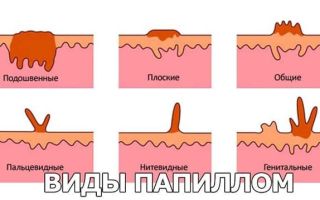
There are many types of HPV. It is classified according to numerical parameters, with each variety characterized by its own level of oncogenicity. If a type 44 virus is diagnosed in women, you should find out what it is first, and only after studying the causes of development can you look for a cure.
The cause of the formation of cancer cells is often the presence of HPV type 44 in the body.
The infection causes various forms of benign, precancerous and neoplastic lesions on the mucous membranes of the genitals and other parts of the body, including cervical cancer.
The pathology is considered the second most common malignant problem in women.
HPV-44, HPV-16 and HPV-18 are responsible for 70% of cancers and most intraepithelial precancerous lesions of the cervix, vulva, vagina, anus and penis.
Routes of transmission of 44 strains
In recent years, there has been a steady increase in the number of cases caused by the human papillomavirus. The exact statistics of the incidence are not yet known, but a massive incidence of condylomas has been diagnosed in patients. There is also a decrease in the average age of the patient.
Condylomatosis occurs in sexually active people.
Genital warts are found on the mucous membranes of the genitals, although they are also found in the mouth or around the anus. In the latter case, their development in women is the result of a secondary infection. Wards near the anus may be a consequence of anal relations.
You can get infected from your partner
Although genital warts are a disease of adults, they are becoming increasingly common in prepubescent children as the infection spreads during childbirth. Another source of infection may be sick family members. For example, as a result of non-compliance with basic rules of personal hygiene.
The incubation period for genital warts ranges from 6 weeks to 8 months. What it looks like depends on the type of virus, location, time of onset of changes and the general condition of the patient.
Clinical picture
HPV has more than 200 serotypes, of which several have outstanding oncogenic potential, whereby infection can lead to the development of cancer.
Among the population aged 19-45, about 80% have been exposed to some type of virus. What contributes to the spread is often the asymptomatic nature of the infection and indicates an easy mode of transmission.
For example, the use of general personal hygiene items.
Infection may be associated with childbirth
A few weeks or months after infection, condylomata acuminata appears. These are single or confluent growths that resemble cauliflower in shape.
They increase in size, but in extreme cases can cause pain during intercourse or prevent urination. Any changes to genital warts should be removed.
This is most often done using laser or cryotherapy.
Such changes serve as a reservoir for the virus and contribute to the infection of sexual partners.
The most serious consequences are oncogenic types of HPV, especially 16, 18, 31 and 44. Most often, the disease is asymptomatic. This pathology is not synonymous with oncology, but significantly increases this risk. A situation that encourages the development of cancer is the presence of a concomitant factor.
Important reasons:
- onset of sexual activity at an early age;
- frequent change of partners without using condoms;
- oral hormonal contraception;
- numerous births;
- smoking.
Not using condoms can lead to infection
Possible complications
Condylomata acuminata in women is a soft growth located on the labia and perineum. They can affect the vaginal epithelium, urethra, anus and cervix. It happens that discolorations combine with each other to create multiple formations. This is a precancerous condition, as there is a risk of degeneration of the rod into squamous cell carcinoma.
Skin changes look like flat spots with a diameter of several millimeters. They are pink or slightly brown, with a smooth surface that is sometimes prone to sticking together. In men, the lesion is located on the head, and in women - on the labia, inguinal folds and in the anal area. Course of the disease: spontaneous or complex and long-term course.
In women, dysplastic lesions associated with HPV infection are found in 75% of cases.
If a person is diagnosed with both Bowen's disease and the HPV virus, the tumor is initially located only under the basement membrane of the epidermis.
Without treatment, this condition can move to tissues located much deeper. In some cases, the pathology metastasizes to the lymph nodes or bones.
In women, the affected areas are flat, red or dark brown, distinct and itchy.
Lack of timely treatment can lead to various kinds of complications
Bowen's disease is found in women over 60 years of age, and for older patients, doctors recommend completely cutting out the vulva.
In younger people with smaller lesions, 5-fluorouracil cream or cryotherapy is used. In case of failure, surgical treatment is used.
In men, small lesions are treated with freezing or 5-FU cream, while larger lesions are treated with surgery or laser removal.
Kairat erythroplasia is a squamous cell carcinoma resembling Bowen's disease. Rarely found on the vulva in women. In most cases, the pathology is caused by HPV.
Vulvar cancer is a rare disease that accounts for 3-5% of all malignant tumors of the genital organs in women. Vaginal cancer problems often occur in scars and skin irritated by long-term inflammation. The pathology is located on the labia majora in close proximity to the clitoris, vestibule of the vagina and perineal skin around the urethra.
Type 44 virus often leads to cancer in women
One of the common symptoms is itching, which requires differentiation from other diseases that provoke the development of the same symptom in this area. The diagnosis of advanced vulvar cancer usually does not raise any doubts. In early periods, when symptoms are not typical, caution is recommended.
The HPV-44 virus is most often mentioned in the context of cervical cancer. And this is correct, because almost 100% of cases of the disease are regenerated by this type of strain. This is confirmed by the results of HPV DNA of patients affected by such a serious disease.
Every year, over 3,500 women are diagnosed with cervical cancer, and half of them die.
Treatment
If a woman notices alarming signs, she should definitely consult a doctor. You should be wary of the following pathologies:
- development of one or more nodules located near the vulva;
- itching;
- bleeding.
It is not uncommon for treatment to require surgical intervention.
HPV-44 infection quickly forms metastases to surrounding lymph nodes. It is important to consult a doctor for any symptoms in the genital area. Lesions caused by contact with the HPV virus often go into remission. If the lesion does not resolve after treatment, surgery should be performed.
In the case of highly dispersed dysplastic growths, the main surgical procedure aimed at eliminating HPV is cervical conization. The uterus is excised when there are other instructions for performing this procedure. For women of productive age, doctors recommend surgical procedures to preserve a normally functioning organ.
Topical chemical solutions are used to remove genital warts (especially on the vulva). The effectiveness of this type of therapy varies, and relapses are common. Another method of treating condyloma is cryostimulation or laser evaporation of the lesions, which gives very good results.
Regular examinations reduce risks
Preventive actions
The risk of HPV infection cannot be completely eliminated, but it can be reduced. Casual sexual contact should be avoided, especially without protection. Using condoms slightly reduces the risk of HPV infection, but does not provide a 100% guarantee. It is important to educate young people not to become sexually active too early.
Doctors recommend regularly testing for HPV DNA. And for girls who have not yet become sexually active, a vaccine is available.
For prevention, patients are advised to adhere to a healthy diet (a diet containing many vitamins) and avoid smoking. In addition, you need to regularly undergo colposcopy and cytological tests.
There are vaccines against some types of HPV, although their effectiveness is still uncertain and cannot be used instead of the above methods. Only inaction creates problems.
The video will talk about the treatment of HPV:
Source: http://bolezni.com/stati-o-boleznyah/papilloma/sorok-chevertyj-tip.html
How is HPV transmitted: all routes of transmission of the human papillomavirus
The papilloma virus can remain in the human body for a long time and not manifest itself in any way. It is activated only when the immune system is weakened.
In most cases, the infection does not pose a particular danger, but some of its strains, under certain factors, can degenerate into cancer. And this already poses a threat to human life. It is impossible to completely get rid of a pathogenic microorganism.
Therefore, it is very important to know how the human papillomavirus is transmitted to reduce the risk of HPV infection.
Characteristics of the virus and its carriage
The human papillomavirus causes the formation of benign neoplasms on the skin and mucous membranes. They have the appearance of a papilla that protrudes several millimeters above the surface.
As a rule, such a growth appears when the body’s defenses are weakened. Usually a person lives quietly and does not even think about “whether I can be a carrier or not,” for the time being.
Why papillomas form:
- frequent hypothermia or overheating;
- presence of concomitant diseases;
- poor nutrition;
- presence of bad habits;
- frequent stress, depression, overwork;
- lack of vitamins, minerals and other nutrients.
90% of the world's inhabitants are carriers of papillomavirus. The question immediately arises whether the human papillomavirus is contagious or not. The answer is yes. No one is 100% immune from infection. Therefore, it is very important to know how you can become infected with HPV (human papillomavirus).
How is human papillomavirus transmitted?
Given that the likelihood of contracting HPV is very high, the question often arises of how the infection (human papillomavirus) is transmitted. Knowing the answer to this question can significantly reduce the risk of infection. Pathogenic microorganisms are transmitted from person to person. These are the most common routes of infection. Methods of infection by contact:
- Transmission of the HPV pathogen through sexual contact (during sex). Very often, this is how the oncogenic microorganism spreads. For example, such as HPV 16 and 18. Strain types 16 and 18 are life-threatening, as they can develop into cancer.
- Contact methods of infection. You can infect a person through touching, hugging, or kissing. The virus enters the body through damage, microcracks in the skin. Therefore, you should not come into close contact with people if you see a wart on their body (if you doubt whether it is contagious).
Transmission routes can also be domestic. How can you get an infection (papilloma) in this way:
- through personal hygiene products (towel, washcloth, toothbrush, etc.);
- human papillomavirus can be transmitted through clothing (infection occurs through lesions on the skin);
- infection can occur in public baths, saunas (the pathogen can be on the floor, benches, etc.).
A newborn baby may also be infected
The disease is not inherited. However, a newborn baby can also be infected. How can a baby become infected with papilloma:
- during fetal development from an infected mother;
- along the birth canal during birth.
Pregnant women need to be very careful to avoid infection or activation of a pathogenic microorganism. After all, not only their health, but also the life of the baby depends on this.
Human papilloma (HPV), how it is also transmitted: infection can occur in medical centers, hairdressers, beauty salons due to insufficient sterilization of instruments. This happens extremely rarely, because such institutions, as a rule, comply with all sanitary standards, but it still happens.
The infected person may not even be aware of it. Therefore, it is recommended to undergo routine diagnostic examinations annually. How infection occurs has now become clear. Thanks to this, you can take preventive measures and avoid infection.
Sexual method
Previously, we figured out how you can become infected with a benign neoplasm (papillomavirus). It became clear that HPV is most often transmitted through intimate intimacy (sexual contact).
Moreover, you can become infected through all types of sex (vaginal, oral, anal). Papilloma through intimate contact (sexual contact) is transmitted through contact between mucous membranes if they are damaged.
Moreover, the risk of infection is higher during anal sex, since it is more traumatic.
Considering that the risk of infection increases during intimate contact, the question arises: is it possible to have sex with HPV if one partner has it? Moreover, during sexual intercourse, infection with oncogenic strains of the virus often occurs.
Sex with HPV is acceptable, but you should always use a condom during it
Sex with HPV is acceptable. But during it you should always use barrier contraception (condoms). According to statistics, protection helps men and women avoid infection in 2 out of 3 cases.
Without contraception, the risk of infection increases to 90%.
If one of the people entering into intimate intimacy is infected, it is necessary to regularly undergo diagnostic testing for the oncogenicity of the pathogen (a healthy partner for the presence of HPV).
However, during sexual intercourse, even with a contraceptive, undesirable events can occur. During sex, the growth may become injured. As a result, another infection or blood poisoning may occur in the wound.
Also, damage to the tumor can cause it to degenerate into malignancy. Thus, it turns out that having sexual intercourse while being treated for HPV is undesirable. If you do do this, be extremely careful.
But it is still better to have contact only after treatment. Sexual life after removal of papillomas is less risky.
There is an opinion that the papillomavirus can be activated during masturbation. Allegedly, this is inferior sexual intercourse, resulting in hormonal imbalance and weakening of the immune system. This opinion is wrong. Masturbation does not in any way affect the body's protective functions.
During oral sex
HPV can be transmitted from woman to man and vice versa through oral sex. This happens through microdamages on the skin and mucous membranes. Through oral sex, strains of HPV are most often transmitted, which can develop into cancer.
A condom during oral sex reduces the risk of infection only if a blow job is performed. With cunnilingus, in 90% of cases it is not possible to avoid infection.
Is the human papillomavirus transmitted from mother to child?
We figured out how adults most often become infected with the papilloma virus. Now it is necessary to understand whether the human papillomavirus is transmitted from mother to her child, how this happens and what it means for babies.
In a newborn baby, infection can occur through the touching and kissing of the mother if she is a carrier of a pathogenic microorganism . The infection enters the baby's body through damage to the skin or mucous membranes.
Infection can also occur during fetal development. From an infected woman to her fetus. Also, infection can occur during childbirth. Although this is rare, it carries serious consequences.
HPV is transmitted through kissing
Through kiss and blood
How is human papillomavirus infection transmitted?
- through saliva;
- through a kiss;
- through blood.
The question immediately arises, if HPV is transmitted through a kiss, is it possible to kiss a person who is infected? This decision is up to you to make.
If you are 100% sure that there is no damage (even microscopic) to your oral cavity, then kissing is completely acceptable. However, this is a rather risky decision.
There may be damage in your mouth that you cannot feel and that you are not even aware of.
The possibility of infection with the human papillomavirus through blood has not been scientifically proven. There have been cases when infection occurred during transfusion. However, this is not proof that the pathogen can be transmitted in this way. It is possible that infection in these cases was caused by poorly sterilized instruments.
Household way
In 85-90% of cases, infection can be transmitted through household means when one of the family members is infected. A pathogenic microorganism at home is very often transmitted from parents to children. The child’s immunity is not yet strong and therefore the baby is more susceptible to infection. Infection through domestic means can occur in the following ways:
In 85-90% of cases, infection can be transmitted through household means when one of the family members is infected.
- if there are lesions on the skin, infection can occur through the use of shared bed linen, towels, washcloths, soap, cosmetics and hugging;
- You can become infected through saliva by using the same utensils, a toothbrush, or by kissing a carrier of the virus;
- when wearing clothes of an infected person (especially underwear);
- In domestic conditions, self-infection can occur during shaving and hair removal.
Also, domestic transmission of the pathogen includes infection in public places. For example, in a swimming pool, bathhouse, sauna. And also with frequent handshakes and friendly hugs.
How to avoid getting infected with papillomavirus
How to avoid getting infected with HPV (papillomavirus):
- avoid frequent changes of sexual partners;
- protect yourself during intimacy;
- do not use other people's things;
- do not wear other people's clothes;
- avoid visiting public baths, saunas, swimming pools (or at least carry a personal towel and spare shoes with you);
- do not drink drinks or eat food from infected people;
- carefully approach the choice of cosmetology, clinic, hairdresser (you must be sure that the institution complies with all sterilization rules);
- do not come into close contact with carriers of the virus.
If you do develop papillomas, consult a doctor. He will conduct the necessary diagnostics, determine the strain of the pathogen and, if necessary, prescribe effective treatment.
If you do develop papillomas, consult a doctor
Does a condom protect?
If one of the partners has HPV, it is necessary to use a condom during sexual intercourse. However, a contraceptive is not a 100% guarantee that the infection will not be transmitted. Of course, the pathogen will not be able to break through the condom, but infection can occur in another way.
Infection can occur during foreplay. Through microcracks in the skin or in the oral cavity. In this case, a barrier contraceptive will not help.
Treatment methods
If you are a carrier of HPV, the infection may lie dormant in the body and not cause any problems. To prevent growths from occurring on your body, you need to monitor the state of your immune system. The stronger it is, the lower the risk of tumor formation.
If growths occur, the doctor may advise not to take any action (provided that the papillomas do not cause discomfort and do not have an oncogenic strain).
If a decision has been made to get rid of tumors, then, as a rule, this is done using conservative methods.
If drug treatment does not produce a therapeutic result or there is a risk of papilloma degenerating into cancer, surgical intervention is prescribed (if there are no contraindications).
Video
HPV infection. Routes of infection with HPV
Source: https://ozppp.com/vpch/papillomavirus-kak-peredaetsya.html
HPV type 44 in women and men: what is this disease, treatment
HPV is a human papillomavirus, it manifests itself in the form of papillary growths on the skin and mucous membranes. In total, there are about a hundred varieties of this virus, some of them affect the skin, and some of them affect the genitals.
HPV is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases. Some types of papillomavirus can provoke cancer; different types have different degrees of oncogenicity.
Reference: according to statistics, about 90 percent of the adult inhabitants of the planet are infected with one or another type of papillomas.
General information about papilloma in women and men
HPV type 44 in women affects the genital organs - the perineum, vestibule of the vagina, cervix, perianal area, vagina, pubis, urethra.
Unlike some other varieties (for example, types 16,18, 45, 56), it belongs to viruses of low oncogenic risk, that is, the likelihood of developing an oncological tumor is low, they can degenerate into a tumor only in very rare cases and only with very serious weakening of the immune system.
Factors and causes of infection
Infection most often occurs through intimate contact, but sexual intercourse is not the only way of infection. Infection can also occur:
- by household means - in contact with a contaminated surface on which the patient’s skin cells remain, or with the patient himself;
- vertically – that is, the virus enters the child’s body through the birth canal.
Infection does not occur through blood or saliva, only through skin cells.
Important!
It is impossible to protect yourself from HPV using barrier methods of contraception or antibacterial agents one hundred percent, since the virus can easily penetrate latex, and HPV DNA molecules are resistant to many antimicrobial agents.
The only way to protect against HPV is to strengthen your immune system.
Factors that provoke the development of infection also include:
- bad habits;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- the presence of pathologies of internal organs;
- long-term use of potent medications;
- hormonal disorders;
- violation of personal hygiene rules.
Stages of the disease
- The incubation period for HPV can range from several months to several years. The duration of the incubation period may depend on the general condition of the body, the presence of concomitant diseases, and lifestyle.
- Clinical manifestation after the incubation period occurs in the form of warts on the genitals.
- The infection is often subclinical, meaning no obvious symptoms are visible, and in many cases this genital infection may go unrecognized.
- HPV is highly contagious, and you can become infected with the first sexual contact, this happens in approximately 60–70 percent of cases.
Important!
It should be noted that infection is also possible if the partner does not have clinical symptoms, that is, there are no warts themselves. The sources of the virus are altered cells in the body of the infected person.
Features of development
HPV is most often transmitted from a sexual partner through microtrauma of the genital organs. Next, the infection enters the mucous membrane and is met by cells of the immune system.
In most cases, these cells manage to destroy the virus. But if the immune system is weakened, then the virus is able to penetrate the cells of the basal layer of the epithelium of the mucous membranes, then the DNA of the virus penetrates the chromosomes of the cells and changes their functioning.
These cells begin to divide too quickly and grow in a certain area, while externally turning into growths - papillomas.
Diagnostic methods
As with any disease, correct and timely diagnosis allows you to avoid a number of health problems. In the case of HPV, this is suppuration in the tissue structure, acute inflammatory processes and, most importantly, cancerous tumors.
Women are recommended to visit a gynecologist once every six months or a year and get tested for the presence of papillomatosis.
Diagnosis of VHF is carried out in several ways:
- Examination by a gynecologist . Often the disease occurs in a latent form and a routine examination will not reveal the infection.
- If the infection already manifests itself in the form of papillomas, a histological analysis of a piece of growth tissue is required. The following methods are relevant if the patient does not have obvious external manifestations in the form of warts.
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction ) is one of the main diagnostic methods. It involves taking a smear from the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix, then using special reagents to determine the presence of DNA infection. This analysis allows you to detect the presence of the virus even in a latent state, as well as determine its concentration. But sometimes PCR can give a false result (both false positive and false negative).
- Cytological examination, also called PAP test, or simply cytology . A smear is taken from the patient, and the presence of pathologically altered cells is determined under a microscope.
- Digene test - Digene testing is a new type of research that allows for a clinically significant concentration of the virus. It is usually carried out in conjunction with a cytological examination.
How to get rid of pathology?
Strain 44 is a low-oncogenic risk virus, so don’t panic, it’s not a terrible disease, but you should approach treatment responsibly and listen to your doctor’s recommendations.
When such a diagnosis is made, antiviral drugs such as acyclovir, cycloferon, isoprinosine, and groprinosin are usually prescribed. These drugs are available in tablet form and are taken orally in certain dosages.
Also, in the presence of genital warts, local drugs (vaginal suppositories) such as genferon, panavir, viferon, papilomin, gepon are prescribed. Sometimes injections of Panavir, Allokin-Alfa, PegAltevin solutions are prescribed subcutaneously or intramuscularly. Parallel treatment of the partner is also recommended. Ointments, gels, and creams are used less frequently in the treatment of HPV type 44.
- Treatment occurs, first of all, by stimulating the immune system and improving the natural protective functions of the body.
- If a patient, in addition to HPV, has other sexually transmitted diseases (herpes, chlamydia and others), a comprehensive treatment regimen is very important, since concomitant illnesses can provoke the risk of complications from papillomavirus.
- Additionally, among folk remedies, douching is sometimes used, washing with a decoction of celandine or calendula, nettle tincture, potato ointment, a decoction of wormwood, raspberry leaves and honey.
Important!
Before using any of the folk remedies, you should consult your doctor, because even medicinal herbs can have serious contraindications!
It is also necessary to remember that it is impossible to cure the papilloma virus 100%, but you can bring it into a latent state, remove external manifestations and reduce its concentration, ensuring that the immune system itself suppresses the infection.
Prevention
Prevention consists, first of all, in strengthening and maintaining the immune system. The best means of prevention include:
- healthy lifestyle;
- compliance with personal hygiene measures;
- avoidance of casual sexual contacts, promiscuity;
- taking vitamins, healthy eating;
- regular visits to a gynecologist.
Thus, human papillomavirus type 44 is a low-oncogenic risk virus. This means that the risk of developing cancer in the presence of this strain is minimal, and is possible only with a very significant weakening of the immune system.
The disease does not always have clearly expressed symptoms, so modern diagnostic procedures - PCP, Digen test, cytological or histological analysis - can identify this disease. The main therapeutic measure in the presence of this type of virus, as well as other types of HPV, is to strengthen the immune system.
Immunomodulatory and antiviral drugs are prescribed as treatment, in the form of tablets and suppositories, and sometimes injections. The best prevention of papillomavirus is refusal of promiscuous sex life (ideally, there should be one regular sexual partner), a healthy lifestyle, personal hygiene, and taking vitamins.
Source: https://vseopapillome.com/papillomy/chto-ehto-vpch-44-tipa.html
Features of the manifestation of HPV type 44 in women: is the strain dangerous?
The prevalence of human papillomavirus infection and associated manifestations is steadily increasing. According to medical statistics, up to 3 million new episodes of HPV type 44 infection in women are registered every year. If you follow the recommendations and advice of doctors, the prognosis for the course of the disease will be positive.
Causes of HPV type 44 in women
In most cases, HPV type 44 infection occurs through sexual contact with the skin of a virus carrier. HPV is contagious and can be acquired after a single sexual contact.
The manifestation of infection is associated with immune suppression.
Factors influencing the activation of the HPV 44 strain:
- bad habits;
- acute or chronic diseases of organs and systems;
- long-term use of immunosuppressants, antibiotics, cytostatics;
- endocrinological disorders;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
Symptoms of virus infection and localization of growths
Type 44 papillomavirus is characterized by damage to the stratum corneum of the epidermis. In women, it is represented by epithelial pathologies of the uterine cervix, which do not give any symptoms for a long time.
When HPV in women becomes active due to decreased immunity, condylomas begin to form in the vagina and inside the cervical canal.
This process poses the greatest danger during pregnancy, as hormonal transformations stimulate rapid growth.
When the virus is activated, condylomas appear on the mucous membranes of the external reproductive organs or near the anus.
These are small skin-colored formations that tend to integrate with each other, modifying into tumor-like elements resembling the shape of a cockscomb or the inflorescences of cauliflower heads.
When damaged by domestic or sexual means, physiological discomfort occurs.
Papillomatosis occurs most severely against the background of sexually transmitted infections of the urogenital tract: chlamydia, gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis.
Features of diagnosing HPV type 44
Typically, condylomas caused by human papillomavirus type 44 in women are diagnosed by a gynecologist. They belong to the group of sexually transmitted infections; differential diagnosis and therapy should be carried out by a dermatovenerologist.
The problem becomes obvious when examining the patient. If characteristic forms of genital warts are detected, verification of the HPV type is not necessary. But it is necessary to exclude diseases: molluscum contagiosum, syphilitic chancre.
Testing methods for HPV 44:
- cytological analysis of a smear from the cervical canal for abnormal cells;
- colposcopy;
- histological examination when removing elements;
- PCR diagnostics to detect DNA and virus concentration;
- determination of antibodies to hpv in the blood.
All patients with condylomas are tested for immunodeficiency virus, syphilis, and other sexually transmitted diseases.
How to cure human papillomavirus type 44 in women
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Currently, it is impossible to completely overcome hpv 44. None of the currently used treatment methods guarantees the absence of relapses.
HPV tends to be reserved in skin cells and mucous membranes. But self-resolution of the situation cannot be ruled out. In maximum cases, removal of condylomas is prescribed.
The procedure is selected based on the medical history, contraindications, and indications of the individual patient.
Basic methods:
- laser coagulation, in which the growth is evaporated to form a scab;
- radio knife - condyloma is cut off without blood;
- cryodestruction using liquid nitrogen;
- coagulation by electricity – pathology is burned out using current.
For local destruction of outgrowths, chemical substances are used: Condilin, Podophyllin, Feresol (it is undesirable to treat mucous membranes). Vaginal suppositories Viferon, Reaferon, Panavir have antiviral and immunomodulatory activity.
Sprays will help relieve vulvar discomfort: Epigen, Panavir.
Immunoenhancing drugs are included in the course of treatment of anogenital warts: Allokin-alpha, Vitaferon, Kipferon, Interferon.
Tablet medications for HPV 44 in women:
- Isoprinosine;
- Gronprinosin;
- Cycloferon;
- Alpizarin;
- Acyclovir.
Is it possible to live fully with virus 44 in the body?
Papillomavirus type 44 is considered low-oncogenic and not life-threatening. This means that the risk of malignancy of condylomas is practically eliminated with adequate and timely treatment.
The patient can continue to live a full life, albeit with some rules. She is recommended to undergo regular examination by a gynecologist or venereologist with quantitative PCR analysis, colposcopy, and removal of growths.
If the analysis is positive, repeat the course of therapy. Pregnancy with this pathology is not contraindicated.
Carrying a virus of any type of HPV 44 does not exclude infection with another strain. Women are advised to avoid indiscriminate sexual contact. Immunity should be boosted by eating vitamin-rich foods, doing as much physical activity as possible, and quitting smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages. If possible, you should live a stress-free life.
All categories of women who have sexual relations must undergo a smear for oncocytology every 2 years. At the onset of menopause, during menopause, the test is performed annually.
How to prevent complications from developing
Women with genital warts caused by type 44 of HPV, after therapy, are advised to be examined by a doctor, undergo tests every three months, then six months, then at least once a year.
After treatment of cellular dysplasia, follow-up is carried out after three or six months, or at least once every six months, by a gynecologist-oncologist to prevent the development of cervical cancer.
For each consultation, the patient performs cytological and virological studies.
Increased attention should be paid to all sexual partners; if possible, they should be examined and treated for STDs and HPV to prevent a woman from becoming infected again with the same or a different strain of pathology. Persons with an atypical course of infection and resistance to standard therapy should ensure that there is no human immunodeficiency virus in their blood.
Finding genital warts on your body, especially the genitals, is unpleasant. Don't panic. It is necessary to visit a doctor as soon as possible and get examined. If type 44 of HPV is detected in women, which poses a low risk of cancer, you need to undergo treatment from a specialist.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Source: https://VashaDerma.ru/hpv/44-tipa-u-zhenshhin
HPV type 44 in women and men: treatment and complications
- Dermatologist of the highest category Inna Vladimirovna
- 30207
- Update date: December 2019
The human papillomavirus (HPV) has more than one hundred strains.
Some of them are dangerous with the risk of developing cancer, some are relatively safe. HPV type 44 is not considered a completely safe strain, so people infected with it must be treated promptly.
What is HPV type 44?
Human papillomavirus type 44 is mainly transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse
HPV type 44 is not a common strain, so it is found quite rarely. This strain is classified as a conditionally safe virus. The DNA of skin cells with HPV type 44 is rearranged in such a way that benign growths form on the skin.
HPV strain 44 is a virus with low oncogenicity. The risk of developing malignant neoplasms when infected with this virus does not exceed 4%.
The virus is transmitted primarily through sexual contact. Infection occurs through unprotected sexual intercourse, with women becoming infected more often than men. As a rule, the HPV virus in men is rarely accompanied by clinical symptoms, so a man may not even suspect that he is a carrier of the papillomavirus, but infect his partner.
Strain 44 is quite easily transmitted through contact and household contact. The transmission of the virus is facilitated by the use of other people's personal hygiene items, especially towels. At the same time, it is possible to become infected with the virus through microtraumas of the skin only if the immune system is weakened. Factors that increase the risk of infection:
- long-term use of antibiotics or corticosteroids;
- recent severe infectious diseases;
- severe stress;
- weakening of the body due to harmful addictions (alcoholism, smoking).
The risk of the virus entering the body increases in the presence of wounds and abrasions on the skin in contact with a potential source of infection, which may be someone else’s personal hygiene items or utensils.
Children can “receive” the virus from their mother while passing through the birth canal. This is observed quite rarely, since most women undergo a comprehensive examination before planning a pregnancy, which makes it possible to suppress a virus potentially dangerous to the child in advance.
Although this strain of the virus is considered harmless in terms of developing cancer, it can cause various other complications. In addition, the virus causes the formation of growths on the skin, which spoil a person’s appearance and are a noticeable cosmetic defect.
Avoiding infection is easier than getting rid of the virus. This is explained by the fact that today there are no sufficiently effective drugs that would destroy HPV in the body.
The main fight against the virus is carried out by one’s own immunity, and medications only temporarily reduce the activity of HPV, giving the body time to suppress it. To avoid becoming infected with HPV, it is necessary to practice protected sex, avoid using other people's personal hygiene products, and prevent a decrease in immunity.
For this purpose, it is necessary to promptly treat any diseases and regularly increase immunity, both with the help of a balanced diet and through special medications.
Symptoms of HPV type 44
Papillomatosis with HPV type 44 is characterized by damage to the mucous membranes and stratum corneum of the epidermis, which is explained by changes in human DNA by this virus. HPV type 44 viruses in women cause changes in the epithelium of the cervix, which can remain undetected for a long time.
When the virus is highly active, warts (papillomas) appear on the skin, as well as condylomas on the mucous membranes of the external genitalia.
HPV type 44 primarily affects the mucous membranes, but often several strains of the virus are found in the body of an infected person. This can lead to the formation of multiple neoplasms both on the mucous membranes and on the skin of the body.
In men, this strain of the virus rarely causes skin changes. Quite often the infection is asymptomatic. In some cases, if a man’s body is severely weakened, strain 44 of the virus can manifest itself as the formation of condylomas on the penis.
They do not pose a danger in themselves, but are a serious cosmetic drawback. If the growths are damaged, their rapid growth may occur.
In addition, growths on the penis are easily injured and can be rubbed by clothing items, which is accompanied by severe discomfort.
In severe cases, men develop papillomas in the urethra. This is accompanied by pain during urination and ejaculation. The body mistakes growths in the urethra for a foreign element, so inflammation may occur.
Diagnosis of HPV
Correct and timely diagnosis of the disease can prevent a lot of health problems
Since HPV type 44 in women often occurs without pronounced symptoms, it can be diagnosed by chance, during a routine examination by a gynecologist or during annual general tests.
Type 44 of the virus causes changes in the epithelium of the cervix. This can be discovered when visiting a gynecologist. The doctor may notice cervical erosion or other signs of pathology. During the examination, a smear is taken from patients for cytology. The smear material can also be used for the PCR reaction.
The presence of the virus can be suspected by the presence of neoplasms on the skin and mucous membranes, but papillomas do not indicate a specific strain of HPV. To determine the strain of the virus, the degree of its activity and the potential threat to health, a PCR analysis and a Digene test are performed.
To carry out PCR (polymerase chain reaction), mucosal tissue samples are examined. Examination of discharge from the cervix or vaginal walls is usually sufficient. The material is examined for the presence of viral DNA in the cells. The result obtained allows you to accurately determine the strain of the virus, even if it is in an inactive state.
Important! PCR analysis often gives a false-positive result, so it cannot be considered completely reliable.
Dijen's research is more accurate, but also more expensive. This method is mainly used to identify oncogenic strains of the virus. The test is also carried out by examining a vaginal smear.
The cost of the Digene test is about 3000-5000 rubles, depending on the clinic. PCR analysis will cost about three times less - about 700-1000 rubles.
The diagnosis is made by a urologist (for men) or a gynecologist (for women). An initial consultation with these specialists will cost 400-900 rubles, depending on the clinic.
It is difficult to name the cost of additional tests, since different prescriptions will apply in each specific case. A smear for women costs about 200 rubles, for men – 300-350 rubles.
Cytology in some clinics is provided free of charge, as part of the program for early diagnosis of cervical cancer.
What complications can there be?
Virus 44 strain almost never causes the degeneration of cervical cells into malignant ones, but is still unsafe. Most often, this strain of HPV affects the cervix, causing changes in the epithelium. As a result, dysplasia of this part of the uterus develops. This disease progresses rapidly and is potentially dangerous for the development of infertility in women.
Important! Cervical dysplasia cannot be detected without examination by a doctor, since the disease is asymptomatic.
Dysplasia is difficult to treat with medication. To get rid of this problem and preserve reproductive function, surgical removal of the altered tissue is necessary.
For men, HPV type 44 is dangerous due to neoplasms in the urethra. This leads to constant inflammation of the urethra, which, in turn, is dangerous due to the spread of the inflammatory process to the bladder (cystitis), prostate gland (prostatitis) or kidneys (nephritis).
How to treat HPV?
After the diagnosis is made, the patient is first prescribed antiviral medications.
Treatment of HPV type 44 in women and men begins with taking antiviral drugs. This is necessary to reduce the activity of the virus. Acyclovir or interferons are usually used.
At the same time, measures are being taken to increase immunity. Patients are prescribed immunostimulants in tablets or injection solutions.
Then a decision is made to remove the existing tumors. This is done using a laser or liquid nitrogen. In women, growths in the vagina and cervix are removed using radio waves or freezing with nitrogen. Men with condylomas on the penis are also prescribed cytostatics in the form of ointments (Podophyllin, Condilin, etc.).
The cost of tumor removal depends on the location and method used. On average, removal of papilloma or condyloma on the skin costs about 500-700 rubles. If the cervix is affected, the decision to perform manipulation is made by the doctor on an individual basis. The cost of the procedure is from 5,000 rubles, depending on the degree of cell damage.
Source: https://DermatologInfo.ru/papillomy/vpch-44-tipa/