Depending on the location, uterine fibroids are divided into several types.
- Submucosal tumor. The formation begins to grow under the mucous membrane inside the cavity. Its development is accompanied by severe pain during menstruation and heavy bleeding.
- Interstitial tumor. This type of fibroid is very common and fibroid formation begins in the middle of the uterine wall. This process provokes an enlargement of the uterus.
- A subserosal formation grows on the outer surface of the uterus. For a long time, the disease does not make itself felt, but only until the growth increases in size and begins to compress the internal organs.
- A rare type of uterine fibroid is a parasitic tumor that attaches to neighboring organs.
- The interligamentous formation is formed between the ligaments that support the uterus.
- A stalked fibroma has a stalk and, if there is a bend, the woman feels severe pain. This type of disease is the most dangerous.
Cause of fibrosis
Doctors do not yet fully know the exact causes of the tumor disease fibrosis. Many experts say that the problem lies in genetic predisposition and hormonal imbalance. The uterine cavity is covered with mucous membrane, and the walls of the organ consist of smooth muscles. The size of the uterus is constantly changing. For example, during pregnancy the size of the organ can increase to the size of a watermelon , and in nulliparous women the reproductive organ is no larger than one's own fist.
The growth of the mucous membrane, which occurs monthly, depends on the hormone estrogen, because it stimulates cell growth.
It is worth knowing that an excess of this hormone can lead to serious problems , including fibrotic disease.
The reason is that with age, the female body becomes more sensitive to various changes, and the risk of developing cancer cells is very high. This phenomenon applies more to the cells of the uterus, which have the ability to grow very quickly.
Typically, uterine fibroids are formed due to hormonal imbalances, and it is the uterus that takes the brunt.
It is worth saying that the reasons for a benign formation can be:
- difficult childbirth and pregnancy;
- absence of pregnancy before the age of thirty;
- taking birth control pills regularly;
- early abortions;
- excess weight;
- diabetes;
- diseases of the thyroid system;
- unstable sex life.
Is it possible to get pregnant with uterine fibroids?
Many women are concerned about this question, but the answer is yes. Experts say that this type of tumor is not an obstacle to motherhood , but they also warn that in some cases this disease can lead to difficult pregnancy and protracted labor. In most situations, the woman does not give birth herself; she has a caesarean section. There are cases where after the first trimester the size of the tumor decreased significantly. Also, a benign formation may decrease or even disappear after menopause.
Symptoms of fibrosis
The most common symptoms are:
- severe bleeding, which is accompanied by sharp pain and cramps;
- pain in the pelvic area due to fibroid pressure;
- heaviness in the bladder area, frequent and painful urination;
- discomfort in the intestinal area, flatulence, constipation;
- increase in weight and abdominal size;
- pain during sexual intercourse.
Diagnosis of uterine fibroids
If none of the types of diagnostics yield results, the doctor prescribes hysteroscopy. The principle of the examination is to insert a very thin probe, with which you can examine in more detail not only the uterus, but also neighboring organs.
Treatment of fibrous tumor
There are several ways to overcome uterine fibroids. Treatment can occur surgically, medications and even folk remedies.
Under no circumstances should you prescribe treatment yourself , and medications should only be prescribed by a doctor. The specialist must assess the size of the fibrous nodes and choose the appropriate type of treatment.
If the disease is accompanied by severe pain, the woman needs careful medical supervision. If the correct treatment is not prescribed in time or surgery is not performed, fibroma can develop into a malignant tumor.
Drug treatment
The treatment course occurs with the help of non-steroidal drugs and hormones that relieve inflammation and restore the woman’s hormonal levels.
With long-term treatment, some women may experience menopause and menstrual irregularities.
Surgical intervention
During this procedure, manipulations are carried out only with the tumor, without touching the uterus itself. This method of surgery is offered to young women and girls who want to have children. But there is also a negative side to this treatment - adhesions and scars that remain after surgery. There is also a small chance of new nodes forming. But despite this, surgery remains the most popular method of combating fibroids.
There is also another type of operation, which is performed under general anesthesia. To do this, several small incisions are made in the patient’s abdomen and and surgical supplies are inserted This operation does not leave any scars.
Folk remedies
The healing properties of white clay, which is dissolved in herbal decoctions and smeared on the lower back, are also known. The application layer should be at least 1.5 cm. Then the back is covered with cling film and wrapped in a towel. Such manipulations must be carried out over seven days.
Uterine fibrosis can be treated with freshly squeezed juices from vegetables and fruits - potatoes, beets, plums, cabbage. These liquids contain elements that destroy excess estrogen hormone.
Traditional treatment includes a variety of recipes.
- You need to take 14 green nuts, pour 0.5 liters of vodka over them and leave them in a cool and dark place for several days. You need to take 1 tsp of the tincture. 3 times a day half an hour before meals.
- If fibroids are accompanied by severe pain, you can take warm baths with herbs. To do this, take 2 tbsp. celandine, hawthorn berries, mint, motherwort herb, rose hips and valerian. All components are mixed and 0.5 ml of boiling water and 2 tbsp are added. Indian onion tinctures. Allow the mixture to steep for 1.5-2 hours and can be added to bathing water.
You should not focus too much on treatment with traditional methods. In any case, treatment should be prescribed by a doctor. Also, traditional medicine will be useful in combination with basic treatment , but it is imperative to consult a doctor. In some cases, herbal infusions only reduce the size of fibroids.
Prevention of fibrosis
As preventive actions it is necessary:
- avoid abortion;
- treat gynecological inflammations and diseases in a timely manner;
- monitor hormonal levels;
- have a regular sex life;
- visit a gynecologist regularly;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- avoid stressful situations.
It must be said that uterine fibroid is not a very pleasant disease, but modern medicine offers many safe ways to treat the disease. The main thing in this situation is to promptly contact specialists and regularly visit a gynecologist.
Source: https://dermatolog.guru/zabolevaniya/novoobrazovaniya/simptomy-fibromy-matki-i-metody-lecheniya-opuholi.html
Uterine fibroid: what is dangerous, symptoms and treatment
Uterine fibroids are a disease known as uterine leiomyoma, a common, non-cancerous growth of the endometrial lining of the uterus. Myomas are muscle cells and tissues, ranging in size from a pea to 12.7-15.24 cm in width.
25-30% of women are diagnosed with fibroids. Although the pathogenesis is not completely understood, fibroids depend on individual fibroid cells and not on a metastatic process.
Fibroids are considered the most common benign solid tumors of the female genital tract. Although often asymptomatic, signs can cause infertility, pain, and bleeding. Gynecology is the field of study of uterine fibroids.
The ICD-10 code (this is a classification of diseases approved by WHO) for uterine fibroids is D25.
Fibroids can outgrow their blood supply and degenerate. The degeneration is described as hyaline, myxomatous, calcific, cystic, fatty, red (pregnancy only), or necrotic. The patient often appears concerned about fibroid cancer; sarcomatous changes occur in less than 1% of patients. A connective tissue tumor is benign.
Where do fibroids grow?
Myoma happens:
- intramural (uterine wall);
- submucosa (under the lining of the uterus);
- subserous (under the outer surface of the uterus).
Causes
The cause of uterine fibroids is unknown. Hormones produced in the ovaries (estrogen, progesterone) are thought to play a role in development according to OWH. Researchers believe that ovarian hormones influence growth. Fibroids rarely occur before a woman goes through pregnancy and menopause.
Fibroids are more common in obese women and menopause. Cigarette smoking is recognized as a provoking factor.
Types of uterine leiomyomas
Onset of symptoms
Often women do not feel symptoms. Submucosal fibroids alter the uterus' ability to control menstrual bleeding, leading to heavy periods associated with blood clots that cause cramps. The difference is that they typically do not cause pain or emergency bleeding between periods.
Nodular and subserous fibroids, unlike others, as a rule, do not lead to difficult periods.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids:
- chronic blood pressure;
- symptom of difficult bowel function;
- lower back pain and pelvic pain;
- pain during sex;
- clothes seem tight.
Based on the listed signs, it is possible to recognize fibroids.
Fibroids can cause anemia, fatigue, and blockage of blood vessels and nerves, causing sharp and severe pain.
Myoma is dangerous by increasing the risk of infertility. During pregnancy, this threatens recurrent spontaneous abortion.
Diagnosis
A critical analysis of the surgical treatment of fibroids compares available myomectomy techniques. Statistical analyzes highlight the advantages of laparoscopic and hysteroscopic approaches.
While open myomectomy results in limited morbidity similar to hysterectomy, the differences of laparoscopic myomectomy result in significant benefits for the patient medically, socially, and economically, with less postoperative pain and shorter recovery time.
Sem and Mettler published the first paper on laparoscopic myomectomy in 1980. Today, the uterine growth is enucleated using the indicated method.
Standard laparoscopic surgery is complemented by robotic support and abdominal entry, often modified to NOS (natural orifice surgery) and natural transluminal endoscopic orifice surgery called single-port entry.
Individual nodes may not be palpable during a gynecologist's examination. Thus, the specialist will not be able to make an accurate diagnosis.
Ultrasound is recognized as the standard method for detecting benign uterine tumors. This helps to see the location and size of the nodes, plus distinguish cancer from fibroids.
Additionally, hysteroscopy and laparoscopy are used.
The examination should show a neoplasm in the ovary and uterine appendages. Data on the period and results of ultrasound examination are required to make an accurate diagnosis.
Complications
Women with subserous uterine fibroids are predicted to have a favorable pregnancy, but this does not reduce the risk of complications. Complications: premature birth in a pregnant woman, the baby is in position, during childbirth there is a possible risk of needing a cesarean section. Select women during pregnancy experience pain during the 1st and 2nd trimester.
Consequences and complications may arise due to the location of fibroids in the uterus. They range from intermittent bleeding to continuous bleeding over a number of weeks, from single episodes of pain to severe pain, from dysuria and constipation to chronic spasms of the bladder and bowels. Peritonitis is extremely rare.
The difficulty of laparoscopic and hysteroscopic myomectomy differs in achieving satisfactory hemostasis using appropriate sutures. Hysteroscopic myomectomy requires an operative hysteroscope and an experienced gynecological surgeon to operate on the connective tissue in the uterus.
Sometimes fibroids can distort and block the fallopian tubes, making it difficult for sperm to pass from the cervix into them.
Treatment
Gonadotropin-containing hormone (GnRH) is used to relieve the symptom of pain.
Myomectomy (to preserve fertility) or hysterectomy for symptomatic fibroid tumors is indicated.
Asymptomatic fibroid tumors do not require treatment. A woman should be examined periodically (every 6–12 months) by a gynecologist.
For symptomatic fibroids, treatment options include ovarian hormone suppression to control bleeding. Opportunities are suboptimal and limited. Physicians should consider medical clinical treatment and discuss other options before performing surgery.
Agonists (GnRH) are sometimes given before surgery to shrink fibrous tissue. These drugs often stop menstruation and allow blood counts to increase.
In the perimenopausal period, it is permissible to wait, because the mature growth decreases in size after menopause or may disappear.
Drugs for fibrous tumors
A number of drugs are used to relieve symptoms, reduce fibrous growth, or both:
- agonists (GnRH);
- exogenous progestins;
- antiprogestins;
- selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs);
- danazol.
Agonists (GnRH) are often the drugs of choice. For large fibroids, they can reduce fibrous size and bleeding.
These drugs can reduce estrogen production. Agonists (GnRH) are most useful if given preoperatively to reduce fibrous and uterine volume, making surgery technically more feasible and reducing blood loss.
In general, the drugs mentioned should not be used long term. Increased recovery to pretreatment size within 6 months is common, and bone demineralization is possible.
To prevent long-term use of the drugs, doctors must give patients extra estrogen.
Exogenous progestins may partially inhibit estrogen stimulation of uterine fibrous growth. Progestins may reduce uterine bleeding but may not reduce fibroids as well as agonists (GnRH). These medications may be taken every day (continuous therapy). Such therapy often reduces bleeding and provides contraception.
Intrauterine device with hormones
Progestin therapy causes the muscle layer to grow in some women's uteruses. A levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device (IUD) may be used to reduce uterine bleeding.
Danazol is an androgen agonist that can suppress fibrotic growth in the early stages, but has a high rate of adverse effects (weight gain, acne, swelling, hair loss, flushing, vaginal dryness), so it is less commonly taken.
Surgery for fibroid tumors
Surgery is usually used for women in the following cases:
- Rapidly growing tumor-like formation of the small pelvis.
- Recurrent uterine bleeding, unresponsive to drug treatment.
- Severe or constant pain or pressure under the skin (requires opioids for control or is intolerable to the patient).
- A large uterus that has a mass effect in the abdominal cavity, causing urinary bowel symptoms or compressing other organs, causing dysfunction (eg, hydronephrosis).
- Infertility (if pregnancy is desired).
- Recurrent spontaneous abortions (if pregnancy is desired).
- Dimensions for mimoma removal surgery.
- Other factors favoring surgery are the completion of the birth of the child and the expressed desire of the patient to choose the exact treatment.
Myomectomy is done laparoscopically or without automated methods.
A hysterectomy can also be done laparoscopically, vaginally, or by laparotomy (an incision in the abdomen).
Most indications for myomectomy and hysterectomy are similar. Patient choice is important, but people should be well informed about the expected difficulties and complications of myomectomy versus hysterectomy.
Removal in sections is done during a myomectomy or hysterectomy. Remove in parts, including cutting fibrous tumors or intrauterine tissue into small parts so that they can be removed through a smaller incision (for example, laparoscopically).
It is extremely rare for women undergoing surgery for uterine fibroid tumors to have an unsuspected, undiagnosed sarcoma or other uterine cancer. If removal is done piecemeal, malignant cells may be disseminated into the peritoneum.
Patients should be advised that if piecemeal removal is used, there is a small risk of dissemination of cancer cells.
If women desire pregnancy or want to keep the uterus, myomectomy is used. In approximately 60% of women with infertility due to fibroid tumors, myomectomy restores fertility and it is possible to become pregnant after approximately 14 months. However, hysterectomy is often necessary or preferred by the patient.
This is a more precise treatment. After a myomectomy, new fibroids sometimes begin to grow again, and approximately 25% of women with myomectomies have a hysterectomy approximately 4-8 years later.
Patients have other pathologies that make surgery more complicated (extensive adhesions, endometriosis).
Hysterectomy reduces the risk of other problems. This includes cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and others.
New procedures may relieve symptoms, but the duration of symptom relief and the effectiveness of the procedures in restoring fertility have not been assessed.
- High intensity focused echography.
- Cryotherapy.
- Radiofrequency amputation.
- Magnetic resonance guided focused ultrasound surgery.
- Detection on x-ray.
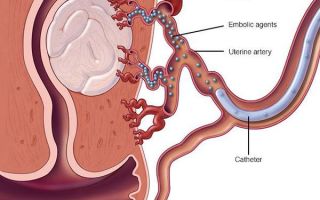
- Uterine artery embolization.
Uterine artery embolization tends to cause infarct formation of fibroid tumors throughout the uterus while sparing normal uterine tissue.
Women recover more quickly after the procedure than after a hysterectomy or myomectomy, but complication rates and return visits tend to be higher.
The treatment failure rate is 20-23%; in such cases, treatment with hysterectomy is required.
Choice of treatment
To treat fibroma, factors are taken into account:
- Asymptomatic fibrous tumors: no treatment required.
- Women after menopause: trial of expectant management, after menopause, fibroids become smaller.
- Symptomatic fibroids provided that pregnancy is desired: uterine artery embolization, another new method (high intensity focused echography) or myomectomy.
- Severe symptoms when other treatment has failed, especially if the pregnancy is unwanted: hysterectomy, possibly preceded by drug treatment (with GnRH agonists).
Treatment of uterine fibroids with folk remedies
Treatment of uterine fibroids with folk remedies is a fairly popular treatment method aimed at eliminating unpleasant symptoms, as well as reducing bleeding.
For treatment, exclusively natural plant components are used, for example, calendula, which is brewed and taken orally.
Other remedies include blue iodine with milk, walnuts, and flaxseeds. But before self-medicating, you need to consult a doctor.
Calendula (2 tablespoons) is poured into an empty bottle, left in the dark for two weeks, shaken daily. Juice gradually appears. After the expiration date, filter the resulting mixture. Drink 1 tbsp. spoon 3 times a day.
Homeopathy helps to get rid of symptoms and tumors so as not to undergo hormonal treatment. This restores balance in the central nervous system. The concentration of estrogen decreases. The preparations are selected by a qualified homeopath. But this does not always achieve a certain effect.
Prevention
- Regular visits to the gynecologist.
- Diet (inclusion of vitamins in the diet).
- Diet involves eating healthy. Fried foods, alcohol, and overeating should be excluded.
- Elimination of bad habits - smoking.
- Check hormone levels.
- Use contraception.
Psychosomatics of fibroids
Psychosomatics greatly influences the course of the disease. If you often experience stress or overeat, this will aggravate the situation, and the cure of the disease will proceed more slowly.
Modern research shows that there is a connection between psychological state and the development of uterine fibroids. This must be taken into account during treatment and explained to women, because with psychological help one can achieve good results, to the point that fibroids can shrink without the use of surgical methods.
Factors influencing the development of a psychosomatic condition:
- unwillingness to become pregnant and making decisions about abortion;
- lack of pleasure from sexual contact;
- stress associated with resentment;
- low self-esteem;
- lack of self-love.
These psychosomatic factors launch a destructive program. As a result, the internal condition worsens and various diseases appear, which include uterine fibroids. Miscarriage also often affects the psychosomatics of the disease. Long-term depression appears, from which fibroids develop.
Uterine fibroids are a serious disease. The course of the disease depends on monitoring your own health. You need to be calmer about everything and not worry about the little things. Then the disease may disappear altogether.
Source: https://onko.guru/dobro/fibroma-matki.html
Uterine fibroid: causes, symptoms and treatment in an article by gynecologist A. Yu Klimanov
Literary editor Elena Berezhnaya and scientific editor Sergey Fedosov worked on the article by Dr. Klimanov A.Yu.
Published February 5, 2018 Updated July 18, 2019
Uterine fibroid is a hormone-dependent benign neoplasm that develops from the cells of the myometrium (the muscular wall of the uterus). At its core, fibroma is a type of uterine fibroid. A distinctive feature of uterine fibroids is the predominant content of connective tissue in the tumor tissue.
Fibroma is a round formation, the structure of which contains connective tissue components, myocytes, blood vessels, plasma cells and mast cells.[1]
According to studies, the peak incidence occurs in the premenopausal period (46-55 years), in some cases this pathology occurs in women of late reproductive age (35-40 years), but in recent years the disease has also been diagnosed in younger patients (25-30 years ). Uterine fibroids can grow, regress and even disappear in postmenopause, but in 10-15% of women the formation increases in the first 10 years of the menopausal period, combined with hyperplastic processes of the endometrium and proliferative diseases of the ovaries.[3]
If you notice similar symptoms, consult your doctor. Do not self-medicate - it is dangerous for your health!
Three main features can be distinguished:
- bleeding and other various menstrual irregularities;
- presence of pain;
- dysfunction of adjacent organs.
Deformation of the uterine cavity by submucosal nodes leads to bleeding and other menstrual dysfunction; patients complain of an increase in the intensity and duration of menstruation, and the appearance of bloody intermenstrual discharge. Simply enlargement of the uterus due to fibroids can also lead to various uterine bleeding.
As the fibromatous node enlarges, complaints of various pains in the lower abdomen may occur. Most often these are pains of a pulling or aching nature. The growth of fibroids may be accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and discomfort, and an increase in the size of the abdomen may occur.
Dysuric phenomena and defecation disorders may be symptoms of subserous localization of fibroma. Acute pain syndrome, increased body temperature and symptoms of intoxication are characteristic of tumor necrosis and torsion of the stalk of subserous fibroma. The severity of clinical manifestations depends on the degree of disruption of the blood supply to the fibromatous node.
So why does fibroma appear? Despite a number of clinical studies, science cannot give a clear answer to this question.
In the development of fibromatous nodes, disturbances in the hypothalamic-pituitary system, changes in the state of the body’s immune system, hereditary predisposition, and the presence of chronic infections in the patient play an important role.
Various changes in the blood supply to the pelvis, which often occur in patients with fibroids, are a favorable factor for the development of the tumor.[4]
In addition, there are risk factors for developing uterine fibroids:
- age;
- early menarche;
- no history of childbirth;
- obesity;
- long-term use of contraceptives.
Often the onset of the disease is asymptomatic, and women learn about their diagnosis during a routine examination with a gynecologist. The manifestation of the clinical picture of uterine fibroids largely depends on its size and location. A growing fibromatous node can become one of the causes of infertility and miscarriage.[3]
The pathogenesis of uterine fibroids is still a subject of heated debate. According to the classic works of K.P. Ulezko-Stroganova, conducted on the morphology of the female reproductive system, the formation of the rudiments of fibromatous areas occurs at the embryonic stage.
Scientific literature data on the importance of sex hormones in the development of uterine fibroids is currently very contradictory, however, numerous clinical and laboratory studies confirm that disruption of estrogen metabolism in a woman’s body leads to mitotic activity, which contributes to the formation of fibromatous nodes. An increase in fibrometry occurs due to hyperplasia of smooth muscle cells and their proliferative changes.
Classifications of uterine fibroids are based on the location and direction of growth of the formation, as well as on clinical manifestations.
1. By localization and direction of growth:
- subserous - growth of a fibromatous node towards the abdominal cavity (intra-abdominal location, intraligamentous location). In this case, the fibroma is located under the serosa of the uterus;
- submucosal - growth of a fibromatous node towards the uterine cavity, under its mucous membrane (endometrium);
- interstitial - the growth of fibroids inside the wall of the uterus, in the thickness of the muscle layer.
2. According to clinical manifestations:
- asymptomatic uterine fibroma (occurs in 70-80% of cases) - fibroma that does not manifest itself in any way. Typically, the early stage of fibroid development is asymptomatic.
- symptomatic uterine fibroid (occurs in 20-30% of cases) - in this case there are various symptoms caused by the tumor. As already mentioned, clinical manifestations of symptomatic uterine fibroids can be: menstrual irregularities - menometrorrhagia; pain syndrome of varying severity and nature (pulling, cramping, dysmenorrhea); various signs of compression and/or dysfunction of the pelvic organs that are located next to the uterus; infertility; habitual miscarriage.
Depending on the number of nodular formations, single and multiple uterine fibroids are distinguished. Multiple uterine fibroids are more common.
A risk factor for the health of patients with fibroids is an increase in the tumor with characteristic signs of pathology - bleeding; pressure of the node on neighboring organs.
The most common complications of uterine fibroids include:
- anemia: due to prolonged and heavy uterine bleeding, the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood decreases. The main symptoms are weakness, fatigue, headaches, dizziness, the appearance of trophic changes;
- infertility: large uterine fibroids significantly reduce the chances of pregnancy. This is due to a number of reasons: the uterine cavity changes and implantation of a fertilized egg becomes difficult; large fibromatous formations can block the mouths of the fallopian tubes, preventing sperm from entering them;
- the birth of a fibromatous node: this complication occurs when the node is submucosal on a stalk, when it exits into the vagina. The onset is always acute and requires immediate hospitalization! If left untreated, it can lead to serious consequences, such as infectious inflammation, peritonitis;
- torsion of the tumor stalk, malnutrition of the formation, leading to subsequent necrosis: uterine fibroids can deform the vessels that provide its blood supply, and thereby cause tissue necrosis. Necrosis can be provoked by physical activity, sexual intercourse, and pregnancy. It is one of the most dangerous complications and requires immediate hospitalization!
- disturbances in the functioning of internal organs , which occur due to excessive pressure on the pelvic organs, which causes the development of chronic diseases (constipation, colitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis).
As a rule, diagnosing uterine fibroids in most cases is not difficult. First of all, it is necessary to correctly identify the medical history and take into account all risk factors for the occurrence of uterine fibroids, and conduct a gynecological examination. The easiest way to diagnose uterine fibroids is a gynecological examination on a chair .
During this examination, subserous fibromatous nodes may be palpated separately from the uterus. Most often in the form of separate formations of a round shape, dense, with varying degrees of mobility. The uterus itself can be of various sizes, but more often it is enlarged, and can be of enormous size.
The surface of the uterus is palpable with a tuberous, fibromatous nodes of a denser structure. If blood circulation in fibromatous nodes is impaired, palpation becomes painful. In women with interstitial fibroma, an enlarged uterus can be felt, the consistency of which will be dense, the surface may be smooth or lumpy.
Malnutrition of the interstitial nodes usually does not occur, so palpation of such a uterus is most often painless.
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the pelvic organs is the gold standard not only for diagnosing primary uterine fibroids, but also for their dynamic monitoring.
[1] The advantage of the method is its information content, accessibility, and safety.
However, it is worth considering the fact that ultrasound is a rather subjective diagnostic method, because the reliability of the results largely depends not only on the qualifications of the specialist, but also on the patient’s preparation for the study.
Ultrasound diagnostics makes it possible to assess the size of the uterus, establish the number of pathological foci and their location, the nature of the shape and contours, size, structure and density; during dynamic observation, compare the data with the results of the previous study, assess the dynamics of the pathological process.
To clarify the location of fibromatous nodes, you can use ultrasound tomographs that provide a three-dimensional ultrasound image. Significant diagnostic data can be revealed by color Doppler mapping (CDC) .
Using it, you can evaluate not only the echographic picture of the structure of the fibroma, but also evaluate its blood flow.
Along with ultrasound diagnostics, methods such as computed and magnetic resonance imaging . However, methods of radiological diagnosis in women of reproductive age are resorted to under strict clinical indications.
In case of menstrual irregularities, patients are advised to undergo diagnostic hysteroscopy - a highly informative method that allows assessing not only the condition of the uterine cavity, pathological processes of the endometrium, the type of node and its location, but also deciding on the possibility of performing transcervical fibromectomy with endoscopic control.[1] Carrying out such a procedure is possible only in patients with fibroids with an enlarged uterus no more than 12-13 weeks of pregnancy.
In addition, to assess the condition of the endometrium for diagnostic purposes, endometrial curettage with histological examination is used. The results of histological examination can significantly affect the management of the patient. Carrying out diagnostic curettage allows you to decide on the continuation of conservative therapy or the extent of surgical intervention.
In special cases, if it is necessary to differentiate between fibroma and giant ovarian and retroperitoneal tumors, diagnostic laparoscopy is used.
There are two main tactics for treating uterine fibroids - conservative and surgical. The only way to completely get rid of the tumor is through surgery.
Conservative treatment methods involve influencing pathogenetic changes to slow the growth of uterine fibroids. This can be achieved by prescribing hormonal therapy.
The main drugs here can be gestogens, gonadotropin releasing hormone agonists, androgens, gonadotropin antagonists.
Correction of metabolic disorders such as obesity and diabetes mellitus, normalization of immune processes, restoration of menstrual function, prevention of inflammatory diseases can also have a beneficial effect on the disease.[5][6]
Despite the positive results of conservative therapy, surgical treatment remains the leading method in the treatment of uterine fibroids.[1] The extent of the operation largely depends on the age of the patient and her desire to maintain the ability to become pregnant, on the location and size of fibromatous nodes, the rate and nature of their growth.
Indications for surgical treatment are:
- symptomatic uterine fibroid (presence of pain, pathological uterine bleeding, signs of anemia);
- submucous location of uterine fibroids;
- subserous node of uterine fibroid on a stalk;
- rapid growth of fibroma and its large size;
- cervical and cervical-isthmus localization of fibroma;
- acute malnutrition of fibroid nodes, severe ischemic and degenerative changes;
- the presence of a fibromatous node in the area of the tubal angle of the uterus;
- compression of pelvic organs by fibroids - bladder, ureters, rectum. Especially if this leads to disruption of their functions.
Previously, the only treatment for fibroids was radical surgery - hysterectomy, that is, removal of the uterus. The modern approach is to remove fibromatous nodes using laparoscopic technologies, which allows preserving not only menstrual function, but also the woman’s ability to bear a child.
Minimally invasive organ-preserving operations include uterine artery embolization, which is both an independent procedure and one of the stages of preparation for surgery. Due to the decrease in blood flow after UAE, the nutrition of the nodes is disrupted, which leads to their reduction and prevents further growth.
[5][6]
With timely diagnosis and treatment, uterine fibroids have a fairly favorable prognosis. Malignization of fibroids, that is, malignancy of the tumor, occurs extremely rarely, in only 2-5% of cases.
Measures to prevent the development of uterine fibroids include timely detection and treatment of gynecological pathologies, reproductive function, adherence to the principles of a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition, and giving up bad habits.[7]
- National leadership. Gynecology Ed. IN AND. Kulakova, I.B. Manukhina, G.M. Savelyeva - M.: GEOTAR-Media. – 2011. – P. 1088
- Clinical recommendations (treatment protocol). Uterine fibroids: diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation. Chief freelance specialist of the Russian Ministry of Health in obstetrics and gynecology, Academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences L. V. Adamyan, 09/21 of 2015
- Sidorova I.S., Kogan E.A., Unanyan A.L./Chapter 4. Uterine fibroids (modern problems of etiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment) ed. Sidorova I.S – M: MIA.-2002.- P.113-127
- Savitsky, G. A., Savitsky A. G. Uterine fibroids: problems of pathogenesis and pathogenetic therapy. – St. Petersburg: ELBI-SPb, 2003. – P. 236
- Pestrikova T.Yu., Yurasova E.A., Yurasov I.V., Chirkov A.V. Rational choice of tactics for managing patients with uterine fibroids. Literature review. Gynecology. 2017; 05:15-19
- Levakov S.A., Borovkova Ekaterina Igorevna Modern aspects of the treatment of uterine fibroids (review of foreign literature) // Archive of Obstetrics and Gynecology named after. V.F. Snegireva. 2015. No. 1. P.13-17
- Chiaffarino F, Cipriani S, Ricci E, et al. Alcohol consumption and risk of uterine myoma: A systematic review and meta analysis. Muka T, ed. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(11):e0188355
Source: https://ProBolezny.ru/fibroma-matki/
Causes and treatment methods for uterine fibroids
Due to the busy life, most women forget to monitor their health in a timely manner, even when the menstrual cycle changes, heavy discharge and pain in the lower abdomen appear. Uterine fibroid is a diagnosis that is most often discovered by chance during a gynecological examination.
A common tumor disease also occurs in young girls of childbearing age. However, the older a woman is, the higher the risk of developing uterine fibroids.
What it is
Since a large number of people are faced with manifestations of uterine fibroids, every girl should know what this is.
A benign tumor consists of connective tissue and muscle fibers. The neoplasm has a round shape and tends to develop slowly.
At the initial stage, the tumor is rarely diagnosed; this mainly happens when the patient already needs surgical intervention.
The size of fibroids can reach up to 30 cm. Women during menopause, as well as teenage girls, do not encounter this disease. The disease most often spreads among patients 35-40 years old.
Fibroma usually does not degenerate into an oncological tumor, but its appearance causes disruption of the functioning of adjacent organs. Whether it is dangerous depends, first of all, on the type of neoplasm:
- Intramural - this is the most famous type of tumor, does not spread beyond the muscle layer;
- Sumbucous - develops in the cavity of the uterus itself, and is much less common. If such a tumor is present, the patient experiences severe symptoms: pain, bleeding.
- Subserous fibroma is a type of neoplasm that grows from the outside. Such a tumor can develop into a knife, sometimes it reaches an impressive length, and when it twists, unpleasant symptoms occur.
- A parasitic type tumor received this name because during the growth process it joins other organs. Cervical fibroma falls into this category and occurs only in rare cases.
Typically, fibroids grow slowly, but if tumor cells begin to divide rapidly, surgical treatment should be performed immediately. The greatest danger is presarcoma.
If the neoplasm has many nodes and is large in size, then sometimes it becomes necessary to remove the uterus. Every woman should understand what uterine fibroids are before problems arise.
What is the difference between fibroids and fibroids?
Myoma is a benign tumor consisting of muscle tissue. Between the fibrous parts there are nodes, their development occurs in the uterine wall.
Tumors of this type do not cause unpleasant symptoms at the initial stage, which makes diagnosing the disease difficult. The difference between such neoplasms lies in the internal composition.
A tumor in which only muscle fibers predominate is called fibroids. If multiple connective tissues are present along with muscle tissue, it is a fibroma. The body of the uterus is affected much more often than the cervix. First, a tumor focus is formed from smooth muscles, after which this nucleus is transformed into a fibroid or myoma of the uterus.
Multiple nodular fibroids are often encountered, growing in different directions. It is extremely rare for nodes to grow into the inner and outer parts. However, if this happens, painful menstruation and heavy bleeding occur. Some types of tumors can disappear on their own after menopause. With this problem, no further treatment is required.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures include an initial interview with the patient; we should not forget about the importance of the presence of concomitant gynecological diseases. Then the following diagnostic methods are carried out to confirm the diagnosis:
- Using ultrasound examination of the pelvic area and abdominal cavity, possible tumor processes can be identified. If necessary, transvaginal diagnosis is performed. This is necessary in order to consider the location of the fibroid node.
- Ultrasound of the uterine cavity allows you to accurately determine the type of fibroid, the number of nodes, and size. This method also determines other endometrial pathologies.
- A biopsy is performed using a special instrument that is directed into the uterine cavity.
- A special camera is placed through the cervical canal into the uterus and examined.
- A special substance is injected into the uterus and tubes for X-ray contrast examination. This allows you to see the contours of the internal organs.
- Doppler ultrasound helps to examine fibromatous nodes, and in particular the integrity of their vessels. The need for the procedure arises before embolization. This is the name of a modern method of removing a tumor without surgery, by blocking the blood flow.
- MRI is performed when a fibroma forms of impressive size, when there is a risk of the tumor becoming malignant.
- Laparoscopic examination is a procedure in which special surgical instruments are inserted through small holes.
Sometimes uterine fibroids are diagnosed during pregnancy. The presence of a tumor during this period creates a significant number of problems for the mother’s body and the fetus. There is a risk of premature termination of pregnancy, placental insufficiency and breech presentation may develop.
Uterine fibroids and pregnancy are not always compatible. This disease poses a danger during childbirth; if the process is complicated, rupture of the uterine wall and bleeding may occur. In most cases, women in labor with this diagnosis undergo a cesarean section, because the natural passage of the child through the birth canal is impossible.
Symptoms
Even when the tumor reaches a large size, sometimes there are no signs of the disease; the location of the uterine fibroid plays an important role. The main symptoms of uterine fibroids:
- Heavy bleeding during menstruation interspersed with clots.
- Constant urge to urinate. This happens because a large fibroid puts pressure on the bladder.
- Gastrointestinal disorders, constipation, due to the fact that the rectum is compressed.
- Heaviness in the abdominal area.
- Pain in the lower abdomen usually appears only during menstruation. However, in the later stages of the disease, pain may be constant.
- The abdomen increases in size, as during pregnancy. However, the weight remains the same.
- Infertility, miscarriage.
If uterine fibroids are detected, symptoms of this type can pose a danger to patients planning a pregnancy. However, with a small tumor, doctors admit the possibility of successful pregnancy.
The appearance of symptoms and signs with uterine fibroids indicates that the last stage of the disease is observed. The development of the tumor is influenced by the following factors:
- absence of childbirth throughout life;
- surgical termination of pregnancy;
- taking medicinal contraceptives for many years;
- chronic inflammation of the appendages;
- various neoplasms on the ovaries, mammary glands, skin around the genitals;
- irradiation with ultraviolet rays;
- constant nervous stress.
You should not ignore the symptoms of uterine fibroids. Especially if such a disease occurs in a woman after 35 years of age and the tumor growth progresses, you should immediately consult a doctor.
How to treat the disease
If uterine fibroids are detected, treatment is most often carried out surgically. The following indications for surgical intervention are distinguished:
- submucosal fibromas grow too actively;
- the dimensions of the nodes exceed all permissible parameters;
- periodic uterine bleeding is observed;
- the tumor stalk becomes twisted, intolerable pain occurs;
- fibroma is combined with inflammation of the ovaries;
- in the tubal angle of the uterus there is a node, which is the cause of infertility.
For women under 40 years of age, if uterine fibroids are detected, removal is performed using laparoscopy. This operation is performed under local anesthesia; upon completion of the process, long-term rehabilitation is not required. However, this procedure is carried out only for small fibroids.
After 40 years, fibroids are often removed along with the uterus and appendages. This is usually necessary if the tumor is large and there are accompanying tumors. Treatment of uterine fibroids in this way allows you to avoid the development of oncology.
In some cases, conservative therapy is carried out, when the development of the disease is stopped with the help of medications. Indications for this technique:
- young patient;
- small tumor size;
- the uterine cavity is not deformed.
Embolization refers to a method of conservative treatment when a special substance is injected into the arteries of the nodes. In this way, further development of fibroids is blocked.
When diagnosing uterine fibromatosis, symptoms, treatment is carried out using hormonal drugs. The following medications are used: hetagens, antigonadotropins, combined oral contraceptives.
Methods for treating uterine fibroids with folk remedies:
- Tincture of celandine. This medicine is prepared on the basis of vodka, start using one drop every day, increasing the dose. The course of treatment is 30 days.
- A decoction of flax seeds, take for 2 weeks, 1 time per day.
- Drink 1 glass of potato juice every day for a month.
Such methods of treating uterine fibroids are auxiliary. They can only be used with the permission of a doctor.
Is fibroid dangerous?
Not all patients know why fibroids are dangerous. With primary fibromatosis of the uterine body, no unpleasant symptoms occur. Therefore, treatment must be started as early as possible.
If fibrotic processes occur, for a long time there is a danger of loss of reproductive functions in a woman. In this case, only a doctor, after preliminary diagnosis, will be able to determine the method of treating fibroids.
Source: https://opake.ru/dobrokachestvennaya-opuhol/fibroma-matki/
Uterine fibroid: its symptoms and treatment
This is a benign oncological formation that consists of connective tissue. Uterine fibroids can come in different sizes.
As a rule, this is a single formation ranging in size from a few millimeters to 30 cm or more. Fibroma is practically not dangerous for the patient and becomes malignant only in rare cases.
Classification
Uterine fibroids come in several types. The classification is based on the location of the tumor.
- mucosal. This formation occurs inside the organ under the membrane. As it develops, bleeding often occurs and is characterized by pain in the lower abdomen and cramps;
subserosal. This tumor is localized on the outer lining of the uterus. There are no symptoms or other manifestations until the uterine fibroid grows to a large size. In this case, it begins to physically affect neighboring organs, interfering with their normal functioning; Main types of uterine cancer
- interstitial. Formed in the wall of the organ. This disease is most common among gynecological cancers. The growth of the tumor itself leads to the growth of the organ;
- interligamentous. This tumor is located in the spaces between the ligaments that support the organ. Treatment of such a disease is associated with the risk of harming the functioning of other organs and damaging blood vessels;
- stalked. The disease develops along with the leg. When the tumor reaches a size that threatens to bend the leg, the disease is accompanied by severe pain;
- parasitic. This uterine fibroid joins neighboring organs.
Each of these types differs in treatment method, localization and some other characteristics.
Differences between fibroids and cysts
It should be remembered that fibroids practically do not appear on the cervix. The cyst is more relevant here. The main difference between a cyst and a fibroma is that the first contains fluid, and the second contains connective tissue. This tumor often occurs in women who have given birth.
Cases of multiple cyst formation are common. The fluid inside a cervical cyst contains a lot of bacteria and viruses that can threaten the patient's health. Cervical cysts have virtually no effect on pregnancy and childbirth.
Uterine fibroids and pregnancy
Small tumors do not prevent pregnancy. However, any tumor will interfere with the process of bearing the fetus.
The consequences can be dire - including loss of the fetus and infertility. Doctors recommend planning pregnancy after completing the course of treatment to avoid adverse consequences.
Causes
Despite the fact that modern medicine has made great progress in the treatment of cancer, the causes of this disease have not been established.
Oncologists believe that the reason for the appearance of this benign formation is the increased hormonal sensitivity of the body. Another reason is hereditary predisposition.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids
In most cases (about 80%), no symptoms appear at all, and the woman feels the first signs only when this nodular tumor grows and begins to interfere with the functioning of other organs.
- prolonged bleeding during menstruation. Bleeding occurs in clots, leucorrhoea is possible;
- pain (in rare cases). This is a symptom that can lead to anemia;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen. This symptom is due to the fact that a benign formation puts pressure on other organs;
- foreign body sensation;
- difficulty defecating or urinating;
- sexual intercourse is difficult.
All these symptoms, as a rule, occur only at an advanced stage of the disease.
Diagnostics
As a rule, uterine fibroids are detected during examination by a gynecologist. An experienced doctor will recognize a benign formation at first glance, however, additional examination is necessary to confirm the diagnosis, determine the form of the disease and treatment tactics.
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound). Ultrasound is performed transvaginally. Ultrasound allows you to identify all defects of the pelvic organs and the main symptoms of diseases. Ultrasound can reveal the location of the tumor. The density of the formation and the size of the affected organ are also detected using ultrasound. Using ultrasound, it is necessary to determine the relationship of the tumor to other structures. Ultrasound also helps to distinguish fibroma from other neoplasms;
- in cases where the information obtained during ultrasound is insufficient, computed tomography is performed;
- X-ray examination.
How to treat uterine fibroids?
There is drug therapy (surgery and conservative therapy) and treatment with folk remedies. Doctors never tire of repeating that self-medication does not lead to anything good and the consequences of such an event can be unfavorable. All manipulations with your health should be carried out only under the supervision of an experienced specialist.
Drug treatment
Conservative therapy (without surgery) is indicated for tumor sizes less than those at 12 weeks of pregnancy. It is also used in cases where removal of uterine fibroids is impossible. This method includes taking the following medications:
- NSAIDs;
- vitamins;
- hormonal drugs;
- iron-based medications.
Surgery is indicated for significant symptoms when the tumor disrupts the functions of other organs. Surgery is also necessary when the tumor growth becomes too active. The combination of a tumor with other inflammations also leads to surgery.
In all these cases, the consequences of ignoring the disease can lead to serious complications, and only surgery can solve the problem. After surgery, recovery is necessary. Surgery may involve either removal of the tumor or removal of the entire organ.
In the first case, the operation is indicated for those who want to preserve reproductive function. The advantage of the second method is that after treatment, tumor recurrence is impossible.
Treatment of uterine fibroids with folk remedies
After surgery and during treatment, you can use herbs, boron uterus, celandine and other folk remedies, subject to the supervision of the attending physician. One of the best herbs for treating this disease is hogweed. Let's describe a few recipes.
- Pour 1 spoon of herb into 200 ml of boiling water. Simmer over low heat for 10 minutes. It is necessary to leave for about 4 hours. Strain and use the infusion of boron uterus 1 spoon 5 times a day;
- Pour 50 g of hogweed leaves into 0.5 liters of vodka. Leave for 20 days in a place where sunlight does not penetrate. Take the herbal tincture an hour before meals three times a day;
- Pour 20 g of crushed leaves of the hogweed into 400 ml of boiling water. Leave for 15 minutes and take 100 ml of boron uterus 4 times a day.
Decoctions of boron uterus can be used for douching. You can also soak tampons in tincture of boron uterus and use it for its intended purpose. This is an analogue of conservative treatment, which promotes tumor resorption.
Source: http://opuholi.org/dobrokachestvennaya-opuxol/fibroma/fibroma-matki.html
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5a5c6286865165fdcc876cb5/5b03a7b98c8be3dd3cd11e01