Human papillomavirus is the most common sexually transmitted disease. Some forms of it can cause cancer, such as cervical cancer. This is why diagnosing HPV is extremely important, because timely treatment can prevent many unpleasant consequences. You can read more about how to diagnose and treat HPV in this article.
What is HPV
HPV, or human papillomavirus, is one of the most common diseases on the planet. According to statistics, in America alone there are about 80 million infected. Not all types of HPV can be considered dangerous to health; some types of the virus do not have any effect on the body. But others can cause cancer, warts and a number of other unpleasant symptoms. HPV in women - what is it? This is a virus that is able to penetrate into the deep layers of the skin and mucous membranes, causing the uncontrolled appearance of cells. Sometimes this process can cause the formation of malignant tumors. Studies have shown that 70% of women diagnosed with cervical cancer had HPV in their blood. Types 16 and 18 of the virus are considered especially dangerous.
How is it distributed?
The main route of transmission of HPV is through sexual contact. During any type of sex, even oral sex, a person is at risk. The virus may not detect itself immediately, but after a few years, when your body is more weakened. Before this, for quite a long time the person does not experience any symptoms at all.
In most cases, the virus does not have a negative effect on the body due to the fact that the human immune system suppresses its activity. But in some people, especially those who are weakened and have suffered a serious illness, the body stops healing itself, and the virus begins to multiply uncontrollably. Here are some additional factors that may contribute to infection:
- Immunodeficiency (primary or secondary).
- Other viral infections;
- A large number of sexual partners.
- Diabetes and other chronic diseases.
- Long-term use of COCs.
- Unprotected sex.
The effect of HPV on the body
Doctors say that in most cases, the papilloma virus is cured by the body on its own. But sometimes this does not happen, resulting in health problems for the carrier. The most common associated symptom of HPV is genital warts.
It is based on these signs that a doctor can suspect a disease and send his patient for diagnosis. There is no need to think that as soon as a person becomes infected with a virus, he immediately develops cancer. No, this process can take years or even decades. So far, there is no way to know what consequences HPV can cause in a particular person.
For one, the problem will be limited to just warts, while the other may acquire a more serious disease.
HPV: diagnosis
It is precisely because of the unpredictable consequences of the papilloma virus that doctors strongly recommend that everyone without exception be examined. After all, with timely treatment, many problems can be avoided. What methods of diagnosing HPV can be identified?
- Inspection. This method allows you to identify the general health of the patient, as well as see the external manifestations of the virus, such as warts.
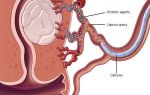
- Colposcopy is a diagnostic method in which, using a special device, the surface of the cervix is examined for the presence of damage or neoplasms. For a more obvious picture, the doctor may use a weak vinegar solution. When applied to the mucous membrane, areas of the mucous membrane affected by the virus begin to foam.
- A biopsy is a study of the tissues on which the virus most often appears. In women this is the cervix, and in men it is the head of the penis. A biopsy allows you to examine the cells of an organ at a microscopic level, identifying any abnormalities.
- Histology is performed primarily as a confirmatory method before diagnosing a patient with cervical cancer. The reliability of this diagnostic method reaches almost 99%.
- What HPV tests should be taken for those who want to make sure that the virus is absent? The PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method currently provides some of the most accurate results. The only condition for obtaining a reliable diagnosis is to choose a good laboratory, or better yet, get tested in several different organizations.
- The Digene test has only recently entered the market, but has already become very popular among doctors and their patients. The main secret of this diagnostic method is that it has extremely high sensitivity. This means that it is able to “catch” even the slightest presence of HPV in the body. The main disadvantage of the test is its cost (about 6 thousand rubles).
On the subject: How to bake buns: step-by-step recipe with photos
Where can I get tested for HPV? In all private laboratories you can find different types of diagnostics (PCR, histology, etc.). Getting tested for free is a little more difficult. To do this, you need to contact a gynecologist at your place of residence and get a referral for analysis. Diagnosis of HPV in men is carried out mainly using the PCR method, Digen test and biopsy. The fence material is taken from the urethra.
Associated symptoms
Most people infected with human papillomavirus are unaware of their illness. Therefore, it can only be determined using high-precision diagnostic methods. However, there are some accompanying symptoms that may directly indicate the presence of HPV.
- The formation of warts or other growths on a person's face, genitals, or mouth.
- Frequent and unexplained illnesses.
- The appearance of condylomas.
The incubation period of HPV lasts about a year. Therefore, it is impossible to draw a clear boundary between a sick and a healthy person without special tests.
PCR
What is the PCR method? This is a polymerase chain reaction that can be used to multiply certain nucleic acid fragments. HPV is a double-stranded DNA virus with more than 8,000 nucleotides.
If it is in the human body, it leaves a noticeable trace, which can be seen using PCR. However, not all types of virus can cause malignant tumors. Only a few of them are recognized as the most oncogenic and dangerous: 6, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 66 and 68.
For women, types 16 and 18 are of particular importance, since they are the ones that cause cervical cancer. Diagnosis of HPV using the PCR method is currently the most popular non-invasive procedure, which with a high degree of probability allows you to determine whether there is a virus in the human body.
PCR allows you to avoid unpleasant and painful diagnostic methods such as colposcopy or biopsy.
Doctors recommend that all women over 30 years old undergo PCR diagnostics for high-oncogenic risk HPV on a regular basis.
Before colposcopy, everyone is recommended to do this test first, and only then, if the virus has been detected, to carry out a detailed examination of the tissues.
No special preparation is required before carrying out PCR, which can also be attributed to the advantages of this method. It is enough just to refrain from water procedures a few hours before the analysis.
Colposcopy
Another method for diagnosing HPV is colposcopy. This procedure is performed by specially trained medical specialists using a low-power microscope - a colposcope. It involves examining the cervix, vagina and vulva while using acetic acid. A vinegar solution makes it possible to more clearly identify changes in tissues that look healthy without the use of acid. The doctor examines all irregularities, neoplasms and, if necessary, takes a biopsy of damaged tissue. Colposcopy is not used very often, mainly in the following situations:
- immunosuppressive conditions;
- the patient has HIV;
- women who have received different test results three times in a row or have an unclear clinical picture;
- positive cervical cytology for malignant neoplasms.
Colposcopy is an invasive procedure, so before going to the doctor you need to refrain from using vaginal suppositories, intimate relations, or using tampons for several days.
Biopsy
Diagnosis of HPV using colposcopy involves taking biomaterial if the doctor suspects the presence of infection in the patient’s body. In fact, a biopsy is part of a colposcopy. A biopsy can be taken not only from the genitals, but also from warts or condylomas.
All manipulations imply that the study is performed using a microscope. The material collection itself is carried out in several ways: using a needle or scalpel. A biopsy assumes the absence of any infectious diseases, since otherwise the risk of inflammation increases.
Doctors consider biopsy not the safest diagnostic method, so they try to perform it only in extreme cases.
Histology
Another method of laboratory diagnosis of HPV is histology of papillomas. HPV, having entered the body once, remains in it for many years. It may not have any effect on humans, but can cause various neoplasms on the skin. It is by examining warts and other growths that a diagnostician can determine whether there is a danger to your health.
Digene test
HPV smear compared to Digene test shows low predictive reliability. The test developed by Digene is currently considered the true gold standard. This method of diagnosing HPV allows not only to determine the presence of the virus in the blood with 98% accuracy, but also to determine its oncogenicity. As a result, the patient receives not only “positive” or “negative” in the test results, but can also find out what type of HPV he is a carrier of - with a high or low cancer risk.
The Digene test is hypersensitive, so it is prescribed in the most complicated cases, when a clear diagnosis cannot be made using classical methods. In addition, this method of diagnosing HPV is used in cases where it is necessary to determine the tendency to develop cervical cancer. What other indications exist for this test?
On the subject: Russian anti-ship missiles: list, types, description with photos
- In a comprehensive examination of the patient to identify cancerous or precancerous conditions.
- To monitor the results of therapy.
- As a preventive diagnosis for women over 30 years of age.
Decoding the results
Test results can only be interpreted by your attending physician. It is he who you need to turn to for help if you want to know the exact result. This happens because tests alone are not enough to make a diagnosis.
Usually the specialist pays attention to complaints, well-being, clinical picture and other factors. However, in many private laboratories, next to the test results, their reference value is indicated, which makes it possible to determine how much they deviate from generally accepted norms.
Ideally, no HPV titers should be detected in a person's blood or tissue. If they are still present, but in small quantities, then it is worth more accurately determining what type of virus you are a carrier of. If this is the type with the highest cancer risk, the doctor will prescribe you appropriate treatment.
But making decisions and medications without the advice of a specialist is highly discouraged.
Treatment and prevention
If a person’s immune system works normally, then no additional therapy is required. If the patient is bothered by warts, or an HPV smear reveals an oncogenic type of infection, then in most cases doctors prescribe the following treatment:
- Removal of tumors;
- A course of antiviral drugs;
- Raising immunity.
Ideally, you need to follow preventive measures that will allow you to stay out of the risk zone.
- Vaccination against HPV significantly increases the body's resistance. The “safest” method for vaccination is 11-12 years old.
- Use barrier contraception (condoms) every time you have sex. This rule must be followed even if you have one permanent partner.
Results
HPV in women - what is it? The papilloma virus can manifest itself in different ways, but only some of its types can cause serious harm to the body. In order to determine the presence of the virus in the blood of women and men, different diagnostic methods are used: biopsy, histology, PCR and Digene test. Each of them has its own pros and cons, so only a doctor can prescribe tests.
- The film “The Painted Veil”: reviews, plot, actors and roles
- Svetlana Zhurova - athlete, politician and amazing woman
- Carrot cake without eggs: recipe with photos, baking secrets
- Darphin: reviews of cosmetics, product range review, composition
- Funny actors' stories - review, features and interesting facts
- Rainbow crab as a pet
- Who invented heels and how they changed
- What to give your wife for her 30th birthday? Birthday script, congratulations, gift ideas
- What does “a log in the bed” mean: how to understand it and how not to become one
- The best eye patches: reviews, rating (top 10)
- By using these products, you will forget about dry skin forever.
- Histamine headache: causes, symptoms and treatments
Source:
Diagnosis of papillomavirus. How to identify? What methods? How is it determined? Which method is accurate?
Source: https://nuzubbelovo.ru/papillomy/diagnostika-vpch-obzor-effektivnyh-metodov-vyyavleniya-virusa.html
Diagnosis of papillomavirus. How to identify? What methods? How is it determined? Which method is accurate?
Published: October 27, 2016 at 08:25 pm
It is recommended for everyone under the age of 30 to get tested for HPV. Up to 25 years of age, a strong immune system can contribute to the complete elimination of HPV, but in some cases the virus remains in the body and affects the cells of the dermis and mucous membranes.
Why is an examination needed? Papillomavirus is dangerous
Human papillomavirus poses a serious danger to the body. Diagnostics in this case is needed in order to correctly determine the strain and viral load. Knowing these characteristics, the attending physician will prescribe effective therapy that will prevent further damage to the epithelium.
HPV is transmitted through contact and sexual contact, depending on the type. Non-oncogenic ones can enter the body even with a handshake if the human dermis is damaged and the immune system is weakened. Such strains are not dangerous in any way and appear as small skin growths that do not differ in color from the dermis.
HPV testing is necessary because the most dangerous strains, when present in a woman’s body for 10-20 years, can cause cervical dysplasia and tumors. A timely and correctly diagnosed disease will prevent the development of malignant processes.
HPV testing – what is it? Diagnostic methods
The examination consists of several stages:
- Examination of the patient for clinical manifestations;
- Collection of biological material;
- Conducting tests for the presence and identification of HPV type and viral load (number of viral particles).
At the end of the 20th century, experts determined how to diagnose HPV. To do this, the suspected area where the virus was located was treated with a 5% acetic acid solution. The lesions took on a grayish-white hue for some time.
This diagnosis of HPV was not correct because it did not provide information about the strain and viral load, and could also give an erroneous result (in the presence of vulvitis, colpitis, herpes, balanoposthitis and other concomitant sexually transmitted diseases).
To more accurately determine the disease, modern diagnostics of the papilloma virus offers the following methods:
- Cytology of cervical smears (Papanicolaou);
- Histology;
- Biopsy;
- Colposcopy;
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR);
- Digene test.
Of these, the most informative are the Digene test and PCR diagnosis of HPV. With their help, the specialist receives a complete picture of the disease, so he can prescribe effective treatment.
It is impossible to completely destroy and remove the virus from the body, but there are a number of drugs that inhibit the development of HPV RNA at the transcription stage. Medicines that increase the patient’s immune status are also prescribed.
Human papillomavirus - Papanicolaou diagnosis
In short, this method of determining HPV is called the Pap test. It is based on taking a smear from the cervical canal, from the cervix. Laboratory assistants examine biological material not for changes in cell morphology. The accuracy of a PAP test depends on the skills of the laboratory technician, the staining method, and the technician's ability to read the test results.
Such an examination for human papillomavirus may give a false negative result if the material was collected from a different area where the largest number of viral cells were concentrated.
Using this method, it is impossible to determine HPV of high carcinogenic risk - only low-oncogenic ones that cause mild dysplasia.
HPV and colposcopy. Other examination methods
The method is based on examining vaginal tissue using a microscope. During colposcopy, specialists pay attention to:
- Mosaic;
- Anomalous transformation zone;
- punctuation;
- Acetowhite epithelium.
If, during colposcopy, a specialist has identified a pathology that may be characterized by papillomavirus, the diagnosis should be more extensive and include other methods.
During a biopsy, doctors remove tissue from the cervix or vaginal walls for further microscopic examination. If cervical cancer is suspected, a histological examination is performed, which has virtually no error and provides a 100% accurate result.
How to test for HPV? PCR method
In order to identify the pathogen in the body using the polymerase chain reaction method, the patient needs to donate blood. In biological fluid, the presence or absence of HPV is determined, as well as its strain and degree of oncogenicity.
Diagnosis of papillomavirus by PCR has many advantages over other laboratory tests.
Method:
- Universal;
- Highly sensitive;
- Specific;
- Provides results quickly.
Using PCR, the pathogen is detected during the incubation period, when no clinical manifestations are observed. The disadvantage of the method is that it does not determine the viral load.
Digen test
If the diagnosis of papilloma is tentatively made due to the discovery of genital warts in a patient, it is very important to identify the load. This characteristic makes it possible to guess when the infection approximately occurred, and whether the increase in the concentration of the virus coincided with a sharp decrease in the patient’s immunity.
If papilloma is detected, the diagnosis must include a method that will indicate the exact concentration of the virus in the blood. This is very important not only for making a diagnosis, but also to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment.
There are currently no similar or more informative methods for diagnosing HPV. With the help of the Digen test, you can prevent malignant processes by starting treatment on time.
Advantages of the method:
- Sensitive;
- Specific;
- Easy to use;
- Fast;
- Informative.
HPV diagnosis – what is it? The answer to this question, as well as step-by-step therapy, must be described by the attending physician. The patient must have a full understanding that self-medication can lead to negative consequences.
After treatment, it is advisable to adhere to general recommendations and periodically carry out prophylaxis, stimulating the immune system.
Interesting materials on this topic!
Recommendations for reading for you personally!
loading…
Irina Shmitko — January 27, 2020, 15:00
I already had problems with HPV activity. About 7 years ago I underwent a course of therapy to eliminate papillomatosis. After the end of treatment, I took care in every possible way and took medications to strengthen the body’s immune system. Recently I became very ill with the flu, which also caused pneumonia.
The immune system weakened, and the papilloma virus made itself felt - small warts appeared all over the body. After being examined by a doctor, I was prescribed the drug Papilite. I inquired about its properties and composition and decided to purchase it. I did everything according to the instructions and this ensured a positive result.
I would never have believed that you could do without all hospital procedures and cope with the problem at home. A very effective product, I recommend it to everyone.
Marina Ivanova — 26 Jan 2020, 14:45
Papillomas in the perineal area have haunted me since I experienced hormonal changes during menopause. Until this time, I had not observed any pathological formations on my body.
I went to the doctor for an examination after the growths began to itch and become very inflamed. The doctor immediately prescribed me the Papilight complex. I bought it. Of course, a little expensive, but the result was not long in coming. In just a few weeks, the growths completely disappeared.
This remedy really relieves a person from the influence of human papillomavirus infection.
Maria - 04 Jun 2018, 18:04
Small growths, similar to pimples, appeared on the hands. How long does it take to do tests and wait for results? Is it possible to remove it painlessly?
Andrey - 06 Apr 2018, 11:34
Digest test is also a good way. But PCR is a little better and more reliable.
Valentin — 03 Apr 2018, 12:40
PCR will show this best. This is the most reliable way to determine the type of papilloma virus and the stage of its development in the body.
loading…
loading…
loading…
loading…
loading…
loading…
loading…
What tests are performed to determine HPV?
Skin growths of different sizes, colors and shapes may appear on the body. They are not only cosmetic defects that can be eliminated and forgotten about forever. Skin growths are a symptom of HPV....
How to determine HPV viral load?
A person under 30 years of age infected with the virus has a high chance of self-healing. This is due to the elimination of HPV from the body due to the influence of the immune system. Older patients have immunity...
NEW! PAPILITE for papillomas!
This unusual two-component drug will allow you to remove papillomas and warts from any part of the body in 1 month!
NEW! PAPILITE for papillomas!
This unusual two-component drug will allow you to remove papillomas and warts from any part of the body in 1 month!
How to identify human papillomavirus?
Papillomavirus is a group of infectious diseases, predominantly sexually transmitted, which is characterized by the appearance of soft, flesh-colored growths on the mucous membranes and skin. About 150 types of virus are known, the common name is...
How to detect human papillomavirus?
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is common among women and men. Externally, it can appear in the form of various growths: papillomas, warts on the skin and on the mucous membrane of the genital organs. How…
Source: https://www.vitiligos.ru/papillomy/diagnostika-2
Methods for diagnosing human papillomavirus
The human papillomavirus (HPV) is very common and is present in the blood of more than half of the country's population. The pathology affects representatives of both sexes; in most, the disease is activated after thirty years.
The pathogen not only injures the surface epithelium, but also threatens with serious complications. An infected woman often has a child who inherits this disease.
Therefore, timely HPV diagnosis and appropriate treatment will help avoid a number of negative consequences.
Various methods can be used to diagnose HPV
Clinical examination
Diagnosis of HPV in both men and women begins with a medical history. The doctor recognizes the patient’s complaints and begins a visual examination.
The method allows you to determine the location and type of neoplasms. Growths on the genitals form both on the surface of the genitals and in the internal zone.
Therefore, cervical examination and urethroscopy are considered mandatory if genital warts are present.
Preparation for laboratory tests
When carrying out diagnostic procedures in a clinical setting, high accuracy of the obtained parameters is important. To avoid erroneous results, you must strictly follow the established rules:
- before taking the test for papillomatosis, you need to stop taking antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications for a month;
- taking a bacterial sample occurs on the fifth day after the end of menstruation;
- three days before the study, exclude sexual intercourse;
- the day before, refuse any intimate hygiene products, wash only with clean running water;
- men should not urinate a couple of hours before the test;
- If a biopsy is ordered, tampons should not be used.
It is recommended to abstain from sex before taking the tests.
Taking biomaterial
Sample collection is considered an important factor for qualitative research behavior.
If negligence was committed during the procedure (foreign bodies got into the analysis, a small amount of necessary material was removed, the instruments were insufficiently sterile, etc.)
d, then the result will be false. To avoid negative consequences, it is important to adhere to the established technique for biopsy of affected tissue.
Sampling scheme for women:
- the cervix is wiped with a sterile solution;
- insert a narrow brush into the canal to a depth of about one or two centimeters;
- make several turns and carefully remove so that there is no contact with the vaginal tissue;
- put the material into a previously prepared test tube with the medium contained in it.
A smear is taken for testing
Collection procedure for men:
- wipe the head of the penis with saline solution;
- a narrow probe is inserted into the urethra four centimeters;
- rotate it for a couple of seconds and take it out;
- the resulting smear is placed in a test tube.
The biological samples collected during the process are immediately sent to the laboratory to further establish the full clinical picture.
How well the papillomavirus diagnosis was carried out can be found out by reading the quantitative indicator of CVM (control of material collection).
If it is below the threshold (four units), it means that there were gross violations during the collection of samples, the result is considered far from reliable.
Colposcopic signs of HPV infection
Colposcopy is a microscopic examination of the tissues of the vagina or cervix.
With its help you can get information:
- what condition is the epithelium of the examined area;
- presence of sources of infection by the virus;
- the emergence of atypical pathogenic processes.
Diagnosis is carried out by colposcopy
The following identified signs are considered a cause for concern:
- acetowhite epithelium;
- mosaic;
- punctuation;
- abnormal zone of transition of the visible portion of the cervix into the canal.
Cytological examination by Papanicolaou test
Taken in accordance with established standards, a smear from the cervical canal is carefully examined, and atypical abnormalities in the cellular structures are revealed.
The sample is stained with a contrast agent and examined under a microscope. As a result of these manipulations, the specialist observes a differential separation of healthy and diseased cells.
The latter acquire a bright color, which indicates the presence of mild dysplasia in the body.
Cytology is used not only in gynecology, the method is also widely used to detect intraductal cancer caused by a virus.
Histological examination
Allows you to diagnose incipient or already progressing oncology against the background of papillomatosis. It is considered key for definitive confirmation of the disease when malignancy is suspected. It is possible to establish a precancerous condition with a 99% probability.
PCR diagnostics can detect the presence of a virus
Typing of papillomaviruses using PCR
This method is considered universal, as it can detect almost any infection in the body. With its help, not only the presence of the HPV pathogen is detected, but also the type of virus.
Affected tissue structures or the patient's blood are suitable for analysis. A special reagent is introduced into the collected material, which easily interacts with foreign DNA. To diagnose each suspected pathology, a specific substance is used, so this method leads to a clear 100% result.
You can find out about the presence of the virus in the body, its type and concentration one week after taking the test; negative indicators become known after two days. The price for the procedure depends on identifying the desired characteristics. PCR for papillomatosis can be qualitative, quantitative and genotyped.
Digene test
Digen research is a modern and highly accurate laboratory method. It allows you to study the parameters of the disease in detail. With its help you can install:
- type of virus – oncogenic or benign;
- appearance of warty structures;
- concentration of infected cells.
An accurate test for HPV is Digene
The sample is collected in the cervical canal, removing previously accumulated secretions.
It is recommended for women who have reached the age of thirty. This category is at risk for the development of cancer processes in the genital organs caused by HPV.
A person can live for a long time with the presence of oncogenic structures that are in remission. For this reason, the disease does not progress and does not have harmful effects.
However, over time, cancer develops, and it can be difficult to detect the activation of the pathological process in the early stages.
The Digen test shows the presence of malignant cells in a frozen state and the likelihood of further progression of the disease.
If there is a suspicion that there is a human papillomavirus in the body, diagnosis is the primary measure to begin the fight against the disease.
Modern research methods make it possible to quickly identify the disease, establish the degree of severity, and indicate the parameters of damage. Based on the results obtained, the doctor decides how to treat the pathology.
Therapy with antiviral drugs that stimulate the natural production of human interferon is often used, or cosmetic and surgical methods are used.
From the video you will learn about HPV testing in men:
Source: http://bolezni.com/stati-o-boleznyah/papilloma/diagnostika.html
HPV analysis - what is it, who is it prescribed for, how to decipher the result?
If there are symptoms and signs of the disease, doctors prescribe many laboratory tests to confirm assumptions and make a diagnosis. In the list of prescriptions, patients can find an HPV test: what it is, why and when it is prescribed - not everyone can answer.
What is HPV?
Human papillomavirus, HPV, is a whole group of virus-like infectious diseases that are widespread. Scientists know more than 100 types of this virus, and not all of them are dangerous to humans.
Most are present in the body unnoticed for a long time, causing carriage. However, about 14 types of this virus are oncogenic - they provoke the development of malignant neoplasms.
When diagnosing, doctors always pay attention to the type of HPV, its oncogenicity, which determines further actions and the nature of the treatment.
Human papillomavirus - types
The papilloma virus is usually divided into types depending on the risk of provoking the development of cancer. Taking this factor into account, there are three main groups of HPV:
- Non-oncogenic - never cause the development of malignant tumors.
- Low oncogenic risk - can, under certain conditions, provoke the development of cancer: 6, 11, 42, 43, 44.
- High oncogenic risk - when infected with these types of HPV, it is difficult to avoid the development of malignant tumors. Oncogenic human papillomaviruses: 16, 18, 31, 35, 33, 45, 58, 59, 52.
How is human papillomavirus transmitted?
Knowing how papillomavirus is transmitted can reduce the risk of infection. However, in practice it is difficult to avoid this.
In the vast majority of cases, transmission occurs with the onset of sexual activity: sexual intercourse is the main method of transmission of the virus.
It can also be transmitted through a kiss, when there are microcracks or scratches on the surface of the lips. You can also become infected if you violate hygiene rules while visiting public places:
- saunas;
- pool:
- baths;
- and also when using someone else’s toothbrush, towel, or razor.
Infection can also occur when the baby passes through the infected tract of the mother during childbirth. Experts do not exclude the possibility of transmission of the virus through contact: it is not stable, but is able to retain some activity. Among the factors that provoke HPV infection:
- early onset of sexual activity;
- a large number of sexual partners;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- reduced immunity.
Human papillomavirus - symptoms
Human papillomavirus can be present in the body unnoticed for a long time. The incubation period, according to experts, can last from 2 months to 2 years.
The disease proceeds unnoticed: there are no clinical symptoms, and basic diagnostic methods show the norm.
Every third patient, thanks to his immune system, recovers within 6-12 months from the moment of infection.
The clinical picture of HPV infection is reduced to the appearance of skin formations. Patients notice papillomas, warts and condylomas on their skin.
Their localization can be different and corresponds to the place where the virus enters the body: genitals, surface of the hands, lips. These formations look like papillary outgrowths, sometimes they look like cauliflower.
The growths are painless, but if rubbed or injured they can cause pain and bleed.
Why do you need an HPV test?
Having talked about the virus, let's move on to information about HPV analysis: what kind of research it is, how it is carried out and in what cases it is prescribed. To begin with, we note that if human papillomavirus is suspected, the analysis helps to confirm or refute assumptions. Research of this kind pursues the following goals:
- identification of HPV of high oncogenic risk;
- confirmation/refutation of persistence of a certain type of HPV;
- assessment of the risk of cancer in patients with dysplasia of the epithelial layer of the cervix.
In addition to the above reasons for the examination, HPV analysis (what it is is indicated above) may be indicated in the following cases:
- Primary screening for cervical cancer in women over 30 years of age.
- Evaluation of the results of surgical treatment of intraepithelial neoplasia.
- Questionable results of cytological examination of gynecological smears.
What tests should I take for HPV?
There are several methods for determining the presence of the papilloma virus in the body. However, in most cases, doctors resort to PCR. If it is necessary to take an HPV test, patients undergo this examination directly. Various biological fluids of the body can serve as material for examination:
- blood;
- urine;
- amniotic fluid (when diagnosing a disease during pregnancy).
When talking about HPV analysis, what it is and how it is carried out, it is necessary to note the possibility of studying tissue material.
So, during colposcopy, the doctor carefully examines the mucous membrane of the cervix. The presence of small papillomas on them is direct evidence of damage to the body by HPV.
To confirm, a small piece of tissue is removed to be examined under a microscope to rule out malignancy.
Diagnosis of HPV is a set of measures aimed at establishing the presence of the virus and determining its type. For this purpose, the following techniques are used:
- Digene test is a modern accurate method. With its help, you can determine the concentration of the virus in the body, the type and oncogenicity. The material for the study is a scraping from the mucous membrane of the urethra or vagina. Often used in conjunction with cytology.
- PCR diagnosis of HPV is a simple and accessible diagnostic method that is widely used. The patient's blood or urine is used as the material. It assumes the detection of traces of viral DNA in the sample.
- Cytological examination - examination of a smear under a microscope. The evaluation criterion is the presence of modified cells in the smear - dyskeratocytes and koilocytes.
- Detection of antibodies to HPV - helps to determine infection with the virus in the early stages. The disadvantage is that it is not possible to determine the concentration and type of virus.
- Histological examination is the examination of a sample of the affected tissue to determine the type of HPV and its oncogenicity.
Human papillomavirus – how to get tested?
Before the examination, even when issuing a referral, doctors tell the patient in detail how they take an HPV test in a particular case.
Depending on the methods and survey materials used, the algorithm for performing the analysis may differ. Direct preparation for the study is important.
Correct implementation of all points of preparatory measures allows you to obtain objective results of the analysis and eliminate the need for repetition.
Preparing for an HPV test
Before an HPV test, the patient must meet a number of conditions. In this case, the examination method and the type of material for analysis are of decisive importance. It serves as:
- blood;
- urine;
- a swab from the vagina or urethra.
Depending on the type of biological fluid being tested, the patient is given recommendations on how to prepare for the analysis the day before. The subject’s task is to fully follow the preparation rules. This will avoid receiving false results, and in some cases, false positives, when the result indicates the presence of HPV when it is not present.
Blood test for HPV
When talking about how an HPV test is performed, it should be noted that in most cases the patient’s blood is used for it.
The study is carried out on an empty stomach: 10–12 hours before the expected time of sampling, the patient is prohibited from eating; plain water without gas can be used as a drink.
2-3 days before the day of analysis, it is forbidden to drink alcoholic beverages, fatty and unhealthy foods. Only in this case, diagnosing HPV by blood will allow you to obtain accurate test results.
HPV smear test
This method is most often used to examine representatives of the fair sex. Before women are tested for HPV, they are prepared for this examination. The doctor introduces the patient in detail to all the rules of preparation. The following important points can be highlighted in this process:
- A smear is taken before starting a course of antibiotics or 2.5 weeks after the end of treatment.
- On the day of collection of the material, toileting of the external genitalia using chemical hygiene products is prohibited.
- It is forbidden to douche or insert vaginal suppositories.
- One day before collecting the material, you must abstain from sexual intercourse.
- It is ideal to take the test in the middle of the cycle; it is prohibited to conduct the study during the period of ovulation.
Decoding the HPV analysis
Only a doctor can correctly decipher the results of an HPV test. The specialist evaluates not only the quantitative value of the indicators, but also the clinical picture and possible signs of infection.
Getting a complete picture of what is happening helps to choose the right medications and choose effective treatment methods.
It is important to take into account the seriousness of timely diagnosis and treatment: as the patient ages, the risk of developing malignant tumors increases.
Quantitative HPV analysis
When an HPV test is carried out, quantitative analysis and decoding involves establishing the concentration of the virus at the time of the study. This helps determine the correct patient management tactics.
The real-time PCR (RT-PCR) method determines the amount of HPV DNA in the test sample.
This is necessary for continuous dynamic monitoring of a specific type of human papillomavirus.
However, even those who know about HPV analysis, what it is and how it is carried out, cannot independently decipher the results. This must be done in conjunction with an examination of the patient and other examinations. When assessing, experts adhere to the following interpretation of indicators:
- lg < 3 – the risk of developing dysplasia is low;
- lg 3–5 – clinically significant result, there is a risk of developing cervical dysplasia;
- lg > 5 – high probability of dysplasia, possibly the initial stage of the disease.
Qualitative HPV analysis
Analysis of HPV of high oncogenic risk is carried out using this technique. Helps identify HPV types 16 and 18.
These forms of the virus often cause genital cancer in women and squamous cell carcinoma, the appearance of genital warts, and cervical dysplasia. The detection efficiency of HPV DNA reaches 98%.
The conclusion assumes an answer indicating each type of virus. There are two possible results: detected/not detected.
Source: https://womanadvice.ru/vpch-analiz-chto-eto-takoe-komu-ego-naznachayut-kak-rasshifrovat-rezultat
What tests are taken for HPV and how to decipher the results of the studies
Many people associate the human papillomavirus with harmless warts on the skin of the hands, feet, or other parts of the body. A good immune system can cope with this problem on its own within 6–12 months.
But not everyone knows that HPV currently has about 170 types, which differ in symptoms, location and effect on the body.
Let's figure out what tests are needed to detect strains of the virus in the body, how to prepare for them, and how to decipher the results obtained.
What is HPV and when are tests prescribed to detect it?
The most serious danger to humans are strains of the virus that can cause cancer, the so-called high-oncogenic risk papillomaviruses. In 50% of cases when cervical cancer is diagnosed, the analysis contains markers of type 16, in 10% (which is also quite a lot) - type 18. These two types of HPV are rightfully considered the most dangerous.
The routes of transmission of the virus can be different - from household (through touch or water in the pool) to infection of the child during childbirth (if the mother has this disease).
But one of the most common ways of contracting HPV is through sexual contact, even such types as oral-genital and anal. This is explained by the fact that the mucous membranes are especially vulnerable to infections, since they do not have a stratum corneum.
By infecting the basal layer of the epithelium, the virus penetrates the body's cells. The further scenario for the development of the disease has two paths: HPV can exist outside the chromosome of a cell, or it can integrate into its genome, causing tissue degeneration.
Exposure to HPV, reduced immunity and the body’s inability to fight infection contribute to the appearance of genital warts (on the mucous membranes of the genitals or mouth) and warts, which can degenerate into malignant formations.
In many cases, HPV is present in the body without making its presence known. But there are a number of indications when it is necessary to be tested for the presence of a virus in the body:
- urogenital infections in acute or chronic form (papillomas, condylomas);
- infertility, miscarriages, pregnancy pathologies;
- having a sexual partner infected with HPV;
- preventive studies of the body.
As mentioned earlier, the human papillomavirus has many specific types. That is why there are several types of tests to detect the disease.
Note: At the moment, there are two types of HPV vaccines - one of them can protect the body from 2 oncogenic strains of the virus (16 and 18), the second from 4 (6, 11, 16 and 18). For the vaccine to work, a course of three vaccinations is required.
What test should I take to detect HPV?
An analysis for the human papillomavirus can show the presence or absence of the disease, and in some cases, accurately determine its type. Having received the results of the study, the doctor (gynecologist, urologist or dermatologist) will be able to develop the right strategy to combat the disease.
- Cytological method, or cytological smear. It belongs to the category of classic safe and simple methods, which allows you to determine the class of disease development. It has a number of disadvantages due to the high probability of error if the material is collected incorrectly and the results are interpreted (specificity of the analysis is 69%, the rate of false negative results is 5–40%).
- Colposcopy. This analysis is prescribed to women based on the results of a cytological examination, in case of suspected presence of altered squamous epithelial cells. Using a special microscope, the doctor examines the surface of the vagina and cervix to identify visible signs of the disease: genital warts.
- Histological method. If suspicious growths are detected on the walls of the vagina during colposcopy, the doctor has the opportunity to take a small sample of tissue for subsequent examination. This reveals the nature of cell changes and disruptions in their functioning.
- ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) . This study is based on studying the activity of the body's immune response to HPV. ELISA can be an additional analysis, but in itself it does not have a pronounced diagnostic value.
- Digene test (amplification) . One of the most modern, fast and accurate tests for HPV. It is carried out on the basis of a tissue sample obtained or scraping of cells from the vagina, cervical canal, or urethra. Shows the degree of oncogenicity of the virus and its concentration.
- PCR (non-amplification) . This research method can give a positive or negative answer to the question of the presence of HPV in the human body. The material for analysis is saliva, blood, vaginal discharge, etc. PCR can detect even hidden infections in the body.
Each patient who has been prescribed a test for human papillomavirus should know how to prepare for taking material for research.
Rules for preparing for biomaterial collection
There are a number of simple rules that a patient must follow to obtain accurate HPV test results.
Women need to know that during menstruation, as well as within 5 days before the start and 5 days after the end, the test cannot be taken.
The day before, you should not douche the vagina; on the recommendation of your doctor, you should stop taking antibiotics. Two days before the procedure, you must abstain from sexual intercourse.
If the biomaterial is samples of cells from the urethra, then at least 1.5–3 hours should pass after the last urination.
The procedure for collecting biomaterial does not take much time. A smear is taken using a cotton swab from the vagina in women and from the urethra in men.
Some types of tests may require a biopsy of the cervix - in this case, the doctor takes a sample of organ tissue with a special instrument.
The patient does not feel pain, because there are no pain receptors on the cervix. But some unpleasant sensations associated with contractions of the organ are possible.
The patient receives the results of the analysis on a special form, which indicates a positive or negative answer, or quantitative data indicating the degree of infection.
Figures and facts In 2008, the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Harold zur Hausen, a German scientist who proved that the human papillomavirus causes cervical cancer.
Interpretation of HPV test results
Many patients who have received test results for the human papillomavirus want to quickly find out whether they should seriously fear for their health or can they breathe easy? There are many options on the Internet for interpreting the results of various tests. It should be borne in mind that only the attending physician, based on the data obtained and general history, can make an accurate diagnosis.
The result of the cytological test is to determine the class of the disease, from 1st to 5th - as the danger increases. Class 1 means the absence of HPV cells in the analysis, class 5 indicates the presence of cells modified by the virus in large numbers.
The results of the Digene test are more difficult to decipher, because what matters here is the number of conventional units in which the ratio of the number of cells susceptible to HPV to the threshold value of the study is measured.
If the analysis is performed for the first time, then any value above the norm indicates a clinically significant number of infected cells in the body.
If the purpose of the study is to track the dynamics of treatment, then a decrease in value is a sign of recovery.
Due to the fact that the human papillomavirus can be in the body, but not manifest itself in any way, everyone who cares about their health needs to undergo regular preventive examinations.
The incubation period of the virus can last up to several years, and only then does the active phase begin. Early detection of the disease is a chance to begin treatment faster and avoid many of the negative consequences of HPV.
Source: https://www.eg.ru/digest/analiz-na-virus-papillomy-cheloveka.html