HPV is one of the most common viruses on the planet today. It has about six hundred different strains, some of which can provoke the development of malignant tumors.
In addition, it should be emphasized that the virus is incurable; it is impossible to remove it from the body of a once infected person. And although it itself does not cause serious concern, only periodically forming small benign growths on the surface of the skin, it spreads very easily among people.
Therefore, HPV prevention remains an important task that requires urgent resolution.
Routes of infection
In order to understand what the prevention of human papillomavirus infection is, you need to know how it enters the body. The route of infection is always the same – contact.
Moreover, it is not necessary to even touch the skin of an infected person, since the virus remains viable for two hours outside the human body.
Therefore, methods of infection include:
- direct contact with the skin of an infected person;
- sexual contact;
- taking shared baths;
- sharing personal hygiene items;
- dirty toilet rim;
- sharing cutlery and crockery;
- transmission from an infected mother to her child during childbirth.
Considering the ease of transmission, the inability to insure against all of these risks, and the incurability of the virus, the extreme prevalence of HPV can be explained.
The appearance of papillomas on the body indicates that the virus has entered the body. From this moment on, the person becomes a carrier of HPV and can transmit it to other people in any of the above ways.
From this point on, infection prevention becomes pointless, and treatment remains unavailable.
In this case, you only need to monitor your own health, remove emerging papillomas and take measures to prevent their re-formation.
It should be noted that the virus, with good functioning of the immune system, may not manifest itself in any way for many years.
Sometimes a person is not even aware of the presence of HPV in his body.
Only over time, when the body weakens due to age, fatigue, nervous and physical exhaustion or illness, various types of papillomas appear.
If they are treated in a timely manner and undergo the necessary examinations for the presence of oncogenic changes in the cells, you can live to a ripe old age without experiencing significant inconvenience.
- strengthening the immune system;
- caution during contact, especially sexual contact;
- use only your own personal hygiene products.
It is worth remembering that using a condom does not prevent HPV infection, since it does not exclude the possibility of contact with the affected areas of the partner’s skin. There is only one precaution in this case - sexual intercourse only with a regular partner.
Modern methods of prevention
The extreme prevalence of the virus forces us to look for effective means of combating it. The growing number of cancers, particularly those caused by HPV, is another reason for this search. The risk of developing malignant tumors is the main danger of HPV, which is what pushes scientists to develop a preventive and therapeutic vaccine against it.
Vaccination
To date, only modest but very important results have been achieved - the creation of a preventive vaccine against four oncogenic strains of HPV. There are several hundred of these strains in total.
Not a single vaccine in the world is capable of protecting a person from all of them. However, even a small opportunity to reduce the risk of cancer can be considered a breakthrough. Currently, preventive vaccines under the trademarks Cervarix and Gardasil are approved for use.
They are used in more than forty countries around the world, including the Russian Federation.
- high cost of vaccination;
- lack of confirmed information about the long-term consequences of vaccination;
- presence of side effects;
- impossibility of use during pregnancy;
- Can only be used in people not infected with HPV.
The vaccine works against the human papillomavirus by immunizing the body. People who have completed the required course of vaccinations develop antibodies in their bodies to the four strains of the virus mentioned above.
This helps prevent primary infection. In addition, the age at which vaccination was carried out is of great importance.
First of all, its feasibility depends on this, since the risk of HPV infection increases every year.
According to official information, the protective properties of the vaccine remain active for at least 4.5 years after the first dose.
Vaccination gives a chance to prevent the development of malignant neoplasms in organs such as:
- Cervix;
- rectum;
- genitals;
- throat.
This type of vaccine is used primarily as a prevention of HPV in women, because the frequency of vaccination is directly proportional to the incidence of cervical cancer. But men are also sometimes given preventive vaccinations against HPV. This is especially true for boys from 9 to 15 years old, as well as people with non-traditional sexual orientation, provided they do not have this virus.
What can you do yourself?
In order to prevent HPV infection, you must first strengthen your own immunity. If the immune system is functioning well, the body will be able to repel a viral attack if one occurs. However, you should not rely only on immunity, because if you are careless about other factors and risks, infection will still occur sooner or later.
And finally, it is imperative to remain vigilant when communicating with strangers: make sure to minimize tactile everyday contacts and be responsible when choosing a sexual partner. It should be remembered that, despite the extremely wide distribution of HPV, it is still possible not to become infected with it, or at least not to be allowed to develop in the body.
Loading…
Source: https://doloypsoriaz.ru/papillomy/profilaktika-vpch.html
Prevention of HPV will save you from an unpleasant disease!
Human papillomavirus is a disease that affects the skin, mucous membranes and internal organs. This infection is transmitted so easily that almost 90% of the population of the entire planet are its carriers.
Warts, papillomas, condylomas are all manifestations of a viral infection that bring a lot of inconvenience to their owners. But a much more dangerous consequence of the virus is the beginning of the oncological process of internal organs. Unfortunately, it is almost impossible to cure the virus.
But HPV prevention allows you to prevent infection or (if infection does occur) activation of the disease.
Content
Prevention as a way to protect yourself from HPV
The papilloma virus is transmitted in three ways: through sexual contact, through household touch and during the birth of a child from the mother. Moreover, in the first two cases this happens to the same extent.
Once an infection enters the human body, it can remain latent for a long time. Activation occurs only after a decrease in the ability of the immune system to resist the pathogen.
Most often, a person has no idea about his illness until its obvious external signs appear.
Treatment of HPV in men and women takes a lot of time and effort. It involves carrying out painful procedures to remove tumors, taking many drugs to fight the virus and restore immune defense. Therefore, it is quite advisable to say that preventing a disease is easier than carrying out a complex of treatment.
There are several preventative methods to protect yourself from contracting the virus.
- maintaining an orderly sex life;
- maintaining the full functioning of the immune system;
- limited contact with an infected person;
- be careful in public places (salons, clinics, swimming pools, saunas);
- observing personal hygiene rules.
Of course, it is impossible to talk about a 100% guarantee of safety if these rules are followed. But it is perhaps possible to help reduce the likelihood of infection.
How to avoid getting a viral infection
Regarding the first, people should avoid casual relationships and always use contraception. Although it is worth noting that even a condom is not able to provide complete protection. The fact is that the particles of infection are so small that they can easily penetrate any obstacles. Moreover, alternating anal and vaginal sex greatly increases the likelihood of infection.
Due to the structure of the genital organs and the frequency of their injury, women are more likely to be affected by the disease. However, HPV occurs at the same rate in men due to homosexual relationships.
Protective measures regarding household contact require complete isolation from potential sources of infection. Prevention of papillomavirus consists of the following actions:
- Use only personal hygiene items. Using someone else's towel, toothbrush, washcloth and other equipment can contribute to infection.
- Visiting tattoos and beauty salons can cause HPV due to the possible lack of sterility of the equipment. You should check how the devices are disinfected and whether the technician wears disposable sterile gloves. If this does not happen, it is better to refuse the services of such a salon.
- You can also become infected while visiting a sauna, bathhouse or swimming pool. Virus particles can remain on the surface of the floor, door handles, etc. To prevent illness, in public places you should wear removable shoes and use only clean accessories.
- Even trivial touching of people carrying the virus can cause infection. It is unacceptable to touch the formations on the skin of sick people.
During pregnancy, women very often notice the manifestation of the papilloma virus. If the patient develops condylomas in the intimate area, the newborn may become infected.
Prevention of HPV in women planning pregnancy is especially important. Since the health of the unborn child depends on the health of the mother.
A person needs to take care of personal hygiene. Take a shower regularly, wash your hands with soap and, if possible, treat them with an antibacterial agent. If any damage to the skin occurs, you should immediately treat it with a special product, preventing infection from entering the wound.
And if a person nevertheless becomes a carrier of the virus and discovers the appearance of papillomas, he should immediately consult a doctor.
In addition, it is not permissible to allow strangers to touch the formations in order to prevent them from becoming infected. Moreover, it is advisable to organize a quarantine zone. Do not share towels or utensils.
The same applies to other people's clothes and shoes. Kissing should also be avoided.
Why is it important to have a strong immune system?
HPV can stay in the body from several months to a couple of years. Moreover, at this time the person does not even realize that he is already sick.
It is with the weakening of the body’s protective function that the external manifestation of the virus begins – the formation of wart growths. Prevention of papillomas is, first of all, prevention of strong immunity.
A strong immune system can even overcome a viral infection so that not a trace remains of it.
To maintain the protective function of your body, a person needs to follow a number of recommendations:
- it is necessary to eat properly and balanced;
- avoid hypothermia;
- avoid stressful situations;
- limit yourself to eating spicy and salty foods;
- protect yourself from infectious diseases;
- take medications with caution;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- do moderate physical activity;
- take walks in the fresh air;
- regularly ventilate the living space;
- provide the required amount of vitamins.
You should be especially careful about your immunity during pregnancy. Since this period is especially important for the baby’s health. If you follow all the recommendations, this will certainly have a positive effect on the immune defense and the body as a whole.
There is no need to let illness take its course. Diseases transmitted to the legs very often become chronic, which will cause a strong weakening of the protective function, and therefore open the way for the activation of the virus.
If a person notices that he has become exposed to various diseases much more often than usual, he should contact an immunologist. If necessary, he will prescribe a course of immunostimulating drugs.
Vaccination as a way to protect yourself from the papilloma virus
There are currently two vaccines of this type. These solutions contain only microparticles of the virus, but its DNA. Therefore, the infection cannot spread and harm a person. However, these particles are enough for the body to develop immunity to them.
Gadrasil is a quadrivalent vaccine that protects against HPV types 6, 11, 16 and 18. It was registered back in 2006. Available in the form of a white suspension for intramuscular administration. This emergency prophylaxis is intended to vaccinate only healthy people. Before vaccination, a person must undergo a thorough examination by a doctor and a series of diagnostic tests.
Cervarix is a bivalent solution for vaccination. Used to produce antibodies to virus types 16 and 18. Registered for use since 2008. Opaque white liquid.
Designed for injection into the muscle. When settled in an ampoule, it gives a white cloudy precipitate at the bottom and a clear liquid at the top.
Just like the previous one, it is used exclusively for people with no symptoms of any diseases.
Thanks to vaccinations, a person can avoid exposure to such an unpleasant disease as the papilloma virus.
This is especially important for women, as it prevents the possibility of developing cancer of the reproductive organs.
In addition, it becomes much easier for a vaccinated woman during pregnancy - she does not need to worry about the appearance of condylomas. Typically, the effect of such a vaccine lasts 8 years.
Human papillomavirus is a dangerous infectious disease. It brings many problems and can provoke the onset of an oncological process on the skin and internal organs.
Even ordinary warts that appear on the face, neck or hands cause discomfort and provoke the appearance of complexes regarding appearance.
Therefore, there is no need to remind you that it is better to prevent a disease such as HPV than to engage in long and labor-intensive treatment.
The article has been verified by the editors
Source: https://CoriumMed.ru/papillomy/vpch/profilaktika.html
HPV prevention: how to protect yourself from the virus
HPV is a common infectious disease that is transmitted only from person to person. Some of its types contribute to the development of malignant neoplasms.
The disease is especially dangerous for women. According to medical statistics, cervical cancer, which is caused by the papilloma virus, ranks third in mortality among all cancers. Prevention of HPV will allow women to protect themselves from such a terrible diagnosis as cancer.
What do you need to know?
Prevention of papillomavirus includes activities of different groups:
- Aimed at preventing infection by a pathogen (taking into account its modes of transmission).
- Aimed at identifying the disease in its early stages.
- Monitoring health status after HPV therapy.
Protect yourself
There are three ways that human papillomavirus can be transmitted. This:
- sexual,
- contact-household,
- vertical.
The main risk factor for infection is promiscuity. To protect yourself from the virus, it is advisable to have one permanent partner. Even using a condom during sexual intercourse, you will not be able to protect yourself from infection. The virus has the ability to penetrate the epithelium through ordinary touch.
What to do? First, after a casual relationship, treat intimate areas with Epigen Intim spray. This is a drug based on glycyrrhizic acid with a powerful antiviral effect. Secondly, women should monitor the condition of the vaginal microflora. If you experience the slightest discomfort, you should consult a doctor and take the probiotics prescribed by him. Vaginal dysbiosis increases susceptibility to HPV.
The second most common route of transmission of the virus is through household contact (through personal hygiene items, bedding, clothing, shoes). The pathogen enters the body of a healthy person from an infected person through microscopic lesions on the skin.
Therefore, when visiting saunas and swimming pools, it is not recommended to use public towels, sheets, slippers; it is better to take your own.
If there are scratches or cuts on the body, they should be treated in advance with any antiseptic and lubricated with medical glue (BF 6).
The vertical method of infection involves infection of the baby from the mother during childbirth.
Women must be tested for the presence of various viruses in their bodies, including HPV, even at the stage of planning a child.
It is possible to “put to sleep” the virus and prevent it from harming the health of the child even during pregnancy. The main thing is that medications are prescribed by a qualified doctor.
Vaccination is an important preventive measure
An important step in the prevention of papillomas is vaccination. There are two vaccines in the world to prevent infection with the most dangerous types of HPV. These are the Belgian-made drug Cervarix and the American Gardasil.
By the way, Gardasil has been included in the compulsory vaccination schedule in countries such as the USA, Germany, Austria and France since 2007.
Both drugs contain viral antibody proteins, which, when entering the body, promote the production of its own specific antibodies. Moreover, neither Gardasil nor Cervarix contain live pathogens. This means that from an epidemiological point of view they are 100% safe. A healthy person does not need to be afraid that after getting vaccinated, he will become infected.
The vaccine is a preventative measure. If a person has been infected, then trying to be treated with its help is pointless.
Immunization is carried out three times with intervals of several months according to the scheme: 0-2-6 (accelerated scheme: 0-1-3 months). The drug is injected into the shoulder. As a rule, there are no side effects. In rare cases, redness and pain at the injection site and an increase in body temperature up to 37.5 degrees are observed. But after a few days, all the unpleasant symptoms go away on their own.
There are several contraindications to immunization:
- acute and chronic diseases in the acute stage;
- allergic reactions to products containing yeast and aluminum;
- pregnancy.
Early diagnosis is the key to successful treatment
Secondary preventive measures are aimed at identifying the disease in the early stages, when the virus has not had time to cause significant harm to a person’s health, and papilloma has not developed into melanoma.
Early diagnosis methods include:
- Examination and palpation by a dermatologist, gynecologist - for women, urologist or proctologist - for men. You should undergo a preventive examination at least once a year. If a specialist sees neoplasms of unknown etiology on the body or changes in the genitals, he will send the patient for tests.
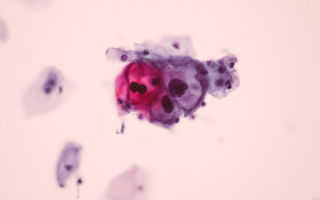
- Cytological screening (for women) - a smear from the cervical mucosa. The collected material is processed using the Papanicolaou method and examined under a microscope. Based on the structure of the epithelial cells, the specialist will determine whether there is cervical neoplasia or a precancerous condition.
- Visual screening (for women) - the cervix is treated with a solution of acetic acid or Lugol. Based on the nature of the reaction, the gynecologist determines whether there is dysplasia (areas with changes will turn white, this phenomenon is called the “acetowhite phenomenon”).
A man should undergo a visual examination by specialized specialists and have an ultrasound of the rectum. If papillomas are diagnosed, the patient will be sent for a biopsy (tumor tissue will be taken for examination in the laboratory).
If during an examination a person is found to have HPV in a “dormant” state, the main task is to prevent the virus from activating. To do this, firstly, you should take simple measures to strengthen your immune system. Secondly, remove tumors on the skin or mucous membranes.
HPV is a virus that does not penetrate deeply into the body. It first settles in the upper basal layer of the skin. If a person has a strong immune system, the virus will not pass further. From the top layer it can be easily removed clinically by destroying papillomas.
To strengthen the immune system, patients are recommended to take immunostimulants (preferably the interferon group: Viferon, Anaferon), antioxidants and vitamin complexes. You can also drink adaptogens of plant origin - alcohol tinctures and extracts (eleutherococcus, echinacea, lemongrass, aralia).
Rational methods of tumor destruction
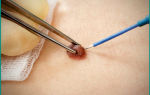
Removal of tumors today is carried out in almost all clinics. Different destruction methods are used. The safest and most effective are the laser method and cryodestruction. Each of them has its advantages.
Laser removal of tumors on the body, face, and intimate places takes about two minutes. The high temperature of the laser beam kills the cells, i.e., eliminating the possibility of secondary appearance of papilloma. A crust remains at the operation site, which disappears on its own after 7-14 days. Moreover, there are no scars or pigment spots left on the treated area.
The cryodestruction method involves removing the growth with liquid nitrogen. In this case, the virus is killed, on the contrary, by low temperature (-196°C). The procedure does not require pain relief. There are no scars left on the body after it, the wound heals very quickly.
A specialist may suggest removing tumors using other methods. For example, electrocoagulation or surgery. It is better to abandon the last method. Because in the process of removing papillomas with a scalpel, the risk of injury increases, i.e., further spread of the virus.
Post-therapy follow-up
After completing the course of HPV treatment, you need to monitor your health. During the first year after completion of therapy, women should undergo a cytology smear every 6 months. In the future, if the test for HPV is negative, once every 12 months. Men should also visit a urologist regularly.
In addition to monitoring with doctors, it is extremely important to adhere to general recommendations for the prevention of papillomavirus:
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Treat inflammatory diseases in a timely manner (do not bring the body to extreme states).
- Avoid stress if possible.
- Do not use antibiotics unless absolutely necessary.
- In immunodeficiency conditions, see an immunologist.
- Avoid visiting public places with high humidity (saunas, baths).
- Adhere to a work-rest schedule.
Like any other disease, HPV is easier to prevent than to treat. To do this, you need to follow simple preventive measures and support your immune system.
At your request they are also reading:
Source: https://opapillome.ru/lechenie/profilaktika-vpch.html
How to avoid becoming infected with the human papillomavirus?
Table of contents
- Risk factors
- Papilloma on the skin?
Risk factors
Doctors note that one of the most significant factors that contribute to the rapid infection and spread of the virus is the body’s weak immunity.
And the second question is what caused the weak immune system: infection, long-term use of antibiotics, chemotherapy, hormones. The sixth and eleventh types of papillomavirus can pose a threat to the life of the fetus.
Infection occurs through the placenta, and also during the woman’s labor.
It can take a long time from infection to the occurrence of severe problems. Skin problems with papillomavirus can be very different. Papillomavirus, especially several of its types, can cause severe damage to the genitals.
Warts in the groin area or acute condylomas are an excellent background for the development of dysplasia or malignant tumors in the cervical area. These can be condylomas in the form of warts on the skin, and flat varieties of papillomas.
Often during infection with papillomavirus, their malicious growth on the skin can be observed while expecting a baby, at a young age, in people with weak immunity, for example, after undergoing chemotherapy or in HIV-infected people.
Papillomavirus is not only an external defect, but also a significant danger to overall health. It is this infection that is closely associated with the occurrence of oncology in the cervical area. Cervical cancer now occupies one of the leading positions.
In addition to the genital area, the papillomavirus can also infect the mucous part of the larynx, thereby causing oncology. When papillomas occur, it is very important to immediately carry out the necessary diagnostics and carry out PCR.
For a more thorough study and research, they turn to a biopsy.
Papilloma on the skin?
You should not expect that papilloma will go away on its own. It is extremely important to entrust the issue of diagnosing and treating papillomavirus to a doctor. Such treatment is now available.
Often, to correct the problem, one of the methods for removing papillomas is proposed, for example, surgery, cryotreatment, diathermocoagulation, radio wave method, local and complex treatment with immune agents.
Thus, advanced papillomas in the anogenital area in the future can cause cracks, bleeding, and the formation of secondary infections, which will significantly complicate the problem. Ignoring the treatment process for papillomas will cause a very rapid spread throughout the body.
How to avoid becoming infected with the human papillomavirus? Link to main publication
Source: https://1papillom.ru/news/kak-ne-zarazitsya-virusom-papillomy-cheloveka.html
What you need to know about HPV and how to protect yourself from an infection that is untreatable and leads to cancer
Human papillomavirus is a very common sexually transmitted infection. It often occurs without symptoms, while some types of HPV can lead to serious consequences in the form of cervical cancer and other cancers.
General practitioner, author of the popular medical blog “Dr. Phil” Philip Kuzmenko tells everything you need to know about the virus and protection against it.
HPV is a large group of viruses that infect the skin. They subsequently develop genital warts. In general, this is not dangerous: despite the fact that most people become infected with this pathogen throughout their lives, most often the infection ends with spontaneous recovery (that is, the virus is simply destroyed by our immune system). However, there are types of HPV that can lead to the development of cancer - and you should be afraid of them.
Currently, more than 190 types of HPV have been described, from which viruses of low and high oncogenic risk are isolated, depending on their ability to cause cancer.
Two highly oncogenic HPV types (16 and 18) account for up to 70% of cervical cancers, as well as 80% of vulvar and vaginal cancers, 92% of anal cancers, 95% of oral cancers, 89% of oropharyngeal cancers, and 63% of penile cancers. .
Non-oncogenic HPV types (6 and 11) do not cause cancer, but are the cause of almost all types of genital warts.
The source is a sick person or carrier. Infection occurs through contact of mucous membranes, that is, during any type of unprotected sexual intercourse. But the virus can also enter the body without sex - just “rubbing” your genitals against the genitals of another person. For example, if you just sleep together.
The risk of transmission even with one single unprotected sexual contact is 80%. Especially in girls who have not reached puberty, during puberty a biotransformation of the reproductive system occurs in the uterus: one type of cell is replaced by another. This “construction” process facilitates the penetration of the virus into cells.
Up to 70–80% of the sexually active population will become infected with HPV during their lifetime. According to WHO, there are about 6 million new cases of infection every year.
However, it is impossible to assess its true prevalence, since most cases of infection are asymptomatic and end in self-healing.
The only symptom is specific warts, but there is no pain or fever with HPV.
In 5-10% of patients, HPV does not go away, which can ultimately lead to the appearance of benign or malignant neoplasms of the mucous membranes where the virus entered and settled: cancer of the cervix and cervical canal, anus, penis, mouth and throat. The interval between HPV infection and progression to invasive cancer is usually 10 years or more.
Symptoms of early stage cervical cancer:
- Irregular spotting or light bleeding between periods in women of reproductive age;
- Postmenopausal spotting or bleeding;
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse;
- Increased vaginal discharge, sometimes with an unpleasant odor.
Who is at risk?
- Early onset of sexual activity (increases the risk of infection by 22 times);
- Frequent change of sexual partners;
- Frequent childbirth and abortion;
- Concomitant urogenital infection and disturbances of the vaginal biocenosis;
- Smoking;
- Immunodeficiency conditions;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Hormonal factors.
If the doctor finds characteristic warts on you, then you already have HPV (but not necessarily that it is oncogenic).
To detect HPV, gynecologists use the cytological method (vaginal smear) - microscopy of exfoliated cells with Papanicolaou staining (Pap test).
However, false negative results are possible, since the sensitivity of the Pap test, according to meta-analyses, is only about 60%. For men, the situation is more complicated - it is impossible for them to be tested for HPV and determine its type.
How is this treated?
If you have been diagnosed with a non-oncogenic type of HPV, then it is enough to be checked regularly by a gynecologist. If it is oncogenic, then under no circumstances should you skip regular examinations with a gynecologist - this is the only way you will have the opportunity to catch precancer in time.
If the doctor prescribed you some pills, IVs or injections in an attempt to cure you of HPV, find another specialist. HPV cannot be treated with medication. Enough to wait and observe. If there are no changes in the cells, the virus will go away on its own.
The basis of prevention is vaccination. It can protect you from HPV, but not all types, only the evil ones that cause cancer. Vaccination is recommended for girls and women aged 9 to 26 years, as well as boys and men aged 9 to 21 years (but up to 26 years).
Many people ask the question: does it really help? Yes, there is high-quality evidence that HPV vaccines protect against cervical cancer in adolescent girls and women vaccinated between the ages of 15 and 26 years.
Which vaccine should I choose?
There are 2 vaccines available on the Russian market - Gardasil and Cervarix. Both are directed against the 16th and 18th strains, but after vaccination, immunity is formed from a number of other subtypes of the virus, since they are very similar to each other. Gardasil also provides additional protection against subtypes 9 and 11.
Vaccination against HPV is not cheap. A full course of vaccination (3 pieces) costs approximately 15-21 thousand rubles. It has not yet been included in the National Vaccination Calendar and is not available for free.
⠀
Vaccines cannot remove the virus from the body if it already lives there. They protect against the very fact of infection. Therefore, vaccination should be carried out before sexual activity begins.
After this, the effectiveness of vaccination decreases, since HPV is very widespread in the population, and most likely you have already been infected. At the same time, there is information that if you get vaccinated after the start of sexual activity (and even after 26 years), the effect will still be there.
Vaccination reduces the risk of developing cervical canal abnormalities and other gynecological problems. So, if you have the desire and extra funds, you can get vaccinated.
Women planning a pregnancy should delay vaccination until completion. If a young woman becomes pregnant after starting the vaccination series, administration of the remaining dose should be delayed until after pregnancy. Breastfeeding is not a contraindication for HPV vaccination.
And yes, it is impossible to become infected with HPV from the vaccine itself. Because they do not contain the virus itself - only its fragmented identification marks, so that the immune system gets to know the enemy and develops antibodies. After vaccination, there may only be side effects - rarely redness, a slight increase in temperature, headache, dizziness, nausea. But nothing criminal.
What else will help for prevention?
As you remember, the virus itself is not dangerous. It is scary because it can cause cancer. Therefore, it is important to visit a doctor and have a PAP test:
- from 21 to 29 years every 3 years,
- + HPV test over 30 years old every 5 years
The HPV test detects the level of concentration of human papillomavirus in the body at which cervical neoplasia develops. The higher the level, the greater the risk.
To reduce your risk of contracting HPV, try to avoid sex with people you don't know well. Condoms provide a 70 percent guarantee of protection against transmission of a viral pathogen to a healthy person during sex.
In addition, this contraceptive helps protect against most sexually transmitted diseases.
Source: http://www.sobaka.ru/health/health/97562
How is HPV transmitted: is it possible to become infected with papilloma?
The probability of the presence of human papillomavirus infection in the body of each person exceeds 50%. By knowing how HPV is transmitted, you can take effective preventative measures against infection.
HPV classification
Today, few people no longer know whether the human papillomavirus is contagious. Considering the high infection rate of the population (70-80%), a positive answer can easily be given. However, not all strains of the virus are equally dangerous to humans. Experts have divided the known types of viruses into several groups depending on the degree of risk of developing cancer pathologies:
- high-risk oncogenic viruses,
- oncogenic medium risk,
- low-risk oncogenic,
- non-oncogenic.
Types of skin growths due to human papillomavirus infection
The clinical manifestation of HPV is the formation of growths on the skin. Depending on the location and external characteristics, these are:
- warts (hardened growths mainly on the face, hands and feet);
- papillomas (softer skin growths on the skin and mucous membranes);
- flat and genital condylomas (a type of papillomas in the anogenital area).
You need to pay close attention to such symptoms of infection. All growths are contagious because they are a source of infection.
How is papillomavirus transmitted?
The main methods of HPV infection are known:
- contact and household (when kissing, shaking hands, using common hygiene items);
- sexual (during intimacy);
- parenteral, through blood (with the infusion of donor blood);
- vertical method (from mother to child during childbirth);
- self-infection (during shaving, hair removal).
The virus is not inherited.
Isolated cases of infection of medical staff by airborne droplets during excision of growths have been recorded, but how papilloma is transmitted in such a situation is still being studied.
The use of poorly sterilized instruments in a medical or cosmetic institution (dentistry, nail salon) can also be dangerous.
Contact and household path
You can become infected with HPV through everyday contact from your loved ones. If someone in the family has skin tags, they are a carrier of the infection. Therefore, it is important not only to treat the sick person, but also to take preventive measures in relation to other family members: use separate personal hygiene products (towels, toothbrushes, razors), and do not skimp on dishwashing detergents.
Some people cannot imagine how one can become infected with papilloma from a sick person through a kiss. Very simple. If there are condylomas on the oral mucosa, the human papillomavirus is transmitted through the saliva of an infected person.
Contact and household transmission of HPV includes infection when visiting public places.
When in a pool, sauna, gym or public bathroom, try to protect yourself as much as possible - do not use other people’s towels or rugs.
It is possible to become infected with papillomavirus even by shaking hands with a sick person, especially if there are untreated wounds or scratches on your hands. They allow the virus unhindered access to cells.
Sexual method
The likelihood of transmitting the human papillomavirus during sexual intercourse is very high. HPV belongs to the group of genital STIs (sexually transmitted infections).
Moreover, a condom does not completely protect against HPV infection, because foci of infection may be located outside the closed area.
And yet, doctors strongly recommend practicing protected sex, which significantly reduces the possibility of becoming infected with the human papillomavirus and other sexually transmitted diseases.
People also become infected with the human papillomavirus during unprotected anal sex: the inner surface of the rectum is easily injured, which opens the door for the virus to penetrate. The result will be the appearance of anal warts.
HPV is also transmitted through oral sex, resulting in condylomas in the mouth and larynx.
Until recently, it was believed that the virus was mainly transmitted from men to women, but this is not the case. The carrier of the virus is identified not so much by his belonging to a certain gender, as by his style of sexual life.
To become infected with the human papillomavirus, one contact with an infected person is enough.
Through the blood
HPV is transmitted parenterally. In medical practice, there have been cases of papillomavirus infection during blood transfusion.
But since the human papillomavirus primarily affects epithelial cells, and even a blood test for HPV is considered by doctors to be uninformative, it can be assumed that in these cases the infection most likely occurred from a poorly sterilized instrument. Although the possibility of transmission through blood cannot be ruled out.
Vertical path
How is papilloma transmitted to children? There is a vertical route of infection when the virus is transmitted to the child during childbirth.
If a woman has condylomas on the cervix, they will not only complicate childbirth due to injury and bleeding, but will also cause re-infection of the female body and infect the child.
The infection will manifest itself in the form of neoplasms in the baby’s mouth and nasopharynx, which will lead to difficulty breathing and problems during feeding. Such tumors must be removed.
If cervical condylomas cannot be removed before the baby is born, gynecologists recommend a cesarean section. This approach reduces the risk of infection of the baby, but does not guarantee 100% safety.
Autoinfection
Infection with the human papillomavirus also occurs through self-infection. Most often this happens during shaving or hair removal, when, as a result of microtrauma, cells become vulnerable to virus entry. This especially happens when existing growths, which are foci of infection, are damaged. Transmission of papillomavirus through blood is unlikely.
Are papillomas and warts contagious when touched?
Untreated wounds, scratches, and all kinds of damage to epithelial tissue are ways to become infected with the human papillomavirus. Any wart is contagious, since this is where the infection lives and multiplies.
But papillomas are transmitted from person to person only if the second person’s body “allows” the virus to itself.
The risk of infection increases when “doors” open on the body - a violation of the integrity of the skin or a decrease in immunity, as a result of which the skin becomes unable to perform its protective function.
When the infection appears
The period of time after infection until the clinical picture appears is called the incubation period. The virus reveals itself after several weeks, months or even years.
The length of this period depends on the person’s health after infection occurs.
A strong immune system prevents the virus from developing, so the disease may never manifest itself.
If the body is no longer able to fight, growths will appear on the skin and mucous membranes caused by the activation of HPV.
Do I need to take tests and which ones?
To prescribe effective treatment for HPV, tests must be taken. Diagnosis of papillomavirus is carried out using:
- biopsy - collection of cells or tissues for cytological or histological studies, respectively;
- colposcopy - examination of the female genital organs using a special device;
- PCR is a highly accurate method that determines the strain of the virus and allows one to predict the development of oncology;
- additional tests to detect other STIs.
Should both partners get treatment?
Mostly papilloma is transmitted sexually. The question of whether it is possible not to become infected with HPV again if only one partner has been treated raises great doubts. Doctors recommend taking the course of HPV treatment together.
If at least one partner has sexual contact with other people, the risk of infection increases again.
HPV prevention
Modes of transmission provide tips on how to avoid contracting HPV in the future. The precautions are not very complicated - you need to monitor your physical and mental health:
- have one permanent partner;
- strengthen the immune system with proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle;
- have enough rest and not get upset over trifles.
Vaccination against HPV
Vaccination against HPV is considered an effective preventive measure. Immunization before sexual activity or HPV infection has been clinically proven to be effective.
Source: https://SkinPerfect.ru/vpch/sposoby-zarazheniya
HPV prevention: risk zone and modern methods of protection
The papilloma virus is a danger that awaits every person, regardless of gender, age and lifestyle. The number of infected people in the world increases more than tenfold every decade.
This is the most common sexually transmitted infection. However, it is not only the sexually active population that is at risk, as HPV can also be transmitted through the sharing of household items.
This group of viruses has been studied quite well. Modern medicine has proven that some types of papillomavirus cause cancer.
Who is at risk
For some groups of people, the chances of becoming infected with HPV are particularly high. These include:
- people with disadvantaged socio-economic status;
- people who often change sexual partners;
- people suffering from immune system disorders;
- people with sexually transmitted diseases (herpes, trichomoniasis, chlamydia and others);
- young people;
- people with vitamin deficiency;
- homosexuals;
- smokers;
- pregnant women.
Most often, infection occurs through sexual contact, and sexual contact without intercourse can also lead to infection. Infection with the virus occurs in 50-75% of women with the onset of sexual activity. Moreover, the likelihood of infection becomes higher with an increase in the number of sexual partners.
HPV is especially dangerous for women, since this virus plays an important role in the occurrence of cervical cancer. According to doctors, almost 100% of women with cervical cancer are diagnosed with an oncogenic type of HPV. Therefore, prevention of papillomavirus is at the same time prevention of cancer of the female genital area.
How does HPV infection occur?
Infection with this virus can occur in different ways. Most often, HPV infection is transmitted through sexual contact, and it does not matter what type of sex you prefer.
You can become infected during vaginal, anal, oral sex, as well as petting. Kissing can also be dangerous.
Even virgins can be infected during sexual contact without intercourse.
The only method of contraception that can to some extent protect against HPV is a condom. Condom protection reduces the likelihood of transmitting HPV from one partner to another, but does not protect against infection by 100%. The fact is that a condom only covers the genital organ, and infection can occur through surfaces located outside of it.
The papilloma virus enters the body not only through the mucous membranes of the genital organs, but also through the skin. This is facilitated by the presence of microtraumas on the skin: cracks, scratches, abrasions. Particularly high concentrations of the virus were found in seminal fluid, urethra, and Bartholin's glands. Of all the types of HPV, of which there are more than a hundred, 35 of its varieties affect the genitals.
There is a possibility of becoming infected with HPV through objects. Sharing clothing (especially underwear) and towels can be dangerous. In a hospital, the virus may end up on medical gloves or biopsy instruments. The problem of virus transmission in this way has not yet been sufficiently studied. The likelihood of infection through sexual contact is much higher.
Rarely do any carriers of the virus know about the infection. HPV may not manifest itself in any way for a long period: from several weeks to ten years. However, all this time the infected person remains a carrier of the disease. On average, after one or two years, the body gets rid of the papilloma virus on its own. If the immune system is weak, this process is delayed.
There is also the possibility of infection of the newborn from the mother during childbirth. The papillomavirus enters the child's body as it passes through the birth canal.
The virus is contained in amniotic fluid, cervical and vaginal secretions.
There have also been cases of infection in children who were removed by caesarean section, so doctors suggest that the infection may also be present in the placenta.
Methods for preventing HPV in modern medicine
What can you do to protect yourself as much as possible from the consequences of infection with the papilloma virus:
- be regularly tested for viruses;
- avoid situations in which infection is possible;
- use barrier contraception;
- get vaccinated against HPV.
Since transmission of the virus most often occurs through sexual contact, it is worth eliminating casual sexual relationships from your life and paying attention to protecting yourself from sexually transmitted infections.
A regular partner can also be a carrier of HPV, so everyone should get tested for the virus.
Condoms are not able to fully protect against HPV, so a responsible attitude towards sexual relations and regular tests for the virus are mandatory for all people who are sexually active.
It is difficult to notice the presence of a virus in the body. HPV infection is not detected in the blood. However, not all patients have an immune system that produces antibodies to it.
The virus has the ability to “hide” from the immune system, due to this it lingers in the body for a long time. The PCR method is the most effective for detecting HPV. It makes it possible to detect viral DNA in cells.
It is recommended to be re-tested for the virus every 3-5 years or when you have a new sexual partner. The examination requires a urogenital smear.
The course of the disease depends on the ability of the immune system to resist infections.
Staying in the body of a highly oncogenic virus for two or more years is a sure path to the development of a precancerous condition of the cervix.
If we are talking about virus type 16, the risk of developing cancer tends to 50%; for HPV type 26, the probability is 30-40%. These are the most dangerous types of virus for women.
To diagnose cervical cancer at an early stage, special programs have been developed that necessarily include the cytological method Pap test (its other name is the Papanicolaou test).
In European countries, such a study is recommended every three years for all women over 21 years of age or 3 years after the start of sexual activity.
The Russian Ministry of Health does not give clear instructions on this matter, but recommends that you undergo preventive examinations with a gynecologist every year, including a smear examination.
There are two vaccines that help prevent infection with the most oncogenic forms of HPV: Gardasil and Cervarix. The most popular vaccine is Gardasil, used in more than 60 countries. The drug is highly effective - immunity is developed in 95-100% of vaccinated people.
Gardasil contains proteins similar to those found in HPV types 6, 11, 16, 18. They are synthesized by drinking yeast and do not pose a health hazard. There are no infectious elements in this vaccine.
Through vaccination, immunity is formed, which also protects against other types of oncogenic HPV. This vaccination is preventive, that is, it will not help someone who is already infected to recover.
But infection with four forms of HPV at once is rare, so the patient can protect himself from other types of papillomavirus.
The best time to get vaccinated is before sexual activity begins. Doctors strongly recommend vaccinating girls and boys aged 9 to 17 years, as well as girls aged 18 to 26 years.
What diseases will the vaccine protect against?
- cervical cancer;
- cancer of the vulva, vagina;
- cancer of the male genital organs;
- genital warts;
- laryngeal papillomatosis.
The vaccination will need to be done three times.
Usual vaccination schedule: 0–2–6 months. An accelerated scheme is also acceptable: 0–1–3 months. Don't worry if for some reason you miss the interval between vaccinations.
If you managed to get three vaccinations within a year, then you have developed immunity.
Side effects from the vaccine are rare and no complications have been reported. There may be a short-term increase in temperature up to 37.5 °C, slight swelling and redness at the injection site.
Gardasil is not recommended for pregnant women and people with allergies to vaccine components (yeast, aluminum). Remember that after vaccination, you still need to stay on guard to avoid contracting other types of the virus.
Prevention of papillomas will protect you not only from cancer. HPV causes neoplasms to appear on the skin and mucous membranes, and it is especially unpleasant when this happens to the genitals. Therefore, follow all safety measures, be attentive to your health and vaccinate your children against the virus.
Source: https://doctoros.ru/dobrokachestvennye-novoobrazovaniya-kozhi/profilaktika-vpch.html