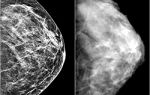
Fissure caries is a pathological condition of tooth enamel, provoked by the accumulation, active activity and proliferation of staphylococci on it.
These microorganisms secrete acids that corrode the upper layers of the tooth (in advanced forms they penetrate to the roots) and contribute to its gradual demineralization. Fissures are small tubercles that are located in the center of the tooth; they are directly involved in the process of chewing food.
This area of the chewing element is most vulnerable to caries, since the spaces between the fissures are very difficult to properly clean from plaque. That is why a similar disease often occurs in the area of the tubercles. They come in open and closed types.
In the presence of this disease, the enamel on the fissures begins to darken, and the chewing side of the tooth gradually deteriorates. Situational pain often occurs during the action of thermal, chemical and mechanical stimuli.
Firstly, the special shape of the grooves or their large size can speed up the process of formation of this type of disease.
The fact is that sometimes there are fissures that expand at their base. It is extremely difficult to get there with a toothbrush, which leads to the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms there over time.
Some people's enamel has low resistance to this type of caries. Accordingly, it will develop in them much faster than in others.
If the saliva contains few immunoglobulins, this is an alarming indicator that caries is bound to appear sooner or later. It is this substance that actively fights bacteria in the oral cavity.
Excessive consumption of carbohydrates leads to the accumulation of saccharides on the teeth, which is an excellent source of food for staphylococci, which cause caries.
An unbalanced diet can affect the reduction of local and general immunity, which will negatively affect the functional state of your teeth.
Fissure caries also appears due to a genetic predisposition to the formation of this disease.
Diagnosis of fissure caries
At the first stage, dark dots and stripes appear along the fissures. Any darkening of the enamel that cannot be removed with toothpaste or professional cleaning is a sign of carious lesions.
Sometimes the darkening is so slight that patients do not attach any importance to it. Moreover, such changes in the enamel can be ignored even by an inexperienced dentist during an examination.
Diagnosis in the dentist's office is carried out using caries markers. These are special liquids containing dye.
In carious cavities there is a denatured protein, which becomes colored when interacting with the components of such a liquid. Only damaged areas of enamel and dentin change color.
Excess can be easily removed with a stream of water. With deep fissure caries, not only the enamel and softer dentin are affected, but also the pulp tissue.
In this case, the question of whether this disease needs to be treated disappears even for people who rarely visit the dentist.
Diagnostic procedures also include visual examination, fluoroscopy and laser diagnostics.
In children, this type of caries often appears even on baby teeth.
Treatment of fissure caries
Most often, in the absence of complications, fissure caries is treated in 5 stages: preparation of the affected cavity, etching, washing and drying of this location, application of sealant and polymerization.
If caries is advanced and the disease has affected the nerve, the sealing procedure is carried out in two steps. At the first visit, a special pulp devitalization agent is usually used. A temporary filling is installed.
When you return to the dentist, the filling material and medication are removed, and the pulp is removed.
After this, the canal is filled, the carious cavity is filled with insulating material, and the surface of the filling is ground and polished to restore the chewing function of the tooth.
Many parents wonder how to treat fissure caries in children with baby teeth? Therapy is carried out in the same way as in adults with permanent analogues.
The fact is that this problem should not be ignored because caries on baby teeth can spread to permanent chewing elements quite easily. In young children, sealing can be performed, but not invasively, using glass ionomer and compomer compounds.
For adults, there is an option to use dental bookmark therapy. They are made individually based on a dental impression.
This design completely follows the shape of the lost tissue and is fixed with special dental cement, which securely holds it inside the cavity.
The materials can be various alloys of gold, palladium, silver, platinum and ceramics.
Many people rack their brains over what is better to choose: a filling or an inlay? The fact is that the fillings in this part of the tooth have a marginal fit.
There is always a gap at the border of contact with dentin and enamel. This is where carious relapses often begin. Unlike fillings, bookmarks fit more tightly.
This significantly increases the tightness of the chewing element.
Also, the average lifespan of an inlay is longer than that of a filling.
And although they are more expensive due to individual production, such expenses are fully justified.
When applying a conventional filling, all stages of treatment are carried out according to the standard scheme, as with other types of caries.
Here it is very important for the dentist to carefully approach the formation of an exact anatomical copy of the tooth and carefully consider the final stage of therapy - grinding and polishing.
Remember, if fissure caries is noticed at an early stage, it is a reversible process and treatment may not be necessary.
In this case, the enamel is loosened, but surgical intervention may not be necessary. It is enough to take preventive measures.
The cost of treatment depends on the complexity of the manipulations performed and the material used for the filling or filling. The price can range from $20 to $1000.
Folk remedies in the fight against this disease
Using folk remedies cannot cure fissure caries, but they can help by reducing inflammation and reducing pain so that you can wait for your appointment with a doctor without any discomfort.
Sage is used as a good antiseptic at home.
Add 15 grams of leaves of this plant to 1 glass of water and let it brew for about 1 hour. A decoction of sage can effectively eliminate bacteria from the teeth.
After filtering, rinse your mouth with the resulting liquid 3-4 times a day.
In a similar way, you can make a medicinal potion from chamomile.
Folk remedies can only bring relief for a short time, but cannot eliminate the disease itself.
Prevention of fissure caries
This is the list of preventive measures that will help prevent the occurrence of this type of caries:
- high-quality oral hygiene through preventive cleanings in the dentist’s office; unfortunately, ordinary toothbrushes are not able to cope with this task;
- regular use of special products for remineralization of enamel, for example fluoride varnish (Bifluoride 12) or preparations based on calcium hydroxide;
- preventive fissure sealing, which is prescribed by the dentist as needed;
- Rinses with antibacterial properties penetrate well into hard-to-reach places on the dental cusps - do not forget to use them;
- consumption of organic food with sufficient content of vital vitamins and minerals.
It is much easier to prevent the occurrence of such a disease as fissure caries than to then spend money and time on eliminating its consequences.
Teach your children to practice good oral hygiene.
Do not forget to take them for preventive examinations to the dentist 2-4 times a year for early detection of ailments and implementation of preventive measures.
Fissure caries - results
Fissure caries occurs due to the entry of pathogenic microorganisms into natural openings, which, as a result of their vital activity, release acid that corrodes the enamel and leads to its demineralization.
Due to the anatomical features of the tubercles on molars and premolars, which facilitate the function of grinding food, food debris often gets stuck in these locations and provokes the active proliferation of staphylococci, which are the main “activators” of caries.
Some people have craters in their teeth, which makes cleaning them with a regular toothbrush very ineffective. Since in the early stages this disease is asymptomatic and does not cause any discomfort, people do not pay due attention to the appearance of darkened areas in the fissures.
Sooner or later, this leads to deepening of the carious areas, penetrating into the soft dentin, and possibly further into the pulp. Only nerve inflammation can force a patient to go to the dentist, as it can cause pain that interferes with the natural process of chewing food.
A genetic predisposition to the formation of this disease is also a common cause of its occurrence. An unbalanced diet, the absence or small amount of fluoride in drinking water and many other factors can accelerate the process of the appearance of this type of caries.
Treatment of this disease is carried out using special headbands or fillings. The first option in this case, most often, is more preferable due to its design features.
Over time, recurrent caries may form under the filling. With screensavers this occurs extremely rarely due to their optimal tightness.
Alloys of silver, gold, platinum and ceramics of various variations are used as consumables during such therapeutic intervention.
You should also not neglect preventive measures that can delay or completely prevent the appearance of caries in this area of the tooth.
If this article was interesting for you and shed light on what reasons lead to the occurrence of such a disease as fissure caries, and what methods of treating this disease are the most effective, you can share it with relatives, work colleagues and friends.
I hope you learned something new and interesting on this topic and were able to find answers to your questions! Check out other materials on our blog, there is a lot of educational stuff there.
Have a great day and stay safe!
Source: https://www.uadent.com/fissurnyj-karies/
Causes and treatment of fissure caries
Fissure caries is a dental disease that many patients face. Not so long ago, due to its practically asymptomatic course, it often led to damage to hard tissues, nerves, and even the entire tooth. But today, thanks to modern methods of diagnosis and work with affected areas, treatment of fissure caries can be carried out quickly, painlessly and effectively.
What is fissure caries?
Fissure caries is a pathological process that develops in the recesses of the tooth (fissures). The latter can be of various shapes - open (grooved or cone-shaped) and closed (drop-shaped). Most often, the disease affects the 6th and 7th teeth. Like other types of this pathological process, this one can lead to damage to the nerve and hard tissues of the tooth.
Visually, the disease is easy to identify by the specific darkening of the cavity. This is especially easy to do with open fissures.
Painful symptoms of the pathology include:
- discomfort when food gets into the cavity, even pain;
- increased tooth sensitivity when eating hot or cold food.
If such symptoms accompany the disease, as a rule, they do not last long and disappear after the pathogen is eliminated.
Fissure caries in closed tooth cavities can occur asymptomatically. Only a doctor can diagnose it using special examination methods. That is why it is so important to visit him regularly so as not to miss the active development of the disease.
What is fissure caries?
Causes of the disease
The main reason for the development of fissure caries is considered to be improper oral hygiene. So, with irregular or insufficiently effective brushing of teeth, food debris accumulates in the fissures, which subsequently begin to rot and destroy the enamel itself. Over time, this process leads to the appearance of caries, which can affect the deeper tissues of the tooth.
Additionally, the causes of this disease include:
- The constant presence in the oral cavity of quickly digestible carbohydrates, as well as bacteria that provoke the development of caries.
- The size of the fissures is too large and their shape is complex.
- Low resistance of tooth enamel.
In the presence of these factors, the disease does not always manifest itself, but its likelihood increases.
People at risk for this disease are advised to visit a specialist from time to time and undergo a full examination, as well as pay maximum attention to the requirements of oral hygiene.
Diagnostics
There are several effective methods for diagnosing fissure caries in modern dentistry:
- Diagnostic device. This is one of the most modern research methods, allowing to identify both internal and external fissures. During this procedure, the patient's teeth are examined using a special laser device. Today this is the most accurate diagnostic method, which, however, is not available in all clinics. In the absence of a laser device, alternative research options are usually used.
- Visual inspection. It is seen by a dentist using a probe. Effective in identifying open fissures. The closed type of formations is not detected in most cases. If they are suspected, the doctor may prescribe additional diagnostics to the patient.
- X-ray diagnostics. The most effective method for examining closed-type fissures in which there are no visual signs of disease yet. It is mainly used as a highly effective adjuvant, especially when patients complain of increased tooth sensitivity or pain. The only drawback of this method is the low diagnostic accuracy in the early stages of the disease.
- Fissurotomy. A technique that involves the use of a set of special soft burs that open the fissure by approximately 0.6-1.1 mm. In most cases, this is enough for a more accurate diagnosis and initiation of treatment.
- Application of caries markers.
For most patients with suspected fissure caries, several diagnostic methods are used simultaneously to obtain the most accurate result.
Treatment
The procedure for working with the affected tooth depends on the stage of the disease, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient, but it can always be divided into two stages:
- drilling the affected areas with a drill;
- filling filled cavities with special materials.
If nerve damage is diagnosed during work with the patient, its removal may additionally be prescribed.
The last stage of treatment - filling the cavity - also depends on several factors: the load on the tooth, the size of the affected area, and the aesthetic requirements for this tooth in the future. The following options are possible here:
- installation of a restorative inlay - a micro prosthesis (the most effective method that gives a high aesthetic effect and long-term results);
- installation of crowns and fillings;
- installation of a therapeutic pin and crown;
- installation of the core inlay and crown.
The procedures are in most cases performed under local anesthesia. If no complications arise during the treatment (for example, the need to remove a nerve), it can be done in one session with a doctor.
Disease prevention
Fissure caries is a disease that can easily be avoided by following general preventive recommendations. Among them:
- Compliance with general recommendations for dental care (regular brushing and flossing, eliminating foods that destroy enamel from the diet).
- Regular dental examinations up to 2 times a year. During this process, a specialist will be able to identify an emerging problem, and then quickly and painlessly eliminate it.
- Carrying out remineralization of teeth every 6 months.
- Taking medications containing calcium and fluoride (especially during the period of teeth formation). Please note - the dosage, as well as the type of product for you, should be selected by your doctor.
For people with a complex fissure structure that does not allow it to be properly cleaned, it may also be recommended to apply a special product - a filler - to problem areas. Your doctor can suggest this option for preventing the disease.
In general, fissure caries responds well to treatment and prevention. In this case, the patient only needs to be attentive to the care of his own teeth and, at the slightest suspicion of such a pathology, immediately contact a specialist.
Source: http://zubyinfo.ru/zabolevaniya-zubov/fissurnyj-karies.html
Fissure caries: manifestation and treatment
Last update: 12/13/2019
Toothache is considered one of the most unpleasant and difficult to bear pain sensations. It can be caused by gum inflammation, caries, poor oral hygiene or poor quality dental treatment.
One of the common subtypes of caries, from which many clients of dental clinics suffer every year, experts call “fissure caries.” What it is and how to treat it – we’ll figure it out in this article.
Fissure caries occurs on the surface of the tooth that is directly responsible for the process of grinding food - on the fissure, i.e. on those natural grooves that are located on the chewing surface of the teeth.
Fissures are divided into “open” and “closed”. “Open” fissures are clearly visible during visual inspection and are easier to clean and can be grooved or cone-shaped. “Closed” fissures appear on the tooth in the form of thin, barely noticeable grooves that expand downward, “inside” the tooth, for example, teardrop-shaped fissures.
As a rule, fissure caries does not spread to the root or neck of the tooth and is activated in its central part.
Why does fissure caries appear?
Dentists identify two large groups of reasons why fissure caries can develop in the human body:
- nonspecific;
- specific reasons.
Nonspecific occurrences of this type of caries include:
- rapid proliferation of pathogenic bacteria that destroy hard tooth surfaces and tooth enamel;
- errors in oral hygiene (incorrectly selected toothpastes and brushes, complete neglect of oral hygiene, etc.);
- nutritional problems (insufficient nutrition, the predominance of “empty” sugars in foods, lack of solid foods and raw vegetables in the diet);
- problems with the concentration of vitamins, micro- and macroelements in the body (hypovitaminosis, excess or deficiency of certain elements);
- disturbance in the formation of teeth (in early childhood, due to poor nutrition in childhood or due to improper formation of dental tissue during gestation);
- reduced immunity;
- problems in the gastrointestinal tract.
Dentists include the following specific causes of fissure caries:
- low level of mineralization of tooth enamel;
- a thinner layer of enamel inside the fissures than on the rest of the tooth surface;
- formation of dental plaque in the fissures and, accordingly, a favorable environment for the development of pathogenic microorganisms;
- mechanical damage to fissures due to specific food products;
- high “depth” of tooth fissures, which is why even thorough brushing with a toothbrush cannot ensure sufficient cleansing.
Diagnosis of fissure caries
This type of caries can be diagnosed in different ways. One of the most common, but far from the most effective diagnostic methods is visual inspection. The presence of caries on the fissures, if they are visible, can even be seen in the photo.
Fissures can only be examined if they:
- open;
- well cleaned.
The examination is complicated by the fact that if the fissures are not sufficiently cleaned, then such a sign of caries as a change in the color of the enamel cannot be a sufficient basis for the diagnosis.
However, if there is a suspicion of the presence of fissure caries, then various additional methods are used for a more accurate diagnosis:
- Using a probe. True, the surface of the fissures itself is rough, which interferes with the passage of the probe. And if the fissure is closed, then when examining it with a probe, the tooth enamel can be damaged. This, in turn, can lead to the appearance of caries in areas where there was none.
- X-ray diagnostics. Suitable for diagnosing caries in closed fissures. However, it is impossible to diagnose caries in the early stages using x-rays.
- Fluorescence using specialized devices.
- Fissurotomy. To determine the degree of caries damage to fissures. It uses a set of special drills that allow you to check the depth of caries as delicately as possible.
- Electrodiagnostics. With it, the electrical resistance of tissues in the area of carious lesions decreases.
- Patient complaints. The symptoms of fissure caries are similar to the symptoms of any other caries (pain, reaction to certain foods and temperature changes). If there are no areas on the tooth that, upon visual inspection, are affected by caries, then we can assume with full confidence that the fissure part of the tooth is damaged by caries.
How is fissure caries treated today?
Considering that fissure caries is one of the most common types of caries today and that this is the first type of caries that affects human teeth, the method of treating it is well known to dentists and has been tested by time and millions of clients.
Stages of therapy:
- First of all, when treating it, it is necessary to remove carious formations.
- Filling those areas of the tooth from which carious formations have been removed.
- Complete filling of the remaining fissures.
- Fitting the filling to the natural “landscape” of the tooth.
- Fissure sealing.
Filling of fissures is carried out very carefully, in two layers and using a therapeutic and prophylactic pad.
If the client wishes, one can resort not to filling, but to using inlays. Dentists call inlays a kind of “microprosthesis” that imitates the chewing surface of a tooth. Fissure inlays are made in a special laboratory from various materials (platinum, ceramics, etc.) by dental technicians.
Installation of a fissure inlay goes through the following stages:
- removal of all tissues affected by caries;
- making a dental impression (anatomically accurate);
- making a special inlay based on a tooth impression;
- placing an inlay on the tooth and securing it with special solutions.
In addition, dentists identify several more methods for treating fissure caries:
- Invasive technique. When implementing it, the teeth are first professionally cleaned, then etched and corrected using sealant. The invasive technique ends with dental fluoridation. This technique is applicable only for adults with already formed tooth enamel.
- Non-invasive fissure sealing using composite substances. It can be used only on teeth that have erupted and on teeth that are susceptible to disease. However, if a significant deficiency of minerals is diagnosed in the body, then non-invasive fissure sealing of this type is not used.
- Non-invasive fissure sealing using compomer and glass ionomer substances. It is most often used to treat fissure caries in new, newly erupted molars (deciduous, permanent). This technique can be used to treat fissure caries even if the patient has a deficiency of minerals in the body.
With non-invasive techniques, there is no need to expand the fissure affected by caries, which significantly reduces the degree of dentist intervention in the tooth tissue.
Are there methods for preventing fissure caries?
Preventive methods for preventing fissure caries are divided into two large groups:
- nonspecific;
- specific.
Experts also divide prevention into primary and secondary.
Nonspecific methods for preventing fissure caries are:
- a balanced diet (the right combination of micro- and macroelements necessary for the body as a whole and, in particular, for the development of teeth; a sufficient amount of vitamins in the body; the presence of an adequate amount of solid food on the menu; limiting the intake of too spicy, salty, sweet foods and carbonated drinks). If your diet does not contain enough vitamins and minerals, take a course of the Asepta vitamin and mineral complex;
- proper oral hygiene - thorough brushing of teeth; using antibacterial toothpastes and mouth rinses. Thus, Asepta PLUS Remineralization paste gently cleanses teeth and helps replenish mineral substances in tooth enamel;
- replenishing the lack of fluoride in the body;
- regular preventive visits to the dental office (every 6 months, at least).
Specific methods for preventing fissure caries are:
- fissurotomy or fissure sealing. This method involves preventive “sealing” of fissures using various components (composite) to block access of bacteria to them. Before using the method, a thorough professional teeth cleaning is carried out so as not to “seal” part of the plaque in the fissure. The composite is applied to the chewing surface, and the dentist files it down so that it imitates the natural “landscape” of the tooth. The consistency of the composite is liquid; it penetrates well into all fissure recesses and protects the largest possible area.
- remineralization of dental molars. Using this method, you can increase the resistance of tooth enamel to negative influences (chemical, temperature, bacterial, etc.). Remineralization is carried out using varnishes based on calcium, fluoride and other micro- and macroelements necessary for preserving teeth.
- direct fluoridation of teeth. Using various suspensions with a high fluoride content, emergency fluoridation of tooth enamel is carried out. To maintain the required level of fluoride in teeth, fluoridated and fluoridated toothpastes are used. Emergency fluoridation of teeth is carried out by a dentist, and maintenance procedures can be carried out independently by patients at home.
- proper oral hygiene. It is important to use toothbrushes of increased rigidity for deep cleaning of fissures and antiseptic mouth rinses, for example, Asepta with chlorhexidine, which reduces the unwanted proliferation of bacteria and reduces the likelihood of developing caries;
- preventive use of medications containing fluoride and calcium. Especially in the autumn-winter period, when the body suffers from vitamin deficiency. Taking fluoride and calcium-containing medications are supportive procedures that will help consolidate the effect of fluoridation and remineralization of teeth.
- regular visits to dentists and independent visual monitoring of dental condition;
- Fissure cleaning at the dentist. If the specialist discovers that the client's fissures are too deep for him to clean them himself on a daily basis, he may suggest periodic visits to the dental office directly for the purpose of cleaning them.
Primary prevention of fissure caries consists of supportive procedures, for example, sealing healthy fissures using non-invasive methods.
Dentists include methods of secondary prevention of fissure caries:
- sealing healthy fissures using invasive techniques;
- preventive filling.
According to internal statistics of dentists, fissure caries is one of the most common types of caries. For example, because people get used to brushing only the outer surfaces of their teeth, achieving a white smile, but they forget about the chewing surfaces, the tongue, and do not clean plaque from them, which, in turn, is the cause of the development of diseases of the teeth and the oral cavity as a whole.
Prevention of fissure caries, according to the observations of specialists, is much more effective and cheaper than its subsequent treatment.
Despite the apparent difficulty of diagnosis, modern dental offices have all the necessary technologies to diagnose fissure caries in the early stages and begin its successful treatment. And modern oral hygiene products will help protect your teeth and gums!
Clinical researches
The active components of the complex help reduce bleeding and inflammation in the oral cavity.
- A unique complex of vitamins, microelements and plant extracts, specially selected to maintain the health of the oral cavity and the body as a whole.
- Coral calcium and coenzyme Q10 in the composition strengthen gums and tooth enamel.
- Vitamins support general immunity.
At the Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, it was proven that the joint use of Asepta dental line products makes it possible to achieve a complex effect.
Taking into account the active components that make up these Asepta products, their clinical properties and the effect they have on the soft tissues of periodontium, they can be used both as independent agents in the initial stages of diseases, and in combination with medications for severe forms of chronic periodontal diseases.
Considering the therapeutic and prophylactic properties of the Asepta line, they can be used for inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa, such as catarrhal stomatitis, glossitis and cheilitis.
Consumer Reviews
Valera (otzyvru.com)
“The dentist recommended the Asepta vitamin and mineral complex for teeth, since the condition of my oral cavity is not the best: my gums are bleeding, my teeth are already beginning to crumble at the age of 30. I started taking these vitamins, not forgetting about other hygiene. I completed the course in two weeks, and my teeth are stronger.”
yuliya1305 (otzovik.com)
“These vitamins contain:
- Coral calcium;
- Coenzyme G10$
- Vitamin C;
- Vitamin D3;
- Vitamins B3, B6;
- Vitamin A;
- Green tea extract
These vitamins come in 721 mg tablets.
To prevent my gums from bleeding, I also use other drugs from this company... By the way, these vitamins are contraindicated for pregnant women. Well, I’ll tell you honestly, I’m very pleased with these drugs and recommend them to everyone. Because Vertex lives up to expectations!”
Sources:
-
The use of new anti-inflammatory drugs in the complex of therapeutic and preventive measures for periodontal diseases (E.D. Kuchumova, A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, L.Yu. Orekhova, S.B. Ulitovsky) E.D. Kuchumova, Ph.D., Associate Professor, A.A. Leontyev, dentist, O.V. Kalinina, dentist, L.Yu. Orekhova, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of Department, S.B. Ulitovsky, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof.
Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
-
The use of drugs from the Asepta line in the complex treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (N.V. Berezina E.N. Silantyeva S.M. Krivonos, Kazan State Medical Academy. Kazan.) N.V. BEREZINA, E.N. SILANTIEVA, S.M. KRYVONOS
Kazan State Medical Academy
-
The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof.
Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
For an accurate diagnosis, contact a specialist.
Source: https://asepta.ru/spravochnik/zubi/fissurnyy-karies-proyavlenie-i-lechenie/
Fissure caries
- home
- Articles
- Fissure caries
Fissure caries is a disease in which fissures, that is, the chewing surface of molars and premolars, are damaged. First, the patient feels pain and “lumbago” in the tooth area, then the caries goes deep inside the tooth. If nothing is done in such a situation, sooner or later the patient will lose his chewing tooth. Fortunately, modern methods of treating dental problems make it possible to qualitatively treat the problem and preserve the dental unit. The main thing is not to delay contacting the dentist.
What are fissures?
A fissure is a groove-like depression on the teeth. Fissures on teeth can be either open or closed. Open – with a visible bottom. Closed – bottle-shaped recesses, that is, when the top of the fissure is visualized as a “neck”, and the bottom expands in the form of a cavity. Diagnosing caries in a closed fissure is much more difficult.
Also, depending on their shape, fissure formations are drop-shaped, cone-shaped and groove-shaped.
Causes and symptoms of caries formation on fissures
The fissure surface is an ideal environment for the accumulation and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. It is for this reason that caries begins to form in such areas and develops dynamically. That is why the main cause of fissure caries in patients is insufficient oral care.
The first symptoms of the disease are pain from hot drinks and foods. The grooves on the teeth gradually darken, the sensitivity of the teeth increases, and there is slight pain.
Diagnosis of fissure caries
To confirm the diagnosis you must do:
- General dental examination. In open fissures, carious lesions are clearly visible. It is more difficult to identify caries in closed areas; for this, the dentist uses various diagnostic methods.
- X-ray. It allows you to determine the presence of caries in the absence of its obvious manifestations. This method is good for damage to closed fissures, but it is not enough in the initial stages of development of carious lesions.
- Research using a device for diagnosing fissure caries. The so-called laser fluorescence. As a rule, the technique is indispensable for caries on closed fissures.
Note! It is very important to identify the lesion at the initial stage of its development in order to prevent further damage to the tooth structures in time. Only in a dental setting can fissure caries be identified in the initial stages, where you will be provided with comprehensive care.
How to cure fissure caries?
- Filling with light-polymer materials
- Recovery tabs
Treatment of fissure caries comes down to drilling out the damaged areas and restoring the integrity of the tooth using light-polymer fillings. Reflective composites make it possible to give crowns an ideal shape; fillings will match the natural shade of teeth, transparency, and enamel texture.
In this case, the dentist works with a microdental prosthesis, which, unlike a conventional filling, is pre-made in a dental laboratory using impressions taken in advance. The inlay is fixed to the tooth using dental cement and is completely biocompatible. The most common are ceramic inlays, which organically fit into the tooth structure both in terms of their “technical” properties and aesthetics. A tooth restored with an inlay is almost impossible to distinguish from a natural one. What is better to treat fissure caries - filling material or ceramic inlay? Dental inlays have a longer service life, they retain their color and texture. The filling (even the best quality) darkens over time, may fall out, and the patient will again have to spend time and money restoring the crown.
Prevention of fissure caries
- Regular oral hygiene
- Fissure sealing
- Remineralization of tooth enamel
This includes daily brushing of teeth, professional hygienic cleaning with removal of soft and hard plaque in the dental office.
This is especially true for those patients who have naturally deep, closed fissures. Sealing involves “sealing” these areas with special seals. This technique is relevant for both school-age children and adults.
Coating the enamel with a special protective layer in the form of varnish, which contains fluorine and calcium. Such compositions are also effective at the initial stage of the formation of carious lesions in order to prevent its further active development.
Was this article helpful? Share the article with your friends!
Source: https://Zuub.ru/fissurnyy-karies.html
What is fissure caries and what methods of treatment are there?
Even if a person brushes his teeth regularly, he may encounter a problem such as fissure caries. We will describe what it is and whether it needs to be treated. Only knowing the nuances and features of the lesion can promptly detect and eliminate the pathology in the initial stages.
Today, dentists note that caries is the most common oral disease. And its fissure variety is much more common than any other. This is facilitated by the structure of the tooth, difficulties in cleaning natural grooves and difficulties in timely diagnosis.
Types of fissures
Fissures are dimples and grooves on the chewing surface of molars. They are created by nature itself for better grinding of food and chewing it thoroughly. With age, these grooves deepen, their structure and shape change, which contributes to more active reproduction of bacteria.
Depending on what the fissure looks like, there are several varieties:
- Gutter-shaped - partially open dimples, with a thick layer of enamel. Of all the existing options, they respond best to cleaning with a toothbrush and visual inspection. Here, bacteria hardly linger, and the sufficient thickness of protective hard tissue prevents disease in a natural way.
- Cone-shaped - due to the recessed shape and narrow bottom, food often lingers and accumulates. It is quite difficult to clean such a space with a brush. And if professional treatment is not carried out periodically, then over time the bacteria will destroy the thin layer of enamel and the development of caries will begin.
- Drop-shaped or polyp-shaped - the most complex and dangerous form, since it is impossible to get inside the cavity with a toothbrush and clean it out. But food debris easily penetrates there and leads to gradual tooth destruction. This form of fissures complicates the whole process by the fact that they are not amenable to conventional diagnostic methods. Even an experienced dentist cannot always identify the problem at the initial stage.
About fissure caries
It is the structure of the tooth and its surface that most often leads to the appearance of the disease, regardless of the quality of daily oral hygiene. It is believed that fissure caries affects people of any age and can appear even immediately after the eruption of molars. In children, due to poor cleaning and the abundance of sweets consumed, the risk of enamel destruction increases significantly.
The disease in this case begins precisely in the deep grooves on the chewing surface of the lateral teeth. But the speed and intensity of destruction depend largely on the structure of the fissures, depth, structure of the enamel, etc. Even if the grooves have a teardrop shape, but the mineralization of hard tissues is able to resist bacteria, then there is no danger of developing pathology.
The peculiarity of the lesion is that at first only the central upper part of the tooth is damaged. And only in an advanced state the disease reaches the pulp or root canals. Therefore, it is advisable to diagnose and eliminate the problem in a timely manner so that you do not have to remove a nerve or an entire tooth.
Causes
The very structure of the chewing surface already provides an explanation for why caries develops in such areas. After all, fissures are quite difficult to clean from plaque and food debris at home. But doctors pay attention to several factors that lead to pathology:
- the shape of the furrows, especially when they are deep and closed;
- poor mineralization of hard tissues, when the natural thickness of the enamel is not enough to fully protect dentin from bacteria;
- excessive consumption of sweets and sugar-containing foods;
- violation of the composition of saliva;
- poor oral hygiene.
More often, the cause of the appearance and active development of fissure caries is not one of these factors, but their combination.
Symptoms
The problem of timely detection of pathology is that in the first stages the disease is most often asymptomatic. And when any signs appear, this indicates more advanced processes and deep damage to the tooth. And even a visual examination by a dentist does not always help to identify fissure caries in time.
Depending on the degree of destruction, you may notice the following symptoms:
- It all starts with the darkening of existing grooves on the chewing side of the lateral teeth.
- If the plaque that appears is not cleared in time, then the fissures begin to deepen.
- When dentin is damaged, sensitivity increases in response to changes in temperature (cold and hot drinks, food) or when consuming acidic foods.
- If the pathology has reached the pulp, then pain occurs with any touch to the tooth.
- When the process of tissue destruction is started, a person feels sharp or throbbing pain even at night.
It is worth noting that deep damage to internal tissues can lead to pulpitis, periodontitis, loosening and loss of teeth, and also, over time, contributes to the destruction of bone tissue and other problems affecting the general condition of the jaw. Therefore, it is important to seek help from a dentist in time.
Do I need treatment?
Of course yes. After all, tissue infection that has begun will not go away on its own. If bacteria begin to actively destroy enamel, and then dentin, then eliminating the darkening of the area with a toothbrush and toothpaste is not enough. Only a doctor can remove all the affected elements and stop the pathological process.
If fissure caries is not detected and treated in time, then it will lead to serious complications - tooth loss, severe pain, spread of infection to surrounding tissues, periodontal damage, etc. And although this process may drag on for months, it is still irreversible and will not stop on its own.
How is treatment carried out?
The choice of therapeutic method of influencing dental tissues strictly depends on the condition of the surrounding teeth, the depth and intensity of the lesion, the age of the patient and the causes contributing to the disease. Only an experienced dentist can decide which treatment option is more appropriate.
To eliminate fissure caries, the following methods are used:
- Filling takes place according to the standard procedure, when all affected tissue is first removed and cleaned using a drill. Then, using glass or light polymers, the open area is filled. And only if the destruction has reached deeper layers, additional removal of the nerve and filling of the root canals is required.
- Using a restoration tab is considered a more reliable method, since such special materials adhere better to surfaces and are characterized by a long service life. Inlays are made individually to suit the structure of the tooth and the affected area, and are attached using dental cement. They exactly replicate the open channel formed after cleansing and treatment. Today they are made from different materials - ceramics, gold, platinum, silver, palladium, etc.
- Fissure sealing is more often used in pediatric dentistry. At the initial stage of enamel destruction, closing the grooves using a special coating made of composite materials helps stop the pathological process.
- If the problem has led to more serious complications and partial or complete tooth destruction, then it makes sense to use other restoration methods:
- Video: what is fissure caries?
Prevention
Since the appearance of fissure caries is largely influenced by the shape and structure of the grooves, it is quite difficult to prevent such damage on your own. All you can do is:
- Take good care of your teeth and follow basic hygiene rules.
- After every meal, rinse your mouth.
- Use pastes with a special mineral composition to strengthen the enamel.
- Visit your dentist twice a year and have it professionally cleaned.
- Avoid sugar-containing foods.
- Sometimes it makes sense to periodically fluoridate the enamel surface.
- Fissure sealing also acts as a preventative measure in childhood.
Source: https://infozuby.ru/fissurnyy-karies.html
Features of fissure caries: from diagnosis to treatment
As the name suggests, the peculiarity of fissure caries is that it affects the so-called fissures - the natural anatomical structures of the tooth, which look like depressions and grooves on the chewing surface. According to statistics, this type of caries is the most common.
Children with baby teeth, as well as adults with very deep or closed fissures, are most susceptible to fissure caries. Even with very thorough cleaning, such cavities cannot be completely removed from plaque and food debris.
Pathology is not always easy to diagnose, so to identify it, sometimes a special apparatus is used to diagnose fissure caries.
At home, seemingly insignificant darkening of the grooves on the chewing surface often goes unnoticed. As a result, going to the dentist too late may result in the need for depulpation and even tooth loss.
Therefore, all darkening in the fissure area should be treated very carefully.
Symptoms and appearance of teeth affected by fissure caries
The photo below shows an example of fissure caries. In the deepest places of the fissures, dark areas of enamel are clearly visible, under which are the main areas of tooth damage:
Fissure caries can develop within a short time after tooth eruption, and the likelihood of the occurrence of pathology depends on several factors, which include:
- great depth and specific shape of fissures;
- low resistance of tooth enamel;
- the constant presence in the oral cavity of easily digestible carbohydrates and cariogenic bacteria.
Fissure caries mainly affects the weakest areas on the chewing surface of the lateral teeth. Most often, pathology develops in children on the first permanent molars (on the sixth teeth).
On a note
The development of fissure caries on the first permanent molars is due to the fact that these teeth erupt in a child at the age of 6 years. Their eruption most often goes unnoticed by parents and is sometimes mistakenly regarded as the appearance of milk (temporary) teeth, which will fall out anyway.
Most often, the lower sixth teeth erupt first, and the upper teeth only after some time, so self-cleaning during chewing does not occur, since there are no contacting areas.
The child cannot ensure proper hygiene of such remote posterior areas on his own; as a result, a kind of “biological garbage dump” arises.
Fissures that are constantly contaminated with carbohydrate residues begin to darken, since zones of demineralization (reduced content of minerals in the enamel crystal lattice) appear under the surface layers of enamel due to the action of organic acids.
- The following photograph clearly shows that fissure caries is localized mainly in the central part of the chewing surface of the tooth. If the disease is not advanced, then the root and neck are not affected:
- The clinical picture of the nosology consists precisely in the staining and further destruction of the enamel in the fissure area.
- Depending on the depth of the carious cavity, fissure caries may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Short-term pain from chemical irritants (sweet, salty, sour) and temperature (cold, hot) with superficial, medium and deep caries.
- Short-term pain from mechanical irritants (when food gets into the cavity), mainly with deep damage to the fissures.
- It is important that with caries the pain goes away quickly, immediately after the irritant is eliminated.
In the early stages, fissure caries often develops asymptomatically (initial and superficial stage), which leads to a late presentation of the patient: when the fissures unite into a full-fledged carious cavity with softened infected tissues and clear symptoms appear.
At the terminal stage, the lesion reaches the pulp. In this case, the pain takes on a completely different character: even after the removal of the irritant, it continues for a long time, spontaneous pain appears (for no apparent reason), nocturnal, radiating or shooting (radiating to any area of the maxillofacial area), long-term aching, throbbing, tearing, unbearable etc.
All of these are complications of caries, called pulpitis or periodontitis, depending on the stage of damage to the “nerve” in the tooth canals.
At this stage, the patient is forced to consult a doctor for emergency help, and treatment is carried out according to the diagnosis.
It is characterized by technically more complex manipulations than in the treatment of caries and often takes place in several important stages before placing the filling itself. In terms of time and financial component, this is a costly undertaking.
The sooner fissure caries is diagnosed, the faster, cheaper and easier the treatment will be.
Diagnosis of the disease: means, devices and methods
Diagnosis of fissure caries in many cases is quite simple, since enamel lesions are clearly visible to the naked eye. But sometimes, especially in deep fissures, they turn out to be completely invisible, and the dental probe does not even linger in them during this instrumental diagnosis.
On a note
The fissures themselves have a darker shade than the rest of the tooth enamel. This is due to the fact that they are filled with plaque, dental plaques, which cannot be completely removed with a toothbrush, and are simply located in the recesses in the shadow of the tooth cusps. All this often masks fissure caries and makes it difficult to identify.
In general, the diagnosis of the disease is carried out in the following ways:
- visual inspection;
- radiography;
- use of caries markers;
- laser diagnostics;
- fissurotomy.
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, which appear when diagnosing caries at different stages.
Visual inspection
The simplest method for detecting fissure caries is a visual inspection.
A dental probe and mirror are used to examine the oral cavity. But if the fissures are closed or the diameter of the lesion is smaller than the diameter of the tip of the probe, it may be impossible to determine the presence of the disease using this method.
Radiography
Radiography can detect hidden fissure caries, even if there are no symptoms. The image clearly reveals the affected areas and their size, but the doctor will not prescribe it without suspicion, and often radiography is not prescribed until pain appears in the tooth.
In addition, X-rays cannot detect fissure caries in the early stages, before the tissue under the surface of the enamel is damaged.
Laser diagnostics
Diagnostics, in which caries is “exposed” with a laser beam, is an almost 100% method for detecting fissure caries (laser fluorescence method). Using this method, caries can be diagnosed at almost any stage of its development.
Although the price of a device for diagnosing fissure caries is quite high, all good dental offices have it. This is explained by the fact that laser diagnostics detects caries even in the initial stages. And for “capsule” type fissures, this option is optimal.
Fissurotomy
When fissure lesions are identified, but their size is not known, an additional technique is used to determine the extent and depth of carious zones - fissurotomy. For this procedure, a set of burs has been developed, with the help of which minimally invasive intervention is carried out in the tooth structure.
With the help of a carbide bur, the darkened fissure is opened by approximately 0.6–1.1 mm. Based on the picture that opens, the dentist decides which treatment for fissure caries will be most effective.
Features of treatment of fissure caries
Treatment of fissure caries is carried out in several stages:
- removal of affected areas;
- installation of a filling or restoration tab.
Removal of the affected areas is carried out using a drill. Using modern filling materials, treated cavities are filled.
If there is a complication of caries (pulpitis), then the “nerve” is removed. Next, the canals are filled, and depending on the clinical situation (size of the cavity, area, position of the tooth, load on it, interaction in the bite, etc.), either a filling is placed or a set of measures is carried out, which may include such options as:
- filling + crown;
- installation by a dentist-therapist of a pin (anchor, fiberglass, titanium, etc.) + filling (or also placing a crown on top);
- recovery tab;
- core tab + crown.
The choice depends on the professionalism of the doctor, his tactics regarding the clinical situation in the oral cavity, since the tooth is not considered as a single organ with its inherent functions, but in a system of interaction with other teeth and surrounding tissues.
An alternative to the well-known filling is a restorative inlay - a microprosthesis made according to the shape of the patient’s tooth. It is created in a dental laboratory from polymer materials, medical alloys, and sometimes from silver, gold or platinum. To make an inlay, a tooth impression is first made. It is fixed using medical cement.
When fissure caries is diagnosed, treatment with a restorative inlay is more promising than a filling, since its service life is longer. If it is made of polymers, it looks more aesthetically pleasing and looks like a healthy tooth.
How to prevent the development of caries on fissures?
Prevention of caries, including fissure caries, is the best way to maintain healthy teeth.
The following areas of prevention are distinguished:
- maintaining oral hygiene;
- fluoridation of teeth;
- timely sealing of fissures;
- regular dental examination.
Thorough cleaning of teeth allows you to maintain a normal pH level in the oral cavity, removes plaque and bacteria, the waste products of which destroy enamel.
But even with regular cleaning, if the mineralization of tooth tissue is reduced, the risk of fissure caries increases. To strengthen the enamel, it is recommended to use fluoride toothpastes or undergo a remineralization procedure at the dentist's office.
A good method of prevention is sealing fissures - they are filled with a liquid composite, which then hardens and prevents bacteria from accessing the tooth enamel. Active substances are added to the material, which further remineralize and strengthen the enamel.
And, of course, it is important to visit the dentist's office regularly. A planned trip to the doctor and timely sanitation will allow caries to be detected in time at the earliest stages of development and effective measures to be taken to eliminate it.
From the practice of a dentist
As mentioned above, at the age of six, the first molars erupt - teeth that are most susceptible to fissure caries, rapid destruction, up to serious complications, and removal.
This cannot be allowed in any way, since orthodontists (doctors who correct bite pathologies) rely on the sixth teeth, calling them the “key of occlusion.” It is the relationship of these teeth that directly affects the formation of a correct bite. Removing the sixth tooth has serious consequences for the development of the jaw and bite.
Therefore, early detection of fissure caries by pediatric dentists and hygienists is important to prevent future complications.
Source: http://plomba911.ru/lechenie-zubov/karies/fissurnyj-karies-i-ego-lechenie.html