- Dermatologist of the highest category Inna Vladimirovna
- 31790
- Update date: December 2019
By the diagnosis of micropapillomatosis, doctors mean benign rashes in the genital area.
This disease occurs in women. In most cases, it does not cause them any discomfort.
But many doctors still recommend treating micropapillomatosis in order to avoid the consequences that the disease leads to in the presence of favorable conditions, although this is rare.
What is micropapillomatosis
Micropapillomatosis in women appears against the background of dysfunction of the reproductive system or a malfunction of the endocrine glands.
The latter are responsible for the production of certain sex hormones, which are produced in both men and women.
If there are too many of them or there is a lack of these substances, then the epithelial tissues in the genital area begin to become covered with a large number of neoplasms, which strongly resemble papillomas in their appearance.
Small rashes on the genitals are not contagious. They have nothing to do with the human papillomavirus. Also, this disease is not considered as a form of dysfunction of the organs of the reproductive system, since it does not affect their tissues and cellular structures.
Causes
Experts identify several main reasons that can lead to the development of micropapillomatosis:
- Hormonal disbalance. A sharp decrease or increase in androgens has a detrimental effect on the condition of the skin in the intimate area. Due to such violations, it may change colors and become covered with small growths;
- Underwear. If it is too tight to the body and is made of low-quality synthetic fabric, then wearing it will cause rashes caused by skin irritation to appear on the body. If the problem is not eliminated, it will lead to the development of the disease;
- Infections. Certain types of infectious diseases may superficially resemble a micropapillomatous rash. Over time, the signs of the pathological process become more pronounced, causing the mucous membrane of the genital organs to become even more inflamed;
- Oral contraceptives. Taking such drugs causes hormonal imbalance, which provokes the formation of micropapillomatosis;
- Anabolic steroid. This reason is not often explained by the appearance of small growths at the vestibule of the vagina and near this area. Anabolic steroids affect the condition of the genital organs, so they may well lead to the growth of micropapillomatosis.
Those women who lead an unhealthy lifestyle and do not take good care of their own health are most at risk of getting sick.
Synthetic underwear, although beautiful, is better to avoid it
Signs of micropapillomatosis
A small rash on and near the labia minora may indicate a serious illness that needs to be treated immediately. But still, there is no need to panic right away. Sometimes such rashes are a sign of a woman’s individual anatomical features. For example, a micropapillomatous rash can hardly be called a serious illness.
Growths caused by this pathology rarely cause discomfort. In addition, they are not sexually transmitted. And most importantly, the disease is not associated with papillomatosis. The two diagnoses are united only by a consonant name.
Skin formations of this type are characterized by the following features:
- Moderate density;
- Painless;
- Symmetrical arrangement;
- No complications;
- Flesh or pale pink shade.
These distinctive features help to recognize micropapillomatosis. If necessary, you can compare the woman’s rashes with the growths in the photo, which depict intimate areas affected by the disease.
Minor rashes do not cause discomfort
Diagnostics
If a woman develops symptoms that indicate a micropapillomatous lesion, she should be diagnosed. It will help you accurately identify the disease and, if necessary, select treatment to eliminate it.
Any rash in the genital area should alert a woman. After all, they do not always turn out to be harmless. Similar neoplasms often warn of the development of sexually transmitted diseases, for example, syphilis. To recognize the pathology, a serological blood test will be required.
A doctor will not be able to give a patient a correct diagnosis based solely on external symptoms. In this case, differential diagnosis is required. A gynecologist deals with it. Initially, he must examine the woman in a gynecological chair and take a smear from her, which is sent for analysis.
Cytological examination allows you to obtain the following information:
- Determination of the cellular structure of the rash;
- The nature of the pathological process;
- Identification of damaged cellular structures;
- The presence of a viral pathogen.
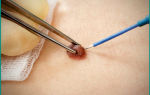
The most accurate information about the disease is provided by the polymerase chain reaction. It allows a specialist to determine the nature of neoplasms at the molecular level.
PCR analysis identifies the pathogen by DNA
Treatment of micropapillomatosis
When diagnosed with vulvar micropapillomatosis, treatment is not always required. To find out, the doctor must only study the examination results that the patient will provide him. If neoplasms bring discomfort to a woman or she simply intends to return the natural surface of the skin in an intimate place, then she is offered a choice of modern methods of therapy.
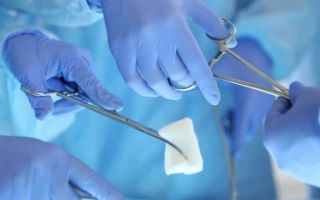
Laser therapy
Vestibular micropapillomatosis of the labia is removed without complications using a laser beam. It instantly excises all tumors in the affected area, thereby gently polishing the skin.
The procedure continues until the surface of the labia becomes smooth. To achieve this result, no more than 2 laser therapy sessions are required.
Sometimes one procedure is enough if the growths are not too dense and are located only in certain areas of the genitals.
Electrocoagulation
During the surgical procedure, the growths are cauterized by exposing them to high-frequency electric current. This method is painful for many women, so anesthesia of the problem area is required before surgery. Complete restoration of the affected tissues will occur approximately 5 days after completion of treatment.
Cryotherapy
Micropapillomatosis that has grown in the vaginal area can be cured with liquid nitrogen. It is applied to problematic growths. This treatment destroys the tumor cells and causes them to simply fall off.
Surgical excision is not performed for benign growths of this type. This is because it is very difficult to remove a small formation with a scalpel, while causing serious harm to healthy skin.
In addition, this treatment leads to bleeding. The period of tissue recovery after the procedure is quite long.
Based on these features, doctors do not recommend surgical excision for micropapillomatosis.
Surgical removal of such small growths is not performed
Traditional medicine
For micropapillomatosis, the use of alternative medicine is allowed. It is best to combat benign rashes with the help of medicinal plants. They improve the microflora of the vagina and do not allow infectious pathogens to penetrate damaged tissues in case of injury to the growth.
When treating micropapillomatosis, it is recommended to use:
- Decoctions of chamomile and oak bark. Their preparation takes a minimum of time. This product is suitable for washing the genitals. Herbal decoctions have antiseptic, antibacterial and antifungal effects, thanks to which a woman can quickly cope with the disease. For the product to work, it must be as concentrated as possible. They are advised to wash every day for 14 days;
- Decoctions of celandine. To prepare it, you need to boil the plant in water for about 5 minutes. A natural remedy should also be used to wash the genitals;
- Herbal decoctions. A remedy that is brewed from mint, chamomile, lovage and linden has proven itself well. Prepare and use the decoction according to the principle described above.
Folk remedies will help prevent the growth of rashes and prevent infection.
Forecasts
Neoplasms caused by micropapillomatosis respond well to treatment. Relapses with this diagnosis occur only in exceptional cases. If a woman carefully monitors the cleanliness of her genitals and avoids factors that provoke the appearance of growths, then this problem will not bother her for a very long time.
Thousands of women live quietly with micropapillomatosis and do not even think about treating it. The situation is different with formations that cause physical or psychological discomfort. In this case, you should contact a competent specialist and ask him to select an effective therapy to eliminate unpleasant rashes on the genitals.
Source: https://DermatologInfo.ru/papillomy/vidy/mikropapillomatoz/
Micropapillomatosis
Micropapillomatosis is a set of symmetrical rashes, predominantly flesh-colored, located on the woman’s labia minora, namely on their inner surface and midline. Somewhat less often they can be diagnosed on the labia majora.
Micropapillomatosis in women is usually detected rarely and its occurrence in medical practice is approximately 4-5% of cases.
Based on the majority of studies, as well as a detailed study of various clinical cases, it was found that these rashes are not initially pathological and rather belong to anatomical changes of an individual nature.
If the development of this anatomical condition is established, vulvar micropapillomatosis is most often diagnosed. Vaginal micropapillomatosis, like other parts of the woman’s reproductive system, does not require specific pathogenetic treatment based on the use of various medications.
What is micropapillomatosis
Micropapillomatosis is small formations of pale pink or flesh color, shaped like papules.
As a rule, these elements are arranged linearly, in rows, symmetrically on both sides, for example, micropapillomatosis of the labia. When they are palpated, a doughy soft consistency and painlessness are determined.
They are most often located in the area of the labia minora, as well as on the midline, which is collectively called vulvar micropapillomatosis.
It has been established that these anatomical changes predominantly develop during puberty. However, despite a large number of studies on this problem, it was not possible to establish a single reason for the formation of these rash elements.
Most scientists are inclined to the possible role in their development of changes in the hormonal system, which inevitably occur in the bodies of young girls, because it is during puberty, according to established data, that these nodules most often begin to form.
Also, factors that may be able to influence their development include mechanical irritation of the external genitalia by wearing tight, tight underwear.
However, this is difficult to attribute to the description of such a condition as vaginal micropapillomatosis, as a result of which another factor is put forward, such as the presence of various chronic inflammatory pathologies of the female reproductive system.
Despite the similar name with such a rather serious disease as human papillomavirus infection, in the process of a large number of laboratory tests, as well as the study of a sufficient number of clinical cases, it was found that these two pathologies have no connection. Although some scientists are still trying to find some connection between these conditions.
During numerous histological studies of micropapillomatosis in women, no signs were identified that could indicate the relationship of these elements with papillomavirus infection. Namely, the phenomenon of coycylotosis, which is characteristic of the human papillomavirus or HPV, has not been identified.
Micropapillomatosis of the labia, as well as any other anatomical area of the female reproductive system, is in no way harmful to her health; it is a variant of the normal anatomical structure; it is not transmitted through unprotected or protected sexual intercourse.
As a result of observations of the course of this condition, the possible development of any complications from these papules has not been established.
According to some data, cases of spontaneous regression and reduction of micropapillomatous rashes without the use of any treatment methods have been identified.
However, the use of all possible methods of removing formed elements is not prohibited and undesirable, since for some women these elements cause some degree of psychological discomfort, although in fact they do not cause any physical suffering or pain.
Symptoms and signs of micropapillomatosis
Micropapillomatosis usually appears most often during puberty, which indicates a possible reason for its formation in the form of hormonal changes in a young body. This process is characterized by the appearance of elements in the form of papules or nodules, small in size, pink in color, and soft to the touch.
Most often they are diagnosed in the vulva area on the labia minora, somewhat less often on the labia majora. When making a diagnosis, it is possible to indicate the specific localization of the elements of the rash, for example, micropapillomatosis of the labia.
It should be noted that the nodules are located symmetrically on both labia; it is also possible to trace some linearity in their location; their localization is often noted as if in rows.
When palpating the elements that have arisen, no reaction in the form of pain is detected, any discomfort in the form of itching, irritation or the possibility of an increase in size is not diagnosed.
In the case of the presence of symptoms such as itching, burning, and even more so pain, and despite the presence of a clinical picture of micropapillomatosis, it is imperative to consult a doctor, since even against the background of this anatomical condition, infections of various types are possible.
It is very important to be able to distinguish between micropapillomatosis in women and the development of genital warts, which are caused by infection with the fairly common human papillomavirus. Condylomas are characterized by a scattered, asymmetrical location in the female genital area.
They are very similar in color to the elements of micropapillomatosis, somewhat denser in consistency, in contrast to anatomically occurring nodules, larger in size, and often form peculiar groups or growths.
An important differential sign that a doctor can immediately identify during a direct examination of the patient is a test with acetic acid, in which, in the presence of condylomas, their significant blanching develops.
If the developed nodules are just micropapillomatosis, then the acetic acid test will always be negative. However, this method is only auxiliary or additional, but in no case determining when making a diagnosis.
It is also always worth remembering that condylomas can also occur when infected with a sexually transmitted disease such as syphilis, which is also characterized by the formation of the above elements. In such a situation, an important step would be to refer the patient for a serological blood test.
Based on the above, we can identify the following signs of micropapillomatosis, which most fully characterize this condition:
— It develops most often in young girls during the period of hormonal changes, that is, during puberty.
- — In this condition, only the woman’s genital organs are affected; as a rule, micropapillomatosis of the vulva is diagnosed; the development of nodules in the vaginal area is somewhat less common.
- — The rashes are pink in color, very small in size, located symmetrically in relation to each other and can most often be found on the inside of a woman’s labia.
- — On palpation, they are completely painless, have a slightly dense consistency, and are not accompanied by burning or itching.
- - Over time, they do not increase in size, do not ulcerate, do not cause any complications, that is, they are completely safe in relation to a woman’s health, that is, in some way they represent only a cosmetic defect, which a woman can sometimes find out about only at an appointment with a doctor - gynecologist during examination.
- — There is no registered fact of transmission of developed elements through sexual contact, that is, they are not dangerous during unprotected sexual intercourse and are not capable of being transmitted to a partner.
Treatment of micropapillomatosis
According to established data, the detected micropapillomatosis does not require any treatment; this condition is usually attributed to peculiar anatomical features that develop as a result of possible hormonal changes or in the case of long-term presence of chronic inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system.
However, quite often women, when this process is established in them, begin to experience some psychological discomfort. In this case, it is recommended to eliminate this peculiar cosmetic defect using electrocoagulation, laser therapy or cryodestruction methods.
During the use of cryodestruction, the formed nodules are destroyed under the influence of liquid nitrogen, while electrocoagulation uses the process of cauterizing the nodules with an electric current. Most popular, however, is the removal of these elements using laser exposure.
This technique does not cause any painful effects, and also promotes rapid restoration of damaged tissue.
However, it is always worth warning the patient that in this condition, the above-described methods are not necessary, and can only be used if desired.
Any medications taken orally have no effect on these nodules. Also, all kinds of topical drugs, such as vaginal suppositories or tablets, are in no way capable of affecting them.
Rarely, but still, cases of independent reduction of developed rash elements without the use of medications of any effect and without the use of the above methods for their removal have been established.
However, before starting any treatment methods, you need to be very carefully examined and make sure that we are talking about micropapillomatosis, and not about such a serious process as the human papillomavirus, as well as syphilis. Unlike the mentioned pathologies, micropapillomatosis does not pose a threat to a woman’s health, and if the diagnosis is incorrect, the prescribed treatment will be inadequate and unnecessary.
To carry out a complete differential diagnosis, an important step is a direct examination of the woman on the gynecological chair, taking from her all the necessary biological materials for microscopic examination.
When conducting a cytological examination in the presence of genital warts caused by a viral infection of the body, such a typical sign as koilocytosis will be detected. This phenomenon is a specific damage to cells when infected with the human papillomavirus.
Cytological examination alone is not enough, since pathological cells can often be located in deeper tissues.
Also, when performing a test with acetic acid and receiving a negative reaction, one can only assume that there is no viral pathology, since this assumption can only be confirmed or refuted using a special polymerase chain reaction technique, as well as during colposcopy. If necessary, to fully confirm the alleged diagnosis, a woman may be sent for a special histological examination.
If micropapillomatosis is detected and suspected in a woman, it is necessary to conduct a study such as PCR. This is a fairly widely known and diagnostically significant method, based on the data of which a final diagnosis can be made and appropriate treatment can be prescribed.
Therefore, if a woman detects any rashes in her genital area, it is imperative to consult a doctor to find out the cause and refrain from any type of sexual intercourse during the diagnostic period.
There are no specific methods for preventing the development of micropapillomatosis, since in most cases the nature of their development is assumed to be based on hormonal changes.
However, it is not superfluous to carefully monitor your health, promptly treat inflammatory processes in the genital organs, maintain personal intimate hygiene, and it is especially important to teach girls this. Also, one of the possible factors for the development of micropapillomatosis is mechanical, that is, possibly associated with wearing tight, synthetic underwear.
We must also remember this and try not to create provoking conditions for the development of such an anatomical condition, which is not dangerous, but still has the characteristics of a cosmetic defect.
Source: https://vlanamed.com/mikropapillomatoz/
Micropapillomatosis. Causes, symptoms and treatment
content
Micropapillomatosis of the vulva (synonyms: micropapillomatosis of the vestibule of the vagina, genital/vestibular micropapillomatosis, lat.
micropapillomatosis labialis, micropapillomatosis of the labia minora) is a small nodular painless rash, usually pale pink in color with slight variation in shade in individual cases, appearing on the labia minora and is currently interpreted as a purely cosmetic problem, and even then quite rare (according to various estimates , in the general population occurs with a frequency of 1-5%).
Noteworthy is the fact that any materials devoted to this topic, especially at the popular science level, are replete with the conjunction “not”: micropapillomatosis is NOT dangerous, it is NOT associated with oncogenic serotypes of the human papillomavirus and is NOT prone to malignancy; this rash is NOT contagious and is NOT a sexually transmitted infection; it does NOT cause any damage to health or well-being, does NOT affect fertility (the ability to get pregnant), the course of gestation (gestation) and the success of childbirth; DOES NOT have complicated or atypical forms; in general, micropapillomatosis is NOT, strictly speaking, a disease, and therefore does NOT require treatment.
This raises a natural question: what, in this case, IS labial micropapillomatosis?
2. Reasons
Etiopathogenesis, i.e. The causes and trigger factors, mechanisms and patterns of development of micropapillomatosis are currently unknown.
The similarity with papillomas and genital warts, not to mention the typical localization for the latter, is so obvious that the viral hypothesis suggests itself and seems to be almost the only reasonable explanation, especially since “papilloma” is clearly heard in the name.
Nevertheless, there are serious histological and physical differences on which differential diagnosis is based (see below).
Perhaps the diagnosis should be changed to micropapulosis or pseudopapulosis, from “papule” - nodule, pimples. However, there is clearly a venereal disease called “bovenoid papulosis”, for which papillomavirus etiology has been proven, and the clinical picture of this disease also does not coincide with the picture of micropapillomatosis.
A competing hypothesis is that micropapillomatosis is caused by fluctuations and imbalances in the hormonal formula.
However, this hypothesis does not yet provide a satisfactory answer to the question of why exactly such pimples appear in this particular area and in the unlucky 1-5% of women, while in the rest, any rashes, polyps, neoplasia, vesicles occur with great frequency , papules, papillomas, condylomas (or nothing similar is observed), but not micropapillomatosis.
Perhaps this is not the main and most pressing question for modern gynecology, but for now it remains open, and research continues.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
The question of whether micropapillomatosis should be considered a disease or declared a variant of the norm is also very controversial.
Most women who have discovered this phenomenon experience significant psychological discomfort, up to depressive-neurotic stuckness on hypochondriacal, cancerophobic, dysmorphophobic dominants, which in turn leads to dyspareunia, low self-esteem and, ultimately, a decrease in quality of life.
WHO defines health as “a state of complete physical and psychological well-being.” The symptom complex described above clearly does not fit into this definition; if micropapillomatosis is perceived by a woman (or her sexual partner) as a problem, then it is a disease.
In addition, micropapillomatosis in any case requires the most careful differential diagnosis, since much more serious diseases, even syphilis or precancerous syndromes, can manifest themselves in a similar way. The following distinctive features of micropapillomatosis serve as differential diagnostic criteria:
- symmetrical, usually linear distribution on the mucosal surface;
- lower density (compared to other externally similar formations, micropapillomatous pimples are noticeably softer);
- lack of color reaction (blanching) to acetic acid;
- absence in histological or cytological examination of signs of koilocytosis, dyskeratosis, parakeratosis, i.e. changes in cellular structure and composition detected during papillomavirus processes;
- isolation of micropapules, lack of tendency to merge into plaques;
- relatively small and non-increasing size of individual elements of the rash.
4.Treatment
It should be repeated that micropapillomatosis, if all other symptomatically similar diseases are conclusively excluded, does not require treatment. This is objective.
Subjectively, such a rash can, as shown above, represent a serious problem that requires psychological correction and elimination of the causes.
Today, fortunately, this problem can be solved quite simply and safely, painlessly and bloodlessly, on an outpatient basis, without general anesthesia and long-term rehabilitation. Mainly three methods of removing micropapillomatous rashes have become widespread: cryodestruction, electrocoagulation and laser therapy. The last approach is the most popular.
Source: https://medintercom.ru/articles/mikropapillomatoz
Micropapillomatosis: causes of rashes on the labia and vagina in women, treatment methods
Small asymptomatic rashes on the labia or vulva in a woman can be a sign of micropapillomatosis.
In terms of external symptoms, this condition is similar to many sexually transmitted diseases, but it is not dangerous and is not sexually transmitted. This anatomical feature is quite rare.
Only a gynecologist can distinguish it from truly serious and dangerous diseases.
Characteristics of the pathology
Experts call micropapillomatosis multiple small rashes on the labia. These formations are benign and do not cause physical discomfort. As a rule, they are located in the vulva area, less often - near the vagina.
Most often, rashes develop in girls during puberty, as well as in women during menopause. Once they appear, they do not grow.
Despite the similar name, micropapillomatosis has nothing to do with the human papillomavirus (HPV) and is not a pathology of viral, bacterial or fungal origin.
However, the symptoms of these diseases at the initial stage can be very similar, so it is recommended to be examined by a doctor.
The rash is not transmitted sexually or through household contact. They are not a disease in the usual sense, but a feature of the physical development of the vestibule of the vagina.
Micropapillomatosis does not pose a threat to a woman’s health and does not affect her well-being. It is treated only because the tumors can cause psychological discomfort to the patient.
Causes
The causes of micropapillomatosis of the labia have been studied very poorly. Rashes most often appear during puberty, when intense hormonal changes occur, so doctors consider these processes to be interrelated. Other risk factors include:
- Poor quality underwear. If it consists of synthetic materials that irritate the skin or is too tight, this can lead to skin pathologies in the intimate area. In this case, eliminating the cause is usually enough to treat the rash.
- Mechanical damage to the genital organs. They can occur both during sexual contact and from other reasons - falls, accidents, accidents. Irritation of the intimate area leads to the occurrence of various pathologies, including micropapillomatosis.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases. They can not only irritate the mucous membrane, but also destroy the structure of vaginal tissue. The consequence of this is often neoplasms and rashes.
- Diseases of the endocrine system. Due to pathologies of the thyroid gland and other organs, changes occur in the levels of various hormones, which, according to doctors, is one of the most likely causes of the development of micropapillomatosis.
- Other conditions accompanied by hormonal changes, such as menopause and pregnancy.
- Taking oral contraceptives. They “deceive” the body by changing the level of hormones to those that correspond to the different stages of pregnancy. This can easily lead to hormonal imbalances, especially if the drugs are not used according to instructions or without consulting a doctor. The consequences of such self-medication can be a variety of ailments, of which micropapillomatosis is considered the most harmless.
- Use of anabolic steroids. These drugs for building muscle mass contain a large amount of hormones, the effect of which on a woman’s body and the condition of her genital organs can be unpredictable. Neoplasms can arise as a result of an imbalance created by drugs.
According to statistics, about 4-5% of women suffer from micropapillomatosis.
This condition is not diagnosed in men. Some doctors tried to establish a connection between the pathology and other diseases of the female genital organs, but to no avail.
Symptoms and signs
As a rule, rashes develop very quickly, without any previous signs or accompanying symptoms. They are usually discovered accidentally by the woman herself or by a gynecologist during a routine examination. Signs of inflammation in micropapillomatosis are as follows:
- the rashes are very small, located symmetrically relative to each other, lining up in rows or lines;
- to the touch, the affected areas are rough, soft or moderately dense;
- there are no inflammatory processes, discharge of pus, burning, itching or other unpleasant symptoms - the disease can only be identified by external signs;
- there is no pain either at rest or when touching or pressing on the rash;
- the rashes do not cause discomfort when sitting, walking, sexual intercourse, playing sports, etc.;
- the color of the neoplasms ranges from merging with the main skin tone to pale pink;
- Over time, the rashes do not change shape or grow, and do not degenerate into ulcers or cancer cells.
Micropapillomatosis does not cause physical discomfort to a woman and does not in any way affect her ability to work, engage in any activity, live a full sex life, or bear and give birth to children. But for many representatives of the fair sex, this pathology causes embarrassment, shame and disgust, so they strive to get rid of it by restoring the natural appearance of the genitals.
Diagnosis and differences from other diseases
Diagnosis of this condition is carried out in order to distinguish the signs of micropapillomatosis from condylomas or papillomas, the initial stages of syphilis, inflammation, malignant neoplasms and other dangerous diseases. The main differences between harmless rashes and HPV infection include the following:
- genital warts that occur with HPV are located chaotically over the entire surface of the vulva or on one side, while micropapillomas are arranged in symmetrical rows;
- condylomas are hard and dense in structure, the rash with micropapillomatosis is much softer and resembles skin elevations rather than warts;
- upon contact with acetic acid, HPV warts change color to a paler color, while micropapillomas do not react in any way to such exposure.
Despite the obvious differences, external examination is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis. Only a specialist can distinguish harmless neoplasms from dangerous ones. He must examine the patient and then take a swab from the affected area to analyze its cellular structure and determine whether the rash was caused by exposure to a virus.
HPV is characterized by fairly specific cell damage (koilocytosis), so it is usually not difficult to distinguish pathologies from each other.
If necessary, more accurate results will be shown by a method such as polymerase chain reaction. To clarify the diagnosis, the patient is also prescribed a serological blood test.
Treatment methods
Micropapillomatosis responds well to treatment. If a representative of the fair sex for some reason decided to get rid of the rashes caused by this condition, she is unlikely to have problems with this. Drugs for neoplasms are not prescribed. The only treatment method known today is physical or chemical removal of the rash.
Removal methods
There are many ways to remove micropapillomatosis in women. 3 methods are considered the most effective and safe:
- Laser therapy. The fastest and safest procedure. Micropapillomas are treated remotely using a laser beam. Its effect is completely painless, and wounds heal quickly and do not become inflamed, which makes this method optimal.
- Cryodestruction. Exposure of neoplasms to cold using liquid nitrogen. The procedure is quick - the rashes are destroyed in seconds. It is safe, but the wounds left behind may bleed or become inflamed.
- Electrocoagulation. Impact on micropapillomas with electric current. The procedure may require local anesthesia. The current cauterizes the blood vessels so there is no bleeding or inflammation, but there is a possibility of burns or discomfort even with anesthesia.
Since the skin on a woman's genitals is very delicate, irritation and other complications may occur after any of these procedures.
Therefore, many doctors advise against treating micropapillomatosis, because it does not harm health and is purely a cosmetic problem.
In addition, in many cases, tumors can disappear on their own without external intervention.
Folk remedies
To treat micropapillomatosis, folk remedies are used, for example, decoctions of medicinal herbs. The good thing about them is that they are easy to prepare at home. Some recipes:
- Celandine decoction. Pour a liter of boiling water over a handful of fresh or dried raw materials, put on fire and hold for 5 minutes. Then cool the broth and strain it through cheesecloth or a fine strainer. Use for washing daily, twice a day.
- Products based on chamomile or oak bark. They need to be made more concentrated than a decoction of celandine. They are used for washing, adding to sitz baths or a regular bath. The course of treatment is about 2 weeks with regular use 1-2 times a day.
- Herbal infusions. You can add sage, eucalyptus, yarrow, string, nettle, celandine, calendula, and chamomile to them. The herbs are dried, crushed, mixed in equal proportions, and then one tablespoon of the resulting mixture is poured with a liter of boiling water and left under the lid for 15 minutes. The product is brought to room temperature and immediately used for washing. It is not recommended to store it.
A contraindication to the use of folk remedies is hypersensitivity to their components. Before applying the herbal decoction to the delicate skin of the vagina, you should conduct a test by spreading a little product on your wrist. It would also be useful to consult a gynecologist.
Preventive measures
The pathology has not been fully studied, so it is difficult to name specific measures for its prevention.
To reduce the risk of developing rashes, it is enough to monitor the hygiene of the genital organs, not wear underwear made of low-quality materials and promptly treat gynecological diseases.
It is known that the development of micropapillomatosis is associated with hormonal imbalance and pathologies of the endocrine system, so their prevention would also be useful.
Source: https://vetryanka.info/papillomy/lechenie-mikropapillomatoza-polovyh-gub
Micropapillomatosis in women on the labia: photos, symptoms and treatment
Time to read the article = 13 minutes
Micropapillomatosis of the labia is a fairly rare disease that affects about 4% of women. The disease manifests itself as many small, flesh-colored rashes on the labia. So, from this article you will learn what other symptoms this disease has and how it can be cured.
Types of rashes on the genitals
The rash on the genitals usually has the appearance of certain skin elements and may appear in the patient suddenly or after an incubation period
The rash on the genitals usually has the appearance of certain skin elements and may appear in the patient suddenly or after an incubation period.
In this case the following appears:
- blisters - they have a short-term course and disappear on their own without treatment;
- pustules are yellow or green in color, contain purulent discharge and appear when the disease is in an advanced stage;
- blisters - they are filled with liquid, located in groups or singly, without treatment they turn into ulcers;
- chancre – has a red color, hard edges and an ulcerated bottom;
- erythema - a very reddened area of the skin that rises above healthy tissue;
- condylomas - they are round lumps above the surface of the skin, they can be either flesh-colored or brown.
- nodes are rashes with a dense structure that lie in the dermal layer of the skin.
- plaques are a rash that consists of grouped small blisters.
These are the most common types of genital rash, but there may be others.
Women's problems: micropapillomatosis
Often the external manifestations of many diseases are confused with a common anatomical feature. However, any pimple that appears, any new spot in an unusual place on a person’s body should be alarming. Especially if the genital and perineal areas are bothering you.
Some women noticed red rashes symmetrically located on the labia. Of course, something that suddenly appears does not lead to anything good. However, there are phenomena in nature whose occurrence does not in any way affect human health. For example, micropapillomatosis in women. Is this your first time hearing this? - here is detailed information about such a manifestation.
What is micropapillomatosis
Micropapillomatosis causes pain
Micropapillomatosis is a multitude of small, light pink or flesh-colored rashes on the labia minora. The shape of the elements resembles papules. Less commonly, the rash appears on the labia majora.
The photo below shows micropapillomatosis of the labia minora, located on their inner surface.
What does micropapillomatosis look like? The photo shows a clear example of flesh-colored rashes on the midline of the vulva. Usually the elements appear symmetrically on the labia, most often they are localized along two parallel lines.
When you touch them, you feel a soft structure. The formations are painless.
The development of the elements occurs during puberty, but the specific causes of the appearance of the rash have not yet been identified. Possible factors in the development of the disease, according to medical scientists, include:
- strong hormonal changes in the body, especially during the maturation of a teenage girl;
- systematic irritation of the genital organs when wearing uncomfortable underwear;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system in the fair sex.
Micropapillomatosis of the labia
Micropapillomatosis of the labia is a fairly rare phenomenon, occurring in only 4% of patients. The origin of the pathology is explained by the anatomical features of the woman. Treatment of micropapillomatosis in women does not require taking special medications.
According to research, micropapillomatosis in women has nothing to do with human papillomavirus infection. Although some medical institutes are still looking for a connection between these pathological processes. The relationship of the disease with the HPV virus is determined during histological and cytological studies for the diagnosis of coycelotosis. This phenomenon is characteristic of the presence of HPV in the body.
Despite similar names, micropapillomatosis has nothing in common with human papillomas and is not viral in nature. Its etiology has not yet been studied, but most experts consider such manifestations to be a variant of the anatomical norm. To finally verify the correctness of this judgment, we propose to consider the differences between viral papillomas and micropapillomatosis:
- Genital warts (condylomas) are hard and rough to the touch. Micropapillomas are soft formations. They resemble small skin elevations of a similar structure.
- The nature of localization. Condylomas are scattered chaotically and are characterized by unilateral lesions. Micropapillomas are arranged in symmetrical rows along a line.
- The vinegar test for warts gives a positive result. Upon contact with acetic acid, the initially pinkish rashes begin to fade. Micropapillomas remain unchanged.
So, micropapillomatosis is a symmetrically located small rash on the labia minora, more precisely on their inner surface along the midline. In rare cases, papules appear on the labia majora. Their color blends with the skin tone, sometimes acquiring a pinkish tint.
Typically, nodular rashes appear during puberty and pregnancy, when hormonal disruption and disruption of the endocrine system occur.
However, cases of occurrence after wearing tight synthetic underwear cannot be ruled out. Micropapillomatosis in women is not a disease. It is not sexually transmitted and does not affect conception or pregnancy.
Unusual rashes on the labia do not cause discomfort, except psychologically.
Manifestations of micropapillomatosis
About 5% of healthy women may notice rows of small pale pink nodules on their labia minora
About 5% of healthy women may notice rows of small pale pink nodules on their labia minora.
They appear most often during puberty, which suggests their hormonal etiology. These nodules, called papules, are soft to the touch and do not cause discomfort or pain to the woman. The color of the formations can vary from pinkish to flesh-colored.
Most often they are located on the inner surface or midline of the labia minora (rarely major) in symmetrical rows.
Micropapillomatosis is not an infectious disease, so it cannot be contracted through sexual or household contact. Unusual changes in the labia do not limit a woman in the sexual sphere, sports or other areas of life.
The reproductive system is not endangered, there is no threat to successful conception and pregnancy. The only inconvenience that micropapillomatous rashes can bring is psychological. Women may consider micropapillomatous pimples a serious cosmetic defect.
This problem can be solved: formations can be removed using simple modern procedures.
Micropapillomatosis and human papillomavirus
The human papillomavirus (papillomavirus, abbreviated as HPV) is not the cause of such changes in the surface of the labia, despite its similar name.
However, it causes another disease, which is sometimes very difficult to distinguish from harmless micropapillomatosis - papillomavirus infection, which affects the external genitalia, perineum and is accompanied by the formation of genital warts (anogenital warts).
HPV affects the growth pattern of vulvar tissue, causing pathological changes in the cellular structure - koilocytosis.
The main differences between viral condylomas and micropapillomas:
- Micropapillomas are located on the labia mainly linearly, in symmetrical rows. Condylomas are scattered over the surface of the vulva.
- Micropapillomatous formations are soft to the touch, the structure of warts is more dense.
- Condylomas are pink, white or red in color and turn pale during the acetic acid test, unlike micropapillomas.
It is extremely important to make a correct diagnosis in the presence of nodular rashes in the vulvar area.
Micropapillomatosis: norm or pathology
According to medical research, the following clinical characteristics of the rash have been identified:
- such damage to any area of a woman’s reproductive system does not harm her health;
- symptoms of vaginal micropapillomatosis refer to normal variants of the anatomical development of the female body;
- the rash is not sexually transmitted;
- the development of complications caused by papules has not been established.
In some cases, this disease resolves itself without the use of any therapeutic measures. Various methods of removing rashes are not prohibited by medicine. For most women, papules cause shame and moral discomfort, although they do not provoke physical ailments; they are often removed. Next in the photo is micropapillomatosis in women.
Micropapillomatosis: photos, symptoms and signs
There is a high probability of this disease occurring due to hormonal changes in a young body. The process is marked by the appearance of rashes on the labia or vulva, similar in appearance to papules, light pink or flesh-colored nodules.
These elements are soft to the touch and do not cause any physical discomfort or pain . The nodules are located symmetrically, and their localization in rows is often noted.
The same symptoms may be present in adult women suffering from hormonal imbalance due to pathology of the endocrine system or in similar physiological conditions, for example, during pregnancy.
Micropapillomatosis of the vulva: photo
If you experience pain, itching in the area of the rash and an increase in the size of the papules, you should consult your doctor.
If you experience pain, itching in the area of the rash and an increase in the size of the papules, you should consult a doctor, since other pathologies may appear during the course of this disease.
In medical practice, it is important to correctly distinguish such a disease from the development of HPV in the body. Condylomas are formations that arise as a result of pathogens of a viral nature entering the body.
They are characterized by asymmetric localization in the genital area. The color of condylomas is often similar to the rashes associated with this disease, but upon palpation a denser structure is felt.
Condylomas are characterized by a group manifestation in the form of multiple growths.
Diagnostics
Often, initially appearing papules can be harbingers of diseases of the reproductive system. Such manifestations resemble the initial stage of syphilis and other sexually transmitted diseases. To clarify the diagnosis, the patient is sent for a serological blood test. The rash can also be confused with genital warts.
External symptoms are not enough to make an accurate diagnosis; differentiated diagnosis is needed. It is performed by a gynecologist. After examining the woman in a gynecological chair, a smear is taken from the affected area, which is subsequently subjected to microscopy.
Cytological examination helps determine the cellular structure of the rash and determine the nature of the phenomenon: whether it is of viral etiology or not.
If the causative agent is the human papillomavirus, koilocytosis is detected (specific damage to cellular structures by viral pathogens). The most accurate results will be provided by polymerase chain reaction.
Using it, you can determine the nature of formation at the molecular level.
Differential diagnosis
Micropapillomatosis is completely harmless for a woman, however, papules are easily confused with condylomas caused by human papillomavirus infection or syphilis
Micropapillomatosis is completely harmless for a woman, however, papules are easily confused with condylomas caused by human papillomavirus infection or syphilis.
Misdiagnosis will lead to the prescription of inadequate treatment. To determine the etiology of changes in the labia, the gynecologist conducts a microscopic examination of a smear taken from the affected area. Cytological examination can detect signs of specific damage (koilocytosis), if present.
Such results indicate that the neoplasms are viral condylomas.
Is treatment necessary?
Such rashes are completely harmless. The only problem a woman may encounter is a cosmetic defect. The fair half of humanity can be confused by micropapillomatosis of the labia. However, in modern medicine this problem can be eliminated.
The principle of treatment is the same as for warts:
- Electrocoagulation . New growths are removed under the influence of electric current. Pinpoint tissue dissection is painless and does not require additional anesthesia. The current has a cauterizing effect, the vessels stick together, so bleeding does not occur.
- Cryodestruction is a popular way to eliminate unwanted tumors. Warts and micropapillomas are frozen under the action of liquid nitrogen and destroyed in seconds. Nitrogen itself is safe, however, after such manipulations, bleeding and infection of the wound cannot be ruled out.
- Laser cauterization . This is the fastest and most accessible procedure. Non-contact interaction with affected tissues makes the manipulation safe. Painlessness, rapid healing, anti-inflammatory effect are the main advantages of laser therapy.
Opponents of physical and chemical treatment methods will not dare to undertake such procedures. Lack of knowledge will push desperate women to seek drug therapy, but any attempt will be in vain. No drug can eliminate these anatomical formations. Even topical medications (vaginal suppositories, all kinds of ointments) will not help solve the problem.
There is no need for treatment of micropapillomatosis. It does not cause pain or itching, and does not lead to any complications.
Throughout life, nodular rashes do not change in color or size. There have been cases where the rash went away on its own over time without prior treatment. Do not immediately resort to eliminating this harmless ailment.
There are no consequences from micropapillomatosis, but after trying to eliminate it, there may be complications. The skin of the genitals is very sensitive, and after physical impact its structure becomes thinner. At any time, if the rules during the rehabilitation period are not followed, an infection may occur. The consequences will be more serious than the initial rash.
Treatment of micropapillomatosis
If the rash makes a woman feel awkward, it is possible to remove the papules by cryodestruction
This process does not require specific treatment. However, if the rash makes a woman feel uncomfortable, it is possible to remove papules using the following modern methods:
- exposure to cold nitrogen – cryodestruction;
- destruction of formations by electric current - electrocoagulation;
- laser burning.
Laser treatment is considered the most popular - a painless method that promotes rapid tissue regeneration. It does not leave visible scars in place of the fallen elements. The recovery process takes up to two weeks. To determine the right method, you should consult your doctor.
How to treat micropapillomatosis at home
Treatment of micropapillomatosis at home involves the use of decoctions of medicinal herbs when washing.
Herbal decoctions help normalize the vaginal microflora and prevent the occurrence of infection in the intimate area.
For the treatment of micropapillomatosis with folk remedies, infusions of oak bark and chamomile are most often used. A concentrated decoction is added to the water before bathing.
This disease can be eliminated on its own; therapeutic treatment is not required, except in cases where a woman wants to remove pathological elements from the genitals due to aesthetic discomfort.
Sources:
- http://www.zppp.saharniy-diabet.com/papillomy/vidy-3/zhenshchin-1
- http://skincover.ru/papillomy/zhenskie-problemy-mikropapillomatoz.html
- http://okeydoc.ru/syp-na-polovyx-organax-prichiny-simptomy-lechenie/
- http://aginekolog.ru/zdorove/polovye-guby/mikropapillomatoz-polovyh-gub.html
Alina Novikova is a dermatologist, graduated from the First Moscow State Medical University. I.M. Sechenov. -2 Loading…
Source: http://papillominfo.ru/papillomy/mikropapillomatoz-polovyh-gub.html