Any pathological condition in the body must be thoroughly examined. The cause of the development of the inflammatory process can be bacteria, fungi and other pathogenic microorganisms.
Urinalysis for prostatitis in men is one of the ways to accurately diagnose the disease, allowing you to find out the cause and identify the characteristics of its course.
In what cases does the doctor refer for a urine test?
Every man needs to have a urine test every year. Urologists issue a referral for this laboratory test for any complaints related to urination. This study is included in the complex of disease diagnostics. Main complaints for which investigation is necessary:
- frequent or difficult urine output;
- sexual disorders - decreased libido, impaired potency;
- discharge of pus from the urethra;
- interruption of the stream of urine during its excretion;
- pain in the groin or area above the pubis.
The results of the study can confirm the diagnosis and determine the degree of neglect of the disease. Based on it, the doctor may recommend home treatment or hospitalization if dangerous symptoms develop - hematuria.
For chronic diseases, urine testing is carried out at least 2 times a year in order to notice at an early stage the transition of the disease into the acute phase and prevent complications.
What does urine analysis show about prostatitis?
Even at an early stage of development of the inflammatory process, its progress can be detected using a urine sample. Doctors may note that the following indicators are abnormal:
- red blood cells;
- protein;
- leukocytes.
In a healthy person, their content in the material sample is minimal; in case of inflammation of the prostate, their amount greatly exceeds the norm. Such changes can show the doctor that inflammation of the prostate gland has begun, disrupting the functioning of other organs.
It is impossible to establish a diagnosis based on analysis alone, but its participation in the differential study is invaluable.
Types of urine tests
Determination of the chemical composition and physical properties of urine is carried out using several methods. For prostatitis, various tests may be prescribed, including several options for diagnosing urine.
Based on this, they also need to be collected in different ways. Sometimes the patient has to provide samples over the course of several days so that the laboratory can check each for individual indicators.
The share of determining the daily amount is used by Nechiporenko analysis. Its essence is that it is necessary to completely collect all the urine excreted by the bladder per day. Typically, this type of diagnosis is resorted to in cases where other tests have already been done and showed abnormalities.
General research
The basis of diagnosis for prostatitis is always a general analysis. It allows you to obtain a clinical picture of the disease and identify abnormalities. This study is ordered first.
It reveals a microbiological picture of the internal state of the body. If the amount of substances in the sample is changed, the doctor prescribes additional tests. The following is taken into account:
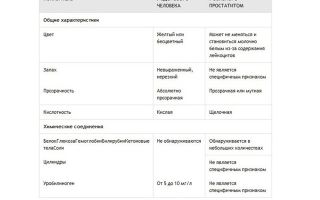
- physicochemical properties - acidity and density;
- appearance – color, smell, presence of foreign inclusions;
- biochemical composition - protein, erythrocytes, leukocytes, oxalates.
For the study, a urine sample is collected immediately after waking up, in the morning.
Only the middle part of the sample will be indicative, that is, first you need to release urine into the toilet, then into a jar and complete the process again not into it. The container must be sterile and filled with at least 100 ml of urine.
If you take an untreated jar, then in a matter of minutes you may observe darkening and turbidity of the sample; the result will no longer be reliable.
A characteristic sign of the inflammatory process is proteinuria, that is, an increase in the amount of protein in the urine. This deviation alone is not enough to make a diagnosis.
Bacteriological diagnostics
It is possible to determine which bacteria contributed to the development of the disease using the bacteriological culture method. To do this, part of the urine sample is placed in a nutrient medium that creates better conditions for the growth of bacteria. Normally, urine should be completely sterile. If this is not the case, then in laboratory conditions a sharp increase in the number of bacteria will be noticed within 5-7 days.
If bacteria are found after the study, the patient will need specific treatment aimed at eliminating them. If the infection is chronic or latent, then a test is performed to determine whether the bacteria are resistant to antibiotics. Analysis is collected differently. The patient needs to collect all the urine excreted in three different containers.
The test result will be ready in 8-16 days due to the need to wait for the bacteria to grow.
Cytological examination
In terms of accuracy, cytological diagnosis of urine is inferior to the examination of a smear from the urethra. It is prescribed if the doctor suspects the development of prostate cancer or the appearance of an adenoma. The study allows you to detect cancerous and atypical cells in the sample.
The peculiarity of this study is that the first morning urine sample is not suitable. A man needs to collect material during his second trip to the toilet, but he needs to wash himself first so as not to distort the result. Simultaneously with this analysis, a scraping from the urethra and ultrasound diagnostics are performed.
Interpretation of analyzes
Disturbances in the functioning of the prostate always lead to changes in the state of urine. The research results can be partially interpreted independently. You can evaluate the following indicators in a urine test for prostatitis:
- Also, normally there is no protein, and in case of disease its amount exceeds 0.033 g/l. This indicator cannot directly indicate prostatitis, since the number of protein compounds increases with other inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system.
- Red blood cells appear in the urine with calculous prostatitis or cancer. Normally, they can be found in no more than 1 unit; with pathologies, the figure is much higher. It changes dramatically.
- Normally, no more than 3 units of leukocytes are detected. Elevated levels are characteristic of a chronic inflammatory process in the prostate gland.
- With calculous pathology, phosphates are found in urine.
Most often, with prostatitis, the urine sample is cloudy, the color of milk tea. The smell of the sample with this disease is pungent and fetid. Acidity levels are also disrupted and the environment becomes alkaline. Density (SG) in diagnosis is of secondary importance; it only allows to exclude other diseases.
It is impossible to determine the presence of prostatitis on your own. This can only be done by a doctor, since he will interpret the research results in a comprehensive manner.
What to pay attention to
Even before submitting the sample to the laboratory, you may be alarmed by the color of the biomaterial:
- dark (orange) – occurs during treatment with certain drugs, consumption of brightly colored foods;
- pink – is a sign of hematuria, the sample contains fresh blood, a sure sign of a pathological process in the organs of the genitourinary system;
- red (dark burgundy, almost black) – occurs in acute prostatitis and other dangerous ailments, color changes occur due to blood stagnation;
- clots and white threads - appear with purulent inflammation of the prostate; the constant presence of such inclusions occurs with an abscess;
- white flakes - observed when protein appears in urine, indicating problems in the functioning of the bladder and kidneys;
- Sticky, foaming or cloudy urine occurs in chronic prostatitis, and the density of the sample increases.
You may also notice an unpleasant smell of urine coming from the sample with prostatitis in men. If already at this stage the material differs from the normal parameters, then this may be a consequence of one of the types of lesions of the genitourinary system.
In 60% of cases, men are diagnosed with prostatitis, and in the remaining cases, other inflammations affecting the bladder or kidneys are diagnosed. In case of pathology, the color of the urine sample may not change for a long time. You should consult a doctor if it remains dark or foams for a long time.
Why does blood appear in urine and what does it mean?
A red flag is the detection of blood in a urine sample. At the same time, its color changes to red or pink. This condition is called hematuria, its causes are:
- Melting of the prostate, in which a blood vessel is affected. In this situation, traces of pus are additionally detected.
- Injury to mucous membranes during research.
- Hyperplasia accompanying chronic inflammation in the prostate. This condition is dangerous because most often the process is malignant.
After the appearance of symptoms of hematuria against the background of chronic inflammation of the prostate, every 15 patient is diagnosed with cancer of the glandular tissue. The appearance of blood often accompanies the development of a malignant tumor, but this is not its only clinical sign.
In every 20 patients, cancer progresses according to the worst-case scenario.
Differential diagnostic methods are aimed at distinguishing a malignant lesion and an acute inflammatory process from urolithiasis, which also often occurs along with prostatitis.
When moving, the stones damage the mucous membranes of the kidneys and bladder, which leads to the appearance of blood in the urine. This disease can be distinguished from oncology only by a combination of laboratory and instrumental methods.
Is preparation required for the test?
It is important to create the right conditions for urine collection. This will allow you to get a reliable result. Failure to follow the urologist's recommendations will lead to a false positive result. For this reason, doctors warn all patients about the need to follow simple preparation rules:
- stick to your normal drinking regime;
- in order not to irritate the urethra, you should avoid eating red meat the day before, do not eat spicy foods and do not drink alcohol;
- if you are taking antibiotics and uroseptics, you need to inform your doctor about them or stop taking the pills, otherwise the picture of inflammation will be blurry;
- You should not go to the gym the day before or expose yourself to serious physical activity.
Many urologists advise having a hearty dinner before collecting material, but you cannot prepare a sample in advance.
Do not store urine in the refrigerator or collect it in unsterile containers. Now pharmacies sell special containers that have been processed; they are ideal for transporting urine samples.
How to properly collect urine
For laboratory tests, urine that has accumulated in a bladder for 5 hours is best suited. You should not have sex at night and in the morning, as this can also affect the quality of the material. Before going to the toilet, be sure to wash the penis and perineum with unscented soap and wipe dry. Urine sample preparation is carried out according to the following rules:
- for general analysis - only “average” urine is collected, the beginning and end of urination occurs in the toilet;
- three-cup sample (for bacteriological research) - a portion of urine is divided into three sterile containers (initial, middle and residual), nothing is poured out;
- a four-cup sample is collected in a medical institution; not only a full portion of morning urine is sent to the laboratory, but also prostate secretion.
Most often, doctors recommend donating urine according to the general scheme or the 4-glass method. In the latter case, there is a chance to make an accurate diagnosis by examining all the samples at once. The material should be on the laboratory assistant’s desk no later than 2 hours later.
If you wait longer, sediment will fall to the bottom of the container, microbes will begin to multiply in the sample, it will become cloudy, and mucus will form in it.
What urologists say about the importance of urinalysis
Doctors consider urine testing an important step in preliminary diagnosis. Only on the basis of data obtained after analyzing samples can a preliminary diagnosis be made, inflammation detected and the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics determined.
Also, based on the analysis, it is possible to detect the initial stage of oncology development against the background of chronic prostatitis.
For patients, determining the composition of urine is one of the few ways to quickly and painlessly clarify the diagnosis. If you approach the collection of research material correctly, you can significantly reduce the list of possible diseases.
At the same time, you need to understand that analysis cannot be carried out in isolation from other research methods.
Source: https://AnnaHelp.ru/prostatit/analiz-mochi-pri-prostatite.html
Urinalysis for prostatitis: indicators for chronic and acute forms
- Urologist-andrologist 1st category Petr Viktorovich
- 44322
- Update date: December 2019
Various laboratory methods are used to diagnose prostatitis.
Urinalysis for prostatitis allows you to determine the very fact of the presence of an inflammatory process and identify calcifications in the prostate gland.
This analysis is not the most informative, but is included in the list of mandatory ones due to the quick results and affordable cost.
Preparing to submit material
Urine is taken only early in the morning, during the first urination
Before taking a urine test for prostatitis, you need to prepare so as not to get a false result. First of all, a gentle diet is recommended, which begins 3-4 days before the test.
True, this point often has to be skipped, since a urine test is most often an examination of the preliminary diagnosis of prostatitis, so there is no time left for thorough preparation.
If the doctor has prescribed a test for tomorrow, it is enough to simply limit your food intake in the evening, excluding meat products, spices, and caffeine-containing drinks from your diet.
Before submitting the material for analysis, you must stop taking all medications that affect laboratory parameters. These include:
- vitamins;
- diuretics;
- antibiotics;
- alpha-blockers;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- some types of analgesics.
As a rule, taking antibiotics should not be skipped, so a man should inform his doctor about all the medications he is taking during the current period.
On the eve of the test, you should limit physical activity and abstain from sexual intercourse. This can lead to changes in the composition of urine, which will distort the test results.
Important! Before collecting material for analysis, you should not drink alcohol.
Any medications used to treat kidney disease may also negatively affect your results. If a man took such medications in the last 10 days before the test, he should definitely tell the doctor.
Urine must be collected in a sterile container. You should purchase a special container with a lid in advance from your nearest pharmacy. Collecting material in a non-sterile cup can lead to foreign components entering the urine, which leads to false results, and then the test will have to be retaken.
How to collect urine?
Urine to study its composition is collected in the morning, on an empty stomach. This should be the first portion of urine after sleep. However, it is necessary to collect the middle part of the fluid that has accumulated in the bladder during the night's rest. That is, a man must go to the restroom, start urinating, wait a few seconds and only then replace the container. For analysis, it is enough to collect 30-50 ml of liquid.
Before collecting the material, it is imperative to toilet the genitals. It is important to thoroughly wash the head of the penis so that mucous secretions do not get into the container along with urine.
It is important to refrain from sexual intercourse or masturbation the day before, as ejaculate will remain in the urethra. If it gets into the material collected for analysis, there is a risk of distorting the results.
Types of analyzes
What tests should be done - the attending physician prescribes himself, based on the symptomatic picture of the disease
There are three types of analysis - general, bacteriological and cytological. Since urine analysis is not reliable enough for diagnosing prostatitis (accuracy does not exceed 65%), three tests are usually prescribed at once.
General analysis is the simplest and fastest. It allows you to obtain only general characteristics - the presence of leukocytes and protein in the urine. In general, such indicators may indicate a number of different diseases of the genitourinary system, including cystitis and nephritis, and therefore are not reliable.
Bacteriological research
Bacterial culture of urine makes it possible to identify the infectious pathogen, but only in the case of acute inflammation, in which pathogenic microorganisms remain in the urethra. In addition, this method is used to diagnose urethroprostatitis.
Normally, urine is a sterile liquid, so in the presence of infectious inflammation with prostatitis, the analysis can detect infection. As a rule, sexually transmitted infections, in particular gonococci, are detected in urine.
The disadvantage of bacteriological research is that the analysis takes a rather long time. The material must be placed in a special nutrient medium and left for several days, waiting for pathogenic agents to appear. If a man neglects personal hygiene before collecting urine, such an analysis may show false results, and therefore its results are double-checked by other methods.
Cytological examination
Cytology involves a microscopic examination of the obtained material for the presence of epithelial particles that would indicate malignant processes in the prostate gland. Such urine tests for chronic prostatitis are necessary for the preliminary diagnosis of oncopathology in the prostate, since advanced inflammation often turns into cancer.
General analysis
The first examination that is carried out in the laboratory is a general urine test. It is done very quickly, so results can be obtained on the day of delivery. In this case, a general analysis makes it possible to establish the very fact of the presence of inflammation, which is the basis for prescribing further examinations in order to clarify the nature of the inflammatory process.
What additional examinations may be needed?
If necessary, an ultrasound examination of the prostate gland may be prescribed
In general, a urine test is not informative enough to diagnose prostatitis. Its advantage lies in the quick results and ease of implementation.
Indeed, in order to get preliminary results of the study, it is enough to give urine in the morning and receive a transcript of the analysis in your hands a few hours later.
These results are the basis for prescribing additional examinations:
- The presence of microorganisms in the urine indicates an extensive infectious inflammatory process and is the basis for prescribing bacterial culture of prostate secretions.
- If epithelial cells are detected during a cytological examination, it is necessary to donate blood to determine the PSA level to exclude oncology.
- If the results of other examinations are insufficiently informative, a semen analysis is prescribed.
In addition, other diagnostic measures are needed - TRUS of the prostate, examination of the bladder, rectal examination of the organ, ultrasound or MRI of the testicles. This allows us to exclude other diseases of the genitourinary system.
Bacterial culture of prostate secretion
Examination of prostate secretions is one of the main methods for diagnosing prostatitis. It allows you to determine:
- type of inflammation (infectious or non-infectious);
- form of the disease (acute or chronic);
- pathogen;
- pathogen sensitivity to antibiotics;
- causes of infertility.
In addition to diagnosing prostatitis, this examination allows you to determine infertility in men by the number of lecithin grains in the prostate secretion. These protein compounds ensure sperm motility after ejaculation. A reduction in their number is observed with congestive prostatitis; the complete absence of lecithin grains in the prostate secretion indicates infertility.
To take material for analysis, a prostate massage is necessary. Before the procedure, the man must do a cleansing enema.
The massage is carried out as follows. The patient lies on his side with his legs pressed to his chest, or leans on his knees and elbows.
The doctor inserts a finger into the anus, feels the septum separating the prostate from the rectum, and stimulates the organ with stroking.
After a few minutes of such irritation, the prostate contracts and a small amount of white fluid is released from the urethra, which is immediately collected in a sterile container. The whole procedure takes no more than three minutes.
The analysis itself takes quite a long time, since it is necessary to “grow” a colony of microorganisms present in the material by placing the prostate secretion in a nutrient medium for 5-7 days. However, a preliminary assessment is carried out by the color, consistency and amount of prostate secretion, since these parameters are different for infectious and non-infectious inflammation.
Before taking the analysis you must:
- refrain from ejaculation for three days;
- stop drinking alcohol;
- stop taking medications;
- stick to a bland diet.
Based on the results of the analysis, it is usually possible to immediately select the optimal treatment regimen.
PSA test
Before the procedure, you must abstain from intimate life for a while.
PSA is a specific antigen produced by the prostate gland only in cases of serious pathologies. Normally, in men the level of this substance is very low; it increases slightly with adenoma, and increases sharply with cancer.
Diagnosis of prostatitis by PSA level is not carried out, since the amount of antigen increases slightly in the presence of inflammation in the prostate, which makes this analysis uninformative.
Blood is given on an empty stomach to determine this antigen. Before taking the analysis you should:
- minimize physical activity;
- exclude meat from the diet;
- abstain from sex for five days;
- stop taking certain medications.
The man receives the results of the analysis quickly. This examination is recommended annually for all men over 60 years of age who are at risk of developing prostate cancer. Also, a PSA test is often prescribed to monitor the progression of prostate adenoma.
When is a semen analysis prescribed?
A spermogram, or ejaculate analysis, is not included in the list of mandatory examinations for prostatitis. This examination is prescribed in two cases: low information content of other tests and suspicion of infertility. Analysis of ejaculate allows us to identify pathological changes in the functioning of the reproductive system that have arisen against the background of chronic prostatitis.
Before taking the test, you should abstain from sexual activity for 4 days. The material is collected directly in the laboratory through self-stimulation of the patient. Seminal fluid must be collected in a sterile container, having previously eliminated all factors that could potentially distort the results of the analysis.
A few days before donating ejaculate, you should stop drinking alcoholic beverages and stop or at least reduce the frequency of smoking.
Interpretation of urine test results
You can always find out what the tests done mean from your attending physician - a urologist.
The main indicators that you should pay attention to as a result of a urine test:
- presence of protein;
- leukocyte count;
- presence of red blood cells;
- presence of phosphates;
- epithelial cells;
- general sterility.
Protein in the urine is an alarming signal indicating a malfunction of the body. This parameter is not always a typical sign of prostatitis, as it may indicate acidosis, pyelonephritis, or inflammation of the bladder. The presence of protein necessitates additional examinations.
White blood cells indicate inflammation. Normally there are less than three of them in the field of view of the microscope. An increase in leukocytes is a sign of prostatitis.
Red blood cells in the urine are a kind of marker of calculous prostatitis. The presence of such cells can also be a sign of cancer. The presence of red blood cells and epithelium in the analysis is a reason for conducting a PSA test.
If the urine is not sterile, it is necessary to additionally make a smear from the urethra to rule out urethritis, check the bladder to rule out cystitis, and take a bacterial test of prostate secretions.
Source: https://muzhik.guru/prostatit/analiz-mochi-pri-prostatite/
Urinalysis for prostatitis: study, chronic, men
Among the many diagnostic methods that are mandatory and help to accurately determine the disease, urine testing is of no small importance. For testing to be reliable, you must adhere to the rules regarding preparation for donating biological fluid. Urinalysis for prostatitis comes in several types and is interpreted taking into account certain indicators.
Referral for testing
Inflammation of the prostate may initially occur without pronounced signs, and only a timely urine test can confirm the presence of pathology.
Urine tests for chronic prostatitis are prescribed to patients with:
- frequent and intermittent emptying of the bladder;
- painful discomfort in the perineum and genital area;
- weakening libido and deterioration of erectile function;
- urinary retention;
- rise in temperature (in acute cases);
- discharge of pus from the urethra.
The disease causes some neurological disorders. In particular, due to frequent urges to go to the toilet at night, a man does not get enough sleep, becomes irritable, depressed and very tired. When urinating, you may notice a change in the color of the urine.
The appearance of purulent or bloody contents in it should alert you.
Particular discomfort is caused by pain that radiates, for example, to the rectum. Pain is often felt during bowel movements, which subsequently provokes problems with bowel movements. In turn, constipation increases the inflammatory process in the prostate.
If you notice any of the above symptoms, it is important not to delay examination by a urologist.
There is also a disorder of sexual function. A man experiences weakening erection and early ejaculation. If treatment is not started, the disease can result in impotence.
To diagnose prostatitis and select effective medications, your doctor will definitely advise you to submit your urine for laboratory diagnostics.
Preparing for the test
In order for these studies to be as accurate as possible, you should adhere to the conditions of the preparatory stage:
- The day before the test, it is prohibited to take medications or drink alcohol.
- You should refrain from serious physical activity.
- It is better to temporarily exclude spicy, salty and fatty foods from the menu. It is not advisable to increase or decrease the amount of liquid you drink per day.
- You should prepare a container for urine - glass or plastic.
It is also necessary to pay attention to water procedures.
Collecting urine for analysis
The optimal time for collecting biomaterial is early in the morning before breakfast. To prevent the test results from being distorted, it is better to refrain from sexual arousal followed by ejaculation before the procedure.
The first drops of urine must be poured into the toilet, and the remaining amount must be collected in a prepared container. It is advisable that the genital organ does not touch the container, which may affect the chemical composition of urine. In general, 5-6 ml is enough for the study.
After collecting biological fluid, it must be delivered to the laboratory as soon as possible. If the patient brings the container with the contents after 3 or more hours, errors in the test data cannot be ruled out.
Types of urine tests to detect prostatitis
Urine examination is a universal diagnostic procedure that allows one to detect pathological processes and differentiate diseases.
For inflammation of the prostate gland, there are 3 types of analysis:
- general – shows changes in physical and chemical parameters;
- cytological – confirms or denies the presence of atypical cells;
- bacteriological – makes it possible to identify pathogenic microorganisms.
Laboratory tests are especially effective at the initial stage, when symptoms are mild.
Urine color for prostatitis
If the man is healthy, the urine will be bright yellow and transparent.
Any changes in color may indicate an inflammatory process in the prostate gland:
- Prostatitis is accompanied by darkening of the urine due to the appearance of red blood cells in it. However, the color also changes due to treatment with drugs or consumption of certain foods.
- If the urine turns pink, which is caused by fresh blood entering it, there may be a serious pathology of the genitourinary organs.
- Red color indicates acute prostatitis, pyelonephritis or renal failure.
- In the purulent form of the disease, white threads are visible in the urine, which slowly precipitate. Immediate assistance is required for a patient with manifestations in the form of white thread-like discharge, increased temperature and pain when emptying the bladder.
- Urine with whitish flakes indicates cystitis, acute prostatitis, pyelonephritis. Flakes can be detected in pathologies of a purulent nature.
- Chronic prostatitis can be recognized by sticky urine with a large amount of cloudy sediment. In addition, it can foam, which sometimes indicates oncology.
Normally, urine does not have a strong odor. If heterogeneous inclusions are observed in it over a long period, and its color changes, you should definitely see a urologist.
General tests
The main goal of the study is to determine the presence of pathology by changes in the color and physicochemical properties of the sample. In particular, the density of the biomaterial and the level of acidity are being studied.
In addition, the content is analyzed:
- leukocytes;
- red blood cells;
- squirrel;
- salt crystals.
If an error was accidentally made during testing, there is a need for re-testing.
Bacteriological analysis
Helps determine the catalyst of the inflammatory process in diseases of an infectious nature. Thanks to bacterial culture, it is possible to identify a pathogen that is sexually transmitted, which allows you to create the most effective treatment plan.
In a healthy body, urine is completely sterile. Infectious prostatitis is diagnosed if pathogenic microorganisms are present in the urine.
Using bacteriological analysis, you can confirm or exclude the infectious nature of the disease. The final decision is made after receiving the instrumental examination data.
Cytological analysis
The need for it is explained by the fact that prostatitis and prostate cancer have similar symptoms. Urine cytology is an opportunity to identify or refute the presence of atypical cells.
If epithelial particles are not detected in the urine, oncology is excluded. The main thing is that the sample is examined by a competent specialist.
Interpretation of urine test results
At the end of the test, the doctor interprets the data in accordance with established standards.
The results of a general urine test for prostatitis may be as follows:
- The presence of red blood cells in urine makes it cloudy. If there is a precipitate in the form of white threads, the inflammation of the gland has become purulent.
- Studying the density of the sample is necessary in order to exclude other diseases. A decrease in the coefficient indicates the development of renal failure, and an increase indicates a lack of fluid.
- Abnormal acidity does not always indicate prostate problems.
If protein is found in the urine, prostatitis is only one of the reasons. The disease is also accompanied by the appearance in urine of a significant amount of red blood cells, leukocytes and phosphates.
Even if there are abnormalities in the general analysis, it is too early to say that the patient has problems with the prostate. Changes in indicators must be persistent, which often requires repeated research.
The reliability of cytological and bacteriological analyzes largely depends on the correct preparation of the subject for the collection of biomaterial. The container for urine must be sterile, and the presence of detergent particles is unacceptable.
If the urine does not contain pathogens or epithelial cells, infectious prostatitis or an oncological process is completely excluded.
Using various types of urine tests, it is possible to determine the presence of an inflammatory process in the gland.
The patient will need immediate help if bloody discharge is detected in the urine. This phenomenon is called hematuria. If only hemoglobin is detected, then we are talking about hemoglobinuria.
There are micro- and macrohematuria. The essence of the first type is that blood particles can be detected using microscopic examination. In the second case, the changes are visible without any devices. The urine turns red and sometimes has a rusty tint.
Hematuria is provoked by:
- inflammatory process in the prostate gland;
- prostate abscess, developing independently or against the background of acute prostatitis;
- malignant neoplasm;
- formation of stones in the organs of the genitourinary system;
- inflammation of the bladder mucosa (cystitis).
After reviewing the results of the study, the urologist begins to draw up a treatment course.
The main thing is not to delay contacting a doctor, but to prepare for the collection of biomaterial in compliance with the established rules. However, the final diagnosis is made only after a comprehensive examination.
Source: https://potenciya.guru/prostatit/analiz-mochi-pri-prostatite/
What will a urine test show for prostatitis?
General, cytological and bacteriological analysis of urine for prostatitis is included in the list of mandatory diagnostic procedures. The results help differentiate inflammation of the prostate gland from other disorders of the genitourinary system.
What kind of urine is there for inflammation of the prostate?
If we look at the anatomical features of a man’s structure, we can see that the urethral canal runs inside the prostate gland. Any disturbances in tissue function lead to changes in urine: its composition, type, color, density, etc.
There are several characteristic signs indicating the presence of an inflammatory process of the genitourinary system and prostate:
- Orange urine is normally a bright yellow fluid. The appearance of red blood cells causes the urine to darken. Your urine may also turn orange after taking medications or certain foods.
- Pink urine indicates the presence of hematuria and the presence of fresh blood in the urine. An unfavorable sign indicating serious disorders of the genitourinary system, in particular prostate cancer.
- Red urine is a characteristic manifestation of acute prostatitis, as well as other inflammations of the genitourinary system. A change in the color of urine indicates the presence of stagnant blood, due to injury to the prostate or the development of renal failure and pyelonephritis - satellites of prostatitis.
- White threads and clots in the urine are a sign of the development of purulent prostatitis. The threads gradually fall into sediment. One of the most characteristic symptoms of purulent prostatitis. If an increase in temperature or pain during urination is diagnosed, you should immediately consult a doctor. Persistent thread-like discharge indicates serious clinical changes: the spread of purulent sacs or the formation of an abscess.
- Whitish flakes are nothing more than protein that appears in urine. White flakes indicate problems with the kidneys and bladder. Changes in the structure indicate cystitis and pyelonephritis, which accompany acute prostatitis. Flakes are also diagnosed with a purulent disease.
- Sticky urine is a characteristic symptom of immunodeficiency conditions. Changes indicate chronic prostatitis, cancer and any other disorders associated with inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system. The density of urine is greatly increased. A large amount of cloudy sediment falls. In some forms of chronic prostatitis and cancer, the urine foams.
Normally, a man should have yellow urine with a clear consistency and no strong unpleasant odors. The structure is influenced by several factors. Visible changes in the urine are provoked by medications, food, and lack of fluid in the body.
If heterogeneous inclusions continue to remain in the outgoing urine, the color changes over a long period of time - this is a reason to consult a doctor for additional diagnosis of the condition. Urine with prostatitis changes, its density increases, and whitish thread-like inclusions appear. The results of the study confirm the presence of inflammatory processes in the prostate gland and urinary tract.
Is it possible to determine prostatitis using a urine test?
Collecting urine for a clinical study allows one to suspect the presence of inflammatory processes at an early stage. A urine test for prostatitis shows the presence of foreign bodies (erythrocytes, leukocytes, protein), which in the normal state are completely absent or present in a minimal amount.
The changes help to conclude that tissue inflammation occurs in the urinary tract, catalyzing disruption of the basic functions of internal organs.
A urine test can determine prostatitis with an accuracy of about 60%.
In other cases, the diagnosed disorders relate to pyelonephritis, renal failure, urethritis, cystitis and other diseases.
Clinical changes in urine are not considered absolute evidence of inflammation of the prostate gland. The results obtained during laboratory tests are used in differential diagnosis using instrumental examination methods.
In addition to cytological, general and bacteriological conclusions, when interpreting the analyzes the following are taken into account:
- The physical properties of urine are data obtained from visual inspection of liquid samples.
- Daily amount of urine - after the onset of dysuric disorders, fluid loss becomes significantly more difficult. Violation of the outflow of urine under unfavorable circumstances leads to a complete cessation of urination.
- Existing signs and symptoms of the disease - if physiological indicators of urine indicate the presence of inflammation and at the same time a man experiences pain when going to the toilet, pain during sex and dysuric disorders, the likelihood of prostatitis increases to 80%.
A urine test alone cannot diagnose prostatitis. But tests can detect inflammation at an early stage and determine the presence of an infectious agent, which is extremely important for making a diagnosis and prescribing adequate therapy.
Types of urine tests to detect prostatitis
To detect inflammation of prostate tissue, several types of examination of urine samples are prescribed. A comprehensive analysis is preferred, since it reveals general changes in the structure of urine, disorders at the cellular level, and the presence of pathogenic microorganisms. As a rule, the following types of laboratory tests are prescribed:
- General clinical analysis.
- Cytological examination.
- Taking samples to identify infectious and bacteriological factors.
To clarify the results with a significantly increased volume of erythrocytes and leukocytes, additional analysis according to Nechiporenko is recommended.
The latter method of research is justified in the case of determining concomitant inflammatory processes: urethritis, cystitis, etc.
General analysis of urine for prostatitis
The main goal is to identify physical and chemical changes in the structure and color of samples taken for analysis. If prostatitis is suspected, a general clinical analysis is required.
During laboratory tests, pay attention to the following:
- Appearance - changes in color and odor, increase in density and the presence of foreign inclusions are taken into account.
- Physico-chemical properties - the acidity of urine is normally 5-7 pH. An increase in values indicates the presence of prostatitis or any other inflammatory process. Density does not play a role in determining the disease, but helps to exclude the presence of related pathologies.
- Biochemical urine analysis - during clinical studies, the number of leukocytes, red blood cells, oxalates and protein is determined. Indicators help to suspect cancer or calculous, acute and infectious prostatitis.
A general urine test gives an idea of the patient’s condition and the presence of inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system. Clinical studies are included in a number of mandatory diagnostic procedures.
Bad urine with prostatitis helps diagnose a form of inflammation. Based on fluid samples, calculous, chronic, purulent and acute processes are identified.
Cytological examination of urine
Chronic prostatitis can develop into prostate cancer. The symptoms of inflammation of the prostate gland and a malignant tumor are identical. Laboratory cytology tests will help differentiate cancer.
Microscopy of urine in oncology reveals particles of epithelium. If there is no malignancy, tissue microcells are not detected in urine during examination.
Together with prostate biopsy, urine cytology is necessary for early detection of cancer
Bacteriological diagnosis of urine
Bacterial culture is necessary to determine the catalyst for inflammation in acute infectious diseases. Prostatitis can be caused by pathogenic microorganisms and candida fungi.
A urine culture test makes it possible to identify a sexually transmitted infection and select the most effective antibacterial therapy in each specific case. Normally, human urine is completely sterile.
If a tank examination reveals traces of fungi or pathogenic agents, infectious prostatitis is diagnosed. In the absence of STIs or fungi, a chronic or acute form of inflammation is diagnosed.
A bacteriological analysis of urine for inflammation of the prostate can show the source of prostatitis or completely exclude an infectious factor. For an accurate diagnosis, you will additionally need to conduct an instrumental study: ultrasound or TRUS, MRI or PET-CT.
How to take a urine test to diagnose prostatitis
Urine is collected for testing using 3-4 glass samples. Each technique has its own characteristics and differences related to information content and accuracy:
- 3-cup sample - morning urine is collected. The vessels are distributed in order with numbers from 1 to 3 pasted on. Urine is collected in each container in turn. A microscopic examination is carried out. The advantage of the three-glass test is the ability to diagnose the localization of the inflammatory process.
- 4-cup sample - in this case, one portion with prostate secretion is added to three portions of collected urine. The results of the study of a four-glass sample are more informative than with a three-glass urine collection.
When diagnosing prostatitis, a 4-glass urine test is usually prescribed. Sample collection is carried out in four stages:
- 20-30 ml of urine is collected in the first container.
- Part of the portion is flushed down the toilet, and the remainder in a volume of 10-15 ml is filled into a second container.
- Now a few drops of prostate juice are taken from the patient.
- About 15 ml of prostatic urine is collected in the last container.
All four stages generally require about 20 minutes of time and do not cause discomfort in the patient, except in cases of acute inflammation, when the collection of prostate juice may accompany pain.
How to properly collect urine
Often erroneous results are associated with incorrect submission of urine samples for testing. There are several basic recommendations that increase the accuracy of diagnosis:
- The first morning urine test is suitable for research. Accurate results are provided by urine remaining in the bladder for about 5 hours. You should not urinate before taking tests. Diagnostic results can be affected by ejaculation during sexual intercourse and masturbation.
- Containers that have been tested for sterility are suitable for collecting samples.
- Before taking a four-cup sample, it is important to rinse the perineum, penis, and towards the anus. Dry the skin with a towel.
- It is correct to give urine for analysis after stopping taking uroseptics and antibiotics. Drinking alcohol and changing eating habits will affect the results.
A three-glass urine sample according to Nechiporenko cannot provide sufficient information for inflammation of the prostate gland, for this reason it is rarely used, only in cases where prostatitis in any form is excluded.
Results of urine analysis for prostatitis
The data obtained from urine testing is difficult to interpret. Deciphering tests requires the experience and professionalism of a urologist. Comparison of the results obtained with the symptoms and manifestations present in the patient.
Some data indicated in the analysis results can be deciphered independently:
- Protein is normally completely absent from urine. Protein in the urine with prostatitis is in proportions above 0.033 g/l. The result does not always indicate the presence of inflammation of the prostate gland. Increased protein in the urine is diagnosed with cystitis, nephritis, urethritis and renal failure.
- Red blood cells in the urine - an increased volume indicates calculous prostatitis and prostate cancer. The normal number of red blood cells is their complete absence during sample examination or the maximum presence of 1 cell.
- Leukocytes - in a normal state, about 3 units are diagnosed. Leukocytes in urine with prostatitis increase above the established values. Particles enter urine from the bloodstream due to the inflammatory process. An elevated white blood cell count indicates prostatitis or cancer.
- Phosphates in the urine are diagnosed with calculous prostatitis.
Deviations in the overall analysis are not a cause for concern. Many factors influence the results. You can talk about suspected prostatitis after re-examining urine samples.
Persistent changes in indicators confirm the development of the inflammatory process in the human genitourinary system.
Signs of prostatitis in urine tests help to suggest the presence of inflammation. It is impossible to draw conclusions based only on urine samples. To clarify the diagnosis, additional biochemical and instrumental studies will be required.
Source: https://ponchikov.net/health/urologiya/692-analiz-mochi-pri-prostatite.html