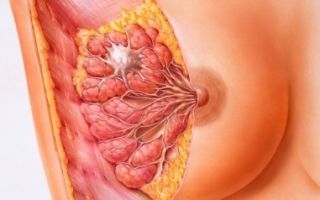
The disease is a pathology of the mammary glands caused by dishormonal processes. As a result, normal cells (alveolocytes of the mammary gland) are replaced by connective tissue, which is fraught with adverse consequences for the woman.
Differences from other types of mastopathy
Diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component is characterized by the highest prevalence among women aged 35 years and older. Fibroadenomatosis is a benign pathology, but under the influence of a variety of factors it can degenerate into a malignant form.
Subsequently, the formation of metastases (distant foci that arise when cells are introduced from the primary tumor form) and their spread to various organs cannot be ruled out. For this reason, this type of mastopathy must be treated.
Important! Oncological danger is represented by those forms of diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component, in which there are signs of atypia. This can only be reliably established through histological examination. To obtain material for it, a breast biopsy is performed at the site of the greatest objective changes.
The lesions formed in the tissue are scattered throughout the mammary gland and do not have clearly defined outlines. Diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component demonstrates the dynamics of symptoms throughout the menstrual cycle. This can lead to some diagnostic errors, and give the woman the false impression that “everything is fine.”
In the second phase (luteal), progesterone begins to be actively produced to prepare the mammary glands for breastfeeding. As a result, the glandular tissue swells and increases in volume, and when a new menstrual cycle begins, estrogens take over and return the mammary glands to their previous state.
Over time, due to hormonal imbalance, connective tissue gradually grows in the tissue, forming cords and nodes that interfere with the functioning of the glands. There comes a moment when the cells stop returning to their previous volumes, a persistent diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component is formed .
In this situation, the glands become unable to perform their normal functions.
Clinical symptoms
1) The occurrence of periodic discomfort, and then constant pain of a stabbing or aching nature in the mammary glands throughout the entire menstruation and in the second half of the cycle. As the disease progresses, the pain syndrome begins to be detected (radiate) in other parts of the body (scapula, shoulder or axillary region). This is due to the fact that diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component leads to a gradual increase in the proliferation of connective tissue between the lobules of the gland, which leads to their compression.
For each woman, the pain sensitivity threshold is determined individually, and it depends on the level of endorphins (pleasure hormones) in the nervous tissue. Edema in the mammary glands compresses the nerve endings, which determines the severity of pain in a woman. Gradually, they not only become permanent, but are also accompanied by an increase in pathological sensitivity (hyperesthesia), when it becomes impossible to touch the patient’s glands during the examination.
2) A feeling of fullness in the mammary glands, an increase in their volume, the appearance of a feeling of heaviness, which is associated with the phase of the menstrual cycle. During the luteal phase, the release of progesterone increases, which has a direct effect on fibrous tissue, which causes an increase in the mammary glands in volume. And against the background of mastopathy, this process intensifies many times over.
3) There is a discharge from the nipples of a liquid resembling colostrum. This is due to a hormonal imbalance when a woman’s prolactin level rises above normal. This hormone is normally responsible for preparing the female breast for feeding a baby and producing milk.
As a result, due to its hyperproduction, when pressing on the areola (areola), a liquid appears, most often having a yellowish tint. If the level of this hormone is much higher than normal, the discharge is white (colostrum).
In the advanced stage of the disease, this secretion becomes brown.
4) Often in a woman, diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component is manifested by engorgement of the mammary glands. This is due to increased edema, which compresses the vessels with which the tissue is richly supplied. As a result, the outflow of blood through the veins is hampered, which is expressed by corresponding symptoms. Because of this, women notice a pronounced venous pattern on the skin of the mammary glands.
5) Upon self-examination, the patient notes the presence of lumps in the mammary glands, which usually disappear after menstruation (in the initial stage) or are observed constantly (with a long-term existence of the disease). It is not uncommon for the shape and symmetry to change due to the formation of compactions scattered throughout the gland and without clear boundaries.
- 6) The woman notes a strong severity of premenstrual syndrome, which was not previously observed, which is characteristic of mastopathy. The main complaints are:
- · severe headache, often similar to a migraine;
- Nausea and possible single vomiting at the peak of the headache;
- · the appearance of swelling of the face and limbs;
- · flatulence;
- · irritability;
- · tearfulness or aggressiveness.
- Treatment of diffuse mastopathy with gestagens >>>
7) Change in skin tone on the chest (especially in the nipple area), which is associated with impaired blood supply to the tissue due to swelling that compresses the blood vessels. As a result, the surface of the mammary glands becomes pale, and the nipple area may acquire a darker shade compared to what the woman had previously observed.
8) There is a change in the appearance of the nipples, which become cracked, and in advanced stages, if left untreated, it becomes retracted. In such a situation, differential diagnosis with oncological processes must be carried out.
9) The menstrual cycle is disrupted. This is an accompanying symptom associated with hormonal imbalance. The stronger the violations, the more noticeable the symptoms of mastopathy.
Sometimes a woman's attention may be attracted to enlarged lymph nodes in the armpit area.
This occurs due to the development of the inflammatory process in the mammary glands or may be a sign of the transition of diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component to a malignant form.
The primary involvement of the axillary lymph nodes is explained by the fact that they are the first on the path of lymph outflow from the chest.
Enlarged lymph nodes are an uncharacteristic sign of mastopathy. Requires the exclusion of complications or other pathologies.
Diagnostics
The appearance of the above symptoms is a reason to immediately consult a doctor. To clarify the diagnosis, certain manipulations should be performed to identify diffuse mastopathy in the early stages.
1) Self-examination is an integral component for diagnosing mastopathy, which is performed monthly. The best day is considered to be the 7th day from the beginning of menstruation, when the breasts are least sensitive to touch and become soft and easily accessible for palpation.
2) Consultation with a mammologist. The doctor assumes a diagnosis based on the collected history, clinical picture and palpation of the mammary glands. Information necessary for diagnosis is previous abortions, miscarriages, pathology of endocrine organs, uterine bleeding, and concomitant gynecological diseases.
When palpating the glands in women with mastopathy, multiple compactions are present in the tissue, without definite boundaries, having different shapes.
3) General blood test, in which, in the presence of inflammatory changes, leukocytes increase (above 10x10*9/l) and ESR increases (over 15 mm/h).
4) Mammography (frontal and lateral projections) is an x-ray method that allows you to see small formations in the mammary glands. The examination should be carried out between 6-12 days of the menstrual cycle. If there is discharge from the nipples, mammography with a contrast agent (sergosine) is used.
5) Ultrasound of the mammary glands allows you to examine the contours, location and size of pathological formations. The technique is advisable when they exceed 1 cm.
It is able to show the structure of the formed tissue, as well as dynamically assess changes in the mammary glands. With its help, material is taken for biopsy under the control of equipment.
It is most advisable to perform an ultrasound before and after menstruation (days 5-10) to monitor the dynamics of formations in the breast.
6) Biopsy followed by histological examination of the compactions to establish the true nature of the disease (benign or malignant course of the process).
7) Ductography is carried out to determine the patency of the ducts in the patient’s mammary glands. It is advisable to prescribe it in the presence of discharge from the nipples.
- 8) If necessary, an MRI is performed to diagnose changes in the glands or regional lymph nodes.
- 9) Cytological examination of breast discharge.
- 10) Consultation with an endocrinologist (diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component is a manifestation of a dishormonal state).
- 11) Consultation with a gynecologist (menstrual cycle irregularities at the onset of the disease can be a manifestation of other pathological conditions).
- 12) Study of the level of progesterone, estrogens, prolactin, and, if necessary, thyroid and adrenal hormones.
- If mastopathy with a fibrous component is suspected of transitioning into a malignant form, a blood test for tumor markers is mandatory.
Treatment
The tactics for managing patients with diffuse mastopathy depends on the stage of the disease and the functional activity of the ovaries. Conservative therapy is carried out for patients who do not have atypical tissue changes in the pathological formations of the mammary glands. Preference is given to hormonal medications, given the endocrine nature of the disease.
The transition to a malignant form or the formation of cysts in place of fibrous tissue is a direct indication for the use of surgical tactics in a particular patient. Removed lesions are subject to mandatory histological examination.
All women with diffuse mastopathy must adhere to a certain diet limiting fatty foods and simple carbohydrates. For this pathology, the best choice is vegetable fats and omega-3 acids. Women should avoid drinking chocolate, cocoa, tea and coffee, which contain methylxanthines, which promote the growth of connective tissue.
An important part of the diet is the consumption of vitamins A, B, C, E and minerals. For a few days, you need to limit your salt intake or eliminate it altogether. It is capable of retaining fluid in the body, which aggravates the course of mastopathy.
If necessary, in the treatment of pathology, the patient is sent for a consultation with a psychotherapist to eliminate certain fears and psychological discomfort in connection with the current situation. You should be careful when choosing a bra, because incorrectly selected underwear will worsen the already impaired blood circulation in the mammary glands.
- The doctor often prescribes massage and physiotherapy, which relieve congestion in the tissues and help prevent inflammation and the progression of diffuse mastopathy.
- Diffuse mastopathy with a cystic component
Source: https://mabusten.com/diagnostika_mastopatii/28.html
What is breast fibroadenosis: its signs and treatment
The fibrous component of the mammary glands is an increase in the volume of soft tissue in the mammary glands. It occurs in mastopathy and provokes the development of a benign neoplasm. Under the influence of some negative factors, it can develop into a malignant pathology.
What is fibroadenosis
The proliferation of the fibrous component of the mammary gland leads to painful phenomena
Fibroadenosis is one of the tumor-like pathologies of the mammary gland. It begins to progress when the body’s regressive processes are disrupted. Therefore, as women approach adulthood, disturbances in the regulation of the mammary glands and their structure occur. At a young age (up to 22 years), this condition is considered normal. This is due to the fact that the hormonal background is just being rebuilt and preparing for childbearing function. Pathology code according to ICD - N 60.2.
Classification of the disease
This type of pathology is usually classified into several forms that differ in symptoms.
- Mastalgia. As a rule, there are no seals. There are only clogged milk ducts. They cause pain. Very often this condition is confused with the imminent arrival of menstruation. Apart from pain, there are no signs of impairment.
- Diffuse fibrocystic form. Accompanied by the presence of tumors and cysts in the breast tissue. They can be felt very well. Pain is felt on palpation. If the condition is too advanced, body temperature may increase.
- Localized fibroadenomatosis. It is characterized by the formation of local compactions that do not spread over the entire area of the mammary gland. Often only one breast is affected. They have clear outlines. Often causes severe pain.
Forms of fibroanematosis are considered the most common among all tumors that can develop in the mammary glands.
The course of the disease is dangerous because it can be asymptomatic and at this time turn into a malignant form. Therefore, women with predispositions to this pathology, as well as those who have reached adulthood, are prescribed regular examinations.
Causes of pathology
The main cause of mastopathy is a malfunction of the pituitary gland and endocrine glands
Specialists in the field of gynecology and mammology believe that breast fibroadenosis can develop against the background of certain conditions. These include:
- Neuroendocrine syndromes. They provoke hormonal imbalances, causing disruptions in menstrual cycles. The influencing factor is the improper functioning of the thyroid gland and adrenal cortex.
- Chronic gynecological diseases. They reduce the activity of the gonads, resulting in infertility and, as a consequence, the further development of fibroadenosis.
- Frequent abortions. Abortions seriously disrupt women's hormonal levels. As a rule, recovery after a miscarriage can be long and difficult. If such procedures are carried out too often, hormones do not have time to recover and cause irreversible processes.
- Taking medications containing estrogen. If their number in the body increases significantly, a malignant process may occur in the mammary glands. In such situations, treatment involves the administration of drugs containing progesterone. They serve as protection against defects in mammary tissue.
- Bad habits and the state of the environment have a detrimental effect on women's health, so consequences such as fibroadenosis are possible.
- Psycho-emotional stress and frequent stress lead to reproductive dysfunction. This affects the condition of the mammary glands: tumors and other neoplasms appear.
Mammologists note that it is often impossible to determine the exact cause at the time a woman complains and when diagnosing fibroadenosis. To eliminate the provoking factor, they try to use broad-spectrum drugs.
Diagnostic methods
There are several main methods by which FCM with a predominance of the fibrous component is diagnosed.
External examination and palpation
The procedure is carried out by an experienced specialist who, during palpation, analyzes the presence of seals in both mammary glands. Sometimes discomfort and pain occur during palpation.
Mammography
This examination is carried out for both mammary glands. This makes it possible to identify or exclude pathological processes in the second breast. They try to conduct the examination only for women over 40 years of age. Younger patients are prescribed ultrasound.
Biopsy
This is a mandatory examination method that will determine how dangerous the neoplasm is and whether it is malignant. This analysis is taken under an ultrasound machine. In this case, a special puncture is performed, and a pinch of biometal is removed through the needle. The analysis takes 14 days.
Lab tests
They are prescribed necessarily after instrumental diagnostics and results have been obtained. A blood test is taken to determine the number of hormones. They can be used to determine whether there is dysfunction in the body.
Breast biopsy Palpation of lumps Blood tests for hormones Mammography
During the menstrual cycle, the structure of a woman's breasts changes, so an ultrasound may show a false positive result. It is recommended to carry out diagnostics before the onset of ovulation.
Features of treatment
Therapy for diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy is carried out using non-hormonal and hormonal therapy, taking anti-inflammatory and other drugs. Each method is selected individually depending on the patient’s condition. Treatment of mastopathy has some features.
- Mandatory intake of vitamins A, B, C, D. Preparations containing minerals are added to them.
- Be sure to adhere to a strict diet, which should exclude salty, spicy and fatty foods.
- You should limit your coffee intake. Strong tea and chocolate.
- Diuretics are prescribed: Furosemide, Veroshpiron.
- Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs are prescribed: Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin.
- To normalize the nervous state, patients are recommended to take tincture of valerian, peony and motherwort.
- If there are chronic female pathologies, they are corrected with medications such as Bromocriptine, Iodine, Iodomarin.
They try to use Utrozhestan and Duphaston as hormonal drugs. They stabilize the background and the menstrual cycle.
Surgical intervention
Only nodular forms of fibrocystic mastopathy are removed
Surgery is used only for nodular fibrous mastopathy. In addition, there are absolute indications for surgery:
- active growth and large tumor size;
- there is a risk of degeneration into a malignant form;
- there are accompanying complications (suppuration, tumor coming out).
During the operation, the tumor tumor is excised and punctured along with a small amount of healthy tissue. Fluid from the tumor is removed from the cavity, after which drugs that promote cell sclerosis are added.
Directly during the operation, a histological examination is performed. If malignancy is confirmed, the tumor is completely removed. Sometimes it is necessary to resort to complete resection of the mammary gland.
Consequences and complications
As a rule, in the first and second months after resection or conservative treatment, the patient is observed by mammologists. At this stage, it is important to exclude the following complications:
- internal bleeding and suture ruptures;
- fluid formation and tumor regrowth.
The repeated development of the pathology can prevent pregnancy and childbirth. This process allows you to adjust your hormonal levels. Experts also recommend adhering to a healthy lifestyle and a strict diet. You should not eat fast food during the rehabilitation period after treatment for a mammary tumor.
Source: https://NogoStop.ru/grud/chto-takoe-diffuznaya-fibrozno-kistoznaya-mastopatiya-s-preobladaniem-fibroznogo-komponenta.html
Diffuse fibrous mastopathy: treatment, signs and diagnosis
Diffuse fibrous mastopathy is a disease that occurs due to the proliferation of fibrous tissue, leading to the appearance of lumps in the breast, located evenly throughout the gland. The female breast consists of glandular, fibrous and adipose tissue.
Fibrous tissue is a subtype of connective tissue that forms the framework of the gland. With mastopathy, connective tissue begins to spread and displace the glandular component. Epithelial cells actively divide and block the milk ducts, resulting in scar formation.
What happens is called tissue fibrosis.
- Fibrocystic mastopathy is noted, when, in addition to tissue fibrosis, a cystic component appears in the gland.
- There is both mastopathy of one breast and a bilateral form.
- As a result, scars form into patches of varying sizes that are benign in nature, but in some rare cases can become malignant.
- According to ICD-10, the disease belongs to code No. 60 “Benign growths of the mammary gland.”
Causes
The main cause of the development of the disease is considered to be an imbalance of hormones, namely progesterone deficiency and extremely high estrogen levels. Factors leading to imbalance are divided into four large blocks.
Reproductive system problems:
- Inflammatory diseases, tumors of the ovaries and other reproductive organs, including those arising from surgical injuries, sexual transmission, birth injuries or poor hygiene.
- Abortion, refusal to have children at fertile age, early cessation of breastfeeding or abandonment of it in favor of artificial feeding.
- Irregular sex life or complete absence.
- Early onset of puberty or late menopause.
- Incorrectly selected hormonal drugs for contraception, treatment of infertility and other problems.
Malfunction of the pituitary gland, which is responsible for the normal functioning of the ovaries:
- Disturbances in the production of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones.
- Increased content of prolactin, which ensures the development of mammary glands and lactation.
A metabolic disorder develops and, as a result, an increase in the amount of adipose tissue capable of producing estrogen and leading to hyperestrogenism:
- Diseases of the thyroid or pancreas, including iodine deficiency and tumors of various types.
- Obesity, diabetes.
External influence:
- prolonged stress or depression;
- exposure to ultraviolet rays on the chest;
- breast injuries of varying degrees;
- smoking;
- unfavorable environmental conditions.
The disease is hereditary and is often detected in close relatives.
Symptoms
Signs characteristic of diffuse fibrous mastopathy:
- Breast swelling and pain before menstruation.
- Pronounced, acute nature of premenstrual syndrome due to hormonal imbalance.
- The appearance of discharge from the nipples.
- The appearance of elastic seals inside the breast tissue, determined by touch.
Breast self-examination
At first, the symptoms are cyclical and highly dependent on the menstrual cycle. In the middle of the cycle or its second half, a woman may experience mild pain and breast enlargement.
Usually this condition is a symptom of premenstrual syndrome and can be characterized as normal. An unusually strong swelling of the breast and a previously uncharacteristic pain syndrome that occurs both from pressure and during exercise becomes alarming.
The pain can be stabbing or aching and often radiates to the neck, shoulder or back.
Upon palpation, uniform swelling of the breast and granular neoplasms in the gland are detected; when pressed, a light or clear liquid is released from the nipple. After the start of menstruation, the symptoms disappear.
A severe form of mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component in the gland is characterized by the fact that the pain becomes constant.
In some women, the disease does not manifest itself, but is detected during a routine annual examination by a mammologist.
Self-examination
Diagnosis of the disease in the early stages is often performed by the patient. A woman performing breast self-examination and palpation may notice an unusual condition of the mammary gland, a change in its density or size, and contact a specialist long before a pronounced form of the disease occurs.
This is the best case scenario. Mammologists recommend that women conduct a monthly breast self-examination a week after the start of menstruation according to the following scheme.
Inspecting the bra for nipple discharge
A woman may not notice minor discharge, but it remains on the fabric of her underwear.
General external examination
It is necessary to examine the chest in a normal position and with arms raised up. Attention is drawn to changes in the shape and size of the chest, its contours, the symmetry of both glands, as well as the uniformity of their movement during raising or lowering the arms.
Skin examination
Checking the condition of the skin includes examination for the presence of bumps, retractions, redness, the appearance of a rash or the so-called “lemon peel”.
Palpation in a standing position
At the first stage, palpation is performed with the pads of three or four fingers in a circular, slightly springy motion. The inspection area extends from the clavicle to the lower rib and from the sternum to the armpit. Attention is drawn to the structure of the breast tissue and enlarged lymph nodes.
Feeling while lying down
The most important stage of the examination. It is necessary to carefully feel the breast tissue, either dividing it into squares or in a spiral. It is important not to miss a single area and remember the normal state of the gland.
Nipple examination
It begins with a visual examination of the nipple and its condition (is it depressed, are there any cracks), then palpation (a tumor may form under the nipple) and ends with squeezing the nipple and checking for the absence of discharge.
Any changes in the condition of the breast are a reason to consult a doctor.
Medical research
When contacting a mammologist, he performs the following procedures:
- Examination and palpation follows the scheme recommended for self-examination.
- Breast ultrasound - reveals formations larger than one centimeter, their location and structure. Sonographic signs of mastopathy: thickening of glandular tissues and changes in their echo density. Safe for pregnant and breastfeeding women.
- Mammography is performed during the second week after the start of menstruation and reveals all changes in breast tissue, even very minor ones. This is an X-ray examination in which neoplasms appear as shadows with blurred edges.
- Ductography – performed in the presence of discharge from the nipples. It involves injecting a substance visible on an x-ray into the milk ducts, and taking pictures to assess the condition of the ducts.
- Cytology of nipple discharge.
- Biopsy and examination of the tumor tissue for the presence of malignant cells.
- Blood tests - general and hormone tests.
As a result of studying the tests and echo data, the mammologist prescribes treatment for mastopathy and, if necessary, refers to a gynecologist, endocrinologist or other specialists.
Since the lumps are benign, doctors usually recommend a conservative approach to the treatment of diffuse fibrous mastopathy. Patients also use folk recipes. The correct combination of two methods increases the chances of curing mastopathy.
Conservative treatment
The causes of the disease are the determining factor for the doctor when prescribing medications. In the treatment of mastopathy, various drugs are prescribed.
Hormonal drugs
Designed to balance hormonal levels. Based on the test results, progesterone-based medications, anti-estrogen drugs, or drugs that reduce prolactin production may be prescribed. Also, when estrogen levels are high, medications are used to reduce pituitary hormones by feedback.
These medications should only be taken with a doctor's prescription; their incorrect use is dangerous and can lead to a worsening of the condition, including the development of cancerous tumors.
Sedatives
They calm and help improve emotional well-being, which also leads to normalization of hormonal balance. The most commonly used teas and infusions are: valerian, mint, lemon balm, motherwort.
Vitamins
Vitamin and vitamin-mineral complexes containing vitamins A, B, C, E are used to improve metabolism and liver function.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Designed to help relieve pain symptoms, used in moderation, only in urgent need on the recommendation of a doctor, and if taken uncontrolled, they can cause harm.
Immunostimulants
Strengthen the immune system.
Hepatoprotectors
They normalize liver function, which helps restore hormonal levels.
Iodine preparations and thyroid hormones
They improve the functioning of the thyroid gland in order to normalize metabolism.
Diuretics
Used to relieve swelling.
Physiotherapy, for example, electrophoresis, is also often used for treatment. It is also recommended to avoid fatty and salty foods, smoked foods, coffee, and chocolate. A ban on alcohol and smoking is prescribed.
Folk remedies
In folk medicine, proven recipes are used to treat mastopathy.
Flax-seed
Contains a lot of phytoestrogens and helps correct a woman’s hormonal levels. Take 1-2 tablespoons per day with plenty of water. You can use dry seeds and add oil to dishes when cooking.
Elderberry juice
Take 1-2 tablespoons twice a day on an empty stomach for two or more months. Helps remove toxins, saturates the body with vitamins and helps slow down the growth of tumors.
Herb tea
The best is considered to be a collection made from part nettle, part sage, part plantain and two parts wormwood. It is infused in the proportion of 1 tablespoon of the collection per glass of water. You should take half a glass three times a day after meals for two months. Designed to balance hormonal levels.
In folk medicine there are other recipes for the treatment of mastopathy. Since most of them, including those mentioned, are based on taking phytoestrogens and neutralizing hormonal imbalances, treatment with folk remedies should be done with caution and only after consultation with your doctor!
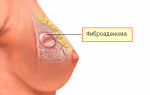
In the case of transformation of diffuse mastopathy into a nodular form, a fibroadenoma is formed, often subject to surgical removal.
Disease prevention
Diffuse fibrous mastopathy of the mammary glands is a disease, the prevention of which is regular self-examination of the mammary glands and visiting a mammologist annually.
To maintain good health, you should choose the right size of underwear and avoid synthetics and slimming materials.
A healthy lifestyle minimizes the likelihood of disease. Proper nutrition, giving up bad habits, feasible physical exercise and emotional health prevent metabolic problems and hormonal imbalances as the root cause of mastopathy. Preventing a disease is easier than treating it.
Source: https://onko.guru/dobro/diffuznaya-fibroznaya-mastopatiya.html
Fibrocystic mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component: what is it and how does it differ from FCM with cystic lumps?
- Fibrocystic mastopathy (FCM) occurs in 50% of women of childbearing age (25-40 years).
- This disease develops for various reasons : stress, frequent abortions, inflammation of the appendages and others.
- FCM is a disease of the mammary glands, which is characterized by the appearance of compactions, tumors, and proliferation of glandular tissue.
- Mastopathy occurs most often in women who have given birth and who have breastfed their child for a long time.
Hide content
What forms of mastopathy are there?
There are several forms of mastopathy:
- Mastalgia. There are no seals at this stage. The thoracic ducts are clogged and inflamed. It causes pain.
Due to pain, patients consult a doctor. Mastopathy at this stage is treated with antibiotics and painkillers.
- Diffuse fibrocystic form. Tumors and cysts appear in the chest; upon palpation, they can be easily felt. Treatment depends on the severity of the disease. In advanced cases, surgical intervention is required.
Highlight:
- mixed type;
- prevalence of cysts;
- predominance of fibrosis;
- predominance of the glandular component.
- Localized fibroadenomatosis. New growths appear locally and do not spread. Their outlines and shape are clearly visible on x-rays or ultrasound.
FCM with a predominance of fibrous component
What is FCM with a predominance of the fibrous component? This form of mastopathy is the most common. It is characterized by the appearance of neoplasms in the breast, but the fibrous component predominates. Fibrosis means:
- an increase in the volume of connective tissue, its growth in the gland;
- blockage of the ducts, up to complete closure of the lumen;
- neoplasms in the interlobular space.
The patient experiences severe pain. On palpation, the tumors are clearly palpable. Fibrous seals are visible on x-rays and ultrasound. The photographs clearly show a “frosted glass” pattern (the seals do not have clear outlines and are drop-shaped in nature.
Important! Any changes in the mammary glands can lead to breast cancer. If pain and lumps appear, you should immediately contact a mammologist or gynecologist.
Areas affected by fibrosis are slightly darkened. There is a feeling that you are looking at the picture through “frosted glass” - hence the name).
Classification according to the nature of neoplasms
FCM has several classifications. Based on the nature of the neoplasms, they are distinguished:
- Diffuse type. It implies that tumors and cysts form randomly. They grow quickly, their outlines change. The diffuse type includes:
- fibrous mastopathy. There are no cysts or tumors, but the connective tissue has grown greatly. The milk ducts are blocked.
- Fibrocystic with a predominance of the glandular component. There are tumors and cysts, but breast lumps predominate.
- Fibrocystic with a predominance of cysts. In this case, many cysts (fluid-filled cavities) are found in the chest. Fibrosis is also observed, but to a lesser extent.
- Fibrocystic with a predominance of fibrosis. Connective tissue compactions are strongly expressed. There are few cysts, they are small in size.
- Mixed type. At the same time, neoplasms and compactions of a fibrous, glandular, and cystic nature are observed.
- Nodal type. Seals and tumors are localized. They form one at a time, but are quite large in size. This type occurs with untimely (or absent) treatment of the diffuse type.
Also, FCM can be proliferating or non-proliferating. Proliferation is the process of cell division and growth with subsequent changes. Such cells are not cancerous, but differ in structure from normal ones.
More nuances about proliferative fibrocystic mastopathy, as well as about the forms of this disease, can be found in our article.
According to the degree of severity, mastopathy is classified into mild, moderate and severe (read more about the differences between severe and moderate FCM here).
Fibrocystic mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component occurs in 30% of cases. It is dangerous because apart from pain, there are no other symptoms. Tumors are mild and may not be immediately noticeable.
Russian women, unfortunately, rarely conduct self-diagnosis, so mastopathy is detected at an advanced stage.
Source: https://LechenieBolezney.com/mammologiya/mastopatiya-m/vidy-mastop/fibrozno-kistoznaya/s-preobladaniem-fibroznogo-komponenta.html
How to identify and how to treat diffuse fibrous mastopathy of the mammary glands?
Mastopathy can be expressed in different forms. They are divided into groups according to the nature of the neoplasms, their composition, and the characteristics of their occurrence.
One of the common options is diffuse fibrous mastopathy, characterized by the formation of a large number of compactions of different sizes and shapes.
In the article we will talk about diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component, what it is and what treatment methods are available.
Various forms of mastopathy are united by their origin. The cause of the disease is hormonal disorders: the amount of estrogen begins to exceed normal levels, while the proportion of progesterone decreases significantly.
- Against this background, breast tissue begins to change, various tumors appear, compressing blood vessels and nerve endings.
- At the initial stage of the disease, patients may feel only slight discomfort in the middle of the menstrual cycle (a feeling of swelling in the mammary gland, mild pressing pain), which completely disappears with the end of menstruation.
- More serious stages are characterized by:
- burning, pulling or pressing pain;
- feeling of heaviness;
- change in breast shape and size;
- pronounced compactions under the skin;
- colorless, cloudy or yellowish discharge from the nipples;
- apathy, drowsiness;
- short-term increase in temperature;
- increased breast sensitivity.
Depending on the nature of the tumors, experts divide mastopathy into nodular and diffuse. The first is characterized by the formation of large tumors localized in one mammary gland or both.
Diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component implies a large number of small formations, evenly distributed in both glands. Depending on the condition and period of the menstrual cycle, neoplasms may disappear and reappear, changing size and shape.
HELP : As soon as you notice signs of diffuse fibrous mastopathy, you should immediately consult a doctor.
The nature of the formations is also important. Depending on their type, mastopathy is:
- Glandular-fibrous . Changes in glandular tissue take the form of compactions and nodes.
- Glandular-cystic . It is characterized by the formation of cysts - cavities filled with clear or cloudy liquid.
- Mixed . Combines cysts and fibromas.
Most often, patients are diagnosed with diffuse glandular fibrous mastopathy, diffuse cystic or nodular fibrous mastopathy.
Diffuse fibrous mastopathy, what is it? Diffuse fibroadenomatosis with a predominance of the fibrous component means that mobile compactions of a benign nature are concentrated in one or both mammary glands.
Experts disagree on the causes of mastopathy. Typically, the appearance of a diffuse form of fibrous mastopathy is influenced by several factors that can disrupt the hormonal balance :
- frequent childbirth;
- late birth;
- breastfeeding for too long or completely refusing breastfeeding;
- chest injuries and injuries;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- abortions and miscarriages;
- dysfunction of the pancreas or thyroid gland, liver disease;
- hereditary predisposition.
The risk group includes women who have recently given birth and are experiencing problems with feeding, as well as those who have experienced a miscarriage or abortion. Mastopathy is often found in women during premenopause or menopause; this condition is characterized by an increased release of hormones.
Diagnostic options
- A whole range of methods are used to diagnose mastopathy; most often they are combined to obtain a more accurate diagnosis.
- Women under 40 years of age are prescribed an ultrasound to determine the presence and shape of tumors.
- This method is not suitable for older patients; mammography is recommended for them.
In some cases, the doctor may prescribe a study of the patency of the ducts by filling them with a colored liquid.
If fibroids are detected, a puncture may be prescribed.
A portion of the tumor tissue is taken for analysis and examined for the presence of cancer cells. Blood tests, as well as a full examination by a gynecologist, will help clarify the diagnosis .
To monitor the condition of the mammary gland, regular palpation at home is useful. The breast and lymph nodes are palpated, mobility and changes in the shape of the seals are noted.
Treatment methods: what to choose?
To treat diffuse fibrous mastopathy, a combination of medications and traditional medicine recipes is used.
At an early stage, homeopathic remedies and light preparations with herbal extracts are used: celandine, burdock, burnet, belladonna, hops, sage, yarrow. For more advanced forms, treatment with hormonal drugs is indicated: creams, ointments, tablets and injections.
- The latest generation of contraceptives, which are taken orally or implanted under the skin, have proven themselves well.
- In severe forms of diffuse fibrous mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component, treatment with steroids or testosterone injections is indicated.
- Among traditional medicines, compresses made from herbs and vegetables are widely used: cabbage, beets, burdock, hemlock, celandine, plantain.
- General strengthening teas and homemade balms based on vegetable oils, propolis, and honey are useful.
- The treatment regimen for diffuse mastopathy with a fibrous component includes a diet.
- It is necessary to exclude fatty meats, hydrogenated fats, fried, canned, smoked foods, as well as drinks containing caffeine from the diet.
Preference is given to whole grain cereals, fish, poultry, dairy products, fruits and vegetables. Vitamin kits and herbal teas are useful. Quitting alcohol and smoking is mandatory .
Nicotine and tar negatively affect hormonal levels, inhibiting the function of progesterone and causing an increase in the number of fibroids.
Doctors note a connection between the formation of benign fibroids and the possibility of breast cancer.
Excess estrogen is an alarming symptom . Against this background, degeneration is possible in the tissues of any organs of the female reproductive system. Already existing fibroids do not degenerate, but malignant tumors may well form next to them.
The problem with the diffuse form is that there are a lot of neoplasms and not all can be detected during a superficial examination. Therefore, you should be especially attentive to your condition, do all the necessary tests and strictly follow the doctor’s instructions.
Diffuse fibrous mastopathy is a disease, the treatment of which can be successful only in the case of complex treatment and timely diagnosis. Therapy is carried out under the supervision of specialists; only in this case is a complete cure and no relapse possible.
You can find more information on this topic in the Diffuse mastopathy section.
Source: https://nesekret.net/mastopatiya/raznovidnosti/diffuznaya/fibroznaya