Transurethral resection of the prostate is a minimally invasive operation to remove pathologically overgrown prostate tissue through access through the urethra . Despite the apparent simplicity of the technique, the operation requires high professionalism of the doctor. The likelihood of developing complications after a TUR of the prostate largely depends on the type of instrument and the patient’s health status.
Indications and contraindications for TOUR
The main indication for TUR is hyperplasia (prostate adenoma). The prostate gland hugs the part of the urethra just below the opening of the bladder. As prostate tissue grows, the lumen of the urethra decreases, as a result of which the neck of the bladder suffers from oxygen starvation.
As a result, the man begins to suffer from urinary retention or leakage. TUR involves the removal of excess tissue that interferes with normal urination . The prostate itself (the capsule with tissue remains) remains in place.
It cannot be removed using the TUR method due to the extensive venous network (important venous plexuses will inevitably be damaged).
When is a TURP of the prostate gland recommended?
- Patients for whom maintaining sexual function is important.
- For obesity and the presence of cardiovascular pathologies.
- In case of relapse of adenoma.
- Localized prostate cancer (which can be completely removed from the gland).
TUR is carried out in cases where previous methods (conservative, hyperthermia) were ineffective.
The operation is performed using a resectoscope - a hollow tube through which instruments are brought into the surgical area.
Resectoscope with loop General scheme of TUR
Contraindications for TOUR:
- Arthrosis and other pathologies of the hip joints that prevent the legs from spreading to the sides (this is the position the patient is in during TUR);
- Urethral strictures (impossible to insert the device);
- Bladder capacity less than 100 ml;
- Tumors and defects of the bladder walls;
- Varicose veins of the urethra and bladder neck;
- Severe concomitant diseases.
Advantages of the TOUR:
- There are no cuts or scars.
- Short recovery period.
- The bladder is not injured.
After a TUR, the tissue can be examined for the presence of malignant cells, and after the laser it is completely evaporated.
Types of TOUR
Depending on the type of cutting element (loop), the following types of TUR are distinguished:
- Monopolar : one pole is the knife, the other is the body. To conduct impulses, liquid must constantly circulate between them. An outdated but still used method. It is fraught with severe bleeding, the development of TUR syndrome, and is dangerous for those suffering from cardiovascular diseases. Used only for TUR of the prostate with a volume of no more than 80 cm3 - to quickly remove tissue, otherwise too much electrically conductive solution will be absorbed into the blood.
Urologist, surgeon Maxim Aleksandrovich Ryabov talks about the indications, the course of the operation, and the consequences of transurethral resection of the prostate
- Bipolar : both poles are at the ends of the loop, resulting in a high temperature, effectively sealing the vessels. Saline solution is used as an auxiliary fluid, which is not dangerous to the body. You can spend more time on the operation and remove the nodes better. The method is suitable for excision of formations with a volume of up to 150 cm3, as well as for patients with cardiovascular diseases.
- Plasmokinetic : a “super pulse” is formed around the loop - a plasma corona, which compacts and seals the cut tissue, but does not overheat the surrounding tissue.
Plasmokinetic transurethral resection of prostate adenoma is recognized by most urologists as the least traumatic and most effective method of treating hyperplasia.
Preparation
List of preliminary tests (valid for 30 days):
Be sure to tell your doctor about all the injuries you have suffered to the brain and spinal cord, and about the medications you are taking. Antibiotics are prescribed before and after TUR. You should not eat food 8 hours before; on the day of surgery you must cleanse your intestines.
Operation technique
For TUR, spinal anesthesia is usually used as pain relief - an injection into the spine. During the operation, the patient may feel pressure and touch, but not pain. If there are contraindications, endotracheal anesthesia is used, in which the respiratory function is performed by a special apparatus.
Spinal anesthesia before TOUR
The patient is placed on a urological chair or operating table with his legs spread apart, the groin area is treated with an antiseptic solution and covered with sterile sheets. The groin must first be shaved or hair removed using hair removal cream.
Urethral zones
A lubricating antiseptic gel is first injected into the urethra, and then the resectoscope itself. The place to which the device is inserted is indicated in the figure below by number 5 (prostatic part of the urethra):
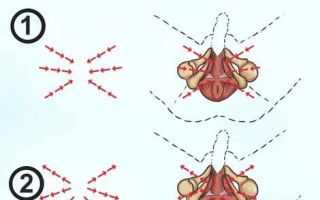
First, the bladder is examined, the condition of the closing sphincter is assessed, and then the hyperplasia is removed (layer-by-layer excision with a loop). Bleeding vessels are immediately coagulated (cauterized) with a loop.
Cutting tissue during TUR
The doctor monitors all actions on the monitor. In a number of clinics there are two of them, one of which is turned towards the patient if he is under spinal anesthesia and wants to see the progress of the operation.
The process of cutting tissue (real operation) with detailed instructions from the doctor. Schematic video of the TUR prostate operation.
The goal of TUR is to restore the patient’s ability to urinate normally. To do this, it is necessary to clear the urethra of growths. This is done in several ways (depending on the direction of growth of education):
- Removal of a small amount of tissue (10-20%) from the bladder neck or middle lobe of the prostate. This method is called “pseudo-TUR”.
- Excision of 30 to 80% of the tissue (partial TUR), in which a cone-shaped passage is formed.
The removed tissue is pushed into the bladder, and then these remains are washed out and removed through a special channel of the resectoscope. Some of them are sent to the laboratory for histology to rule out cancer through cellular analysis.
With hyperplasia, the PSA level increases. After TUR it will drop (but not to zero), since there will be much less tissue producing this antigen.
Monopolar TUR should last no longer than an hour, otherwise the risk of postoperative complications will significantly increase. It is important not to go beyond the spermatic tubercle (inferior landmark) and the neck of the bladder. Otherwise, the orifices of the ureters and the walls of the bladder will be damaged, which will also lead to serious postoperative complications.
To speed up the healing of the urethral walls after surgery, a catheter is inserted into the bladder - a thin flexible tube through which urine will be drained randomly within 2-3 days. The doctor regularly checks its quality. When the urine becomes light, the catheter is removed.
Postoperative period
After TUR, resuscitation is not required; the patient is immediately transferred to a regular ward. There should be no pain even after recovering from anesthesia. Your legs won't move for about two hours - this is normal. On the first day, it is advisable not to get out of bed to avoid headaches. After 3-4 days the patient is discharged home.
After the catheter is removed, urination will be painful. To relieve symptoms, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and painkillers are prescribed for a week.
Early rehabilitation lasts about two weeks . During this time, it is recommended to drink at least 8 glasses of liquid per day to flush out the bladder.
You can have sex and start doing Kegel exercises after 3 weeks.
For 2-4 weeks after TUR, the patient will be bothered by frequent urination and dripping of urine caused by severe irritation of the receptors. There is no need to worry about this as it is a natural phenomenon. The problem of leakage can be solved with the help of urological pads.
Immunologist Ermakov Georgy Aleksandrovich talks about rehabilitation after TUR of prostate adenoma
After excision of hyperlasia, a fairly deep wound remains, covered with burnt tissue.
Subsequently, it will begin to be rejected, which may lead to intravesical bleeding. The patient may detect blood in the urine on days 7, 14 and 21 after TUR.
Complete cleansing of the wound from damaged tissue and restoration of the epithelium occurs after 6-18 months.
For the first 3-6 weeks, you should not lift anything heavier than 2.5 kg or drive. After a TOUR, it is generally advisable to sit less and not on a hard one (it is recommended to use a donut-shaped pillow with a hole for the perineum to avoid pressure). To activate blood flow, you definitely need to move.
It is important to follow nutritional recommendations. No special diet is required, but spicy, salty, smoked and fatty foods, as well as alcohol and coffee should be excluded from the diet to avoid urethral irritation. Eat less potatoes, rice and animal protein to prevent constipation.
Complications after surgery
Complications after TUR are due to the specifics of the technique.
Hyperplasia almost always occurs against the background of chronic prostatitis, therefore, after excision of part of the tissue, inflammation in the remaining tissue often worsens (in 13% of patients).
Damage to the excretory ducts of the gland also occurs, so the organ may become non-functional - the prostate will no longer enrich sperm with its secretion in the same volume, which will complicate natural conception.
Retrograde ejaculation diagram
An obstacle to conception is also retrograde ejaculation, which occurs in 75-93% of patients (when seminal fluid flows into the bladder instead of the urethra). The complication arises due to cutting of the muscle that closes the lumen of the bladder neck (this is necessary to expand the lumen).
The second common problem after TUR is the formation of the so-called pre-bladder. This is a cavity that remains in place of the removed prostate tissue, a widening of the area of the urethra under the bladder.
Chronic inflammation often develops and is maintained in the prevesicle, stones are formed, which is why the patient periodically suffers from painful urination (dysuria).
In this regard, open adenomectomy is better.
Immunologist Ermakov Georgy Aleksandrovich on possible complications after TUR of prostate adenoma
A significant disadvantage of TUR: most clinics use resectoscopes with a large tube caliber (24 or 27), so patients have to bougienage (dilate) the urethra, which is traumatic. When the instrument is forcibly advanced, the mucous membrane is damaged, and scar tissue and strictures subsequently develop (in 18% of patients).
The most dangerous consequence of the operation is TUR syndrome. This is a severe violation of the body’s water and electrolyte balance, fraught with death in the absence of emergency measures. The reason is excessive absorption into the bloodstream of the irrigation fluid used during monopolar TUR.
Life after surgery
Many men are afraid of becoming impotent after a tour. According to doctors, this is possible if the operation is performed with a monopolar instrument in the hands of a not very competent surgeon. If TUR is done correctly, the erection will even improve due to increased blood flow. The quality of orgasm will also not be affected.
As for retrograde ejaculation after TUR, in this case it is necessary to strengthen the tone of the smooth muscles of the bladder neck. Kegel exercises combined with deep squats, as well as special medications, will help.
Urination will be completely restored within a maximum of 6 weeks. During this period, it is important not to fall into depression, otherwise not only erectile function, but also health in general will suffer.
You can drink alcohol (not strong and in small quantities) no earlier than six months later, but it’s better not to. Alcohol provokes inflammation, weakens the effect of medications, slows down the healing process, and weakens the immune system.
Prices and where the operation is performed
Below are approximate prices from clinic websites. The exact cost of the institution is not indicated, since it depends on the category of complexity of the operation, which is determined by the volume of the gland, the age of the patient, and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Examples of clinics and costs:
- GMS Hospital (Moscow): RUB 385,720;
- Network of “SM-clinics”: from 60 thousand rubles;
- Center for Endosurgery and Lithotripsy (Moscow): 105 thousand rubles.
In state clinics and city hospitals, the cost of a monopolar TOUR starts from 13 thousand rubles.
Patient reviews
Alexander, 47 years old: “I did a TOUR in Moscow City Clinical Hospital No. 50. My wife is 12 years younger, I thought that the end of my family life had come, but after a couple of months I fully recovered. To eliminate problems with urination, I took a course of Vesicare.”
Evgeniy, 44 years old: “My father had a rather large adenoma removed at the Pirogov clinic in St. Petersburg using a bipolar loop. There were no special complications. We struggled with the natural consequences of urine leakage for about 3 months.”
Conclusion
Doctors consider TUR the most precious operation of all transurethral endosurgery methods, since it requires talent and specific knowledge from the specialist. The effectiveness of the manipulation and the patient’s condition after it depend on this. When choosing a clinic, be sure to clarify what method and who performs the removal (reviews of doctors are on the forums).
Sources:
Source: https://muzhchina.info/prostata/adenoma/tur
Indications for surgery for prostate adenoma and methods of surgical treatment
Content
Share on VKontakte Share on Odnoklassniki Share on Facebook
Prostate adenoma is a benign tumor. Surgical treatment is still required for at least 1/3 of all patients with this pathology. Please note that conservative therapy provides only a temporary effect. It is possible to completely get rid of the tumor and improve the quality of life only with the help of surgery.
Stages of the clinical course of the disease
Prostate adenoma is characterized by stage-by-stage development. Certain symptoms appear as the size of the tumor increases. Over time, the signs only intensify and become more pronounced. Depending on the severity, treatment for prostate adenoma is selected. Main stages of disease development:
| Stage | Characteristic symptoms | Recommended Treatment |
| Compensated |
|
Taking medications that stop the development of prostatic hyperplasia, normalize the process of urination and prevent further changes in the kidneys and ureters. Main groups of drugs used:
|
| Subcompensated |
|
If the stage proceeds without complications, then conservative treatment is carried out, but the likelihood of success of such therapy is low. In this case, surgery is prescribed. |
| Decompensated |
|
Surgery |
Types of surgery
All operations to remove adenoma are divided into open and minimally invasive. The former are considered more radical and traumatic, the latter give fewer complications, but do not allow treating patients with multiple tumors. For prostate adenoma, the following types of operations are performed:
- Adenomectomy. The surgical area is treated with an antiseptic, the hair is shaved, and then an incision is made into the skin and subcutaneous tissue. Then the walls of the bladder are cut and the adenoma is removed through it.
- Transurethral resection of the prostate. A resectoscope is inserted into the urethra. Using a special loop, the overgrown epithelium is scraped out, and the vessels are cauterized using electrodes.
- Laser vaporization. Special equipment is inserted through the ureter, then the tumor is dissected with a laser beam.
- Transurethral incision. A resectoscope is inserted into the urethra, which at the end has a camera, a light bulb and a special knife. When the instrument is at the level of the prostate, the doctor makes two incisions from the neck of the bladder to half the length of the prostate gland. As a result, the lumen of the urethra is freed from compression.
In what cases is it necessary to remove prostate adenoma?
- Each operation to remove prostate adenoma has its own indications, since the techniques differ in the degree of impact.
- In some cases, it is possible to cope with the tumor using minimally invasive methods, in others, more radical intervention is required.
- Absolute indications for surgery to remove adenoma:
- chronic kidney failure;
- bladder stones;
- repeated acute urinary retention;
- severe narrowing of the urethra, leading to disruption of the bladder and urinary retention;
- bleeding;
- inflammatory changes and infections of the genitourinary system.
Adenomectomy
In case of complications, the only possible method of removing the adenoma is adenomectomy. This type of operation is also called abdominal surgery, because it is carried out through the open bladder. The patient is under general anesthesia. Indications for adenomectomy:
- malignant tumor transformation;
- the tumor is large - more than 80 ml;
- the presence of concomitant diverticula and bladder stones;
- high risk of malignant tumor transformation.
Transurethral resection of the prostate
Transurethral resection is considered the “gold standard” in the treatment of prostate adenoma. It is prescribed to most patients, but the operation is complex and requires special skill from the surgeon. The main advantage of the technique is the absence of postoperative sutures and scars, but large tumors cannot be dealt with in this way. Indications for transurethral resection:
- The planned duration of the intervention should be no more than 1 hour.
- The volume of the adenoma is no more than 80 ml.
Laser vaporization
The main advantage of laser vaporization is the low risk of postoperative bleeding, since the tissue is cauterized with a laser. Indications for surgical intervention:
- tumor size up to 60-80 cubic meters. cm.;
- concomitant hemostasis disorders, in which the risk of bleeding is high.
Transurethral incision
This method of surgical treatment can be used when there are contraindications to other operations, but the prostate is greatly enlarged and causes serious problems with urination. Transurethral resection is performed only if the prostate adenoma is not complicated, and the patient wants to preserve sexual function. Indications for surgery:
- frequent urination;
- difficulty urinating;
- frequent inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract;
- inability to completely empty the bladder.
Video
Found an error in the text?
Select it, press Ctrl + Enter and we will fix everything!
Attention! The information presented in the article is for informational purposes only. The materials in the article do not encourage self-treatment. Only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis and give treatment recommendations based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient.
Source: https://vrachmedik.ru/2648-pokazaniya-k-operacii-pri-adenome-prostaty.html
What operations are performed on a man for prostatitis?
Prostatitis is almost always treated with conservative methods, and therefore surgical intervention is not required. However, a course of the disease is possible in which the quality of life deteriorates significantly or a serious threat to the man’s life arises. The operation helps combat such complications of prostatitis.
Let's talk about in what cases surgical treatment is indicated. We will also talk about the types of operations and the actions of men in the postoperative period.
Indications for surgery
Men over 45 years of age begin to experience changes in their bodies that can lead to health problems. The reproductive system suffers greatly - erections can become sluggish, libido decreases, and pathological processes begin in the prostate gland.
In men of pre-retirement and retirement age, prostate adenoma and chronic prostatitis of various etiologies are not uncommon. These conditions in themselves are not indications for surgery, but may be accompanied by various disorders that can only be eliminated through surgery.
Indications for surgery for prostatitis are:
- acute urinary retention - a man cannot relieve himself even by straining the muscles of the abdominal wall;
- detection of stones in the prostate;
- severe pain in the perineum or pubic area that cannot be treated;
- urinary incontinence due to prostate dysfunction;
- development of renal failure.
Also, an indication for surgical intervention is bleeding from the penis for unclear reasons.
In this case, surgery can be performed both for diagnostic purposes and to stop bleeding.
However, bleeding with prostatitis and prostate adenoma is quite rare; it predominates in the calculous form or may be a consequence of improper rectal massage.
If the doctor suggests surgery, it means the problem is serious, you should not refuse. This method is used in extreme cases.
Contraindications for surgery
When preparing for surgery, the doctor carefully studies all the dangers and makes an informed decision - the benefits of surgery for prostatitis should be higher than the risk of possible complications. Therefore, the patient is examined for contraindications, which are:
- acute inflammatory processes in the intestines and organs of the genitourinary system;
- renal or liver failure;
- severe cardiovascular diseases;
- blood clotting pathologies;
- cerebral atherosclerosis;
- some nervous system disorders;
- pathologies in the respiratory system.
Some contraindications are relative - surgery is possible after recovery or with strict monitoring of the patient’s condition by medical personnel.
You cannot remain silent about existing chronic diseases and allergies to medications - excessive “modesty” can cost your life.
How to prepare for surgery
Surgeries on the prostate gland are not considered difficult, but you need to properly prepare for them. A detailed list of rules and necessary measures depends on the technique of the operation, and therefore the attending physician will familiarize you with them during the consultation. Let's consider the general points:
- A man must undergo a full examination - blood tests, ECG, allergy tests for anesthetics, etc.
- If necessary, antibiotics are prescribed, especially if there is a risk of infection during surgery.
- The last meal is possible the evening before; on the day of surgery, the patient may be allowed to drink water as an exception.
- The day before you need to do a cleansing enema.
- You should not take sedatives without a doctor's prescription.
On the day of surgery, the patient needs to wash himself, shave his pubis and perineal area. The doctor will discuss the remaining requirements regarding medication preparation, examination and other aspects at the appointment.
The duration of preparation depends on many factors and can reach several weeks.
What operations are performed for prostatitis?
For prostatitis, various operations are possible, including laparoscopic ones. The choice of technique depends on the localization of the pathological process, the equipment of the clinic and the preferences of the doctor. Open access operations on the prostate are rare in modern surgery. Let's look at the basic techniques.
Transurethral resection of the prostate
Transurethral resection (TUR) is a modern method during which the prostate is removed completely or partially through the urethra. To achieve this goal, the surgeon can use electric current or laser (laser vaporization). TURP has a number of advantages:
- there is no need to cut the skin and muscle tissue;
- recovery occurs quickly;
- minimal risk of bleeding.
TUr is used primarily for the removal of prostate adenoma and, when using bipolar technology, allows the removal of tumors with a volume of up to 120 cm3.
Transurethral incision
The method is used to restore normal urination, impaired due to BPH or chronic prostatitis. All manipulations are carried out through the urethra, as in the case of TUR, but the prostate is not removed. During the operation, the prostatic urethra is incised.
The method is well tolerated by most patients. Possible complications include retrograde ejaculation, in which sperm during sexual intercourse is ejected not outward, but into the bladder. The problem is solved by taking special medications. Short-term complications include urinary retention or incontinence.
Prostatectomy
The method is considered outdated, and therefore is used only in the case of the formation of large-sized benign hyperplasia or the presence of serious complications of chronic prostatitis, in which minimally invasive operations cannot be performed. During surgery, muscles and skin are cut, blood vessels are damaged, and therefore the man takes longer to recover.
Prostatectomy carries a risk of bleeding and infection. The rehabilitation period is long, a man may face erectile dysfunction, early ejaculation, infertility and other problems in the reproductive system. Therefore, prostatectomy is considered a last resort and is used more often to treat older patients.
If small stones or tumors are found and there are no serious complications, laparoscopic surgery may be used for prostatitis.
This is a gentle technique in which all surgical procedures are performed through 2-3 punctures in the skin.
Video equipment is inserted into one hole for visual control, surgical instruments are inserted through the remaining holes and excised tissue and blood are removed.
After laparoscopic surgery, there are practically no scars left, the patient recovers quickly and can return to his normal life. Potential complications include some pain after surgery, infection if asepsis is not followed, and a slight risk of bleeding.
During the recovery period
Whether it will be possible to cure prostatitis or adenoma with surgery also depends on the progress of the rehabilitation period. If a man neglects the doctor’s instructions or medical personnel do not show due care, relapses, complications and other problems may develop.
Each method of surgical treatment has its own recommendations for the postoperative period, but there are some general points:
- monitor the cleanliness of the skin, catheter, wound, dressing;
- take antibiotics in the dosage prescribed by the doctor, without shortening the course time;
- observe bed rest for 2-3 days, depending on the technique used;
- remove fried and fatty foods from the diet;
- do not lift heavy objects, do difficult work and do not have sex for a month or two.
The first few days there may be pain in the perineum, and there may be small flakes of blood in the urine. This condition is considered normal, but a man needs to be attentive to his well-being.
The appearance of severe bleeding, drops of blood on underwear, and an increase in temperature indicate the development of a complication, which the attending physician should be aware of.
Conclusion
Surgeries for prostatitis are possible, but are carried out only in extreme cases - when there is a serious threat to the life or health of the patient.
Typically these conditions are stones in the gland or the development of a large tumor. Various techniques can be used - from laparoscopic surgery to open prostatectomy.
To reduce the likelihood of complications, you must follow your doctor’s instructions, especially during the rehabilitation period.
You might be interested
Source: https://prostatits.ru/lechenie/operatsiya-pri-prostatite.html
What are the indications for surgery for prostate adenoma?
In recent years the situation has changed. In the early stages of the disease, treatment is carried out with medications. In most patients, conservative therapy makes it possible to eliminate urinary disorders, slow down further growth of the tumor, and avoid surgery altogether. Even if surgical intervention is unavoidable, it is possible to choose a less traumatic method in which there is no need to completely remove the prostate.
When is surgery required for prostate adenoma, and what methods of performing it can be offered to the patient?
Stages of development of hyperplasia and possible methods of treatment
The clinical course of prostate adenoma is divided into three stages of development. The initial stage is characterized by urination disorders: the number of urges increases, the outflow of urine worsens, and an imperative urge is observed with the need to immediately empty the bladder.
When diagnosing uncontrolled proliferation of prostate tissue at the initial stage, the patient is recommended to take medications.
As a rule, their use makes it possible to stop the increase in hyperplasia and even reduce its size, normalize urination processes and prevent further structural changes in the kidneys and ureters.
At the second stage of prostate hyperplasia, as a result of deterioration of urine outflow, partial atony of the bladder and the appearance of residual urine after emptying occurs, changes are observed in the upper urinary tract, and the disease gradually affects the condition of the kidneys, causing renal failure. If the second stage proceeds without complications, the patient may also be offered conservative treatment, but the likelihood of eliminating symptoms and improving the condition with drug therapy alone is much less likely.
With stage three prostate adenoma, chronic renal failure develops, and there is a high risk of complete cessation of urine outflow. The disease can be eliminated at this stage only by performing surgery.
Indications for urgent surgery
The absolute indications for performing the operation are as follows:
- development of acute urinary retention;
- the course of the disease is complicated by stones formed in the bladder;
- severe renal failure;
- the presence of recurrent infectious diseases in the organs of the urinary system;
- blood has been present in the urine for a long time;
- a sharp increase in the amount of residual urine.
Contraindications
Before performing the operation, a complete examination of the patient is carried out and the presence of possible contraindications is clarified. These include such background pathologies as heart failure, atherosclerosis, and severe forms of renal dysfunction.
If chronic inflammatory processes in the kidneys and bladder are detected in a patient, surgical intervention is performed after a preliminary therapeutic course.
Types of surgery
For prostate adenoma, several methods of surgery are used.
The main ones are open removal of the gland, transurethral resection, vaporization, incision:
| Adenomectomy | The most traumatic surgical treatment for prostate hyperplasia, which involves complete removal of the gland through an incision in the abdominal wall. Indications for using this method: the presence of complications in the form of stones, large adenomas. The operation is performed under general anesthesia, the postoperative period lasts up to 2 weeks. |
| Transurethral resection of the prostate | When using this surgical method, an endoscopic medical device is used, at the end of which a loop-shaped electrode is placed. The instrument is brought to the prostate along the urethra. A resectoscope is used to remove excess prostate tissue and cauterize the blood vessels. Depending on the volume of hyperplasia, from 10 to 40 sections are performed. After the operation, the bladder is washed with a solution through a catheter for 1-3 days. The advantage of TUR is minimal damage to the tissue of the abdominal wall and a shorter rehabilitation period. The outflow of urine is normalized 1-2 months after the manipulations. |
| Laser vaporization | Endoscopic methods for removing prostate hyperplasia include vaporization. The method consists of layer-by-layer evaporation of excess tissue with a directed beam of laser light. As a result of laser cauterization, simultaneous coagulation of blood vessels occurs, which significantly reduces the risk of postoperative bleeding. |
| Transurethral incision | This method is used if there are indications for surgical intervention, but the prostate gland is not very enlarged, there are no complications, and the patient wants to maintain sexual function. The method involves making incisions at the point of contact with the urethra and its subsequent release. |
Rehabilitation period and possible complications
Regardless of what indications caused the surgical intervention and what method was used to perform the operation, rapid restoration of damaged tissue is possible provided that several basic rules are followed:
- avoid constipation, as tension in the pelvic muscles can lead to prolonged healing;
- observe drinking regime;
- do not subject the body to intense physical activity, avoid sudden movements.
After any surgical treatment there is a risk of complications. Early postoperative complications include:
- TUR syndrome, in which part of the solution for washing the bladder enters the patient’s blood vessels;
- development of bleeding;
- development of inflammatory processes, including infectious etiology, in the organs of the genitourinary system;
- complications typical for any type of surgical treatment: blood clots, pneumonia and others.
In some cases, the consequences of surgery appear a month or later after it is performed.
Among the possible late complications of prostate adenoma, the following disorders may be noted:
- sclerosis of the bladder neck;
- improper functioning of the sphincter, as a result of which the patient develops urinary incontinence;
- the appearance of scars on the urethra, which leads to a narrowing of the urethra;
- the development of retrograde ejaculation, in which seminal fluid is released not into the urethra, but into the cavity of the bladder;
- all kinds of sexual function disorders.
Timely surgical treatment and the correct choice of surgical method can restore the normal functioning of the urinary system and significantly improve the quality of life.
Source: https://kaklechitprostatit.ru/diagnostika/podgoovka-k-operatsii.html
Prostate surgery: in what cases and how is prostate surgery performed?
Prostate diseases, previously considered age-related pathologies, are now diagnosed in 35-40 year old men.
Despite the efforts of specialists, it is not always possible to manage with conservative treatment methods; 30% of patients require surgical intervention.
And prostate surgery, according to statistics, firmly holds 2nd place in urology. Let's consider what types of surgical intervention there are and what indications exist for them.
Indications for surgical treatment methods
Surgery on the prostate gland often becomes the only possible method for a man to get rid of painful spasms when urinating, as well as eliminate the growth of the tumor.
Prostate surgery is performed in the following cases:
- Prostate tissue growth – prostate adenoma.
- Purulent prostatitis or abscesses in the body of the prostate gland.
- Narrowing of the urethra (urethra).
- Delay or absence of urination.
- Prostate tumors – both benign and malignant.
- Bloody discharge from the urethra.
- Rapid proliferation of connective tissue – sclerosis or fibrosis of the prostate.
- Urinary incontinence.
Urologists or andrologists are the names of specialists who should be contacted if alarming symptoms appear. At the same time, urologists deal with pathologies of the urinary system as a whole, while andrologists study disorders of the male reproductive system. But a doctor of both first and second specialization, after all examinations, can recommend prostate surgery.
Note! Prostate surgery is performed strictly in a hospital setting by surgeons under anesthesia.
Surgery on the prostate gland is performed in a hospital setting
What types of operations are there?
The types of operations depend on the degree of prostate damage. In case of voluminous tumors (more than 80 mm), the presence of multiple stones in the urinary system, developed diverticulosis of the bladder membranes, preference is given to a radical method - surgery to remove prostate growth or adenomectomy.
If the tumor size is less than 80 ml, a more gentle operation on the prostate is performed - excision of the adenoma. With mild inflammation and a small adenoma, surgeons tend to use low-traumatic endoscopic methods.
Regardless of what type of prostate surgery is planned, there are a number of contraindications to surgery:
- Severe forms of cardiac, renal and pulmonary failure (there is a risk of intolerance to general anesthesia).
- Cystitis, pyelonephritis in the acute stage.
- Infectious diseases.
- Serious pathologies of the cardiovascular system and brain.
Depending on the degree of intervention and penetration into the affected area, there are several methods for surgical tumor removal.
The operation varies in form of intervention
Open or traditional surgery
Operations to remove glandular growths of the prostate, carried out in the traditional open way, 30 years ago were practically no alternative method of tumor removal.
Currently, other methods are widely practiced, but open adenomectomy has not lost its relevance as a way to cope with large tumors and prevent the degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one.
The operation is also indicated for significant accumulation of stones and proliferation of diverticula in the urinary system.
The operation is classified as abdominal, since the intervention occurs through an open bladder under general anesthesia.
To predict possible complications and recovery time before surgery, general and biochemical blood and urine tests, a blood test for AIDS and sexually transmitted diseases are required. The list of preliminary preparation also includes an ECG and ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
The course of the operation, which requires certain skills and qualifications of the surgeon, includes a number of stages:
- After the necessary hygienic procedures, a longitudinal or transverse incision is made in the abdomen, penetrating through the dermis and subcutaneous fat tissue.
- Dissection of the anterior wall of the bladder allows the contents of the bladder to be analyzed for the presence of stones and diverticula.
- The third most crucial moment of the operation is palpation of the detected tumor and its isolation.
- Penetrating into the internal opening of the urethra, the surgeon uses his index finger to remove tissue growth that interferes with the normal functioning of the gland itself.
- After the tumor is isolated, it is carefully removed through the opened organ, being careful not to damage adjacent structures. The excised tumor is certainly sent for histological examination.
Like any type of surgical activity, open surgery has undeniable advantages, but also has its disadvantages.
The main advantage of the traditional open method is radicalism, that is, the final and irreversible cutting off of the tumor with all aggravating symptoms.
The main negative consequence of the method is the likelihood of bleeding in the initial postoperative period. The danger is not so much blood loss as the possible blocking of the outlet hole in the bladder by a blood clot. To prevent this situation, the organ is washed with sterile saline through a catheter.
Getting rid of a tumor also has its price - the consequences of anesthesia, a long recovery period (up to 3 months), the risks of complications (suppuration and bleeding of the wound, the formation of fistulas). The postoperative suture does not paint either.
Source: https://prostatu.guru/lechenie/kak-delayut-operatsiyu-na-prostate.html