15.08.2018
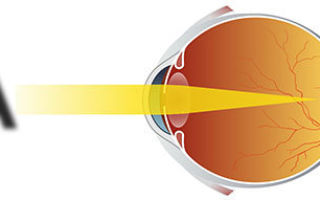
Farsightedness (hypermetropia) is characterized by a pathology of the visual organs, which is accompanied by fixation of images of distant objects not on the retina, but on a plane located behind it.
This visual impairment in the initial stages of development has reversible consequences. Experts recommend farsightedness correction for patients of any age.
In the absence of competent treatment, serious complications can occur:
- Glaucoma
- Lazy eye syndrome
- Inflammatory processes in the tissues of the organs of vision.
In most cases, farsightedness develops in people of middle age, and after 50 years, the presence of this pathology is regarded as the norm. It is worth noting that hyperopia also occurs in children.
Treatment methods
There are several methods for treating farsightedness:
- Performing special exercises
- Wearing glasses
- Surgery.
Read more about all methods of treating farsightedness in this article.
Conservative
Glasses
The most common and simplest way to restore vision in case of farsightedness without surgery is to wear glasses that need to be worn:
- When working at a computer
- When reading
- While watching TV
- In any other case when concentration of gaze at a close distance is required.
Contact lenses
A modern alternative to wearing glasses is to correct farsightedness using contact lenses. They are used both during the day and at night.
For people leading an active lifestyle, it is, of course, preferable to wear contact lenses. However, they are not intended for the correction of farsightedness in pediatric patients.
Hardware methods
The complex of measures for conservative therapy also includes the use of modern hardware methods of vision correction:
- Electrical stimulation
- Vacuum massage procedures
- Ultrasound therapy
- Wearing massage glasses.
Taken together, these methods make it possible to achieve excellent results in restoring vision in case of farsightedness without surgery.
Vitamins
Conservative treatment of farsightedness also involves prescribing patients to take appropriate vitamin complexes that can maintain the muscles of the visual organs in good shape. Read more about what vitamins are necessary for eye health and clear vision in this article.
Farsightedness and surgery
The surgical method for treating farsightedness involves moving an image onto the retina of the eye. Many people will probably ask whether this result cannot be achieved by wearing contact lenses or glasses.
The fact is that when using these methods for correcting farsightedness, depth and three-dimensional vision undergo significant changes - they worsen. As a result, this can have a negative impact on the patient’s quality of life, because deep and three-dimensional vision is necessary, for example, for working on a computer and driving a vehicle.
To treat farsightedness with surgery, laser techniques are usually used and LASIC laser vision correction is often used.
The essence of laser surgery
The essence of the technique is the precise and gentle impact of excimer laser beams on corneal tissue, which, due to such exposure, evaporate only 1/8 of its thickness.
With the help of new computer developments in the field of esimer laser vision correction, specialists obtain an “ideal new corneal profile.”
In this regard, it becomes possible to correct pathologies of almost any type and severity.
Scientifically speaking, new high-precision technologies make it possible to carry out the procedure of “photochemical ablation” (evaporation) of the layers of the cornea of the eye. If corneal tissue is removed from its peripheral part, the center of the cornea acquires a “steeper” relief. This allows hypermetropia to be corrected.
Restrictions on laser correction for farsightedness:
- The period of pregnancy and breastfeeding. This is due to the need to completely restore the hormonal levels of patients.
- Children and teenagers up to 18 years of age. This is due to the fact that until this age the eyeball is not fully formed.
Absolute contraindications:
- The presence of systemic pathologies that can affect the healing processes.
- Immunodeficiency conditions (primary and secondary).
- Autoimmune pathologies (arthritis, collagenosis, etc.).
- Retinal detachment that has undergone surgery.
- Herpes simplex.
- Cataract at any stage of its development.
- Myopia in the acute stage.
- Keratoconus in combination with thinned corneal tissue.
- Glaucoma.
- Herpes zoster.
- Insufficient thickness of the cornea (less than 450-440 microns).
Relative contraindications:
- Psychoses of endogenous etiology.
- Pregnancy and lactation period.
- The patient has a pacemaker.
- Diabetes.
- Changes in retinal tissue that require preventive laser coagulation procedures.
- The presence of pronounced changes in the fundus.
- The presence of penetrating scars in the tissues of the cornea (in the optical area).
- Diseases of the lacrimal apparatus, posterior and anterior parts of the eye, occurring in the acute stage or chronically.
If farsightedness is of a high severity, its treatment is carried out starting from the preparatory stage, which is collagenoplasty or scleroplasty. These procedures make it possible to create a new corset for the sclera, consisting of donor tissue.
Only after the progression of the pathology has completed is it permissible for the patient to treat farsightedness using laser surgery.
Extremely severe farsightedness and age-related farsightedness are treated with surgery, in which an implant in the form of a multifocal or phakic lens is implanted into the eye. It is advisable to use this method of treating hypermetropia only when other methods are powerless.
Source: https://fedorovmedcenter.ru/stati/oft-blizorukost-i-dalnozorkost/operacia_i_dalnozorkost/
Causes of farsightedness and methods of its correction. – eye microsurgery clinic
Normal vision
Vision with farsightedness
Farsightedness, hypermetropia is a deviation from the normal refraction of the eye, in which a person sees poorly near, but quite well at distance. But with medium and high degrees of farsightedness, vision decreases not only near, but also at distance.
The cause of farsightedness is that the eyeball has an irregularly compressed shape, resulting in the image being focused behind the retina.
Very often, farsightedness occurs in a combination of two reasons: the irregular shape of the eyeball and insufficient optical power of the cornea.
However, much less often, farsightedness is caused by the weakness of the optical system of the eye with a normal length of the eyeball.
Farsighted people often have trouble seeing close up, but their vision can also be blurred when looking at distant objects.
Many young people with mild to moderate farsightedness do not have vision problems because their natural lens can accommodate or adapt to increase the optical power of the eye.
But accommodation is gradually lost and people notice a progressive deterioration in near vision as they age.
Degrees of farsightedness
- weak hypermetropia - up to +2 diopters
- average hypermetropia - up to +5 diopters
- severe hypermetropia - above +5 diopters
Why is farsightedness dangerous?
Farsightedness, if ignored, is fraught with such unpleasant complications as strabismus; frequent inflammatory eye diseases (conjunctivitis), “lazy” eye - the eye is outwardly healthy, but sees poorly and this cannot be corrected either with glasses or contact lenses. The progression of farsightedness can lead to disturbances in the outflow of intraocular fluid and, as a consequence, the development of glaucoma. And the advanced stage of glaucoma leads to irreversible vision loss.
Treatment of farsightedness
Depending on the stage, nature and nature of the disease, both conservative and surgical methods of treating farsightedness are used. Conservative include glasses and contact lenses. Surgical operations include a whole range of operations: conductive keratoplasty, multifocal excimer laser ablation, ACE - anterior laser expansion, intraocular correction. Read more about treating farsightedness
Farsightedness in children
With farsightedness in children, the eyeball is shorter than normal, so after the rays are refracted, the focus is behind the retina. In this case, a fuzzy, blurry image is formed in the fundus. Almost all newborns have childhood farsightedness of about 3 diopters.
However, as the child grows, the eyeball increases in size and the optical focus moves to the retina. In some cases, due to various reasons, children's farsightedness can be higher than 3 diopters. Children have to strain their eyes to see objects clearly.
Not in all cases the body is able to compensate for childhood farsightedness. Very often this leads to a decrease in the functions of cells in the visual cortex of the brain, because they do not receive a clear image and therefore lack the stimuli for proper neuronal development.
This leads to decreased visual acuity and the development of amblyopia.
Amblyopia is a visual impairment associated with changes in the cerebral cortex, in which vision is reduced even with glasses. Amblyopia can develop exclusively in children, because... in childhood, the visual system is very plastic and any negative influence leads to developmental disorders.
Treatment of farsightedness in children
Treatment of farsightedness in children, as well as accompanying amblyopia, is carried out against the background of spectacle correction. Glasses for farsightedness and amblyopia are prescribed for constant wear. As a rule, the power of glasses is lower than the degree of hypermetropia. This technology is justified in childhood, as it stimulates eye growth and helps reduce hypermetropia.
We also conduct courses of hardware treatment for children's farsightedness, including various methods of vision stimulation. The course of treatment for farsightedness in children consists of five to six different methods. All methods of treating children's farsightedness are painless, well tolerated by children and include playful aspects.
Treatment courses for farsightedness in children should be carried out 4-5 times a year.
Modern technologies for conservative hardware treatment of childhood farsightedness make it possible to cure amblyopia in farsightedness in most cases. In addition, with proper treatment of farsightedness in children with amblyopia, in many cases it is possible to save the child from constant glasses correction.
Often children do not notice that they have reduced vision, so even if there are no complaints, the child should be shown to an ophthalmologist at least once a year. This will allow you to identify the disease in time and begin treatment.
Read also:
Source: https://mocentro.com/dalnozorkost/
Correction of farsightedness. Treatment of farsightedness
Treatment of farsightedness (treatment of hyperopia) is one of the most important areas of refractive ophthalmology.
Correction of farsightedness is constantly being improved, and the treatment of hyperopia currently has a huge surgical arsenal, using all the latest high-tech methods of surgical treatment.
However, the specific method of correcting farsightedness is determined for each patient individually, taking into account the state of the organ of vision at the time of examination, the patient’s lifestyle and the nature of his work, the advantages and disadvantages of each method.
Often, patients with farsightedness (hyperopia) have difficulty choosing glasses or contact lenses or problems with their intolerance. In this situation, as a rule, surgical treatment of farsightedness is the only possible solution to comfortable vision for patients.
Read about farsightedness
Correcting farsightedness has one single goal - changing the optical power of the eye so that the image is focused accurately on the retina.
The most widespread are spectacle and contact correction of hypermetropia. However, correcting farsightedness with glasses or contact lenses does not allow you to radically get rid of hyperopia.
Many patients experience significant difficulty using them.
Currently, this problem has been successfully solved by introducing methods of surgical treatment of farsightedness into the daily practice of an ophthalmic surgeon. And hundreds of thousands of patients suffering from hypermetropia were given the opportunity to look at the world with their own eyes.
Below we will try to give a complete description, describe the advantages, advantages and disadvantages of each of the methods of surgical treatment of farsightedness.
Surgical treatment of farsightedness
The term “surgical treatment of farsightedness” means surgical intervention or laser correction of farsightedness. Surgical treatment of hyperopia, regardless of the technique used, is the fastest and most effective way to correct farsightedness.
Surgical correction of farsightedness lasts for several minutes under local anesthesia, and the patient can be discharged home on the same day. Surgical treatment of farsightedness, regardless of the method, consists of enhancing the refractive ability of the farsighted eye. Each of them has its own indications and contraindications.
Taking into account all the examination data, the doctor will suggest the most optimal operation for your eyes.
Surgical correction of farsightedness
Thermokeratoplasty - the refractive effect is achieved by applying a metal needle heated to a certain temperature of coagulates along the periphery of the cornea, as a result of which the latter contracts, increasing the refraction of the central optical zone. Laser coagulation - the essence of the operation is the same as keratoplasty, the difference is that instead of a heated needle, laser energy is used.
Laser correction of farsightedness (hyperopia)
In the last decade, laser treatment of farsightedness has been the most effective, safe and predictable method of treating hyperopia. Laser correction of farsightedness is achieved by evaporating a layer of the cornea of a certain thickness with an excimer laser. To correct hypermetropia, a procedure called hypermetropic laser keratomileusis is performed.
Hyperopic laser keratomileusis
It has wide limits for the correction of hypermetropia and hypermetropic astigmatism, as well as a short rehabilitation period.
The essence of the intervention is that the increase in corneal curvature necessary for the correction of hypermetropia is achieved through ablation (“cold” evaporation) with an excimer laser of the middle layers of the cornea on its periphery, as a result of which its refractive power changes, which makes it possible to obtain the refractive effect of the operation.
The main advantages of laser keratomileusis
- rapid restoration of visual functions (within 1 - 2 days after surgery),
- minimal restrictions in visual load after surgery,
- preservation of the anatomical structure of the cornea,
- absence of an open healing wound,
- minimal pain (2 - 3 hours after surgery),
- laser correction of farsightedness has stable results and a lasting refractive effect,
- treatment of farsightedness can be performed on both eyes at once, without applying bandages,
- absence of corneal opacification in the postoperative period,
- the ability to correct high degrees of farsightedness (including astigmatism).
Progress of excimer laser keratectomy surgery
The operation is usually performed on both eyes at once. Before the operation, anesthetic drops are instilled. No general anesthesia is required.
The patient is placed on the operating table, the skin around the eyes is treated with a special germ-cleaning solution and covered with a sterile delineating bandage.
Painkiller drops are instilled once again. Next, the following stages of the operation are carried out:
| To provide access to the middle layers of the cornea, using a special “microkeratome” device, a flap (“lid”) is cut out from the surface layers of the cornea and turned to the side. To achieve optimal results in forming corneal flaps of the required size, a computer method is used to calculate the operating parameters of the device. | |
| The laser then evaporates the middle layers of the cornea at its periphery, changing its curvature. | |
| At the end of the operation, the “lid” is placed in its original place. The flap is fixed without suturing, due to the adhesive properties of the cornea's own collagen. |
Install Flash Player to watch the movie.
- It is better to spend the first day after surgery in our hospital under the supervision of experienced staff. It is not recommended to touch the operated eye or rub the eyelids to prevent displacement of the corneal flap. It is also not recommended to wash your face at this time. During these days, eye drops are instilled.
- The next day after examination by our specialist, eye drops (antibacterial and anti-inflammatory) are prescribed for a period of 2 - 3 weeks, and if there are no problems, the patient is sent home.
- In the first two weeks after surgery, it is not recommended to rub your eyes or put pressure on them; it is advisable for women not to use makeup on the eyelids and eyelashes, sprays or hairspray. It is not recommended to visit the sauna or swimming pool for 2 - 3 months.
- Visits to your doctor after surgery usually occur the next day, 2 weeks, one month, 3 months, and 6 months after surgery.
- Vision after surgery begins to recover within a few hours and reaches a sufficient level the next morning. In the next 2 to 4 weeks, vision reaches its maximum.
Correction of hypermetropia using intraocular methods
The operations listed above are not abdominal operations, since during them the surgeon’s knife does not penetrate the eye cavity. In cases where there are contraindications to excimer laser operations on the cornea, hypermetropia is corrected through intraocular surgery (implantation of a phakic IOL or lens replacement for refractive purposes).
Removal of the clear lens of the eye with implantation of an artificial lens
Clear lens removal (CLR) differs from the vision correction methods described above in that the operation is performed not on the cornea, but on the lens. Instead of reshaping the cornea, the lens is removed and replaced with an artificial eye lens.
The operation is the same as cataract removal, only the clear lens is removed rather than the cloudy one.
Like other refractive surgeries, clear lens removal is often performed on an outpatient basis through a small incision. The lens is removed using ultrasound (phacoemulsification).
Instead, an intraocular lens (IOL) of the required optical power is implanted. There are no stitches. Vision is usually restored within 24 hours.
UPC is used to correct hypermetropia of any degree. The method is most suitable for patients over 40 years of age, because at this age the ability of accommodation begins to be impaired in most people.
Phakic lens implantation
Phakic lens implantation (IOL) involves placing an additional diverging (“positive”) lens directly onto the lens, which focuses light rays entering the eye onto the retina. Usually, phakic lens implantation is carried out at a young age and with large degrees of hypermetropia, which cannot be corrected by excimer laser vision correction.
The IOL is implanted into the eye cavity through a puncture, without suturing. The biocompatibility of the lens material minimizes the risk of complications. The operation and postoperative period are painless, vision improves within a few hours after the intervention.
The advantages of this operation include, among other things, the possibility of removing the lens, that is, returning the eye to the preoperative state.
If there is opacification in the lens due to hypermetropia, the lens is replaced for refractive purposes. This operation is similar to that performed for cataracts.
Currently, when carrying out such an intervention, the method of phacoemulsification, or crushing the lens using ultrasound, is used.
The natural lens is removed through a 2-3 mm puncture, and a soft artificial lens is implanted in its place, designed in such a way that the patient no longer needs distance correction.
And recently, a number of large manufacturers have developed and are introducing multifocal artificial lenses, which allow one to see well not only near or far, but to combine sufficiently high vision for both near and far. This happens due to the fact that each such IOL has several focal lengths. True, quite often the patient needs to get used to such a correction.
The choice of tactics for surgical treatment of farsightedness is strictly individual and is determined based on the results of a complete ophthalmological examination. Since refractive surgery is the method of choice, the decision to undergo correction is made by you.
We will help you find your way - recommendations depend on your age, general health, existing or pre-existing eye problems, your glasses or contact lenses, lifestyle, profession, work goals and the results you expect from the operation.
Prevention and treatment of complications of farsightedness
If you have developed complications of farsightedness such as amblyopia, impaired binocular vision or strabismus, you need comprehensive treatment to improve visual acuity.
Treatment includes various types of stimulation: laser, magnetic, classes on computers equipped with unique programs, as well as a number of other latest devices.
If indicated, no earlier than 1 month after excimer laser surgery, you may be recommended to undergo surgical correction of strabismus.
You can find out more about lens replacement in the treatment of astigmatism here
Source: http://www.ophthalm.com/content/Hirurgiya_gipermetropii.php
Treatment of myopia
- With nearsightedness (myopia), a person sees objects closer to the eye better, while distant objects appear blurry and indistinct.
- Myopia should not be confused with farsightedness, in which, on the contrary, distant objects are clearly visible, but close objects are not.
- In a myopic eye, the relationship between the optical power of the cornea (the main structure of the eye that refracts light rays), the lens and the length of the eye is disrupted.
In myopia, light rays are collected in front of the retina, and not on it as in a healthy eye.
As a result, a blurry image is transmitted to the brain.
- In a normal eye, light is focused on the retina; the owner of such a healthy eye sees objects clearly at any distance
- Because of its elongated structure, a nearsighted eye focuses light in front of the retina, causing objects in the distance to appear blurry.
There are three degrees of myopia: weak, medium, high. The stronger the degree of myopia, the lower the distance visual acuity.
With myopia above 4 diopters, a person begins to see objects at close range poorly, and working on a computer and reading becomes difficult.
Our myopia specialists
- There are stationary and progressive myopia.
- In childhood and adolescence, myopia increases over time, which is associated with the growth of the body and the eyeball, in particular.
- This kind of myopia is called progressive.
- If the progression of myopia exceeds 1 diopter per year (that is, the eye grows significantly faster than normal), it is necessary to treat progressive myopia.
- The goal of this treatment is to stop the progression of myopia and prevent the occurrence of retinal tears, detachment, and other unwanted diseases.
Later in this section we will talk about stationary myopia.
You can find out more about the treatment of progressive myopia in the section of the site dedicated to it.
Laser vision correction using the Femto-LASIK method
- The leading method of treating myopia is laser vision correction using the Femto-LASIK (Laser-Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis) method.
- Femto-LASIK is recommended for patients of any degree of stationary myopia, in the absence of contraindications that are identified during the examination.
- The leadership of this method of vision correction is due to its high safety, efficiency and reliability, the absence of pain after surgery and the achievement of high visual acuity within the first day after correction.
- Detailed information about vision correction using the Femto-LASIK method is available in the “Vision Correction” section.
- In our center, operations using the Femto-LASIK method are performed on the Technolas Z100 Zyoptix excimer laser system using the Victus femtosecond laser produced by Technolas Perfect Vision (Germany).
- Most LASIK operations in the world are performed on the Technolas system; the Zyoptix Z100 is an advanced model of this laser.
- The operation lasts approximately 15 minutes:
- First, using the Victus femtosecond laser, a so-called flap is formed on the surface of the cornea.
- Next, using the excimer laser directly, a microscopic layer of tissue is evaporated, the volume of which is designed specifically to obtain the corneal curvature necessary for vision correction.
- That is, we can say that the surface of the eye turns into a lens, which creates the desired correction.
- A superficial flap on the cornea is formed in order to increase the safety of the operation, speed up the healing process, and improve the results obtained.
- LASIK allows you to see clearly almost immediately after the procedure, and unpleasant sensations (similar to those that occur when cleaning an onion) remain for only a few hours.
- The Technolas Z100 Zyoptix system for laser vision correction uses innovative dual “scanning/flying spot” technology, which allows the most accurate and, accordingly, the most safe and effective treatment of corneal tissue.
- A special tracking system constantly monitors and follows the slightest fluctuations of the eye, fully controlling each point of influence of the laser beam, with the help of which ideal precision and accuracy of corneal profile correction are achieved, which, accordingly, gives an excellent correction result.
- The Technolas Z100 Zyoptix excimer laser system also has special software that allows laser correction of farsightedness and presbyopia with a high degree of safety and efficiency, which is not available with a number of similar devices.
- The core of this program is the direction of laser exposure to the periphery of the cornea using the double “scanning/flying spot” method, which achieves an increase in the optical power of the cornea in its center.
- An advantage of the Technolas Z100 Zyoptix laser model is also the use of the Planoscan software package, which allows the laser to work in conjunction with a diagnostic station, including Orbscan and Zywave devices, with the help of which the doctor receives data on the smallest anatomical features of the patient’s cornea and transmits this data directly to the laser.
- Thus, the treatment takes into account the smallest details of the structure of each patient’s eye, thereby achieving the best treatment result.
- Laser vision correction using the LASIK method is carried out on an outpatient basis: the patient is under observation in the clinic for an hour, and then can safely go home.
- The very next day you can start work, watch TV, use a computer, drive a car and continue to lead a normal lifestyle.
- There are only a few exceptions:
- Do not rub your eyes, take a steam bath or swim in a pool for 2 weeks
- Do not drink alcohol for 1 week after surgery
You should visit your doctor for postoperative examinations once a week for the first month after surgery.
In order to protect yourself during the postoperative period, you must:
- To protect against infections, instill Tobrex antibiotics for 1 week.
- to improve healing and prevent unwanted dry eye from antibiotics, instill Oquis 0.3% for 1-2 months.
Implantation of an intraocular lens
- Sometimes (if the patient is about 50 years old, with high myopia of more than -12 diopters), it is advisable to use a different approach to vision correction - phacoemulsification of the lens with intraocular lens implantation (that is, replacing the native lens with an artificial one).
- New generation artificial lenses - Acrysof Restor from Alcon (USA) have several focuses, which allows the patient who has such a lens implanted to see near and far without glasses.
- The advantage of this method is that by the age of 50, most people’s own lens becomes cloudy - a cataract occurs, which still has to be removed using phacoemulsification and the lens also replaced with an intraocular lens.
- And at an earlier age, surgery is safer, since the transparent lens is easier to replace, and the risk of complications is lower, also due to the fact that a younger body is more resilient.
- More information about phacoemulsification can be found in the section on cataract treatment.
Methods of the past and others
PRK, LASEK, EPI-LASIK
- In the 80s, ophthalmologists Pollikaris (Greece) and Burrato (Italy) developed a method of laser vision correction, in which the radius of curvature of the cornea is changed using a laser, as a result of which the image moves to the retina.
- When performing an operation using this method, the laser beam acts on the surface layers of the cornea and “evaporates” the cornea until the required curvature is achieved.
- As a result of such exposure, the surface layer of the cornea, which performs important protective functions - Bowman's membrane, is inevitably damaged.
- Due to such damage, the recovery period is delayed, creating the potential for various complications to arise, and various side effects arise, for example, a halo around luminous objects, deterioration of twilight vision.
- The LASEK and EPI-LASIK methods can be called a variation of the PRK method, since their use also causes damage to Bowman's membrane and, in general, does not eliminate the disadvantages of the PRK method.
Radial keratotomy
Another way to change the radius of curvature of the cornea is surgically.
Operations of this type began in the 70s at the Eye Microsurgery MNTK under the leadership of S.N. Fedorov.
During this intervention, called “keratotomy” (from the Greek “keratos” - cornea, “tomia” - cut), non-penetrating radial incisions were made on the peripheral part of the cornea.
Keratotomy is an outdated method, much less effective and safe than LASIK.
"Super LASIK" and others
Among laser vision correction services, there are also other names, in particular, “Super LASIK”, “REIK”. These are the names that clinics use for their modifications of certain aspects of the LASIK method.
It should be noted that practically every surgeon modifies various aspects of the operation in his own way, trying to achieve the best result, but the leading core of laser vision correction today remains the LASIK method, and the greatest role in its use is played by the skill of the surgeon and the quality of the equipment.
Treatment of progressive myopia
Conservative treatment of progressive myopia
Conservative (non-surgical) treatment includes various types of visual simulators for the external and internal muscles of the eye to improve their blood circulation.
These procedures include electrical stimulation of the eye muscles, reflexology, which improve blood circulation in the eye and vision. Such procedures are comfortable and safe for the patient.
Surgical treatment of progressive myopia
- Sometimes conservative treatment is not enough, and myopia continues to increase by one diopter or more per year.
- In such cases it is necessary to carry out scleroplasty surgery (“scleroplasty”) to prevent the development of severe eye diseases associated with a high degree of myopia.
- The essence of sclera-strengthening surgery is the implantation of a special biomaterial on the back surface of the eye, as a result of which it becomes more difficult for the eye to grow in length, creating an obstacle to the progression of myopia.
Sclera-strengthening operations in many cases make it possible to achieve almost complete stabilization of myopia.
This procedure is tolerated very easily by patients, is painless and has the highest level of safety due to its non-penetrating nature.
First, anesthetic drops are instilled into the eye, then a small pocket is cut in the mucous membrane of the eye, through which an implant is placed behind the eyeball with a special tool.
With such interventions, it is important to use safe implants. We use the biomaterial "Xenoplast", which, today, is the safest scleroplastic implant, since it is completely sterile and biocompatible.
The patient can go home immediately after the operation; this procedure does not affect the general condition of the body.
But unfortunately, in a relatively small group of patients, myopia, even after scleroplasty, slowly but steadily grows, reaching more than 10 diopters.
This condition is called “myopic disease” . It is characterized by severe degenerative changes (thinning) in the inner membranes of the eye, accompanied by degeneration, hemorrhages, ruptures, and sometimes retinal detachment.
Patients suffering from myopic disease must undergo an ophthalmological examination annually (or even more often as recommended by a doctor) with a thorough examination of the fundus of the eye and strictly follow all the instructions of the ophthalmologist.
When thinning of the retina and breaks occur, it is necessary to carry out preventive laser strengthening of the retina to prevent retinal detachment.
Source: https://vostok-prozrenie.ru/treatment/myopia
Presbyopia - treatment of age-related farsightedness
Presbyopia (age-related farsightedness) is an eye condition in which vision deteriorates at close range, making it difficult for a person to read small print and perform any work at close range.
Causes of presbyopia
Thanks to the ability of the lens to change focal length (accommodation), a person can distinguish objects at different distances - both near and far. With age, the lens becomes more dense and gradually loses its elasticity, which reduces its ability to increase its curvature when viewing objects close to the eye.
In addition, as a result of aging, the muscles that hold the lens weaken . That is, they are no longer able to sufficiently change the shape of the lens to focus the image on nearby objects. As a result, a person sees blurred and unclear.
Presbyopia in both eyes and its symptoms
The development of presbyopia is an inevitable process directly related to the aging of the body. It affects both eyes at the same time and is manifested by the following symptoms:
- difficulty viewing objects close up;
- blurred and unclear vision, decreased contrast;
- the need to move the object away from the eyes to make the image clear;
- difficulty reading, writing and small work (sewing, embroidery, etc.);
- the need to turn on brighter lights than usual;
- frequent headaches;
- eye fatigue.
Symptoms of presbyopia in both eyes are expressed differently depending on the initial visual acuity. If a person suffers from farsightedness, the ability to see becomes even worse, both far and near.
At-risk groups
Presbyopia is an irreversible condition. And, unfortunately, this disease sooner or later affects absolutely all people, even those who have had excellent vision all their lives. But this disease can progress at different rates - for example, in people with farsightedness, presbyopia, as a rule, begins much earlier than in everyone else.
Presbyopia Treatment Methods
Correction of presbyopia largely depends not only on the state of the patient’s visual system, but also on the lifestyle the person leads, his age, and type of activity.
Optical correction
For those who have poor near vision, but good distance vision, it is most convenient to use glasses for working at close range . This is perhaps one of the simplest and most accessible methods for correcting age-related farsightedness today.
But if a person is also myopic, then he sees poorly both at close and far distances. In this case, it is necessary to choose bifocal glasses , which have two zones: one zone of the glasses is designed to correct distance vision, and the other is intended to correct near vision.
You can also use two pairs of glasses designed for visual work at different distances.
Contact correction
In modern ophthalmology, patients with presbyopia (age-related farsightedness) are offered various types of contact correction. Multifocal contact lenses , which have become widespread recently, have peripheral and central zones that are responsible for clarity of vision. This type of lens makes it possible to increase the field of vision without deforming it, and the innovative material from which the lenses are made allows the eyes to “breathe.” With such lenses, a person does not need glasses for good vision both far and near.
Contact correction along the “monovision” path implies that one eye is corrected for near vision, and the other - at a distance, as a result of which the person does not need glasses. However, this type of correction requires getting used to and has a significant disadvantage, namely the lack of binocular vision.
Laser correction of presbyopia
Treatment of presbyopia with laser is based on changing the shape of the cornea. The operation is carried out similarly to the correction of farsightedness.
If this technique is effective at a young age, then when the operation is performed on older people, the result may be unstable; the procedure will not eliminate the need to wear glasses.
That is why doctors at the Excimer Clinic offer to get rid of presbyopia by implanting an artificial lens.
Surgical treatment of presbyopia at the Excimer Clinic
The problem of presbyopia can be radically solved surgically by replacing the lens, which has lost its elasticity, with an intraocular lens .
This operation is carried out in a “one day” mode for 15–20 minutes, under local drip anesthesia and consists of replacing the natural lens with an intraocular lens.
The ophthalmic surgeon performs all manipulations through a self-sealing microaccess measuring about 1.6 mm. Sutures are not required after this type of surgery.
multifocal and accommodating lenses can be used to correct vision for age-related farsightedness (presbyopia) .
Multifocal intraocular lenses have a special design of the optical part of the lens, which allows them to imitate the work of the natural lens.
Having several focuses rather than just one, a multifocal lens makes it possible to clearly see objects located at different distances .
After implantation of such a lens, a person may not use glasses or contact lenses for reading, writing, or when working with small parts.
An accommodating lens is as close as possible in its properties to the natural human lens. Thanks to the unique design, accommodating lenses, using the eye muscles, “move” and “flex” like a natural lens, which allows you to imitate natural focusing ability, restoring natural accommodation.
The optical power of the artificial lens is calculated for each patient individually - depending on the state of the visual system, age, type of activity and other related factors. Surgical treatment of presbyopia (age-related farsightedness) is also the prevention of cataracts, since the intraocular lens (artificial lens) can no longer become cloudy.
Preventing presbyopia
Presbyopia is a natural process that accompanies aging. Accordingly, it is impossible to prevent it, but slowing it down is quite possible. To do this, you need to follow a few simple recommendations:
- maintain visual hygiene: take regular breaks when working at the computer, ensure proper lighting of the workplace;
- regularly perform a set of eye gymnastics to train the ciliary muscle;
- get enough sleep: adequate sleep slows down the aging process;
- eat right, don’t forget about vitamins (especially A and E) and microelements;
- Visit an ophthalmologist regularly to check your eye condition and visual acuity.
What is important to remember?
Quite often, people attribute the appearance of the first signs of vision problems to age or fatigue, thus extremely risking the health of their eyes. After all, after 50 years, the body becomes very vulnerable to various kinds of diseases .
And deterioration of vision can be not only a symptom of presbyopia (age-related farsightedness), but also cataracts or retinal diseases, being, for example, a manifestation of an endocrine disease such as diabetes.
That is why it is necessary to regularly visit an ophthalmologist and therapist, without avoiding the necessary examinations and tests.
It is very important to select glasses after a thorough diagnosis and consultation with an ophthalmologist, because when making glasses, not only diopter is taken into account, but also many other parameters that seriously affect the quality of vision.
Article rating: 4.7/5 (246 ratings)
Source: https://excimerclinic.ru/long-sight/presbiopy/
Laser correction of farsightedness: is it possible to replace the lens with age-related hyperopia, is it possible to undergo vision surgery
If a person has any disturbances in visual function, then the optical power of the eyes changes, as well as their accommodative ability. This means that in the initial stages of the development of farsightedness, the body fights the disease and includes additional reserves in the form of increasing the refractive power of the lens.
However, the gradual deterioration of vision makes itself felt and even the compensatory capabilities of the body are no longer enough to ensure that the focus of light refraction is on the retina and the surrounding world does not become increasingly blurry with the onset of a new day.
Therefore, it is very important to consult a doctor in time in order to eradicate the sources of inflammatory processes and undergo surgery.
Indications for surgery for farsightedness
Before the operation, a person must undergo an examination by an ophthalmologist, an ENT doctor, and also a therapist. Based on the reasons for the development of the disease, the ophthalmologist draws up an eye map and prescribes additional examinations in the form of tests (blood, urine, for the presence of viruses and infections). This material will tell you about zero glasses for image.
Surgical intervention is an effective method of vision correction.
The operation is carried out as follows:
- The man lies down on the couch and is given sedatives.
- An eyelid holder is inserted into the eyelid.
- The surgeon, using a diamond knife and other instruments, corrects the surface layer of the cornea under a microscope.
- Potent drops are instilled into the person.
Types of surgical elimination of the disease - surgical treatment
Patients who have a chronic disease, people for whom the use of drops, ointments and tablets will be useless, are prescribed surgical elimination of farsightedness. This article will tell you about anti-glare glasses for drivers.
Implantation of phakic lenses into the eyes
The use of phakic lenses is a real salvation for those people who have a high degree of hypermetropia. Surgical intervention is also possible for astigmatism and myopia.
Laser vision correction is contraindicated in patients whose visual system, due to individual characteristics, does not allow the procedure. In this case, doctors recommend implantation of phakic lenses.
Implantation is carried out only in cases where a person’s vision is not completely lost. This allows the patient's natural lens to be preserved.
Thanks to excimer laser correction, refractive replacement occurs.
However, such a method does not guarantee that a person will not develop a new disorder in the visual system - accommodation (a person sees the picture of the world unclearly and blurred, both at close and long distances). For this reason, in order for a person to work, read and see at least at a close distance, he needs to wear glasses.
An artificial lens replaces the lens of the eye, and the lens is completely removed.
People aged 40 and over are most at risk of complete loss of natural accommodation.
A doctor may prescribe phakic intraocular lenses if a person has:
- thin cornea of the eye;
- high degree of hyperopia (farsightedness) up to +20 diopters;
- high degree of myomia (myopia) up to -25 diopters;
- high degree of astigmatism of about 6 diopters.
Existing infectious diseases (sinusitis, otitis, caries) must be treated before surgery in order to avoid secondary infection.
Correction with contact lenses is essentially an example of installing intraocular phakic lenses without surgery.
The difference between phakic lenses and contact lenses is that phakic lenses are implanted in the anterior or posterior chamber of the eye (inside the eye), while contact lenses are placed on the cornea (outer part of the eye).
The retina is responsible for normal vision.
If the sun's rays are refracted outside the plane located on the border of the retina, then a person, depending on the focus, sees objects either far away or near the eyes. Find out what the disease is called when you can’t see well up close here.
In order for the image to focus on the retina of the eye, and thus save a person from myomia (myopia) and hyperopia (farsightedness), it is necessary to implant positive or negative lenses, depending on the type of disease.
There are several types of implantable contact lenses:
The use of these models allows you to improve the optical power of the eyes. Phakic contact lenses are placed in front of the lens behind the iris. Such models are posterior chamber.
Thanks to the self-sealing micro-access (its size is 1.6 mm), there is no need for stitches. The operation does not last long, on average 10–15 minutes, and hospitalization is not required.
An ophthalmologist can prescribe drip anesthesia (does no harm, does not create stress on the heart, and is well tolerated by people of all ages).
This operation is often called “one-day surgery”, since after a short procedure a person can do his usual activities on the same day. Find out how to distinguish farsightedness from nearsightedness here.
The doctor will not allow a person to undergo surgery if the patient has complications such as cataracts, corneal opacity, glaucoma, as well as in cases where the person has already had similar operations on the retina.
Radial keratotomy
Anterior dosed radical keratotomy is the first external method of microsurgical vision correction. Previously, it was widely used, but in the course of scientific and technological progress, radical keratotomy has lost its original meaning.
Patients with 1st and 2nd degree myopic refraction, as well as people with astigmatism and abnormalities in the structure of the cornea, can correct their vision using radical keratotomy. Find out how to choose the right glasses for farsightedness at this link.
Contraindications: persons under 18 years of age cannot perform the operation. Also, people with malignant formations in the eye, infections and inflammation of the intraorbital location, as well as those patients with dermatitis (since there is a possibility of secondary infection) are not allowed to undergo surgical intervention.
The operation is carried out as follows: the surgeon makes marks on the pupil, then, using a diamond knife, non-through microsections are made in the designated areas.
Intraocular pressure reduces the refractive power of the cornea, causing it to become flatter. The depth and number of incisions are determined after individual diagnostics for each patient.
The surgery is painless and is carried out using eye drops. The duration of the operation is from 2 to 5 minutes. No hospitalization required.
Keratoplasty operation
If the cornea of the eye has suffered any injuries, diseases, defects or deformations, and its function and shape gradually loses strength, then the ophthalmologist will prescribe surgery in the form of keratoplasty.
The operation is carried out by introducing material to replace the cornea. Using a microsurgical instrument, the flap is placed on the eye shell and sutured. After this, a special protective lens is applied to the cornea.
Corneal transplantation using keratoplasty is the best solution in case of eye damage.
The donor graft replaces portions of the cornea of the eye. The depth of foreign body penetration depends on the degree of damage to the cornea of the eye, so a dorograft can be placed on the deep and superficial layers of the cornea.
The material that replaces the cornea takes root well. This means that cloudiness should not occur after operations.
The main tasks that keratoplasty solves are:
- improve the appearance of the cornea, reconstruct its congenital or acquired deformations and defects;
- restore damaged cornea, stop progressive diseases;
- improve the transparency of the cornea, which improves visual acuity.
There are two types of keratoplasty: according to the layers of the cornea that need to be replaced (anterior, posterior layer-by-layer, through); according to the size of the areas of the cornea to be replaced (subtotal, local, total).
The duration of the rehabilitation period after surgery ranges from 3 to 12 months. During this period, the stitches are removed. Physical stress on the operated eye is not allowed.
Keratoplasty cannot be performed if a person has any inflammatory diseases in the eyeball, obstruction in the lacrimal canal, diabetes mellitus, hemophilia (the body will reject the transplant), and also if the patient’s eye pressure is increased.
Cardiovascular diseases are a serious obstacle to surgery, so surgical interventions are carried out with extreme caution.
Is it possible to replace the lens (lensectomy) with a laser?
The peculiarity of this surgical intervention is that the natural (natural) human lens is subject to removal, and in its place an optical lens with the required number of diopters is introduced.
Lansectomy is used to treat high degrees of farsightedness.
The following diseases may be indications for lanceectomy:
- myomia (from 20 D);
- contraindications to laser vision correction;
- the refractive ability of the lens is lost;
- prespiobia (hypermetropia in old age).
An ophthalmologist may not prescribe a lens replacement if a person:
- have retinal diseases;
- the presence of a recent heart attack or stroke;
- inflammatory processes on the membrane of the eye.
When replacing a lens, patients can choose different lenses, but the most popular ones are: a regular yellow lens (does not allow age-related diseases to develop); multifocal lens (increases visual acuity, over time makes it possible to abandon glasses); an aspherical lens with a yellow filter (visual acuity increases, there is protection from ultraviolet rays).
The operation lasts on average half an hour under general anesthesia. Next, phacoemulsification occurs (the eyes are opened with an eyelid speculum, a small incision is made, a solution is injected to remove the natural lens; then an artificial lens is installed - a lens with the necessary optical power).
Recovery period and results of the intervention
After any operation, a further course of treatment is required to help improve visual acuity.
After phakic lens implantation
Implantation of a phakic lens in surgery is the only completely reversible operation, since the lens can be removed from the eye at any time. Implantation of phakic intraocular lenses does not require hospitalization, this is a “day 1” operation. After surgery, the doctor may prescribe drops. The operation improves the optical power of the eyes.
You can remove lenses from your eyes after surgery only with your doctor’s permission.
After radial keratotomy
After the operation, the doctor prescribes antibacterial therapy, so the person must take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for 4–5 days. You can find out whether the operation was effective using visometry and computer refractometry.
After radical keratotomy, in some cases, reverse astigmatism develops, and the refractive ability of the eyeballs also gradually decreases. Visual acuity after surgery improves significantly.
After keratoplasty
The sutures on the eye may come apart, so the recovery period after keratoplasty lasts from 3 to 12 months. It is necessary to be observed by a specialist for a year until complete healing.
After lanceectomy
The recovery period after surgery lasts no more than a month, but if there are complications, the duration of treatment may increase. The result of replacing the lens is that a person can clearly see objects located at close and far distances.
Possible complications
Let's consider the key types of postoperative complications for each of the procedures described above:
- Implantation of phakic lenses. The operation is safe, its results are reversible and predictable. The most common complications may be inaccuracies in the calculation of lens power, as well as decentralization of the optical zone.
- Radial keratotomy. Due to the fact that the density of corneal endothelial cells decreases after surgery, its depletion occurs. Other complications are also possible in the postoperative period: the development of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cornea, as well as traumatic rupture of the keratotomy scar.
- Keratoplasty. Complications after keratoplasty are divided into 2 types: early (capillary hypertrophy, delayed epithelization, uveivitis, intraocular pressure, iris prolapse) and late (retrocorneal membrane, cysts and glaucoma, transplant rejection by the body).
- Lansectomy. After lanceectomy, secondary cataracts, cystic macular edema, corneal edema, increased intraocular pressure, astigmatism, and displacement of the artificial lens may occur.
Video
This video will tell you about how vision correction occurs through surgery.
Conclusion
- If you detect any disturbances in the visual function of the body, you should immediately consult a doctor, since timely treatment will help to avoid serious problems in the future, as well as correct your vision with glasses for myopia and farsightedness, and make sure that it does not fall.
- For farsightedness, the following types of operations can be performed: implantation of phakic lenses, radial keratotomy, keratoplasty, lanceectomy.
- Each procedure has its own contraindications and requires preliminary tests and analyses.
Source: https://OkulistPro.com/bolezni/ametropii/dalnozorkost/lechenie-dal/operatsiyu.html