied by an inflammatory focus under the skin, swelling, and pain on palpation.
Symptoms in children
In children, the clinical picture has pronounced symptoms, as the disease develops rapidly. Initially, the baby is worried about chills and malaise, then other symptoms appear. Signs of infection in children under 6 months:
- The child refuses to eat.
- Runny nose with copious greenish or yellow discharge.
- Tearfulness, irritability, restless sleep.
- Nausea and vomiting.
Enlarged lymph nodes in children are one of the signs of pathology
Children of preschool and school age experience drowsiness, loss of appetite, and enlarged lymph nodes.
The main symptoms include:
- Complaints of pain and sore throat.
- Headache and dizziness.
- Obsessive coughing.
- Heat.
Beta hemolytic streptococcus is especially dangerous in children, as it can cause diseases such as laryngitis, scarlet fever, rheumatoid arthritis, endocarditis, otitis media, tonsillitis, and vasculitis.
Treatment of hemolytic streptococcus
Therapy for streptococcal infections is carried out using antibacterial drugs, which can quickly eliminate the number of bacteria, reduce the risk of complications and prevent damage to other internal organs.
Penicillin group:
- Benzylpenicillin - injections are administered intramuscularly.
- Penicillin V - the course of treatment depends on the severity of the disease and the age of the patient.
- Flemoxin Solutab - taken 1 g in the morning and evening.
- Amoxiclav is prescribed for children in the form of a suspension, for adults injections or tablets.
Group of cephalosporins:
- Ceftazidime - intramuscular injections 2 times a day.
- Cefuroxime-axetine is prescribed intravenously or intramuscularly.
These groups of drugs are most effective against hemolytic streptococci. However, before prescribing a specific type of antibiotic, it is necessary to conduct a laboratory antibiogram, which will determine the sensitivity of the bacterium to a particular type of drug.
The duration of treatment is 7-10 days, depending on the severity of the disease. In combination with antibiotics, other drugs are prescribed that relieve characteristic symptoms:
- Solutions for gargling and rinsing the throat.
- Antiseptic absorbable tablets and lozenges.
- Antipyretic drugs.
- Vasoconstrictor nasal drops.
When diagnosing group A beta hemolytic streptococcus, treatment should only be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. Since it is necessary to monitor the restoration of intestinal microflora, monitor the strengthening of the immune system and the reduction of intoxication.
To increase the effectiveness of treatment, traditional medicine recipes are added to drug therapy. Teas with rose hips, cranberries and raspberry leaves will help reduce inflammation and increase immunity. For gargling, it is useful to use decoctions of string, oak and willow bark.
During treatment, patients are advised to remain in bed, avoid physical activity and maintain fluid balance to remove toxins from the body.
If your throat is affected, you should review the menu and exclude hot, cold and hard foods that will injure the inflamed mucous membrane.
Group A beta streptococcus, if left untreated, can cause complications such as liver and kidney abscesses, pneumonia, meningitis, sepsis and toxic shock. Such consequences often occur 7-27 days after the onset of infection and require hospitalization.
In order to avoid the development of streptococcal infection, it is necessary to strengthen the body's defenses, avoid contact with infected people, and promptly treat possible foci of infection: caries, boils, inflammation of the adenoids and tonsils.
Source: https://101parazit.com/mikroorganizmy/bakterii/streptokokk/beta-gemoliticheskij-streptokokk.html
Hemolytic streptococcus: causes, symptoms, treatment
Hemolytic streptococcus is a gram-positive bacterium with a specific shape. Belongs to the lactobacilli family. Often it simultaneously coexists with Staphylococcus aureus. The bacterium can infect the body of any person - both an adult and a small child.
Online consultation on the disease “Hemolytic streptococcus”.
Ask a question to the experts for free: Infectious disease specialist.
Classification
In medicine, streptococci are divided into three types:
- alpha-hemolytic streptococcus;
- gamma streptococcus;
- beta-hemolytic streptococcus group A-U.
The first type (alpha) is also called viridans streptococcus. It received this name because of its ability to color the blood environment green. This is due to the fact that the pathogenic microorganism produces incomplete hemolysis of red blood cells.
Alpha and gamma streptococci are considered less dangerous to health and life. Almost all known throat ailments are mainly provoked by beta-hemolytic streptococcus. It is extremely dangerous because in the process of its life it performs complete hemolysis of red blood cells (erythrocytes).
The incidence of bacterial throat diseases depends on the time of year, as well as the age of the patient. In children, the incidence of general morbidity is higher during the cold season. This is due to a decrease in local and general immunity.
The lowest coefficient is recorded in children in the first six months of life, and the highest in children from 6 to 14 years old. In adult patients, the incidence directly depends on the growth and “aggressiveness” of viral diseases in the autumn-winter period.
This is often due to the fact that it is during this period that people experience an exacerbation of pharyngitis, tonsillitis, and other throat pathologies already existing in the body.
Causes
Most often, the causative agent of streptococcal sore throat, pharyngitis, and pharyngotonsillitis is Streptococcus pyogenes.
In children, the main reason for the progression of the pathology is the primary infection of the body with bacteria or a weakening of the immune system as a result of previously suffered viral diseases.
In this case, bacteria that are localized on the mucous membrane of the throat begin to actively multiply and increase the number of their colonies.
Streptococcal sore throat
The main causes of infection activation in adults:
- bad habits - drinking alcohol and smoking;
- decreased immunity due to previous viral diseases;
- damage to the throat mucosa by foreign bodies.
Factors that increase the risk of progression of infectious pathologies of the throat:
- chemotherapy;
- long-term use of hormone-containing medications;
- heartburn;
- immunodeficiency states.
Group B hemolytic streptococcus is one of the bacteria localized in the genitals of the fair sex. The number of these microorganisms can increase several times during pregnancy.
The infection can also manifest itself in a newborn, since he was already infected with it while passing through the mother’s birth canal. In 50% of cases, if a mother has this bacterium, it will be passed on to her child. But children can also become infected at any age.
Most often, infection occurs through airborne droplets or household contact.
Symptoms
The latent period is usually only 1–4 days. The picture of the disease may differ slightly depending on the age of the patient. If this is a child, then the disease develops rapidly. First, chills and malaise appear, after which pronounced symptoms appear. A child under 6 months of age experiences the following symptoms:
- vomiting and nausea;
- crying, irritability;
- the baby is capricious;
- Discharge appears from the nose. Most often they are green or yellow;
- the child refuses to suckle the breast or eat other foods (complementary feeding, supplementary feeding).
An older child sleeps most of the time, he is lethargic, and his appetite decreases sharply. Lymph nodes may become enlarged.
The main complaints of older children:
- a sore throat;
- soreness;
- headache;
- coughing;
- temperature rise to high levels.
Upon visual examination of the throat, it can be noted that the tonsils are enlarged and hyperemic, and pustules or plaque have appeared.
As soon as purulent processes begin, the patient’s general well-being worsens - intoxication of the body increases.
If a patient's streptococcal pharyngitis progresses, a dry cough appears, which after a certain period of time becomes wet. If it is not cured in a timely manner, the disease will develop into tracheitis.
In adult patients, streptococcal tonsillitis is usually very severe. They show all the same signs that were mentioned above. But they are more pronounced. Exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis occurs more smoothly. Most often the patient is concerned about:
- low-grade fever;
- swelling of the throat;
- weakness;
- a sore throat;
- enlargement of the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes.
Complications
Complications are rare but do occur, especially in people with weak immune systems. All of them can be divided into two groups – early and late.
Early complications appear 4–7 days from the onset of infection progression. This group includes:
- sinusitis;
- otitis;
- pneumonia;
- bronchitis.
Late complications may manifest themselves 2–4 weeks after the patient’s apparent recovery. As a rule, they are directly related to non-compliance with therapy and lack of antibiotic therapy. This group includes:
- osteomyelitis;
- myocarditis;
- endocarditis;
- meningitis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- rheumatism.
Treatment
Streptococcal throat diseases can be cured only with the use of antibiotics. Correctly prescribed treatment is the key to a quick recovery of the patient, as well as to avoid the development of complications.
It is important to first diagnose the disease. Typically, BAK seeding is used for this purpose. A swab is taken from the patient’s throat and sown on a nutrient medium to identify the pathogen.
Until the results are obtained, the patient is prescribed broad-spectrum antimicrobial drugs.
Taking a throat swab
The duration of antibiotic therapy ranges from 7 to 10 days. If the disease is severe, then not tablet forms of these drugs are prescribed, but solutions and powders for intramuscular administration.
Preference is given to antibiotics from the penicillin group. If the patient is allergic to drugs from this group, preference is given to cephalosporins.
As scarlet fever progresses, macrolides are also added to the general course of therapy.
Treatment of streptococcal infection should also be aimed at eliminating the main symptoms of the pathology. For this purpose, the following drugs and procedures are prescribed:
- rinsing the throat and tonsils;
- drinking liquid (warm);
- vasoconstrictors;
- antipyretic drugs;
- resorption of antiseptic tablets.
ethnoscience
This infection can be treated at home, supplementing the prescribed drug therapy with folk recipes. They will help eliminate unpleasant symptoms of pathology, relieve inflammation and increase immunity:
- raspberry and rose hip leaves;
- willow bark and succession grass;
- propolis.
Source: https://SimptoMer.ru/bolezni/infektsii-parazity/1110-gemoliticheskij-streptokokk-simptomy
Hemolytic streptococcus: treatment of hemolyticus
Microorganisms that cause diseases can enter the human body under the influence of unfavorable factors.
Streptococci are the most common cause of infectious diseases. Quite often, as a result of the ingestion of these pathogenic organisms, a person develops upper respiratory tract diseases.
In addition, streptococci provoke the development of sore throat, pharyngitis, and along with them tonsillitis and scarlet fever.
Description of hemolytic streptococcus
Hemolytic streptococcus (streptococcus haemolyticus) belongs to the group of gram-positive pathogenic microorganisms . Experts classify it as a member of the lactobacilli family. A characteristic feature of these bacteria is their round shape. The process of their reproduction occurs in pairs. Or these microorganisms form colonies during their life activity.
When examining sick people, this bacterium is most often found on the mucous membrane of the nose, throat, as well as in the genitourinary organs, respiratory tract and large intestine. At first, an infected person does not experience any discomfort from the presence of bacteria.
In normal health, every person has a small amount of this bacterium. However, when a person’s immune system weakens or his body becomes hypothermic, this provokes an increase in the activity of these microorganisms.
Currently, experts identify several types of streptococci :
- alpha-hemolytic;
- beta-hemolytic;
- gamma hemolytic.
The greatest threat to human health is beta-hemolytic streptococcus. A characteristic feature of this type of bacteria is their high resistance to chemical attack.
They can exist under the influence of a temperature of 70 degrees for 2 hours.
These bacteria are resistant to low temperatures and can remain in dried blood or pus without losing their viability for a long period of time.
Reasons for appearance
In most cases, these bacteria enter the human body through the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract. Often a sick person is the main source of infection.
In addition, infection of a healthy person can occur if he uses personal belongings, as well as household items of a sick person.
People who communicate with a person suffering from pharyngitis or a sore throat are at risk of contracting the infection.
The bacterium streptococcus haemolyticus can be transmitted through unwashed or not fresh food. Hemolytic streptococcus can settle in dairy products, as well as in semi-finished meat products that have expired. The infection can also enter the body through scratches on the skin. It can also appear on the skin as a result of abrasions or an insect bite.
Sexual transmission is one of the ways of transmitting infection. A woman who carries it can infect her partner during sexual intercourse. Experts say there is a serious possibility of transmission of infection from mother to child.
If beta-hemolytic streptococcus enters the human body, this can lead to the following diseases :
- angina;
- otitis;
- pharyngitis;
- erysipelas;
- scarlet fever;
- meningitis.
Carrying out their vital functions in the human body, bacteria produce certain toxins, which, once in the bloodstream, become the main reason provoking the occurrence of specific symptoms.
Symptoms
When infected with hemolytic streptococcus, the latent period lasts about 4 days . Symptoms can vary and largely depend on the age of the patient. During the first days after infection, the patient complains of chills and malaise. Later, other symptoms are added to these symptoms.
Streptococcal infection that occurs in children under six months of age can manifest itself with symptoms such as vomiting and nausea. Yellow or green discharge appears from the nose. The baby becomes capricious and refuses breastfeeding and complementary foods.
Older children and adults may experience the following symptoms:
- sore and sore throat;
- coughing;
- temperature increase;
- enlarged tonsils;
- swelling of the throat.
The appearance of these symptoms indicates that a person has streptococcal tonsillitis. With the development of complications of the disease in the form of purulent processes, a sharp deterioration in the patient’s well-being occurs. There are signs indicating intoxication of the body.
With pharyngitis, the mucous membrane becomes swollen and the color changes to reddish. In addition, a runny nose appears, and the doctor may detect a grayish coating on the surface of the mucous membrane.
Scarlet fever is most often encountered by children aged 2 to 10 years. In most cases, this disease occurs only once. After the disease is cured, children develop a stable immunity to this disease.
High temperature is a characteristic symptom of scarlet fever. In addition, the patient may experience nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Small papules appear on the skin. The tongue becomes coated, and the skin becomes dry and changes its color to white.
In addition to this, the tonsils become inflamed.
Characteristic signs of erysipelas are skin lesions with a bright color and the appearance of a clear boundary. In addition to this, fever develops, chills, a state of weakness and muscle pain appear.
The development of osteomyelitis occurs in very rare cases. A characteristic feature of the disease is that the resulting inflammatory process during the course of the disease spreads to the bone marrow.
Against the background of hemolytic streptococcus, the development of sepsis is associated with the spread of infection throughout the body through the bloodstream. This pathology poses a great danger to human health, as it can be fatal.
Diagnostics
If you detect symptoms characteristic of sore throat, pharyngitis or other diseases caused by hemolytic streptococcus, you must immediately consult a doctor to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. In order to determine the cause of the disease, doctors usually prescribe urine and blood tests.
In order to determine the type of pathogen that caused the disease, a bacteriological study is prescribed. The material is taken from infectious foci - on the skin, tonsils, sputum.
He is sent for examination, and based on the results, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis. In order to determine the type of pathogen that caused the disease, a smear is also taken from the vagina, and mucus is collected from the urethra.
The collected material is placed in a nutrient medium for a day, where it is kept at a temperature of 37 degrees. Next, a specialist uses a microscope to evaluate the results obtained and identify the colony of bacteria that have appeared.
If more pathogens were found than normal, then an antibiotic program is prescribed in order to determine how sensitive the bacteria that have entered the patient’s body are to drugs.
Using this method allows the doctor to determine a list of antibiotics that a sick person can take to prevent the growth of microorganisms. However, sensitivity testing lasts for several days. During this time, the infection will progress, and the patient’s condition will noticeably worsen.
In order to determine antibodies to the hemolytic streptococcus streptococcus haemolyticus in the blood, diagnostics are carried out, thanks to which their quantity can be determined. Express methods for diagnosing streptococcal infections are gluten reaction, latex agglutination and enzyme immunoassay .
Drug treatment of infection
Treatment of diseases caused by streptococcus haemolyticus involves the use of drugs that have an antibacterial effect.
, penicillin antibiotics are mainly prescribed . Doctors make a choice in their favor, since bacteria do not demonstrate high resistance to the components contained in these drugs. Such drugs include Ampicillin, Benzylpenicillin , as well as Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav .
If a patient experiences an allergic reaction during treatment with the above drugs, then in this case a number of erythromycin drugs are used: Erythromycin, Oleandomycin and others.
When treating diseases caused by streptococcus streptococcus haemolyticus, tetracyclines are not used. They only relieve the symptoms of the disease, while the person continues to be a spreader of the infection. The duration of treatment with antibiotics should not exceed 10 days.
Even if after 3 days of taking the drug the condition has improved, then in this case you should not stop the course of therapy. It needs to be completed.
If you stop taking medications ahead of time, this can lead to a relapse or provoke possible complications.
To treat the throat, topical medications are used. Doctors prescribe antiseptic sprays, as well as solutions intended for rinsing. Most often prescribed are Bioparox, Hexoral, Chlorhexidine and others.
Bioparox has a wide spectrum of action. This drug is used in the form of inhalations and has a strong antimicrobial effect. It must be used as soon as the first symptoms are detected.
To relieve the symptoms of a sore throat, you can use alcohol tinctures of calendula or chamomile . These compositions have strong antiseptic properties. Medicines can be purchased at a pharmacy or prepared at home. They are used as an adjunct to primary therapy.
After completing the use of antibiotics, it is necessary to take a course of probiotics. This is necessary for this. To normalize the intestinal microflora. You need to take the following medications: Bactisubtil, Linex, Bifiform and others.
In severe cases of the disease, streptococcal bacteriophage is prescribed. This virus is created artificially with the sole purpose of destroying streptococci that have settled in the body.
Prevention measures
In order to completely prevent streptococcal infection from entering the body, it is necessary to adhere to certain rules of personal hygiene.
If we talk about preventive measures against streptococcus, the main ones include the following:
- it is necessary to regularly clean the premises, carry out wet cleaning and do not forget to ventilate the room;
- periodically carry out procedures aimed at hardening the body;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- fight bad habits;
- promptly treat the skin with antiseptics;
- nutrition should be complete and balanced in terms of vitamins and microelements;
- during periods during which the incidence of respiratory infections peaks, it is recommended to wear a special mask to avoid them, and in addition to treat dishes and other surfaces where microorganisms could get in, using special compounds;
If a person follows all preventive measures, the risk of infection with streptococcus is significantly reduced.
Conclusion
Streptococci are a pathogenic microorganism, the entry of which into the body leads to human infection and the occurrence of various ailments.
When the first symptoms of a painful condition appear, you should not self-medicate, but rather consult a doctor.
The specialist will conduct an examination and prescribe a series of tests, the results of which will allow you to accurately diagnose and prescribe appropriate treatment.
It should be noted that streptococci are a pathogen that causes many diseases. Most often it is the cause of scarlet fever, meningitis, as well as tonsillitis and other ailments.
A wide range of medications are prescribed to eliminate the symptoms of the disease.
Many of the medications that are intended to treat diseases caused by streptococci quite quickly relieve the symptoms of the disease.
However, despite this, you should not stop taking medications. If you do not complete the course of therapy, then after some time a relapse of the disease may occur. In order to completely cure the disease and not have to deal with it again, it is necessary to carry out treatment in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations.
Source: https://lechim-gorlo.ru/zabolevaniya/gemoliticheskiy-streptokokk-lechenie-gemolitikusa
Causes and symptoms of development, tests and examinations of beta-hemolytic streptococcus in children and adults
The streptococci in question, when breeding colonies, destroy blood cells due to the released chemicals. In this regard, the term hemolysis is used. Since this type of bacteria destroys cells in a special way, it is called beta-hemolytic. This streptococcus completely destroys red blood cells. This is its main difference from other microbes of this genus.
There is another important term - pyogenes, which refers to a type of spherical gram-positive bacteria. The pyogenic microbe causes purulent inflammation in the human body.
The presented variety of streptococcus can get on the mucous membranes of the throat of both children and adults.
In this case, bacteria can be destroyed by a well-functioning immune system or spread quickly, causing various throat diseases and other infectious and inflammatory disorders in the upper respiratory tract.
As a rule, streptococcal infections are easily treated with antibiotics, but sometimes the disease can become chronic.
Most often, this type of microbe, belonging to group A, either does not provoke any diseases or leads to sore throat. Basically, the person recovers without any negative consequences or complications. But sometimes this infection carries a serious danger.
In some cases, the disease caused by beta-hemolytic streptococcus can spread to other areas. For example, when a sore throat develops, the infection can affect the ears and paranasal sinuses. The appearance of abscesses in the throat is also possible.
Diseases caused by this type of microbe should be treated promptly and appropriately. For this, antibiotics are used, and in some cases surgery may be prescribed. Such diseases are easy to treat and, if everything is done correctly, no complications will arise.
In addition to throat diseases, beta-hemolytic streptococcus can provoke other serious and severe diseases. They are not discussed in this article, since it is entirely devoted to diseases associated with the throat.
Beta-hemolytic bacteria can cause serious complications in these organs. In adolescence and in adults, such consequences remain extremely rare. The same applies to those who are carriers of this type of streptococcus.
Most often, complications are recorded in recently infected children. At the same time, they developed a sore throat and symptoms similar to a cold.
Negative consequences are caused by the production of antibodies that fight not only the disease itself, but also affect healthy human organs. This action of the body leads after some time to inflammation of the joints and heart in children.
Accordingly, the first complication does not pose a serious threat, the second can lead to severe disruptions in the functioning of the organ, and sometimes to death.
- 1 The child began to notice pain, redness and swelling in large joints;
- 2 There is a loss of strength and heavy breathing after minor physical activity;
- 3 Pain appeared in the chest near the heart;
- 4 Small knots formed under the skin.
- If signs of complications are detected, you should consult a doctor.
Another severe effect on the body of group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus is acute glomerulonephritis. It occurs in some children who become ill due to this bacterium.
In this case, antibodies are also the culprits. They are produced to fight streptococcus, but when combined with them they harm the body, affecting the kidney tissue, which ultimately leads to inflammation of the kidneys.
Such exposure often leads to disruption of organ functioning.
- Complications on the kidneys can be identified if, after a certain period of time after a sore throat, the following symptoms appear:
- 1 There is swelling in any part of the body or near the eyes;
- 3 Weakness appeared and the temperature increased.
- If the described symptoms are observed, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Among children who become ill from group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus and have complications, in rare cases, disorders in the psyche and musculoskeletal system are observed.
This is because the infection sometimes affects certain centers of the brain that control speech, emotions and movement. This condition is called PANDAS syndrome. Most children suffering from this complication recover.
This often takes months. For others, the disorders have been observed for a long time.
- 1 The child’s views on food have changed for unknown reasons - he began to eat a lot or stopped eating altogether;
- 2 Tearfulness or aggression appears for no apparent reason;
- 3 Academic performance has decreased;
- 4 Involuntary urination at night;
- 5 Strange abnormal movements appeared.
- In this case, medical assistance is also necessary.
Methods of infection with beta-hemolytic streptococcus, where does it come from?
The microbe is transmitted from an infected patient or carrier to a healthy person. It has been scientifically confirmed that every 5th child infected with this type of streptococcus is a carrier of the infection.
Infection occurs when a person with a sore throat coughs or sneezes. Such people are more contagious than carriers of streptococcus.
A healthy person becomes infected when particles of a sick person's saliva enter the body through the mouth, nose or eyes. Transmission of infection occurs through dishes or food. Cases of infection through food are very rare.
It is impossible to get the infection from pets, since they are not its carriers.
Most often, diseases spread strongly in all seasons except summer. This is often associated with attending school, when many children gather in one room and the risk of streptococcus transmission increases.
How long is the incubation period of beta-hemolytic streptococcus?
The infection first manifests itself after entering the body no earlier than 2 and no later than 5 days. You can become infected from such a person at the same time that symptoms appear. Infectivity remains for a long time if antibiotic treatment is not started promptly. After taking these drugs, a person ceases to be infectious within a day.
Symptoms of infection development (beta-hemolytic streptococcus)
There are often no symptoms of beta-hemolytic streptococcus. But it happens that the infection manifests itself as a sore throat, which is accompanied by high fever, purulent plaque on the tonsils, and enlarged lymph nodes in the neck.
In some cases, red spots appear in the throat, the tongue turns red and the stomach hurts.
It should be noted that this condition occurs not only with sore throat, which is caused by beta-hemolytic streptococcus, but also by other pathogens.
If, with a sore throat, a dark reddish rash forms on the skin, then in this case we are talking about scarlet fever. Rashes with this disease may not always occur or occur after some time.
With streptococcal infection, children under 3 years of age may not have a sore throat or plaque on their tonsils. At this age, infection is characterized by fever and nasal congestion.
Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus is almost impossible to distinguish from other types of infection. This is explained by the fact that no special symptoms occur when these bacteria are present in the body. To determine this streptococcus, appropriate studies are prescribed.
Tests and diagnostics, examinations to detect streptococcus
All people with a sore throat should be tested for streptococcal infection. Some patients may be at risk for complications, and beta-hemolytic streptococcus often does not exhibit symptoms specific to it. Experts recommend undergoing a study to prescribe subsequent treatment.
Depending on the age, time of year when the person fell ill, the presence of a rash and possible contacts with sick people, the likelihood of developing a sore throat due to the type of streptococcus in question is determined. Therefore, it is important to undergo certain tests to determine whether there is an infection in the body.
Research on beta-hemolytic streptococcus is not necessary if the child has already reached the age of three and has symptoms of a viral infection, or if the child is younger; in such children it is extremely rare that the microbe can cause complications in various organs.
Description of the test to detect streptococcus
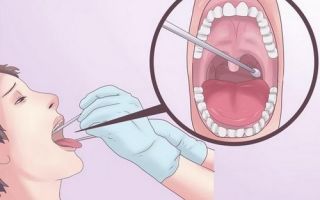
For analysis you need a special swab. The doctor runs it along the mucous membrane of the throat to collect the necessary material. Such actions often cause discomfort. This is explained by the appearance of a gag reflex when touching the back of the throat.
The presence of beta-hemolytic streptococcus is checked by reacting the resulting material in a special solution. To conduct the test, the swab is immersed in a special chemical in a test system. You can find out about the results of the analysis no later than in 40 minutes.
Explanation of beta-hemolytic streptococcus test results
If the result is positive, we can say that the person has a streptococcal infection. Otherwise, there is no infection. More accurate results can be obtained by sowing. It is prescribed if there is a suspicion that the first test has given a false answer, to confirm the diagnosis. If group A streptococcus was not detected during culture, then the person is not infected with it.
Do relatives of a patient with streptococcus need to be tested?
Testing is usually not required if relatives of the affected person do not have any symptoms of beta-hemolytic streptococcus.
If you suspect that the infection occurred from one of the family members, it is advisable for all of them to undergo a test for beta-hemolytic streptococcus. Doctors also recommend that children who may have been infected and are at risk of complications be tested.
Sometimes an infection is discovered after it, although there were no symptoms, so the necessary treatment is prescribed.
The smear is more effective in detecting beta-hemolytic streptococcus from the first days. A blood test for antibodies to streptococcus can show their presence only after a certain time after infection. It should not be carried out in the early stages of infection. The feasibility of this study is confirmed after several weeks of the disease.
Treating a throat infection (beta-hemolytic streptococcus)
It is necessary to treat throat diseases, which, according to test results, were provoked by beta-hemolytic streptococcus. Treatment is with antibiotics.
It is necessary to use drugs as soon as possible after identifying the disease. This has a positive effect and prevents complications associated with joints, heart and kidneys. But with the latter organs, things are a little different. Even with proper treatment, kidney damage can occur if it is started more than a week after the onset of the disease.
- Antibiotics are also indicated for people who have been in contact with patients and belong to one of the following groups:
- 1 Elderly people;
- 2 Patients with diabetes mellitus;
- 3 People with weakened immune systems.
Penicillins and cephalosporins are the main types of antibiotics that are used in the treatment of diseases caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus. They have shown high effectiveness in fighting infection.
The medicine is available in the form of tablets and injections. The antibiotic injection is very painful and is used when the child does not take the pills. The drug is administered intramuscularly once.
Amoxicillin should be taken three times a day for at least 1.5 weeks. The course of treatment is determined by the doctor and if relief occurs before completion, therapy cannot be stopped. The medicine should be taken as much as was prescribed for at least 10 days in a row. This is a necessary condition for preventing undesirable consequences of the disease.
If a person is allergic to the above antibiotics, then the use of macrolides is allowed. But this group of drugs is not always effective enough against streptococcus.
You can determine whether the treatment has worked by reducing the temperature and improving the patient’s condition after a couple of days. Otherwise, treatment is defined as ineffective.
- Such situations have no explanation due to the lack of relevant research and arise due to:
- 1 Incorrect treatment;
- 2 Streptococcus resistant to the drug;
- 3 The sore throat was not due to beta-hemolytic streptococcus, but due to other pathogens.
When treatment does not produce results within 48 hours, you need to consult a doctor. The doctor may change the dosage of the drug or prescribe a medicine that belongs to a different group of antibiotics.
What to do if after treatment the sore throat appears again?
Often, the appearance of sore throat is again provoked by other pathogens. But re-infection with streptococcus is quite likely. Therefore, if symptoms of the disease appear, you should consult a doctor.
Factors that provoke the development of beta-hemolytic streptococcus are determined by the doctor during the examination and based on test results. If the disease caused by beta-hemolytic streptococcus recurs, then it is necessary to undergo treatment again.
It is also possible that the doctor will recommend that family members undergo tests to identify the carrier of the infection, from whom the infection occurs not for the first time.
Carriers of streptococcus need treatment if they pose a threat of transmitting the infection to people around them. Therapy is prescribed despite the absence of any symptoms. In the treatment of beta-hemolytic streptococcus, already known antibiotics are used.
Repeated smear after completion of treatment for streptococcus
- Experts recommend getting tested a second time after treatment has ended in the following cases:
- 1 After a treatment course, a person is still bothered by the manifestations of a throat disease;
- 2 The child is predisposed to complications related to joints.
- If streptococcus is detected after completion of treatment, antibiotics are prescribed again.
All people who had contact with sick people and who became ill after that should undergo appropriate testing. If the presence of beta-hemolytic streptococcus is confirmed, treatment is prescribed.
Family members are at greatest risk of getting sick. Most people who become infected become ill and require treatment.
Rheumatic fever due to streptococcal infection
Rheumatic fever affects connective tissues and is a complication of throat diseases caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus.
Genetically predisposed people most often suffer from rheumatic fever at the age of 7-20 years. It all starts with the fact that streptococcal infection affects the heart, triggering an autoimmune process.
Rheumatic fever can last from 6 to 12 weeks, and begins 2-3 weeks after the infection.
For rheumatic fever, especially if it does not happen for the first time, a long course of treatment with antibiotics is prescribed. This is necessary to prevent recurrence of complications in the joints and heart.
Rheumatic fever affects the heart, which is manifested by stabbing and aching pain in its area. The pain is especially felt with minor physical exertion.
As a result of carditis, some people develop a heart defect. If the organ was not severely affected, then long-term treatment with antibiotics is prescribed for 5 years or until the patient turns 21 years old.
For significant heart damage, medications must be taken for life.
If treatment is started early, success can be achieved. It is important to seek help from a doctor in time (as soon as signs are noticed). Rheumatic fever requires hospital treatment. If carditis is suspected, the patient must remain in bed.
Prevention of rheumatic fever
- To prevent this complication, you must:
- 1 Carry out activities to increase the body’s immune forces;
- 2 Apply preventive measures against streptococcal infections;
- 3 Promptly identify and treat diseases associated with beta-hemolytic streptococcus.
- To prevent relapses and complications, clinical observation and treatment of chronic infections are carried out.
Source: http://vevolife.ru/prichiny-i-simptomy-razvitiya-analizy-i-obsledovaniya-beta-gemoliticheskogo-streptokokka-u-detej-i-vzroslyx.html