Aphthous stomatitis is a disease accompanied by a vivid clinical picture. The pathology makes it difficult to eat and affects a person’s quality of life.
Lack of treatment leads to the transition of the disease to a chronic, intractable form. There are many types of the disease, each of which requires its own approach to treatment.
For this reason, it is necessary to combat aphthous stomatitis under the supervision of a doctor.
What is aphthous stomatitis
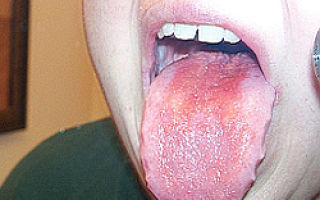
The name of the disease comes from the word “aft,” or ulcer. A characteristic sign of the problem is damage to the mucous membranes of the mouth with the formation of ulcers of various shapes and sizes. Formations occur in the mouth separately or in groups, affecting large areas of mucous structures.
Aphthae are most often localized in the front of the mouth, on the inside of the lips and cheeks. These areas are more susceptible to damage, friction, and accidental bites. Less commonly, stomatitis on the tongue is noted. The disease may be accompanied by a slight increase in temperature and general weakness. Aphthous stomatitis lasts on average 8-12 days.
Aphthae in the mouth are round in shape and resemble erosions with a white or gray coating, surrounded by a bright red membrane. The size of the wounds does not exceed 1 cm in diameter. With a mild course of the disease, 1 ulcer appears in the mouth, with a severe one - from 3. Touching the affected areas gives the person acute pain and discomfort, so eating with the problem is very difficult.
Development mechanism
Medicine has not established the exact mechanism for the development of stomatitis of this type. Two factors have been identified that contribute to the development of the disease: autoimmune disorders in the body and the influence of pathogenic microflora.
In its development, aphthous stomatitis goes through several stages. Pathogenic flora, entering the oral cavity, provokes a change in the composition of saliva.
The condition is not accompanied by characteristic symptoms due to the fact that immune cells do not recognize the pathogen. At the next stage, the body begins to produce lysocytes, which attack the foreign substance.
As a result, erosions appear on the mucous membranes of the mouth.
The following factors are of great importance in the mechanism of development of stomatitis:
- poor nutrition;
- use of oral hygiene products with aggressive chemical composition;
- non-compliance with the work and rest schedule;
- bad habits - smoking, biting the inner surface of the cheeks;
- lack of vitamin D in the body;
- disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- uncontrolled use of antibiotics and non-steroids.
Advanced form of aphthous stomatitis caused by dental caries
Kinds
In addition to the chronic course of the disease, there are several other types of aphthous stomatitis:
Treatment of purulent stomatitis
- Fibrinous. Ulcers on the mucous membranes have a grayish tint and disappear on their own after 1-2 weeks. In the chronic form of the course, the pathology recurs 3-4 times a year.
- Necrotic. Develops due to infectious and viral pathogens. When the disease occurs, mucosal cells die. In the recurrent form, the size of the aphthae increases with each new exacerbation, making it difficult to eat and speak. The healing process of large wounds lasts up to 1 month.
- Glandular. Occurs with damage to the salivary glands. The neoplasms are large and appear again after healing.
- Scarring. Aphthae reach 1 cm in diameter, and after healing they leave noticeable scars on the surface of the mucous membranes. Erosion takes a long time to heal – from 3 months.
- Deformable. It is considered one of the most severe types of pathology. Ulcers deeply affect the mucous membranes, which causes scarring and changes in the structure of the oral cavity. Recovery takes a long time - from 2 months.
- Herpetic. It is more often diagnosed in children who become infected with the virus from their mother in utero or during childbirth. Aphthae are small blisters and appear in the plural (up to 30 pieces at a time). The mucous membranes of the child’s mouth become inflamed and acquire bright red shades.
- Recurrent. Often diagnosed aphthous stomatitis in adults. This type of pathology practically does not occur in children. The wounds merge with each other, forming large lesions. The ulcers become covered with a white coating and are accompanied by pain and burning.
- Spicy. It is more often observed in children under 3 years of age and occurs against the background of infectious diseases - whooping cough, diphtheria or measles. Acute aphthous stomatitis is accompanied by increased salivation and bad breath.
- Mixed. Common among children over 4 years old. Erosion during the disease causes burning and pain. With each relapse the disease becomes more pronounced.
The photo shows changes in the structure of the mucous membranes resulting from the deforming form of stomatitis
The danger of the problem and how it spreads
Is the disease contagious? The answer to this question depends on the cause of canker sores. An illness of viral, infectious and fungal etiology is easily transmitted from one person to another through common objects: dishes, toys, etc. The viral type of disease can be contracted through airborne droplets: when talking, while sneezing.
Infectious aphthous stomatitis is dangerous for children, since the local immunity of their mucous membranes is not sufficiently developed. The infection is transmitted in the same way as the virus: by contact and airborne droplets. Adults become infected with the pathology if they have abrasions and microdamages in the oral cavity.
Fungal stomatitis is not transmitted by airborne droplets. This type of disease develops when sharing utensils, water and food with the patient. People with weakened immune systems and diabetes are especially vulnerable to fungal pathogens.
Fungal stomatitis is characterized by large affected areas and the formation of a white coating on the tongue
Aphthous stomatitis, provoked by vitamin deficiency, mechanical damage and stress, is not contagious. Forms of the disease that are transmitted from one person to another are especially dangerous for infants. Their immunity cannot fully cope with the introduction of a foreign agent. Which leads to severe forms of the disease with damage to internal organs.
Symptoms of aphthous stomatitis vary depending on the stage of its development. Initially, the condition is accompanied by inflammation of the lymph nodes, malaise, fever and worsening fever.
Then redness of the oral mucosa and the appearance of ulcerative rashes up to 5 mm in diameter are noted. As the pathology progresses, erosions become covered with a yellowish or gray coating.
The general symptoms of the disease, hyperthermia and malaise, persist.
The initial stages of the disease are characterized by severe inflammation and redness of the mucous membranes
Signs of the problem disappear in the final stage of stomatitis: the patient stops feeling burning and itching in the mouth. Usually, after the acute stage, a person’s condition normalizes, and after wounds there are no scars left (with the exception of the deforming form of the disease).
Aphthous stomatitis in adults begins abruptly. The disease is accompanied by:
- the formation of small bursting bubbles that leave behind aphthae;
- soreness in the mouth when consuming foods with a pronounced taste;
- general weakness and fever up to 39 degrees;
- inflammation of the mucous membranes and looseness of its structure;
- the appearance of a white coating on the tongue.
It is recommended to treat the problem under consideration under the supervision of a dentist, since there is a possibility of the problem becoming chronic (recurrent) form.
In this case, the mucous membranes swell and become pale. Ulcers affect the inside of the cheeks, the area under the tongue and lips, and less commonly the palate and tongue.
The lesions can reach 1 cm in diameter and become red. With extensive damage, the aphthae protrude above the surface.
Extensive lesions due to the merging of several afts into one
An exacerbation in the chronic form of the problem is observed for 12-15 days. Without proper treatment, erosion affects the deeper layers of the oral cavity with each relapse. In this case, the wounds may bleed, causing the person even more discomfort. The condition is dangerous due to the possibility of infection. In addition, deep erosions leave behind non-healing scars.
An experienced doctor will be able to make the correct diagnosis after a visual examination of the oral cavity.
To confirm assumptions, the dentist collects detailed information about the disease: the time of the first symptoms, the intensity of symptoms, the presence of mechanical and thermal injuries to the oral cavity, allergies to food and medications, and the presence of similar problems in close relatives.
To identify the causative agent of aphthous stomatitis, they resort to laboratory diagnostic methods - a smear on the flora. It is important to diagnose stomatitis with herpes lesions, since these diseases have a similar clinical picture.
| Criteria | Aphthous stomatitis | Herpes |
| Primary signs | Painful spot | Bubble with clear liquid. Aphtha forms only after the vesicle has opened |
| Number of ulcers | 1-2 | Up to 3 for a mild form of the disease and more than 25 for a severe one |
| Related Issues | Enlarged lymph nodes | Manifestation of signs of gingivitis and lymphadenitis |
| Location of rashes | Skin and mucous membranes of the mouth | Inner and outer lips |
Treatment methods
Aphthous stomatitis in adults should be treated comprehensively and under the supervision of a specialist. Therapy is not stopped even after visible signs of the problem disappear. This can provoke a re-exacerbation of the disease and its transition to a chronic form.
Drug treatment
For local treatment of the oral mucosa, patients are prescribed antimicrobial sprays and gels with anti-inflammatory effects. Medicines are prescribed depending on the type of aphthous stomatitis and its severity. To irrigate canker sores, dentists prescribe Miramistin spray. It suppresses the proliferation of viral and infectious pathogens and normalizes the microflora of the oral cavity.
The choice of antiseptics for a problem depends on the age of the patient and his sensitivity to the components of the drugs
To lubricate wounds at the initial stage, Cholisal gel is recommended. The drug is used after antiseptic treatment of aphthae with sprays or solutions. The procedure is performed 3-4 times a day.
In addition to Cholisal, other ointments with an anesthetic and anti-inflammatory effect can be prescribed: Kamistad, Kalgel, Trasylol, Clobetasol, Benzocaine.
Treatment with ointments should not last more than 7-10 days, as these drugs have side reactions.
In case of secondary manifestation of signs of aphthous stomatitis, treatment of the mucous membranes is carried out with antibacterial sprays: Tantum Verde, Orasept, Hexoral. For quick and effective treatment of aphthous stomatitis, use Stomatofit-A gel. It contains medicinal herbs and an anesthetic substance. The gel is applied to the lesions using a cotton swab.
After the wounds disappear, agents with a regenerating effect are used, for example, Solcoseryl. The drug prevents the formation of scars after pathology. Stomatitis therapy is supplemented with antihistamines - Diazolin, Claritin, Tavegil. The course of taking allergy medications is 10-14 days.
A common cause of aphthous stomatitis is dental diseases of the oral cavity: gingivitis, periodontal disease, advanced caries. For this reason, treatment of the problem should begin with the sanitation of infectious foci in the mouth. Their elimination will reduce the duration of stomatitis and prevent its recurrence.
Oral sanitation is especially important in cases of a chronic form of the problem. Dental plaque and caries are favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic flora.
Sanitation of the oral cavity is an important aspect in the treatment of aphthous stomatitis
Strengthening local immunity
Fermented pastes are prescribed to patients as immunomodulatory agents. Hygiene products contain lysocin, lactoferrin or lactoperoxidase. Substances help strengthen the defenses of mucous membranes and accelerate the death of pathogenic flora.
For the same purpose, lollipops are purchased, for example, Imudon. The drug is dissolved up to 6 times a day for 10 days. Drug treatment can be carried out using natural plant components: ginseng, echinacea and propolis or preparations containing these plants (Immunal).
Diet
Due to the fact that ulcers are accompanied by pain, preference is given to warm and liquid foods. For aphthous stomatitis, you can eat: soups, liquid porridges, pate, vegetable purees. The diet is saturated with proteins and carbohydrates so that the body can fully fight the pathogen.
During therapy, avoid eating foods with a pronounced taste: sour, sweet, bitter. A mandatory condition for treatment is complete cessation of smoking and alcoholic beverages.
The following types of products restore the oral microflora:
- olive oil;
- sea buckthorn oil;
- carrot;
- greenery;
- potato;
- oatmeal;
- honey.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis in adults is similar to the treatment of pathology in children. You can learn more about treating problems in younger patients here.
Honey accelerates the regeneration of wounds with stomatitis and promotes the death of pathogenic flora in the mouth
Control methods at home
How to treat aphthous stomatitis at home? Traditional methods of combating aphthous stomatitis are used as an addition to the main therapy regimen. Some natural ingredients have anti-inflammatory effects, which speeds up the healing process.
- Chamomile tincture. Quickly helps in the treatment of any inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, including chronic stomatitis. Decoction recipe: 1 tsp. dry plant, pour 200 ml of boiling water and leave until cool. The liquid is filtered from the cake, 2 tsp is added to it. honey and drink 30 minutes after eating.
- Raw potatoes. The vegetable is peeled, chopped on a fine grater and placed in cheesecloth. The resulting paste is applied to the erosions 3 times a day for 15-20 minutes. For each procedure, a new mixture is used.
- Garlic. Several cloves of the plant are squeezed through a press and mixed with 2 tbsp. l. curdled milk. The resulting mixture is kept in the mouth for 2-3 minutes and then spat out. The procedure may cause burning wounds, but this is not a reason to stop the procedure. Treatment of the oral cavity is performed 3 times a day after meals.
Preventive actions
Prevention of aphthous stomatitis involves careful oral care. Mechanical damage to the mucous membranes should also be avoided.
Identification of the cause of the disease is important in the prevention of pathology. Chronic stomatitis cannot be cured without eliminating provoking factors, for example, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, vitamin deficiency.
If aphthae appear frequently, you should visit specialists in several fields - a psychologist, a gastroenterologist, a dentist. To prevent chronic stomatitis, it is important to follow a diet and exclude too solid foods from the diet.
Source: https://pcvoice.ru/bolezni/aftoznyy-stomatit
Effective treatment of aphthous stomatitis - list of drugs
Effective treatment of aphthous stomatitis - list of drugs4.5 (90%) 2 votes
Aphthous stomatitis is accompanied by the appearance of round ulcerative formations on the mucous membrane, covered with a yellow or gray coating on top.
The disease occurs in both adults and children. It does not occur against the background of acute infectious processes, and therefore does not pose a threat to others.
But in any case, treatment of aphthous stomatitis should be carried out by a dentist.
Only this specialist can thoroughly understand the causes of the disease and identify possible connections with concomitant dental diseases.
Causes of the disease
Aphthous stomatitis appears due to excessive activation of the human immune system, as a result of which it begins to destroy the oral mucosa. Most often, α-hemolytic streptococcus acts as an antigen.
It is this that causes the production of specific antibodies, which cross-react with the mucous membrane and provoke the formation of long-healing aphthae.
The risk of aphthous stomatitis increases if you have the following diseases:
- autoimmune conditions;
- vitamin deficiency, especially deficiency of B vitamins;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- Crohn's disease;
- reactive arthritis.
Hemolytic streptococcus can provoke the appearance of aphthae on the mucous membrane. Among the predisposing factors, experts identify damage to the oral epithelium during eating, when using dentures, and braces.
How is aphthous stomatitis diagnosed?
To understand how to treat aphthous stomatitis, it is necessary to correctly diagnose and determine the possible causes of the development of the pathology. With aphthous stomatitis, specific symptoms appear that make it possible to assess the severity of the patient’s condition with a high probability. Additionally, laboratory tests may be prescribed.
In HIV infection and other immunodeficiency conditions, aphthous stomatitis often recurs and is severe. Therefore, in the chronic course of the disease, it is necessary to test the blood for viral infections.
Symptoms of aphthous stomatitis
Unlike other forms of stomatitis, aphthous stomatitis does not cause difficulties in making a diagnosis. The main symptom of the disease is clearly limited aphthae. On top they are covered with a necrotic film in the form of a gray-yellow coating. Ulcerative defects are necessarily round in shape, with a red rim around the circumference.
Small ulcers heal quickly within a few weeks. There are usually no scars left on the mucous membrane. But in some patients the diameter of the ulcerative defects is more than a centimeter, and a significant depth of damage is observed.
In this case, tissue epithelization takes a long time, up to a month or more, with the formation of scar deformities.
Typical locations for aphthae are the inside of the cheeks and lips, the lateral surfaces of the tongue and the tonsils. The later treatment for aphthous stomatitis at home begins, the higher the risk of chronic disease and complications.
Aphthous stomatitis can be treated at home, but under the supervision of a specialist. Symptoms of stomatitis in children, who may have hidden immune disorders and endocrine pathologies, require special attention.
Principles of treatment of aphthous stomatitis
Treatment in adults and children has the same principles. Medical tactics depend primarily on the severity of the clinical picture, the frequency of relapses and the effect of specific predisposing factors.
Before treating aphthous stomatitis, you must consult a doctor!
In the acute period, treatment is aimed at reducing signs of inflammation, pain, as well as combating associated symptoms. In the future, it is necessary to heal the mucosa and pay attention to preventing relapse in the future.
Drugs effective for the treatment of stomatitis in adults and children
Local treatment - the use of antiseptics to remove ulcers and prevent the development of additional infection:
- Chlorhexidine – low cost, high efficiency;
- Miramistin.
Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs - used in conjunction with local treatment, most of them are in gel form, for example:
- Cholisal – has a powerful anti-inflammatory effect, suitable for children and adults.
Occlusive preparations based on bismuth subsalicylate have an epithelializing effect and reduce pain. Used after the antiseptic.
- Bismuth subsalicylate - sold in tablets, has no age limit.
Glucocorticosteroid local agents are the “heavy artillery” of drugs aimed at treating stomatitis. Aphthous stomatitis is treated with them only in special cases.
Healing drugs - prevent the appearance of scars on the mucous membrane.
- Solcoseryl gel – has a healing and antiseptic effect.
Systemic drugs are used when there is a likelihood of a chronic course of the disease and the possibility of complications. These include the group of glucocorticosteroids. And also immunostimulants:
Video:
Medicines for stomatitis - TOP-11 drugs for treatment
The mucous membrane in aphthous stomatitis is inflamed and reacts sharply to food and temperature irritants. Therefore, throughout the course of the disease, it is necessary to avoid the consumption of foods and drinks that may increase signs of epithelial damage.
It is recommended to avoid crackers, hard bread, sour juices and carbonated drinks, sauces, pineapples, marinades and smoked foods. You cannot drink alcohol in any form.
Local treatment
Local effective drugs are the main ones in the fight against aphthous stomatitis. With their help, you can quickly treat ulcerative defects and prevent the addition of a secondary infection.
It is necessary to rinse with antiseptics several times a day. For young children who do not know how to rinse their mouths, spray antiseptics can be used. Chlorhexidine and Miramistin have just such a dosage form. These drugs are also suitable for adults.
You can buy chlorhexidine in a regular solution, which has a low price but is quite effective.
Antiseptic treatment of aphthous stomatitis using rinsing has a rule - compliance with the required duration of each procedure. This will destroy pathogenic microorganisms and stop the inflammatory process. It is recommended to rinse the mouth for aphthous stomatitis in adults and children 4-5 times a day for a minute.
After rinsing, you need to let the mucous membrane dry a little and apply an anti-inflammatory gel locally to the aphthae.
Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs
Such preparations are often released in the form of a gel, which is easily distributed throughout the tissues and quickly absorbed. An example of such a drug is Cholisal. It contains choline salicylate and cetalkonium chloride.
These components relieve pain in the first minutes after use and have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect. Gel Cholisal has no age restrictions. It is actively used to treat all forms of stomatitis, including aphthous stomatitis in adults and children.
Occlusive preparations based on bismuth subsalicylate
They have an epithelializing effect and can reduce pain. Such products are applied to ulcerative defects of the mucous membrane, after which they form an upper protective layer and thus protect inflamed and sensitive tissues from various irritants.
Occlusive agents are produced in the form of a gel, suspension, or chewable tablets. It is advisable to use them after antiseptic treatment.
Glucocorticosteroid local agents
Drugs from the group of glucocorticosteroids are prescribed for severe aphthous stomatitis, when other drugs do not give the desired effect. The course of treatment is limited due to possible complications. Glucocorticosteroids accelerate the healing of ulcers, even the deepest ones, quickly eliminate pain and remove signs of inflammation in the oral cavity.
Healing drugs
If you ignore the use of healing agents and treat exclusively with painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, deep scars may form on the mucous membrane.
An example of such a medicine is Solcoseryl gel . It not only heals ulcerative defects, but is also an anesthetic. The gel is not used in the acute period, but is prescribed 3-4 days after the first signs of aphthous stomatitis appear.
Systemic drugs
For aphthous stomatitis, systemic drugs are prescribed according to indications when the disease occurs with pronounced clinical manifestations, is chronic and is accompanied by a high risk of complications. Medicines used include antihistamines, immunostimulants and glucocorticosteroids.
Antihistamines eliminate swelling and inflammation. Aphthous stomatitis can recur against the background of a hidden course of chronic allergies. Often patients do not even suspect the presence of such a disease.
It is recommended to use the latest generation products that do not cause drowsiness or other adverse reactions. Antihistamines are prescribed for a week or a little more.
Glucocorticosteroid drugs in the form of drugs for oral use are not prescribed to everyone, but mainly to patients with severe aphthous stomatitis.
The tablets are taken for a week from the onset of the first symptoms of the disease. In severe cases, treatment continues for up to a month.
An example of a glucosteroid drug is Prednisolone. But the dosage of such drugs is selected only by a qualified specialist. The doctor must monitor the progress of treatment and, if necessary, make adjustments to it.
Immunostimulants are used to increase general and local immunity and prevent frequent relapses of aphthous stomatitis. Examples of such drugs are Methotrexate and Cyclosporine. Immunostimulating agents are effective for recurrent stomatitis. Medicines in this group restore the functions of the protective immune system.
Drugs with systemic effects are used as part of complex therapy and must be combined with local treatment. Without antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs, anesthetics, the risk of infection and its spread to healthy tissue increases sharply.
Oral care during illness
Many patients perceive soreness of the mucous membrane during exacerbation of aphthous stomatitis as a reason to refuse oral care. But during this period, it is extremely important to brush your teeth properly with soft-bristled brushes. They are usually recommended for use when gums are vulnerable and prone to bleeding.
Toothpastes should ideally contain anti-inflammatory herbal extracts. For relapses of aphthous stomatitis, it is recommended to choose products with licorice and lactic enzymes that can restore the microflora of the oral cavity.
At the first signs of illness, you should contact a dentist, and not a therapist or pediatrician. Unfortunately, pediatricians sometimes use outdated drugs and methods to combat inflammatory processes in the oral mucosa, and the need to identify a specific pathogen based on laboratory diagnostic results is often simply forgotten.
But aphthous stomatitis is not a disease that can be treated with outdated methods (borax, blue). But even modern drugs will not always help with this form of pathology. For example, antiherpetic drugs will be useless.
The main emphasis in the treatment of aphthous stomatitis is on antiseptic treatments and primarily prescribing antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs. And antibiotics, which are often used by patients without prior consultation with a doctor, can further reduce local immunity and worsen the condition of the mucous membrane.
Therefore, the success of treatment primarily depends on the correctness of the diagnosis. A qualified dentist can accurately determine the form of stomatitis.
The author of the publication is dentist Stanislav Vladimirovich 32 years of experience. Place of work: “Dentistry ECT”. Graduated from SamSMU (1985) Date of placement: 2018-12-12
Source: http://stomatita.ru/lechenie-aftoznogo-stomatita/
Aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis is an inflammatory process of the oral mucosa, accompanied by disruption of the surface layer of the mucosa and the formation of aphthae (erosions).
The formation of aphthae is accompanied by severe pain, a burning sensation in the mouth, especially while eating, enlarged lymph nodes, and sometimes an increase in temperature. Aphthae heal without a trace in 7-10 days.
With weakened immunity and the presence of concomitant diseases, aphthous stomatitis can occur with relapses.
Aphthous stomatitis is an inflammatory process of the oral mucosa, accompanied by disruption of the surface layer of the mucosa and the formation of aphthae (erosions).
The formation of aphthae is accompanied by severe pain, a burning sensation in the mouth, especially while eating, enlarged lymph nodes, and sometimes an increase in temperature. Aphthae heal without a trace in 7-10 days.
With weakened immunity and the presence of concomitant diseases, aphthous stomatitis can occur with relapses.
Chronic aphthous stomatitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa. A characteristic clinical manifestation of such stomatitis is the appearance of aphthae with a whitish-yellow fibrous plaque against the background of general hyperemia of the mucous membrane. The disease is sluggish in nature with periodic remissions and exacerbations.
The pathogenesis of aphthae formation in chronic aphthous stomatitis is not fully understood, however, in all patients there is a strong connection between the progression of the disease and the reaction of the immune system.
Today, the generally accepted theory for the formation of aphthae on the oral mucosa is the theory according to which the human immune system cannot identify the molecules of the substance present in saliva. This causes activation of lymphocytes, since the immune system, not recognizing the chemical agent, attacks it as foreign.
As a result, aphthous ulcers are formed; the inferiority of the immune system and the constant presence of chemicals contribute to the chronicity of the process and aphthous stomatitis takes a long, sluggish course.
In patients who use oral care products containing sodium lauryl sulfate, aphthous stomatitis was diagnosed more often.
The likely cause is the foaming component sodium lauryl sulfate, which has a drying effect, which can negatively affect the oral mucosa.
And in the future, when the upper layer of the mucosa is damaged, the lower layers become more sensitive to irritants, especially to substances with high acidity.
Mechanical damage to the oral cavity is also a provoking factor, since patients themselves note a connection between oral trauma and the onset of the disease.
Chronic aphthous stomatitis can begin after biting the tissues of the oral cavity, after damage to the mucous membrane by the sharp edge of a tooth or hard food.
Approximately 40% of patients with chronic aphthous stomatitis confirm the presence of trauma before the onset of the disease.
Neuropsychic stress in itself rarely causes chronic aphthous stomatitis, but the appearance of aphthous stomatitis during exacerbations often coincides with periods of increased psychological stress.
Most patients with chronic aphthous stomatitis have various nutritional disorders and nutritional deficiencies.
Lack of vitamin C, B vitamins, iron, zinc, folic acid and selenium negatively affects the condition of the oral mucosa, which contributes to the occurrence of aphthae.
An allergic reaction to food can cause an outbreak of canker sores, so patients are advised to keep a diary to make it easier to find out the allergen that caused the aphthous stomatitis in the future.
Among the products that are the most likely allergens are cereals with a high content of gluten protein: wheat, rye, barley, buckwheat.
Citrus fruits, pineapples, apples, tomatoes, figs, strawberries, chocolate, seafood, spices, as well as dairy cheeses and food additives are the main causes of aphthous rashes in the mouth.
In women, the frequency of rashes is associated with the menstrual cycle, many of them observe clinical recovery or remission during pregnancy. However, the relationship between pregnancy and remissions of aphthous stomatitis has not yet been studied.
The genetic predisposition to the development of aphthous stomatitis is confirmed by the facts that in a third of patients, one or both parents also suffered from chronic aphthous stomatitis.
Identical twins suffer from aphthous stomatitis in 91% of cases, while fraternal twins suffer from aphthous stomatitis only in 57% - this also confirms the genetic cause of chronic aphthous stomatitis.
Bacterial and viral agents were identified in the contents of aphthae.
Often, upon complete examination, systemic diseases of the blood, gastrointestinal tract and immunodeficiencies are revealed in patients with aphthous stomatitis.
The connection between them and the formation of aphthous stomatitis is confirmed by the fact that after correction of the underlying disease, clinical recovery from aphthous stomatitis or stable remission occurs.
Long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antiarrhythmic and antihypertensive drugs as a side effect causes the development of chronic aphthous stomatitis.
In the fibrinous form of aphthous stomatitis, primary disorders of blood microcirculation in the epithelial layer come first. As a result of these changes, single aphthous rashes appear, covered with fibrous plaque. After 1-2 weeks, the aphthae epithelializes.
The rashes are localized mainly on the mucous membrane of the lips, the lateral surfaces of the tongue and in the area of transitional folds. At the first stage of the disease, relapses occur 1-3 times a year. As stomatitis progresses, it becomes permanent.
Moreover, if at the beginning relapses are provoked by exacerbations of systemic pathology or trauma to the mucous membrane, then as they progress, minor stress is enough for the appearance of aphthae.
In the necrotic form of aphthous stomatitis, primary destruction of the epithelium occurs, while ulcerations of the oral mucosa cause dystrophic disorders that occur against the background of necrosis and necrobiosis of epithelial tissue.
Necrotizing aphthous stomatitis is diagnosed in persons with severe somatic diseases and blood diseases.
The emerging aphthae are practically painless, over time they turn into ulcers, the period of epithelization of which is from 2 weeks to a month.
Grandular aphthous stomatitis develops due to primary damage to the ducts of the minor salivary glands. This causes hypofunction of the glands and provokes the appearance of aphthae, which are localized next to the salivary glands. Aphthae are painful and epithelialize after 1-3 weeks; their further appearance can be provoked by hypothermia, respiratory diseases and exacerbation in foci of chronic infection.
With cicatricial aphthous stomatitis, the acini of the minor salivary glands are affected, the layer of connective tissue is involved in the pathological process, and over time, elements of the rash are observed both in the location of the salivary glands and on the mucous membrane of the pharynx and anterior palatine arches. Mostly young people suffer.
The primary element is aphthae, but they quickly transform into deep painful ulcers, reaching one and a half centimeters in diameter. Cicatricial stomatitis is not associated with somatic diseases, and the pathogenesis is a genetic deficiency of the secretory apparatus.
The process of epithelization of ulcers is long, up to 3 months; after healing, clearly visible scars remain.
The deforming form of aphthous stomatitis is considered the most severe, since the destructive changes in the connective tissue are deep, and the ulcers are persistent. Ulcers epithelialize slowly; the healing process leads to deformation of the soft palate, anterior palatine arches and lips. If the ulcers are localized in the corners of the mouth, then during healing a microstoma may form.
The goal of treatment is either stable remission or clinical or complete recovery. The complex of therapeutic measures includes general and local therapy; the choice of drugs depends on the severity of the manifestation and dominance of individual symptoms.
Local treatment consists of treating the oral cavity with hydrogen peroxide, nitrofural and chlorhexidine. If there is pain, then the aphthae is treated with a 5-10% glycerin suspension with lidocaine or novocaine. If there is an allergic component in the pathogenesis of stomatitis, then a mixture containing trasylol, heparin, novocaine and hydrocortisone is used.
During exacerbations, enzymes are used topically - trypsin, chymotrypsin and RNase. Solutions of citral, vitamin C and P, preparations with Kalanchoe and propolis juice accelerate the process of epithelization. The use of corticosteroid ointments can interrupt the further development of aphthae and speed up the healing process.
Internal use of antihistamines is indicated - clemastine, loratadine, fexofenadine; and desensitizing drugs - quifenadine and histamine with immunoglobulin. If sensitization of the body to a specific microbial agent is detected, then specific desensitization is used. According to indications, antiviral drugs and an antiherpetic vaccine are prescribed.
All patients are recommended to undergo a course of vitamin therapy with a high content of vitamins B and C. Immunomodulators and immunoprotectors are indicated.
If there are neurological disorders, sedatives and tranquilizers are used. It is recommended to include phonophoresis, electrophoresis and laser therapy in the treatment complex.
During treatment and during remissions, it is necessary to follow a hypoallergenic diet with the exception of rough, traumatic foods.
With timely treatment and compliance with the prescribed regimen, stable and long-term remission can be achieved, although complete recovery from chronic aphthous stomatitis is extremely rare.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_stomatology/aftoznyj_stomatit
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis in an adult, symptoms of the disease and ways to combat the disease
Stomatitis in adults has several varieties, and one of them is aphthous. It manifests itself in the form of small ulcers in the mouth, causing some discomfort. Treatment can take a very long time. With aphthous stomatitis, the oral mucosa becomes covered with formations in the form of ulcers, forming a small wound. Eating food or just talking gives a person painful sensations.
What is aphthous stomatitis?
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis in adults should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, who prescribes it taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, his age, and the strength of his immune system.
Causes
Aphthous stomatitis often occurs if a person has a weakened immune system as a result of the harmful effects of bacteria, viruses and microbes.
The following infectious diseases can cause the formation of aphthous stomatitis:
- Measles.
- Flu.
- Adenovirus.
- Herpes virus.
- Diphtheria.
- L-form staphylococci.
In addition, this oral disease occurs for the following reasons:
- If the human body lacks vitamins.
- For diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- For diseases of teeth and gums.
- As a result of trauma to the oral cavity, for example from biting the cheek or eating too hot food.
- With hereditary predisposition.
- From allergic reactions.
Symptoms of the disease
In aphthous stomatitis, the symptoms are similar to the first manifestations of acute respiratory infections :
- Weakness and malaise appear.
- Body temperature rises to 38 degrees.
- Appetite decreases.
- Lymph nodes may become enlarged.
After this, redness appears on the oral mucosa. As the disease develops, aphthae form , which cover the entire oral cavity. Symptoms such as high fever and general malaise continue to persist. Talking, eating, laughing - all this causes pain in the oral cavity.
Pathogens
If, as a result of unsuccessful brushing of teeth, the oral mucosa is injured , then the causative agent of aphthous stomatitis quickly penetrates through this damage. Weak immunity cannot resist infection, and it begins to multiply quickly.
Infection can enter the body not only from the outside. The oral cavity has normal microflora, which contains streptococci, bacteroides and fusobacteria, which do not cause harm to a healthy person. If the body's protective functions are reduced , this microflora can contribute to the development of the disease.
Aphthous stomatitis can be caused by viruses and bacteria. Viral pathogens include measles, herpes, and chicken pox. Bacteria not only cause diseases, but also contribute to the development of complications. This can be tuberculosis, streptococcal and scarlet fever infections.
Forms of the disease
The following forms of aphthous stomatitis are distinguished based on the nature of aphthae damage to the oral mucosa:
- Necrotic.
- Scarring.
- Deformable.
The necrotic form occurs in adults who have any blood diseases or suffer from severe forms of somatic diseases. Provoking factors are hypothermia and respiratory diseases. Ulcers may not heal for about a month, even with treatment.
With the scarring form, ulcers form on the palate and pharynx, reaching a size of 1.5 centimeters. Healing takes a very long time, sometimes taking up to three months. As a result, scars form on the affected areas.
The deforming form is considered the most severe, in which the connective tissue is subject to destruction. The ulcers heal very slowly, after which deformation of the lips, palate, and nerve arches occurs.
Depending on how the disease progresses, aphthous stomatitis can be acute or chronic.
In the acute form, single or multiple ulcers affect the oral mucosa. After 1-2 weeks, aphthae disappear, but if left untreated, this form becomes chronic.
The chronic form lasts longer. In the acute form, aphthae can heal within 5 days without leaving scars. In the chronic form, ulcers do not heal for a very long time, and if they heal, they tend to form again. As a result, the oral cavity constantly breaks out.
This form is characterized by suppression of the immune system due to concomitant pathology, for example, AIDS. The body cannot cope even with a common cold, as a result, all chronic diseases worsen.
The chronic form is often of allergic origin , because the mucous membrane reacts sharply to all irritants. New ulcers form, and the old ones do not even have time to heal.
This condition is typical for people suffering from urticaria, bronchial asthma and migraines.
Studies have been conducted during which it was found that a large number of eosinophils enter the blood, and this confirms the allergic nature of stomatitis.
The development of aphthous stomatitis can be triggered by toxic substances that accumulate in the intestines due to constant constipation. Therefore, it is necessary to follow a diet and adjust your diet in order to normalize intestinal function. People who suffer from diseases of the large intestine are susceptible to the chronic course of the disease.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis
If an adult develops aphthous stomatitis, he should adhere to the following rules:
- It is necessary to avoid eating rough foods, such as chips, which easily get stuck in the cheek and can deepen the ulcers.
- Teeth should be brushed very carefully so as not to damage the inner surface of the mouth.
- You should avoid sour and spicy foods.
- This type of stomatitis is not contagious, so it is not necessary to use separate dishes.
- You can purchase toothpaste that does not contain sodium lauryl sulfate and other substances that cause irritation to tissue in the mouth. It is also advisable to buy toothpaste that can delay the growth of irritating plaque.
The following effective remedies are used to treat aphthous stomatitis:
- To disinfect the oral cavity, it is treated with hydrogen peroxide , furatsilin, chlorhexidine.
- Clobetasol ointment should then be applied immediately to soothe the damaged tissue and repair it.
- Additionally, you can use medications that are intended for internal use. These are prednisolone, azotopyrine and betamethasone . They can be in the form of tablets and injections for intravenous and intramuscular administration.
A popular treatment method is cauterization of aphthae. For this purpose, medications are used that dry out ulcers and erosions, and this promotes their healing. These medications include:
- Lugol containing iodine. Can be sold in the form of applications and sprays.
- Fukortsin, this product is made on the basis of phenol. It should only be applied to the middle of the ulcer. This drug is a universal remedy; it is used to treat all types of stomatitis.
After the inflammation stops, the ulcers become covered with dense crusts. Removing them causes severe pain and may cause bleeding. To prevent this, dried crusts should be removed during the following procedures:
- First, rinse your mouth with an infusion of medicinal herbs . This softens the crusts and makes them easier to remove.
- A cotton swab is moistened with an oil solution , for example, sea buckthorn oil. It is necessary to lubricate the sores with it, pressing lightly on them.
- After all dry crusts have been removed , you need to rinse your mouth with a disinfectant solution. For repeated procedures, use new cotton swabs.
- Then thoroughly rinse the mouth with an antiseptic and lightly dry it using a bandage or cotton wool.
- After all procedures are completed, the damaged areas are lubricated with a medicine that has a wound healing and restorative effect. These are vinylin, mundisal gel, carotolin, stomatophyte, olazol.
Folk remedies for the treatment of aphthous stomatitis
Treatment of this disease should include strengthening the immune system, taking vitamins, and using folk remedies.
- Since ancient times, to rinse the mouth : take half a teaspoon of salt, a third of a teaspoon of ordinary soda and mix in half a glass of boiled water at room temperature. If the pain is very severe, you need to rinse your mouth every 2 hours. This will relieve inflammation and soothe pain.
- Chamomile relieves inflammation very well To use its healing properties, you need to take 1 teaspoon of the flower and pour one glass of boiling water. The product should cool at room temperature, then it is filtered and mixed with 1 teaspoon of honey. You should rinse your mouth with this infusion 3-4 times a day.
- The following remedy also helps very well. Take burdock seeds and grind them. The resulting slurry is salted, heated, and butter or pork fat is added. It is necessary that the gruel is as thick as sour cream. This ointment is used to lubricate ulcers in the mouth.
- For the treatment of aphthous stomatitis, the following medicinal collection : chamomile flowers, peppermint leaves, medicinal sage leaves and fennel fruits. All ingredients are mixed and crushed. Then 2 tablespoons of the mixture are poured with water and boiled over low heat for about 20 minutes. The broth is cooled, filtered and warm, rinsed in the mouth 5-6 times a day.
- A decoction of oak bark helps a lot . It is crushed, a tablespoon is poured into a glass of water and boiled over low heat for about 15 minutes. Cool, filter and rinse the mouth with it. The resulting volume must be used at a time.
- Ulcers can be treated well with the following tincture . Take dry herbs of mint, paprika and chamomile, one tablespoon each, put it all in a jar and pour a glass of alcohol. The jar is closed with a tight lid and infused for 2 weeks, then filtered and added 3 drops of mint oil. This tincture is necessary to cauterize the ulcers twice a day.
Disease prevention
In order to suffer from aphthous stomatitis as little as possible, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system. For this, immunocorrectors and immunomodulators , as well as vitamin complexes, which contain large amounts of vitamins B and C. The diet should consist of a gentle diet, without salt, spices, hot and sour foods.
In order for the body to be able to actively resist various infections, it is advisable to undergo hardening, start playing sports and quit all bad habits. In addition, do not forget to monitor the condition of your gums and teeth, and regularly visit the dentist for treatment and prevention.
- Anastasia Petrovna Olkhovskaya
Source: https://stoma.guru/polost-rta/stomatit/aftoznyy-stomatit-u-vzroslyh-simptomy-i-lechenie.html