Systematic therapy - what to do when allergies have already begun. It is necessary to remove the allergen or reduce contact with it. Start taking antihistamines, use drops in the nose and eyes, sprays in the throat. Such therapy will help relieve the severity and severity of the moment, but will not solve the problem.
“It all depends on the specific cases of allergy. It’s one thing when a child has only an allergy to birch, and even then not a pronounced one. And it’s completely different when there is a reaction to everything, and the child not only has a stuffy nose and sneezes, but he also has conjunctivitis, asthma, Quincke’s edema, and urticaria.
In this case, medical drug activity will be completely different, up to the prescription of hormonal drugs, IVs, home or hospital treatment.
There are people who have a very strong reaction, and they are forced to simply not go outside at a time when it is dry, windy and when the warm weather first lingers and then suddenly gets warmer,” said the head of the pediatric center of the GMS Clinic.
Immunotherapy is prevention using injections, drops or capsules containing an allergen. Even before the plants begin to generate dust, a small amount of an allergen, for example, birch, is introduced into the child’s body.
Protective factors are formed in the body, and the child does not show an allergic reaction to this allergen.
It is believed that three years of such therapy will save a person for 12 years from severe manifestations or, at a minimum, from significant drug-induced aggression.
“If a person does not have many allergens, and he follows a diet at the right time and follows the recommendations of doctors, then soon he may completely forget what an allergy is, that he should always carry nasal drops and antihistamines with him,” noted pediatric allergist Nadezhda Magarina.
A factor influencing the occurrence of an allergic reaction is plant pollen. Provocateurs of the disease can be not only flowers, but also trees, wild and cultivated cereals, and weeds. On the territory of Russia, plant dusting can be divided into three periods:
- Spring period (starts at the end of April and continues until the end of May). The following trees are dusted: birch, hazel, poplar, alder, oak.
- Summer period (summer months - June and July): dusting of wheat, rye, oats, timothy and other plants.
- Summer-autumn period (starts in July and ends in September): dusting of chamomile, quinoa, wormwood and the very dangerous ragweed plant.
- The highest concentration of allergen in the air occurs during the daytime, when there is wind and minimal air humidity.
- We also recommend reading:
- Signs and treatment of alcoholic coma, first emergency aid Mercury poisoning: why the consequences of intoxication are dangerousHelping a dog poisoned by rat poisonIntoxication of the body: methods of treatment at home
Some people believe that allergies to plant dust manifest themselves only in the form of conjunctivitis and rhinitis. This is not entirely true. In addition to these symptoms, a person may experience allergic manifestations on the skin, damage to the respiratory tract, bronchial asthma, and hay fever under the nose. All these diseases are treated by a doctor.
Allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis
How to stop vomiting at home for adults
Rhinitis is almost always accompanied by conjunctivitis. In this case, there is significant redness of the eyelids and conjunctiva of the eyeballs, burning and itching in the eyes, profuse lacrimation, and sometimes even photophobia.
Respiratory tract damage
Allergic damage to the upper respiratory tract manifests itself with characteristic symptoms. These include:
- sore and itchy throat, dry cough (the disease is called pharyngitis);
- hoarseness of voice, cough is paroxysmal in nature (laryngitis);
- dry, hacking cough that causes pain (tracheitis).
Bronchial asthma caused by hay fever is exacerbated during the season that coincides with the flowering of certain plants. If a person has been suffering from seasonal allergic rhinitis or tracheobronchitis for several years, he may develop bronchial asthma.
When the bloom of allergens ends, bronchial patency normalizes. As a rule, there are no asthma attacks in winter.
Even if a person has bronchial asthma of a different etiology, during dusting of allergen plants, the severity of attacks may increase.
Skin allergies
It should be noted that it is rare to find hay fever affecting only one organ. An example of this is the combination of allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis. When allergenic plants bloom, most patients complain of the same symptoms: general weakness is felt, the person sleeps poorly, has a headache, sweating increases, and there is also a slight increase in body temperature that lasts for a long period.
Allergenic plants are dangerous not only during their dusting period.
Many of them are medicinal plants and are included in various medicinal preparations that are sold in pharmacies and used both internally (in the form of decoctions and infusions) and externally (for bathing and inhalation).
A significant amount of pollen is included in honey. Those who drink alcohol should be aware that some of them contain herbs. For example, herbs are present in many balms, tinctures, vermouth and other alcoholic beverages.
Why did you lose your sense of smell when you had a cold and how to get it back?
Allergy skin tests are then taken to determine the specific plant that is an allergen to humans.
As a rule, tests are performed during the period when the disease is in remission (no earlier than 15-20 days after the patient stops taking antihistamines).
Skin tests are performed simultaneously with 5-10 types of allergens, and sometimes with a large number, it depends on the state of health, age and other individual characteristics of the patient. This research method helps to identify the allergen that causes hay fever in a person.
Therapy of the pathological process
For hay fever, treatment with medications should only be prescribed by a doctor.
The disease is treated with antihistamines, inhaled glucocorticosteroids, vasoconstrictors (anti-inflammatory and symptomatic drugs).
The doctor prescribes the dosage of these medications according to the age of the patient. Treatment should continue as long as the allergen plant blooms. It is not allowed to take medications unsupervised.
Hyposensitization - treatment method
The principle of therapy is that the patient is injected with an allergen, gradually increasing its dose. This leads to a decrease in the body's sensitivity to it. Injections are performed for several months 1-2 times a week intra- or subcutaneously, sometimes intramuscularly or intranasally.
Such long-term therapy is necessary in order to be able to very slowly increase the dose of the allergen. If the dose is increased quickly, this may cause the development of local or general complications. With local complications, swelling may appear at the injection site, with general complications - Quincke's edema, skin rashes, an attack of bronchial asthma, and sometimes anaphylactic shock.
Treating food poisoning at home
Timely diagnosis and correctly prescribed treatment help the patient not experience significant inconvenience. But you just can’t prescribe medications for yourself; this should be done by a specialist.
Sometimes an allergist recommends consulting with a pulmonologist, ENT specialist, ophthalmologist or dermatologist. If a person has a chronic form of the disease, it will be useful to contact an immunologist, as well as a nutritionist.
Measures to prevent the disease
It is better to refuse bouquets of both fresh and dried flowers, and also not to grow flowering plants at home. It is recommended to remove all soft toys and carpets from the room where a person suffering from hay fever lives.
Experts recommend excluding foods that cause cross-allergy from the patient’s diet. These include:
- some fruits and berries (strawberries, currants, citrus fruits, etc.);
- chicken eggs;
- bee products, including honey;
- products containing dyes.
If the cause of hay fever is flowering cereal crops, then during the period of their dusting the consumption of baked goods and cereals (semolina, pearl barley, wheat, oatmeal) should be reduced. If this is not done, the fever may worsen.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely get rid of hay fever. But if you follow all the doctor’s instructions, monitor your health and eat right, this will help prolong remission as much as possible.
Hay fever is a complex of seasonal allergic reactions to plant pollen. The disease manifests itself as rhinitis, dermatitis, conjunctivitis, and allergic asthmatic bronchitis.
It is characterized by swelling of the mucous membranes of the nose and eyes, nasal congestion, runny nose, sneezing, coughing, suffocation, impaired sense of smell, itching and skin rashes. Without appropriate treatment, it will have a progressive course and may develop into bronchial asthma.
Diagnosed using rhinoscopy, allergy tests, and rhinocytogram examination. Treatment - antihistamines, topical corticosteroids, ASIT.
Hay fever (“hay fever”) comes from the Latin word “pollen” - pollen. As a rule, the disease develops in childhood or young adulthood.
The disease occurs cyclically, worsens when the allergen appears and goes into remission when it disappears. According to scientists, 10-15% of the world's population suffers from pollen allergies.
Most often, hay fever occurs in dry and warm climates, in regions where many species of pollinated plants grow. Most of the patients are young people 10-30 years old living in big cities. Hay fever is observed less frequently in rural residents.
Hay fever develops more often in women (in some regions of Russia, every third woman is affected). The incidence rate is influenced by environmental, climatic and geographical factors.
The diagnosis of hay fever is made on the basis of a characteristic history (seasonality of exacerbations, hereditary predisposition), data from an objective examination by an otolaryngologist and additional studies.
During examination of the nasal cavity (rhinoscopy), swelling of the mucous membrane and narrowing of the nasal passages are revealed. When vasoconstrictors are instilled into the nose, swelling of the mucous membrane persists.
The detection of eosinophils when examining prints of the mucous membrane of the eyes and nose confirms the allergic nature of the disease.
To identify the specific allergen that caused the development of hay fever, a series of provocative tests and skin allergy tests are performed.
Causes
The main cause of the disease is an allergic reaction to pollen from flowering plants. During the flowering period, pollen is deposited on the surface of the skin, mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, eyes, and penetrates the bronchi, causing the development of an allergic reaction in people with a corresponding predisposition.
Interesting to know!
Until recently, it was believed that hay fever was associated with poplar fluff, but this opinion turned out to be unfounded. Poplar seeds are not an allergen, but they can carry pollen from other plants. Pets can also spread pollen.
Symptoms
The main signs of a bloom allergy include:
- sneezing, clear discharge, nasal congestion and itching;
- lacrimation, redness and itching in the eye area;
- dry tongue, itching of the palate;
- manifestations of pollen asthma - difficulty breathing, coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, attacks of suffocation;
- skin allergic manifestations in the form of rash, itching.
The general condition of the patient resembles a cold, but is characterized by the absence of fever. In the most acute period, symptoms of pollen intoxication appear:
- fatigue;
- irritability;
- decreased appetite;
- migraine-like attacks;
- depression;
- weight loss.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on the results of skin (or otherwise, scarification) tests carried out with a set of allergens characteristic of the patient’s area of residence. Determination of immunoglobulin E (specific and total) in blood serum can also be used.
Treatment methods or how to survive the flowering period
The comprehensive therapeutic program includes:
- elimination measures (limiting contact with the allergen);
- diet;
- drug treatment;
- specific immunotherapy.
Elimination measures:
- exclusion of visiting city squares and parks, traveling to the countryside during the flowering period;
- hanging window openings with wet cloth;
- ensuring, if possible, that doors and windows are closed;
- ventilation of premises only after rain;
- daily wet cleaning;
- use of air purifiers;
- when walking, protect your eyes with tight-fitting glasses and your body with long sleeves and trousers;
- changing clothes, washing eyes, nose and mouth after a walk;
- lack of plants in the room.
The diet involves the exclusion of honey and products that can cause an effect similar to a flower allergy when reacting to pollen:
- trees - apples, nuts, carrots, etc.;
- cereals - bread, pasta, strawberries, peanuts, etc.;
- weeds - sunflower oil and seeds, mayonnaise, herbs, watermelon, chicory, etc.
To relieve allergy attacks, the latest antihistamines are used, acting locally or systemically.
In autumn and winter, “allergy vaccination” is carried out - specific immunotherapy: the introduction of small doses of allergens into the body according to a certain scheme.
Approximate flowering schedule of the main allergenic plants
- Tree Pollen:
- until April 30 - alder, willow, poplar, aspen, elm, hazel;
- from May 1 to May 20 - maple, birch.
- Pollen of cereals: wheat, oats, barley.
- Weed pollen: quinoa, ragweed, wormwood (first 15 days of September).
- Depending on climatic conditions, flowering times may vary by 1-2 weeks.
- Read other useful articles on medical care
What laboratory tests help establish the diagnosis of an allergic disease?
- Determination of total IgE level
- Determination of eosinophil cationic protein level
- Examination of nasal secretions for eosinophils
- Determination of specific IgE to specific allergens or panels of allergens
These studies are most informative when there are signs of an allergic disease. This is due to the short circulation time of general and specific immunoglobulins E in the blood.
Preventive measures in the presence of hay fever:
- Travel to other climatic zones during the flowering period.
- Closed windows and doors during the dusting period, use of air conditioning, air purification.
- Walking is advisable in cloudy weather, after rain (at this time the concentration of pollen in the air decreases).
- Exclusion from the diet of foods with cross-allergenic properties.
- The best method of prevention and treatment:
- Timely consultation with a doctor to diagnose hay fever and prescribe adequate treatment
- ASIT (allergen-specific immunotherapy) as prescribed by an allergist
Remember, all patients with pollen allergies must be registered at the dispensary under the supervision of an allergist.
Source: https://healthage.ru/poleznye-sovety/lechenie-boleznej/pollinoz-prichiny-simptomy-lechenie-i-profilaktika/
Hay fever
Hay fever is a complex of seasonal allergic reactions to plant pollen. The disease manifests itself as rhinitis, dermatitis, conjunctivitis, and allergic asthmatic bronchitis. It is characterized by swelling of the mucous membranes of the nose and eyes, nasal congestion, runny nose, sneezing, coughing, suffocation, impaired sense of smell, itching and skin rashes. Without appropriate treatment, it will have a progressive course and may develop into bronchial asthma. Diagnosed using rhinoscopy, allergy tests, and rhinocytogram examination. Treatment - antihistamines, topical corticosteroids, ASIT.
J30.1 Allergic rhinitis caused by pollen
Hay fever (“hay fever”) comes from the Latin word “pollen” - pollen. As a rule, the disease develops in childhood or young adulthood.
The disease occurs cyclically, worsens when the allergen appears and goes into remission when it disappears. According to scientists, 10-15% of the world's population suffers from pollen allergies.
Most often, hay fever occurs in dry and warm climates, in regions where many species of pollinated plants grow. Most of the patients are young people 10-30 years old living in big cities. Hay fever is observed less frequently in rural residents.
Hay fever develops more often in women (in some regions of Russia, every third woman is affected). The incidence rate is influenced by environmental, climatic and geographical factors.
Hay fever
Allergic diseases develop with sensitization (increased sensitivity) to the effects of a certain environmental factor. In case of hay fever, pollen from grasses and trees plays the role of such a factor. Small pollen measuring only 10-50 microns settles on the skin and mucous membranes of the patient, causing a specific reaction in the body.
The period of exacerbation of hay fever coincides with the flowering period of certain trees and grasses. Patients with allergies to hazel, oak, alder and birch pollen experience an exacerbation of hay fever in April and May.
In June and July, patients who have developed an allergy to grass pollen (timothy, foxtail, fescue, wheatgrass and bluegrass) suffer.
In August and September, symptoms of the disease appear in people with allergies to ragweed, quinoa and wormwood pollen.
The severity of clinical manifestations depends on the weather. In windy, dry weather, the concentration of pollen in the air increases, and the symptoms of hay fever intensify. In rainy, damp weather there is a small amount of pollen in the air, and the manifestations of the disease become less pronounced.
The decisive role in the occurrence of hay fever belongs to hereditary predisposition.
If both parents suffer from allergic diseases, the probability of developing an allergy in the child is 50%, if one - 25%, if the parents do not have allergic diseases - about 10%.
The risk of hay fever increases if a child at an early age is constantly in an environment contaminated with allergens, eats improperly, or often suffers from viral diseases.
Typically, hay fever develops in two stages. At the first stage, transient clinical manifestations of the disease occur. Patients complain of itching in the nose, throat, ears and tracheal area.
The patient's eyelids become swollen and hyperemic. Characterized by prolonged bouts of continuous sneezing. Mucous discharge appears from the nose.
Allergic conjunctivitis develops, accompanied by photophobia, lacrimation and a feeling of sand in the eyes.
After 6-8 hours from the moment of exposure to the allergen, the next phase of hay fever begins. The inflammatory reaction intensifies. The discharge from the eyes becomes purulent. Hyperthermia is possible. Some patients develop hives or difficulty breathing due to asthma. In some cases, angioedema, contact or atopic dermatitis, cystitis or inflammation of the external genitalia may develop.
Hay fever can be accompanied by the phenomena of so-called “pollen intoxication” - fatigue, increased irritability, decreased appetite, depression and migraine attacks. If the patient for some reason ingests pollen (for example, with honey), nausea and vomiting may occur, which are accompanied by severe abdominal pain.
The diagnosis of hay fever is made on the basis of a characteristic history (seasonality of exacerbations, hereditary predisposition), data from an objective examination by an otolaryngologist and additional studies.
During examination of the nasal cavity (rhinoscopy), swelling of the mucous membrane and narrowing of the nasal passages are revealed. When vasoconstrictors are instilled into the nose, swelling of the mucous membrane persists.
The detection of eosinophils when examining prints of the mucous membrane of the eyes and nose confirms the allergic nature of the disease.
To identify the specific allergen that caused the development of hay fever, a series of provocative tests and skin allergy tests are performed.
It is necessary to minimize contact with the allergen. A patient with hay fever is advised to reduce the time spent outside, especially in dry and windy weather. It is not recommended to open windows.
You should use special air purifiers designed to capture plant pollen, and exclude certain foods from your diet that can cause cross-allergies.
In case of mild hay fever, the patient is prescribed antihistamines (for oral administration - astemizole, fexofenadine, loratadine, locally - levocabastine and azelastine sprays).
A patient suffering from moderate hay fever is recommended to use topical glucocorticosteroids (nasal sprays triamcinolone, fluticasone, mometasone, beclomethasone, etc.).
For bronchial asthma, inhaled glucocorticosteroid drugs are used.
With concomitant severe viral, bacterial, fungal infections and immune disorders, glucocorticosteroids should be used with caution.
In severe hay fever, local glucocorticosteroids are combined with general antihistamines. If the patient is concerned about severe nasal congestion, it is possible to prescribe vasoconstrictors (naphazoline, xylometazoline, oxymetazoline) for no more than a week.
It should be remembered that long-term use of such drugs can lead to the development of drug-induced rhinitis. Severe hay fever combined with narrowing of the nasal passages is an indication for surgical treatment.
The operation consists of partial removal of the nasal turbinates and can be performed in various ways, including using a laser and cryodestruction.
The most effective remedy in the fight against hay fever is allergen-specific immunotherapy. The treatment regimen involves introducing increasing doses of the allergen into the patient's body. As a result of treatment, the patient's body's sensitivity to the allergen decreases. Specific immunotherapy can be carried out simultaneously with taking medications.
Patients with hay fever are advised to take measures aimed at limiting contact with allergens:
- If possible, it is worth going to another climate zone during the flowering period.
- Patients are strictly not recommended to travel outside the city during the flowering period.
- It is better to ventilate the room in damp, windless weather. In order to prevent the allergen from entering the apartment, you can hang a dampened thick cloth on the window.
- Patients with hay fever should take a shower after coming in from outside.
- During an exacerbation, it is recommended to wash your eyes and gargle several times a day to remove the allergen.
- After washing, clothes should not be dried outside to avoid pollen settling.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_lor/pollinosis
Hay fever - symptoms, causes, prevention and treatment
Hay fever refers to a group of diseases that arise from contact with plant pollen. The manifestations of hay fever are very diverse: swelling of the mucous membranes of the nose and eyes, conjunctivitis, runny nose, sneezing and cough are typical. Without appropriate treatment, it can develop into bronchial asthma.
Symptoms of hay fever
The development of hay fever usually occurs in two stages.
- Stage No. 1 – the first manifestations of the disease, which are transitory. The person will complain of severe itching in the throat, ears and nasal passages. Eye inflammation often occurs. Conjunctivitis, among other things, is accompanied by a fear of bright light, a feeling of sand in the eyes and lacrimation. After 5-8 hours from the moment of contact with the irritant substance, the second phase begins.
- Stage No. 2 – all allergic reactions intensify. High fever is possible. The eye compartments become purulent. In some individual cases, the breathing process may become very difficult. An allergy to pollen often manifests itself as hives. There is also a high probability of developing angioedema, inflammatory reactions of external organs, cystitis, allergic or contact dermatitis.
Another manifestation of hay fever can be “pollen intoxication”: frequent migraine attacks are replaced by a depressive state, irritability greatly increases and appetite decreases. If a person swallows pollen with honey, he may feel nausea and sharp pain in the abdomen1.
Hay fever in children
Allergies are especially pronounced during the flowering period: plants actively spread pollen, and children with a tendency to allergies react especially sharply. Symptoms may include:
- itching in the eye area;
- lacrimation and redness of the mucous membrane of the eye;
- severe cough and sneezing;
- runny nose in the form of clear, copious discharge;
- nasal congestion;
- attacks of suffocation.
Such symptoms indicate an exacerbation.
In addition, the flowering period of plants in children can cause redness, irritation and rashes on the surface of the skin. This reaction is given by the body upon contact with pollen grains2.
Treatment of hay fever
The first thing to do when treating hay fever is to limit contact with the allergen plant.
- You should be outdoors as little as possible, especially in strong winds.
- At home, you need to install special filters to catch plant pollen.
- Remove certain foods from your diet that often lead to the appearance of these symptoms.
- For inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose and throat, antihistamines should be used. For example, Cetrin®. blocks H1-histamine receptors. Prevents the development and facilitates the course of allergic reactions, has antipruritic and antiexudative effects. It has virtually no anticholinergic and antiserotonin effects. In therapeutic doses it practically does not cause a sedative effect. The onset of the effect after a single dose of 10 mg of cetirizine is 20 minutes, lasting more than 24 hours3.
- When the disease manifests itself in moderate severity, glucocorticosteroids are used (glucocorticoids are hormones formed in the adrenal cortex that affect protein and carbohydrate metabolism in the body). For bronchial asthma, a course of inhalations is prescribed.
- In case of severe disease, antihistamines are used in parallel with glucocorticosteroids.
To completely cure the disease, specific immunotherapy is performed. It involves the body receiving gradually increasing doses of a specific allergen. Upon completion of treatment, a significant decrease in sensitivity to the irritant substance will be observed.
When diagnosing the disease in children, provocative and contact tests are used. Doctors also prescribe serodiagnosis (PCR and ELISA).
As for contact skin tests, they are not carried out during the flowering phase. Preliminarily stop taking medications. When treating hay fever in children, it is important to restore the immune balance, and therefore emphasis should be placed on the comprehensive intake of restoratives4.
Diet for hay fever
One of the effective methods of combating the symptoms of hay fever is a hypoallergenic diet. The principles of dietary nutrition are the same, but there are adjustments for the individual characteristics of the person and the type of hay fever.
Experts recommend sticking to the prescribed diet from the end of March until May. This time period determines the flowering period of wormwood, ragweed and quinoa (from mid-July to early September).
To prevent hay fever, it is recommended to exclude from the daily diet:
- fruits and freshly squeezed juices;
- Birch juice;
- bee products (for example, honey);
- berries with seeds (cherries, apricots, cherries, etc.)
- alcoholic drinks;
- nuts and all food products containing this component;
- corn;
- carrots, paprika and celery;
- plant-based products (for example, infusions and herbal decoctions);
- legumes;
- products related to fermentation.
Particular care should be taken when eating foods such as tomatoes, onions, potatoes and cucumbers. You should also add homemade flour products to this list.
As for citrus fruits, they act as an allergen all year round, not only during the period of acute activity of hay fever.
In case of exacerbation of pollen allergy, it is recommended to reduce the consumption of easily digestible carbohydrates as much as possible. This group includes chocolate, sugar, confectionery and syrups.
Cheeses are on the list of prohibited foods. The most allergenic varieties are cheddar, Roquefort and Camembert. To ensure that the diet is as varied as possible, foods should be introduced gradually, in small doses. At the same time, observe the body’s reaction. When a food product is absorbed normally by the body, it is removed from the list of allergens.
To avoid the development of an allergic process in the form of swelling of the nasal mucosa, throat and the development of conjunctivitis, it is recommended to build a diet on the following products:
- butter;
- lean meats (rabbit, turkey, chicken);
- cereal porridge (buckwheat and rice);
- mineral water and dried fruit compotes;
- cottage cheese, yogurt, fermented baked milk and kefir5.
Prevention of hay fever
Preventive measures are relevant for people who do not have an allergic disease, but are at risk. And secondary measures apply to everyone suffering from allergies.
Primary methods of preventing hay fever:
- it is necessary to undergo regular examinations by an allergist, both children and adults;
- it is necessary to exclude or minimize contact with household chemicals;
- and the person should also be protected from the possible allergen (this especially applies to pregnant women).
Secondary methods of prevention:
- regularly carry out wet cleaning in the living space;
- do not use household chemicals;
- you should weigh the pros and cons when getting a cat or dog at home;
- it is necessary to minimize the consumption of fruits (especially citrus fruits), nuts, spices, and plant-based drinks (chicory, vermouths, balms)6.
It is important to understand that allergic hay fever, if left untreated for a long time, can lead to serious complications (for example, bronchial asthma - an allergic-type disease, characterized by a repeated attack of shortness of breath, which occurs when bronchial obstruction is impaired). If there is a possibility of developing an allergic disease, then it is necessary to take measures and not bring the situation to the hospital ward.
Bibliography
- Mikhailenko A. A. Allergy and allergic diseases / A. A. Mikhailenko, G. A. Bazanov. – M.: Medical Information Agency, 2009. – 304 p.
- Revyakina V. A. Features of hay fever in children in modern conditions / V. A. Revyakina // Attending physician. – 2012. – No. 4. – 12-15 s.
- Instructions for use of the medicinal product for medical use Cetrin®. – Registration number: P N013283/01.
- Allergology. Clinical recommendations developed by the RAACI Working Group / ed. R. M. Khaitova. – M.: Farmarus Print Media, 2013. – p. 126 p.
- Savelyeva Yu. Allergy. Treatment and prevention (electronic book) / Yu. Savelyeva. – M.: Scientific book publishing house, 2013
- Research Institute of Pediatrics: Diet for hay fever. – Access mode: http://www.kdcenter.ru – (Date of last access: 10/16/17).
Source: https://cetrine.ru/allergiya/vidy-allergii/pollinoz
Hay fever: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Watery eyes, runny nose and cough are not always symptoms of a cold. In the warm season, these signs indicate the presence of hay fever. This is an allergic reaction of the body to the flowering of a plant. Without treatment of this pathology, bronchial asthma develops. For this reason, many people want to know what the symptoms and treatment are for hay fever.
What is hay fever?
It is known that itching in the nasal passages and sneezing occur with hay fever, that this is not an infectious disease and cannot be infected by airborne droplets. Hay fever is an allergic response of the human body to the influence of pollen from various plants. The reaction has a clearly recurring seasonality. Most often, the disease manifests itself as inflammation of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract and eyes. In addition, the disease is also commonly called:
- pollen bronchial asthma;
- pollen rhinopathy;
- hay fever;
- spring catarrh;
- allergic rhinoconjunctivitis.
The most correct term is hay fever.
Risk factors
The disease usually appears in the female half. Climatic, environmental and geographic factors influence infection rates. Rural residents often suffer from hay fever.
An important role is played by hereditary predisposition. If two parents are endowed with allergic diseases, then the risk of the baby developing the disease will be 50%. If only one is sick, then the percentage drops to 25%. If both parents do not suffer from this pathology, then the risk of the disease is 10%.
The risk of illness increases significantly if a child from early childhood is constantly in an environment contaminated with allergens. Malnutrition and viral diseases also lead to the disease.
Causes of hay fever
The disease progresses when the body is overly sensitive to the action of a small stimulus. The irritant is pollen from wind-pollinated plants. To enter the human body, one inhalation or the deposition of small particles on the conjunctiva, nasal mucosa or oral cavity is enough.
The reason for the active action of pollen is permeability factors that facilitate the entry of microscopic elements into the epithelium. After the onset of the local acute inflammatory process, soluble allergic particles are quickly absorbed into the blood and various parts of the body.
They cling very strongly to cells and stimulate the release of histamine. The result is a reaction in the form of spasms of smooth muscles, swelling of the mucous membrane, and difficulty breathing. After contact with the irritant, literally 20 minutes pass, after which the allergic reaction begins to progress.
In case of weakened immunity, allergies begin to appear in different parts of the body.
Plants to which pollen is most often allergic:
- Trees at the time of flowering such as poplar, alder, willow, maple, birch.
- Trees during leaf fall.
- Meadow and cereal grasses.
- Flowers such as buttercups, asters, lilies of the valley.
- Weeds.
An allergic reaction may begin to appear when eating plant products that contain pollen antigens. But Dr. Komarovsky believes that if the immune system is strong, then no allergies or hay fever will be scary.
Symptoms of hay fever
Signs of the disease appear at the same time every year. The main symptoms are:
- itching in the nose, ears and throat;
- sneezing;
- the appearance of discomfort in the eyes such as itching, lacrimation, photophobia;
- itching in the genitals;
- rhinitis with discharge of a fair amount of mucus;
- increased fatigue.
Later, the following signs begin to appear:
- increased body temperature;
- labored breathing;
- the appearance of urticaria on the epidermis;
- symptoms of cystitis.
A dry paroxysmal cough appears. With hay fever, this phenomenon is associated with irritation of the respiratory tract. When the first signs appear, you must urgently contact a specialist to avoid undesirable consequences.
Diagnosis of hay fever
A patient with these symptoms should be examined by a specialist. This is done by an otolaryngologist. When examining the nose, ear canals and oral cavity, the doctor must exclude ARVI. After this, a diagnosis of hay fever is made. Only after examination by an ENT specialist does the patient undergo a venous blood test for immunoglobulin levels. Next, the patient goes directly to the allergist.
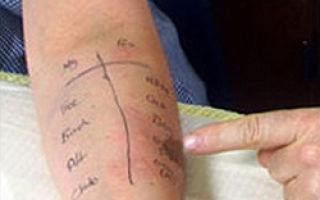
In the cold season, after the symptoms disappear, the doctor will be able to do allergy tests. Such tests will help determine which product a person is experiencing such a reaction to. Samples include:
- small notches are made on the forearms;
- diluted allergen is dripped onto each notch;
- an allergen that provokes bright and prolonged redness is the cause of the disease.
After identifying the allergen, the doctor prescribes an effective treatment for the disease.
Treatment of hay fever
At first, treatment of the pathological condition is carried out throughout the year:
- in warm weather, patients take measures to eliminate symptoms;
- during the cold period, the irritant is determined.
Only then is it possible to keep hay fever under control. After a couple of years, you can reach the minimum amount of funds used. To reduce symptoms you need to:
- change your lifestyle;
- stick to a diet;
- take medications against illness.
Lifestyle adjustments
At the time of exacerbation, the patient must be protected from pollen. During the warm season it is recommended:
- rinse your nose and mouth with a sodium chloride solution;
- shower constantly;
- regularly perform wet cleaning;
- ventilate the room at night;
- do not leave the house during the hot period of the day;
- do not travel during flowering to places where there are many irritants;
- the air should always be slightly humid.
During the cold period, you do not need to take pills for hay fever. It is important to simply strengthen your immune system. To do this you need:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- do hardening;
- exercise.
Diet
The diet for hay fever consists of eliminating foods containing the allergen from the diet. At the time of exacerbation, it is necessary to exclude cow's milk, seafood, bee products, chocolate, and citrus fruits from the diet. You should also avoid those foods that may cause cross-allergies. You should exclude beer, bananas, melon, potatoes, watermelon, margarine, apricots, red apples and much more.
Drug treatment
The main drugs in the treatment of the disease are those that block the release of histamine from immune cells. During the period of acute allergies, tablets are indicated:
- Tavegil;
- Suprastin;
- Diazolin.
Third generation medications may also be prescribed:
- Erius;
- Cetirizine;
- Loratadine.
Antihistamines for this pathology must be taken as a whole course. They provide excellent relief from symptoms. During pregnancy, it is extremely difficult to treat this disease. All medications are contraindicated for use. It would be optimal for a pregnant woman to change her place of residence.
Symptomatic treatment
This is a therapy that is prescribed depending on the symptoms that appear:
- For difficult nasal breathing, vasoconstricting medications are indicated: Nazol, NOC-Spray, Lazolvan-rino.
- In case of symptoms of bronchial asthma, Singulair and Acolat are prescribed.
- For watery eyes, Ketotifen eye drops are prescribed.
Homeopathic treatment
Official medicine does not approve of the treatment of this pathology using homeopathy. This is extremely dangerous and self-medication is not recommended. It is only possible to turn to experienced homeopaths. You can use certain homeopathic medicines that can alleviate the patient's condition. A positive result is shown:
- Cinnabsin;
- Sinupret;
- Nux vomica.
Treatment in children
If hay fever is diagnosed, treatment in children is carried out using the same methods as in adults:
- Walks should be in places where there are not many flowering plants.
- Do wet cleaning daily, hang moistened gauze on the window.
- In spring, summer and autumn, take a bath after each walk, but do not use herbal decoctions.
- Follow a strict diet, just like adults. If you are ill, you should not add new dishes to your diet.
- When taking medication, listen to all the doctor’s recommendations. Not all drugs can be used for therapy in children.
- After a walk, be sure to rinse your nose with saline solution.
- Do not use homeopathic medicines.
- ASIT can be used in children from 5 years of age.
Prevention of hay fever
Doctors offer several preventive measures that will help prevent the disease. Prevention methods are as follows:
- Primary. Prevent negative reactions and eliminate harmful factors. It is necessary to harden the body, eat right, and succumb to physical activity.
- Secondary. It is important to reduce negative symptoms and prevent their manifestation. It is necessary to undergo a timely course of therapy.
The causes of hay fever, what it is, and the symptoms of the disease are known, so it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner to get help. You should not resort to self-medication, as the consequences may be undesirable. Treatment with traditional methods is possible only after preliminary consultation with a specialist.
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/59f9a0235a104fe1e0d6eaf6/5a89dc6fa815f1f98d8ffaa0
Hay fever | Symptoms | Diagnostics | Treatment – DocDoc.ru
Hay fever is a seasonal allergic reaction to pollen that can manifest as conjunctivitis, rhinitis, asthmatic bronchitis or dermatitis. It is characterized by nasal congestion, inflammation of the mucous membranes of the eyes, cough, shortness of breath, and skin rashes.
More often, allergic hay fever is diagnosed in children and young people. The disease is cyclical: during the period of exposure to the allergen on the body, it worsens, after its disappearance, it goes into remission.
The most common allergen for hay fever is pollen from wind-pollinated plants (weeds, cereals, trees). Depending on the period of their flowering, allergists distinguish three forms of the disease:
In some cases, patients have increased sensitivity to all types of pollen. Then their allergic symptoms persist from May to September.
Causes of hay fever
Hay fever in children and adults is a consequence of sensitization (high sensitivity) to the effects of a specific environmental factor - grass or tree pollen. Fine pollen, falling on the mucous membranes and skin of the patient, causes a specific reaction of the body.
An exacerbation is observed during the flowering period of the “provoking plant”. Thus, spring hay fever (April, May) is observed in persons who cannot tolerate pollen from alder, hazel, birch, and oak; summer (June, July) - in those that respond to the flowering of wheatgrass, foxtail, timothy, and fescue. Autumn hay fever occurs in people who are allergic to pollen from quinoa, wormwood, and ragweed.
The severity of clinical manifestations is determined by weather conditions. When there is a strong wind, the symptoms become pronounced; during rain, they weaken as the pollen settles. In cases where hay fever occurs in parallel with allergic food reactions, cross-allergy is diagnosed.
9.2 25 reviews Allergist Immunologist Doctor of the highest category Elvira Viktorovna Azarova Experience 19 years 8.8 85 reviews Allergist Immunologist First category doctor Elena Evgenievna Gorbunova Experience 32 years 9.5 149 reviews Irina Dmitrievna Baranova Experience 28 years Candidate of Medical Sciences 8.6 39 reviews Allergist Pulmon ologist Doctor of the highest category Elena Arkhipova Gennadievna Experience 15 years 9.2 172 reviews Allergologist Pulmonologist Doctor of the highest category Panina Irina Valentinovna Experience 21 years 9.2 131 reviews Allergist Gastroenterologist Cardiologist Therapist Pulmonologist Immunologist Rheumatologist Fedorova Lyudmila Grigorievna Experience 37 years 9.5 102 reviews Allergist Immunologist Doctor member of the highest category Sergeev Andrey Viktorovich Experience 20 years Candidate of Medical Sciences Sciences 8 (495) 185-01-01 8 (499) 116-78-78 8.9 16 reviews Allergist Immunologist First category doctor Bilibina Svetlana Vladimirovna Experience 15 years Candidate of Medical Sciences 8 (499) 519-39-10 8 (495) 185 -01-01 9 13 reviews Allergist Immunologist Doctor of the first category Starostenkova Irina Igorevna Experience 22 years 8 (499) 519-39-10 8 (495) 185-01-01 8.6 135 reviews Allergologist Immunologist Doctor of the first category Tsarevsky Kirill Lvovich Experience 13 years
Symptoms of hay fever
- Seasonal hay fever develops in two stages. The disease begins with:
- Afterwards allergic conjunctivitis, lacrimation, photophobia, and a feeling of sand in the eyes appear.
- The second stage is observed 6-8 hours after the onset of the first symptoms. It is characterized by:
The discharge from the eyes becomes purulent.
The development of atopic/contact dermatitis, Quincke's edema, inflammation of the external genitalia, and cystitis is possible.
Hay fever is often accompanied by pollen intoxication, the symptoms of which include:
If pollen is ingested, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain may occur.
If you notice similar symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
Diagnosis of hay fever
Diagnosis of seasonal hay fever includes:
- examination of the patient, during which the doctor listens to complaints, assesses the severity of symptoms and the characteristics of their manifestation;
- medical history. It is determined at what time symptoms appear. The period specified by the patient correlates with the list of plants blooming at this time;
- anamnesis of life. The allergist asks under what conditions the patient works, whether he has bad habits, intolerance to any medications, whether any of his relatives suffer from hay fever due to ragweed or pollen of other plants;
- study of external respiration function. Relevant if the patient complains of attacks of suffocation or difficulty breathing. Allows you to evaluate the conductivity of the respiratory tract, lung capacity and other important parameters;
- blood test for IgE antibodies (class E immunoglobulins, which are responsible for fighting allergic reactions);
- allergic skin testing. Allergens are applied to the patient's skin - substances that cause an allergic reaction and are perceived by the body as foreign. To do this, the skin is scratched with a special instrument (scarifier) and then treated with compounds containing allergens. It is also possible to introduce the latter into the body by performing prick tests (shallow injections). Afterwards, the reddened areas are used to determine which allergens the body reacts to most acutely;
- cytological examination from the nasal cavity. It is performed for seasonal hay fever of the nose. During diagnosis, an increased content of eosinophils is revealed;
- determination of the level of allergen-specific xIgE in blood serum. Performed when skin testing is unable to accurately identify the allergen (for example, if the group of suspected allergy-causing substances is large);
- general blood analysis. In case of allergies, it shows a high content of eosinophils.
When examined by an ophthalmologist, signs of inflammation of the conjunctiva (swelling/redness of the mucous membrane of the eye) may be detected. A consultation with an otolaryngologist may reveal redness of the nose, inflammation of the pharynx, and the presence of mucous discharge from the nose.
Treatment of hay fever involves stopping contact with the allergen. To do this, the patient is recommended:
- do not go outside (especially in windy weather);
- do not open windows in the house;
- use special air purifiers that capture pollen;
- Avoid eating foods that may contribute to the development of cross-allergy during hay fever.
If the course of the disease is mild, the patient is prescribed antihistamines:
- Azelastine, Levocabastine - locally;
- Fexofenadine, Astemizole, Loratadine - orally.
For moderate illness, it is necessary to use local glucocorticosteroids:
- Fluticasone;
- Triamcinolone;
- Beclomethasone;
- Mometasone, etc.
If symptoms of bronchial asthma are severe, hay fever is treated with inhaled glucocorticosteroid drugs. However, they should be used with caution if hay fever is accompanied by fungal, bacterial or viral infections, or immune disorders.
Severe allergic disease requires the combined use of antihistamines and glucocorticosteroids.
For nasal congestion, Naphazoline, Oxymetazoline, Xylometazoline drops can be instilled (treatment with them should not exceed one week, otherwise allergic rhinitis may occur).
If the nasal passages are significantly narrowed, surgical treatment (cryosurgery, laser) is indicated, during which partial removal of the nasal turbinates is performed.
Doctors consider specific immunotherapy, carried out simultaneously with taking antihistamines, to be the most effective way to combat hay fever. It involves introducing increasing doses of the allergen into the body. As a result, sensitivity to substances that cause hay fever gradually decreases.
Treatment of hay fever with folk remedies
Treatment of hay fever at home can be carried out using folk recipes. According to reviews of people suffering from this type of allergic reaction, the following herbal infusions help achieve the best results:
- 6 tbsp. licorice root, 3 tbsp. Combine viburnum flowers with 2 tbsp. elecampane, 2 tbsp. medicinal sage, 2 tbsp. peppermint, 5 tbsp. horsetail. Mix the herbs. 2 tbsp. collection, pour a glass of boiling water. Leave for 8 hours. Strain. Drink 1/4 cup 3 times a day. The herbal collection helps get rid of swelling of the nasal sinuses and runny nose caused by hay fever;
- combine 1 tsp. rhizomes of marsh calamus, 1 tsp. rhizomes of Potentilla erecta, 4 tsp. St. John's wort herb, 1 tsp. comfrey roots. Mix. 2 tbsp. pour a glass of boiling water over the herbal mixture. Boil over low heat for 5 minutes. Strain. Gargle with the resulting medicine and rinse your nose;
- mix 2 tbsp. St. John's wort herb, 1 tbsp. tansy flowers, 3 tbsp. comfrey roots, 2 tbsp. herb eyebright sprout. Boil 1 tbsp. collection, poured with a glass of boiling water, 10 minutes. Strain. Gargle with the product and rinse your nose.
It is also recommended for patients with hay fever:
- drink freshly squeezed celery juice 3 tsp. 3 times a day;
- drink half a glass of juice made from two apples, three carrots, two cauliflower inflorescences half an hour before each meal;
- place 5 drops of dill oil on a piece of sugar and dissolve it half an hour before meals before each meal (at least 3 times a day);
- drink 100 ml of decoction made from nettle leaves (pour 2 tablespoons of crushed leaves with a glass of boiling water and leave);
- chop 4 onions, pour a liter of cold boiling water over them and drink the resulting infusion a few sips the next day before meals.
Diet for hay fever
The diet for hay fever due to ragweed and pollen of other plants involves the exclusion of certain foods from the diet. The fact is that in some cases, a reaction to pollen has the same symptoms as a food allergy (cross food allergy). Eating the “wrong” foods leads to a severe deterioration in well-being.
To understand which products are dangerous for each individual patient, you should study the information below.
If you are allergic to weeds (wormwood, sunflower, calendula, ragweed, chicory, etc.
), it is advisable to avoid consuming spices, herbs, vegetable oil, mustard, eggplant, watermelon, zucchini, halva, seeds, melon, and drinks in the preparation of which wormwood was used (for example, balms, vermouth).
You should also be careful with garlic, honey, citrus fruits, bananas, and carrots. Medicinal plants such as tansy, wormwood, coltsfoot, dandelion, chamomile, yarrow, and calendula can cause harm to health.
If you are allergic to tree pollen (alder, apple, birch, hazel, etc.
) you can expect allergies from eating nuts, carrots, some fruits and berries (pears, apples, cherries, cherries, olives, kiwi, olives, apricots), dill, celery, parsley, birch sap.
It is also advisable to exclude the negative effects of tomatoes, cucumbers, potatoes and onions on the body. When treating various diseases, you should not use medicinal alder cones, birch buds and leaves.
If you are allergic to grass pollen (wheat, rye, corn, feather grass, oats), the symptoms of hay fever may worsen after eating beer, baked goods, bread kvass, coffee, cocoa, smoked sausage, porridge (corn, barley, rye, oatmeal, rice). You should be more careful with citrus fruits and strawberries. Among medicinal herbs, it is recommended to avoid using bluegrass, foxtail, wheatgrass, fescue, feather grass, timothy, rye, millet, barley, oats, corn, rice, and wheat.
Danger of hay fever
Hay fever can lead to the development of:
- inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane of the eyes (bacterial conjunctivitis);
- inflammation of the cornea and mucous membranes of the eyes (keratoconjunctivitis);
- anaphylactic shock (a life-threatening reaction that occurs when an allergen is perceived by the immune system as a foreign substance).
If a patient experiencing anaphylactic shock is not provided with competent medical care, death is possible. Therefore, hay fever cannot be called an absolutely safe disease.
Risk group for seasonal hay fever
Women are most often affected by hay fever. However, among rural residents the disease is much less common.
The decisive role in the occurrence of pathology belongs to hereditary predisposition. So, if both parents suffer from a pollen allergy, the probability of symptoms occurring in the child is 50%, if one of the parents is 25%. If no one in the family suffers from hay fever, the risk of getting hay fever is reduced to 10%.
Children who are exposed to allergen-contaminated environments from an early age, suffer from viral diseases, and are malnourished are more likely to experience allergic reactions. If you begin to notice allergic reactions in your child, you need to come to any allergy medical center as soon as possible.
Prevention of hay fever
Preventive measures to prevent the development of hay fever include:
- refusal to travel to nature during the flowering of a plant to which you are allergic to pollen;
- ventilate the room through a window hung with a damp cloth;
- departure for the time of flowering to a populated area located in a different climatic zone;
- washing the eyes and gargling to wash out allergenic substances;
- drying things after washing indoors.
It is also necessary to avoid contact with chemicals and tobacco smoke. During the flowering season of the allergen plant, it is advisable to take medications aimed at eliminating the symptoms of hay fever.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Source: https://illness.DocDoc.ru/pollinoz