Tuberculosis
9 hours ago
Hello, please tell me, I’m 34 years old, I was treated for tuberculosis for a whole year, in the end I was discharged with unhealed tuberculoma (they said that it was slow, but it was dragging on), almost every evening the temperature was 37.1-37.5, ESR was 38, for three months the ESR was 48, then it dropped to 20, but...
Dmitriy
Hello, the issue of disability group is resolved individually. Take a referral for a consultation to the regional or republican tuberculosis dispensary. If they give you a written opinion that you can work, then you can. If your ability to work is reduced or you are disabled, then they will form a group.
Mantoux in a 1 year old child
11 hours ago
Hello! The child is 1 year old. They did a Mantoux test, 13 mm. The child has a history of allergic dermatitis. On the recommendation of a gastroenterologist, all dairy products are excluded. Staphylococcus and Klebsiella are present in the stool above normal. The pediatrician insists on repeating Mantoux and…
Olga
Hello. First, you can do a repeat. It does not harm the baby. And secondly, you have a positive reaction to allergic dermatitis, the Mantoux test also reacts to BCG, plus the onset of acute respiratory infections. Therefore, there is no point in repeating the test now. Do it when there is no acute respiratory viral infection, acute respiratory infections, under the cover of antihistamines for at least 10-14 days.
Diaskintest and x-ray
yesterday, 08:04
200.00 rub.
Good day, dear specialists! A question that has been keeping me awake for a couple of days now. Please tell me if Diaskintest and Mantoux did not show the presence of tuberculosis, but on the x-ray (Before the tests) they wrote the presence of infective foci. Can I request a certificate from the PTD about...
[email protected] , St. Petersburg
The question is closed
You must have a CT scan. If, after a CT scan of the chest, the TB doctor does not confirm the diagnosis, then it is necessary to exclude systemic diseases: vasculitis, SLE, sarcoidosis, interstitial lung diseases, this should already be dealt with by a pulmonologist
Is it necessary to do BCG?
January 27
Good evening! Now the child is 7 years old; he was not vaccinated with BCG at birth, because he had honey. withdrawal, then after consultation on immunoprophylaxis, some vaccinations were given, except for BCG. Mantoux test negative. Next was honey. Diversion due to allergic bronchitis, bronchial…
Nikolai
Nikolay, this issue is decided by a pediatrician and an allergist after a thorough examination and in-person examination of the child.
Diaxin test positive in a 4 year old child
January 26
200.00 rub.
Hello. The child tested positive for manta and was sent to a phthisiologist. They did a Diaxin test, which was also positive. They took a picture, the roots were enlarged, there were shadows on both sides, signs of acute bronchitis. They sent me for a CT scan and a consultation with a republican phthisiologist. No contact with patients...
Olga
The question is closed
Olga, I am confused by the presence of shadows in the roots of the lungs and the conclusion of Bronchitis in the absence of complaints and the child’s normal condition. Changes in the roots can occur both with tuberculous bronchoadenitis and with allergies.
It is necessary to donate blood for immunoglobulin E and blood for Eosinophilic cationic protein (we will look at the level of allergies) and a CT scan of the lungs, specifically examining the roots of the lungs and lymph nodes. A swab from the throat and nose for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics. Blood testing for Mycobacterium tuberculosis using PCR.
According to the analysis of the Mantoux test, even if it was negative, a 4 mm papule is not tubinization, but a positive diaskin test requires exclusion of the tuberculosis process. The test results can be sent to us on the website (you don’t have to close the question). Best regards, Olga
Positive reaction mantoux
January 26
The child is 6 years old, 3 months old, the first mantoux is doubtful, the second one is positive 8 mm. Purpose of OAC, OAM and x-ray. Is it possible to determine anything from these tests and is it possible to do without x-rays? Or do the test again?
Veronica
The question is closed
Hello, 8 mm hyperemia or papule?
Is it possible to get tuberculosis?
January 24
300.00 rub.
Hello, I had contact for two days with a patient with tuberculosis. He says that it is a closed form and not contagious, but less than a year ago he was operated on, the affected area was removed, and now the place is healing. He took the medicine for 120 days, he doesn’t take it anymore, although he should. Is it true...
Elmira, Almetyevsk
The question is closed
Hello, there is practically no risk, or rather, minimal. Neither x-ray nor chemical therapy is advisable in your situation. And your baby too. Yes, if the patient has undergone surgery and has taken medication for 120 days, this is very good.
But in order to achieve stable remission, after surgery it is necessary to take anti-tuberculosis drugs (300 doses) for at least 300 days. Therefore, it poses an indirect, but nonetheless, threat.
I do not advise you to communicate with him, try to avoid contact.
Help with the diagnosis
January 24
I am diagnosed with bronchial tuberculosis. According to bronchoscopy and CT scan of the lungs without pathology. Because I had a sore throat and I tested sputum and it showed MBT+. But according to other tests, sputum, urine, blood, which I donated at the hospital, they showed nothing. What should I do? What to do? I was put in...
Elena
The question is closed
Hello. Did you take a PCR test for Mycobacterium tuberculosis, what was the culture for TB? Diaskin test positive?
Positive diaskintest, negative t-spot
January 24
200.00 rub.
Hello, please help me figure it out. Positive diaskin test and negative t-spot in an adult. Which of these is most likely to be incorrect? First, blood was donated, then the Diaskin test. One day.
Evgenia, Novosibirsk
The question is closed
Good afternoon Did you rent it out in absolutely home condition? No ARVI, allergic reactions? Of course, t spot is considered more accurate, with more than 97% specificity of this test. The Diaskin test can be false positive.
What were the tests done for?
Pulmonary tuberculosis
January 24
Hello. I was treated for tuberculosis of the right lung for six months. The picture shows that I am improving, and when I took the control test, they found a rod. How so? There was always a minus. What, back to the hospital?
Natalya, Vladivostok
The question is closed
Hello, The tuberculosis bacillus could be “stuck” in the bronchi. Treatment should be continued until complete abacillation
Mantoux vaccination for hydronephrosis
January 23
Good evening! The child is 1 year 11 months old, congenital hydronephrosis, we are seeing a urologist, observation. Urinalysis is always normal, the pediatrician insists on 2 Mantoux vaccinations per year, is it necessary? Diaskintest was done at 1 year and 3 months. Or seek advice from a urologist? Thank you.
Julia
The question is closed
Julia, you need to contact your doctor. If he deems it necessary (for clinical reasons, laboratory tests), he will give a medical exemption. If the data are satisfactory, neither the Mantoux nor the Diaskin test is contraindicated.
Do you need a medical exemption from vaccinations?
January 22
200.00 rub.
Hello! Our grandmother was diagnosed with tuberculosis. There is a stick in the sputum. We, as contacts, checked. There was contact every Sunday, especially close with the child. All tests for us and the child are good, the Diaskin test is negative. We don’t have any preventative treatment...
Taisiya
The question is closed
Yes, you can... there are no contraindications
What to do?
January 22
200.00 rub.
Hello! My father was diagnosed with acute bronchitis, tuberculosis was called into question, and he died the next day. The cause of death has not been established, histology was taken, the answer will be in 1-1.5 months. What tests can be taken to check who was in contact?
Victoria
The question is closed
Everyone to the tuberculosis dispensary to take the Diaskintest. Referral Children need to take a children's clinic to an adult clinic. Good luck to you
Is it possible to become infected with tuberculosis?
January 22
200.00 rub.
At work, several times I talked with a person for about 20 minutes in a room, sitting next to each other. Yesterday I found out that he was diagnosed with tuberculosis, an infiltrate with dissemination and decay in the lungs, according to him. I don’t know about MBT + or- yet. But I read on the Internet that if there is decay...
Victoria, Kyiv
The question is closed
Hello! No, you won’t get infected, don’t worry.
Mycobacteriosis
January 21
300.00 rub.
Hello, since October, after a medical examination at work, a darkening was detected on the lung, they were admitted to the hospital with pneumonia, then they were sent for a CT scan, they discovered a cavitary formation in the lower lobe of the left lung, they sent them to a tuberculosis clinic, took all the tests there - everything was negative;...
Yuri
The question is closed
Source: https://sprosivracha.com/questions/ftiziatr
What is the name of a pulmonary tuberculosis doctor?
Phthisiatrician is the name of a doctor who specializes in tuberculosis (once in Rus' it had another name - consumption). This disease is dangerous; at the last stage of development it can lead to death, so you should know in what cases it is worth visiting a phthisiatrician in order to prevent the development of pathology in case of infection.
What does a phthisiatrician treat?
A phthisiatrician is a doctor who treats tuberculosis, deals with disease prevention and rehabilitation measures. But first of all, the specialist examines the patient and makes a diagnosis.
Doctors of this specialization conduct consultations in phthisiology departments of hospitals, specialized dispensaries and specialized sanatoriums.
You can get professional advice at any of these medical institutions.
You should not think that this doctor treats tuberculosis, and therefore only deals with the lungs. Koch's bacillus, which is the causative agent of the disease, affects the entire body. A phthisiatrician diagnoses and treats the following diseases:
- tuberculosis, affecting the skin, mucous membranes, and lymphatic system;
- extrapulmonary form of the disease, in which the kidneys, bones, vision, intestines, and genitals are affected;
- leprosy, which is an infectious pathology (it is often called leprosy);
- meningitis of tuberculous origin;
- pulmonary sarcoidosis.
If the local physician has sent the patient for a consultation with a phthisiatrician, this cannot be ignored. If a pathology is diagnosed, the phthisiatrist takes additional measures to determine the type and form of the disease. For this purpose the following examinations are carried out:
- Mantoux test;
- MRI or CT;
- examination of secreted sputum;
- tests - skin, liver;
- culture – microbiological, urine, etc.
Tuberculosis can be completely cured only if the disease is at the beginning of its development, which is why it is so important to identify the pathology as early as possible. In Russia, the population is required to undergo fluorography every year. This examination helps to detect changes in the lungs, in the presence of which a person is referred to a phthisiatrician.
Features of the work of a pediatric TB doctor
If a child is suspected of being infected with tuberculosis, he or she is examined by a pediatric specialist. A referral to a phthisiatrician after Mantoux is given by the attending pediatrician if the tuberculin test is positive.
Phthisiatricians treating children have a double responsibility. Such specialists must have knowledge in the field of phthisiology and understand pediatrics, since diagnostic, therapeutic and preventive measures are carried out taking into account the patient’s age.
Tuberculosis is not a death sentence! Our regular reader recommended an effective method! New discovery! Scientists have identified the best remedy that will instantly relieve you of tuberculosis. 5 years of research!!! Self-treatment at home! After carefully reviewing it, we decided to offer it to your attention. Read more >>
The Mantoux reaction is not a vaccination, but a test during which the drug Tuberculin is injected into the child’s skin to detect the causative agent of the disease. This makes it possible to detect pulmonary tuberculosis at an early stage. The size of the papule formed after the test determines the presence of infection in the body.
If a child was sent to a phthisiatrician after Mantoux, this does not mean that he is infected with Koch's bacillus.
A positive reaction may occur in those who have recently had a cold or have been vaccinated with BCG.
A similar thing is observed in the presence of worms in the body. A pediatric tuberculosis doctor will conduct a full examination of the child to identify the disease, and if the diagnosis is confirmed, he will begin treatment.
Types of specialty
In case of tuberculosis, the doctor deals not only with the lungs, but also with other organs and systems, therefore in phthisiology there are the following specializations:
- pulmonologist - a specialist who deals with the respiratory system, including the lungs;
- ophthalmologist - a doctor who treats the organs of vision affected by tuberculosis;
- urologist - able to cure the kidneys and genitourinary system affected by Koch's bacillus;
- gynecologist – works with women whose reproductive health has been affected by tuberculosis;
- otolaryngologist - a doctor who knows how to help patients suffering from ENT pathologies caused by the causative agent of tuberculosis;
- pediatrician – a specialist in the treatment of children and adolescents under 18 years of age;
- surgeon - a doctor who performs operations if there are indications for this.
The disease, which has been spreading widely over the past few years, requires a large number of tuberculosis specialists. But their number does not increase, but decreases, which is associated with many factors, including an increased risk of contracting a dangerous disease.
Phthisiology is not popular among medical students. The choice of specialization of future doctors is influenced by the opinions of loved ones who consider this profession dangerous.
You may also be interested in: Important information: Features of immunity in tuberculosis ( 2 ratings, average 5 out of 5 )
Source: https://ProTuberkulez.info/lechenie/kak-nazyvaetsya-vrach.html
Who is a phthisiatrician and what does he do?
The spread and treatment of tuberculosis has remained an important medical challenge for several centuries.
As the rhythm of life increases, the number of factors that weaken the body increases - ecology, harmful substances. At the same time, the pathogen turns out to be much more resistant (resistant) and dangerous.
That is why, to combat this pathological condition, a separate category of doctors is provided - these are phthisiatricians.
What does a doctor do?
So, a phthisiatrician specializes in identifying, treating and preventing tuberculosis. Despite the rather narrow specialization, the organs of study are not only the lungs. This is due to the fact that the infectious pathogen (Koch bacillus) is able to infect both this system and many others.
This is not an exaggeration, because there is not a single “component” in the human body that is not susceptible to the negative effects of tuberculosis. This could be bones or joints and even the genitourinary system.
What does a phthisiatrician treat?
It is necessary to consider in more detail which diseases are within the competence of the doctor:
- leprosy (leprosy) is a chronic infectious pathology that affects the skin and peripheral nervous system;
- extrapulmonary form of tuberculosis, affecting the bones or intestines, eyeballs, even kidneys;
- open type of disease - pulmonary;
- external form, affecting mucous surfaces, skin, lymph nodes;
- sarcoidosis is a non-inflammatory pathology that affects the lungs and other physiological systems;
- adrenal tuberculosis (Addison's disease);
- a specific form of meningitis.
In 90% of cases, the phthisiatrician focuses on tuberculosis. Its manifestations and forms may differ depending on the specific type.
Related professions
Taking into account the different localization of both primary and secondary foci of the disease, a specialist can deal not just with tuberculosis, but have a more narrow specialization. These can be phthisiourologists and -gynecologists, -infectious disease specialists, -surgeons, -otolaryngologists (they treat tuberculosis of the ear or nose and throat).
It may be necessary to consult a phthisiatrician-dermatologist if a skin form has developed or an orthopedist who deals with damage to joints or bones.
You can also make an appointment with an ophthalmologist or pediatrician. Each of them is able to prescribe complete treatment not only for the disease itself, but also for the complications that arise.
Alarming symptoms
There is a whole list of clinical manifestations that are a reason to visit a phthisiatrician. First of all, it is a cough that bothers a person for 30 days or more. In some situations, mucous discharge occurs during expectoration, and in case of complications, blood is mixed.
You need to make an appointment with a phthisiatrician if:
- painful manifestations in the area of the shoulder blades, if they are not associated with diseases of the spinal column;
- unusual sensations in the sternum, constant lack of comfort;
- increased wheezing, difficulty swallowing, worsening breathing;
- poor appetite;
- unmotivated weight loss.
You cannot do without visiting a phthisiatrician if a person’s general condition worsens. If there is weakness or apathy, rapid fatigue when doing the most ordinary things. Increased body temperature and constant sweating during sleep at night should also not be ignored.
Diagnostic methods
A visit to a TB specialist is associated with certain examinations. Based on existing complaints and to clarify the diagnosis, the phthisiatrician insists on the following diagnostic methods:
- tuberculin skin test - Mantoux test, which allows you to determine whether or not a person has tuberculosis;
- microbiological seeding of biomaterial, including pus, exudate, the upper layer of ulcerative lesions;
- a complete analysis of sputum during expectoration to determine the presence of a viral infection in saliva;
- liver test;
- examining the eyeballs for the presence of visible changes;
- Urine testing is carried out when Koch bacilli penetrate the kidney area.
These are so-called specific methods prescribed when a certain pathology is suspected.
The main examinations are control fluorography (x-ray of the sternum), tomography of the lungs. With their help, the presence or absence of inflammation is detected.
After the results of all diagnostic examinations are received, the phthisiatrician prescribes an individual rehabilitation course.
How is the appointment going?
A mandatory precondition before consulting a doctor is to undergo fluorography and a general blood test. The patient needs to prepare a list of his complaints and alarming symptoms. Next, the phthisiatrician will refer the person for a full examination, including laboratory and instrumental testing methods.
After studying the results, the doctor decides whether the patient has tuberculosis or not. If the disease is confirmed, it is necessary to determine its type. For example, the open variety is the most dangerous, because in the “affected zone” is not only the TB doctor himself, but also the patient’s family, friends, and colleagues.
Next, the phthisiatrician works out a treatment plan, which involves treatment in a hospital. If a chronic form of tuberculosis has been identified, the skin and internal organs are examined to identify complications. Depending on whether they are found or not, the recovery course can vary dramatically.
Children's phthisiatrician
Separately, I would like to consider how a consultation with a pediatrician proceeds. The child is asked to undergo a special test - quantiferon. To do this, the phthisiatrician takes blood from a vein.
The advantage of the test is its high accuracy, because it is carried out to identify specific pathogens, for example, only Koch's bacillus.
After this, the pediatrician can determine whether the child has tuberculosis or not.
Early diagnosis is extremely important because children's bodies are not strong enough to cope with this disease given its duration.
In children, tuberculosis develops more rapidly, the likelihood of complications is higher, while cleansing the body of medications takes longer.
In this regard, it is necessary to make an appointment with a TB specialist at the first suspicion and begin treatment as early as possible.
Source: https://stop-kashel.ru/kto-takoj-ftiziatr-i-chem-on-zanimaetsya/
Consultation with a pediatric TB specialist
If, based on the results of the Mantoux reaction, a child required consultation with a pediatric TB specialist and was referred to a TB specialist, this does not mean that the child has tuberculosis. The child was referred for consultation, just as they are referred to other specialists.
Currently, the phthisiatric service is trying to organize the appointment of children by a phthisiatrician in children's clinics at their place of residence, on certain days 1-2 times a month. Preference is given to children under 3 years of age. It would be a good idea to ask your clinic about this before going to the tub with your child. dispensary.
It is advisable to show the child to a TB doctor as quickly as possible. It is recommended within 6 days from the date of Mantoux. So that the phthisiatrician has the opportunity to look at the papule.
A papule with an infectious allergy is different from a papule with a post-vaccination allergy (after BCG). It differs in color, leaves behind pigmentation, etc.
The phthisiatrician must understand these subtleties, but he must be given this opportunity.
Consultation with a pediatric TB specialist You must have with you
- An extract from form 112 (child’s outpatient card) indicating information about the BCG vaccination, the presence of a scar and its size, information about all Mantoux tests performed on the child, indicating the size in mm, information about previous consultations with a phthisiatrician (if any), information about chronic diseases if the child is sick with them.
- The result of a general blood and urine test of the child.
- If your child has had a chest x-ray within a year: take the x-ray with you.
- Results of fluorography of parents and other adult (over 14 years old) family members living with the child.
The phthisiatrician will find out your medical history. What illnesses did the child have during his life, what conditions does he live in, how does he eat. Could he have had contact with tuberculosis patients? Will evaluate the results of all the child’s Mantoux tests, tests, and fluorography of the parents.
Examine the child: Mantoux mark, BCG scar. He will examine the peripheral lymph nodes and listen to the lungs.
In some cases, the TB specialist then diagnoses a post-vaccination allergy. This concludes the examination for the child. And he is sent home with recommendations to repeat Mantoux in 1 year.
In some cases, the doctor and parents doubt the correctness of Mantoux. Then treatment of other diseases of the child is indicated: sanitation of foci of infection, deworming, achieving remission of chronic diseases, treatment of allergies, adherence to a hypoallergenic diet and repeated p. Mantu after 1-2 months (if necessary against the background of antihistamines).
Consultation with a pediatric TB specialist X-ray examination
Most children are prescribed an x-ray examination. To rule out respiratory tuberculosis, the most common form of tuberculosis. This form of tuberculosis is divided into tuberculosis of the lungs, bronchi and intrathoracic lymph nodes.
In children, compared to adults, tuberculosis of the intrathoracic lymph nodes without changes in the lungs occurs much more often (about 1/3 of all cases of respiratory tuberculosis). This is the so-called “minor form of tuberculosis”. Its prevalence in children is currently associated with the protective effect of BCG vaccination.
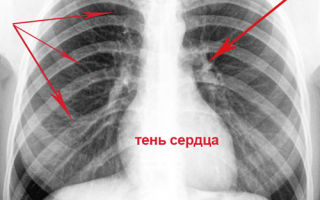
As a result, the child’s body limits the spread of infection. The intrathoracic lymph nodes are located in the root of the lung. In standard X-ray images of the chest organs in AP projection, the roots of the lungs are partially covered by the shadow of the heart.
At the onset of the disease, radiological signs may not be obvious, but indirect: slight expansion of the lung root, increased vascular pattern, etc.
Therefore, to diagnose this and other forms of tuberculosis, X-ray tomography is also used: an image of a section of the lung at the depth that interests the doctor.
In order for the X-ray examination to be the most useful and informative, a specific type of examination is prescribed (survey radiography, X-ray tomography, or a combination of both).
And it is the TB specialist who evaluates the results, and not the pediatrician in the children's clinic at the place of residence.
If the X-ray images are without pathology, this means that the child does not have respiratory tuberculosis.
Consultation with a pediatric TB specialist Diagnostic minimum
Thus, the diagnostic minimum to answer the question of whether or not a particular child (and adult) is currently sick with tuberculosis today includes:
- Mantoux reaction.
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Inspection data.
- X-ray examination.
Most often, children are diagnosed with tubal inversion. samples or primary tuberculosis infection.
This means that tuberculosis bacilli from the environment have entered the body, as evidenced by an increase in the Mantoux test, but the child has not yet fallen ill with tuberculosis, this is indicated by the normal results of the examination of the child. That is, the diagnosis is a tube turn. samples means that the child is allowed into the children's group and is not infectious to others.
But the possibility of developing the disease exists, and the younger the child, the greater the risk (see article tuberculosis in children). Therefore, the child is taken under dispensary observation by a TB doctor.
In order to prevent the transition of infection into disease, children were previously always prescribed the drug isoniazid.
Now, in order to verify the need for this treatment, a diaskintest is performed (more about diaskintest).
Currently, with a negative result of the diaskintest, according to order No. 109 of M.Z. “On improving anti-tuberculosis measures in the Russian Federation”, children diagnosed with: Virage tuberculosis.
Mantoux test results and a negative diaskintest result do not prescribe preventive treatment with isoniazid, but it is recommended to repeat the test over time after 2 months.
A negative test result does not eliminate the diagnosis; it means that the child’s body is currently coping with the infection without treatment.
A positive result of the diaskintest means that mycobacteria in the child’s body are in a state of active reproduction, which means there is a possibility of developing the disease. If the result is positive, the drug isoniazid is prescribed.
Should I give isoniazid to my child or not?
Isoniazid treatment is prophylactic and is aimed at preventing the development of tuberculosis in a child. The doctor’s prescriptions in this case are advisory and not mandatory.
Isoniazid reduces the risk of developing the disease in a child in case of primary tuberculosis infection by 8 times.
This drug belongs to the group of antibacterial drugs; Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the reproduction stage is sensitive to it, acts on intracellular and extracellular pathogens, and penetrates all tissues of the body. Most effective for recent infections. It has no pronounced effect on other bacteria (causative agents of other diseases and normal human microflora).
Has contraindications:
- epilepsy,
- past polio,
- liver and kidney dysfunction
— the drug is not prescribed for these diseases.
Side effect
- Allergic skin reactions - the drug is discontinued.
- Nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, in rare cases, drug-induced hepatitis. These side effects are due to the fact that isoniazid is metabolized in the liver (broken down and then excreted from the body; as a result of its breakdown, a hepatotoxic substance (monoacetylhydrazine) is formed. In order to minimize this side effect, children are always prescribed hepatoprotectors - medications along with isoniazid , protecting liver cells from toxic effects, for example - karsil.
- Headache, dizziness, increased excitability, poor sleep. To reduce the effect of isoniazid on the central and peripheral nervous system, B vitamins (B1 and B6) are prescribed along with it.
Side effects of isoniazid occur with large doses of the drug, combinations with other anti-tuberculosis drugs and long-term use.
For preventive treatment, it is prescribed in a minimum dose: 5 mg/kg, in a short course of 3 months. For comparison: its therapeutic dose is up to 15 mg/kg, the course of treatment is from 6 to 12 months.
Isoniazid is given to parents free of charge.
The doctor can only recommend preventive treatment. The final decision whether to conduct it or not is made by the parents. Parents have the right to issue a written refusal of treatment. But in this case, the child is at risk of contracting tuberculosis.
Observation
In any case, the child requires further observation by a TB specialist. Most often, children referred for consultation with a phthisiatrician regarding Mantoux turn fall into the following dispensary observation groups:
- Group 0: children for whom the final diagnosis has not yet been established, i.e., those who are under examination. The duration of observation in this group is up to 3 months, then a diagnosis must be made and the child is either removed from the register by a TB doctor or transferred to another observation group.
- Group IV: children who have had contact with a patient with tuberculosis with bacterial excretion. The entire period of contact and at least 1 year after its cessation are observed; in the case of contact with a person who died of tuberculosis - 2 years. They undergo a comprehensive examination 2 times a year: Mantoux test, Diaskintest, blood and urine tests. X-ray examination and sputum examination - according to indications.
- Group VI - children with an increased risk of tuberculosis: children in the early period of infection (turns), children with increasing tuberculin sensitivity, children with hyperergic reactions to tuberculin. A comprehensive examination is carried out 2 times a year (see paragraph above). The duration of observation in this group is no more than 1 year, in the case of the presence of medical and social risk factors (lack of BCG vaccination, presence of chronic diseases, low-income and large families, refugees) - 2 years.
A child diagnosed with Virage tube testing is required.
- Establish a daily routine - diet, provide time for proper rest and walks.
- Provide adequate nutrition. A child’s daily diet must include meat or fish, milk or fermented milk products, cottage cheese, cheese, fresh vegetables and fruits - in the quantities recommended for children of this age.
- The child should walk for at least 2 hours every day.
- The child must have sufficient physical activity (sports or just active games).
- It is necessary to sanitize foci of infection (treat teeth, consult a child with an ENT specialist) and treat chronic diseases.
- Spa treatment is recommended for children at high risk for tuberculosis from the age of 4, without changing the climate zone and without prolonged exposure to the sun.
Specialized kindergarten
For preschool children, there is a network of specialized kindergartens for children with an increased risk of tuberculosis.
A TB doctor gives a referral for registration to such a kindergarten only to children registered at a tuberculosis dispensary. It is impossible to become infected with tuberculosis in such a kindergarten.
Because children in the active stage of tuberculosis are not allowed there. On the contrary, all children here are examined very carefully.
A phthisiatrician can offer parents to enroll their child in such a kindergarten - the decision remains with the parents. Having agreed to enroll a child in such a kindergarten, parents must agree to carry out preventive treatment for the child if it is recommended by a doctor.
These kindergartens are considered sanatorium-type institutions. A child goes to such a kindergarten, just like a regular one, every day. The child's stay in them is free for parents. The food is fortified and is equivalent to that in a sanatorium.
Medical supervision of children in such a kindergarten is carried out by a phthisiatrician. Monitors preventive treatment with isoniazid, Mantoux testing, and carries out additional appointments. If the child needs them: physical therapy, massage. All these procedures are carried out for the child directly in kindergarten. In such kindergartens, children are also engaged in physical therapy and breathing exercises.
This concludes the series of articles about tuberculosis, vaccinations and examinations related to it.
This is all on the topic of consultation with a pediatric TB specialist. The sources of information are the same as in previous articles.
Source: https://mamadoktor.ru/38-92/konsultatsiya-detskogo-ftiziatra.html
Phthisiatrician
A phthisiatrician is a doctor whose specialization is the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis, an infectious disease caused by the Koch bacillus (Mycobacterium tuberculosis).
What does a phthisiatrician treat?
Tuberculosis is a potentially fatal airborne disease.
The main organ that affects tuberculosis is the lungs, however, this disease can also destroy other systems of the human body: kidneys, bones, liver, prostate gland in men, fallopian tubes and ovaries in women, abdominal cavity, etc.
Phthisiatricians call this condition extrapulmonary tuberculosis.
Mycobacteria of the disease can be excreted in sputum (in case of damage to the respiratory system), in feces (in case of damage to the gastrointestinal tract), in semen or urine (in case of damage to the genitourinary system), in menstrual fluid (in case of damage to the female genital organs), in breast milk (for tuberculosis of the mammary glands), etc. You can become infected with tuberculosis by inhaling air containing particles of saliva from a patient.
The main diseases treated by a phthisiatrician are:
- Lupus;
- Eye tuberculosis;
- Intestinal tuberculosis;
- Tuberculosis of the musculoskeletal system;
- Tuberculous meningitis;
- Tuberculosis of the genital organs;
- Tuberculosis of the kidneys and urinary tract;
- Acute glomerulonephritis.
When should you make an appointment with a TB specialist?
The main symptoms of tuberculosis include weakness, poor health, cough with a small amount of yellowish or greenish sputum, increased sweating at night, shortness of breath resulting from the presence of fluid or air in the pleural cavity. As the disease progresses, the amount of sputum increases and may contain traces of blood. If you find characteristic symptoms in yourself or your loved ones, you should go for a consultation with a phthisiatrician.
If tuberculosis is suspected, the TB doctor prescribes the following tests:
- Mantoux test (or tuberculin skin test), indicating the presence of infection;
- Examination of sputum for the presence of microbes;
- Microbiological cultures of sputum, pus, urine, cerebrospinal and pleural fluids and other biological material;
- Sowing on Lowenstein-Jensen medium;
- Liver test;
- Eye examination;
- Hearing acuity test;
- Urine culture to detect renal tuberculosis.
During the consultation, the phthisiatrician suggests conducting an X-ray examination (fluorography), which allows for differential diagnosis between tuberculosis and other lung diseases - silicosis, abscess, pneumonia, to determine the nature of tissue damage (focal, infiltrative, cavernous, disseminated), the localization and extent of the process. In addition to fluorography, a phthisiatrician can prescribe such types of diagnostics as:
- Biopsy;
- Microbiological diagnostics;
- Tuberculin diagnostics;
- Diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis;
- Cerebrospinal fluid examination;
- MRI;
- CT scan.
In large medical institutions, a phthisiatrician may specialize in the treatment and diagnosis of certain organs. For example, pulmonary tuberculosis is dealt with by phthisiopulmonologists, kidney tuberculosis - by phthisio-urologists, and phthisio-otolaryngologists - of the larynx. Children with tuberculosis are treated by a pediatric phthisiatrician - a phthisiopediatrist.
Scope of activity of a pediatric phthisiatrist
A pediatric phthisiatrist deals with the problems of identifying, treating and preventing tuberculosis in children. During the consultation, the phthisiatrist finds out what the child has been ill with throughout his life, evaluates his living conditions, the results of Mantoux, fluorography, and examines the peripheral lymph nodes.
Most often, primary infection is detected in children, which means that Mycobacterium tuberculosis enters the body, but not direct infection with the disease.
However, the likelihood of developing the disease in children with a “tuberculosis test” exists: young patients with a positive tuberculin skin test regularly come to see a TB specialist and undergo preventive treatment.
Recommendations from a phthisiatrician
In order to protect yourself and your children from tuberculosis, TB specialists recommend following a number of preventive measures. These include:
- Activities that increase immunity (nutritious and varied diet, active lifestyle, work and rest schedule, cessation of drinking alcohol and smoking);
- Activities aimed at improving living and working conditions (ventilation of premises, support of sanitary and hygienic standards, etc.);
- Prophylactic administration of chemotherapy drugs to prevent the onset of the disease (prescribed to persons who are in constant contact with bacteria-shedding patients, as well as in the presence of unfavorable living conditions, chronic diseases, etc.);
- Anti-tuberculosis vaccination.
Phthisiatricians claim that it is impossible to become infected with tuberculosis by shaking hands with a patient - the bacteria are transmitted only by airborne droplets, however, rooms with stale, immobilized air, the use of shared household items and tactile contact significantly increase the risk of infection.
Found an error in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Source: https://www.neboleem.net/ftiziatr.php
Patients suspected of having tuberculosis were required to register with a TB specialist
Federal Law No. 314-FZ dated August 3, 2018 “On Amendments to the Federal Law “On Preventing the Spread of Tuberculosis in the Russian Federation” was adopted.
- Now a person who, during the provision of medical care, during a medical examination or medical examination, reveals signs of possible tuberculosis is considered a “person with suspected tuberculosis.”
- a number of responsibilities for persons suspected of having tuberculosis :
- — undergo a medical examination for tuberculosis;
- — register (dispensary observation) with a TB doctor at a tuberculosis clinic;
- — observe the frequency of dispensary appointments;
- - take medications;
- — observe sanitary and epidemiological rules and not interfere with sanitary and anti-epidemic measures.
Let us recall that a year ago a new Procedure for conducting preventive medical examinations of citizens in order to detect tuberculosis came into force (Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated March 21, 2017 N 124n).
- According to the document, in order to detect tuberculosis, children undergo immunodiagnosis, adults undergo fluorography or chest X-ray.
- From the meaning of the new law, it turns out that attending physicians at clinics (generalists and pediatricians) must pay close attention to persons suspected of tuberculosis (based on the results of fluorography and tuberculin testing) and refer them for further examination.
- Phthisiatricians can now register (dispensary observation) not only patients with tuberculosis, but also “suspected persons,” “contact persons,” and those who have recovered—dispensary observation schemes in the tuberculosis dispensary must be adjusted accordingly.
claim may be filed against a citizen who deliberately evades examination for the purpose of identifying tuberculosis or treating tuberculosis involuntary in a medical anti-tuberculosis organization (Part 1 of Article 281 of the Code of Administrative Proceedings of the Russian Federation).
Dear readers, if you liked the article, do not forget to like and subscribe to new articles and reviews, and also tell the news to your colleagues!
You can ask all questions regarding the document to medical lawyer Vadim Sergeevich Berezinsky.
Source: https://zakon.ru/Blogs/podozritelnyh_na_tuberkulez_pacientov_obyazali_vstat_na_uchet_ftiziatra/74745
Frequently asked questions | "Clinical anti-tuberculosis dispensary"
Answers to the most frequently asked questions
Phthisiatricians of the children's dispensary department No. 1 of the KPTD KUZOO answer.
1. I have a small child, and a homeless person is constantly warming himself in the entrance. He coughs and spits all the time. Elderly neighbors told about him that he lived in a neighboring house, periodically spent time in prison and was sick with tuberculosis. If so, can I or my child get this disease.
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease, the source of infection is people and animals (cattle, goats, dogs) with an active form of tuberculosis. The most dangerous are patients with pulmonary tuberculosis with the presence of bacterial excretion and/or destructive processes in the lungs.
The pathogen is transmitted by airborne droplets.
The causative agents of tuberculosis are distinguished by very high resistance to environmental factors: they are able to retain their pathogenic properties for quite a long time in the ground, in household dust, in snow, in ice. On the pages of books, Koch sticks can remain viable for 3-4 months, in street dust for 10 days, in water for up to a year, and in a dry state for up to 3 years.
First of all, a homeless person is a person who is in a critical life situation and needs help. It has not been proven that he has tuberculosis. Information must be sent to the county social service website. If he really is sick with tuberculosis with bacterial excretion, then infection (infection) of others is real.
2. Why give manta to children, if even with its increase, this does not mean that the child is sick??? Why injure everyone!!??
The Mantoux test is not a vaccination against tuberculosis, it is a diagnostic test for detecting infection with tuberculosis, early detection of preclinical (latent) forms of tuberculosis in children! It is carried out at intervals of 12 months or 6 months in the presence of aggravating factors in the form of chronic pathology.
When a positive Mantoux test is detected for the first time, a consultation with a TB doctor is carried out, an additional examination is prescribed, since this is a turn of the tuberculin test - a period of early tuberculosis infection, and observation by a TB doctor is required for at least one year; if necessary, anti-tuberculosis drugs are prescribed . Since infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis (latent form of infection) is a risk of developing an active form of tuberculosis. Detection of infection is necessary for timely initiation of observation and, if necessary, treatment, since without treatment, tuberculosis-infected children have a risk of developing active tuberculosis of about 10-15%.
3. Why do you need to give BCG to a newborn if he can still get tuberculosis later? I personally wrote a refusal.
Vaccination helps protect people, especially infants and young children, from developing generalized forms of tuberculosis.
The incidence of tuberculosis in the Russian Federation exceeds the epidemic threshold by 20.0%; in the Siberian Federal District and Omsk Region, the excess of the epidemic threshold is more than 50.0%.
Vaccination of a newborn against tuberculosis in such a tense epidemiological situation is mandatory and is included in the National (State) calendar of preventive vaccinations.
Only when a newborn is vaccinated against tuberculosis does the state guarantee the protection of infants and young children from generalized forms of tuberculosis, including tuberculosis of the central nervous system.
Vaccination does not prevent infection; the development of an active form of respiratory tuberculosis is possible, but we emphasize once again that vaccination prevents the development of generalized forms of tuberculosis. By refusing to vaccinate your newborn with BCG, you are putting the health and life of your child in serious danger!
4. We ask you for advice on how to protect yourself and your children from this terrible disease.
In the Russian Federation, the system of specific prevention of tuberculosis in children is a state task. Its components are as follows:
1) First of all, this is an examination of people in the immediate environment of the pregnant woman and newborn for tuberculosis within an interval of no more than a year after the last examination.
And subsequently, an annual examination for tuberculosis of persons from the child’s immediate environment (parents, grandparents, nannies, all apartment surroundings from the age of 15 years) is also necessary.
If a patient with tuberculosis is identified in a family with the release of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, it is necessary to completely separate the patient and the child until the patient completely stops isolating Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
2). Mandatory vaccination of newborns against tuberculosis in the maternity hospital.
3) Further, from the age of 1 year, annually at intervals of 12 months.
The Mantoux test is performed - this is a diagnostic test to detect infection with tuberculosis, early detection of preclinical (latent) forms of tuberculosis in children! In the case of a positive test for the first time, with a timely consultation with a TB doctor, further examination and, if necessary, anti-tuberculosis drugs are prescribed. This generally prevents the development of active forms of tuberculosis in children.
5. Please tell me if there is an alternative to the Mantoux test and the Diaskin test in Omsk today. The child had an allergy to Mantu, they used to take a quatiferon test (quite expensive, though), but for the last two years they haven’t done it in Omsk - there is no drug.
The Mantoux test is a diagnostic intradermal test (delayed hypersensitivity test for tuberculin) to detect early infection; it establishes the fact of infection (with the exception of post-vaccination allergies). A positive reaction is detected after 6-8 weeks after infection.
Diaskintest (recombinant tuberculosis allergen) - a diagnostic intradermal test with a questionable and positive reaction indicates not only infection, but also that mycobacteria “live and multiply” in the body; a negative reaction in no way excludes the presence of infection.
After the fact of infection, a positive reaction to Diaskintest is detected no earlier than 3-4 months. Hence the conclusion - these methods are not alternative.
An alternative to Diaskintest are diagnostic tests based on the release of interferon-gamma by cells of the immune system (quantiferon test, determination of the level of interferon-gamma), which are carried out as prescribed by a TB doctor.
Contraindications for the Mantoux test when performed in organized groups are as follows: skin diseases, acute and chronic infectious and somatic diseases (including epilepsy) during an exacerbation period; allergic conditions, rheumatism in the acute and subacute phases, bronchial asthma, idiosyncrasies with pronounced skin manifestations during an exacerbation. When children are hospitalized, the list of contraindications is significantly narrowed.
By refusing to perform a Mantoux test on your child, you are giving up the possibility of early detection of tuberculosis infection; in such cases, when infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the risk of the child developing an active (clinical) form of tuberculosis increases.
6. Please tell me that preschool educational institutions require a Mantoux test for a child, we don’t want to do this (we don’t want to introduce foreign harmful substances into the child’s body). They did blood PCR. It's enough? What is necessary in order to obtain a phthisiatrician’s conclusion on a child’s admission to a preschool educational institution?
This method determines the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA in the test material. If there is DNA of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (or DNA fragments), the result of this method is positive. If not, negative.
Used to detect the DNA of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in pathological biological material (sputum - in case of damage to the respiratory system, urine - in case of kidney damage, etc.). And even in such cases, it can be negative in the presence of active tuberculosis.
Even with generalized tuberculosis, a blood test using PCR for the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA gives a negative result.
The PCR method may not detect tuberculosis (for example, intrathoracic lymph nodes), even if it is present and has a complicated course. Children with tuberculosis secrete Mycobacterium tuberculosis extremely rarely.
A child can die from tuberculosis without ever isolating Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Consequently, the detection of tuberculosis in children by blood PCR cannot be a replacement (alternative) to the tuberculin diagnostic method (Mantoux test) and a TB doctor cannot, based on a negative blood PCR result for tuberculosis, give a conclusion about the absence of active tuberculosis in your child.
It is not recommended to independently choose one or another method to identify the disease, since the results may be false and repeated testing simply cannot be avoided.
7. Hello! I am interested in the following question: why are children sent to a phthisiatrician even with a slight redness of the mantu? Why, if the child is healthy, should he jostle in lines there? After all, there may be sick children there. And without a phthisiatrician they threaten us in the kindergarten that they won’t let us in? And in general, is it legal not to let children go to kindergarten?
For the purpose of early detection of tuberculosis in children, tuberculin diagnostics are carried out on children vaccinated against tuberculosis from 12 months of age until they reach the age of 18 years. An intradermal allergy test with tuberculin (hereinafter referred to as the Mantoux test) is performed once a year, regardless of the result of previous tests.
The Mantoux test is a diagnostic intradermal test (delayed hypersensitivity test for tuberculin) to detect early infection; it establishes the fact of infection (with the exception of post-vaccination allergies) - this is the course of a latent tuberculosis infection.
In accordance with the sanitary and epidemiological rules SP 3.1.2.3114-13 “Prevention of Tuberculosis”, the following categories of children are sent for consultation to the TB dispensary at their place of residence within 6 days from the date of the Mantoux test:
- - with a newly detected positive reaction (papule-infiltrate 5 mm or more), not associated with previous immunization against tuberculosis;
- — with a long-lasting (4 years) reaction (with an infiltrate of 12 mm or more);
- - with increasing sensitivity to tuberculin in tuberculin-positive children - an increase in infiltrate by 6 mm or more;
- - an increase of less than 6 mm, but with the formation of an infiltrate measuring 12 mm or more;
- - with a hyperreaction to tuberculin - infiltrate 17 mm or more;
- - with vesiculo-necrotic reaction and lymphangitis.
Children who have not passed the annual scheduled examination using the tuberculin diagnostic method (Mantoux test) should be referred for consultation to a phthisiatrician. This is regulated by clause 5.7., section V.
“Organization of early detection of tuberculosis in children” Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated October 22, 2013. No. 60 “On approval of sanitary and epidemiological rules SP 3.1.2.
3114-13 “Prevention of tuberculosis” (hereinafter referred to as the Sanitary Rules):
“Children sent for consultation to a tuberculosis dispensary, whose parents or legal representatives have not submitted a phthisiatrician’s conclusion about the absence of tuberculosis within 1 month from the date of the Mantoux test, are not allowed into children's organizations.
Children who have not undergone tuberculin diagnostics are admitted to the children's organization if they have a phthisiatrician's conclusion about the absence of the disease.” The decision to admit a child to an educational institution is made by the head of the institution.
Compliance with the Sanitary Rules is mandatory for individuals and legal entities.
The risk of a child contracting tuberculosis when visiting children's dispensaries of the state health care institution of the Omsk region "Clinical Anti-TB Dispensary", located not only in separate buildings, but also geographically separated from dispensaries for adults, is no greater than when visiting children's clinics and other diagnostic centers.
8. Tell me if the child is not given a r. Mantoux, which analysis other than the Diaskin test is the most informative?
There is no alternative to the Mantoux test; each diagnostic test has different tasks.
9. Is the hype around tuberculosis related to the fact that WHO decided to end tuberculosis in the world by 2030??? Why do TB doctors in different parts of the country have no clear instructions on what examinations children who refuse Mantoux, Diaskintest, or radiography should undergo?????????
- WHO has developed a global control strategy; the successful solution of the WHO global goal of defeating the tuberculosis epidemic (not ending tuberculosis) by 2035 is determined equally by the commitment of each person and the readiness of the state to contribute to solving the global task.
- (Strategy – “End the TB Epidemic”).
- WHO for countries with a high burden of tuberculosis infection recommends the tuberculin diagnostic method (Mantoux test) to monitor the detection of early infection in children (latent tuberculosis infection).
In no other country do parents allow themselves such a “luxury” of refusing to participate in government programs for vaccination, tuberculin diagnostics, etc.
In our country, “intoxicated” by the freedom of informed consent, parents, refusing effective methods of preventing infectious diseases, are putting the health and even the lives of their children at great risk.
10.
Why is it that for the widespread diagnosis of tuberculosis in children, only methods harmful to health are used, such as the Diaskin test, Mantoux, X-ray and fluorography, and more accurate and safe diagnostic methods, such as CFT, T-spot, tubinferon, PCR, test for antibodies to tuberculosis and other blood and macro tests are accepted by a very small number of TB specialists and with great reluctance?
It should be emphasized that each method has its own tasks. You can list a dozen more methods; the state phthisiatric service, when conducting a comprehensive examination of patients to exclude the presence of tuberculosis, is guided by orders approved by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, sanitary rules, standards, methodological guidelines, and federal clinical recommendations.
The myth that the Mantoux test is harmful to a child is one of the most dangerous and ignorant ideas that doctors are actively fighting against.
According to Rospotrebnadzor, tuberculin is an absolutely safe drug that has passed state registration, has been thoroughly studied and is incapable of harming the patient when used correctly.
The experience of using this substance in medicine is more than 100 years.
In addition, in the Omsk region, for more than five decades of conducting intradermal Mantoux tests with tuberculin 2TE PPD-L, not a single case of complications as a result of the tests has been recorded.
Yes, the composition of the drug used in skin testing for children does contain phenol. The fact is that tuberculin is based on a protein isolated from mycobacterium tuberculosis and is unsuitable for long-term storage.
In order for the drug to be stored and used for a long period from the date of manufacture, it is necessary to add a preservative. At the same time, the dose of phenol that a child receives when injecting tuberculin is, by definition, incapable of harm, since it is negligible - only 0.25 milligrams.
For comparison, the body of each person naturally produces 250 milligrams of this substance from the moment of birth, that is, one thousand times more.
In addition to phenol, tuberculin also contains the surfactant Tween-80 (polysorbate), which is non-toxic and approved for use in children's cosmetics, i.e., the child encounters it every day.
Phthisiatricians of preschool educational institution No. 1 KUZOO "KPTD"
Source: http://kptd55.ru/informaciya-dlya-naseleniya/chasto-zadavaemye-voprosy/