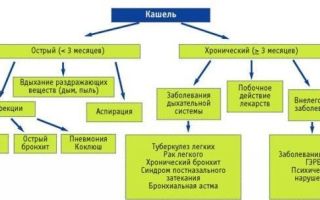
Coughing attacks are a symptom characteristic of many diseases. Different types of cough in children and adults can accompany different pathologies and require a special approach to treatment, so determining the specifics of this symptom plays an important role in recovery.
Varieties of symptoms
Coughing in children and adults can be both physiological and pathological. Physiological coughing is normal at any age: this process is necessary to regularly clear the respiratory tract of sputum particles and minor contaminants.
Pathological cough attacks are associated with the development of the disease. The presence or absence of sputum is of greatest importance in making a diagnosis and determining an appropriate treatment regimen.
If it separates, then we are talking about a wet (productive cough); if not, it is a dry (non-productive) cough.
Some experts also distinguish a low-productive type, in which coughing occurs with difficulty, and sputum is expectorated in small quantities.
According to the etiology of occurrence
When answering the question of what a cough is, experts point out that it is necessary to determine the type of this symptom based on the causes of coughing attacks.
Based on etiology, infectious and non-infectious types of cough are distinguished. Infectious is divided into viral and bacterial. If a child suffers from a cough, then most often the reason lies in the activation of viruses or bacteria.
In addition, cough attacks in children can be of a non-infectious nature, for example, allergic. This symptom also occurs when a foreign body enters the respiratory tract.
In adults, phenomena such as “smoker’s cough” and “heart cough” are often observed, the causes of which are also attributed to non-infectious factors.
By duration
When treating cough, it is necessary to take into account the duration of the disease. The cough may be:
- Spicy. This type is most typical for respiratory diseases. The duration of the course is up to 3 weeks.
- Lingering. If it lasts more than 3 weeks and has a wave-like manifestation (it is absent, then it appears again, it can occur only at night or in a certain position of the body), then they speak of a protracted course of the pathology.
- Chronic. The cough becomes chronic if it lasts more than 3 months.
It is much easier to cure acute cough attacks than protracted and chronic ones, so the treatment regimen will vary depending on the type of cough.
Other classifications
In addition to the above-mentioned types of cough symptoms, there is the following classification of cough:
- by time of occurrence (morning, evening, night);
- by frequency of occurrence (constant, periodic);
- according to the rhythm (individual cough impulses, a series of impulses, paroxysmal);
- according to the nature of the attacks (barking, bitonal, hoarse, silent).
Experts identify several other forms of cough, depending on the conditions under which the symptom occurs or what phenomena it is accompanied by. Thus, some diseases are characterized by coughing attacks that occur when changing body position or associated with eating food, while others end with vomiting or the release of a large amount of sputum.
Methods of treating the disease
Cough is not an independent disease, but one of the signs accompanying the disease, therefore, in order to successfully get rid of cough attacks, it is necessary first of all to influence the source of their occurrence. Along with this, symptomatic treatment should be carried out.
A dry cough that accompanies respiratory diseases must be converted into a productive cough as quickly as possible. For this, expectorants are used.
As soon as the cough becomes wet, it is necessary to take mucolytics, which thin the mucus and accelerate its removal from the bronchi. If the cough is caused by a bacterial infection, the only way to get rid of it is with antibiotics.
For ARVI accompanied by coughing attacks, treatment should be carried out using antiviral drugs.
In some cases, for dry coughs, antitussive drugs are prescribed to suppress attacks, but they can be taken strictly as prescribed by a specialist. Indications for the use of such drugs are bronchial asthma, emphysema, bronchitis, bronchopneumonia and some other diseases.
If the cough is associated with an allergic reaction, you should be treated with antihistamines - Claritin, Zyrtec, Zodac. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe inhalations with bronchodilators (Pulmicort, Eufillin). For therapy to be effective, contact with the allergen should be avoided.
With the permission of a specialist, cough treatment can be carried out using folk remedies. It is recommended to use the following alternative medicine recipes:
- Mix in equal proportions dry crushed grass of plantain, chamomile flowers, linden flowers, coltsfoot. Take 1 tbsp. l. collection, pour 1 cup of boiling water, leave for 1 hour. Take the product 3 times a day, 2 tbsp. l.
- Add ½ tsp to a glass of boiled water cooled to room temperature. alcohol tincture of eucalyptus. Take in small portions several times a day.
- Place 1 fig in 200 ml of milk and cook for 20 minutes. Have a drink at night.
- Take a fresh black radish fruit, cut off the top, cut a hole in the flesh with a knife, without cutting through the vegetable. Place a few teaspoons of honey into the resulting cavity and wait for the juice to appear. Drink the resulting liquid 1 tsp. 3-4 times a day.
- To stop a severe coughing attack, you need to use burnt sugar. To do this, pour granulated sugar into a metal spoon and hold it over the fire until the grains dissolve and form a caramelized amber-colored mass. The resulting product must be absorbed until completely dissolved.
Treatment with folk remedies can only be used as an additional measure to relieve cough attacks. It is important to identify the cause of the cough and eliminate it. Only in this case can you effectively get rid of the symptom and avoid complications.
Source:
Types of cough, classification and treatment in children and adults
- Any irritation of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, both in children and adults, entails a cough.
- This process is not only a sign of the disease, but also a way to cleanse the bronchi from sputum or foreign bodies accumulated in them.
- In order to find out whether a cough is a symptom of a child’s illness, you need to familiarize yourself with what types of cough there are and what causes their occurrence
When to worry
It is worth remembering that the body of a child and an adult produces a small amount of sputum every day, and coughing it up is a natural process. However, you should be concerned if:
- cough is accompanied by symptoms of allergies;
- shortness of breath appears (this is especially true for children);
- the person has not stopped coughing for two weeks;
- the sternum and the area behind it hurt;
- coughed up sputum is greenish in color or contains blood;
- body temperature rose.
If a child develops shortness of breath or severe coughing attacks are caused by an allergy, it is necessary to treat immediately - call an ambulance. Delay in such a situation can be fraught with consequences.
What types of cough exist in children and adults
A cough cannot be an independent disease, but only a symptom of existing health problems. Diagnosis of the disease largely depends on the type of cough, since different diseases are characterized by different types of cough reflexes. Depending on the intensity, time of manifestation and presence of sputum, there is the following classification of cough in both children and older people:
- dry and wet;
- manifests itself in the morning, evening or night;
- permanent and periodic;
- convulsive;
- barking;
- spastic;
- bitonal;
- sharp or silent;
- coughing
Various dry types of cough do not bring any relief to the patient.
The occurrence of this type can occur due to many diseases, including pneumothorax, diffuse and disseminated processes.
This could be pneumonia, tuberculosis, cancer, etc. But such a cough in children and adults also appears if various foreign objects enter the bronchi.
A wet cough in children and adults appears when fluid (pus, sputum, mucus) accumulates in the bronchi. After a person clears his throat, he feels better. A wet cough appears with colds, pneumonia, bronchitis, etc. A wet cough can also be a viral type of disease.
Cough in the morning is observed in patients due to the fact that sputum has accumulated in the respiratory tract overnight. The bronchi are cleared of it after the body awakens.
This cough is typical for people suffering from pneumonia, tuberculosis or even an abscess. Separately, it is worth noting the morning cough of a smoker, which is characterized by high intensity.
It occurs only in adults who smoke, or in those who have recently given up this bad habit.
An evening cough may not bother a person all day, but only appear in the late afternoon. It is characteristic of bronchitis and pneumonia. At night, the cough reflex often occurs due to hypertonicity of the vagus nerve, which leads to bronchial spasm. However, this may also be a manifestation of asthma or bronchitis.
If you are interested in what kind of cough a child has, you should know that it also varies in its frequency. A constant cough is characteristic of chronic diseases of the trachea, larynx, bronchi and pharynx, diseases associated with poor circulation. Periodic types of cough bother patients:
- emphysema;
- acute respiratory disease;
- asthma;
- pneumonia, etc.
Also, such a cough reflex can be observed in smokers in the morning.
A convulsive cough in a child is often accompanied by vomiting, which can be explained by irritation of the vomiting center. This type of cough reflex is characterized by a high frequency of coughing, between which a deep breath takes place. Often a convulsive cough occurs at night.
Source: https://kinder-medcentr.ru/protsedury-i-operatsii/kashel-u-vzroslyh-simptomy-vidy-kriterii-sravneniya-vidy.html
How to determine the type of cough in an adult
Co-author, editor and medical expert – Maksimov Alexander Alekseevich.
Last updated: 10/22/2019
This symptom can accompany various diseases. When does cough occur and with what diseases? Tracheitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis (including laryngitis) and bronchitis can cause it in adults.
Everyone coughs differently, depending on the characteristics of the disease. In the same person, the cough may be different at different times depending on the reason it is caused. It is important for the doctor who makes the diagnosis to know the symptoms and be able to determine the type of cough.
There are many symptoms that help to correctly determine the type of cough, for example, you need to find out its timbre, duration of attacks, time of appearance, appearance of sputum, etc.
Today we will talk to you only about some of the most common types of this symptom that accompanies various diseases, and we will also learn to distinguish a cold type of cough from others.
Comparison criterion 1 - quality and quantity of sputum
- It is not accompanied by sputum production and does not bring relief.
- This cough can be a symptom of the following diseases:
- Sometimes, depending on how a dry cough sounds, you can determine what disease it is a symptom of.
- In the case of the diseases mentioned above, the doctor may prescribe the use of a syrup that can transform a dry type of cough into a wet one.
A not too obtrusive dry cough caused by drying out of the pharyngeal mucosa or accumulation of mucus at the entrance to the larynx most likely indicates a disease such as pharyngitis.
With this, the doctor may prescribe inhalations, warm drinks and lozenges and lozenges to soothe a sore throat.
Accompanied by sputum production. This is a viscous liquid that is produced by the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract: lungs, bronchi, throat, nasopharynx. Microbes and their metabolic products are removed from the human body with sputum.
- Yellow discharge can be a symptom of sinusitis, bronchitis or pneumonia. Sometimes a yellow tint is given by pus, which is mixed with sputum.
- White, curd-like sputum may indicate fungal diseases in the respiratory tract.
- Sputum that is white but watery in appearance indicates a viral infection or chronic respiratory disease.
- Brown discharge is a symptom of viral or bacterial diseases accompanied by inflammation. It can appear with pneumonia, bronchitis and even with a common cold.
To cure a wet cough, it is necessary to remove accumulated phlegm from the lungs and bronchi. In this case, doctors prescribe expectorant or sputum-thinning syrups and tinctures for adults.
It is contraindicated to treat a wet (productive) cough with antitussive drugs, that is, those that suppress the cough reflex.
Comparison criterion 2 - cough character
Paroxysmal cough most often occurs in the first days of illness, becoming more active in the evening and at night. The attacks follow one after another, there is no way to clear the throat, and between these moments it can be difficult to take a breath. The cause of the problem is dry airways and lack of mucus. The throat becomes irritated and attacks occur again and again.
A recurrent cough can occur suddenly and persist for both short and long periods. If you notice that you cough from time to time, but for quite some time, then you need to find the reason. It could be an allergy to animals, dust or flowers, sometimes even to the presence of a certain person or to a certain situation. This cough is usually called psychosomatic.
A short or one-time cough can occur when you inhale smoke or any other irritants or when pieces of food get into the respiratory tract.
Comparison criterion 3 - cough timbre
A barking cough is a dry cough , similar, as one might imagine, to the loud barking of a dog. This situation is due to the fact that the sputum becomes viscous and is difficult or impossible to cough up.
A hoarse or hoarse cough with dull and whistling sounds indicates diseases such as laryngitis, tracheitis, bronchitis or pneumonia. With laryngitis and tracheitis, the cough is accompanied by a hoarse voice, and with bronchitis and pneumonia - chest wheezing.
Silent cough
Source: https://lkray-promo.ru/kashel/kak-opredelit-vid-kashlya-u-vzroslogo/
How to determine what kind of cough a child has
Cough (lat. tussis) is a strong and usually loud exhalation. Coughing (expectoration, expectoration) is a protective reflex action aimed at freeing the airways from mucus, sputum and other foreign bodies that block or irritate them.
Usually the reflex occurs due to chemical or mechanical irritation of receptors on the mucous membrane. It begins with a short inhalation followed by a strong exhalation.
Determining the presence (absence) of expectorated sputum, sound and other characteristics is a way to determine the type of cough in a child and an adult. The duration is also taken into account (acute, chronic cough).
Cough in adults
A sick person hears sounds from the throat, aimed at relaxing the respiratory tract. The accompanying symptoms depend on the factor that provoked this reaction (choking, hoarseness, etc.).
There are many causes of cough. In addition to conditions associated with disorders of the respiratory tract (colds, bronchitis), they include diseases of the digestive system, circulatory system (secondary etiology) due to their connection with the respiratory system.
The most common causes in infants:
- aspiration;
- obstructive bronchitis;
- laryngotracheomalacia;
- compression of the airways by blood vessels;
- cystic fibrosis;
- viral infections (RSV, parainfluenza, adenoviruses);
- whooping cough (rare);
- pneumocystis;
- tuberculosis (from mother);
- congenital heart defects;
- idiopathic cardiac hemosiderosis;
- influence of passive smoking.
The most common causes in children under 5 years of age:
- aspiration;
- bronchial asthma;
- bronchiectasis;
- cystic fibrosis;
- primary ciliary dyskinesia;
- immunodeficiency;
- ARVI;
- chronic sinusitis, otitis;
- tuberculosis.
The most common causes in schoolchildren, adolescents, and adults:
- bronchial asthma;
- bronchiectasis;
- primary ciliary dyskinesia;
- immunodeficiency;
- chronic sinusitis;
- otitis;
- active or passive smoking;
- influence of the work environment;
- tumors of the lungs and mediastinum;
- psychogenic factors.
This pathology has a specific development scenario. Conventionally, the process of emergence and development is divided into the following stages:
- The infection enters the body through the mouth and nose.
- Pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, bacteria) provoke the onset of an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane that covers the inside of the above-mentioned parts of the face. The following factors contribute to inflammation of the mucous membrane: hypothermia, weakened immunity.
- When the health of the lungs is normal, the “secretory fluid” regularly formed in the bronchi is a reliable protector against microscopic dust particles and pathogens. The daily volume of such mucous bronchial secretions can reach 100 ml.
- Ciliated epithelium is a layer of corresponding cells with mobile “cilia” located on the inner surface of the respiratory tract. Responsible for the movement of bronchial mucus up the bronchi, towards the pharynx. In other words, it pushes mucous secretions out of the respiratory system. Subsequently, they are quietly swallowed, the person does not feel it at all.
- With respiratory disease, there is a sharp increase in mucus formed in the bronchi. The volume of produced bronchial secretions is tens of times higher than the permissible values. The activity of ciliated epithelial cells decreases sharply with the development of the inflammatory process. The upward movement of mucus is inhibited.
- Excessive amount of sputum provokes “congestion” in the bronchi, creating favorable conditions for the proliferation of microbes. Independent cleansing of dust particles and pathogens becomes impossible, and the body “calls for help” with a cough.
Finally, we come to the final stage - the process itself. The chronology of actions is as follows:
- inhale, cover your mouth
- respiratory muscles are tense
- air pressure increases in the lungs
Source: https://onsmeta.ru/kak-opredelit-vid-kashlya/
Types of cough in adults
Constant cough in an adult: normal or pathological? Any cough that does not go away for a long time, for example, for a month or more, should alert everyone. A cough in an adult is a protective reaction of the body that occurs for a specific reason, so every conscious person must identify the provoking factor and choose options for eliminating it.
In most cases, people go to the doctor when severe advanced diseases are already diagnosed, and the cough becomes prolonged, and the person cannot even clear his throat.
What can cause a persistent cough?
In medical practice, it is customary to distinguish between infectious and non-infectious causes of severe cough.
- Chronic forms of rhinitis, sinusitis, sinusitis, in which the nasal mucosa is constantly swollen. Sputum does not come out and descends into the bronchi and trachea.
- Due to the consumption of excessive amounts of spices, acidity in the stomach may increase and heartburn may occur. It may manifest itself as a cough.
- Allergic reactions of the body to irritants. In this case, the cough will be dry and prolonged.
- The body's reaction to certain medications that have already caused addiction.
- Polluted air in the workplace or in a populated area.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Presence of tumors in the airways or lungs.
Types of prolonged cough in adults
With any cough, the manifestations will be different. Therefore, it is worth knowing that there are several types of pathology:
If at this stage you don’t help the immune system recover, then the cough will go straight to the bronchi. This leads to the development of acute bronchitis, which takes a long time to treat, and in many cases becomes chronic. If proper treatment is not provided, a prolonged cough causes deformation of the bronchial walls, which leads to asthma, lung abscesses and pneumonia.
- When visiting a doctor, many patients indicate pain in the side, shortness of breath, and fever that accompany the main symptom.
- A cough with wheezing or whistling is characteristic of whooping cough.
- Barking - tracheitis or laryngitis.
Source: https://0p3.ru/kasel/vidy-kashlja-u-vzroslyh.html
We determine the disease by the nature of the cough
Causes of cough. Does cough always mean damage to the respiratory tract?
Indeed, in most cases, a cough indicates damage to the respiratory tract by some disease. At the same time, cough is often the symptom of the disease that forces the patient to see a doctor. The question: is a cough always a symptom of a disease of the respiratory system, is very interesting for a more detailed consideration.
This is especially true for chronic cough. Before considering the list of diseases that can cause cough, we will provide a description of some characteristics of cough, in order to subsequently describe the different types of cough in various diseases.
Knowledge of the basic features of cough in various diseases can be extremely important not only for medical specialists, but also for all people faced with this problem.
In order to determine the type of cough and whether it belongs to any disease, you need to pay attention to its main characteristics: duration, strength of the cough, the moment of the day when the cough is strongest, the cough is wet or dry, the nature of the sputum released when coughing, the timbre of the cough , the presence of other symptoms of the disease.
How long does the cough last? From the point of view of clinical development, we distinguish between acute, protracted and chronic cough.
Acute cough – present for a period of time up to 3 weeks. Acute cough is characterized by constancy of symptoms, that is, the cough is present almost all the time.
Acute cough is characteristic of most acute respiratory viral infections (influenza, parainfluenza, MS infection, adenovirus infection), acute bronchitis, pneumonia, pharyngitis.
An acute cough, as a rule, is purely protective in nature and helps cleanse the body of germs and phlegm.
Persistent cough. Unlike an acute cough, a persistent cough lasts from 3 weeks to 3 months. A persistent cough is less persistent than an acute cough. It is quite possible for the cough to develop in waves (the appearance and disappearance of a cough after a few days) or for it to appear only at certain times of the day (for example, in the morning or at night). A lingering cough also most often indicates damage to the respiratory tract, however, unlike an acute cough, a lingering cough indicates a slow course of the disease and the possibility of its becoming chronic. Chronic cough. The diagnosis of chronic cough is established when the cough continues for more than 3 months. Let us immediately note that a chronic cough can be a sign of very dangerous diseases: chronic bronchitis, bronchial asthma, heart failure, tumors of the lungs and respiratory tract, tuberculosis. Therefore, patients with chronic cough need the most careful examination and treatment. In some cases, chronic cough can occur in nervously ill people (without certain diseases of the respiratory system), as well as in people exposed to adverse environmental factors: dust, smoke, caustic gases. In smokers, a chronic cough can be either a sign of prolonged irritation of the bronchi by tobacco smoke, or a sign of one of the complications of smoking (bronchitis, lung cancer). Chronic cough is usually not persistent. Chronic cough is characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission, as well as cough fixation, that is, the occurrence of cough at a certain time of day. Exacerbations of chronic cough are associated with exacerbation of the disease that caused it or with exposure to any irritating factors (cold air, dust, allergens) on the body.
Chronic cough, as a phenomenon, loses its protective role and can cause the development of certain disorders of the respiratory system: emphysema, bronchiectasis, spontaneous pneumothorax, cardiac dysfunction, hernia of internal organs, etc.
Strong or weak cough? Typically, the strength of the cough depends on the severity of the disease: acute respiratory tract diseases are accompanied by a strong, “hysterical” cough. Chronic diseases are manifested by a mild cough (coughing).
A particularly severe cough is typical for respiratory diseases such as whooping cough (convulsive cough), acute tracheitis or acute bronchitis caused by influenza or other acute respiratory viral infections. Coughing is often observed in chronic smokers, patients with chronic bronchitis, tuberculosis, and lung cancer.
With a chronic cough, the transition from coughing to a hysterical cough always means a worsening of the disease.
At what time of day does the cough appear? The appearance of a cough at a certain time of day can be a fairly characteristic sign of a particular disease.
A cough that lasts all day is characteristic of acute respiratory infections (influenza, parainfluenza, whooping cough), as well as acute laryngitis, acute tracheitis, acute bronchitis. A cough that occurs in the morning is typical for patients with chronic bronchitis, bronchiectasis, and lung abscess.
Night cough is typical for patients with heart failure, lung cancer patients, and tuberculosis patients. Often a night cough is the only symptom of gastroesophageal reflux, chronic sinusitis or chronic rhinitis.
An allergic cough occurs any time upon contact with an allergen. Allergic cough and cough of asthmatics are characterized by a seasonal appearance in spring or autumn.
Wet or dry cough? What type of sputum? The terms “dry” or “wet” cough require further clarification. It is customary to talk about a dry cough in cases where during a cough either no sputum is produced at all, or very scanty amounts of sputum are produced. A wet cough is accompanied by copious sputum production.
Sputum is produced by the bronchi and trachea. Together with sputum, when coughing, microbes and their poisons are removed from the body. During many diseases, a transition from a dry cough to a wet one is often observed, as well as a change in the nature of sputum (for example, from watery to purulent). This change in the nature of the cough, as well as the change in the nature of sputum, depends on the natural development of the disease.
With many viral infections (influenza, parainfluenza, MS infection), the cough is initially dry; the appearance of purulent sputum indicates that a bacterial infection has joined the viral infection - this development is typical for most acute respiratory viral infections.
Dry cough is also characteristic of chronic pharyngitis, the initial stages of pneumonia, lung cancer, initial forms of tuberculosis, gastroesophageal reflux (gastric juice from the stomach into the esophagus), chronic sinusitis, pleural diseases (systemic connective tissue diseases, tumors), for patients with heart failure , for allergy sufferers.
An important cough with copious discharge is characteristic of the final stages of pneumonia (lobar pneumonia), chronic bronchitis, and tracheitis. Very copious sputum production is observed with bronchiectasis.
The nature of the sputum also indicates the nature of the disease - watery sputum at the beginning of an acute respiratory infection indicates a “purely viral” infection, while purulent sputum is a clear sign of a bacterial infection. In heart failure, the small amounts of sputum produced when coughing is usually foamy and may be pink in color.
The cough of patients with bronchial asthma is also accompanied by the release of scanty viscous, glassy sputum. The appearance of sputum mixed with blood (hemoptisia) is always an unfavorable sign. If there was bloody sputum only once or several times, then this is most likely a consequence of a blood vessel bursting during coughing.
Chronic cough with bloody sputum may be a sign of heart failure, pulmonary tuberculosis, or lung cancer.
Timbre of cough In some diseases, the timbre of cough can be quite characteristic. In acute tracheitis, for example, a loud, chesty cough.
With whooping cough, the cough is painful, periodically interrupted by pauses with a loud sigh, which again turn into a cough. The cough with laryngitis is rough and barking.
Usually, along with a cough, patients with laryngitis also complain of hoarseness. In chronic bronchitis, the cough is deep and muffled.
Patients with bronchial asthma complain of a severe, muffled, suffocating cough.
All of the cough characteristics described above may change during the course of the disease.
Comment
Source: https://www.BabyBlog.ru/user/Ulia_Ulia/3010191
Reasons why a cough occurs without a cold in an adult and a child, for what diseases
The reasons for a cough without a cold in an adult can be different. It is necessary to identify the disease or factors that caused the development of this condition in time in order to begin treatment correctly.
Symptoms of cough without cold, fever and sore throat
Sometimes a person may experience this symptom without signs of a cold. There is an incomprehensible cough at night, which goes away in the morning, but does not allow you to sleep. It often occurs on its own without significant symptoms. It happens due to an illness not related to a cold.
In children
In children under 1 year of age, cough occurs less frequently than in older children. Breastfeeding reduces the risk of developing colds in babies.
If a child coughs, but there is no snot, and the body temperature is +36.6 ° C, then you should suspect an allergy to some substance or the development of whooping cough.
You cannot make a diagnosis on your own and self-medicate, because the respiratory system in children under 1 year of age is poorly developed, and sputum is difficult to cough up, which leads to stagnation of mucus in the lungs and bronchi.
This provokes the development of complications including pneumonia.
In an adult
There are many diseases that are accompanied by cough. Without a cold in an adult, this symptom can cause a permanent deterioration of the condition, developing for the following reasons:
- Heart failure.
- Allergic reactions.
- Bronchospasms.
- Exacerbation of obstructive pulmonary disease.
- Stagnation of mucus in the bronchi after acute respiratory viral infections or acute respiratory infections.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease.
- Lung pathologies resulting from long-term smoking.
- Lung cancer or tuberculosis in any form.
- Problems related to the nervous system.
- Development of pleurisy.
Type of cough
There are productive (wet) and non-productive coughs. When productive, coughing or coughing provokes the expulsion of accumulated mucus from the bronchi. Unproductive is dry; during its attacks, the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract are irritated. In order not to miss the development of pathology, you need to know the signs of dangerous diseases.
With sputum
You need to pay attention to the color of the mucus. Blood or pus is a signal for a full examination. An alarming symptom is an increase in the volume of sputum produced. If you have a runny nose without a cold, you should be alert to the following signs:
- increase in body temperature (+37.5…+38 °C) for 5-7 days;
- shortness of breath, pain in the chest area;
- severe weakness, chills, sweating, weight loss;
- a coughing attack that does not stop for an hour.
Dry
A severe, dry cough for a long time is not always associated with a cold. It can be caused by viruses, the development of an infection, or the initial stage of a dangerous disease. The following signs indicate the absence of a cold:
- An elevated body temperature along with a severe, dry cough may be due to the flu or an infection caused by bacteria. This condition often develops into asthma or bronchitis.
- Internal pathologies, the presence of foreign bodies or tumors in the respiratory tract can also be accompanied by a nonproductive cough.
- Allergies can also cause a dry cough associated with seasonal flowering of plants or other factors.
Possible causes not related to ARVI
An unreasonable attack, when the throat does not hurt, can be caused by dry air in the room or other internal or external factors. It doesn't matter when he appeared - at night or during the day. It is necessary to undergo an examination and eliminate the cause that provoked this condition.
Tuberculosis
With tuberculosis, the cough does not appear constantly, and with the focal form of the pathology it is completely absent. The symptom is pronounced in miliary tuberculosis. It can be dry, accompanied by a small amount of sputum. Destructive tuberculosis is characterized by a dull cough with a high metallic timbre due to the resonance of the cavity.
Worms
The first signal indicating the presence of worms is discomfort and sore throat, accompanied by a dry, unproductive cough.
With helminthic infestation, a cough may appear, which is often confused with ARVI. Parasites are able to migrate throughout the body through the bloodstream, localizing in the lungs and bronchi. Inflammation develops as a result of the vital activity of helminths; a dry cough appears, turning into a wet one with the discharge of sputum.
Children are at risk because they come into contact with each other in kindergarten and school and can quickly become infected with helminths. A cough that develops due to worms can cause mental and physical development delays. It is necessary to undergo examination and begin treatment if the following symptoms are detected:
- sudden increase in body temperature, chills, fever;
- muscle pain;
- inflamed lymph nodes, which cause pain when palpated;
- nausea, pain in the upper abdomen;
- a feeling of a full stomach with rapid saturation, but the feeling of hunger comes quickly;
- change in the size of the liver and spleen (increase);
- insomnia, increased fatigue, severe irritability.
Laryngitis, tracheitis and bronchitis
By the nature of the cough and some signs, you can determine the disease:
- With laryngitis, this symptom is barking, unproductive, and exhausting. It appears most often at night. If left untreated, severe irritation of the laryngeal mucosa occurs, accompanied by pain. In a child, such a cough can provoke laryngeal stenosis or false croup.
- Tracheitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the trachea) is accompanied by a dry hacking cough that is paroxysmal in nature. Appears at night or in the morning. The condition can be caused by laughter, a sharp deep breath, a rapid change in air temperature (going from a warm room to a cold one in winter). The attack is accompanied by severe pain in the trachea and chest. Breathing becomes shallow and quickens.
- In case of bronchitis, it helps remove phlegm, therefore it is protective. If the disease is identified correctly and the treatment is adequate, then within 3-5 days from the onset of the pathology it becomes productive. When listening to the patient, moist rales are heard. It lasts about 2 weeks until the bronchial tree is completely cleared of sputum.
Post-infectious
Post-infectious (residual) cough appears after acute respiratory infections. Its duration is 3-8 weeks. During this period, a person reacts sharply to any irritant (smoking, dust, cold air) and remains vulnerable to infections because the inflamed mucous membrane cannot fully perform protective functions.
Presence of a foreign object in the respiratory tract
If a foreign body enters the respiratory tract, frequent bouts of severe coughing and hoarseness may occur. The duration and intensity depend on the size of the foreign object, its shape, nature and location. When it is fixed in the larynx, the symptom will be less intense.
When a foreign body moves freely through the respiratory tract (for example, a watermelon seed), a paroxysmal intense cough appears, which can increase when the object comes into contact with the walls of the trachea. May be intermittent, worsening at night or when the child is restless.
The attack may be accompanied by vomiting, blueness of the face, often the symptoms resemble whooping cough, and the diagnosis may be made incorrectly.
Allergy
An allergic cough is the body’s response to the penetration of an allergen; the symptom is not associated with viruses and colds. It can last for several weeks, in severe cases - months.
If you ignore this condition without eliminating the allergen, complications may arise that can develop into asthma.
It is difficult to distinguish a cough from a cold. You need to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- appears suddenly at night;
- cough: dry, transparent secretions from the bronchi can be coughed up in small quantities only after a long attack;
- characterized by severe soreness that appears in the larynx, making breathing difficult;
- shortness of breath due to spasms of the smooth muscles of the bronchial walls;
- normal body temperature with a runny nose and severe cough;
- decreased blood pressure due to a sharp decrease in the tone of the artery walls;
- Often a rash may appear on the body due to nervous irritation of areas of the skin, itching.
Source: https://lechim-gorlo.ru/gorlo/prichiny-ot-chego-byvaet-kashel-bez-prostudy-u-vzroslogo-i-rebenka-pri-kakih-zabolevaniyah
How to determine the type of cough in adults. Types of cough: characteristic signs
A cough is a voluntary or involuntary sharp exhalation. It is needed to clear the airways of foreign particles, microorganisms, liquids and mucus. We can all cough at least 1-2 times a day to clear our throat.
But this cannot be considered the norm: a cough always signals that something is wrong with us. Because there are different types of coughs, it can be difficult to diagnose the problem.
To choose the right treatment, you need to know when and what to look for.
Why does cough occur?
The most common causes of cough are prolonged exposure to cold and the penetration of harmful microorganisms into the respiratory system. With weakened immunity, they cause increased mucus production in the bronchi.
The ciliated epithelium cannot cope with the volume of secretions secreted by the bronchi and reduces the reflex protection of the respiratory tract. Mucus accumulates in the bronchi and an infection develops, which causes inflammation of the airways.
The body can no longer clear itself of phlegm on its own, and a cough begins.
Types of cough and what diseases they are typical for
Types of cough in adults can be classified according to several criteria.
By the presence or absence of sputum:
- Dry appearance, characteristic of tuberculosis, allergies, bronchial asthma, whooping cough, pneumonia, pleurisy and tumors.
- Wet appearance - occurs with bronchitis, pneumonia, acute respiratory viral infections.
Based on the duration of the cough, cough can be divided into types:
- acute form - lasts no more than two to three weeks and occurs with a respiratory tract infection;
- chronic type - lasts longer than 3 weeks, occurs due to mental disorders or long-term use of medications, as well as bronchitis.
To understand what kind of cough occurs in children, you need to know its causes, which are very different from the reasons for its appearance in adults.
In infants, it occurs due to milk entering the respiratory system after feeding. When teething, babies produce a lot of saliva, which, if swallowed, can also cause coughing.
This type of symptom is not considered a disease and does not need to be treated.
Many people wonder how to determine the type of cough on their own, without medical help. Here are some tips.
Dry
If you and your surroundings do not smoke, are not exposed to chemical irritants, and you have a type of symptom that has been bothering you for a long time, that is, a cough for no reason, then it signals the development of asthma, reflux esophagitis, heart diseases, benign and malignant tumors. This is the main and often the only symptom characteristic of these pathologies.
The dry appearance appears as a result of inflammatory processes in the mucous tissues of the larynx; cough suppressants are used to treat it.
The following types of dry cough are distinguished:
- Tubercular appearance. Usually, a person’s strong immune system copes with Koch’s bacillus on its own, but if it is weakened, the tuberculosis bacterium is activated and affects the lungs and bronchi. The cough impulse in tuberculosis is dry, accompanied by frequent coughing, general weakness and an increase in temperature to 37.5.
- Allergic type. Caused by an excessive reaction of the immune system to dust, animal hair, pollen, and household chemicals. It is characterized by attacks of suffocation, which are provoked by anaphylactic shock.
- For helminthic infestations. It's incredible, but worms also cause coughing. This happens when the larvae migrate through the bloodstream, due to which they penetrate the lungs, trachea and bronchi. There, irritating cough receptors, they cause bouts of dry cough.
- For diseases of the digestive system. This type of cough appears after eating. Due to organic changes such as protrusion of the esophageal wall, reflux esophagitis, fistulas between the esophagus and trachea, pieces of food enter the respiratory passages or are thrown from the stomach into the esophagus.
- Medicinal type. Usually caused by blood pressure and heart medications.
- Cough due to cancerous tumors in the lungs, bronchi, trachea and throat.
- For lesions of mycoplasma and chlamydia, causing wave-like attacks of atypical pneumonia and bronchial pathology.
Wet
It is important to determine what diseases cause cough with sputum in order to correctly diagnose and treat it.
This type of symptom develops with seasonal colds, bronchial lesions, pneumonia, bronchial asthma and allergies.
After coughing, the temperature rises, shortness of breath appears, appetite decreases, sometimes the sputum is greenish in color and contains blood clots. The wet appearance usually bothers you at night and causes wheezing and chest pain.
The wet appearance occurs due to the fact that a lot of sputum accumulates in the bronchi, so expectorant medications are used to clear it.
Whooping cough
This type is more common in children under 10 years of age, who can get whooping cough (adults rarely get sick). Its presence in adults indicates tuberculosis or pharyngitis in a chronic form.
Cough with whooping cough bothers the child at night. The accumulation of too viscous mucus in the respiratory passages prevents the child from breathing.
The presence of a foreign body in the respiratory tract also causes such suffocation. To push it out you need a strong cough push.
Barking
The barking appearance occurs more often in children than in adults, since the respiratory passages of an adult are much wider than those of a child. Breathing is difficult, hoarseness appears. Debilitating attacks do not help the patient to cough. They are symptoms of ARVI, false croup, whooping cough, laryngitis, diphtheria (a very dangerous disease), and also occur due to the inhalation of small objects by children.
Paroxysmal
Attacks of suffocation, which greatly torment the patient, especially at night, are most often signs of bronchial asthma. The insidiousness of this type of cough is that it is rarely associated with the onset of a serious illness. Only a thorough diagnosis will reveal the true cause of the attacks.
Staccato
This type develops in newborns and is caused by chlamydia infection of the respiratory tract. It is dry, short, sonorous and sharp. It is not accompanied by an increase in temperature and goes away quickly when the underlying cause of the disease is eliminated.
With loss of consciousness
Bettolepsy is when a person loses consciousness during severe coughing. With prolonged and intense coughing, a spasm of the lungs occurs and intrathoracic pressure rises. This impairs cerebral circulation and causes brief fainting, convulsions, amnesia and severe headaches.
This type is characteristic of pulmonary emphysema, bronchial asthma and chronic bronchitis.
Other options
In medical practice, there are other, rarer types of cough:
- The dry psychogenic type manifests itself only in the daytime; by the evening its symptoms subside. At night and during conversation he disappears. It is distinguished by rapid and frequent coughing. The cause is stress. It usually affects children living in families with irritable and restless environments.
- Residual view. It remains in a person after a sore throat, bronchitis or pneumonia. Due to the fact that the normal function of the mucous membranes of the respiratory organs is restored for at least a month after the illness, during this period they are extremely vulnerable to cold, high humidity, cigarette smoke, and dust.
Diagnostics
Depending on the stage of cough, the patient’s well-being and the course of the disease itself change.
- At the initial stage, it is dry, causing headaches, chest pain, and sore throat.
- At the climax stage, the frequency and number of coughing impulses increase, disturbing even at night. They become loud, and pain in the peritoneum and chest area intensifies.
- During the fading stage, it becomes moist and accompanied by a large amount of mucus, then recovery occurs.
Making a diagnosis begins with collecting an anamnesis, ordering laboratory tests, the results of which may indicate the following additional examinations: X-ray of the lungs, bronchoscopy, echocardiogram, ultrasound, sputum culture. If necessary, consultations with an ENT specialist, TB specialist, neurologist, or cardiologist may be required.
Why is a dry cough dangerous?
When the first signs of cough appear, we rarely immediately go to the doctor and try to calm it down on our own. If after 2-3 weeks you cannot get rid of the attacks, it means that serious inflammation is developing.
- A prolonged cough provokes an increase in blood pressure.
- The cough “descends” into the bronchi, becomes wet, causes wheezing and high fever. Pneumonia develops due to respiratory failure.
- The sputum becomes thicker, stagnates, and microbes multiply in it.
- A symptom that lasts more than 3 weeks becomes a chronic disease and cannot be cured on its own.
Treatment
Types of cough and their treatment are closely related to the cause of the underlying disease:
- If a person coughs due to hypothermia, home treatments will be enough to get rid of it.
- If a foreign object gets into the respiratory tract, it is necessary to rinse and rinse the nasopharynx and throat.
- An allergic type will require the prescription of antihistamines.
- If the symptom occurs as a result of infections or chemical damage to the respiratory system, then treatment with medications will be required, which can only be carried out by the attending physician.
For any type of cough, the patient needs to drink a lot, eat a balanced diet and ventilate the air in the room.
Medications
If the patient suffers from a dry cough, then drugs are prescribed that suppress the excitation of the cough center. Glauvent, Stoptussin, Tusuprex, Libexin, Codeine will help here. The doctor prescribes the dosage and duration of taking the drug individually.
Do not take cough suppressants at the same time as expectorants or when there is sputum!
When it is wet, mucolytics are prescribed, which facilitate the discharge of sputum. These include Ambrobene, Ambroxol, Bromhexine, Carbocysteine, Acetylcysteine. These products are incompatible with codeine-containing medications; asthmatics should take them with caution.
Herbal preparations Mukaltin, Tussin, Solutan, Pertusin also dilute sputum and facilitate its evacuation.
No matter how simple a cough may seem, self-medication can lead to serious pathologies. If you do not know the exact cause of its occurrence, choosing medications on your own will only worsen your condition. For example, symptoms may be caused by bronchospasms or pneumonia, and you will need not just products to thin and evacuate mucus, but antispasmodics and antibiotics.
ethnoscience
At the first signs of a cold, you need to start rinsing your mouth and throat with disinfectant solutions:
- Place 1 tbsp in a glass of warm boiled water. sea salt and 1 tbsp. baking soda, stir thoroughly until the ingredients are completely dissolved, then gargle. Depending on how you feel, you can do up to 5-7 rinses a day.
- If a dry cough bothers you, prepare the following healing drink. Mix 1⁄2 cup lemon juice, 2 tbsp. honey, 1 tbsp. glycerin. Shake everything until smooth and take 1 tsp. half an hour before meals 7 times a day.
- If you have a cough with phlegm, prepare a decoction based on elecampane rhizomes. 1 tbsp. pour a glass of water over the herbs, boil for 15 minutes, then let it brew for 3 hours. Take 1 tbsp of the strained broth. 30 minutes before each meal.
- To speed up the separation of mucus, you can do inhalations. Boil the potatoes in their jackets, pour the broth into a separate bowl, and, covering your head, breathe in the steam for 10-15 minutes.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is used to speed up recovery. It not only has a local effect on diseased organs, but also strengthens the entire body. Basic physiotherapeutic techniques for cough are as follows.
Breathing adjustments
- Coachman - a person sits on the edge of a chair, spreads his legs, puts his elbows on his knees, his back should be straight and his gaze directed forward. Breathing is free, without tension.
- Prayer: you need to get on all fours, put your forearms on the floor, and put your head on your palms. Relax the breathing muscles.
- You can simply lie down with your upper body hanging over the edge of the bed. Place your head on your crossed arms.
Massage
For a person suffering from a persistent cough, it is better to have a massage in the evening, for half an hour, with a warming ointment. It relaxes well and speeds up the removal of phlegm. The massage begins with pinching, moving from the spine to the sides. Then they move on to light tapping. Finish with stroking. The spine itself is not massaged.
Other methods
Cough of any kind is annoying and disturbing. Therefore, immediately after its appearance, the question arises - how to treat it.
Sanatorium methods will help cope with severe attacks.
- For bronchial asthma and chronic pneumonia, dry carbon dioxide baths are indicated, which eliminate bronchospasms and suppress cough.
- Normobaric hypoxytherapy or treatment with mountain air is the inhalation of gas mixtures with low oxygen content, which increases physical endurance and prevents acute respiratory diseases.
- Halotherapy is a treatment with special salt aerosols that are sprayed indoors. They purify the air of allergens and microorganisms, normalize the microflora of the respiratory system, and in patients with asthma, reduce the severity of the disease and increase periods of remission.
- To speed up recovery, the patient is recommended to visit the bathhouse, but only if the body temperature is normal. Bath procedures increase the body's immunity and strengthen lung function.
Prevention
A person needs a cough to clear the airways, but it is better to prevent other types of cough.
- You will have to quit smoking. Smoking is a source of chronic cough, and it can be very difficult to cure a smoker's cough.
- Make changes to your diet. People who get plenty of fiber and flavonoids suffer less from chronic coughs.
- Stay away from those with contagious diseases, wash your hands frequently, and do not share cutlery, towels or pillows.
The cough can often go away on its own. But if it continues for a long time and gets worse, you should still talk to your doctor.
The types of cough differ depending on its cause, the location of the pathological focus, the presence of sputum, time of day, duration... It is a specific diagnostic sign for various diseases: ARVI, bronchitis, pneumonia, lung cancer... Treatment for each type of cough is different.
Source: https://duyc.ru/kak-opredelit-vid-kashlya-u-vzroslyh-vidy-kashlya-harakternye.html