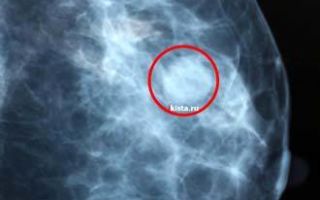
A common disease that requires special attention is bilateral fibrocystic mastopathy (BCM). It is known that this pathology often precedes another more serious disease - breast cancer.
For this reason, treatment for fibrocystic mastopathy should be started as soon as possible.
Reasons for the development of mastopathy
The main reason for the development of FCM is a hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body. Estradiol and progesterone have the greatest impact on women's health. A disruption in hormones that causes the development of mastopathy can occur for the following reasons:
- Early puberty. If the hormonal levels are updated too quickly, then the body does not have time to adapt to such changes. This can provoke the development of pathology in the structure of the mammary gland tissue.
- Late menopause under the influence of hormonal therapy or due to a hereditary factor.
- Breast injuries. Long lactation Stress
- No pregnancies.
- Constant stress.
- Absence or short period of lactation.
- Frequent abortions can cause sudden changes in hormones.
- Age after 40 years.
- Diseases associated with metabolic disorders: diabetes mellitus, obesity, endemic goiter.
- Malfunctions of the endocrine organs - hyper- or hypothyroidism, thyrotoxicosis.
- Liver dysfunction.
- Ovarian diseases of an inflammatory nature, for example adnexitis.
- Uncontrolled use of drugs containing hormones, including contraceptives.
- Bad habits. Bad habits Taking medications
- Hereditary factor.
- Bad ecology.
- Diseases of the genitourinary system leading to reproductive dysfunction.
The mammary gland is an organ that is very dependent on the cyclical physiological processes occurring in the female body. Breasts always react to any changes in hormonal levels.
Even the emotions that a woman experiences can affect the condition of this organ. The appearance of a problem in an emotional background can easily provoke the development of a neoplasm in the mammary gland, in particular fibrocystic mastopathy.
Usually, in the presence of this pathology, the amount of estrogen in the body increases significantly, while at the same time the level of progesterone decreases.
It has been noted that with this type of mastopathy there is often an increase in the concentration of prolactin.
This hormone is responsible for the onset of proliferative processes, that is, it promotes the pathological proliferation of tissue in the mammary gland and the expansion of the milk ducts.
Signs of development of FCM
The main sign of the presence of the disease is pain. However, her character may be different. Unpleasant sensations can be permanent or in accordance with the phase of the menstrual cycle, usually in the second half.
Often, fibrocystic mastopathy begins to manifest itself in the form of chest pain before the next period, and women mistake it for PMS. In this case, the following accompanying symptoms should alert you:
- swelling, swelling of the mammary gland; Breast enlargement Breast swelling
- the breasts increase in size, the underwear begins to press;
- the mammary gland is painful to touch.
Signs indicate the presence of mastodynia. If you do not take active action at this stage, then over time the pain becomes more intense and begins to radiate to the shoulder, arm or armpit area. In this case, unpleasant sensations are constantly present and do not depend on the phase of the menstrual cycle.
If, in the presence of all these symptoms, a nodular compaction is detected in the chest during examination, then it is more likely that fibrocystic mastopathy occurs.
- In the diffuse form of the disease, the detected neoplasms will be small in size, but there will be many of them. A characteristic feature is also symmetry; there are seals in both glands.
- Before the start of the critical days, neoplasms can increase in size, and after they end, they can completely disappear. In the nodular form of FCM, the nodules are most often clearly defined, not connected to the skin, but located singly. In some women, the disease manifests itself in a mixed form.
- The appearance of the nipples may change; they often become inverted. Sometimes cracks appear on them. Some patients may experience discharge from the nipples. At the beginning of the disease they are usually clear or milky. But if the pathology is not treated, then over time they acquire a brown and even greenish tint.
- Another characteristic but rare sign of fibrocystic mastopathy is enlarged lymph nodes in the armpits.
FCM forms
Fibrocystic mastopathy can manifest itself in a moderate and severe diffuse form. According to the official classification, there are the following types:
- with a clear predominance of the ferrous component;
- with a significant predominance of the fibrous component;
- with a predominance of the cystic component;
- diffuse mastopathy in mixed form.
Bilateral mastopathy, in which the glandular component significantly predominates, is most often detected in young girls and is characterized by the presence of uniform compaction. The same form often occurs in women in the first trimester of pregnancy.
If the fibrous component predominates, then pain in the mammary gland is pronounced. Upon palpation, a solid compaction can be determined. This form of mastopathy provokes the development of an inflammatory process in the interlobular connective tissues, which causes the milk ducts to significantly narrow.
If a clear predominance of the cystic component is revealed, then upon examination by a specialist, numerous formations with clear contours will most likely be identified. The seals have a pliable, soft consistency.
When a mixed form of the disease is detected, hyperplasia of the mammary gland lobules with sclerosis of the connective tissue is observed. Often this pathology leads to rapid atrophy of some alveoli. The milk ducts are unnaturally expanded. The disease provokes the formation of a large number of cysts. These are neoplasms containing secretions.
Diagnostics
The following diagnostic methods help to identify fibrocystic mastopathy:
- examination by a doctor with palpation of the mammary glands;
- An ultrasound will help not only determine the presence of formations, but also find out their parameters, as well as their quantity;
- biopsy - collection of biological material from an area with pathology for subsequent examination;
- Mammography in two projections will help distinguish nodular mastopathy from cancer; Radiothermometry Ductography
- cytological examination is used if fluid is released from the nipples;
- radiothermometry helps detect rapidly growing tumors;
- ductography is an x-ray examination that involves the injection of a contrast agent into the milk ducts.
To make a more accurate diagnosis, a specialist may conduct additional studies. Tests are prescribed for hormones (gonads and thyroid), cytology and histology.
Treatment of fibrocystic mastopathy
To eliminate the disease, conservative and surgical treatment methods are used. When treating nodular and diffuse forms, various techniques are used.
When treating fibrocystic mastopathy, the main emphasis is on stabilizing hormonal levels. The same goal is pursued by therapy for the diffuse type of the disease. With the nodular type of mastopathy, surgical intervention is most often performed.
Conservative treatment involves the use of the following methods:
- taking hormonal medications;
- special diet;
- folk remedies.
When following a diet for mastopathy, you should avoid caffeine-containing foods and drinks. It is recommended to increase the consumption of fresh vegetables and fruits, bran and reduce the amount of fat. It is also necessary to give up bad habits - smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
Folk remedies Diet
It is useful to exercise to normalize weight and eliminate stress. It is recommended to take vitamins, especially E, A, C and group B.
For non-hormonal therapy, the following is also indicated:
- drugs that affect the central nervous system - antipsychotics, sedatives and tranquilizers;
- immunostimulants;
- homeopathic remedies and herbal remedies;
- NSAIDs;
- iodine preparations;
- drugs for enzyme therapy.
In the treatment of this form of mastopathy, physiotherapeutic procedures are used: electrophoresis with potassium iodide, magnetic and laser therapy.
Sometimes you cannot do without taking hormones - progestogens, antiestrogens and androgens. Drugs that inhibit the production of prolactin are also used.
Progestogens can eliminate the effects of excess estrogen, so they are an ideal solution to this problem. They influence the very mechanism of the appearance of bilateral mastopathy, preventing its development.
There is no specific regimen for taking these drugs. In each specific case, the doctor develops a specific treatment plan based on research and analysis data.
Fibrocystic mastopathy - video
Source: https://mastopatiya.su/klassifikacii/dvuxstoronnyaya-fibrozno-kistoznaya-mastopatiya.html
Causes of diffuse mastopathy, its symptoms and treatment
Frequently changing hormonal levels in women lead to the development of diffuse formations in the breasts. Connective and epithelial tissues change their ratio, the structure of mammary gland cells is disrupted. Diffuse mastopathy (DM) causes discomfort and pain; when the nipple is compressed, there is pathological discharge. The danger of the disease lies in the risk of oncology developing in its place.
What is diffuse FCM?
Benign dishormonal changes lead to the occurrence of diffuse mastopathy, code N.60.1 according to ICD-10. The mammary gland contains 3 types of tissue: adipose, connective (stroma), glandular (parenchyma).
When a woman’s body is healthy, their ratio is maintained in constant balance.
If one or two types of tissue predominate over the third, then a pathology is diagnosed - mastopathy, fibrocystic disease or benign mammary dysplasia.
When changes in the glands are observed in one place (focal in nature), then the type of pathology is nodular. Diffuse FCM spreads throughout the mammary gland. Bilateral or unilateral mastopathy occurs in the presence of two forms of the disease.
Fibrocystic breast disease is observed by surgeons, oncologists, gynecologists, and mammologists. Methods and methods of treatment depend on the type of mastopathy (diffuse, nodular or mixed). The doctor may prescribe a complex of medications or surgical intervention (for nodular form) followed by hormonal therapy.
Previously, of the patients suffering from mastopathy, 30-70% were women 35-50 years old, 75-95% were representatives of gynecological diseases. Over the past 10-20 years, pathology has become increasingly common in adolescents and women after menopause.
Causes
The reproductive organs, including the mammary glands, function and develop under the control of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian system. Changes in its work occur during puberty, and cyclical processes occur during childbearing years.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the changes in the female body are significant. They occur due to the influence of hormones of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland, hypothalamus, pancreas, adrenal glands and ovaries.
If for any reason the functioning of various parts of the neuroendocrine system is disrupted, a hormonal imbalance occurs. Against this background, mastopathy of any form develops.
The causes or factors that provoke hormone imbalance are considered to be:
- Heredity. The presence of malignant or benign diseases in blood relatives on the maternal side. Stress and depression.
- Overstrain at work, family/work conflicts, poor personal life.
- Diseases of the neuroendocrine system. Functional circulatory disorders of the brain, slow metabolism, diabetes, tumors of hormone-producing organs.
- Failures of reproductive functions. Frequent pregnancies, vacuums, abortions, long-term lactation. As well as IVF, gynecological diseases, irregular sex.
- Cholecystitis, liver and gastrointestinal tract damage lead to a delay in the removal of excess estrogen from the body.
- Constant poisoning from alcohol and tobacco products. Taking products containing large amounts of methylxanthines - strong coffee or tea, chocolate, Coca-Cola, cocoa.
Often, the factor causing the formation of diffuse mastopathy is the earlier onset of menstruation in girls (up to 12 years of age). And also in women with late menopause.
Classification
In medicine, diffuse breast mastopathy is divided into several types, each of which has its own characteristics.
Only a specialist who has the necessary results of an additional examination can distinguish one form of pathology from another. In practice, doctors often use N.I.’s classification.
Rozhkov, consisting of 5 types of diffuse mastopathy. It is based on x-ray examination of the structures of the mammary glands.
Fibroadenomatosis with dominance of the glandular component
This form is characterized by the presence of a benign neoplasm in the breast, formed due to the proliferation of parenchyma. Both glands are affected, rarely - a certain area of one in the upper outer quadrant.
With fibroadenomatosis with a predominance of the glandular component, the woman feels swelling of the bust, pain, and hardening upon palpation. Fibroadenomatosis is more often diagnosed in the first trimester of pregnancy and in adolescents.
Mastopathy with dominance of the fibrous element
Mastopathy with a predominance of fibrous component (DFM) is a pathology in which small neoplasms from unchanged tissue are localized inside the mammary glands. They can be located at the top of the mammary glands and collect in one area.
Due to the proliferation of fibrous tissue, scars form in the connective tissue fibers, and fibrosis of tissue structures develops. Active division of stromal cells promotes the displacement of glandular cells.
As a result, the number of lobules and ducts decreases. In DFM, cells from the outer epithelial layer penetrate the milk ducts, blocking them.
This is how scar compactions of different sizes and volumes are formed, which can be clearly felt in the chest during palpation.
Sometimes scar matter transforms into cysts. The diffuse fibrous form of the disease is typical for women 35-45 years old and develops in one or two glands at the same time.
Mastopathy with a cystic element
Fibrocystic mastopathy occurs in 60% of women. A common cause is an imbalance of steroid hormones. Estradiol and progesterone act cyclically on the mammary glands.
The first, during ovulation, causes natural tissue proliferation, indicating that the body is ready for fertilization.
If conception does not occur, the concentration of progesterone in the blood increases, which slows down the growth of the glands.
With an excess of estrogen or a lack of progesterone, the tissue continues to increase, and disturbances in trophic functions and microcirculation in cells occur. Tissue fluid stagnates, forming edema - the precursors of cysts.
Sclerosing adenosis
Adenosis is characterized by the proliferation of breast tissue, the number of lobules increases, and the shape of the breast changes. This can lead to lobular or ductal carcinoma.
Despite this, adenosis is considered the simplest form of dishormonal disorders. The parenchyma remains virtually unchanged, the structures are limited, and the basement membranes remain the same.
The resulting lumps are sensitive during manual examination of the breast, and in some cases moderate pain is observed.
The initial stage of sclerosing adenosis occurs at the age of 30-40 years. There are cases of pathology being detected in elderly women and girls. Those who have had abortions and vacuums are at risk.
Mixed form
With a mixed type of mastopathy, both lumps and cysts form in the mammary glands. More often in women of childbearing age, fibrocystic mastopathy predominates. On palpation, compacted areas, small and large formations are felt.
Pathology includes signs of nodular and diffuse forms. Liquid is released from the nipples, the pain can be mild or persistent, occur on its own or only when pressing on the chest. 3-4 days before menstruation, the pain intensifies.
Symptoms and signs
Each stage of the menstrual cycle is characterized by its own signs indicating diffuse mastopathy. The main manifestations of the pathology are considered to be pain and discomfort that occur on days 14–30 of the cycle. Key features of DM:
- The size of the glands is increased.
- The bust looks swollen.
- Round and oval seals can be felt. With the onset of menstruation they disappear, and after 5-10 days they appear again.
- In the fibrocystic form, the formations roll during palpation and contain fluid inside.
- Discharge from the nipple when pressed is yellow, white, brown or mixed with blood. Green liquid indicates the presence of infection.
Every woman should listen to her body and feel her breasts on the 8-9th day of the cycle. Timely recognition of symptoms of breast diseases will facilitate treatment and maintain health. With diffuse mastopathy the following are observed:
- Before critical days - moderate pain in the mammary glands. The pain is aching, tingling, bursting. Affects the chest, neck, back, shoulders.
- Gastrointestinal disorders - bloating, gas, constipation.
- Slight dizziness, migraine-like pain.
- The nervous system becomes sensitive - excitability, fear, anxiety, and insomnia appear.
Rarely described symptoms include: irregular menstrual cycle or lasting more than 30-31 days, scanty/heavy discharge, constant fatigue. A woman may experience dull hair and dry skin.
Diagnostics
First of all, the doctor collects anamnesis and listens to the woman’s complaints. This is followed by an examination of the chest with palpation of the glands. Next, the doctor refers the patient for additional examination. This may include tests and instrumental diagnostics. This includes the following:
- Ultrasound is a safe procedure and is permitted for pregnant and lactating women.
- Mammography. The diagnostician will be able not only to see the pathology, but also to assess the condition of the affected area using a special scale: BI RADS categories 2 and 1 do not pose a danger.
- Puncture. The doctor, using a thin needle, collects biomaterial. Sends the extracted contents to the laboratory for histological examination.
- Detailed biochemical blood test. The level of sugar and enzymes produced by the liver is important.
- Blood test from a vein for hormones of the adrenal glands, thyroid glands, progesterone and estrogen levels.
If necessary, the doctor prescribes MRI and ductography. Also, for the integrity of the clinical picture, it is suggested to undergo auxiliary procedures - laser or digital mammography, and evaluate thermal radiation.
Treatment regimen
There is no general treatment regimen for diffuse mastopathy. The doctor’s task is to identify and eliminate the cause of the pathology. Sometimes conservative treatment methods are sufficient. Disciplined use of medications under the supervision of a mammologist eliminates the problem.
It is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, engage in moderate physical activity and balance your diet. Treatment with physiotherapy, dietary supplements, vitamins, and adaptogens is encouraged.
In order to increase the effectiveness of traditional therapy, related treatment with folk remedies is used. Here you need to be careful and use only healthy recipes:
- Tincture of immortelle, wormwood, or take echinacea and aloe. You can prepare it yourself or buy it at a pharmacy chain. For 1 part herb there are 10 parts 4% alcohol.
- Burdock compress. Clean sheets are applied to the chest before going to bed, duration is 1 month.
- Camphor oil. Lubricate the breasts with a small amount.
For diffuse mastopathy, surgical treatment is not used. Only in the presence of large cysts that cause pain and discomfort are they removed to avoid their degeneration into cancer.
Oral hormone-containing contraceptives are widely used, which will restore the balance of hormones in the body. Contraception can relieve symptoms and restore the menstrual cycle.
Going to solariums and saunas and using warming compresses are prohibited. To relieve symptoms, it is allowed to treat diseased areas of the breast with Progestogel gel on a hormonal basis.
In addition, Duphaston, Zoladex, Tamoxifen, Bromocriptine or their analogues will help cure DM.
At the late stage of cystic mastopathy, Wobenzym is prescribed, an enzyme group drug that strengthens the walls of blood vessels and reduces swelling. It has immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties.
Forecast
Diffuse mastopathy is not very dangerous if it is diagnosed early. The pathology can be successfully treated with drug therapy, has a high cure rate, and the neoplasms are benign.
However, if not treated in a timely manner, an advanced form of mastopathy tends to transform into an oncological tumor.
Periodic visits to a mammologist increase the chances of recovery, especially for women with a cystic form of the disease.
Prevention
A consultation with a mammologist is required once a year. Every month, on the 8th–9th day of the cycle, the woman herself is able to palpate the breasts. So at an early stage it is easy to detect changes in the breast in the form of small lumps and begin earlier treatment. Doctors advise against going through with abortion. This is severe stress for the body, and the result is a high risk of developing DM.
The list of preventive measures includes taking care of your bust. Injuries, bruises, wearing a tight, pressing bra are provocateurs of breast diseases. During lactation, the formation of cracked nipples, stagnation of milk, and poor hygiene should not be allowed.
Source: https://mammolog.guru/zabolevaniya-grudi/mastopatiya/diffuznaya.html
Diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy: symptoms, treatment
Changes in hormonal levels can provoke the development of diffuse changes in the mammary glands in a woman. As a result, the normal ratio of epithelial and connective tissue elements is disrupted. The disease causes soreness of the mammary glands, the appearance of discharge from the nipples, reminiscent of colostrum (secretion of the mammary glands). These symptoms cause a woman considerable discomfort, so it is worth understanding what diffuse mastopathy is, what its manifestations are and methods of treatment.
Classification of the disease
Doctors distinguish 2 degrees of pathology:
- Diffuse fibrous mastopathy. The disease leads to the replacement of epithelial structures with connective tissue. The pathological process can be one- or two-sided. Pathology provokes the development of dysplasia, scarring, and the appearance of round or oval elastic seals. The disease is easily amenable to drug therapy, so a complete cure is possible.
- Diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy (dfcm). The disease often develops against the background of menstrual irregularities and lack of ovulation. What is diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy? Pathology leads to the proliferation of glandular lobules with the formation of compactions with clear boundaries. The neoplasms are mobile upon palpation and gradually increase in size.
- fibroadenosis (diffuse fibrosis). This type is characterized by a predominance of fibrous changes;
- fibrocystic disease This is cystic mastopathy with a predominance of cavities filled with fluid;
- adenosis (glandular mastopathy) – mastopathy with a predominance of the glandular component;
- sclerosing adenosis;
- a mixed form of the disease, combining signs of several types of mastopathy.
Depending on the localization of pathological formations, there is unilateral and bilateral diffuse mastopathy.
Clinical picture
The following signs of diffuse mastopathy are distinguished:
- Development of pain syndrome. The appearance of moderate pain during palpation is typical. The pain can be aching, bursting, tingling or radiating to the neck. Pain in the mammary gland is noted before the appearance of menstrual flow.
- Lumps in the mammary gland. Diffuse fibrous changes in the mammary gland provoke the appearance of round or oval-shaped lumps, which disappear by the end of menstruation. At the beginning of a new cycle, formations arise again. With diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy of the mammary glands, mobile formations filled with fluid appear.
- Swelling and increase in the volume of the mammary gland.
- Severe symptoms of premenstrual syndrome: constipation, increased gas formation, migraine-like headache, increased excitability, fear and anxiety.
- The appearance of white, yellowish or pink discharge from the nipples. If the discharge is greenish in color, then an infection may be suspected.
There are also less common symptoms of diffuse mastopathy: weight gain, prolonged menstrual cycle, dysmenorrhea (heavy discharge or menorrhagia, amenorrhea, irregular cycle), dry skin, decreased performance.
Do you use folk remedies?
Features of therapy for diffuse mastopathy
Many patients are interested in how to treat diffuse mastopathy. Therapy of the disease involves the use of conservative treatment methods (hormonal and non-hormonal drugs), traditional medicine recipes, and surgery may be prescribed for the treatment of diffuse cystic mastopathy.
Symptoms and treatment methods for breast cysts
Non-hormonal therapy
Diffuse mastopathy of the mammary glands involves the following treatment tactics:
- change in diet. If symptoms of the disease appear, you should limit your consumption of coffee, chocolate, spicy foods and cola. The listed products contain methylxanthines, which provoke the proliferation of fibrous tissue. It is recommended to introduce fiber-rich foods (fresh fruits and vegetables) into your diet. It is also required to adhere to the water regime - drink at least 1.5 liters of water or herbal tea per day;
- lifestyle change. Diffuse mastopathy of the mammary gland is a dishormonal pathology. To normalize hormonal levels, doctors recommend exercising regularly, normalizing sleep, minimizing stressful situations, maintaining personal hygiene, giving up smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs;
- taking vitamin complexes. It is recommended to take vitamins B, A, C, E, which normalize metabolic processes in the mammary glands and restore liver functionality;
- use of immunomodulators. The drugs will increase immunity and overall body resistance;
- taking homeopathic remedies. Diffuse mastopathy can be treated with drugs based on herbal components: Mastodinon, Klamin, Fitolon;
- taking hepatoprotectors. This group of drugs normalizes the functioning of the liver, where hormonal metabolism occurs. Essentiale, Legalon, Hofitol, Karsil are widely used;
- prescription of sedatives. Constant stressful situations can provoke the development of diffuse cystic mastopathy. Therefore, patients need normalization of their psycho-emotional state. It is recommended to take preparations based on hops, valerian, motherwort;
- taking diuretics. In case of severe swelling of the breast tissue against the background of diffuse cystic mastopathy, it is recommended to use mild diuretics;
- use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Medicines can effectively eliminate pain, slow down the production of substances that contribute to the growth of tumors, swelling of the mammary glands and impaired blood flow. It is recommended to take Naproxin, Acetylsalicylic acid, Indomethacin in the second half of the menstrual cycle;
- ethnoscience. Therapy involves ingesting tinctures, infusions and decoctions based on medicinal plants (horsetail, St. John's wort, string, yarrow, valerian, corn silk, nettle, eucalyptus, wormwood, celandine, bearberry, plantain). Applications, ointments and compresses for external use are also widely used;
- physiotherapeutic methods. Diffuse mastopathy of the mammary glands involves electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, and laser therapy.
Treatment of fibrocystic mastopathy with folk remedies
Use of hormonal drugs
When fibrous mastopathy is detected, normalization of hormonal levels is required. For this purpose, the following drugs are widely used:
- Gestagens (Duphaston, Utrozhestan, Norkolut, Primolut, Norethisterone). The drugs are prescribed in the second phase of the menstrual cycle.
- Prolactin synthesis inhibitors (Parlodel). Prescribed for severe hyperprolactinemia. The drug is taken from 10 to 25 days of the cycle.
For diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy in women under 35 years of age, estrogen-gestagen contraceptives (Zanina, Marvelona) are used. The drugs will normalize the luteal phase and resume ovulation.
If echo signs of diffuse fibrous mastopathy appear in patients over 45 years of age, then androgens (Methyltestosterone) or antiestrogens (Tamoxifen, Fareston) are used. If therapy for diffuse nodular mastopathy is carried out against the background of endometriosis, then Danazol is indicated.
The use of the drug leads to inhibition of the synthesis of pituitary hormones.
It is important to remember that before prescribing hormonal drugs, it is necessary to examine the patient’s hormonal status.
When is surgical treatment indicated?
If drug treatment for diffuse cystic mastopathy is ineffective for 6 months, they resort to surgical removal of the seals. The following indications for the operation are distinguished:
During surgery, the following techniques can be used:
- Sclerosis. The method involves the introduction of a sclerosing substance, which leads to the healing of defects in the mammary gland.
- Resection. The operation involves excision of the affected area. The resulting tissue is sent for histological examination to rule out breast cancer.
Forecast
Diffuse mastopathy has a positive prognosis - the pathology is easily treatable with medication. However, in advanced cases, benign tumors may degenerate into cancerous tumors. Therefore, it is important to promptly begin therapy with a qualified mammologist if cystic mastopathy of any form appears.
Prevention
Preventive measures include an annual examination by a mammologist. It is important to promptly treat any gynecological and extragenital pathologies in order to reduce the risk of developing hormonal disorders. Experts strongly recommend avoiding abortions, which are a serious stress for the body and increase the risk of developing mastopathy.
An important stage of prevention is monthly breast self-examination, which allows you to promptly identify minor lumps in the structure of the mammary gland. It is also necessary to minimize the risk of developing injuries and bruises to the chest, and give preference to comfortable bras.
Diffuse mastopathy provokes changes in the structure and functionality of the mammary gland. Therefore, when the first signs of the disease appear, you must contact a mammologist or gynecologist. This will allow the pathology to be identified in time and therapy to begin.
Source: https://ikista.ru/grud/diffuznaya-kistoznaya-mastopatiya.html
What is bilateral diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy and how is it treated?
Women of reproductive age are at risk of developing various diseases of the mammary glands. One of these is bilateral FCM - fibrocystic mastopathy. Pathology is considered benign if adequate treatment is applied to it. The disease is divided into several forms.
Symptoms and forms
FCM mastopathy occurs in 30-70% of women over the age of thirty. The disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- soreness (not in every patient);
- engorgement of the mammary glands;
- the presence of seals in several places;
- redness on the skin of the chest;
- increase in body temperature.
Forms of pathology are classified as follows:
- Diffuse - occurs in every third case. It predominantly occurs in both mammary glands. It represents the presence of fibrous or cystic components in the soft tissues. However, tumors in each mammary gland may differ in classification.
- Nodal. These include diffuse and separately fibrocystic forms. To the touch you can feel the presence of single or multiple nodules located under the skin. Less commonly, this type of pathology affects deep tissues. Occurs in one or two mammary glands at the same time.
To accurately establish the class of the disease, it is necessary to conduct a full diagnosis, determine the level of development of the pathological process and damage to soft tissues. All changes in the breasts, regardless of their shape, occur due to hormonal imbalance.
Causes of bilateral DFCM
Lack of iodine affects the functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary system and leads to mastopathy
In addition to natural age-related changes that can affect the development of pathology, there are also a lot of negative factors. As a rule, the formation of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy is preceded by a number of the following reasons.
- Endometriosis is one of the common diseases of the female genital organs. Occurs due to the inability of the body to consistently reject the overgrown endometrium in the uterus with menstruation.
- Venereal diseases. Recent infection or chronic carriage of HIV or AIDS most often becomes a prerequisite for the development of various types of mastopathy.
- Menstrual irregularities and hormonal imbalances. These could be age-related changes, as well as problems with hormones after a failed pregnancy, miscarriage or other problems with the uterus.
- Decreased frequency of intimacy. Irregular sex life affects the decreased production of the hormone estrogen. In this regard, the appearance of neoplasms in the breast is possible.
- Bad heredity. If women in the family had a predisposition to developing such diseases, the likelihood of pathology in females in the next generation increases.
- Uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives and hormone replacement therapy can also cause diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy.
- Early cessation of breastfeeding affects the development of any kind of mastopathy. It is advisable not to stop feeding for 6-12 months.
- Malfunctions of the endocrine system.
Infertility, injuries and previous surgeries can also cause neoplasms, as they cause incorrect hormone production.
The onset of pregnancy can stabilize processes in the body and spontaneously destroy tumor cells. Women who have given birth two or three times have a good chance of not encountering this disease.
Diagnosis and treatment
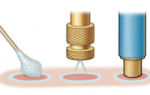
Biopsy reveals abnormal cells in breast tissue
When the first signs of the disease appear, it is necessary to undergo an urgent examination and, if possible, consult a professional. Diagnosis of pathology will consist of several stages.
- General examination, examination and palpation of the mammary glands. This procedure is performed by a mammologist. If any kind of lump is found, the patient is referred for instrumental studies.
- Ultrasound or mammography. Women under the age of 40 are advised to undergo ultrasound. Representatives of mature age are examined by mammography. After receiving the results, determine the stage of the disease using the images.
- Lab tests. A general blood and urine test is performed. It is also necessary to donate blood for tumor markers and biochemistry. This will reveal the exact clinical picture of the tumor.
- Needle biopsy. This analysis involves taking biomaterial through a special puncture. A small area of the tumor is removed. This makes it possible to determine the quality of the neoplasm.
After obtaining a general clinical picture, adequate therapy is prescribed. First of all, they try to remove the disease using conservative methods, and then, if there is no effectiveness, they may prescribe surgery.
Drug treatment
The drug reduces the effect of estrogen in diffuse mastopathy
Hormonal medications are indicated for background correction. Tamoxifen and Torymifene Citrate are sometimes prescribed to treat fibrotic dysfunction. They help reduce the effect of the hormone estrogen on the mammary glands.
Before taking medications, an additional consultation with a gynecologist and endocrinologist is prescribed.
The tablets are taken according to the regimen specified in the instructions or as individually prescribed by a specialist. As a rule, at least two tablets per day.
Patients may also be prescribed Vitamin E capsules. It is taken 1 tablet three times a day, but not less than every 4 hours.
Traditional treatment of mastopathy
Patients with diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy are treated with extreme caution using herbal remedies. Some formulations may cause an allergic reaction.
To prepare tea based on St. John's wort and valerian, take 1 tsp. dry valerian, caraway seeds, fennel and St. John's wort, as well as 0.3 tsp. table soda. Mix all these ingredients and place in a dry, dark place. Use after steaming with hot water in a ratio of 1:6. You need to drink before each meal at least three times a day.
Operation
After tumor removal, the biomaterial is sent for histological examination
Surgical intervention is necessary to remove the nodular form of mastopathy. During the operation, the affected tissue is excised. Subsequently, the biomaterial is sent for histological examination.
After surgery, the patient is required to take anti-inflammatory drugs. This ensures that no complications will arise after tumor removal.
During treatment, a woman must adhere to a diet. It is forbidden to eat food with large amounts of carbohydrates and fats. Fatty, sour, spicy and salty foods are also contraindicated.
Preventive measures
To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to monitor the state of your own hormonal levels and promptly treat pathologies associated with women's health. It is important to avoid:
- hypothermia or colds of the pelvic organs;
- any trauma to the uterus;
- hormonal imbalances:
- taking medications without consulting a doctor;
- use of hormonal contraceptives;
- increase in body weight.
Regular drinking of alcohol or smoking will sooner or later lead to problems with reproductive function. It is better to get rid of bad habits at a young age.
MFCM of both mammary glands is a common diagnosis in women of reproductive and mature age. In each individual case, individual treatment is prescribed. In the initial stage, they cope with conservative methods. An annual instrumental examination is required to check for the presence of a recurrent tumor.
Source: https://NogoStop.ru/grud/lechenie-dvustoronnej-diffuznoj-fibrozno-kistoznoj-mastopatii.html
Bilateral diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy: causes, clinical picture and diagnosis of the disease
Diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy is a benign disease of the female breast, which is characterized by a violation of tissue histology. In addition, this problem is called chronic cystic mastitis , Reclus disease, fibroadenomatosis.
Appears in 30-70% of women of reproductive age, and with certain gynecological problems, the risk reaches 90%. Often affects two mammary glands at once. The risks of the disease increase after 40-45 years.
Hide content
Causes of fibrocystic mastopathy
The main role in the onset of the disease is played by changes in the hormonal levels of the body. Under the influence of hormones, breasts change - from the onset of puberty and breast growth to the period of pregnancy and lactation.
When any hormonal imbalance occurs in such processes, dysfunction of the mammary glands and changes in tissue develop. As a result, cystic or fibrous neoplasms appear.
Important: there is a factor that increases the chances of developing the disease many times over. This is breastfeeding for less than 6 months.
Imbalance in the hormonal levels of women is caused by the following factors:
- stress;
- excessive fatigue;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- hereditary factors;
- liver diseases;
- irregular sexual relations;
- diseases in the gynecological field;
- disorders in the endocrine system.
But the most important reason for the appearance of bilateral mastopathy is an increase in estrogen levels , as well as a decrease in progesterone. Estrogen causes the growth of stroma and epithelial tissue of the ducts, and progesterone prevents this process from happening and differentiates the epithelium.
When there is not enough progesterone, swelling occurs in the breasts and connective tissue increases. Due to the proliferation of ducts, cysts appear, and prolactin (lactation hormone), increasing outside the lactation period and in the 2nd phase of the cycle, causes swelling, engorgement, and pain in the chest.
There are diseases that are combined with fibrocystic mastopathy:
- fibroids in the uterus;
- endometrial hyperplasia;
- endometriosis;
- inflammation of the uterine appendages;
- diseases of the thyroid gland and liver;
- scleropolycystic ovarian disease;
- diseases accompanied by high levels of estrogen.
Clinical picture
The clinical picture of such processes in the chest does not have pronounced symptoms . The main complaint is pain in the chest. They can be constant or periodic, intensifying during PMS or during the 2nd phase of the cycle.
What are the symptoms of bilateral diffuse FCM?
The most common symptom of bilateral fibrocystic mastopathy is the detection of a dense area of tissue upon palpation in the tissues of both mammary glands. In the 2nd phase of the cycle and before the onset of menstruation, the lump may hurt, characterized by pulling and aching pain, sometimes burning.
During self-examination or with a mammologist, single lumps or multiple nodules in the form of grape clusters are revealed . The diffuse form of the disease most often affects the upper parts of the glands.
The following symptoms are also noted:
- swelling and increase in the size of the mammary glands;
- fluid from the nipples (clear or bloody);
- change in the size of the lymph nodes in the armpits.
Approximately 15% of women who suffer from this disease report no pain. This is due to different levels of sensitivity and the special location of nerve endings in the chest.
In addition, cysts may not appear on palpation at first . The same thing happens when fibrous elements predominate. For this reason, for diagnosis and timely detection of the disease, it is necessary to regularly visit a mammologist.
Attention: in the first stage, symptoms are observed only on specific days of the cycle. The late stage is characterized by pain that does not depend on the days of the cycle.
You can read about the symptoms of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy with a predominance of the cystic component here.
Is the disease dangerous for women?
Mastopathy in itself is not a life-threatening disease . But it worsens a woman’s quality of life. In addition, mastopathy is not considered a precancerous condition, that is, it does not develop into it. But nodular varieties can simulate breast cancer.
Often mastopathy acts as a background for the occurrence of cancer (it is important to take into account some similarities in the risk factors for cancer and mastopathy).
Diagnosis and treatment
The diagnosis is made based on the results of an examination by a mammologist, mammography, ultrasound, and tests. Sometimes a biopsy and breast MRI are required.
External changes in the breast do not appear in the diffuse type of the disease . Palpation reveals painful neoplasms of different sizes and lengths, without obvious limitations, with a lobulated and granular surface.
- Mammography reveals a heterogeneous tissue structure with small lumps or cysts.
- This study helps to exclude a malignant tumor in the breast and identifies a form of mastopathy.
- As for treatment, for the diffuse type of the disease, conservative treatment is indicated, as well as monitoring over time.
- It is recommended to change your diet:
- add more plant-based fiber;
- consume dairy products;
- limit the intake of animal fats from food.
If intestinal dysbiosis is present, which disrupts the process of absorption of nutrients, intervention by a gastroenterologist is required.
Vitamin and mineral complexes , potassium iodide, homeopathic medicines, dietary supplements, herbal adaptogens are prescribed. As for non-hormonal therapy, the doctor can prescribe sedatives, diuretics and enzymatic drugs.
Important: treatment with hormones should only be prescribed and under the supervision of a doctor. Self-medication is unacceptable!
With a diffuse form, physical activity should be increased. Among the physiological procedures allowed:
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- galvanization;
- balneotherapy;
- electrophoresis.
Hormone therapy is aimed at eliminating “breakdowns” in the hormonal background; it includes taking dydrogesterone and progesterone, thyroid hormones.
In conclusion, it should be said that prevention is always better than cure . To avoid the development of such a disease, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle, undergo regular check-ups with a doctor, and follow the rules of hygiene. It is important to ensure that there are no chest injuries, maintain proper nutrition, avoid stress and get enough sleep.
Source: https://LechenieBolezney.com/mammologiya/mastopatiya-m/vidy-mastop/diffuzno-kistoznaya/dvustoronnyaya.html