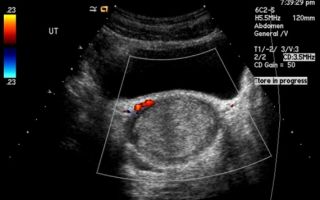
Nowadays, the most popular diagnostic method is ultrasound. It allows you to quickly, accurately and without harmful consequences determine the disease in the initial phase of development.
When analyzing the condition of the genitourinary system in men and women, transabdominal ultrasound is widely used.
Let's consider what this procedure is, what pathologies can be detected with its help, how wide the scope of its application is, and whether special preparation is required before it is performed.
Preparing for a transabdominal ultrasound
The prescribed procedure does not require long preliminary preparation. 60 minutes before the start you need to drink at least half a liter of liquid.
A full bubble will act as a kind of screen and create good conductivity for sound. In this case, the intestines shift and the necessary organs become visible.
Another condition is the elimination for several days of foods that lead to increased gas production.
For what symptoms is it prescribed for women and men?
Abdominal ultrasound of the pelvic organs is prescribed for diseases of organs located in the peritoneum; in women, these are the uterus and its appendages, and in men, the prostate.
The reasons for prescribing a transabdominal ultrasound examination in women will be:
- conception that occurred outside the uterus, stopped pregnancy;
- adhesions (after abdominal surgery);
- tumor formations (fibroids, cysts and polyps) - examined at the beginning of the cycle (first 10 days);
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes (additional studies will be needed);
- endometritis – inflammation of the uterine mucosa (examined twice: in the first and second phases);
- inflammatory processes in the appendages;
- adenomyosis (gynecological ultrasound is performed in the second phase);
- endometriosis (detection even after childbirth) - the presence of benign nodes, best visualized in the second phase of the cycle;
- fluid formation in the fallopian tubes, which leads to their inflammation;
- fluid in the pelvis that does not go away for a month or more;
- polycystic disease - hormonal imbalance, leading to cycle disruption, increased hair growth, obesity;
- multifollicularity – excessive monthly maturation of follicles;
- reproductive function disorders of various origins.
Men, no less often than women, suffer from various diseases of the genitourinary system, but, unlike the fair half, they usually do not rush to the hospital. They can be sent for both a transabdominal examination and TRUS - a method primarily for studying the prostate, the manipule is inserted anally.
Indications for visiting the ultrasound room will be:
- erectile dysfunction;
- suspicious discharge or blood from the urinary canal;
- pain in the groin area;
- discomfort in the scrotum;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- disturbances in the functioning of the organs of the reproductive system;
- diseases of an infectious nature.
What is transabdominal ultrasound
Transabdominal ultrasound is a diagnostic method that involves the penetration of ultrasound waves through the anterior wall of the peritoneum using a manipulator to analyze the condition of internal organs.
The work uses the effect of ultrasound reflection from obstacles, that is, the inverse piezoelectric effect. Some of the reflected waves return to the device’s sensor, where they are converted into electrical signals.
They are processed by the device and displayed on the screen as a black and white image.
During the procedure, the sensor is located on the surface of the anterior abdominal wall, which makes it possible to study the contents of the abdominal cavity and organs located in close proximity to it. To obtain the most objective results, the process uses linear or convex sensors with a frequency of 3.5 to 7.5 MHz.
Typically, transvaginal ultrasound is not performed independently, but is combined with alternative diagnostic techniques: bimanual palpation, other forms of ultrasound (for example, transvaginal or, less commonly, transrectal), MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), laparoscopy.
Contraindications
Despite the safety of the examination method, there are cases in which ultrasound scanning cannot be performed. It is contraindicated for HIV (human immunodeficiency virus), open wounds, ulcers, viral hepatitis and fistulas.
How to carry out the procedure
The examination procedure is the same for everyone. The patient lies on the couch either on his back or on his side. A special gel is applied to the skin in the area to be examined. By eliminating air between the device's sensor and human skin, the signal will be of higher quality.
It is advisable not to make any movements until the doctor asks you to (for example, take a deep breath or hold your breath). The sensor is moved over the skin in the area under study, and the resulting image is viewed on the monitor. The results can be printed for later analysis by other specialists.
What organs are being examined?
The transabdominal ultrasound diagnostic method for women helps to non-invasively determine the condition of the uterus and its appendages (ovaries and fallopian tubes).
In addition, it shows the cervix, which helps to analyze it for the presence and dynamics of pathology. In men, they look at the prostate, bladder and seminal vesicles.
In addition, the abdominal examination method is used in obstetrics.
Application in obstetrics
In the field of childbirth, ultrasound examinations performed through the abdominal wall have found their niche.
The transvaginal method is not suitable for pregnant women from the twelfth week, as it can stimulate the tone of the uterus and, as a result, cause premature labor or miscarriages.
That is why the transabdominal diagnostic method is today the only method used in obstetrics to study the condition of a woman’s reproductive organs and fetal development.
Routine diagnostics for a pregnant woman are indicated at least 3-4 times (more often in case of deviations). Usually a 2D examination is carried out, but when you need to get a more informative picture, 3D and 4D are used.
You can find out about pregnancy in the third week after conception. The period is determined with an accuracy of two to three days by measuring fetometric values, in particular, CTR (coccygeal-parietal size). It is possible to find out the sex of the unborn child only from the middle of the gestation period (18-20 weeks). This diagnostic method allows you to identify such deviations as:
- risk of miscarriage;
- stalled pregnancy or pregnancy occurring outside the uterus;
- child developmental defects;
- anembryony – fertilized egg without an embryo;
- placental anomaly and others.
Decoding: norm and pathology
When conducting an examination, the specialist pays attention to the location of organs, their shapes and contours, sizes and structure. The width and length of a woman’s uterus in a normal state of the body should not exceed 4-5 cm.
Moreover, such a parameter as the thickness of the endometrial walls varies depending on the day of the cycle. For example, it will be larger before the start of your period. The oval shape of the ovaries, the clarity of their contours, and the average density of the structure indicate the health of these organs.
Evenness is another sign of normality.
When conducting a study of the male organs of the genitourinary system, the prostate gland and seminal vesicles are studied. In a healthy man, the prostate normally should not exceed a volume of 24-30 cm3, the transverse size is 43 mm, the superoanterior size is no more than 41 mm, and the anteroposterior size is 23 mm.
When assessing the condition of the seminal vesicles, it is necessary to take into account that their normal size is up to 1 cm. An oval, smooth bladder with a wall thickness of 5 mm, with clear contours, will be qualified as a healthy organ.
Despite all the advantages of this examination method, it cannot detect changes in the structure of organs in the initial phase due to the low accuracy of the apparatus and the limited nominal length of ultrasonic waves (on average, 7 inches).
It is possible to identify a variety of developing abnormalities using transabdominal ultrasound in both sexes. Due to its non-invasiveness, painlessness, accurate results and a small number of contraindications, it occupies a leading position in the list of examinations recommended by doctors.
This procedure should be used not only when raising the question of the presence of pathological changes, but also for preventive purposes. This is especially important for women aged 40 and older, and men over 50.
Source: https://iDiagnost.ru/uzi/primenenie-transabdominalnogo-uzi-dlya-diagnostiki-zabolevanij
What is transabdominal ultrasound
Today, the successes of diagnostic medicine are determined by the emergence and improvement of various research methods that make it possible to obtain images of internal organs.
One of these methods is ultrasound examination, the information content of which, in many aspects, exceeds the results of x-ray examination, and, often, allows you to supplement the information picture obtained using computed tomography.
Despite its somewhat limited capabilities, transabdominal ultrasound (examination performed through the anterior abdominal wall) is successfully used to diagnose diseases of the upper and lower urinary tract, pelvic organs and digestive organs.
General concepts
Ultrasound diagnostics is based on the ability of human body tissues to reflect sound waves with varying degrees of intensity. Since the speed of passage of an ultrasound wave depends on the density of a specific biological tissue, the main amount of information is obtained when the echo signal passes through sections of tissue environments.
Table: Velocity of echo signal propagation in various biological media
| Biological tissues | Unit change | Speed indicator |
| Soft tissues (including the brain) | m/s | 1530 |
| Fat | ** | 1450 |
| Liver | ** | 1550 |
| Kidneys | ** | 1560 |
| Muscle | ** | 1585 |
| Skull bones | ** | 4080 |
| Concretions (gallbladder stones) | ** | 5000 |
| Water | ** | 1500 |
| Air | ** | 340 |
Thus, the higher the tissue density, the higher the ultrasound speed, and, accordingly, the stronger the reflected sound signal. The acoustic resistance of each specific area is reflected on the monitor in the form of different shades of gray. The higher the density of the area under study, the lighter its image on the monitor.
When areas with high acoustic density that are not typical for the area under study are detected, the term “zone of increased echogenicity” is used.
For example, stones are displayed on the monitor in white, and objects filled with fluid (cysts) are shown in black.
The average penetration depth of the ultrasound beam during transabdominal ultrasound, depending on the frequency used, is 8–20 cm, which makes the study difficult in obese patients.
Possibilities
Many experts consider transabdominal ultrasound not so much a diagnostic method as a way of selecting patients for further research.
This position is explained by a number of limitations that make it difficult to obtain complete diagnostic information. For example, the presence of air in the intestines can significantly distort the results.
Technically, ultrasound allows you to obtain the maximum possible amount of information about the morphological structure of the abdominal and pelvic organs, as well as pathological foci.
During the research process the following is determined:
Abdominal ultrasound of the abdominal cavity
- localization of an organ or pathological focus in the structure of an organ;
- dimensions;
- shape;
- smoothness and clarity of the external contour;
- internal structure of organs;
- the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity or pericardium.
When examining hollow organs, you can obtain information about the thickness and presence of seals in the wall, for example:
- slight compaction accompanying an increase in wall thickness is characteristic of an acute inflammatory process;
- a strong increase in the density of the entire organ wall, with a simultaneous increase in its thickness, indicates a chronic inflammatory process;
- the appearance of focal thickenings of the wall, with uneven changes in structure, may indicate hyperplastic changes of a benign or malignant nature.
Ultrasound examination performed through the abdominal wall, due to its high sensitivity to changes in the density of various media, allows one to study the condition of parenchymal organs (liver, kidneys, pancreas, prostate), which is difficult to do when using x-ray diagnostic methods. An undoubted advantage of the transabdominal method is the ability to monitor the development of the fetus during pregnancy, starting from 5–6 weeks from the moment of conception.
Important! The quality of ultrasound examination results depends to a much greater extent on the doctor’s experience than when using other diagnostic methods.
An ultrasound image reveals a fertilized egg at a gestational age of 5 weeks
The transabdominal ultrasound sensor performs two functions at once, one of which is the generation of a low-frequency sound wave, and the second is the registration of the intensity reflected from the internal organs.
Therefore, to obtain the most informative image, the doctor must move the sensor in specified directions, changing the angle of inclination, and, accordingly, the projection of a given point on the monitor.
When conducting transabdominal scanning, transducers with a frequency of 2 MHz are used, which corresponds to a 10–20 cm depth of beam penetration.
The use of a generally accepted orientation when performing transabdominal ultrasound allows for standard interpretation on an ultrasound monitor.
The sensor (transducer) is held in the right hand, while the thumb should be on the side of the groove (regulator) located on one of its sides.
A gel is applied to the patient's skin to facilitate sliding and prevent air from penetrating between the sensor and the contact surface and position it perpendicular to the surface of the body.
The position of the sensor on the right side of the patient's body is reflected in the form of a cone-shaped image on the monitor, the narrow part of which is directed to the left or up, and the widening part is directed to the right or down.
In this case, the left or upper corner of the image (small angle) reflects structures located close to the ultrasound transducer, and the lower or right (expanding part) displays structures located further from the transducer.
Scanning begins with the most interesting area, moving the transabdominal sensor first along the center of the body, for example, from the womb towards the navel (when examining the pelvic organs), and then from both sides of the abdomen, until satisfactory image quality is obtained. When a suspicious area is detected, scanning is performed from many positions, and with the help of manual settings, the best visualization is achieved.
Important! The design of the ultrasound device provides the ability to adjust the penetration depth of the sound wave, as well as the brightness level on the monitor, which allows you to examine the anatomical area of interest in detail.
Preparation for a transabdominal ultrasound is, first of all, preparation of the intestines, since gases, which cannot always be eliminated, significantly reduce the quality of diagnostic information.
In this regard, a mandatory stage of preparation, regardless of the field of study, is the rejection of products that can cause gas formation.
Good results in preventing the formation of gases in the intestines can be achieved by taking enzyme preparations (Festal, Mezim) with every meal.
Prevention should begin 2–3 days before the scheduled procedure. Further preparation is aimed at improving visualization of the anatomical area of interest. So, when examining the pelvic organs, a full bladder is required. To do this, the patient must refrain from urinating for 3–4 hours or drink 1–1.5 liters of water 1–2 hours before diagnosis.
Due to the increase in volume, the bladder pushes back the intestinal loops and moves the uterus in a central direction, which makes it easier to examine.
Examination of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and gallbladder is carried out on an empty stomach. You should stop eating 6-10 hours and drinking 2-3 hours before the procedure.
Routine ultrasound during pregnancy for more than 9 weeks does not require special preparation.
If there is an urgent need for diagnostics, it is advisable to take Espumisan the day before
Urinary tract organs
Assessment of the condition of the urinary tract organs includes examination of the following organs:
- kidneys;
- adrenal glands;
- ureters;
- bladder.
Ultrasound of the kidneys performs a comprehensive assessment of the size of each organ individually and in comparative relation to each other, the state of the pyelocaliceal system (PCS), the presence or absence of hyperechoic structures in the PSC and the condition of the renal parenchyma.
Table: Main ultrasound signs of kidney pathology
| № | Name of pathology | Ultrasound signs |
| 1 | Aplasia | Absence of echostructures of one kidney and increase in size of the other |
| 2 | Kidney duplication | Doubling of the echo signal from the CLS or significant dilation of the pelvis |
| 3 | Polycystic | Detection of a large number of echo-negative foci of various sizes in the renal parenchyma |
| 4 | Trauma, hematomas | General changes in the structure of the kidney associated with a violation of its integrity: changes in structure or density |
| 5 | Urolithiasis | Detection of fragments with increased echogenicity in the CLS |
| 6 | Hydronephrosis | Increasing the volume of the CLS and dilating the ureters |
| 7 | Pyelonephritis | Increased CL, thinning of the parenchyma with normal ureter sizes |
| 8 | Tuberculoma, carbuncle | Changes in the external contour of the kidney due to the formation of large foci with a heterogeneous echostructure |
The adrenal glands are not always detected during transabdominal ultrasound. Normally, they are defined as triangular-shaped structures. An increase in the size of the adrenal glands to 2 cm or more indicates tumor-like changes. Ultrasound examination of the bladder includes assessment of the following indicators:
- form;
- uniformity of the wall structure;
- symmetry;
- amount of residual urine after urination;
- the presence of a communicating cavity (diverticulum);
- the presence of stones and intracavitary cysts.
Digestive organs
The digestive organs, to one degree or another determined by ultrasound examination, include the stomach, pancreas, liver, gallbladder and ducts, and intestines.
The stomach and intestines are hollow organs, so their condition is assessed based on the wall thickness, which usually does not exceed 1 cm, and the thickness of the echo-positive lumen, which is no more than 3 cm.
Signs of the disease are a uniform or uneven change in wall thickness and a decrease in lumen.
The ultrasound image shows the stomach and upper intestinal loops
The acoustic properties of the pancreas are practically no different from the acoustic properties of the liver.
Pathological signs indicating the development of pancreatitis, the formation of hematomas or cysts are: enlargement of the gland, blurred contours, heterogeneous compactions of the parenchyma, accompanied by an increase in the echo signal, identification of the pancreatic duct, which normally should not be visible.
A healthy liver on a sonogram looks like a homogeneous structure with weakly positive acoustic properties. Vessels, veins and bile ducts look denser against the background of parenchyma. The appearance of lighter lesions on the liver sonogram, accompanied by an increase in the thickness of the portal vein, may indicate cirrhosis, and a general darkening of the parenchyma may indicate fatty liver degeneration.
The appearance of echinococcal cysts is a fairly common pathology. A characteristic difference between such a cyst and a hygroma is the presence of a dense membrane, characterized by an enhanced echo signal.
A normal gallbladder has an elongated shape and a wall thickness not exceeding 0.4 cm.
Its examination makes it possible to detect various kinds of structural deformations (diverticulum, duplication, septum formation), polyps, stones and inflammatory processes, expressed in thickening and compaction of the wall.
Important! Optimal results in diagnosing digestive diseases can be achieved using equipment that operates in real time and at scale.
The diagnostic capabilities of transabdominal ultrasound in the study of the genital organs in men and women are extremely high. However, the diagnosis often requires clarification using other methods.
Perhaps this situation is associated with a wide variety of pathologies and the associated need to differentiate diagnoses.
The study of the prostate gland in men comes down to assessing its size, condition of the capsule, symmetry, severity of the periprostatic venous plexus and parenchymal structure.
To obtain information about the size of the gland, each lobe is measured in two directions, and then the volume is calculated.
Symmetry is judged by its location relative to the urethra, which should visually divide the prostate into two equal parts.
An increase in one of the lobes most often indicates a malignant neoplasm. With benign hyperplasia, the gland increases in volume symmetrically.
Schematic image of the prostate gland on an ultrasound image
Changes in the echostructure of the parenchyma indicate a fairly wide range of diseases, from inflammatory to oncological, so this sign is assessed comprehensively. When diagnosing the organs of the female reproductive system, transabdominal ultrasound allows you to visualize:
- external contours of the uterus and cervix;
- vagina;
- uterine cavity;
- ovaries (only in half of the cases);
- thickness of the endometrial mucosal layer;
- folliculogenesis.
Ultrasound can also be used to detect all types of fibroids larger than 1 cm (intramural, subserous, submucosal) and endometrial cysts.
When diagnosing pathologies of the female reproductive system, the best results can be achieved using transvaginal ultrasound. The widespread use of ultrasound diagnostics is due, first of all, to its accessibility and safety.
However, one cannot deny the high information content of the method, which makes it possible to identify pathological conditions of some organs with 80% accuracy.
The disadvantages of the transabdominal method, such as difficulties in visualizing various anatomical structures (ovaries, fallopian tubes, bile ducts, ureters), recognizing only large tumors, false positive results, are successfully compensated by the use of transurethral, transvaginal and other ultrasound methods. However, all of the listed methods have some limitation in the viewing range, and in addition, they are invasive, which means that transabdominal ultrasound will retain its position as a first-line diagnostic method.
Source: https://apkhleb.ru/uzi/chto-takoe-transabdominalnoe
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the uterus and appendages (transabdominal)
Unlike the male body, the female body has a number of features. It is more fragile and requires specific care and attention.
- To find out what is happening in the body and check the condition of the pelvic organs, doctors often prescribe ultrasound examinations for women.
- Most women are afraid of such diagnostics, but there is nothing wrong with that.
- Let's figure out what transabdominal ultrasound diagnostics is and how it works.
In what cases is transabdominal ultrasound diagnostics of the uterus and appendages prescribed?
Transabdominal diagnostics is an instrumental study of the condition of organs. Any organs can be examined, but we are interested in the uterus and appendages, so let’s find out when such diagnostics are used in gynecology: to determine the volume of a woman’s genital organs.
It is the size of the uterus and appendages that can tell about the possible pathological processes that occur in them; for timely diagnosis of neoplasms and adhesions; for diagnosing and establishing the duration of pregnancy; to control the process of bearing a baby.
There is such a thing as an ultrasound examination of the uterine cavity, which allows you to: diagnose an ectopic pregnancy in a timely manner; record fetal freezing; diagnose pathological processes in the fetus (even the most severe ones, such as Down syndrome and hydrocephalus of the brain); location and size of fibroid tumors; identify a malignant tumor; diagnose the proliferation of endometrial cells outside the uterus; record the displacement of the spiral; diagnose chronic endometriosis; diagnose the growth of polyps and other pathological structures; diagnose cancer of the inner mucous membrane of the uterus.
The doctor may also notice various deviations in the shape, size and weight of the uterus and its appendages. An ultrasound examination can show how patent the fallopian tubes are.
Diagnosis is carried out by introducing an echographic solution. It is inserted into the uterine cavity.
How to prepare for an ultrasound examination?
Today there are several types of ultrasound examination, and each of them has its own preparation rules. There are also general rules, for example:
- Two to three days before the test, you are prohibited from consuming foods that cause severe gas formation. You should also avoid dairy products. This can have a significant impact on the results.
- If before the ultrasound examination the patient underwent other diagnostic measures by administering a contrast agent, then the ultrasound examination should be rescheduled.
- On the day of diagnosis, it is advisable to do an enema to cleanse the intestines.
Before the start of the transabdominal ultrasound examination, it is necessary to fill the bladder. How to do this correctly? Half an hour before the ultrasound, you need to drink one liter of plain water. If there is no time to wait, the doctor can administer fluid using a catheter.
If the patient suffers from gas formation or constipation, then two days before the ultrasound examination she is prescribed special enzymes. On the day of the diagnostic procedure, you should not take any medications.
Doctors also recommend diagnosis within the first 6 days after menstruation.
There are no special contraindications to such procedures. The only thing is that doctors do not perform transabdominal ultrasound examinations on patients during their menstrual cycle.
Transabdominal examination and its features
Such an ultrasound examination belongs to the traditional methods of diagnosing the pelvic organs. Its work is that the ultrasonic wave is directed at the abdominal cavity and passes through it.
To examine the uterus and its appendages, it is necessary to place special sensors on the patient’s abdomen that can provide detailed information.
I wonder how this happens? During the procedure, a reverse piezoelectric effect occurs, that is, the outer shell of the uterus and appendages begin to reflect ultrasonic waves. During reflection, particles are formed that turn into electrical impulses. These impulses form the image on the screen.
Often, during a transabdominal ultrasound examination, doctors resort to additional diagnostic measures, which take the form of bimanual palpation, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, and laparoscopy. This research methodology has a number of advantages, let's look at them.
Benefits of transabdominal ultrasound
During the diagnostic procedure, the screen receives a picture of not only the organ being examined, but also the one that is nearby. This way you can get a general panorama of the pelvic organs. This will allow doctors to make a more accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Unlike other types of ultrasound, transabdominal allows you to diagnose voluminous and wide uterine tumors and neoplasms on the appendages.
Ultrasound examination does not require special preparation. It also does not have any negative effects on the pelvic organs and is absolutely painless.
This is an effective way to assess the condition of the uterus and appendages in virgins.
Disadvantages of transabdominal ultrasound scanning
Above we described how this technique works. So, it is sometimes difficult for ultrasonic waves to pass through the peritoneal tissue. Therefore, in some cases the image does not turn out as clear as we would like.
Compared to other ultrasonic scanning sensors, this one is considered weaker.
During diagnosis, certain difficulties may arise, for example, the patient is overweight and has a thickened abdominal wall. In this case, the uterus and its appendages are more difficult to visualize. Also, the image quality may be unclear due to adhesions that are located in this area. As a rule, adhesions are a consequence of abdominal gynecological operations.
It is also worth taking into account the fact that, compared to other ultrasound scans, this method provides less information, but at the same time it perfectly shows the condition of the organs being examined, without causing discomfort or pain.
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the uterus and appendages (transabdominal)
updated:
June 12, 2018
Source: https://FoodandHealth.ru/diagnostika/uzi-matki-i-pridatkov-transabdominalnoe/
What is transabdominal ultrasound in men and women? – UZI.ONE
Transabdominal ultrasonography (TAUS) is a harmless and painless transperitoneal method for diagnosing the condition of shallow organs and tissues, including the prostate gland in men and the pelvic organs in women.
Features of transabdominal ultrasound
Transabdominal examination allows you to visualize the abdominal and pelvic organs and obtain information about their functioning. The device's sensor, lubricated with gel, is placed on the anterior abdominal wall. The specialist moves it and turns it at different angles in order to most accurately assess the condition of the organs and exclude the presence of pathologies.
To obtain an image, ultrasonic waves are directed to the area under study and, reflected from the organ, are converted into electrical impulses. Thus, a picture appears on the device’s monitor. This imaging method is called the piezoelectric effect. To conduct transabdominal ultrasound, sensors with a wave frequency of 2.5-3.5 MHz are used.
Advantages and disadvantages of TA ultrasound
Transabdominal ultrasound is used to assess the functions of the abdominal organs, retroperitoneum and pelvis. The advantages of this type of diagnosis include:
- A non-invasive method, that is, transabdominal access does not require disruption of integral structures of the body or interference with the functioning of organs and tissues.
- Ultrasound examination does not require complex or lengthy preparation.
- Ultrasound during pregnancy does not pose any danger to the fetus and can be performed even in the early stages of gestation.
- This method allows you to assess the condition of several nearby organs.
- Transabdominal ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women makes it possible to visualize large tumors of the uterus and appendages.
- This method is especially in demand when examining children, as it is not only safe, but also absolutely painless. The entire procedure takes no more than 5-7 minutes.
- Today, transabdominal ultrasound of the prostate is the simplest and most informative method that allows you to obtain the most complete information about the condition of the prostate gland.
- Using TA ultrasound of the uterus and appendages, the condition of the pelvic organs is diagnosed in virgins and women suffering from acute infections of the genitourinary system or bleeding.
Read more
How is endosonography performed?
Disadvantages of this method:
- Some of the ultrasound waves are absorbed by the tissues of the abdominal wall, and therefore the image may not be clear enough;
- The quality of the image is also affected by the patient’s excess body weight, the presence of adhesions in the gastrointestinal tract or pelvic organs.
Transabdominal ultrasound is somewhat inferior to other diagnostic methods in terms of information content, and therefore is often accompanied by additional procedures, for example, laparoscopy or bimanual palpation. A combined examination allows you to get a complete picture of the patient’s condition.
When is TA ultrasound prescribed?
Indications for TA ultrasound may include abdominal pain, impaired urine outflow, and pregnancy. The patient is referred for an ultrasound examination either by a local physician or by a specialist, for example, a gynecologist or urologist.
Men should have a scan if they are concerned about:
- Pain in the groin and scrotum.
- Diuresis disorders, burning or itching during urination.
- Discharge from the urethra.
- Urinary dysfunction.
- Hematuria, sediment in urine.
With such symptoms, the doctor prescribes a transabdominal ultrasound of the prostate gland for the patient. Thanks to this procedure, it is possible to assess the condition of the organ and its blood supply, exclude tumors and pathological changes.
For women, a transabdominal pelvic ultrasound is prescribed to identify dysfunction of the uterus and appendages. In addition, scanning allows you to diagnose uterine polyps, tumors, cysts and other neoplasms.
Transabdominal ultrasound during pregnancy
In addition, a gynecological ultrasound is mandatory for women expecting a child. What is transabdominal ultrasound during pregnancy? This is a study that allows you to verify the normal development of the fetus, exclude the development of gross defects in it, and make a forecast regarding the future course of labor.
Visualization of the embryo during transabdominal examination of a normal pregnancy is mandatory by the end of the 6th week of gestation, when the fertilized egg reaches 5-7 mm in length. If at this stage the embryo is found outside the uterus or not detected at all, then there is a high probability of an ectopic or frozen pregnancy.
Read more
How is a stomach ultrasound performed?
After the end of the first trimester, only TA ultrasound is used to assess fetal development, since transvaginal scanning can cause premature birth.
From 8-9 weeks you can distinguish the head of the embryo, from 12-13 - most of the internal organs, visualization of the fetal kidneys with transabdominal echography occurs at 15-16 weeks. Ultrasound allows not only to determine the location of the embryo and the number of embryos, but also to identify various pathologies: absence of the brain, spinal cord herniation and skeletal abnormalities.
If the baby is developing normally, then with the help of a scan the doctor will determine the breech presentation of the fetus and will be able to guess the approximate date of birth.
Preparing for an ultrasound
What does it mean: preparation for ultrasound examination? When prescribing an ultrasound, the doctor must give the patient a leaflet with recommendations. You should drink at least 1 liter of water 1-2 hours before the procedure.
A full bladder will provide access for the sensor waves to the organs and displace the intestines from the pelvis.
In addition, a few days before the examination, you should stop eating foods that increase gas formation: fruits, brown bread, cabbage, legumes and dairy products.
Source: https://uzi.one/zhkt/transabdominalnoe-uzi-u-muzhchin-i-zhenshhin-kak-jeto.html
Ultrasound of the prostate gland, abdominal and transabdominal
Thanks to ultrasound, it has become easier to identify pathologies that are difficult to recognize from the clinical course or other research methods. Transabdominal ultrasound of the prostate is a diagnostic examination through the abdominal cavity.
An ultrasound of the prostate is often performed in conjunction with an examination of the bladder and kidneys.
Function of prostate ultrasound
The main purpose of the examination is to identify defects that may occur in the male prostate gland. An ultrasound examination will determine the size of the prostate and the presence of tumors in it. Adenoma and inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system are also detected during examination.
Who is it shown to?
If a man has the following symptoms, the urologist refers him for an ultrasound examination:
- pain in the lower abdomen,
- painful urination,
- dysfunction of the reproductive system,
- erectile dysfunction.
Transabdominal ultrasound of the prostate is indicated:
- If a specialist detects disorders in the function of the gland.
- If the results of a clinical analysis deviate from the norm.
- Before the operation.
- During the period of drug therapy, to record the progress of recovery.
The reasons for ordering an examination are any signs of dysfunction of the genitourinary organs:
- clinical symptoms of inflammation of the abdominal organs;
- difficulties associated with urination, inflammation of the urinary organs;
- detection of the tumor marker PSA in blood tests;
- impotence, infertility;
- other indications discovered by the doctor during examination and palpation.
pros
The advantage of the study is that it does not harm the health of the subject.
- Rapidity. The procedure does not require much time.
- Availability:
- low cost of research;
- An ultrasound machine is available in every medical institution and most urology departments of hospitals.
Advantages of the method
- Allows you to visually assess the condition of organs.
- Transabdominal examination of the prostate is not accompanied by penetration. Injections and surgical interventions are not performed.
- Safety. No exposure.
- You can see processes in nearby organs, and early diagnosis of serious diseases, including cancer, is achieved.
- When performing an ultrasound, it is possible to collect cerebrospinal fluid or tissue for biochemical and histological analysis.
- No contraindications.
What pathologies are detected by ultrasound examination?
When examining the prostate in men, the following parameters of the gland can be assessed:
- size;
- density;
- structure;
- presence or absence of tumors.
Pathologies that are revealed during examination:
- Prostatitis is an inflammatory process in the prostate gland. With its increased size, this diagnosis can be made.
- Prostate cancer is predominantly a disease of older men. Characterized by an asymptomatic course.
- Prostate adenoma is a benign tumor. With this pathology, urination disorder occurs.
- Cyst. The presence of a cavity filled with liquid on ultrasound indicates its formation;
- Stones in the genitourinary system.
How to prepare
The main requirement during preparations for an ultrasound of the kidneys is diet.
For three days, the patient must exclude from the diet foods that contribute to the formation of gases in the intestines. Bread, dairy products, fruits, vegetables, legumes, fatty meat and fish dishes that can cause temporary changes in the functioning of the digestive organs.
It is recommended to eat cereals, boiled meat, and low-fat cheeses. The specialist will prescribe sorbents during meals - activated carbon, Espumisan, Smecta. Patients with constipation should take a mild laxative the day before to have a bowel movement.
30 minutes before the session, the patient should drink half a liter of still water, since ultrasound of the kidneys is performed with a full bladder.
Prostate ultrasound
- when examining through the abdominal wall - abdominally, the preparation is no different.
- The transrectal method (through the anus) has its own peculiarities.
- You don’t have to fast before the procedure - a light dinner the day before and cleansing the intestines on the day of the procedure will be enough. Various methods are used to empty the colon:
- Esmarch's irrigator;
- microenemas;
- candles;
- laxatives.
Esmarch's mug is an enema with a volume of 1.5-2 liters. with its help, a drug prepared from chamomile decoction or a saline solution with oil is injected into the rectum.
The procedure takes 15-40 minutes and is performed on the day of appointment.
bladder ultrasound
Preparations for scanning are carried out similarly to the abdominal method. it is required to restrain the urge to urinate for 3-4 hours. if the desire is intolerable, partial emptying with subsequent replenishment of fluid is permissible.
If an emergency examination is necessary, the sonologist conducts it without preliminary procedures, but always with a full bladder.
conducting a survey
The wave generated by the device penetrates the human cavity and is reflected from the tissues. At this time, an image appears on the device monitor.
If you have recently had an X-ray with a special substance, tell your doctor.
Research methods
In urology, several types of ultrasound examinations are used, which differ in the technique used.
- Abdominal - through the abdominal cavity.
- Transrectal - through the rectum.
- Transurethral. It is performed using a cystoscope. The probe is inserted into the urethra. Local anesthesia is required first. The method requires special equipment and conditions, so it is rare.
Abdominal ultrasound of the prostate
Ultrasound with an abdominal probe is performed directly through the abdominal cavity. The method is the most convenient and painless for patients.
- The patient assumes a supine position.
- A gel is applied to the subject’s abdomen, which creates a transitional environment between the skin and the device.
- The sensor is placed on the abdominal area, and by controlling the device, organs are scanned in different planes.
However, this survey method is not reliable enough. It is used to get the overall picture.
Transrectal ultrasound of the prostate
The next type is rectal. It is carried out using a rectal sensor. It is inserted into the anus and into the rectum. It has high accuracy and efficiency, since the device is located close to the prostate.
- It is performed in a position lying on your side, with your knees brought to your chest.
- An ultrasound sensor is inserted through the anus into the rectum, several cm deep.
- Before invasion, a condom is placed on the sensor. If you are allergic to latex, tell your doctor.
Simultaneous inspection
It is advisable to conduct a study of the prostate and nearby organs. Inflammatory processes can cause pathological changes in all organs of the genitourinary system. To determine the interdependencies, an ultrasound of the prostate gland is performed to determine the amount of residual urine.
Kidney and bladder examination
Joint ultrasound is usually performed transabdominally. The patient lies on his back, and a special gel is applied to his lower abdomen for better contact with the equipment.
By moving the sensor, the diagnostic specialist scans the abdominal cavity. During the procedure, the patient turns over alternately on the right and left sides, holds his breath and follows other doctor’s recommendations.
The session lasts about 10 minutes.
Simultaneous examination of the prostate and bladder
In the absence of contraindications, scanning is performed transrectally. The patient is positioned on the couch on his side, with his legs pressed to his chest. The sensor is inserted into the rectum to a depth of about 6 cm. To avoid infectious infections and discomfort, a condom is first placed on the sensor.
The person being probed feels virtually no discomfort. Men's fears about this are greatly exaggerated, and the benefits of the study far outweigh the discomfort.
Normal indicators
The prostate should be described as follows:
- Symmetrical.
- Have the shape of an oval or triangle.
- Dimensions:
- Length - 2.5 -3.5 cm.
- Thickness - 1.5-2.7 cm
- Width - 2.7-4.3 cm
The volume is calculated manually or in a program. To calculate, length, thickness and width are multiplied, the resulting number is multiplied by 0.54. Normally, the volume is 25-30 cm^3. The weight of the prostate in healthy people is 26.5 - 30 g.
The main criteria by which the condition of the genitourinary system organs is assessed:
- smooth, clearly visible contours of organs, clear edges. Roughness may indicate inflammation;
- homogeneous structure of organs - absence of formations, bubbles, etc.;
- normal uniform echogenicity (the ability of tissues to reflect an ultrasound signal). High echogenicity indicates chronic diseases or stones in the gland;
- the condition of the seminal duct is normal patency without blockage, good visibility.
The compliance of the results obtained with the normative ones confirms the absence of abnormalities of the prostate gland and urinary tract.
The procedure is not prescribed if the patient has recently undergone an X-ray, colonoscopy, or gastroendoscopy. If there are open wounds in the examination area, the procedure is performed only after they have healed.
Where is it held?
Ultrasound diagnostics can be performed both for a fee and free of charge - under the compulsory medical insurance policy in a clinic at your place of residence. The doctor must write a referral.
You can first consult with friends or read reviews about medical institutions on websites.
Urologists on the accuracy of ultrasound examination
Transabdominal (abdominal) prostate examination is convenient for patients. But this type of diagnosis does not guarantee accurate results. Urologists recommend undergoing transrectal ultrasound.
Ultrasound examination has long remained the only method for quick and accurate diagnosis of pathologies of the prostate, bladder and other abdominal organs. After interpreting the ultrasound, prostatitis, adenoma, benign and cancerous tumors, stones, etc. are detected in the early stages.
Conclusion
An ultrasound examination of the prostate and other genitourinary organs is recommended for all men over 40 years of age on an annual basis, regardless of the detection of symptoms. It allows you to start fighting the disease using gentle methods long before pain manifests itself.
Source: https://my-urolog.ru/uzi-predstatelnoj-zhelezy.html