Shortness of breath (dyspnea) is a change in the frequency and depth of breathing, designed to increase the amount of oxygen entering the body. At this moment, a person experiences a feeling of lack of air, and rapid breathing and heartbeat are also observed.
Impairment of inhalation and exhalation is not a disease in itself and may occur in response to changes in the environment or physical activity. If you are concerned about shortness of breath at rest, and difficulty breathing is a common occurrence, you should consult a doctor.
These symptoms may indicate serious health problems.
The article will help you understand what shortness of breath is, describe the causes of poor breathing and ways to eliminate the disease.
Etiology of the problem
The only reason why shortness of breath occurs and the heart rate increases is the lack of oxygen in the blood and tissues. In this way, the body tries to restore balance in order to prevent serious disturbances in the functioning of organs.
A feeling of lack of air can occur in a healthy person. It is provoked by:
- excessive physical activity (especially in untrained people);
- in rarefied air conditions (at high altitudes);
- excitement, stress;
- late pregnancy;
- confined spaces;
- foreign body in the airways.
Chronic bad breathing is observed in people suffering from osteochondrosis, intercostal neuralgia or herniated intervertebral discs.
The main pathological reasons that make it difficult for a person to breathe are diseases:
- respiratory organs (bronchitis, asthma, pneumonia, pneumosclerosis, lung cancer);
- heart (arrhythmia, ischemic heart disease, pericarditis, heart attack, heart failure, neoplasms);
- nervous system (trauma, tumor, edema, stroke);
- anemia.
Factors that provoke heavy breathing and rapid heartbeat include physical inactivity, obesity, and smoking.
Shortness of breath in children occurs for the same reasons as in adults. But due to the fact that a young body is more vulnerable, even minor disturbances in homeostasis can cause rapid breathing.
Shortness of breath in a child can be recorded against the background of:
- hyperthermia;
- high temperature;
- excitement, stress;
- allergies;
- rhinitis;
- physical activity;
- laryngeal edema, laryngitis;
- diphtheria;
- bronchial asthma;
- pneumonia;
- emphysema;
- heart disease;
- anemia;
- diseases of the immune system;
- virus infections;
- hormone imbalances;
- entry of a foreign object into the respiratory system;
- cystic fibrosis (congenital anomaly).
Important! Rapid breathing, like rapid heartbeat, in childhood is not always an alarming symptom. A healthy child makes more breathing movements than an adult.
Physiological norms of respiratory frequency
| Age | Quantity per minute |
| Newborn | 50-60 |
| 0.5-1 year | 30-40 |
| 1-3 years | 30-35 |
| 5-10 years | 20-25 |
| Puberty | 18-20 |
If your baby's breathing differs from average norms or causes concern, you should contact your pediatrician. Only a doctor can reliably determine whether a child has shortness of breath.
Symptoms
Dyspnea is characterized by general and specific symptoms. The latter are caused by pathology, which results in difficulty breathing.
Shortness of breath and lack of air have the following clinical picture (in both sick and healthy people):
- pain and pressure in the chest;
- unusual sounds during inhalation and exhalation (wheezing, whistling);
- problems with swallowing;
- feeling of a lump and constriction in the throat;
- breathing through the mouth;
- high blood pressure;
- cough;
- yawn.
Choking, most people begin to panic, so fear, nervous tremors, and inappropriate behavior are added to the main symptoms.
Shortness of breath in sick people is accompanied by symptoms specific to a particular pathology.
Breathing disorders due to heart disease
Shortness of breath and lack of air are accompanied by pain in the chest and behind the shoulder blade. Cyanosis of the skin and swelling of the lower extremities are observed. The patient does not have enough air when inhaling, and shortness of breath at rest is a common occurrence. In severe cases of the disease, a feeling of lack of air may occur in a lying position (at night while sleeping).
Breathing disorders due to diseases of the lungs and airways
Cough and shortness of breath in a person indicate a violation of the respiratory system.
The patient lacks air to the same extent when inhaling and exhaling. In the first stages of the disease, rapid breathing appears only during physical exertion, then shortness of breath occurs when walking and minimal movements.
When the disease reaches an extreme or irreversible stage, chronic bad breathing is recorded.
Shortness of breath with bronchial asthma is a familiar phenomenon for almost 10% of the world's population. It is accompanied by attacks of suffocation, which most often occur in the morning or at night. The patient experiences a feeling of lack of air, accompanied by chest pain, arrhythmia, and enlarged veins in the neck.
At the same time, I suffer from a dry cough. Choking, a person may lose orientation in space and the ability to respond adequately. Sometimes an attack leads to convulsions and loss of consciousness.
Breathing disorders due to pathologies of the nervous system
The respiratory centers are located in the brain. Rapid breathing can result from structural disorders in the medulla oblongata. When the central nervous system is infected, tissue acidification occurs and oxygen levels decrease, causing the patient to experience heavy breathing (frequent and noisy).
Lack of air during breathing is observed in people suffering from vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD), due to impaired blood supply to organs and tissues.
Rapid breathing is accompanied by numbness in the fingers, ringing in the ears, and dizziness. In people with VSD, shortness of breath is very common when walking, especially fast, and when walking up stairs.
Patients suffering from attacks of hysteria and other neurotic disorders may also experience shortness of breath. But such a violation of inhalation and exhalation is only superficial and directly depends on emotions. A person may scream “I’m choking,” but there will be no signs of hypoxia.
Lung diseases in humans: list and their symptoms
Types of breathing disorders
Shortness of breath occurs:
- Physiological. Shortness of breath during physical exertion, in the mountains or in a stuffy room.
- Pathological. Occurs due to disruption of internal organs. Lack of air during breathing is felt not only when playing sports or other efforts, but shortness of breath also appears at rest.
Based on when shortness of breath occurs when breathing, the following types of shortness of breath are distinguished:
- inspiratory;
- expiratory;
- mixed.
Inspiratory dyspnea is diagnosed when there is not enough air when inhaling. Problems arise against the background of narrowing of the airways. In childhood, inspiratory shortness of breath is a sign of diphtheria or another throat infection.
A distinctive feature of the second type of shortness of breath is difficulty in exhaling. It appears due to a decrease in the diameter of the bronchi and bronchioles. This type includes shortness of breath in bronchial asthma.
Causes of mixed shortness of breath - heart failure and serious lung diseases
In medical practice, it is customary to distinguish 5 stages of the disease.
To determine the severity of the disease, the doctor finds out how often and under what conditions lack of air occurs when breathing:
- Initial. Shortness of breath during physical activity, running, or playing sports.
- Easy. Shortness of breath is noted when walking over rough terrain or walking in the mountains.
- Average. Heavy breathing occurs when walking at a normal pace and a person is forced to stop to recover.
- Heavy. A person needs rest every 3-5 minutes.
- Very heavy. Shortness of breath occurs at rest.
Diagnostics
Heavy breathing, which occurs even with minor exertion, is a reason to consult a therapist. Only after an examination and thorough diagnosis will the doctor give an answer as to why there is not enough air when breathing and what to do next.
Diagnostics involves a survey and an initial examination. The doctor finds out whether the patient was injured and what chronic diseases he has. The patient is examined using a phonendoscope, which reveals the presence of wheezing and whistling. To clarify the clinical picture, laboratory tests are prescribed:
- blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
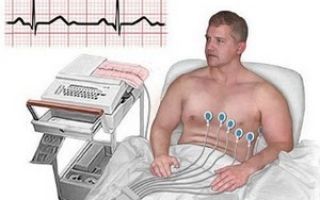
- chest x-ray;
- electrocardiogram;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- pulse oximetry (determines the degree of oxygen saturation of hemoglobin);
- spirometry (measurement of breathing volume and rate);
- capnometry (measuring the amount of carbon dioxide during inhalation and exhalation).
If the patient’s indicators are normal at rest, then load tests are performed. Such studies will help identify the causes of shortness of breath when walking and exercising. To do this, use a bicycle ergometer, or ask the patient to climb the stairs.
To make a correct diagnosis, the patient is examined by specialists from different fields: pulmonologist, cardiologist, surgeon, allergist, neurologist.
Treatment of shortness of breath
It is important for every person to know not only what shortness of breath is, but also to be able to provide first aid if necessary.
Algorithm of actions before the arrival of doctors:
- comfortably sit the patient or lay him on his side;
- remove clothing that may make breathing difficult;
- provide additional oxygen supply (open a window or give (if available) an oxygen cushion);
- try to warm the limbs (massage, heating pad).
Carbon monoxide poisoning
People suffering from bronchial asthma should:
- avoid contact with the allergen;
- Always have medications with you (inhaler, mucolytics).
Drug therapy
Treatment of shortness of breath primarily involves treatment of the disease itself that caused it. But to improve the patient’s quality of life, medications are used to relieve the unpleasant symptom. The patient is given an appointment:
- means that dilate the bronchi (Atrovent, Berodual, Ipratropium native);
- beta-adrenergic agonists (Salbutamol, Indacaterol);
- methylxanthines (Theotard, Teopek);
- inhaled steroid hormones (Ingacort, Pulmicort, Becotide);
- mucolytics (Bizolvon, Lazolvan, Ambrosan);
- antispasmodics (Hyoscyamine, Buscopan);
- sedatives (Persen, Novo-passit);
- multivitamin complexes (Aerovit, Polivitaplex).
Surgery
Surgical treatment is resorted to if it is necessary to remove a tumor that affects the parameters of inhalation and exhalation.
Treatment with folk remedies
What a breathing disorder is has been known for a long time, so traditional medicine has accumulated a lot of advice on how to eliminate shortness of breath.
- If a person does not have enough air when inhaling, it is recommended to use an infusion of honey, lemon and garlic to alleviate the condition. To prepare it, take 0.5 liters of honey, 5 lemons and 5 heads of garlic. The juice is squeezed out of the lemons, the peeled garlic is crushed, and then everything is mixed with honey. The mixture is infused under a lid in a dark place for a week. Take 4 tsp. once a day for a course of 2 months.
- If you are concerned about shortness of breath at rest (especially important for people with excess body weight), you can take an infusion of garlic and lemon juice. 175 grams of peeled and mashed garlic are mixed with the juice of 12 lemons. The infusion is left in the jar for a day (covered with gauze on top), remembering to shake regularly. Take 1 tsp. before going to bed, after shaking it in a small amount of water.
- Fresh goat milk has great benefits for the respiratory system as a whole. It should be drunk on an empty stomach several times a day.
Important! The use of folk remedies must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor!
Exercises
To make breathing easier, doctors suggest doing the following:
- sit up straight and straighten your shoulders;
- place your palms on the chest (bottom);
- breathe through your nose without taking very deep breaths.
The exercise is performed every 40-45 minutes throughout the day.
Prevention
There are no recommendations that could 100% protect against shortness of breath. You can reduce the likelihood of its occurrence if:
- stop smoking;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- exercise;
- control your weight;
- avoid stress;
- timely treatment of diseases that cause shortness of breath;
- undergo regular preventive examinations.
Forecast
The prognosis for life is favorable. The exception is inspiratory dyspnea, which occurs due to the entry of a foreign object into the respiratory tract, as well as shortness of breath at rest, which occurs against the background of severe diseases of the respiratory system, heart, or injury.
Videos on the topic
Source: https://tvojajbolit.ru/pulmonologiya/odyishka-ee-vidyi-prichinyi-vozniknoveniya-simptomyi-i-osobennost-lecheniya-uchashhyonnogo-i-zatrudnyonnogo-dyihaniya/
Cough and shortness of breath
Mechanism of symptom formation
In the overwhelming majority, it is coughing attacks that are the source of lack of air. Due to cough and bacteria on the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, very severe irritation appears. And the air becomes the same pathology as bacteria.
For this reason, it pushes out air along with mucus and phlegm. And as a result, the patient simply physically cannot take a breath and severe shortness of breath appears. The stress that a person experiences in this case further aggravates the situation and shortness of breath becomes stronger.
The state of lack of air is also called dyspnea. How it is formed:
- virus or bacteria enter the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract;
- swelling of the bronchi develops, spasms begin;
- the volume of mucus increases;
- the body, with the help of a dry cough, tries to get rid of phlegm;
- it is difficult for a person to breathe, there is not enough air - shortness of breath appears.
Such symptoms may indicate the development of bronchitis or asthma. In a healthy person, when you inhale, oxygen comes in, and when you exhale, carbon dioxide comes out.
But with pneumonia, asthma or other respiratory diseases, obstacles arise. The blood does not receive enough oxygen and breathing becomes difficult.
In addition to coughing, shortness of breath can also cause the following symptoms:
- increased heart rate;
- strong fear;
- shortness of breath;
- yawning;
- fainting.
Depending on the disease, these symptoms may vary in duration.
Causes of difficulty breathing
Whatever the cause of the cough and lack of air, you need to get rid of it as quickly as possible.
Bronchial asthma. This disease is characterized by:
- dry cough;
- shortness of breath;
- difficulty breathing;
- wheezing with whistling.
You may be interested in the article - The main symptoms of cough with VSD.
Asthma attacks occur for various reasons:
- contact with an allergen;
- hypothermia;
- previous cold;
- exercise stress.
Chronical bronchitis. Accompanied by a constant productive cough and periodic shortness of breath. But lack of air is observed less frequently. Mostly it occurs during an exacerbation of the disease or after physical training.
You may be interested in the article - What are the reasons that a child coughs and chokes?
Attacks of suffocation are also observed in the following diseases:
- pneumonia;
- tuberculosis;
- emphysema;
Source: https://nasmork.net/kashel-i-nehvatka-vozduha/
Cough and difficulty breathing: what to do and causes, dry cough
In most cases, shortness of breath occurs from long and painful coughing attacks. The mucous membranes of the respiratory tract are severely irritated.
They consider the air to be the same pathogenic environment as multiplied bacteria, so it is expelled along with sputum. The person simply does not have time to take a breath before the next attack.
Due to hypoxia, the brain releases stress hormones, which make shortness of breath worse.
The mechanism for causing breathing difficulties is as follows:
- bacteria have entered the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract or the body has been attacked by a virus;
- due to the development of infection, swelling of the bronchi appears and spasms occur;
- an increase in the amount of mucus constricts the bronchi;
- the body tries to get rid of the mucus that interferes with it - a dry cough occurs;
- these processes prevent a person from breathing, so he experiences a lack of oxygen.
It's hard to breathe: heart
When there is enough oxygen in the environment and the lungs are in order, but the heart is not working properly, it will be difficult to breathe due to impaired blood supply and insufficient saturation of the body with oxygen.
With the following disorders in the cardiovascular system and heart function, it is difficult to breathe due to:
- Heart diseases - acute heart attack, coronary artery disease, heart failure, etc. As a result of diseases, the heart muscle is weakened and cannot push a sufficient amount of oxygenated blood through the circulatory system to organs and tissues;
- Anemia. Lack of red blood cells - red blood cells that bind and transport oxygen through the cardiovascular system, or in the case of red blood cell pathology, in which the process of binding and releasing oxygen is disrupted.
Due to serious damage to the blood supply system and heart, it becomes difficult to breathe due to the acceleration of the heart rate.
Attacks of dry and unproductive cough do not occur as an independent symptom. The cause of these symptoms lies in viral, infectious or bacterial inflammation of the respiratory system. Often a debilitating cough is accompanied by severe wheezing in the throat and pain in the chest.
Impaired breathing is especially dangerous during pregnancy. Therefore, cough should be treated at the first attack.
If discomfort is accompanied by breathing problems, the patient must urgently seek medical help. Otherwise, there is a risk of pneumonia, tuberculosis, acute or chronic bronchitis and other, but no less dangerous diseases.
Attacks of shortness of breath and breathing problems occur as the first symptom of bronchitis, laryngitis, tracheitis and other inflammations. As a rule, at this time the patient is tormented by a non-productive process. It is extremely rare to experience a wet cough, which is accompanied by an outflow of sputum due to viral or infectious inflammation. Most often, the cause of the pathology lies in bacterial proliferation in the mucous membrane.
Let's determine why a cough is accompanied by breathing problems.
Acute bronchitis
The main reason for holding your breath when coughing is acute bronchitis. Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bronchi or bronchial tree is accompanied by severe pain, an unproductive process and other symptoms. Most often, patients complain of the following symptoms:
- weakness, fatigue, feeling of weakness, fatigue;
- a sharp increase in body temperature;
- acute rhinitis;
- increasing the functioning of the sweat glands;
- frequent headaches.
In addition, patients note the formation of shortness of breath. The appearance of such a symptom indicates a severe course of the disease.
To avoid a chronic form of development, the patient must follow the rules of treatment and exclude independent decision-making.
Hypothermia, infectious inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, and a decrease in the immune system predispose to the formation of the disease. In addition, a common cause of bronchitis is smoking.
Acute bronchitis can be an independent disease, but it usually occurs against the background of the development of an acute respiratory disease. In order not to complicate the pathology, bronchitis should be treated using a comprehensive approach. Otherwise, there is a risk of the acute form transitioning to the chronic stage.
The main sign of the development of acute bronchitis in adults and children is the formation of a painful cough. It occurs as a defensive reaction to a certain irritant that causes inflammation in the respiratory tract. At first, the cough is dry and unproductive, but after a few days it changes into a wet form.
Laryngitis
A person may begin to choke from coughing due to laryngitis. Inflammation of the larynx most often occurs as a consequence of the development of a cold or infection of the respiratory tract. In addition, the reason for the formation of laryngitis lies in measles, scarlet fever and whooping cough.
The development of the disease occurs due to long walks in the cold season, frequent breathing through the mouth, excessively dusty air, as well as smoking and regular consumption of alcoholic beverages. In addition, inflammation of the larynx is accompanied by overstrain of this area. Singers and teachers are at risk.
The main sign of inflammation is a cough. It occurs as a natural reaction of the immune system, during which the body tries to eliminate inflammation and restore patency of the airways.
Cough due to laryngitis can last up to three weeks. Quite often at this time, patients complain of severe pain and the inability to support breathing. Over time, inflammation changes its character and the cough transforms into a productive form.
At this time, active production of mucus or sputum occurs, which can clog the airways. If the treatment rules are violated, a wet cough will not provide relief, but will only provoke the development of the disease.
Problems in the vascular-cardiac system can also cause shortness of breath. The patient complains that he does not have enough air during any exercise or even a normal walk. Fever is not typical for heart disease, but general weakness, shortness of breath, cough may well be symptoms of such diseases:
- Ischemia;
- Vices;
- Valve malfunctions;
- Heart failure.
- Chest pain: constant, aching, stabbing, with a deep breath;
- Fainting;
- Heavy heartbeat.
It should be remembered that only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Diagnosing yourself and self-medicating is unacceptable.
A child's cough is a concern for parents!
The peace of mind of parents greatly depends on the health of their baby.
At the first manifestations of deviations from the norm, a number of often unnecessary measures are taken, which leads to bad consequences in the future, but it is much better to never let your guard down with your child.
Heavy breathing in a child and cough, although not common, are often a sign of some pathological processes in the body.
Coughing is a reflexive defense process of the body against the presence of any foreign bodies or masses in the respiratory system. It occurs due to a mechanical effect on the receptors in the wall of the respiratory tract, which leads to a sharp contraction of the muscles of the chest and diaphragm, which leads to a sharp exhalation.
Cough often occurs with bronchial asthma, viral or inflammatory diseases. When making a differential diagnosis, attention is paid to other symptoms: runny nose, fever, etc. If a child has a cough and heavy breathing, it can lead to a lack of oxygen in the body, leading to harmful effects.
Upper respiratory tract cough should be treated comprehensively. It is important to remove the cause of the cough, and not just hide it through pharmacological support. For example, the use of antibacterial therapy for infectious pathologies or heart failure, which is the cause of COPD.
After treatment, preventive measures must be taken. Cough and difficulty breathing are usually treated for up to several months to compensate for pulmonary failure due to the pathogen.
After drug therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures and breathing exercises for cough are often prescribed. The latter, for example, do not require much time and can be done at home, but it is important to do them regularly. Only then can shortness of breath and cough be cured completely.
To alleviate the condition, as well as to relieve coughing when inhaling air, Strelnikova’s cough breathing exercises are recommended. Unlike other systems, a positive result is achieved by squeezing the chest when turning the body, bending, etc., which causes a reflex increase in the depth of breathing.
This technique shows remarkable results in the prevention and relief of the following pathologies:
- Chronic pathologies of the sinuses, bronchi and lungs;
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Heart disease (see)
- Peptic ulcers during remission;
- Pathologies of neurological origin;
Some parents note that thanks to these exercises it is possible to help a child with stuttering that has not been cured by any other means. Thus, the spectrum of beneficial influence is truly enormous.
| Exercise "Palms" | Body position: straight stand with bent arms, palms out; When inhaling, the palms are clenched into a fist, imitating a grasping movement. The exercise is done in sets of 4 repetitions, and the total number of repetitions should be 96. |
| Exercise "Epaulettes" | Body position: upright posture with arms placed freely along the body with palms clenched. When you inhale, your palms unclench, simulating the repulsion of air towards the floor. The number of repetitions is similar to the previous exercise. |
| Exercise "Pump" | Body position: the child stands straight, legs slightly apart, arms down. While inhaling, bend forward with rounding of the lower back. During exhalation, the body straightens. The total number of repetitions is 96. |
| Exercise "Cat" | Body position: vertical with legs apart, narrower than shoulder width. When inhaling, a slight semi-springy turn to the side is performed. During inhalation, the body takes its original position. The exercise is repeated as much as the previous movements. |
These exercises are basic, which can relieve coughing when inhaling air. Each movement is performed in several approaches, the number of repetitions in each should be a multiple of 4. The intensity of the training gradually increases and movements are performed according to the 4x24 pattern.
Strelnikova’s full complex of breathing practice consists of 14 exercises, however, coughing and shortness of breath are significantly weakened when performing basic exercises. It is recommended to perform the practice together with the child in the form of a game, which will not only increase the little patient’s involvement in the process, but will also allow him to evaluate the complexity of the movements. This way you can understand the movements yourself.
How to treat a severe cough
- bright yellow, rich color of sputum indicates that the person has developed bronchial asthma;
- orange sputum indicates lobar pneumonia;
- black sputum occurs with pneumoconiosis;
- yellow sputum with bloody streaks indicates activation of tuberculosis or bronchiectasis;
- colorless, light yellow or greenish sputum occurs with mild respiratory diseases, and the color indicates the stage of the disease.
Almost always, when a severe cough is already accompanied by phlegm, this is a clear sign of recovery. True, how long it will last is unknown. If a severe cough is not accompanied by phlegm, it is dry and hysterical, and the pain in the chest area is very severe, then all measures should be taken to make it productive.
In some cases, heavy cough plagues heavy smokers. The sputum in such cases has a yellow color and a very viscous consistency.
A severe cough has similar symptoms and it must be treated thoroughly, regardless of the cause of the disease, so that in one case it does not worsen the disease, or in the second case, it is necessary to get rid of it completely.
In order to relieve a severe cough, taking medications alone will not be enough. Therefore, it is recommended to drink plenty of herbs, both sold in pharmacies and collected independently. An excellent assistant for removing phlegm are decoctions of: viburnum, raspberry, mint, rose hips, thyme, licorice, chokeberry, plantain.
When thinking about how to treat a severe cough, you should also not forget about inhalations. They will not only help remove mucus, relax muscles, but also have a beneficial effect on the respiratory tract. Even ordinary inhalation in the form of boiled potatoes or steamed eucalyptus can have a beneficial effect on the situation.
It is strictly forbidden to treat a severe cough with drugs that suppress it. This will only worsen the situation and delay the healing process.
Often, a runny nose is a concomitant symptom of the disease. In this case, it is difficult to breathe, the cough intensifies and emergency measures must be taken. In this case, inhalations can also help. But, at the same time, it is necessary to follow a simple breathing technique: inhale through the nose and exhale through the mouth. This way, all airways will be cleared.
Source: https://onsmeta.ru/kashel-trudno-dyshat-prichiny/
Difficulty breathing: causes of lack of air and treatment
Difficulty breathing is a fairly common manifestation that indicates a wide variety of pathologies. In humans, the disorder may manifest as harsh, noisy, or too quiet breathing. The depth of manifestation may also vary. With this symptom, the patient feels a strong lack of air, difficulty in inhaling or exhaling.
Dyspnea is the most common presentation and is also characterized by difficulty breathing. However, it can manifest itself from the usual lack of air after exercise, walking or running. The appearance of a symptom in a calm state may indicate the development of a pathology that threatens human health.
Etiology
Difficulty breathing is a common occurrence that occurs for various reasons. This symptom is typical for those people who suffer from asthma. The appearance of this symptom is normal for them and can be eliminated with special medications.
The causes of difficulty breathing may be the following:
- a foreign body in the respiratory tract, which prevents the passage of air;
- emotional stress;
- lung pathologies;
- disease of the cardiovascular system;
- allergies;
- serious infectious blood lesions;
- physical inactivity;
- excess weight;
- panic attacks and fears;
- hernia;
- change in the environment;
- smoking.
Pulmonary diseases that can trigger the development of difficulty breathing include asthma, pneumonia, COPD, thromboembolism, pulmonary hypertension, croup, epiglottitis, hiatal hernia.
If a person often has difficulty breathing, then he may develop severe heart pathologies. Pulmonary system disorders can develop under the influence of the following ailments:
Difficulty breathing in a child of an older or younger age category can also manifest itself on the basis of respiratory diseases. Also, the reasons for the development of the symptom may be hidden in croup, bronchitis, or pneumonia.
Difficulty breathing in a child
The risk of developing such a symptom increases in those people who are often exposed to stress, allergies, or have chronic lung or heart diseases. The disease can also manifest itself from excess weight and extreme sports.
Shortness of air can occur both during the day and at night. During sleep, the cause of the symptom is hyperventilation syndrome. If a person develops severe drowsiness, but at the same time restless sleep, headaches and rapid heartbeat, then the reason definitely lies in the pathological process. It is difficult for a patient to breathe with the following disorders:
Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of heavy breathing is not that difficult. A person begins to experience inhibited communication and finds it difficult to concentrate on a conversation. Lack of air also manifests itself in the following indicators:
- lowering the head;
- brain function deteriorates;
- deep breathing;
- cough;
- darkening of the eyes;
- blurred objects.
Cough and difficulty breathing can manifest itself in several forms - constant, infrequent, debilitating.
An urgent visit to a doctor is possible if the patient experiences additional symptoms and shortness of breath is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- burning sensation in the sternum and painful attacks;
- heavy breathing at rest;
- discomfort in a lying position;
- wheezing and whistling are heard during sleep;
- unpleasant sensation when swallowing;
- feeling of a foreign body in the throat;
- high body temperature;
- sudden attacks of heavy breathing;
- dyspnea.
If difficulty breathing is detected, the patient should under no circumstances self-medicate. It is enough to identify such a symptom and seek the help of a doctor.
Diagnostics
To diagnose prolonged difficulty breathing, a person needs to know the rate of inhalations per minute. A healthy adult normally has about 17–20 respiratory movements, but children breathe much more frequently. They can take up to 35 inhalations and exhalations in a minute. The breathing rhythm should be counted by the number of one movement - the rise and fall of the chest.
If the patient has asthma or any of the ailments listed above, then his breathing may be significantly faster. An altered respiratory rate can lead to a significant deterioration in the patient’s general condition.
Carrying out an ECG
Difficulty in nasal breathing can occur in a person of any age and gender, so if there are frequent relapses, it is important to immediately inform the doctor. The causes of the symptom can be very diverse, so you need to quickly establish the provoking factor. Depending on the suspected illness, the patient is prescribed laboratory and instrumental diagnostics:
- blood analysis;
- chest x-ray;
- tomography;
- echocardiogram;
- ECG.
Therapy for the symptom is prescribed after diagnosis.
Treatment
If the patient has difficulty breathing through his nose, he can be given first aid before the doctor arrives. To provide emergency support, the patient should remain in a sitting position, but with the spine and shoulders retracted. You can place pillows under your back, but your shoulders should always be open so that your lungs can take in as much air as possible.
Treatment of the symptom can also be done with exercise. The patient can restore breathing with a simple action:
- you need to lie down or sit down with your shoulders back;
- place your palms on your chest;
- breathe through your nose and mouth alternately.
By repeating this exercise several times, the lack of air will decrease and the patient will feel much better. However, it is worth remembering that taking too deep breaths can cause dizziness. After the exercise, you can rest a little.
In case of suffocation, an asthma attack, allergies or stress, doctors advise going out into the fresh air or opening a window. You can also drink cool water or make a compress to slightly relieve the heat from difficulty inhaling and exhaling. In case of allergies, it is important to immediately eliminate the allergen so that there are no relapses.
If cardiovascular diseases are detected, the cardiologist prescribes the patient to spend more time in the fresh air, not be constrained by clothing, maintain a calm state and use diuretics.
Prevention
To normalize breathing during osteochondrosis, stress, allergies and other problems, doctors advise adhering to preventive measures:
- eliminate all negative habits;
- play sports and lead an active lifestyle;
- control weight;
- take medications to improve breathing.
If any of the above signs and difficulty breathing are detected, a person is advised to consult a doctor to find out the exact causes of the symptom and relieve an attack of suffocation.
Source: https://SimptoMer.ru/simptom/zatrudnenne-dyhanie
Difficulty in exhaling
Difficulty in exhalation (expiratory shortness of breath) is a violation of respiratory function with a significant prolongation of exhalation, accompanied by a subjective feeling of fullness and tightness in the chest. The symptom is pathognomonic for bronchial asthma. Expiratory shortness of breath is also observed in broncho-obstructive diseases, chronic lung diseases, and some tumors. To identify the causes of difficulty in exhalation, radiography, spirography, bronchoscopy, and laboratory tests are performed. To relieve symptoms, bronchodilators, glucocorticosteroids, antihistamines, and expectorants are used.
Expiratory shortness of breath is caused by impaired patency of the bronchial tree and is a symptom of the obstructive form of chronic respiratory failure.
Bronchial blockage can develop both due to organic pathologies of the respiratory tract and when a foreign body enters. Difficulty in exhalation also occurs in the second stage of asphyxia, when compensatory reactions are exhausted and the respiratory center in the medulla oblongata is depressed.
More rare causes of shortness of breath: bronchospasm in Mendelssohn syndrome, tracheal tumors located near its bifurcation.
Bronchial asthma
The disease is characterized by sudden difficulty in exhaling after contact with provoking substances. A few minutes before the attack, a sore throat, nasal congestion, and itchy skin are felt.
Then suddenly there is a feeling of tightness in the chest, an acute lack of air and the inability to perform normal breathing movements. The inhalation is short, convulsive, the exhalation is significantly prolonged. When exhaling air, whistling sounds and wheezing are heard.
To alleviate the condition, patients sit with their legs dangling, lean their hands on their knees or lean on the bed.
During an attack, the patient's appearance is typical: his eyes are wide open, his face appears puffy, and the nasolabial triangle is noticeably blue. When you inhale, the neck veins swell.
Due to difficulty in exhaling, active movements of the chest and abdominal tension are noticeable. In mixed bronchial asthma, shortness of breath is provoked not only by contact with allergens, but also by stress and exposure to cold air.
Attacks of difficult exhalation that occur exclusively at work are pathognomonic for occupational asthma.
Prolonged paroxysms of difficulty breathing, which are not relieved by conventional medications, are observed in status asthmaticus. The person is constantly in a forced position (orthopnea), there is a sharp cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, and blue discoloration of the fingertips.
Patients are restless, convulsively inhale air, and some patients experience fear of imminent death. As respiratory failure progresses, breaths become increasingly rare, and the person loses consciousness.
Failure to provide emergency medical care can result in death.
Obstructive bronchitis
The disease is accompanied by bronchoconstriction, which causes constant breathing disorders of varying severity. In acute obstructive bronchitis, shortness of breath on exhalation often occurs during a coughing attack.
The exhalation phase of air is significantly prolonged, patients complain of chest tightness and suffocation. The pulse quickens, cyanosis of the lips is possible. Similar attacks of shortness of breath occur throughout the entire period of illness - about 2-3 weeks.
Difficulty in exhalation also indicates a complicated course of chronic bronchitis.
Shortness of breath with minimal physical exertion occurs with bronchitis of smokers, dust bronchitis. In this case, it is difficult exhalation that becomes one of the first symptoms and appears against the background of normal well-being.
Young children are characterized by a special form of expiratory suffocation due to narrowing of the smallest bronchi - acute bronchiolitis, complicating ARVI, respiratory syncytial infection.
The child has difficulty wheezing, swelling of the wings of the nose, and bluish skin.
Other obstructive diseases
In addition to inflammation of the bronchial tree, other organic pathologies of the respiratory tract can cause difficulty in exhalation.
Disturbances in these diseases develop gradually, imperceptibly, so patients do not go to doctors for a long time, which is fraught with a complicated course.
The main link in pathogenesis is changes in the structure of the bronchial wall, excessive growth of connective or scar tissue, causing bronchoconstriction. Expiratory shortness of breath is accompanied by:
- COPD . At the onset of the disease, there is slight shortness of breath during physical activity, which is often overlooked. With the progression of morphological changes in the bronchi, difficulty breathing with prolonged exhalation develops at rest. During an attack, patients take a forced position, severe cyanosis of the skin is noted, and a paroxysmal painful cough is bothersome.
- Bronchiectasis . The appearance of difficulty in exhalation indicates the presence of respiratory failure. With bronchiectasis, symptoms can occur regardless of the time of day. Attacks of shortness of breath are prolonged, and in the terminal stages they are extremely difficult to control with the help of bronchodilators. In addition to difficulty in exhaling, a severe cough develops with the release of copious purulent sputum and pain in the chest area.
- Stenosis of the trachea and bronchi . Expiratory stridor is typical - a noisy, difficult exhalation, preceded by a short, convulsive inhalation. The severity of breathing difficulty depends on the cause of the obstruction and the degree of stenosis. When the trachea is narrowed against the background of shortness of breath, short-term fainting is possible, associated with reflex effects on the nerve endings. Bronchostenosis occurs as recurrent bronchitis.
- Osteochondroplastic tracheobronchopathy . There have been no complaints for a long time. With massive replacement of the walls of the respiratory tract with bone tissue, difficulty exhaling, noisy wheezing is noted, and patients experience a lack of air. Respiratory disorders are combined with dull pain in the chest cavity and sore throat. Gradually, shortness of breath intensifies, and in severe cases of the disease, attacks of suffocation appear.
- Williams-Campbell syndrome . With this congenital disease, respiratory disorders appear already in the first months of a child’s life. Parents note that the baby becomes restless, breathing is noisy and stridorous. Severe shortness of breath is indicated by retraction of the intercostal spaces and supraclavicular fossa, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle. The child refuses the breast or pacifier, the crying becomes quiet.
Breathing difficulties are caused by both obstructive and restrictive mechanisms. Patients complain of the inability to take a deep breath, prolonged exhalation with wheezing, which can be heard from a distance. The symptom sometimes occurs with prolonged pneumonia and other chronic nonspecific lung diseases. The most common causes of shortness of breath are:
- Emphysema . Difficulty in exhalation is initially noticed only during physical exertion or climbing several flights of stairs. Patients exhale air through tightly closed or folded lips, while strongly puffing out their cheeks and “puffing.” Unlike other diseases, with emphysema the skin has a healthy, pink color. A similar clinical picture is also observed in the ventilation form of McLeod syndrome.
- Pneumosclerosis . When the pulmonary parenchyma is replaced, difficulty breathing occurs both during exercise and at rest. There is a prolongation of exhalation, a feeling of lack of air, and with prolonged attacks the fear of death is expressed. Respiratory disorders are accompanied by diffuse cyanosis of the skin. Shortness of breath can occur at any time of the day, but painful suffocation is more common at night or in the early morning.
- Pulmonary ascariasis . Difficulty breathing with prolongation of exhalation develops against a background of severe chest pain and general intoxication. Typical complaints are frequent and prolonged episodes of shortness of breath, provoked by the allergic effect of helminths. At the time of the attack, a dry cough with loud wheezing begins. The patient sits up on the bed, leans forward and rests his arms bent at the elbows on his knees.
- Alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency . Symptoms occur in young people with predominantly lung damage. Difficulties first occur when playing sports, running, or climbing stairs above the 3rd floor. Subsequently, prolongation of exhalation manifests itself even at rest. During paroxysm, there is a feeling of lack of oxygen and the need to tense the abdominal muscles for a full exhalation. Perioral cyanosis appears, the wings of the nose swell.
Occupational diseases
Difficulty in exhalation is characteristic of byssinosis, which develops upon contact with dust from spinning raw materials. Respiratory disorders become noticeable after breaks from work - vacations, weekends, which is called “Monday syndrome”.
Expiratory shortness of breath is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and pressure in the chest and a sore throat. The symptom also occurs with massive gasoline pneumonia.
In such cases, prolongation of exhalation is combined with coughing, wheezing, and general symptoms of intoxication.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
Attacks of expiratory dyspnea occur in so-called aspirin-induced asthma. Symptoms appear immediately after taking the medication: patients experience painful convulsive inhalations and whistling long exhalations.
A similar clinical picture is observed with the bronchial type of allergy to salicylates; in this case, difficulties during exhalation persist for 1-3 days after taking the medication.
The symptom manifests itself in severe cases of citrate intoxication - long-term episodes of respiratory disorders are characteristic, in the most severe cases apnea occurs.
Survey
Patients with complaints of difficulty in exhaling most often turn to a pulmonologist or therapist.
Expiratory shortness of breath indicates serious disorders in the respiratory system, so a comprehensive laboratory and instrumental examination is necessary.
During the diagnosis, the specialist evaluates the morphological features of the trachea, bronchi and lungs, and also examines the functional state of these organs. The most informative are:
- X-ray examination . To study the features of the anatomical structures of the chest cavity, a standard chest x-ray is performed in two projections - frontal and lateral. The method helps to detect deformations of the bronchi and trachea, signs of sclerosis and emphysema. For better visualization of the respiratory tract and neighboring organs, CT is prescribed.
- Bronchoscopy . Endoscopic examination is aimed at studying the structure of the mucous membrane, identifying pathologically altered areas of tissue and cicatricial stenoses. According to indications, the method is supplemented with forceps biopsy and bronchoalveolar lavage, followed by microscopic and bacteriological analysis of rinsing water.
- Spirometry . The nature of breathing difficulty can be established by studying the main indicators - forced expiratory volume in the first second, functional vital capacity of the lungs, Tiffno index. For differential diagnosis between bronchial asthma and other obstructive pulmonary diseases, a bronchodilator test is recommended.
- Lab tests . The degree of respiratory failure is determined according to blood tests - the level of hemoglobin oxygen saturation and the concentration of carbon dioxide are determined. In the presence of a general infectious syndrome, a bacteriological blood test is indicated. To clarify the type of pathogen, serological reactions are carried out (RIF, ELISA, PCR).
To determine the etiological factor of bronchial obstruction in the remission phase, allergy tests are prescribed. If a congenital disease of the respiratory system is suspected, consultation with other specialists is required.
Symptomatic therapy
Difficulty in exhaling often indicates organic diseases of the respiratory system, so qualified medical care is necessary. If the disorder occurs for the first time and is severe, you should urgently call an ambulance.
Before doctors arrive, it is important to provide the patient with peace and sufficient flow of fresh air, place him in a semi-lying position, and limit contact with possible allergens.
To reduce emotional stress, you can offer mild herbal-based sedatives.
If an attack occurs in a patient with an established diagnosis of bronchial asthma, you should immediately take previously prescribed bronchodilators in the form of an aerosol (beta-adrenergic agonists, anticholinergics, myotropic antispasmodics).
For inflammatory diseases, expectorants can be used, and for allergic conditions, antihistamines can be used.
In other cases, special medications can be used only after examination by a doctor, taking into account his recommendations.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/symptom/dyspnea/exhalation-difficulty