Papillomas on the chest, as one of the manifestations of human papillomavirus infection, do not cause oncological alertness, but cause a lot of inconvenience and aesthetic discomfort. For pregnant and lactating women, the issue of treatment and removal of growths is especially acute. In addition, the problem of recurrence of tumors adds difficulties in the fight.
Papillomas growing in the ducts of the mammary glands, on the nipple and breast have a completely different prognosis and approach to diagnosis and treatment. This type of neoplasm is regarded by some experts as a precancerous condition.
Types of papillomas on the chest and the reasons for their appearance
The clinical manifestations of cutaneous human papillomavirus infection are varied, and the breast is no exception. On the skin of the mammary glands, papillomas are located in various places and are provoked by several factors. Localization and growth factors of viral formations on the skin of the chest:
- Papillomas under the breasts bother patients most often. The main factor that provokes the growth of warts under the mammary glands is intense sweating. In obese people, the number of growths can be very large. Their growth is especially common in diabetes mellitus combined with obesity. Weight gain during pregnancy also contributes to the appearance of elements.
- Papillomas on the nipple are rare and are mainly localized on the skin of the areola. Microtrauma to the skin of the nipple, for example, when feeding a child, contributes to the introduction of the virus and the growth of the tumor.
- Warts on the chest tend to grow when wearing tight underwear and clothing.
Types of growths on the chest:
- Filiform warts are usually located under the breasts.
- Flat tumors grow both on the skin of the breast and in the nipple area.
Warts vulgaris rarely affect the breasts. The initiator of the growth of these elements of any localization is human papillomaviruses. HPVs are ubiquitous, but they don't cause warts in every person.
HPV enters the human body only through contact from a sick person. For the virus to penetrate, there must be trauma and damage to the skin (diaper rash, maceration). Activation of a viral infection occurs with a decrease in immune strength.
Indirectly, the state of immunity can be judged by the number of growths: if there are many of them, then this is evidence of insufficient work of the antiviral link. As a rule, single papillomas on the chest regress on their own several months or 1.5-2 years after their appearance.
The reasons for the growth of papillomas on the chest also lie in decreased immunity:
- Pregnancy is one of the leading causes of the growth of warts on the chest. Natural physiological suppression of all parts of the immune system during gestation leads to the primary appearance or spread of papillomatosis that already existed before conception.
- Diseases accompanied by suppression of the body's resistance:
- diabetes;
- chronic infectious diseases (viral hepatitis, streptococcal infections, tuberculosis);
- alcoholism;
- herpes virus infections (recurrent herpes simplex, cytomegalovirus infection, infectious mononucleosis).
The appearance of papillomas on the chest is promoted by malignant neoplasms of any location, as well as radiation therapy, especially carried out in the chest area. In this case, human papillomavirus infection is widespread and affects a large area of the skin.
Intraductal papillomas of the mammary glands
intraductal papilloma
The insidiousness of this disease lies in the absence of specific symptoms. Common breast lesions such as fibroadenoma, cystic formations, intraductal papilloma and breast cancer can manifest in exactly the same way.
Symptoms:
- The presence of bloody, bloody discharge from the nipple. The discharge may turn black.
- The presence of a palpable round formation in the chest.
- Painful sensations when pressed.
The reasons for the growth of such elements are not only problems with the woman’s immunity, but also a number of other factors:
- Burdened hereditary history.
- Conditions associated with increased estrogen production (polycystic ovary syndrome, obesity, endometriosis).
- Early puberty and late menopause.
| Diagnostic plan for suspected intraductal papilloma | |
| 1 | Mammography |
| 2 | Ultrasound |
| 3 | MRI |
| 4 | Blood test for the presence of mutations of the BRSA1, BRSA2 genes. |
| 5 | Tissue biopsy with immunohistochemical analysis and FISH test. |
| 6 | Ductography. |
| 7 | Cytological examination of nipple discharge. |
Treatment is carried out exclusively surgically. The scope of the operation is determined individually. In some cases, sectoral removal is performed, but sometimes the entire gland has to be removed, since intraductal papilloma is considered a precancerous condition. Treatment can be supplemented with radiation therapy, immunostimulants and cytostatics.
Every woman should perform breast self-examination at the beginning of her menstrual cycle. After 35 years, preventive mammography and ultrasound are required.
Mammography will detect formations up to 1 cm in size, which is impossible with ultrasound examination of the mammary glands.
Modern screening methods will make it possible to determine the malignancy of a tumor in the early stages and save the patient’s life.
Methods for treating and removing papillomas on the chest
breast papillomatosis
Removal of a viral tumor is carried out at the request of the woman or according to medical prescription. Papilloma on the chest requires complex treatment: getting rid of unwanted elements is carried out in parallel with drug support to prevent relapse.
In what cases is breast papillomas removed?
- Multiple warts on the skin of the mammary glands.
- Papilloma on the nipple during pregnancy must also be removed, since breastfeeding can infect the baby with HPV.
- Papillomas under the breasts in obesity tend to spread and can cause severe discomfort to a woman, so doctors recommend getting rid of such growths.
Considering the connection between cutaneous papillomatosis and the activation of the virus in the body, in parallel with getting rid of warts, drug correction of immunity is carried out using interferon inducers. A single papilloma on the chest does not require the use of immunomodulators.
Methods for getting rid of growths are divided into chemical and physical (cryodestruction, radio wave and laser removal). Electrocoagulation to get rid of unwanted elements on the nipples is not used in modern dermatology due to scarring after the procedure.
Chemical method for removing warts on the skin of the mammary glands
photo of flat papillomas on the chest
Substances for removing warts based on acids and phenol can be used both independently and in a clinic. Women can cauterize individual elements themselves. The exception is the skin of the nipples. Removal of papillomas on the nipples is carried out only by physical methods.
Papillomas under the breasts are not removed using phenol-based drugs. Their use is contraindicated in skin folds due to the risk of burns. All chemicals are applied exclusively to the wart, since the concentration of active substances is very high.
It is possible to remove growths during pregnancy using a chemical method. The drugs are applied topically and do not affect the developing fetus.
After removing the tumor, the lesions are treated with alcohol. If one course of treatment does not lead to the expected result, then repeated removal is carried out after a month. Scar formation is not typical.
Physical methods for removing warts in the chest area
- Cryodestruction .
Getting rid of multiple warts using liquid nitrogen requires several treatments at intervals of several weeks. A single wart is removed in one step. Liquid nitrogen is applied to the elements within 1 minute. The most accurate application is achievable only when using special equipment. If cryodestruction is carried out with an applicator or a cotton swab, then in such cases areas of healthy skin are often affected, which significantly delays the healing process. Depending on the area of the lesion, healing lasts from 4 to 8 weeks. The process of exposing a large number of warts to low temperatures requires local anesthesia. When removing single formations with liquid nitrogen, scars do not form. - Laser removal.
Most often, carbon dioxide laser is used, which is the most effective way to get rid of viral tumors on the skin. The method requires pain relief by subcutaneous injection of an anesthetic. The session lasts from 5 to 20 minutes. As a rule, laser excision of papilloma on the chest is carried out in one procedure. Repeat sessions are extremely rarely required. After removal, a crust forms, which disappears after 2-2.5 weeks. Healing lasts on average 1-3 weeks, and if the papilloma is localized on the skin of the nipples, this period is extended. Cryodestruction and laser methods for removing viral formations of the skin of the nipples and breasts during pregnancy are preferable. - Radio wave method.
Removal of viral tumors on the skin of the chest using low-frequency radio waves is characterized by maximum accuracy and low trauma. The effect does not involve the use of high temperatures, so a burn scab does not form, which accelerates the rate of healing. The procedure lasts from 10 minutes to half an hour and requires local anesthesia. This method is prohibited during pregnancy. A removed papilloma under the breast is characterized by prolonged healing due to difficult aeration and constant friction of clothing and linen. Therefore, using the radio wave method to get rid of warts under the mammary glands is the most effective. For the same reasons, this method is preferable for excision of growth on the skin of the nipples.
Antiviral drugs and immunomodulators
Removal of the tumor by physical method is carried out on the 3-5th day of taking the immunomodulatory drug.
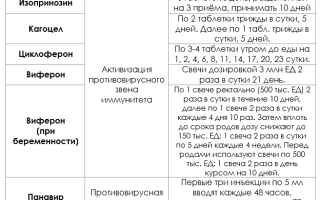
The main means for correcting immunity when getting rid of warts are interferon inducers (Isoprinosine, Kagocel, etc.) and human interferon preparations (Viferon, Genferon, etc.)
Regimen for taking immunomodulators and antiviral drugs in the treatment of breast papillomas
In case of extensive damage to the skin, antiviral drugs for systemic use (Panavir) are prescribed. Also, according to the doctor’s decision, such products can be used topically in the form of a gel or cream (Panavir, Vartotsid, Aldara). Local antiviral medications are not used during pregnancy and in persons under 18 years of age.
For the speedy healing of affected lesions after removal, it is recommended not to take a general bath, not to sunbathe, and to change bandages regularly. After treating the wound and changing the bandage, you should thoroughly wash your hands with soap to prevent the spread of the virus to healthy areas of the skin.
Source: https://vysypanie.ru/herpes/papillomy/papillomy-na-grudi-prichiny-vozmozhnaya-opasnost-i-sposoby-lecheniya.html
Papillomas on the chest: treatment methods and causes of appearance
Breast papilloma is a benign neoplasm caused by HPV, which is localized on the mammary gland on the skin and in the ducts. Usually the growth is white and does not cause pain. But when the virus becomes active, the papilloma can begin to grow rapidly, causing discomfort in the woman.
Content
Are papillomas on the chest dangerous?
What to do if you notice changes and unpleasant symptoms? Growths can grow not only on the surface of the epidermis, but also inside the gland ducts. It is impossible to detect them in a timely manner through visual inspection. It is recommended to periodically conduct breast examinations to identify abnormalities and neoplasms.
The presence of a growth inside the mammary gland is indicated by a painful round nodule that is felt when pressed. Such neoplasms are found in large ducts near the nipple and in the area of the areola.
Papilloma on the chest can have different appearances and colors:
- dark brown to flesh-colored wart;
- thick base with soft round growth;
- a group of small “papillae” or single ones;
- growths of different diameters, attached to the skin with a thin stalk.
The location may also vary. Neoplasms grow on the side of the mammary gland, are observed under or above the breast, on the nipple and inside.
At the first signs of the presence of a virus, consult a doctor who will diagnose, identify the strain, and prescribe appropriate treatment, including breast papillomas.
It is important to do this quickly if you notice dangerous changes:
- discharge from the nipple mixed with blood;
- changes in the density and structure of the growth;
- external changes in color, diameter;
- the appearance of pain at the site and throughout the mammary gland;
- increased nipple sensitivity.
We recommend reading:
- Papillomas on the nipple
- Removal of papillomas during pregnancy
- Cervical papilloma
Causes of skin growths in the chest area
The appearance of papillomas on the chest can be caused by various factors. Most often they begin to grow during pregnancy. The culprits are hormonal changes in the body. Over the 9 months of bearing a child, the immune system weakens and cannot resist infections. Papilloma occurs during pregnancy. During this period, you should observe her without resorting to radical treatment, which could affect the baby.
Growths begin to appear as a result of:
- neglect of hygiene standards;
- physical injuries to the chest;
- wearing uncomfortable, tight clothing for a long time;
- the appearance of microcracks in the nipples and between the mammary glands;
- polycystic ovarian dysfunction;
- increased work of the sebaceous glands;
- taking oral contraceptives;
- menopause;
- stress;
- period of puberty.
There are many reasons for the development of abnormal epithelial growth; to identify them, you must consult a doctor. For successful treatment of papilloma under the breast, it is important to use surgical techniques, take medications, and eliminate the provoking factor.
The growths appear due to a weakening of the immune system; patients need its strengthening and stimulation. After this, you can plan how to remove the growth.
It is worth noting that if there are neoplasms, you can breastfeed the baby if this does not cause discomfort to the woman.
Diagnosis of occurrence
The extent to which the treatment of papilloma that has arisen in the breast will be successful, and the patient will be able to completely get rid of all tumors, depends on the timeliness of diagnosis. Experts warn that the longer the growth remains in the chest or on its surface, the faster it will multiply and affect the healthy tissue around it.
To undergo an examination to identify the cause of papilloma under the breast, you need to contact a mammologist.
Diagnosing papilloma inside the duct is not difficult; it is enough to use an ultrasound machine or perform a mammogram. X-ray examination is considered one of the effective methods for identifying nodules in the chest cavity. Thanks to it, you can confirm the presence of skin growths, accurately determine their diameter and location.
The woman must have a blood test taken. It will help identify the strain of papilloma on the chest. This step is important to rule out oncology and not waste time that could cost your life.
Locations
Neoplasms are localized on:
- nipples and halos;
- in the area under the breast;
- in the milk ducts.
Many papillomas on the nipples indicate a weakened body. They may cause discomfort when wearing underwear or not be felt at all.
The occurrence of such growths is also caused by disruption of internal organs or prolonged use of antibiotics.
Papillomas under the breasts in most cases cause pain.
Regular friction with clothing, underwear, sweat, and lack of air circulation leads to permanent injury. The situation is aggravated by poor hygiene and excessive sweating.
Intraductal papillomas are difficult to identify by visual examination. They require the use of special equipment. When they grow, they can be felt by carefully palpating the chest. There may also be clear discharge from the nipples, sometimes with blood clots.
How are skin tumors treated?
All growths must be removed surgically. This measure is mandatory and helps eliminate the risk of cells degenerating into cancerous ones. It is prohibited to get rid of growths on your own. If the head becomes detached from the stem, serious complications may occur.
Manipulations to remove papillomas on the nipple, neck and under the breast should be carried out by a specialist using modern equipment.
- Laser technology is widely used for elimination. It is safe for health, does not cause pain and does not require a long recovery period. After treatment, there are no scars or marks left on the skin of the neck and other areas.
- To accurately eliminate the manifestations of papillomavirus, the electrocoagulation method is also used. It is based on the use of high-frequency electric current, which cuts out the growth and seals the treatment site, preventing bleeding.
- Flat growths are eliminated using liquid nitrogen, which burns the formation to the base without scars or scars.
- Radiosurgery is a popular modern method. To cut small papillomas and large neoplasms, a special scalpel is used that emits radio waves, which allows you to carefully, quickly and painlessly get rid of the papillomas that have appeared. At the same time, the incision is cauterized, which eliminates bleeding and further relapses of the disease in this area.
- The endoscopic method is used to remove skin lesions on the chest and intraductal nodules. The surgeon makes incisions along the areola and inserts an endoscope, which allows you to monitor every movement and remove the papilloma inside or under the breast in women without unnecessary trauma. The material removed during the operation is sent for histological examination.
Is it possible to remove papillomas on the chest using these methods only? These methods are not used independently, since it is important to undergo a course of drug treatment as a supplement. This will help put the virus into a calm state and prevent relapse.
At the first symptoms of HPV, contact a medical facility. Only a qualified doctor knows how to remove and treat papilloma on the delicate skin of the chest in each specific case.
Remember that there are life-threatening strains that cannot be neutralized by traditional methods.
It is possible to remove papillomas and eliminate the virus in a short time if you undergo the appropriate studies and adhere to the planned treatment plan.
The article has been verified by the editors Link to the main publication (2
Source: https://CoriumMed.ru/papillomy/tipy/papilloma-na-grudi.html
Papillomas on the chest and in the milk ducts
Papillomas on the chest occur almost as often as on the body. Moreover, the favorite place for their formation is the folds under the breast. But in addition to damage to the epidermis above the mammary gland, they often form in the areola area, on the nipple, and even inside the ducts.
This localization causes anxiety, pain and requires special attention, especially during pregnancy and breastfeeding. At the same time, the possibility of the growths degenerating into a malignant tumor cannot be ruled out, so they must be treated in a timely manner.
How to get rid of papillomas on the mammary glands?
Papillomatosis – what is it?
A disease characterized by the appearance of papillomas, warts, and condylomas is called papillomatosis. The cause of its occurrence is the human papillomavirus, which penetrates epithelial cells and causes their rapid growth. This is a side effect of the virus multiplying because in order to replicate, it inserts itself into the genome, changing its structure.
The prevalence of papillomatosis is very high; the human papilloma virus infects most of the world's population. It has been revealed that there are different types of HPV, some of them develop only on the skin, others can also affect mucous membranes.
Infection occurs through household contact and sexual contact. Once on the skin and mucous membranes, HPV penetrates the epidermis through small wounds and microcracks. You can become infected even by shaking hands or using handrails on public transport.
Children can become infected from their parents and transmit the virus to other children by playing with them in kindergarten.
Papilloma on the chest of a young mother is a very dangerous localization, since during feeding the virus can pass to the child.
Why do papillomas appear on the nipples?
If such a large number of people are infected with the virus, then why doesn’t it manifest itself in everyone? This is explained by the fact that a person’s increased immune status prevents the virus from quietly multiplying and spreading. Some people develop 1-2 warts or papillomas, which may disappear over time, while for others they constantly appear in different places, covering more and more new areas.
Growths on the chest may appear due to:
- transfer from other areas of the skin;
- infections during lovemaking;
- using someone else's underwear, towel, breast pump;
- while feeding the baby.
Infection in baths and saunas is also possible. Moreover, papillomas most often occur under the breasts. This is the most favorable place for their development. Increased humidity promotes growth and spread.
The area of the areola and nipple is also quite often affected by HPV. This is due to the fact that the skin in this area is more delicate, microcracks appear on it, and in the presence of discharge from the ducts, even more favorable conditions are created for the spread of papillomavirus.
The ducts of the mammary gland are lined with epithelium, so papillomas can also be found in the breast. They are difficult to diagnose on their own, but they require mandatory treatment, as they can develop into a cancerous tumor.
Papillomatosis occurs against the background of reduced immunity, which can lead to:
- chronic infectious diseases;
- smoking and drinking alcohol;
- unhealthy diet (diet, fasting);
- endocrine diseases;
- hormonal imbalances;
- pregnancy;
- stress, depression;
- use of antibiotics;
- vitamin deficiencies.
Papillomas appear after infection after 3-6 months, the intensity of their manifestation depends on the general condition of the body and immunity.
Clinical picture
Neoplasms can appear on the skin in any part of the body. Papilloma under the breast is detected by palpation. It is usually flesh-colored or light brown and often has a stalk. It can become inflamed and painful due to irritation and friction. Such papillomas quickly spread throughout the skin under the breasts and under the arms.
If the formation is located in the area of the areola or nipples, then it causes pain, increased sensitivity, and burning. Intraductal papillomas are more difficult to identify; this requires instrumental examination of the mammary glands.
Upon palpation, a lump can be detected; it is usually located near the nipple. There may be discharge from the mammary gland. They are usually light, whitish, but if they become yellow-green or pink, you should immediately consult a doctor, as this indicates an inflammatory process or degeneration.
How to make a diagnosis
The papilloma virus can be detected using special tests that detect specific antibodies produced by the body against the virus. They can be used to determine the type of virus; this is important, since some strains are highly oncogenic.
Examination of the mammary gland ducts is carried out by:
- ultrasound examination;
- mammography;
- galactography;
- ductography;
- cytological studies of nipple discharge.
Therapy methods
Treatment of papillomas that affect the area of the breast or mammary ducts is carried out using both conservative and surgical methods. Intraductal formations can only be removed surgically. Under anesthesia, a small incision is made, the duct is opened and the growths are excised.
To remove tumors from other locations, use:
- laser therapy – the wound heals within 1-2 weeks, leaving an invisible scar;
- diathermocoagulation is a painless, effective procedure, but after it a small scar may remain;
- cryodestruction – removal using liquid nitrogen;
- Radio wave therapy is an expensive procedure, but it is very effective and does not leave scars.
At home, to get rid of papillomas, you can use the following drugs: Super Celandine, Cryopharma, lapis containing silver nitrate. It is useful to simultaneously take antiviral medications, immunomodulators, and use traditional methods of increasing immunity.
It is necessary to remove formations located under the mammary gland with caution; it is advisable to do this in the clinic, since sequential removal can cause pain, and if the breast is large, heavy, or excessive sweating, then suppuration of the wound may occur.
Features during pregnancy
Papillomas often occur during pregnancy, even in apparently healthy women. The fact is that pregnancy causes a decrease in immune status, this is a normal condition, and it is necessary for the fetus to implant and develop in the uterus.
In addition, favorable conditions are created for HPV, since the mammary glands are prepared for feeding, grow, and colostrum is released drop by drop. Breasts and nipples become more sensitive, swell, and microcracks may form.
If papilloma occurs on the chest during pregnancy, you should consult a doctor; he will prescribe antiviral ointments that will prevent the growth of the formation. Removal is possible only after childbirth.
Treatment of formations on the nipples and breasts is not always necessary: the decrease in immunity during pregnancy is temporary, the woman’s immune status is gradually restored, and papillomas can disappear as quickly as they appeared. But consultation with a doctor is still required to exclude the development of a malignant neoplasm.
Folk recipes
Removal of papillomas can also be carried out using folk remedies, for example, the juice of medicinal plants (celandine, dandelion), but they should not be used in the folds under the breasts.
You can lubricate the formations with castor oil or specially prepared solutions. For example, an infusion of green walnuts on kerosene, which is kept in a dark place for 3 weeks, or an infusion of onion peels.
You can also wipe the affected areas with an alcoholic infusion of dandelion flowers.
To increase immunity, decoctions of medicinal herbs (plantain, sage, immortelle, chamomile), mixtures of honey with walnuts, lemon, and dried apricots are used. Proper healthy nutrition has a good effect on stimulating the immune system.
It is recommended to use beef liver, eggs, seafood, fresh herbs, lactic acid products, and seasonings in the diet. You need to watch your weight, exercise, get enough sleep, and avoid stress.
At your request they are also reading:
Source: https://opapillome.ru/vidyi-papillom/papilloma-na-grudi.html
Papillomas on the neck and under the breasts
The human papillomavirus is one of the insidious and dangerous diseases that affects the human body. The insidiousness of the disease lies in the fact that even after the virus has penetrated the body, it may not show its aggressiveness for a long time and “wake up” under certain conditions.
Activation of the virus provokes the appearance of growths on human skin, which can appear on any part of the body. Papillomas under the breast are especially dangerous, which significantly increases the risk of their degeneration into a malignant formation.
Papillomas under the breasts are benign neoplasms that consist of epithelial cells of the excretory ducts. Women of reproductive age, as well as those who take contraceptives or hormonal medications for a long time, are at risk for developing this condition.
The presence of papilloma under the breasts in women always causes concern and is the main reason for visiting a mammologist. Experts in the field of oncology, papillomas under the breasts are often classified as precancerous conditions, especially in cases where, in addition to the growth itself, nodes or discharge from the nipples are felt on the mammary glands.
Penetrating into human blood plasma, this virus infects internal organs and external epithelium, causing the development of skin outgrowths. The incubation period for HPV ranges from 2 to 24 months, and during this time the insidious disease may not show signs of its existence.
The reasons for its active growth in the area of the mammary glands can be various factors affecting the human body both from the inside and from the outside. The first group of internal causes of papillomas between and under the breasts includes:
- Changes in the functioning of the endocrine system (hormonal fluctuations in adolescents, women during menopause or pregnancy).
- Decreased immune defense of the body.
- Presence of concomitant diseases (obesity, diabetes).
Appearance
Papillomas under the breasts, if you look at the photo of the problem, can often be confused with birthmarks. In shape and color, such formations do have a certain similarity, but if we talk specifically about the consequences of exposure to HPV, then the formation is attached to the skin with the help of a small stalk.
This is the first sign by which birthmarks can be distinguished from such formations. Benign growths have a light brown color, can reach different sizes, be flat, oblong, round, or have non-standard shapes.
If we talk about mammary gland papillomas, they most often appear in the following areas:
- on or around the nipples;
- under the breasts, where the greatest skin friction occurs;
- in the ducts of the mammary glands.
Internal breast papillomas are slightly less common than external ones; in order for the virus to leave its signs on the skin in this particular area, a woman needs to encounter some kind of provoking factor, and there are many of them and it would be worth knowing more about each of them.
Pathogenesis
The surface of the body, unfortunately, does not remain soft and velvety throughout life. The skin is especially susceptible to changes in those areas where there are folds, high humidity and friction from linen and clothing.
The etiology of the growths is different, although to a non-specialist they seem similar in appearance. Types of skin tumors under the breast:
- manifestations of human papillomavirus (HPV);
- basal cell papilloma;
- verrucous nevus;
- seborrheic keratoma;
- atypical nevus;
- acrochordon.
The appearance of papilloma under the breast is the result of epidermal proliferation of the epidermis. This is how viral dermatoses, developmental defects, benign and malignant skin lesions manifest themselves. The nodules are soft, pedunculated or broad-based, similar to a thread or mushroom.
The word “papilloma” itself means “papilla”. They get rid of benign tumors under the breasts not for medical reasons, but for aesthetic reasons. Proper skin care before and after removal of papillomas is very important, especially in areas of folds and increased sweating. External factors:
- Wearing uncomfortable tight underwear.
- Failure to comply with hygiene standards for skin care.
- Hyperactivity of sweat and sebaceous glands.
Constant friction with clothing, lack of air circulation and accumulation of sweat in the folds of skin under the breasts create favorable conditions for the active growth of virus cells. Accidental mechanical damage and microtrauma can provoke the transformation of benign growths into malignant tumors, so it is important to pay special attention to the fight against a dangerous disease.
Risk factors
The occurrence of papilloma can be caused by a combination of one or more reasons that provoke hormonal imbalance in women of different ages:
- Puberty;
- Menopause;
- Pregnancy;
- Long-term use of hormonal contraceptives;
- Obesity;
- Problems with the ovaries (dysfunction, polycystic disease);
- Experienced stress.
Any of these factors not only affects the production of female hormones, but also leads to a weakened immune system. This increases the risk of contracting HPV. Wearing tight, uncomfortable clothing and frequent visits to public baths and swimming pools are also causes of infection.
Benign formations under the mammary glands are such a common occurrence that many women do not even pay special attention to this and, as it turned out, in vain.
It is this location that becomes the reason for suspicion of the presence of cancer.
Papillomas in the chest area very often degenerate into malignant tumors, which is no longer anything good.
The following factors can lead to such consequences from the human papillomavirus in a woman:
- wearing underwear that is too tight, which gradually chafes;
- long-term use of antibiotics or other potent pharmaceutical drugs;
- unprotected sexual contact;
- excessive sweating of the skin under the breasts;
- the presence of minor injuries during the period when a woman is breastfeeding;
- lack of vitamins and other useful microelements in the body;
- hormonal instability;
- frequent presence of stressful situations in the life of a female representative.
You can become infected with breast papillomas even completely accidentally if you injure the skin and do not treat the wound. In this case, the virus will be able to freely enter the body, wait for the moment of its exhaustion, and bring such consequences.
Localization
The most “popular” places in the chest area where papillomas appear.
The area under the mammary glands is often subject to friction, lacks normal ventilation and produces a large amount of sweat.
All these are excellent conditions for the development of the virus. Papilloma under the breasts can occur as a result of wearing tight underwear or ignoring simple rules of personal hygiene.
Warts on the sternum appear in women with a weak immune system. If the beard does not come into contact with the underwear, then it is not injured and does not cause severe discomfort.
On the chest
Papillomas on the chest can occur for internal and external reasons. In the first case, formations are formed as a result of mastopathy. During such a disease, the milk ducts are dilated, which leads to disruption of the epithelial structure.
REFERENCE. Infection can occur during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
At this time, a complete hormonal change in the body is observed. Sometimes the infection penetrates through microcracks or the child’s bite site.
Neoplasms are localized on:
- nipples and halos;
- in the area under the breast;
- in the milk ducts.
Many papillomas on the nipples indicate a weakened body. They may cause discomfort when wearing underwear or not be felt at all. The occurrence of such growths is also caused by disruption of internal organs or prolonged use of antibiotics.
Intraductal papillomas are difficult to identify by visual examination. They require the use of special equipment. When they grow, they can be felt by carefully palpating the chest. There may also be clear discharge from the nipples, sometimes with blood clots.
Breast diseases
Benign refers to a neoplasm that appears as a result of a failure in the processes of cell division and growth.
Their main feature is their slow growth and lack of aggressiveness: in this case, metastases do not form, the tumor itself is limited to damage to one organ.
Depending on the structural features and origin, the following types of benign breast tumors are distinguished:
- Fibroadenoma is a breast tumor that is formed from fibrous tissue of the gland.
- Intraductal papilloma is a tumor growing inside the gland and is characterized by the appearance of formations (papillomas) of connective tissue containing blood vessels.
- Lipoma is a benign breast tumor that forms from adipose tissue. It has a round shape and soft consistency. These tumors reach large sizes.
First of all, we are talking about intraductal papilloma in the chest area. Synonyms: Mintz disease, bleeding mammary gland, intraductal papilloma. The tumor can reach several centimeters and is located in the lumen of the duct.
The danger of the disease is that papilloma is an obligate precancer that requires surgical treatment. One form of the disease is cystadenopapilloma. The tumor originates from the milk ducts, outwardly it looks like papillae located in the dilated duct; similar growths can be found in a mammary gland cyst.
This disease is classified as mastopathy. The first and important symptom is pathological discharge from the nipple. They may be whitish, bloody, or greenish. In some cases, the patient herself detects the tumor by palpation. Typically, the tumor is localized in the peripapillary zone.
Additionally, ultrasound and mammography are performed. The methods do not allow one to accurately differentiate the disease, but they make it possible to distinguish it from other pathologies. The method of ductography, or galactography, has great informative value.
A contrast agent is injected into the duct, after which pictures are taken in two projections. The method makes it possible to assess the location of the tumor, since MRI and mammography do not have such capabilities.
Ductography is indicated only for those women who complain of brownish, green or bloody, whitish discharge from the nipples. In nulliparous women, discharge from both glands may indicate a side effect of hormonal drugs or a pathology of the pituitary system.
Many female representatives are actively trying to eliminate a problem of this nature on their own, at home. Women use aggressive methods to burn out warts, but they cannot achieve long-term results. That is why you should not waste time self-medicating, further aggravating the situation, but it is better to immediately go to an experienced doctor.
A medical specialist, if the formation turns out to be benign, will be able to offer his patient the following ways to eliminate the problem:
- surgical excision of papillomas on the chest or under the breast;
- correction using laser or liquid nitrogen;
- antiviral therapy with drugs.
Many patients are inclined to believe that it is best to deal with the problem through the mediation of a laser. This process is truly as fast, comfortable, painless, and does not leave scars.
Modern pharmacological companies are actively engaged in the production of medications that are aimed at combating the human papillomavirus.
The drugs are available in the form of tablets, injection solutions, ointments and creams, gels and sprays, and patches.
How to get rid of papillomas under the breasts cannot be determined on your own, and if the problem is internal, then the woman is even more powerless.
An unpleasant disease can strike an absolutely healthy person at any time, but therapeutic measures almost always produce positive results.
If the problem is neglected, the woman runs the risk of facing cancer, and then she will greatly regret that she did not go for an examination in a timely manner.
Papillomas under the breasts can appear in women of any age, but this situation should not be made into a real tragedy.
Modern medicine has in stock a lot of good techniques and drugs that will definitely help cope with papillomas and restore health.
First of all, it is worth getting rid of the virus itself, and then you can take other therapeutic measures aimed at correcting the consequences of HPV activity. If you start solving a problematic situation in a timely manner, then the issue will definitely be resolved positively, as time and the experience of many people have already proven.
Forms of papillomas
Three types of growths can appear in the chest area: thread-like - appear with age, although they can occur under the influence of hormonal imbalances and excess weight, during pregnancy, diabetes and menopause. They grow up to four centimeters.
They are also called keratomes; flat in shape - appear most often in childhood and adolescence, have a pale color, and disappear with age under the influence of changes in hormonal balance. Removing papillomas under the mammary glands on your own can have negative consequences and is therefore undesirable.
The virus easily enters the blood, the growths begin to multiply and increase in size at high speed. You should be careful not to accidentally injure the warts, which is very easy to do in this area.
Benign breast tumors - classification
Only certain types of warts appear on the chest: flat, senile and filiform. Flat warts. Such neoplasms occur most often in children, adolescents and young adults. In shape they resemble a mole, but differ in flesh-colored or yellowish color.
The appearance of this type of wart most often becomes possible after forty years. The round, protruding or flat shape of the neoplasm resembles a mole, but unlike a mole, it is devoid of pigmentation. This is the only type of wart that is not viral in origin.
The neoplasm is a skin growth - a keratoma. The danger of such an anomaly is that it can be either benign or malignant. Filiform warts. In shape, such formations resemble pointed growths up to four centimeters long.
The occurrence of such warts is closely related to the hormonal levels of the body. Filiform warts under the breast are dangerous due to the frequent risk of injury, which results in further spread of the disease and an increase in the size of the tumors.
Routes of infection
- Sexual.
About half or more of patients become infected through this route;
- Household: through clothes, towels, dishes, shoes, any hygiene products;
- Public places: gyms, handles in transport, water parks, baths, solariums, swimming pools;
- Infection of a child from the mother;
- Through saliva during a kiss.
It is known that the human papillomavirus is considered more dangerous for the female half of the population. Certain types of the virus with a high oncological risk can cause cervical cancer, the formation of papillomas inside the mammary ducts, and papillomas under the breasts.
Some types of papillomas protrude above the surface of the body, for example, on the nipples in the chest area, in the armpit, on the neck, causing great inconvenience for women, constantly being injured. The color of papillomas ranges from pink to dark brown.
Source: https://5059696.ru/blog/papillomy-na-shee-i-pod-grudyu/