In appearance, this formation is similar to a long growth, equipped with a large number of villi on the sides.
If there are difficulties in urinating and suspicious signs appear, the disease requires contacting a specialist.
General description of the disease
Despite the fact that this formation is benign in nature, under the influence of external factors it can take a malignant form, therefore it is necessary to carry out a set of diagnostic measures in a timely manner and prescribe a treatment process.
At the initial stage of development, the disease has the appearance of a growth formed on a thin stalk. When its development is observed, it takes root in the tissue and causes certain symptoms. Bladder papilloma in men appears much more often than in women.
Transitional cell papilloma
Transitional cell papilloma in the bladder area is a neoplasm containing altered cellular epithelial elements in its structure.
Usually the phenomenon looks like a red growth, is soft and is equipped with villi located on a thin stalk.
Sometimes the tumor does not have a stalk and grows from the mucous membrane; it has a wider base. Papilloma contains elongated villi, due to which it resembles a fern.
Manifestation of the disease in men
In males, the urinary system is structured in a special way; incomplete emptying of the bladder occurs, so they are more likely to suffer from this disease.
Characteristics of the female disease
As for the female half of humanity, in this case, HPV is no less dangerous than the disease in men. If development occurs within the bladder, the neoplasm becomes cancerous and spreads to the reproductive system, affecting the vaginal walls, covering all neighboring organs.
In the initial stages, the disease does not manifest itself, but in later stages there is a dysfunction of urination, pain and a burning sensation, and streaks of blood in the urine.
Causal factors of the phenomenon
Despite the benign nature of the disease, it is dangerous because it can sometimes transform into a malignant process.
Degeneration can be caused by poor quality removal. As already noted, at the initial stage of the disease, you can notice a leg that is fixed in the area of the inner wall of the bladder.
After some time during the course of the disease, it becomes shorter, and the general appearance of the formation is similar to a large growth. Most often, men aged 40-60 years are at risk. Papilloma formed in the bladder area occurs in 10% of cases compared to other similar phenomena. The causes of formation have not been studied, but there are several risk factors:
- smoking,
- weakened immunity,
- neglect of healthy lifestyle,
- work in hazardous conditions.
Due to the difficulty of identifying the cause, problems arise with diagnosing the phenomenon.
Symptomatic picture
- Blood in the urine
- hematuria,
- frequent urge to urinate,
- pain when going to the toilet.
In order for treatment of growths to be started in a timely manner, it is necessary to consult a specialist in time.
Diagnostic complex
Large formations can be detected by a specialist through palpation. In other cases, ultrasound and CT are most often used. However, they make it possible to identify neoplasms ranging from 1 cm in size.
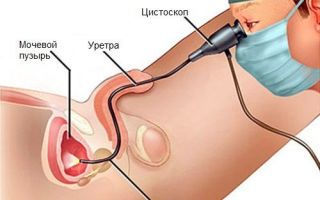
If the sizes are smaller and characteristic of the initial stages of pathology, they can only be recognized by cystoscopy. Endoscopy today is increasingly used to determine the disease.
In this procedure, the device is inserted into the cavity being examined and produces an image using a camera. The method allows you to take a tissue sample for the purpose of histological examination in the future.
Therapeutic measures
- Surgical intervention involves removal by a specialist of the affected areas of the organ. If the tumor is malignant, the bladder is completely resected. In its place, an organ is formed from parts of the small and large intestines.
- Radiation therapy is prescribed for patients with cancer; the method involves complete removal of the organ. Due to the presence of side effects, therapy is not always justified. If the signs are severe, it is necessary to stop this type of therapy and move on to another type of treatment.
Alternative Treatments
If a pathology is detected in the bladder, treatment can be anything. In practice, the following types of measures are most often used:
- the medicinal method involves its use after surgery: the patient is prescribed chemotherapy for carcinoma, as well as drugs for drug prophylaxis in order to prevent relapse,
- radical therapy is carried out in women and involves complete resection of the organ - its uterus and the anterior part of the vagina, urethra; in men, meanwhile, the bladder, canal and prostate are completely removed.
Treatment does not always involve resection. If progressive human papillomavirus is detected in a timely manner, drug therapy without surgery is sufficient.
But when the disease is advanced and the growth penetrates into the muscle structures, there is a high probability of the tumor developing into a malignant type.
In this case, the cells are damaged at an active rate, so it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor.
Loading…
Source: https://beauty-love.ru/dermatologiya/vpch/osobennosti-terapii-papillomyi-v-oblasti-mochevogo-puzyirya
Transitional cell papilloma of the bladder
Symptoms of bladder urothelial tumors in the early stages of their development are expressed in micro- or macrohematuria, dysuria, and suprapubic pain.
As a rule, the area of the base of the bladder (Lieto's triangle) is affected, and by the time of cystoscopic diagnosis in half of the patients the tumor does not exceed 2.5 cm in diameter.
The currently accepted fluorescent cystoscopy exceeds conventional cystoscopy in diagnostic efficiency by 20%; it allows identifying not only very small papillary tumors, but also small areas of carcinoma in situ.
Like papilloma . Likewise, bladder cancer can recur after radical removal. Moreover, relapse often has a different localization, for example, instead of the bottom in the vault of the bladder. When cancer of this organ is initially recognized, less than 10% of patients have metastases.
Exophytic transitional cell papilloma of the bladder
Exophytic transitional cell papilloma of the bladder
Exophytic transitional cell papilloma (syn.
papillary transitional cell carcinoma grade 0, papillary urothelial cancer grade 1) * - benign epithelioma, protruding in the form of a “bush” into the lumen of the bladder and consisting of papillae, in each of which the fibrovascular core is covered with transitional cell (transitional) epithelium. This tumor accounts for up to 25% of all cases of transitional cell neoplasms. The prognosis for urothelial papilloma varies greatly.
A small and delicately villous neoplasm (0.1-0.8 cm in diameter), growing on a narrow base or thin stalk, can be accompanied by relapses, usually several years after radical removal. Malignancy is extremely rare.
It should be noted that such a complete papilloma falls into the field of morphological research extremely rarely due to the widespread use of endovesical electrocoagulation. Much more often, a morphologist studies the smallest fragments of a tumor obtained in the sediment after centrifugation of urine.
Therefore, to obtain a complete picture, you need to focus on cystoscopic descriptions.
Larger (up to 2 cm in diameter) and coarse villous papilloma on a wider base has a worse prognosis. It is almost always accompanied by relapse and, in approximately 20% of patients, malignancy.
Under a microscope, thin villi of a small papilloma . growing on a narrow base, as normal, they have a lining of 5-8 layers of cells with more or less clear differentiation into three zones: integumentary, intermediate and basal. The cells forming each zone are almost normal.
Their mitotic index fluctuates within limits not much higher than normal (0.29-0.40%). Mitotic figures are found in the basal, less often in the intermediate zone. The coarse villi of a larger papilloma, located on a relatively wide base, are lined with urothelium, the thickness of which does not always, but often exceeds 8 layers of cells.
The above-mentioned three-zone differentiation of the lining is disrupted almost everywhere.
signs of cellular atypia or polymorphism, but the mitotic activity of epithelial cells is higher than that of the previous form of papilloma. Mitotic figures can be found in all layers of the lining of the villi.
In both forms of papillomas, the degree of lymphoid and lymphomacrophage infiltration of the villous stroma and tumor base varies greatly.
Both of these forms should be differentiated from papillary transitional cell carcinoma.
Transitional cell papillomas
Transitional cell papillomas of the bladder have the appearance of villous formations, pale pink or red. The tumors are soft, located on a thin stalk, some are more dense and have a wide base, sometimes there is no stalk and the tumor seems to come directly from the mucous membrane.
Papillomas consist of highly elongated villi, resembling a fern, but sometimes the villi are short and the tumor looks like a sponge. Each of the numerous papilloma villi has a delicate, well-vascularized stroma, forming a connective tissue core that is covered with stratified transitional epithelium.
Transitional cell papilloma of the bladder
The tumor consists of numerous villi with a delicate, well-vascularized stroma. The villi are covered with multilayer epithelium, arranged in several rows. Epithelial cells are homogeneous. X160.
Transitional cell papilloma of the bladder
Cross section. The villi are built from large, homogeneous, elongated epithelial cells arranged in several layers. The surface cells are flattened. X320.
The epithelium is located on the basement membrane and is represented by a rather thick layer of cells, repeating all the bends of the papillary eminence.
The basal layer of cells, as a rule, is located perpendicular to the villus axis, the cells are elongated or cubic, the surface cells are flatter. In general, the cells are quite uniform and form regular rows.
In some areas of the epithelium, vacuolated cells are found, which may contain mucin or fat.
In contrast to a normal bladder, with papillomas the cells of the mucous membrane are larger, in general it is thicker, especially in the depths of the folds, both due to an increase in the cells themselves and the number of their rows. The number of mitoses in cells varies, but in benign papillomas they are always biopolar.
Some researchers designate papillomas of the structure described above as simple papillomas, in contrast to the so-called atypical papillomas, in which the cells are more polymorphic, hyperchromatic, contain large nuclei, and form irregular cell rows. However, taking into account the growth characteristics of bladder papillomas, which are not related to the nature of the histological structure, it is hardly correct to divide papillomas into typical and atypical.
Papillomas are located on the mucous membrane and do not grow into the wall of the bladder; the basement membrane remains intact. The absence of destructive growth is the most significant feature that distinguishes papilloma from cancer.
In this regard, it is necessary to very carefully examine the stalk of the papilloma: germination of the epithelium into the base of the stalk indicates the beginning of infiltrative growth.
At the base of the stalk of the papillary processes, muscle fibers are sometimes found.
According to some researchers, the presence of bundles of muscle fibers in these areas indicates penetration of the tumor into the depths of the bladder wall, which is alarming regarding the malignancy of papilloma.
Examination of the base of the papilloma is often crucial to rule out malignancy, but unfortunately, the base of the papilloma is damaged during tumor isolation, especially with an electric knife.
The stroma of papillomas, in particular in the base area, can be infiltrated with lymphoid cells, leukocytes, and plasma cells. Roussel's bodies and foam cells are also occasionally found here.
Some authors believe that the stroma of papillomas is also tumorous, so they suggest calling them fibroepitheliomas or mixed tumors. This concept is untenable.
The prognosis for transitional cell papillomas cannot be considered favorable due to their characteristics.
Transitional cell papillomas, inverted type
The tumor has the same structure as transitional cell papilloma, but with pronounced endophytic growth. As a result, multiple invaginations of layers of transitional epithelium are formed into the submucosal layer of the bladder wall, but without destruction of the basement membrane.
Squamous papillomas
The tumor villi are covered with stratified squamous epithelium.
“Bladder cancer”, V.I. Shipilov
Bladder papilloma - localization of HPV in the area of the urinary organ - is very rare, but under unfavorable factors the formation may appear, and treatment in this case will require immediate treatment.
Human papillomavirus is an incurable infection.
The formations on tissues that this virus provokes are in most cases benign, but there are types of the virus (66, 16, 31, 39) that provoke the development of cancerous tumors.
Bladder papilloma appears as a growth on a thin stalk, from which filamentous processes can grow (transitional cell papilloma). Initially, papillomas of the bladder are localized on the surface of the organ, but as they develop, they can grow inside the tissues of the bladder and transform into thick keratinized plates.
Symptoms of bladder papilloma
Symptoms of the appearance of papilloma at the initial stage appear very little or may be completely absent. While the bladder papilloma is small, it does not interfere with the functioning of the organ, which means it does not manifest itself in any way.
As the papilloma grows and grows deep into the walls of the bladder, the first characteristic symptoms of this disease appear:
- blood in the urine;
- pain in the groin area.
Bloody spots in urine may appear regularly or be an isolated symptom. The blood itself may be a lot or a small amount. If such a symptom appears, you must consult a doctor to find out the cause.
The appearance of a formation in the area of the urinary organ can manifest itself in the form of lower back pain. Many people perceive this symptom as a natural sign of a “strained back,” hypothermia, osteochondrosis, myositis, but not a papillomavirus infection.
This is why self-medication is so dangerous, which can lead to complications of the disease and longer (and not always effective) treatment later.
Symptoms of papilloma in the bladder area when another infection is attached will manifest itself in the form of itching and burning during or after urination, pain during sexual intercourse. Most often, cystitis occurs due to HPV of the bladder, but sometimes another infection, including a sexually transmitted infection, can occur.
It is impossible to independently see the papilloma inside the urinary organ. This can only be done by a doctor during examination using palpation (if the formation has grown through the epithelial cells of the organ) or using ultrasound.
Using ultrasound, you can see large papillomas, the size of which exceeds 10 mm. Small tumors are diagnosed using cystoscopy. Be sure to examine papilloma tissue by performing histological analysis.
All these procedures will help determine the type of HPV and the stage of development of the disease in order to select the most appropriate treatment.
Treatment of papillomas on the bladder
Treatment for bladder growths caused by HPV depends on the type of virus and the stage of development of the disease. If the papilloma has not grown into the muscle layer of the organ, then transurethral resection is used as treatment. This is an endoscopic operation, and it involves electrical resection of the area of the bladder that is affected by the growth.
When transitional cell papilloma has penetrated the muscle layer, radiation therapy or surgery is used as treatment.
Removal of papilloma using surgical excision. Surgical intervention to remove the affected part of the urinary organ is carried out when the disease is advanced and it is impossible to remove papillomas with medication.
In particularly severe cases, the bladder is removed and replaced with part of the large or small intestine.
The operation is not easy and is fraught with various complications, so it is better to treat papillomas at an early stage.
Radiation therapy is used as the last stage of treatment, followed by organ removal. Since a targeted effect directly on the papilloma tissue is impossible, the bladder mucosa suffers after radiation therapy.
This is fraught with a number of side effects, such as severe pain during urination, frequent urge to urinate, and burning in the lower abdomen. Due to inflammation, the patient's temperature rises and blood appears in the urine.
Sometimes these symptoms are so unbearable that there is talk of stopping radiation therapy.
Drug therapy is prescribed after removal of papillomas. It increases the protective functions of the immune system, due to which the risk of reappearance of papillomas, which tend to recur over the next 4 years, is reduced to a minimum. Drug prevention consists of catheter administration of special drugs into the cavity of the urinary organ.
Complete cystectomy is used for deeply ingrown tumors, which often affect neighboring organs. This operation involves removing the bladder and reproductive organs in women and the urethra and prostate in men.
All these procedures are dangerous due to subsequent complications, so you should be careful about your health and treat the disease in the early stages.
If possible, you should protect your body from the penetration of HPV: protect yourself during sexual intercourse with a condom, do not use other people’s hygiene products, and refrain from visiting public places.
Harmful professions where a person is constantly exposed to substances hazardous to health can also subsequently provoke papillomas on the bladder.
This disease cannot be treated with folk remedies. You can prevent HPV activation at home by strengthening your immune system with a healthy lifestyle and good nutrition. Giving up bad habits will only benefit you.
What to do if papillomas do not go away?
- Have you tried all the means to combat it, but the disgusting warts keep coming back again and again?
- You almost decided on surgery or removal with nitrogen, despite the fact that it is terribly painful and expensive, but you have no choice, because papillomas are not only a discomfort, but also a risk of cancer.
- Perhaps you are trying to remove the effect when you need to treat the cause?
Sources: http://medicalplanet.su/oncology/248.html, http://www.medchitalka.ru/rak_mochevogo_puzyrya/patologicheskaya_anatomiya/28943.html, http://bezpapillom.ru/papillomy/mochevogo-puzyirya.html
No comments yet!
Source: https://www.luchshijlekar.ru/mochevoj-puzyr/perehodno-kletochnaja-papilloma-mochevogo-puzyrja.html
Transitional cell papilloma of the bladder: treatment with folk remedies
.
HPV is one of the most common diseases. More than 60% of the world's population are carriers of a dangerous infection. Bladder papilloma brings discomfort to a person’s normal life. In a brief review, we will talk about the main causes of the disease and how to effectively treat it.
Papillomas grow on mucous membranes and can appear inside the bladder
reference Information
HPV is a benign tumor that is infectious in nature. The disease is quickly transmitted from one carrier to another through household objects, sexual contact or a banal handshake.
With strong immunity, patients do not know about the presence of the disease for a long time, but once they get sick, the virus becomes active. Bladder papillomas tend to degenerate and undergo various transformations.
An abnormal growth of tissue on the mucous membrane of an organ under unfavorable conditions mutates into cancer. Main symptoms of the disease:
- blood in urine;
- pain and burning when urinating;
- frequent urge to go to the toilet (including false ones);
- you need to tense your abdominal muscles so that all the liquid comes out.
These signs characterize many diseases, so you do not need to wait for the condition to improve, but immediately visit a doctor. There are many reasons why virus cells begin to actively multiply, so let’s look at the main ones.
- Weakening of the immune system. A serious illness or low-grade inflammation (dental, for example) destroys the body’s protective properties, which contributes to the rapid proliferation of tissues.
- Long-term use of medications. Hormonal drugs and antibiotics weaken the body, which activates the infection.
- Bad habits. An unhealthy lifestyle undermines your health.
- Working with chemicals. The production of paints and varnishes, paper and other items negatively affects the body. Carcinogens have a habit of accumulating, so they continue to affect a person several years after a change in activity.
- Late visit to the toilet. If you ignore the natural urges of the body, then transitional cell papilloma of the bladder in men develops rapidly.
A small nodule in an internal organ can only be detected during a routine examination or during an ultrasound. Without clear signs, the disease does not bother patients for a long time. The appearance of blood in urine is a signal that the tumor has begun to grow into the inner walls of the mucous membrane.
If any unpleasant symptoms occur, then you need to immediately visit the clinic. The professional will carefully check the patient and prescribe appropriate tests. In the early stages, a special device with an optical camera and a flashlight – an endoscope – is inserted into the organ. The equipment allows the smallest to see seals.
If papillomas in the bladder of men and women have grown over 1 cm in diameter, then it can be recognized by ultrasound.
Restraining the urge to urinate provokes the rapid growth of formations
Therapy
Is it possible to cure HPV of the bladder with folk remedies? The nodules will not resolve on their own, so using only herbs to destroy the infection will not bring a positive result. All actions must be coordinated with the attending physician, as there is a risk of the tumor degenerating into cancer. If the seals have penetrated deeply into the muscle layer of the organ, then two removal methods are recommended.
- Surgical excision. During the operation, the affected area of the bladder is removed. In the most advanced cases, you have to get rid of the diseased organ.
- Radiation therapy. It is the last chance for recovery if removal is necessary. During this period, you need to give up bad habits and reconsider your lifestyle. Dietary nutrition and regular exposure to fresh air become mandatory.
Deeply infiltrating tumors are treated with radical cystectomy. This operation involves complete removal of the bladder, uterus, anterior vaginal wall and urethra (in women), or removal of the bladder along with the prostate and urethra (in men).
After surgery, papilloma treatment follows the traditional scenario.
- Restoring the body's defenses. To help the body survive the consequences of the intervention and cope with the infection, you need to take medications to boost immunity.
- Vitamin therapy. The lack of important trace elements and minerals negatively affects health. A regular course will protect against relapses.
- Virus suppression. Anti-infective drugs prevent HPV cells from multiplying.
If nothing is done after surgery, then the prognosis for recurrence of the disease increases by 80% within three years after removal. Regular examination by a supervising doctor will prevent relapse in the early stages, which will make therapy less painful and lengthy.
HPV should be suppressed with antiviral drugs
Prevention
It is easier to prevent a disease than to spend a long time getting rid of it and recovering. If you have pedunculated nodules on your skin, then we recommend that you visit the clinic immediately. The specialist will determine the nature of the disease to rule out malignancy of the tumor.
Remember: bladder papillomatosis is much less common in women than in men. Representatives of the stronger half of humanity are required to undergo examination by a urologist every six months. Especially those working in hazardous industries and smoking people. We recommend not to get sick on your feet.
If you are treated in an office or at an enterprise, then your health is undermined, which becomes a catalyst for the awakening of HPV.
If you have inflammation of the genitourinary system, it is better not to self-medicate, but to seek help from a professional. The doctor will determine the therapy and advise what to do.
From folk recipes, you need to use products that increase the body's defenses and allow the immune system to suppress the virus. Decoctions of rosehip and chamomile have a positive effect on health. A course of taking tinctures of echinacea, ginseng or eleutherococcus will help predict the disease.
Papillomas on the bladder are a dangerous infection that has a tendency to develop into cancer. Timely seeking medical help and regular monitoring by a specialist will eliminate surgical intervention.
If the disease is detected in the early stages, then drug therapy is sufficient.
Source: https://kozhmed.ru/papillomy/mochevogo-puzyrya.html
Bladder papilloma: causes, treatments and types
After overcoming the 40-year mark of their lives, many people begin to develop diseases that they did not even suspect about before. One of these pathologies is bladder papilloma. The appearance of tumors in the urinary tract often affects men.
All benign formations of the urinary system and urothelial papilloma according to the ICD 10 code (international classification of diseases) are assigned a code corresponding to D 30.X, where X is a number from 0 to 9, determining the location of the formation. So, a bladder polyp will correspond to the code D 30.
3, urethral polyp – D 30.4, etc.
Content
What is papilloma in the bladder and the causes of its occurrence?
Bladder papilloma, its classification, is a benign formation characterized by the proliferation of epithelial tissue.
It is a growth located on one of the walls of the bladder, has an irregular shape and consists of elements of the mucous membrane.
A polyp is a benign neoplasm, but the specificity of growths that arise in the bladder is their high risk of malignancy - degeneration into cancer.
The causes of bladder papillomas in women and carcinoma in men are quite diverse. The vast majority of them are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), but there are a number of factors that both contribute to the activity of the virus and independently lead to the appearance of tumors:
- Bladder papilloma in men occurs more often due to the anatomical and physiological features of the structure of the genitourinary system. The presence of prostatitis is very often accompanied by the appearance of a neoplasm.
- Urolithiasis disease. Crystals and stones that fall into the cavity of the bladder injure its mucous membrane, promoting the proliferation of HPV.
- Chronic or frequent inflammation processes - cystitis, urethritis, lead to the proliferation of affected tissues.
Symptoms and diagnosis of bladder papillomas
When a foreign body appears in the bladder, the following symptoms come to the fore:
- The appearance of blood in the urine. There can be either a small amount of blood, which slightly stains the urine pink, or quite heavy bleeding, when the urine completely loses its transparency and acquires a pronounced red color.
- Pain at rest and when urinating. Most often they appear with large tumors. The patient complains of pain in the lower abdomen, above the pubis.
- Difficulty urinating, false urge. They occur when a tumor completely or partially blocks the urine outlet from the bladder.
Unfortunately, all these symptoms are not specific to polyps located in the bladder. They can be due to formations of the urethra, urolithiasis, cancer, mental disorders, and in women – with diseases of the internal genital organs.
Due to such low information content of symptoms, a lot of instrumental research methods have been developed, the main of which is ultrasound. The ultrasound procedure is performed exclusively on a full urinary tract and allows a more detailed study of the cause of the complaints.
Using ultrasound, you can recognize whether it is a stone or a polyp, which, unlike the first, will be motionless during examination.
When performing an MRI or CT scan, based on indirect signs (the presence of metastases, growth into surrounding organs and tissues), it is possible to judge whether a malignant or benign tumor is developing in the body. However, this difference is unreliable and in the early stages all types of tumors look the same on CT, MRI and ultrasound. They can be definitively determined only after removal and examination under a microscope.
Types of papillomas
There are several of the most common types of urinary papillomas, different in cellular composition and prognosis regarding further treatment.
We recommend reading:
- Papilloma in the rectum
- Papilloma on the lip
- Small papillomas on the neck
Transitional cell
The most common type, most often removed in men over 40 years of age. Transitional cell papilloma of the bladder is formed exclusively from components of the transitional epithelium lining the entire urinary tract. In 90% of cases, its cause is HPV acquired through sexual contact. With timely treatment, the formation rarely turns into cancer.
Urethral papilloma
Located in one of the parts of the urethra. Often accompanies prostate diseases - prostatitis, adenoma.
This can all arise due to the same HPV, a chronic focus of inflammation, or prolonged carriage of sexually transmitted diseases. After removal, malignant forms are rarely detected.
Very often, such polyps are mistakenly diagnosed as prostatitis or prostate adenoma and lead to chronic and acute urinary retention.
Squamous
The presence of cellular atypia (discrepancy between the cells detected during microscopic examination and the cell of a given organ) is inherent in the early stages of cancer and carcinoma. Squamous cell papilloma can be a so-called cancer in situ - the appearance of malignant cells that have not yet had time to spread beyond the epithelium and affect other organs and tissues and have not begun to hurt.
Inverted papilloma
The difference between this type of neoplasm is that, while remaining benign, they grow inside the tissues, and not into the lumen of the organ. Inverted papilloma of the bladder occurs against the background of chronic inflammation. It is asymptomatic for a very long time, and the reason for its detection is a routine ultrasound.
Can bladder papilloma develop into cancer?
In order to prevent the occurrence of such dangerous diseases, undergo an annual examination after 40 years. Men must undergo an ultrasound of the urinary and prostate, and women must undergo an ultrasound of the pelvic organs. If you find blood in your urine, difficulty urinating, pain in the lower abdomen, immediately seek help from qualified specialists. Any delay will contribute to the progression of the disease and worsen the chances of a successful outcome.
Treatment and removal methods for women and men
To date, many methods have been developed to remove polyps from the urinary system. Some of the latest methods do not even require the formation of incisions in the lower abdomen - all manipulations are performed using special, thin devices inserted through the urethra. The recovery process after such operations
Removing bladder papillomas using folk remedies is impossible, since none of the proposed tinctures or herbs is capable of eliminating pathologically overgrown tissue. Moreover, when using folk remedies, it is impossible to differentiate whether this tumor is benign or cancer.
After removal of the bladder papilloma, it is sent for histological analysis to exclude the presence of carcinoma. If nothing is detected, the patient is soon discharged from the hospital. In the first days after surgery, it is necessary to use a urinary catheter to avoid irritation of the fresh wound with uric acid salts.
The article has been verified by the editors
Source: https://CoriumMed.ru/papillomy/tipy/mochevogo-puzyrya.html
Diagnosis and removal of bladder papillomas
01.05.2017
Papilloma is a benign tumor that can form both on the skin and on human organs, such as the bladder. Bladder papilloma is a disease that remains virtually asymptomatic for a long time. But this pathology is dangerous and poses a threat to human life.
Papillomas in the bladder are a common formation that, in the absence of medical intervention, can turn into a cancerous tumor. The wart is attached to the walls from the inside of the organ, has the appearance of a small growth with a branch of villi and is determined using ultrasound diagnostics.
Main characteristics of papillomatosis
It is important to detect HPV at an early stage
Little attention is always paid to the health of the urinary system; many people do not take the problems seriously. Experiences begin to arise when the first unpleasant symptoms become noticeable. Warts can form in any part of the body or organ of the human body.
In the genitourinary system, neoplasms account for only 1/10 of the generally known cases of papillomas. To prevent a growth on the bladder from turning into a malignant formation, it is necessary to diagnose the disease in time and begin comprehensive treatment.
Bladder warts often occur in people over 40 years of age. Statistics show that the disease occurs more often in men than in women. The growth in the female bladder has a structure than the formation in the male organ. This is explained by the fact that the genitourinary organs are located in representatives of different sexes.
Benign tumors that form in the female body have a homogeneous structure consisting of epithelial cells, of which the bladder and urethra. Bladder papilloma in men consists of a large number of tightly adjacent villi. Such transitional cell papilloma of the bladder can form in both male and female bodies.
Causes of papillomas in the gallbladder
Causes of papilloma in the bladder
In medicine, there is no exact list of causes for the appearance of such a disease as papillomatosis of the bladder. Papilloma can develop for various reasons, which will determine the form, speed of the disease, as well as the prognosis. But we can identify several common factors that influence the formation of growths in the urinary system. It could be:
- work in enterprises with hazardous working conditions. Cancer can develop even long after leaving such an enterprise;
- serious kidney problems;
- the presence of bad habits such as smoking, drinking alcohol in large quantities;
- consumption of chemical or biological carcinogens, which are found in many modern foods;
- inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary organs;
- autoimmune diseases, constant stress;
- presence of HPV in the human body;
- the occurrence of stagnant processes in the body - prolonged abstinence from urination.
To avoid the appearance of such a disease as bladder papillomas, it is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, drink at least 2 liters of water daily, and empty the bladder in a timely manner.
How do papillomas develop in the rectum?
Signs of warts in the bladder
The process of development of papilloma in the bladder in the initial stages is asymptomatic and only when it has already grown and taken root in the walls of the organ, some symptoms may begin to appear that alarm the patient.
A clear sign of a urothelial neoplasm in the urinary system is the appearance of blood clots in the urine. At first, this symptom is not very pronounced, but over time the blood clots become larger and more noticeable. Sometimes a slight remission may occur, but after a short time the disease relapses.
Blood clots in the urine may indicate the presence of papillomas in the bladder
Other, no less important, symptoms of the development of papillomatosis of the bladder include:
- urination is accompanied by painful and unpleasant sensations;
- there is an increased urge to urinate, which can often be false;
- to relieve physiological need, you have to make some effort;
- painful sensations appear in the groin and lower back areas;
- Due to weakened immunity, other diseases may appear, for example, cystitis. They are accompanied by itching, burning, and painful sensations.
If at least one of the signs appears, you need to contact a urologist for diagnosis. Even if there was blood in the urine only once, this is already a reason to worry and go to the clinic.
Reasons for the development of papillomas in the esophagus
Diagnosis of the disease
When you go to a medical facility with suspected bladder papilloma, you will have to undergo an examination and undergo a series of tests. A urologist can detect a tumor using palpation if the tumor is on the outside of the bladder.
If it begins to grow through the epithelial cells of the organ. Otherwise, papilloma can only be detected using ultrasound or cystoscopy.
Cystoscopy is an accurate way to diagnose a tumor in the bladder; an ultrasound machine only shows a growth with a diameter of more than 10 mm. If a growth is detected, the doctor gives a piece of papilloma tissue for histological analysis to determine the type of human papillomavirus, the stage of development of the pathology and selecting an appropriate treatment method.
The root causes of papillomas in the ear
Methods for removing a tumor from the bladder
Cystoscopy is used to diagnose HPV in the bladder
If a papilloma in the urinary system has been identified, it is subject to immediate treatment in order to prevent its malignancy. The treatment method can be of several types and is selected depending on the characteristics of the formation and development of the appendix. The following methods can be used to get rid of warts:
- transurethral resection. It is carried out in the case when the wart has not yet affected the muscular part of the organ;
- radiation therapy method. Radiation intervention is the only way to preserve the bladder, but it is very low in effectiveness. In addition, this type of treatment has a number of complications: increased body temperature, severe pain during urination, the formation of blood clots in the urine;
- surgical intervention. It involves partial or complete removal of an organ. And after its removal, a new urinary bladder is created using a small part of the patient’s large (or small) intestine;
- cystectomy. This method of removing warts is used in situations where the tumor has grown deeply and has begun to spread to organs that are located nearby. During this operation, the urethra with the prostate in men or the bladder with the uterus, urethra and part of the vagina in women are removed.
After the operation, the patient is prescribed a number of medications and immunotherapy is prescribed to reduce the risk of relapse of the disease.
Bladder papilloma cannot be cured with folk remedies, so if symptoms occur, you need to make an appointment with a doctor to get rid of the problem in the initial stages.
Treatment methods for papillomas in the throat
Video about removal of bladder tumors
Source: https://telemedicina.one/zhkt/papilloma-mochevogo-puzyrya.html
Transitional cell papilloma of the bladder
Bladder papilloma - localization of HPV in the area of the urinary organ - is very rare, but under unfavorable factors the formation may appear, and treatment in this case will require immediate treatment.
Human papillomavirus is an incurable infection.
The formations on tissues that this virus provokes are in most cases benign, but there are types of the virus (66, 16, 31, 39) that provoke the development of cancerous tumors.
Bladder papilloma appears as a growth on a thin stalk, from which filamentous processes can grow (transitional cell papilloma). Initially, papillomas of the bladder are localized on the surface of the organ, but as they develop, they can grow inside the tissues of the bladder and transform into thick keratinized plates.
Symptoms of bladder papilloma
Symptoms of the appearance of papilloma at the initial stage appear very little or may be completely absent. While the bladder papilloma is small, it does not interfere with the functioning of the organ, which means it does not manifest itself in any way.
As the papilloma grows and grows deep into the walls of the bladder, the first characteristic symptoms of this disease appear:
- blood in the urine;
- pain in the groin area.
Bloody spots in urine may appear regularly or be an isolated symptom. The blood itself may be a lot or a small amount. If such a symptom appears, you must consult a doctor to find out the cause.
The appearance of a formation in the area of the urinary organ can manifest itself in the form of lower back pain. Many people perceive this symptom as a natural sign of a “strained back,” hypothermia, osteochondrosis, myositis, but not a papillomavirus infection.
This is why self-medication is so dangerous, which can lead to complications of the disease and longer (and not always effective) treatment later.
Symptoms of papilloma in the bladder area when another infection is attached will manifest itself in the form of itching and burning during or after urination, pain during sexual intercourse. Most often, cystitis occurs due to HPV of the bladder, but sometimes another infection, including a sexually transmitted infection, can occur.
It is impossible to independently see the papilloma inside the urinary organ. This can only be done by a doctor during examination using palpation (if the formation has grown through the epithelial cells of the organ) or using ultrasound.
Using ultrasound, you can see large papillomas, the size of which exceeds 10 mm. Small tumors are diagnosed using cystoscopy. Be sure to examine papilloma tissue by performing histological analysis.
All these procedures will help determine the type of HPV and the stage of development of the disease in order to select the most appropriate treatment.
Treatment of papillomas on the bladder
Treatment for bladder growths caused by HPV depends on the type of virus and the stage of development of the disease. If the papilloma has not grown into the muscle layer of the organ, then transurethral resection is used as treatment. This is an endoscopic operation, and it involves electrical resection of the area of the bladder that is affected by the growth.
When transitional cell papilloma has penetrated the muscle layer, radiation therapy or surgery is used as treatment.
Removal of papilloma using surgical excision. Surgical intervention to remove the affected part of the urinary organ is carried out when the disease is advanced and it is impossible to remove papillomas with medication.
In particularly severe cases, the bladder is removed and replaced with part of the large or small intestine.
The operation is not easy and is fraught with various complications, so it is better to treat papillomas at an early stage.
Radiation therapy is used as the last stage of treatment, followed by organ removal. Since a targeted effect directly on the papilloma tissue is impossible, the bladder mucosa suffers after radiation therapy.
This is fraught with a number of side effects, such as severe pain during urination, frequent urge to urinate, and burning in the lower abdomen. Due to inflammation, the patient's temperature rises and blood appears in the urine.
Sometimes these symptoms are so unbearable that there is talk of stopping radiation therapy.
Drug therapy is prescribed after removal of papillomas. It increases the protective functions of the immune system, due to which the risk of reappearance of papillomas, which tend to recur over the next 4 years, is reduced to a minimum. Drug prevention consists of catheter administration of special drugs into the cavity of the urinary organ.
Complete cystectomy is used for deeply ingrown tumors, which often affect neighboring organs. This operation involves removing the bladder and reproductive organs in women and the urethra and prostate in men.
All these procedures are dangerous due to subsequent complications, so you should be careful about your health and treat the disease in the early stages.
If possible, you should protect your body from the penetration of HPV: protect yourself during sexual intercourse with a condom, do not use other people’s hygiene products, and refrain from visiting public places.
Harmful professions where a person is constantly exposed to substances hazardous to health can also subsequently provoke papillomas on the bladder.
This disease cannot be treated with folk remedies. You can prevent HPV activation at home by strengthening your immune system with a healthy lifestyle and good nutrition. Giving up bad habits will only benefit you.
Source: https://fazaa.ru/medicina/papillomy/perehodno-kletochnaya-papilloma-mochevogo-puzyrya.html