A prostate cyst is an abnormal cavity in which there is an accumulation of pathological secretion. The disease is usually diagnosed in men after 55 years of age. But sometimes a cyst develops at a younger age. If symptoms of pathology occur, consult a urologist.
Causes
A cyst develops in healthy tissue. It contains a liquid that has different viscosities. The shade of the secret also varies. The walls of the cavity are lined with abnormal fibrous tissue. They consist of a special epithelium - it can be cylindrical or cubic.
Sometimes a prostate cyst is congenital. However, acquired formation is more often diagnosed. Key factors that cause problems include the following:
- Chronic pathologies of the prostate. Usually the disorder occurs due to the lack of adequate treatment for prostatitis. Also, the cause of the pathology can be advanced prostate adenoma;
- Influence of harmful production factors. If a man is constantly exposed to vibration or constantly in contact with chemicals, the risk of developing a cyst increases significantly;
- Lack of systematic sexual intercourse. This leads to congestion in the pelvic organs, which negatively affects the functioning of the prostate. But it is worth considering that too much activity also provokes problems;
- Physical inactivity. With a lack of physical activity, stagnant processes in the pelvic organs are observed. This increases the likelihood of developing a cyst or inflammation of the prostate. The risk of developing an adenoma is also high;
- Bad habits. All kinds of prostate lesions often develop in men who smoke or drink large amounts of alcohol. The same applies to people with drug addiction;
- Poor nutrition. Excessive consumption of harmful foods negatively affects the functioning of the prostate and can provoke hormonal imbalance;
- Sleep deficiency. Disturbances in work and rest schedules adversely affect men's health;
- Venereal diseases. Syphilis, gonorrhea and other diseases in this category often provoke complications, one of which is a cyst in the prostate gland.
Classification
For reasons of appearance, there are two main types of the disease, which have certain characteristics:
- False cyst - its formation is associated with severe compression of the prostate, which causes expansion of the organ and accumulation of fluid in these areas;
- True cyst - the appearance of a cavity is caused by various diseases.
Based on the nature of the pathology, the following forms of cysts are distinguished:
- Congenital. Its appearance is due to the pathological structure of the Müllerian canals. If you consult a doctor in time, the anomaly is easily diagnosed. The key sign of the disorder is the abnormal structure of the genitourinary organs. The formation resembles a drop and reaches 5 cm in diameter. The cyst usually affects the base of the prostate. If the pathology is localized in the urethra, a significant increase in the size of the prostate is observed.
- Purchased . Such cysts are much more common. Typically, formations appear in old age and are associated with tumors, injuries, and foreign objects in the prostate. The size of the cavity can reach 3 cm. When infection penetrates into the cyst, there is a threat of dangerous disorders.
Symptoms
In most cases, a cyst in the prostate progresses asymptomatically. In such situations, it is diagnosed accidentally during a medical consultation for other reasons. Key symptoms of a prostate cyst include:
- increase in temperature parameters to subfebrile parameters;
- problems at the beginning of urination - in this case the person experiences pain and burning;
- accelerated ejaculation;
- discomfort during ejaculation;
- feeling of insufficient emptying of the bladder;
- weak urine stream;
- discomfort in the genitals;
- frequent urination at night;
- erectile dysfunction.
Diagnostics
To detect a prostate cyst in men, diagnostic tests should be performed. The most informative procedures include the following:
- Palpation of the prostate. The manipulation is carried out by a urologist through the intestines.
- Ultrasonography. Thanks to this procedure, it is possible to get an idea of the structure of the prostate and the presence of cysts in it. The manipulation also allows one to assess the size and location of tumors. To obtain more accurate information, you can do a transrectal ultrasound. However, this procedure causes significant discomfort. In addition, it is prohibited to perform it for hemorrhoids, anal fissures and intestinal obstruction.
- Blood and urine examination.
- Analysis of prostate secretions.
- Prostate puncture. After the procedure, the doctor examines the obtained material;
- Magnetic resonance imaging. With its help you can get a complete picture of the structure of the organ. It is important to eat right before the procedure. This will help reduce flatulence and gas.
Treatment
The treatment regimen is selected depending on the severity of the manifestations and the type of disease. The presence of inflammatory changes and other lesions of the genital organs is of no small importance.
If the diameter of the cavity is no more than a few millimeters, and it does not cause any symptoms, specific treatment is not required - it is enough to monitor the patient’s condition. In other situations, treatment for prostate cysts is selected.
Drug therapy
A small cyst usually does not cause discomfort and most often becomes the result of acute prostatitis. In such a situation, medications are prescribed. The following categories of funds are usually prescribed:
- antibiotics;
- bioregulatory peptides;
- alpha-blockers.
During the therapy period, you need to regularly visit a doctor who monitors the dynamics of the disease.
Puncture
This technique is used for relatively large cysts. In such a situation, the patient experiences severe symptoms. Such formations often compress the intestines or affect the bladder.
To perform the manipulation, a puncture is made in the cyst using a special puncture needle. After this, the specialist pumps out the exudate and injects sclerosant in its place. This element glues the walls of the cyst. This method of therapy belongs to the category of minimally invasive procedures, so it is the most harmless and effective.
Surgical intervention
This is a radical manipulation, which is used for large cyst sizes, rapid growth of the formation and the appearance of purulent complications. To remove a prostate cyst, an excision technique is used.
Taking into account the location of the formation and its characteristics, access to the cavity can be through the urethra, peritoneum or intestines. After the procedure is completed, the patient needs to stay in the hospital for some time.
This is required to monitor its condition.
Folk remedies
In addition to standard methods, folk remedies are often used to treat prostate cysts. However, such recipes can only be used as prescribed by a doctor. The most effective means include the following:
- Add 100 ml of vodka to 400 ml of burdock juice. Infuse the composition for 10 days, then consume 1 large spoon before meals;
- Mix equal parts of field steel roots, flaxseeds and birch leaves. Add 1 liter of boiling water to 3 large spoons of the composition and leave for 6 hours. It is recommended to infuse the composition in a thermos. Drink 100 ml of the drink. This should be done three times a day;
- Take the shells of 15 nuts, add 0.5 liters of vodka and leave for 1 week in a dark place. Drink the finished composition 1 large spoon. This should be done in the morning on an empty stomach.
Consequences
If treatment is not started immediately, there is a risk of dangerous complications. The main consequences of a cyst in the prostate include the following:
- Serious difficulty urinating - is a consequence of compression of the urethra or bladder by a large cyst;
- The formation of pus - this occurs due to the entry of infected urine into the prostate and cyst;
- Rupture of an abscess - this can lead to the entry of purulent masses into the abdominal cavity or bladder;
- Compression of the intestines, nerves, blood vessels.
Prevention
To avoid problems, you need to follow these recommendations:
- Do not lift heavy objects if your bladder is full;
- After 40 years, do an ultrasound of the prostate every year;
- Reduce consumption of alcoholic beverages and coffee;
- Avoid hypothermia;
- Treat pathologies of the reproductive system.
The formation of a prostate cyst is associated with a variety of factors. To cope with pathology, you need to carry out diagnostic procedures in a timely manner. To do this, you need to consult a doctor for any disorders in the reproductive system.
© 2018 – 2019, MedProstatit.ru. All rights reserved.
Source: https://MedProstatit.ru/kista-prostaty.html
Causes of cysts in the prostate gland in men: description of symptoms and methods of treating the prostate
A prostate cyst is found in 20% of the stronger sex and most often appears as a consequence of prostatitis.
Her education requires close attention and competent treatment.
Hide content
Prostate cyst
Prostate cyst: what is it? A pathological cavity occurs in the tissue of the male prostate gland and is filled with fluid. Typically, the tumor occurs in males over 55 years of age. But sometimes it can appear in young men who have no health problems. The reasons for the development of the disease are different.
Causes
Cystic formation can be congenital. It can occur at any time, under the influence of various factors.
- Often, the appearance of a cavity is promoted by a chronic form of prostatitis. If it is present, the amount of secretion produced by the male prostate gland increases.
When its outflow worsens, the appearance of a prostate cyst is inevitable.
The process is accelerated by constant psychological stress, low or, on the contrary, high sexual activity, in addition, prostate adenoma and heavy physical activity with a full bladder.
- The cavity appears when the excretory ducts of the prostate gland are compressed and blocked by stones and various types of malignant formations, as well as fibrous tissue.
- Congenital cysts are rare. They are usually the result of abnormal development of the Müllerian ducts and are multiple.
When the cavity is filled, its contents vary. There are cysts filled with prostate secretion, inflammatory and non-inflammatory fluid. Infection of the formation occurs when there is an abundant accumulation of purulent fluid, in which pathogenic microbes and leukocytes are present.
Classification
Prostate cysts in men are classified differently:
- Infectious and non-infectious cystic formations. In the first case, the neoplasm occurs during infectious inflammation provoked by pathogenic microorganisms. In the second - in the presence of non-infectious inflammations in the body, which are most often caused by physical phenomena.
- Non-inflammatory and inflammatory. A prostate cyst in men often occurs after acute inflammation, then there is pus inside it, sometimes in quite large volumes.
- Plural and singular . The name speaks for itself. Formations may appear in a single copy or in several.
If we talk about the reasons for development, then there are 2 types:
- False. Appear when the duct of the male gland is compressed, pinched or blocked. The lobules of the prostate expand and fluid begins to accumulate.
- True. A pathological cavity occurs due to diseases of the prostate gland. We are talking, first of all, about tumors and prostatitis.
The intensity of the symptoms of a prostate cyst in men depends, first of all, on the parameters of the cavity formed, as well as on its pressure on the tissues located around it. When the tumor is relatively small, the disease does not manifest itself in any way.
But when it starts to grow, the following signs appear:
- Burning in the urethra, pain symptoms during urination and at the time of ejaculation;
- The urge to urinate: frequent or even constant.
- Pain in the back and pelvic organs.
- Constant feeling of incomplete emptying.
- The urine stream is weakened.
- Difficulty emptying the bladder.
Diagnostics
Prostate diseases are characterized by similar symptoms. How can one determine the presence of a cyst in the prostate among them?
The diagnosis is established using the following methods:
Treatment
Before you begin treatment, you need to make sure that treatment of prostate cysts in men is really necessary. If the neoplasms do not exceed 5 mm in size, they are not dangerous and do not affect the man’s health in any way. Usually in this case they are congenital, detected by ultrasound and do not subsequently increase in size.
IMPORTANT! Physician intervention should be mandatory in cases where the disease progresses and the cavity is constantly growing, squeezing surrounding tissues and provoking suppuration. The size of the tumor and its contents require constant medical supervision.
If the cystic neoplasm has reached a certain size, the patient may be prescribed:
- Taking painkillers.
- Antibiotics (if the cavity is of infectious origin).
- Taking alpha-blockers.
Ultrasound-guided puncture of the prostate gland is practiced in particularly difficult cases. The tumor is punctured and special medications are injected into it to connect the walls to each other. A purulent cavity sometimes requires radical surgical intervention.
Traditional methods
Treatment of prostate cyst in men with folk remedies:
- Before meals, it is recommended to take 1 tbsp every day. spoon of burdock tincture. To prepare the infusion, 400 ml of juice from the leaves of the plant is poured with 100 ml of ordinary vodka and infused.
- You can take 1 tbsp on an empty stomach. tinctures of walnut shells. The shells of 15 nuts are placed in a jar with 500 ml of vodka and infused for at least a week.
- The collection of medicinal herbs is widely used for treatment: flax seeds, birch leaves, roots of field steel. To prepare the decoction, you need to take 3 tbsp. collection, pour 1 liter of boiling water and leave in a thermos for 2 hours. Drink the decoction three times a day, 100 grams.
- Cystic neoplasm can be cured by pumpkin juice (1 glass twice a day: evening and morning for a month).
- Young larch bark is crushed, 5 tbsp. pour 1 liter of boiling water and leave tightly closed for 12 hours. The infusion is taken one glass on an empty stomach 4-5 times a day for six months. Every 2 weeks there is a week break.
Treatment of prostate cysts with folk remedies goes well with medications. But they should only be practiced under the supervision of a specialist.
- Cystic neoplasms provoke the development of prostatitis and significantly complicate its treatment.
- Pain in the back and groin.
- Painful frequent urination.
- The appearance of stones in the prostate.
- Impotence.
- Acute urinary retention.
- Prostate abscess.
- Infertility.
- Compression of healthy tissue and blood vessels of the prostate.
- Spontaneous opening.
Read the article about how to check the prostate through the rectum.
And also how to treat the prostate gland with electrical stimulation - here.
For preventive purposes, you need to follow a few simple tips:
- Treat infectious male diseases in a timely manner.
- Do not lift heavy objects alone if your bladder is full at that moment.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Do not endure the urge to urinate for too long. It is recommended to empty the bladder in a timely manner.
- Do not drink coffee and alcohol too often.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Practice a balanced diet.
- Men over 35 years of age should undergo regular examinations for prevention purposes.
Conclusion
Male diseases require a serious approach. It is impossible to self-medicate if neoplasms occur; it is best to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Source: https://samec.guru/zabolevaniya/urologiya/zabolevaniya-prostaty/kista.html
Prostate cyst in men: causes, symptoms, treatment with herbs and drugs, removal
Prostate diseases are, unfortunately, not a rare phenomenon. And such a formation as a cyst occurs in a fifth of men on the planet. This disease cannot be classified as fatal, but it causes considerable discomfort and pain.
Prostate cyst - what is it?
From a physiological point of view, a cyst is a limited cavity filled with fluid; it can form in the thickness of any tissue, and the prostate is no exception.
In most cases, the disease is diagnosed in elderly men over 55 years of age, but this is associated not so much with age as such, but with dysfunction of the prostate - excessive secretion formation or obstructed fluid outflow.
Accordingly, the disease occurs in both young healthy men and the elderly. Moreover, in 10% of cases, prostate cyst is a congenital disease.
The dimensions of the formation are, as a rule, small - from 1 to 4 cm, although exceptions have been observed - cavities containing almost a liter of liquid. The cyst itself does not create painful sensations.
If the cyst is large, it puts pressure on the surrounding tissues and, accordingly, causes discomfort, pain and corresponding pathologies caused by compression. Most often, this is difficulty urinating, weakening of erection, and discomfort during sexual intercourse.
If you suspect a prostate cyst, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. The fact is that if you get an infection, which is not uncommon for the genitourinary tract, there is a high probability of cyst suppuration and abscess. And these processes pose a great threat.
Kinds
The cyst can be congenital or acquired:
- congenital pathology - usually located at the base of the gland, have a drop-shaped or spindle-shaped shape. The cyst does not exceed 4 cm in size, is thin-walled, usually has 1 chamber, but can have several. Unfortunately, it is rarely isolated. Quite often, a congenital cyst develops together with cryptorchidism and hypospadias;
- acquired - occur much more often (90% of cases), usually solitary, with a size of about 2.5 cm. Most often, its appearance is caused by compression of the duct or its blockage by a scar, stone, tumor. In such cases, the unremoved fluid, the secretion of the prostate, accumulates in the duct, stretches it and forms a cyst with viscous, colorless or gray-brown contents.
Another classification is related to the number of formations:
- single - there is only one cyst, although its size can be either large or normal;
- multiple – formed in several areas.
Depending on the cause of occurrence, formations are divided into false and true:
- false – formed when the gland duct is blocked, compressed or pinched. The secretion accumulates in the prostate lobe, it expands and forms a cyst;
- true - it has nothing to do with blocking the duct and is usually a consequence of a disease - prostatitis, for example.
The cause of formations may be infection. On this basis they distinguish:
- infectious – the impetus for the formation of cysts is inflammation caused by pathogenic microorganisms;
- non-infectious – formed against the background of non-infectious inflammatory diseases or caused by physiological phenomena.
Inflammatory and non-inflammatory cysts are considered in the same way:
- inflammatory – arise as a result of an acute inflammatory process, often contain pus and are very dangerous;
- non-inflammatory - formed as a result of other physiological processes.
The cyst can transform. Thus, a formation that appears against the background of the prostate, as a result of the addition of a secondary infection, can fester and turn into an infectious one.
Reasons for education
But there can be many conditions for creating such a situation:
- the most obvious are corresponding organ ailments, such as prostatitis or prostate adenoma;
- any other diseases leading to compression of the ducts - tumor, fibrous tissue, large calculus, stones in the gland;
- unfavorable working conditions - dragging heavy objects and vibration. The latter becomes the cause much more often than heavy physical labor. So the cyst is literally an occupational disease of drivers;
- Young people who lead an overly active sex life, as well as those who have sex too rarely or not at all, are also at risk.
Clinical picture
It often happens that a small cyst does not affect the functionality of the gland or urination. In such cases, the formation is discovered by chance during an examination of other organs - most often on an ultrasound.
However, with large sizes and a “successful” location, the cyst makes itself felt quite quickly.
Typical symptoms are:
- difficulty urinating at the first moment of the act - the cyst partially blocks the lumen of the urethra. There may be no symptom, as it depends on the location of the cyst;
- increased urge to urinate, especially at night - in a horizontal position, the cyst exerts more pressure, which leads to increased urination;
- premature ejaculation, weakened erection. Unpleasant sensations may appear during ejaculation - if the cyst puts pressure on the seminal canals;
- pain - in the perineum, in the rectum, in the lower spinal region. The localization of pain depends on the location and size of the cyst. The formation can completely block the lumen of the urethra or rectum, which leads to acute dysfunction. When the nerve endings are compressed, the pain increases noticeably;
- impotence may develop with large lesions;
- in some cases - an inflammatory or infectious cyst, an increase in temperature is observed. This is due to general intoxication of the body.
The above symptoms are not specific. The picture almost completely coincides with the signs of prostate adenoma, for example, or acute prostatitis. Therefore, treatment without preliminary diagnosis is impossible.
To diagnose a cyst or separate it from a similar disease, it is necessary to conduct additional examination:
- Palpation – if there are no contraindications to a rectal examination, then the urologist first palpates the gland. If compacted elastic nodules - lumps - are detected, a preliminary diagnosis can be considered established. However, such a simple method is only available if the cysts are formed on the surface of the gland facing the rectum.
- Uroflowmetry is an examination that allows you to determine the speed of urination and its nature, difficulties at the beginning or end, stream pressure, type of urination - intermittent, smooth, and so on.
- Tests - blood, urine, semen, and prostate secretions. These data make it possible to differentiate a cyst from other ailments, since the formation itself, unlike prostatitis, for example, does not affect the chemical composition of secretions or urine.
- TRUS – transabdominal or transrectal ultrasound. To detect and study cysts of any kind, ultrasound is the most accessible and most informative method. An ultrasound is performed against the background of a full bladder through the skin of the abdomen. The method allows you to determine with absolute accuracy the location of the cyst, size, shape, structure. Unfortunately, in case of hemorrhoids, intestinal obstruction or posterior fissures, ultrasound is prohibited.
- CT and MRI are the most informative, although expensive, methods. It is prescribed, as a rule, in case of ambiguous ultrasound data, as well as in cases where there is a suspicion of the presence of tumors and circulatory disorders of the pelvic organs.
- Biopsy - puncture is prescribed in cases where a prostate tumor is suspected or detected and its nature needs to be determined. The same procedure can be carried out to examine the contents of a cyst, if its infectious origin is suspected, for example.
- Urethrocystography is an X-ray examination of the bladder and urethra against the background of a contrast agent. It is undertaken when the presence of stones is suspected.
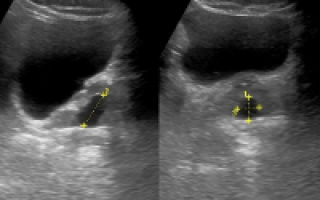
Prostate cyst on ultrasound
Treatment
The method of treatment is determined by the severity of the disease: the size of the cyst, its nature, location in the prostate:
- Observation - if a cystic formation was discovered by chance, does not cause discomfort, does not affect functionality in any way, and upon examination it is determined that its size does not exceed 5 mm, then all treatment comes down to observation. Once every six months or a year, if pain symptoms do not appear or urination is not difficult, the patient undergoes an examination to determine the size of the cyst.
- Medication – prescribed when symptoms of the disease appear.
- Puncture – in case of a large size of a single cyst and in cases where it interferes with functions, a puncture may be prescribed. This is the safest method of removing growth.
- Sclerotherapy is usually combined with puncture.
- Surgical intervention is prescribed in especially severe and advanced cases - with suppuration, for example.
Drugs
Therapeutic treatment is largely determined not so much by the disease itself as by its cause.
With an inflammatory cyst, it is necessary to first stop the inflammation itself; with an infectious cyst, first of all, suppress the activity of bacteria. Accordingly, the drugs and the schedule for their use are selected by the doctor in each specific case.
In general, the conservative treatment regimen includes:
- painkillers – mainly non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Antibiotics – prescribed for infectious cysts. The nature of the antibiotic and the duration of use is determined by the type of pathogenic microflora that became the cause. There can be no general recommendations here;
- alpha-blockers - dilate blood vessels, reduce blood pressure, and help reduce blood glucose levels. For prostate cysts, medications are prescribed to improve the tone of the muscular walls of the bladder and prostate muscles. This improves the flow of urine and the removal of any waste products. Adrenergic blockers are required if the formation is inflammatory or infectious. They are also prescribed in other cases if there are difficulties in urinating.
Traditional methods
Traditional methods are aimed, rather, at alleviating symptoms and relieving inflammation. Decoctions have little effect on the size of the cyst.
Treatment with folk remedies is recommended to be combined with medicinal drugs, but only after consultation with a doctor:
- Burdock tincture - 400 ml of plant juice is poured with 100 ml of vodka and infused for a week. The product is taken before meals once a day.
- Tincture on walnut shells - shells from 15 nuts (young), pour 500 ml of vodka and leave for a week. The infusion is taken on an empty stomach, 1 tablespoon.
- Pumpkin juice - drink a glass 2 times a day for a month.
- The bark of young larch is used both as a remedy and as a preventative. 10 tablespoons of crushed dry bark are poured into 1 liter of boiling water and left for 12 hours. Drink 1 glass of the decoction on an empty stomach up to 4-5 times a day. Drink the infusion for 2 weeks, then take a week break and repeat the course for six months.
It is worth immediately noting that herbal treatment is applicable in cases where the disease requires conservative treatment. If any surgical intervention is recommended, herbs will no longer help.
Surgical removal
This category includes all types of cyst removal, both minimally invasive and surgical:
- Puncture is the simplest and safest method of removal. It is carried out in cases where the formation, due to its size, makes urination difficult and affects erection. The procedure is very simple: under ultrasound guidance, a puncture is performed and the contents of the cavity are removed.
- Sclerosis is the actual puncture, but supplemented by the following stage: after removing the liquid, a drug is injected into the cavity - alcohol or another similar substance, which causes the walls of the cavity to stick together - sclerosis. The procedure is very effective and has virtually no restrictions.
- Actually, surgical intervention is resorted to in the most extreme cases - with the onset of an abscess, with very large cysts, and the like. In this case, the formation is excised during surgery.
In the video, surgical removal of a prostate cyst:
Complementary therapy
Physiological procedures for cysts are rarely prescribed. The cavity has rather thin walls, so many manipulations in such cases are prohibited.
- Massage is not performed for the reasons mentioned. When answering the question whether it is possible to massage the prostate with a cyst, it is worth recalling that there is a high probability of the membrane rupturing and fluid entering the surrounding tissue, and in such cases inflammation is inevitable.
- Hirudotherapy - most pelvic diseases are caused by blood stagnation. Leeches solve this problem to some extent, but this does not in any way affect the condition of the cyst. It makes sense to resort to this method only to relieve painful symptoms or when several ailments are combined.
- Warming - in cases where the cysts are of inflammatory or infectious origin, heating is strictly prohibited. Such procedures are prescribed for chronic prostatitis, which may be accompanied by the formation of a cyst. In general, this is not the best solution, since the cyst under the influence of temperature can transform into something much more dangerous.
- Physical activity is preferable to active sports that improve blood circulation in the pelvis: fast walking, running, joint exercises. Heavy lifting, sudden squats, and extreme sports are undesirable.
Complications and consequences
As a rule, the cyst is quite successfully cured. In mild cases, this requires a therapeutic course. Even with large sizes, the matter ends with puncture or sclerosis. However, if the problem is ignored, the cyst can lead to serious complications:
- acute urinary retention - the cavity blocks the lumen of the urethra;
- compression and deformation of the vessels of the prostate gland - various disorders in the blood circulation lead to ischemia of the organ, and then to atrophy;
- opening of the cavity - the contents enter the surrounding tissues and cause inflammation;
- secondary infection - often leads to suppuration and abscesses;
- degeneration of a cyst into a malignant formation is quite rare.
Prevention
The likelihood of this disease occurring can be significantly reduced if you follow the most common recommendations:
- If your bladder is full, refrain from lifting anything heavy;
- avoid hypothermia, both general and local;
- empty your bladder as needed rather than waiting for it to become full;
- Avoid excessive consumption of coffee and alcohol;
- treat infectious diseases of the pelvic organs in a timely manner - this is one of the main causes of cysts;
- undergo examination once a year. This is especially true for men over 40.
Prostate cyst is a relatively harmless disease that responds well to treatment. But this does not exclude the need to immediately consult a doctor if relevant symptoms appear. Otherwise, the treatment will no longer be so simple and easy.
Source: http://gidmed.com/urologiya/zabolevaniya-urolog/prostaty/kista-prostati.html
Prostate cyst
A prostate cyst is a congenital or acquired formation of the prostate gland, which is an encapsulated cavity with fluid. Often small cysts do not have clinical manifestations, and in only 5% of patients symptoms include pain in the pelvic region, hemospermia, painful ejaculation, and dysuric disorders. The gold standard for diagnosis is TRUS. To exclude a malignant tumor process, an MRI of the prostate and a blood test for PSA levels are performed. Management tactics vary from dynamic observation to surgical intervention: TUR, laser marsupialization, puncture with sclerosis, open surgery.
N42.8 Other specified diseases of the prostate gland
Prostate cysts occur in less than 1% of men. With the availability of imaging modalities, some researchers believe this figure could be increased to 5-8.6%. Congenital cystic cavities are diagnosed in 10% of cases, acquired ones - in 90%. With age, the likelihood of the occurrence of this pathology increases.
Men who have casual sex without a condom are at greatest risk. Parasitic cysts in the prostate have been described, they occur in endemic areas and are secondary to an infectious disease. The sizes of cystic cavities are variable and average 0.5-1.2 cm.
There are giant cysts up to 7 cm, they are mostly congenital.
Prostate cyst
The causes of congenital and acquired prostate cysts vary. In the first case, the pathology is caused by developmental anomalies during embryogenesis, in the second - by a number of conditions that have a negative impact on the functioning of the prostate gland:
- Urological diseases . Long-term chronic prostatitis with frequent exacerbations, fibrosis, prostatolithiasis lead to the formation of a cystic neoplasm. Cysts in the gland form in some forms of prostate cancer. In men with BPH and underlying atrophy, small cystic cavities may also be visible on ultrasound.
- Behavioral factors . Anything that creates stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs (sedentary lifestyle, tendency to constipation, lack of regular ejaculation) disrupts the functioning of the glandular structures of the organ. Prostate juice thickens and remains in the acini. Further secretion leads to the formation of a cyst.
- Traumatization . Any operations on the prostate can be complicated by an inflammatory process with the proliferation of fibrous tissue, which negatively affects the production of secretions. The prostate gland can be injured during medical procedures: cystoscopy, bougienage of the urethra, catheterization, and when performing transrectal biopsy. The cavity of such a cyst is filled with blood.
A prostate cyst can be localized in any area of the prostate. The mechanism of formation depends on the pathogenetic factor. With severe inflammation, bacteria and leukocytes are present in the contents of the cyst; in this case, the cystic neoplasm is the body’s desire to limit the infectious process.
A non-infectious prostate cyst is formed under the influence of damage and accompanying proliferation processes aimed at tissue restoration. Scar changes do not allow the secretion to come out; it accumulates in the glandular lobules and is then encapsulated. The developing tumor compresses the acini, which leads to inadequate drainage of the gland.
Congenital pathology is caused by impaired differentiation of the Müllerian ducts due to a deficiency of anti-Müllerian hormone produced by the testes.
Possible negative factors influencing the lack of reduction of these ducts and low AMH levels include exposure to alcohol, drugs, radiation, and certain diseases suffered in early pregnancy.
If several multi-chamber cysts form, the formation of combined defects of the genitourinary system is likely.
A unified classification that would take into account all aspects has not been developed in modern andrology. Prostate cysts can be true (primary, congenital) or false (secondary, acquired, retention). The following types of formations are distinguished:
- Midline cyst (Müllerian duct). The formation is located along the median line above the seminal tubercle. There is no communication with the urethra. Median cysts also include a cyst of the prostatic uterus (utricular cyst, located closer to the urethra), and the ejaculatory duct.
- Parenchyma cyst . A simple prostate cyst is detected as an isolated lesion in the thickness of the gland. It is acquired due to a violation of the outflow of prostate juice. Accompanied by inflammatory changes. There may be multiple cysts of the prostate parenchyma. More often they are localized in the transition or peripheral zone.
- Complex cysts . This group includes infectious cysts, including those of tuberculous etiology, complicated (purulent) forms and hemorrhagic formations (due to necrosis, infarction of the gland, bleeding after a biopsy). Any localization.
- Cystic tumor . Cystic carcinoma is a complex malignant tumor of large size, most often located in the midline, involving the seminal vesicles. Cystadenoma is a rare benign tumor that also originates from the glandular epithelium and forms a cystic cavity during development. This also includes a dermoid prostatic cyst containing keratinization elements.
- Prostate cyst secondary to certain diseases . The cavity is formed during infectious parasitic diseases (echinococcosis, schistosomiasis). The size depends on the duration of infection. Any location.
The clinical picture depends on the size of the cyst: if it is less than 5 mm, there are no symptoms. The location of the cystic neoplasm also affects the manifestations of the pathology.
With a median cyst larger than 5 cm, obstructive and irritative symptoms of the urinary tract appear: frequent urination in small portions, the inability to immediately begin urination, discomfort, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Some patients have hematuria, pain in the lower abdomen and rectum.
Dysuria and blood in the semen are typical for ejaculatory duct cysts. If a cystic formation of the prostate parenchyma puts pressure on the neck of the bladder, urination disorders appear, and the cyst is less than 3 cm in size. With all large cysts, pain during ejaculation and pain in the perineal area during sexual intercourse are possible.
In patients with concomitant pathologies that affect the weakening of the immune system (HIV, diabetes mellitus, condition after chemoradiotherapy), a prostate cyst can fester and transform into an abscess.
At the same time, the temperature rises to 38-39°C with chills, general health suffers (weakness, fatigue), pain in the perineum and during urination is significantly pronounced.
A prostate cyst supports chronic pelvic pain syndrome, which impairs quality of life. When infection occurs in weakened patients, purulent melting of tissue occurs. A large cavity compresses the tissue of the prostate gland, which is manifested by deformation of the organ with dyspareunia. In some men, the cyst ruptures and bleeds.
Large neoplasms can lead to acute and chronic urinary retention with frequent recurrent infections of the urogenital tract. Prostate cysts are considered as a cause of obstructive azoospermia with 2-sided lesions. At the same time, a cystic cavity also forms in the ejaculatory duct.
In most cases, a prostate cyst is diagnosed accidentally when a test is performed for another reason, for example, when the PSA level increases. On palpation, the cystic cavity is round in shape and elastic, but digital rectal examination does not always reveal a cyst. The diagnostic algorithm includes:
- Visualization methods . TRUS makes it possible to establish a diagnosis with high accuracy; shows dimensions, contours, content density, partitions. MRI of the prostate is performed if a tumor form of the disease is suspected; tomograms demonstrate the relationship of the formation with surrounding tissues.
- Laboratory diagnostics . To determine the concomitant inflammatory process and its cause, the secretion of the prostate gland is examined. If the number of leukocytes is increased, PCR tests for STDs are prescribed. With an ejaculatory duct cyst, oligospermia may be detected in the spermogram. Sowing biomaterial is justified to determine microflora and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with prostate cancer. To do this, the blood is assessed for prostate-specific antigen over time, and if its level increases, a transrectal biopsy is performed. A cyst in the prostate is suspicious for malignancy if its contents are heterogeneous, there is calcification, septa.
Small asymptomatic cysts do not require active management and are monitored with ultrasound. Patients are managed by a urologist, but consultation with an andrologist or geneticist may be required.
Surgical treatment is indicated for large tumors and complications, including expected ones. Open operations are rare due to their high morbidity.
Interventions that can be performed for prostate cysts:
- Drainage . Transrectal or transperineal puncture is performed to evacuate exudate. In order to prevent relapse, upon completion of the manipulation, a sclerosant is introduced, causing “gluing” of the walls. The resulting liquid is sent for morphological examination.
- TOUR (TURED). Transurethral resection of the ejaculatory ducts is one of the methods for treating median prostate cysts in obstructive male infertility. Disadvantages include the likelihood of developing repeated stenosis of the orifices and a decrease in the intensity of orgasm.
- Laser marsupialization . The cyst is opened with a holmium laser to form a wide anastomosis. Access is through the urethra, under transrectal ultrasound control. The operation is low-traumatic, has a lower percentage of complications, and does not interfere with orgasmic sensations, since it does not affect the seminal tubercle.
The prognosis for life is favorable with the correct management tactics. Prevention includes a healthy lifestyle, regular sex, and avoidance of casual sex.
A visit to a urologist and timely, adequate treatment of inflammatory prostate diseases are important aspects in preventing the formation of cysts.
Experts recommend avoiding situations that provoke congestive phenomena in the pelvis: monitor the regularity of bowel movements, do not use interrupted sexual intercourse as a method of contraception, and exercise.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_andrology/prostatic-cyst