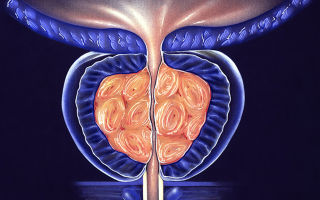
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced in a man’s body (in the prostate gland) that performs the function of liquefying sperm.
The amount of protein increases with age, with prostatitis, and neoplasms. Therefore, PSA serves as a tumor marker for prostate cancer or other pathological process.
All men should periodically undergo a PSA test for prostatitis in order to promptly detect oncology or adenoma.
The need for diagnostic tests
To establish the correct diagnosis and recognize negative changes in prostate diseases, a set of examinations is prescribed. PSA in chronic prostatitis makes it possible to detect inflammatory processes and oncology in the prostate, so it is mandatory for diagnosis.
It is necessary to examine the patient to assess the condition of the affected organ, then ultrasound to examine neighboring organs. Chronic prostatitis can affect the bladder and urinary system, kidneys, testicles, and rectum. An examination of the inflammatory process of glandular tissue will help to distinguish prostatitis from similar ailments such as urethritis, vesiculitis, etc.
If the doctor has all the information on the disease, he will be able to prescribe the appropriate treatment. Without research and a blood test for PSA, you can make a mistake in making a diagnosis and incorrectly prescribe medications. Therefore, it is necessary to complete all test orders and strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations in the future.
Prostatitis and symptoms
Prostatitis is a disease of the prostate gland accompanied by an inflammatory process. It occurs due to a sedentary lifestyle, previously untreated infections, non-compliance with diet, long-term abstinence from sex, etc.
Symptoms of the disease can be different: severe pain in the pelvis, delays in urination, problems in bed. It happens that prostatitis does not make itself felt, so you need to visit a doctor once a year in order to promptly detect the onset of the disease.
Prostatitis is determined by examining urine, blood, and prostate secretions. Palpation and ultrasound are performed, and in case of a controversial situation, other examinations are also prescribed.
Determining the PSA level in chronic prostatitis is a necessary test for diagnosing the disease. Having studied its results, you can immediately determine whether everything is in order with the gland.
An analysis is prescribed for the following symptoms:
- Pain involving the groin, perineum, external genitalia, lower abdomen.
- Premature (in the early stages of the disease) or delayed (in later stages) ejaculation.
- Difficulty urinating, accompanied by pain and burning.
- Frequent urge to go to the toilet, especially at night. With advanced pathology, urine comes out with pus, blood, and thread-like discharge.
- Some men may have mild or no symptoms at all. In this case, prostatitis is determined only by test results or examination.
After effective treatment, the antigen level gradually normalizes - after about a month. If after therapy the level remains the same high, the development of prostate cancer is suspected. Therefore, after completing a course of treatment, it is necessary to retake a general PSA blood test. In chronic forms of prostatitis, examinations are prescribed every three months.
PSA level analysis
Elevated protein does not mean that a person has cancer. PSA viscosity increases with heavy physical exertion, after bladder surgery, and prostate biopsy.
Protein is measured in nanograms per milliliter. Its norm changes according to age:
- from 20 to 25 years the norm is 2.5 ng/ml;
- from 25 to 40 - not higher than 3 ng/ml;
- from 45 to 65 - no more than 3.5 ng/ml;
- from 65 years old - should not exceed 4 ng/ml;
- in old age, the protein may not be produced at all due to the cessation of prostate function.
In healthy men, the indicator is very small, since the presence of the antigen is scanty. As soon as the process of degeneration of healthy cells into malignant cells begins, its production increases. The growth of the indicator occurs for other reasons:
- For benign prostatic hyperplasia. Overgrown tissues of the organ put pressure on healthy ones, as a result, the penetration of protein into the blood is activated.
- During infections and subsequent inflammatory processes, the barrier protective functions of the gland tissue are disrupted, and the substance also enters the bloodstream.
- Thus, the PSA norm for prostatitis is 5-6 ng/ml, during periods of exacerbations - up to 10 ng/ml. If the indicators exceed this figure, malignant formations are present in the body (prediction accuracy is approximately 70%).
If the protein in the blood is 20 ng/ml, cancer of the lymph nodes in the prostate area is suspected; if the marker reaches a value of 50 ng/ml, cancer is fully developed; at 100 ng/ml, metastases are possible.
Bacterial type prostatitis is determined by a figure reaching up to 34 ng/ml, while the stagnant type shows 4 ng/ml, which is difficult to diagnose even by analysis.
The PSA level increases due to an increase in the volume of prostate tissue; the larger it is, the more antigen it produces. Therefore, a PSA test for prostate disease is necessary.
Conducting research
Urologists recommend that all men over 45 years of age undergo a general blood test for PSA every year, as it can detect cancer even before symptoms of the disease appear. The study is especially necessary for those men whose immediate relatives were susceptible to this disease.
Often, using a rectal examination or ultrasound, it is impossible to determine the presence of a malignant pathology due to small changes in the gland tissue, while an increased PSA value shows the opposite. When diagnosing dangerous organ diseases, medicine primarily focuses on the presence of prostate-specific antigen in the blood.
Laboratory tests are prescribed:
- To track the progress of prostate cancer. This checks the correctness of the chosen treatment.
- If there is a suspicion of a malignant tumor of an organ.
- For preventive purposes, for men over 45 years of age.
- After completing a course of therapy prescribed for cancer diagnosis.
All patients in urology departments need to be aware of the importance of timely diagnosis of disorders in the functioning of the prostate. By regularly undergoing examinations and tests, you can identify the disease at an early stage and successfully treat it.
Before donating blood for antigen detection, a man must follow the doctor’s recommendations for preparing for the procedure to avoid errors in the test results. The patient should consider the following points:
- For 8 hours before blood sampling, you should not eat anything other than juice, water or tea.
- Avoid cycling, long-distance walking 24 hours before the examination, and do not use an exercise bike.
- A week before the test, refrain from sexual intercourse and eating smoked and spicy foods.
- If a transrectal ultrasound of the prostate, digital examination of the rectum, colonoscopy or catheterization of the bladder was performed, then only after a week it will be possible to determine PSA in the blood.
- After a biopsy of the gland or massage, you should wait two weeks.
Only by following all these recommendations can you get a reliable result of protein levels. The study is carried out in laboratory conditions during the day.
Preventative tips
If the blood test result for protein exceeds 10 ng/ml, you should reconsider your lifestyle.
It is recommended to avoid drinking alcoholic beverages, smoking, taking walks in the fresh air, and regularly consulting with a urologist.
It must be remembered that timely testing and detection of an increased value of total PSA in the blood makes it possible to determine prostate cancer at the first stage.
Prostatitis is an insidious disease that brings a man not only physical suffering, but also psychological one.
The first cause of pathology is an infection, the development of which is facilitated by the position of the gland relative to the pelvis.
This part concentrates the paths through which the infection can easily penetrate: the urethra, bladder, rectum, lymphatic and blood vessels of the pelvis.
For the development of infection (the prostate fights small ones on its own), other contributing factors are needed. The infection develops into prostatitis if the following recommendations are not followed:
- Avoid hypothermia of the body. This can happen due to swimming in an ice hole - “winter swimming”, or being in a cold vehicle or room for a long time. Do not sit on cooled concrete or stone.
- Avoid frequent constipation.
- You cannot work sitting for a long time. Office workers and programmers, drivers are at risk.
- Excessive activity or long abstinence from sex negatively affects the body and primarily the prostate gland.
- Regularly contact a urologist to avoid developing urethritis or gonorrhea, which contribute to the occurrence of prostatitis.
- Do not suppress the body's immune system. This means not overloading yourself when playing sports, getting good sleep, eating regularly and efficiently, and avoiding stress.
If you do not follow these recommendations, microbes will easily penetrate the prostate gland. Malicious organisms will find themselves in a favorable environment for reproduction, and this leads to an inflammatory process.
Manifestations of prostate disease
There are three types of prostatitis: acute, chronic bacterial and chronic non-bacterial. The first type is rare. It is easily diagnosed and can be treated without problems. Acute prostatitis is characterized by an acute onset of the disease. It occurs due to hypothermia or ARVI.
In this case, the body temperature rises to 40 degrees. There is pain in the groin, perineum, lower abdomen, acute pain when urinating, sometimes with blood. Infection is always the root cause of prostatitis. If this form of the disease is not treated, complications may arise: inflammation of the testicles and their appendages, prostate abscess, chronic prostatitis.
Chronic bacterial is as rare as the acute form of prostatitis, only in 10−15% of all cases. The main reasons influencing the occurrence of this disease are foci of chronic infections: urinary tract, ENT organs, untreated acute form of prostatitis. This is facilitated by frequent hypothermia, irregular sexual intercourse, and working in a sedentary position.
Nonbacterial prostatitis is accompanied by constant chronic pain and occurs in 8 out of 10 cases of the disease. It has such an abundance of symptoms that it is difficult to establish its diagnosis: from slight deviations in urination to constant severe pain.
Another difficulty lies in the lack of facts about how such a disease occurs. After therapeutic treatment, non-bacterial chronic prostatitis can develop again.
The main symptom by which this form of the disease can be diagnosed is constant, unremitting pain, as well as urination problems, aching pain in the perineum, and sexual dysfunction of varying degrees. This negatively affects the quality of life of any man.
The causes of the disease are very different. These also include a violation of the barrier function of the prostate gland caused by a lack of zinc and lysozyme in the body. Pathology usually begins with an infectious-inflammatory process, and then covers autoimmune mechanisms.
Share with your friends and rate the publication. It’s not difficult for you, but it’s nice for the author.
Thank you.
Source: https://manbe.ru/muzhskie-bolezni/obshhiy-analiz-psa-pri-prostatite-i-uroven-antigena-v-krovi.html
PSA analysis for prostatitis: norm and deviations, interpretation of indicators, recommendations
- June 10, 2019
- Prostatitis
- Marina Star
A general PSA analysis is a determination of the levels of prostate-specific antigen, which is produced by prostate tissue. The protein PSA is necessary to thin a man's sperm. It should be noted that malignant neoplasms produce larger amounts of this substance. For this reason, the analysis is used as a tumor marker for prostate cancer. In addition, the amount of this protein produced can be affected by absolutely any pathological process that occurs in a man’s body. That is why a PSA test for prostatitis must be performed. Thanks to it, it is possible to detect the development of oncology or prostate adenoma. So, let's look in more detail at what a PSA analysis is for prostatitis, what its norms are, and also for what reasons deviations from it occur.
Why does protein increase?
How is the amount of this element determined? To determine protein levels, it is necessary to take a free PSA test. The norm of this antigen should be no more than 4. With existing malignant cells in the body, protein production begins to increase significantly. Otherwise, with a general blood test, PSA for prostatitis, the norm will increase for the following reasons:
- The antigen level may increase due to existing infections, which are also accompanied by an inflammatory process in the male body. In such a situation, the barrier function of the tissue is disrupted, due to which the substance gradually enters the blood.
- The prostate protein PSA can actively enter the bloodstream if the overgrown tissues of existing benign prostatic hyperplasia put pressure on other tissues of the organ.
It should be noted that antigen analysis for a disease such as prostatitis reveals any deviation and disturbance in the entire functioning of the male body. The majority of patients who had an elevated antigen level do not suffer from cancer.
In a general blood test, PSA for prostatitis, the norm may increase due to surgery on the bladder or due to a prostate biopsy. In addition, the amount of antigen in the blood increases during ejaculation or after prolonged physical activity.
When is it necessary to get tested?
As mentioned earlier, a PSA test is taken for prostatitis. However, this is also done in other cases. The specialist prescribes these laboratory tests in the following situations:
- To watch how prostate cancer develops. Thanks to this, you can check the effectiveness of the selected treatment tactics.
- If there is a suspicion of a neoplasm on the prostate gland. However, this can also be detected using other diagnostic methods: ultrasound, digital rectal examination, and others.
- For preventive purposes, an antigen test is prescribed to patients over 40 years of age to detect an increase in protein levels.
- After antitumor therapy, which was carried out after the diagnosis of prostate cancer. As a rule, after such treatment, experts recommend that patients undergo this examination at least once every 3 months.
Preparing for the test
In order to donate blood for a PSA test for prostatitis, you should carefully prepare for this procedure. If you ignore this step, the protein antigen indicator will be incorrect. For this reason, experts recommend following the following rules:
- Approximately 8 hours before blood sampling, do not eat food, and also avoid drinking alcoholic beverages, strong tea, coffee and juice.
- It is also necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse approximately 5-7 days before blood sampling.
- The analysis must be taken 12-14 days after examination by a urologist or before his visit.
If a prostate massage, bladder catheterization, transrectal ultrasound or cystoscopy, digital rectal examination or other mechanical effect on the prostate was performed, then blood is taken 2 weeks after such research methods, and if a biopsy of prostate tissue was performed, then the analysis is taken after 1 month after this procedure.
The PSA analysis is interpreted within approximately 1 day. To get tested, a specialist must give a referral to a man, after which the patient prepares and then donates blood from a vein. Sometimes it is necessary to determine either the free antigen or the total indicator. This is necessary in order to more accurately diagnose the patient.
Decoding the results
We have already discussed what a PSA test means for prostatitis. But how is it deciphered? Antigen testing for this disease can be interpreted by several methods. The level of antigen in the blood is usually measured in nanograms per 1 ml of blood.
Some experts say that the minimum threshold for this indicator should be reduced to 2.5. Thanks to this, it will be possible to detect more prostate diseases. However, there is a risk that specialists, as a result of this test, will treat cancer that has no clinical significance.
During diagnosis, three types of protein should be taken into account:
- Free prostate specific antigen. This antigen is found in the blood, making up about 20% of the total PSA value.
- A protein that is associated with A1-antichymotrypsin or A2-macroglobulin. Only the first type of antigen can be determined in a laboratory setting.
- General indicator of PSA analysis. This indicator includes the total amount of protein entering the blood.
Dog and prostatitis
This disease, in fact, cannot be called a malignant disease. After all, prostatitis does not even increase the likelihood of developing prostate cancer.
But with the help of regular monitoring of antigen levels, it is possible to correctly adjust the treatment, which is aimed at combating the inflammatory process.
If the antigen indicator is in the range from 4 to 10, then this may indicate the development of the following diseases:
- Prostatitis.
- Prostate oncology. In this case, the risk of diagnosing the disease increases by approximately 25%.
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia.
It should be noted that experts among themselves call this indicator of the antigen level the gray zone. If the protein concentration increases more than 10, then the probability of developing cancer appears by approximately 67%.
Quite often, the level of common antigen is directly related to the type of prostate disease. This analysis is often used for differential diagnosis.
How is the disease determined?
If the test was taken and carried out correctly, and the antigen level is between 45 and ten, then when making a diagnosis, specialists pay attention to the following protein fractions and ratios:
- A decrease in the concentration of free antigen increases the risk of developing cancer. This is due to the fact that malignant cells produce much more A1-atichymotrypsin.
- An increased concentration of free antigen, on the contrary, reduces the risk of developing cancer. In this case, this indicator may indicate the presence of chronic prostatitis.
Other data
A general test to determine the antigen in the blood for prostatitis, the price of which will vary depending on the clinic, is recommended for patients over 50 years of age once a year. To improve test results, additional indicators are used that allow you to consider the protein depending on various parameters.
Antigen density should be taken into account during testing. Thanks to this, it is possible to calculate the protein concentration in relation to the size of the prostate gland itself, which is determined using transrectal ultrasound. The low density of the antigen may indicate that the main reason for its growth is hidden in the development of prostatitis.
In addition, the speed of antigens is also taken into account. It represents a comparison of antigen over a certain period of time. If the indicator increases quickly, then the specialist can diagnose the patient with prostatitis, which occurs in an acute form. This may also indicate the initial stage of oncology.
Protein control
You can only monitor blood protein levels using the analysis discussed in this article. A specialist should study the features of this test in detail.
For example, as a result of recent studies, it has been proven that a disease such as prostatitis can lead to an increase in the serum level of this antigen.
It is necessary to take the test even if there are no signs of inflammation, and a digital rectal examination does not reveal any abnormalities.
First of all, such phenomena indicate that the prostate is not working well due to certain disorders. If the analysis indicators jump sharply, then doctors in this case recommend:
- If the antigen level has increased significantly, then it is necessary to check for symptoms of prostatitis, as well as any genitourinary infection.
- After treatment for prostatitis or after genitourinary infections, it is necessary to retake the PSA test.
Price
The price of such a test is from 600 rubles. and more. In some clinics, the patient may also pay additionally for blood sampling from a vein. In order to give a more accurate price, in any case you will have to contact the laboratory in your clinic.
Conclusion
There is no direct evidence that prostatitis causes prostate cancer. But the histological signs of this disease are often diagnosed by doctors during the study of cancerous prostate tissue.
Source: https://cureprostate.ru/424796a-analiz-psa-pri-prostatite-norma-i-otkloneniya-rasshifrovka-pokazateley-rekomendatsii
General PSA blood test for prostatitis: norm and deviations (transcript)
PSA is a special protein produced by the epithelium of the prostate gland and helps liquefy the ejaculate. The blood of healthy men contains this prostatic antigen in low concentrations.
However, a general PSA blood test can also show an increased level of this enzyme against the background of the development of certain chronic diseases.
Experts recommend that men periodically undergo a general PSA blood test for prostatitis; deviations in protein concentration indicators in the transcript make it possible to timely determine the possible development of a malignant tumor.
Timely PSA analysis helps prevent malignant processes.
Types of antigen
PSA, after absorption from the prostate epithelium into the man’s blood, can be present in it in three different forms: Types of antigen When to donate Preparation Consider the results What changes after radical therapy
- A free protein that is present in the blood in its pure form and is not combined with any plasma proteins.
- A protein associated with the highly active blood enzyme chymotrypsin.
- An enzyme associated with the plasma transport protein macroglobulin.
This prostate epithelial enzyme classification is used as the basis for diagnostic tests:
- General PSA blood test. This diagnostic test determines the concentration of free and chymotrypsin-bound protein.
- Free PSA concentrations are determined.
- Laboratory analysis of venous blood for the level of ratio of free specific antigen to total.
The ideal option is when the doctor specifies what kind of diagnostic test a man should undergo - a general PSA blood test or another type of test for this antigen. It is better to go for a consultation to a knowledgeable, competent specialist.
When to take it
A general capillary blood test, biochemical studies, general and sometimes targeted (specific) urine analysis are a standard set of diagnostic procedures.
It is used to identify pathologies of internal organs, severe disorders of the functioning of organs and systems.
A study on the level of enzyme concentration of the prostate epithelium is recommended in the following cases:
- Regular monitoring of men with prostatitis, prostate cancer and assessment of the effectiveness of therapy for these diseases.
- Confirmation of the development of a benign or malignant tumor in the prostate gland after a course of treatment and in a comprehensive diagnostic study.
- If a doctor has prescribed a patient antitumor tests for prostatitis, he must take a diagnostic test to determine the amount of PSA once every three months.
- As a preventive examination for people over 40 years of age. Such measures make it possible to promptly determine the increased amount of enzyme and the causes of the deviation, and prescribe adequate treatment.
If the doctor has prescribed a test for prostate-specific antigen after prostatectomy, then in no case should this laboratory diagnosis be ignored. Even if nothing overshadows your well-being, then find time to donate blood for a test.
Preparation
A general PSA blood test (its interpretation) in some cases can show false positive results (in which deviations will be higher than normal) if a man underwent any procedures on the prostate, urethra or bladder before taking the test. Also, in order to obtain the most reliable research result, you should:
- 12 hours before donating blood, completely eliminate natural juices, tea, coffee, and alcohol from your diet.
- 48 hours before collecting material, refrain from sexual contacts that may cause deviations in the results.
- If a man undergoes a massage course for prostatitis, then he should get tested no earlier than three days after completing the course. In addition, biological material for laboratory diagnostic studies should not be submitted immediately after a rectal examination.
Be sure to follow these rules, because to get an incorrect result is to expose yourself to the risk of receiving an incorrect diagnosis, which will entail drawing up an unnecessary treatment plan. Remember that proper preparation for tests serves as a starting point, so treat this procedure responsibly.
Considering the results
Normal PSA levels vary depending on a man's age. The level of this protein in plasma increases with age. Over time, the prostate grows. This phenomenon directly affects the increase in the amount of enzyme. The critical norm that the decoding of the general PSA analysis should contain is determined by the following indicators:
- In representatives of the stronger sex aged 40 to 49 years, the specific antigen should not exceed 2.5 ng/ml.
- Age group from 50 to 59 years - the PSA norm is up to 3.5 units.
- For patients aged 60 to 69 years, the level of this type of protein should not exceed 4.5 ng/ml.
- At the age of 70 years and older, the norm of this enzyme is up to 6.5 units.
After 40, PSA tests are recommended annually.
For people over the age of 40 who periodically take a complete PSA blood test for preventive purposes, the specific antigen should be below the level of 2.5 units, and a digital examination of the gland should also show a good result. In this case, the patient is considered completely healthy, and laboratory tests for PSA levels are repeated after a year.
If the laboratory determination of the level of a specific protein (antigen) is above 2.5 units, and an examination by a doctor shows a normal (or pathological) result, in this case the patient is recommended to undergo a prostate biopsy. This is a more informative test than an antigen test.
In addition, it is worth considering that an excess of the enzyme, which was shown by laboratory studies of plasma, can manifest itself in prostatitis. These deviations also indicate the presence of inflammatory processes in the patient’s body.
Decoding the analysis of biological material for the amount of PSA, namely, how much protein is exceeded in the plasma, allows the doctor to determine the pathology. For example, a specific antigen (only slightly higher than normal) after 40 years can appear with prostatitis.
PSA concentration indicators:
- From 4 to 10 units – observed with prostatitis, which has turned into a malignant tumor.
- From 20 to 40 units (decoding of the general blood test PSA, which shows abnormalities) - indicates that the patient’s oncological process has been developing for quite a long time.
- Results above 40nk/ml – deviations indicate metastasis of a malignant tumor in prostatitis.
However, it is worth considering that for people who take the drugs Finasteride, Dutasteride, Avodart or their analogues for prostatitis, the interpretation of the general analysis of biological material for PSA concentration will be false. After all, the effect of these drugs reduces the concentration of this enzyme by 50%.
What changes after radical therapy
As practice shows, after a radical prostatectomy, a general PSA blood test shows a sharp decrease in its concentration, namely no more than 0.2 units.
In the first year after removal of the prostate gland, most patients experience no change in PSA levels. And this is the norm for the body. In this case, a deviation of up to 0.3 units is allowed.
This indicator is also normal; after removal of the prostate (prostatectomy), the antigen (more precisely, its level) changes. If deviations from this norm exceed 0.4 nc/ml, then this indicates:
- Progressive cancer disease.
- Development of the metastatic process.
It is worth noting that the overall PSA level, even after radical therapy, is an individual indicator for each patient. But if, a year after surgery, the analysis, namely its decoding, showed deviations from the norm, this can only indicate a relapse of the oncological disease.
A PSA blood test is one of the necessary examination methods during the diagnosis of serious diseases, as well as in the treatment of prostatitis. Decoding the analysis together with the results of other diagnostic methods makes it possible to promptly determine possible deviations and identify pathological processes in the body.
Source: http://Mprostata.ru/diagnostika/analiz-krovi-psa-obshhij-pri-prostatite
Why do you need a PSA blood test for prostatitis?
PSA is best known as a tumor marker that signals the development of prostate cancer.
Many men are wary when a doctor prescribes this type of study as part of the diagnosis of prostate pathology.
There is usually no reason for concern - a PSA test for prostatitis is needed not only to exclude cancer, but also to determine the phase and dynamics of the development of inflammation .
General information
PSA is a prostate-specific antigen. This is a special protein synthesized by prostate tissue, both healthy and tumor. The larger the prostate volume, the higher the PSA . That is why exceeding the norm of this substance is a reason to suspect the appearance of neoplasms in the gland, but it is not a fact that they are malignant.
The very presence of prostate-specific antigen in the blood is normal (as is its absence), since this protein is part of the juice produced by the gland and carries an important functional load: it liquefies sperm, which ensures sperm motility, and takes part in the regulation of testicular function .
When is a PSA test needed and how is it done, says venereologist-urologist Sergey Gennadievich Lenkin
In case of prostatitis, a PSA test is done with the aim of drawing up a more complete clinical picture of inflammation and excluding a malignant tumor process . Main indications:
- Frequent urination at night;
- Poor heredity in terms of oncology;
- Difficulty or intermittent urination, a constant feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- Chronic pain in the groin.
The analysis is also used to track the health status of patients with the following pathologies:
- With operated prostate cancer or during its treatment.
- When changes in the structure of the gland are detected during a digital examination.
- For prostate adenoma.
- Vascular pathologies of the gland (ischemia, infarction).
This type of research is relevant for men over 40; it is usually not prescribed for younger men.
Preparation
Many factors influence the amount of antigen in the blood. For a reliable result, it is important to fulfill a number of conditions before submitting the analysis:
- Sexual rest for at least 2 days. Ejaculation leads to an increase in antigen levels;
- For 3-4 days, stop eating fatty, spicy, fried foods, completely eliminate alcohol, drinks with nutrients (for example, sports drinks);
- Wait at least 3 days after any intervention on the prostate (massage, diagnostic manipulations) and a week after TRUS (rectal ultrasound), otherwise the PSA value will be significantly elevated. After prostate surgery, the test can be taken after 6 months;
- Refrain from physical activity for 3-4 days, especially those that stimulate the prostate (biking, rowing, weighted squats).
Preparing for tests (click on the image to enlarge)
Failure to comply with the above rules will lead to a distortion of the result, the prescription of incorrect treatment with subsequent side effects.
How the analysis is done
Provided proper preparation, the test result will reflect the actual volume of antigen. It is best to donate blood in the morning (10-12 hours of fasting). You can drink plain water. It is recommended to avoid physical and nervous overload and stop taking medications. Do not smoke about an hour before the procedure.
Immediately before taking blood, you need to completely relax. The injection is made into a vein in the bend of the elbow . Approximately 5-10 ml of blood is drawn into the syringe, after which the puncture site is closed with a cotton swab soaked in an antiseptic.
PSA levels are measured by enzyme immunoassay. The results are sent to the doctor for study and interpretation. The result will be ready the next day . If the doctor has doubts about the accuracy of the indicator, the test is retaken at approximately the same time interval as the first time.
Free and bound forms
PSA circulates in the blood in 3 molecular forms:
- Free (fPSA). Occupies 20% of the total. The norm is in the range from 0.04 to 0.5 ng/ml, the limiting threshold is 0.93 ng/ml. This indicator is most important for diagnosis. When it exceeds the regulated value, there is a good reason to suspect prostate cancer.
- Associated (cPSA). 1 type of connection - with alpha-1-antichymotrypsin. Exceeding the level indicates the development of a tumor. Type 2 - with alpha-2-macroglobulin. An increase in value indicates the presence of chronic or acute prostate pathologies. The total bound rate is from 3.5 to 3.96 ng/ml.
- General (the totality of free and also bound by antichymotrypsin).
The analysis first determines the amount of total PSA. If the result is elevated, then the volumes of each molecular form of the protein are deciphered and determined.
Average prices for analysis:
- General PSA – from 400 to 610 rubles;
- Free – from 515 to 610 rubles;
- Calculation of the index (ratio) – from 800 to 950 rubles.
Of the private laboratories, the cheapest analysis will cost you at Mobilmed, and the most expensive at Invitro.
Decoding
Standard values for the volume of the antigen were derived during many years of observations and examinations of men with cancer, subject to different concentrations of this protein in the blood.
Some experts recognize a value of 4 ng/ml (nanograms per ml) as normal, others – 2.5 ng/ml.
Since elevated values require a prostate biopsy (serious intervention) to clarify them, the standards were revised and adjusted according to age (Table 1).
Table 1. PSA norms depending on the age of the man
| Age | Standard (upper limit), ng/ml |
| 40-44 | 2-2,3 |
| 45-49 | 2,4-2,7 |
| 50-54 | 2,8-3,2 |
| 55-59 | 3,3-3,7 |
| 60-64 | 3,8-4,4 |
| 65-69 | 4,5-5,1 |
| 70-74 | 5,3-6 |
| 75-79 | 6,2-7 |
| After 80 | 7,2 |
1 g of adenomatous tissue increases the PSA concentration by 0.3 ng/ml, and cancer tissue by 3.5 ng/ml. Measuring the rate of protein growth over the course of a year helps determine the quality of the tumor: if the indicator has increased by more than 0.75 ng/ml, then there is reason to suspect the development of a malignant process of the gland .
If total PSA exceeds 10 ng/ml, a biopsy is prescribed. In this case, the ratio of the free form of the antigen to the total form should be less than 15%. If the level is elevated, but does not cross the limit of 10 ng/ml, then the index (Ipsa) is calculated: (free bound) x 100%. Normally the value should be 15%. The lower the percentage of the ratio, the greater the likelihood of developing a malignant formation.
An important indicator is PSA density. It is calculated as the ratio of the total volume of antigen produced to the volume of the gland. The safe threshold is up to 0.15 ng/ml per 1 cm3 of tissue.
Dangerous values of total PSA : from 10 to 20 ng/ml - likely cancerous damage to the lymph nodes in the area of the gland, at 50 the presence of a malignant neoplasm is practically beyond doubt, at 100 extensive metastasis is usually diagnosed.
Reasons for the increase
PSA increases when exposed to factors that are not always pathogenic. For example:
- Age-related changes. The older a man is, the larger the prostate becomes due to slower functioning and benign tissue growth;
- Passion for some sports (motorsports, cycling);
- Failure to comply with the rules of preparation for analysis;
- Enlarged prostate size (genetic).
An elevated PSA value is always considered in conjunction with the results of other studies . This is an organ-specific marker - it reflects the condition of the organ, not always indicating its specific diseases.
An increase in the indicator can occur due to infectious prostatitis, adenoma, and diseases of other pelvic organs. PSA also increases against the background of insufficient blood supply to the gland (ischemia), with atrophy of its vessels.
Successful drug therapy reduces the volume of antigen.
PSA for prostatitis
An increase in the level of antigen during inflammation of the prostate is due to the fact that due to swelling of the tissues, the ducts are blocked, the release of the protein is difficult and the main part of it is absorbed into the blood. Infectious processes disrupt the structure of cells, reduce their barrier functions, as a result of which the antigen penetrates in large quantities into the blood vessels.
As a result of urological examinations of patients with chronic prostatitis, the following PSA values were identified:
- In the bacterial form – from 4.6 to 34 ng/ml. The ratio of free antigen to total is from 13 to 25%.
- In the abacterial (non-infectious) form – from 0.8 to 4.2 ng/ml. The ratio of free and total antigen is from 19 to 28%.
- For prostate sclerosis (replacement of normal tissues with rough connective tissue due to chronic inflammation) - from 0.3 to 1.1 ng/ml.
In nonbacterial prostatitis, the PSA level before and after treatment does not change significantly. The average value is 4 ng/ml. In the infectious form, antibacterial therapy helps to reduce the volume of antigen, so in this case, PSA indicators are convenient for monitoring the phases of exacerbations and remissions. Average values: 5-6 ng/ml during remission, 10 ng/ml for acute prostatitis.
How to normalize PSA for prostatitis
If the risk of cancer is excluded, and the cause of the increase in PSA is prostatitis, then the following methods can be used to reduce the antigen level:
- Medicines (except prescribed antibiotics). Thiazide diuretics – lower blood pressure and remove PSA in the urine. 5-alpha reductase inhibitors – slow down the growth of glandular tissue. Lipid-lowering drugs - lower cholesterol levels, normalize weight, help reduce PSA. All of the above remedies can be used only on the recommendation of a doctor;
- Diet . Reducing consumption of saturated fats (full-fat milk, meat, butter). Introduce vegetables, berries and fruits. The most useful: tomatoes, pomegranates, grapes;
Urologist and andrologist of the highest category Roman Borisovich Mazo on nutrition for prostate diseases
- Preparations based on mint, chaga, nettle, hemlock, wormwood, plantain, fly agaric . For prostatitis, pumpkin seeds are an effective auxiliary measure for reducing PSA. Bee products and flax seeds are useful for adenoma.
Normalization of PSA is facilitated by moderate physical activity, which accelerates blood flow in the prostate area (allowed only during periods of remission or in case of abacterial prostatitis).
Importance and frequency of examinations
A PSA test helps to detect prostate cancer in a timely manner and also prevents its development by signaling borderline conditions of the prostate tissue. Exceeding standard values is often the only indicator of pathologies in the pelvic area.
For men over 40 years old, doctors recommend donating blood for antigen once a year, after 50 – twice a year . It is safer to use the services of the same laboratory so that there are no discrepancies in results due to the quality of equipment, personnel qualifications, and research methods.
To explore the infographic, click on the image
Conclusion
An excess of PSA due to prostatitis is not yet a reason to panic. Even high values may be the result of improper preparation for the study or the influence of non-pathogenic factors. The advisability of taking a PSA test for prostatitis is determined only by the attending physician, who also interprets the results.
Source: https://muzhchina.info/prostata/prostatit/analiz-psa
A dog's general blood test for prostatitis: what is the norm?
One of the ways to diagnose inflammation in the prostate gland is to donate blood for the PSA tumor marker. Knowing the normal indicators, an experienced doctor will not only confirm the preliminary conclusion about the disease, but also predict the risk of developing prostate cancer. Read the article about what PSA is, which indicators are considered normal, and which indicate the development of pathology.
What is PSA
Prostate specific antigen PSA is a complex polypeptide protein consisting of many amino acids. The production of the substance occurs in the cells of the prostate gland. And it doesn’t matter what origin they are. Normal and cancer-induced - produce PSA in equal amounts.
In the absence of pathologies in the prostate, PSA is excreted from the body with ejaculate and prostate secretions.
In this case, prostate specific antigen acts as a secretion diluent, thereby increasing sperm motility.
A small amount of PSA enters the blood; it is on this property that diagnostics using the okomarker is based. The presence of antigen is measured in nanograms per milliliter.
When pathology occurs in the prostate gland (tumor or inflammation), the organ increases in size. New cells are formed, their number increases, followed by an increase in PSA production.
Due to the narrowing of the excretory channels and their deformation, the excretion of the antigen decreases, therefore its presence in the blood increases. PSA analysis allows you to identify the onset of the pathological process in the early stages.
It becomes possible to detect the following diseases and pathologies:
- prostate tissue infarction;
- inflammatory processes and foci of infection;
- prostate cancer in different stages;
- benign prostate hyperplasia (adenoma);
- prostatitis in various forms.
The normal amount of PSA in the blood serum depends on age. This factor is taken into account by a urologist when diagnosing and differentially diagnosing prostatitis in men.
What is a digital prostate examination?
PSA levels in the blood at normal and abnormal levels
It has been established that the older the man, the higher the upper threshold of the normal PSA value in the blood serum. Such analysis is rarely performed in young men.
This is due to the fact that PSA levels are measured when prostate cancer is suspected.
The disease most often occurs over the age of 45, so not all urologists consider checking antigen levels in young men to be necessary.
For normal PSA levels in the blood, see the table.
| Age | Indicator ng/ml |
| Up to 44 | 2,5 |
| 45-60 | 3,5 |
| 61-70 | 4,5 |
| 71 and older | 6,5 |
In men under 45 years of age, PSA may be absent altogether. This is considered normal, because such a study is not the only one for diagnosing prostatitis and prostate cancer.
If the PSA level is elevated to 10 ng/ml during analysis, the ratio of total to free antigen must be taken into account. The normal indicator in this case is a value greater than 15%.
With a lower ratio, there is a suspicion of the development of prostate cancer, which serves as the basis for prescribing an organ biopsy. If research is necessary, the PSA density index is also calculated.
The value is determined by dividing the antigen value by the volume of the prostate gland.
Changes in the level of PSA in the blood in diseases are different:
- Above 20 ng/ml – pathologies in the regional pelvic lymph nodes.
- Above 50 ng/ml – in addition to damage to the lymph nodes, prostate cancer.
- More than 100 ng/ml – the appearance of cancer cell metastases.
With prostatitis of any form, blood levels increase slightly. After the course of treatment, the indicators return to normal and there is no reason for concern.
Considering the factors that provoke an increase in antigen in the blood serum, we can say with confidence that a change in the indicator does not always indicate cancer.
A similar picture is typical for infectious and chronic prostatitis, as well as for prostate adenoma.
What are the consequences after a prostate biopsy?
How to prepare for the PSA test
With prostatitis, as with other pathologies of the prostate gland, preparation for blood donation is important. There are several known factors that provoke an increase in antigen in the blood:
- ejaculation less than 2 days before the test;
- prostate massage less than 3 days before blood collection;
- TRUS performed in a week or less;
- cytoscopy and catheterization also increase PSA levels.
When preparing for a PSA blood test, it is necessary to exclude these factors in order to obtain a reliable picture.
If inhibitors, for example, dutasteride, were prescribed for the treatment of prostate BPH, the value of the onomarker decreases after a year. When testing for prostate specific antigen, this point must also be taken into account.
A PSA test for prostatitis is carried out simultaneously with a general blood test. The material is taken from the vein of a sick man.
In order for all indicators to be reliable, you must stop eating and drinking alcohol 8 hours before taking the test. Tea, coffee and juice are also undesirable.
Violating the rules for preparing for a PSA test will distort the results and make it difficult to diagnose not only prostatitis, but also prostate cancer.
Conclusion
A blood test for total PSA is a reliable test for detecting prostate cancer at an early stage.
Men over 45 years of age are recommended to visit a urologist or andrologist once a year to monitor the rate of change in the indicator. With prostatitis, the level does increase, but only slightly.
Therefore, additional examination is necessary to diagnose the prostate gland.
If the PSA blood test reaches more than 10 ng/ml, adjust your lifestyle. Stop smoking and drinking alcohol, spend more time outdoors, and visit your doctor regularly.
Remember that timely detection of an increase in total PSA in the blood makes it possible to detect prostate cancer at the first stage.
Source: https://oprostatite.info/urologiya/prostatit/diagnostika-prostatit/norma-obshhego-psa-v-analize-krovi-i-otkloneniya-pri-prostatite