✅Skin NEW EDUCATIONS can be benign, malignant, precancerous. Why do they appear, how to diagnose and treat them?
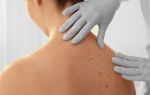
Pathological growths of cells can appear anywhere, in the internal organs; a growth often forms in the nose, mouth, or genitals, but most often the skin is affected.
Growths are various defects formed on the skin, which may include papillomas, various types of warts, cutaneous horn, intradermal nevi and others.
Among them there are dangerous ones that require immediate treatment, so it is important to seek advice and determine the nature of the origin.
Types of growths on the skin
- Benign formations
- Malignant growths
- Precancerous growths
- What causes growths to appear and how do they manifest themselves?
- Diagnosis and treatment
- Complications and prevention
Neoplasms are:
- Benign
- Malignant
- Precancerous.
The main reasons may be frequent damage to the epidermis, solar radiation, and genetic predisposition. Each form of growths has its own subgroups.
Benign formations
- Formations of the first type do not themselves pose a danger to humans if they are not subjected to mechanical stress.
- Subscribe to our INSTAGRAM account!
- A cause for concern may be tumors on the face or other visible part of the body, as well as their large size, which can compress blood vessels.
- Benign growths on the skin can be of the following types:
Fibroma
If a growth appears on your toe, it is most likely a fibroid. Its development occurs slowly from connective tissue cells, externally it looks like nodules with a smooth or warty surface.
It has a flesh-colored, pink, blue-black, gray or brown tint; under the influence of carcinogens and mechanical damage, it can transform into malignant fibrosarcoma.
It is mainly formed on the skin, in rare cases on internal organs.
Neurofibroma
The development of pathology occurs from the nerve sheaths and can appear on the skin or internal organs. Externally, the formation is convex, has a light brown color and does not cause discomfort if it does not press on a nerve; most often there are multiple tubercles.
Lipoma
Lipoma is characterized by the content of adipose tissue and can appear on almost any part of the body. Another name is a wen, it tends to grow, which brings discomfort to a person and can threaten life; in other cases, surgical removal is the patient’s desire.
Atheroma
Externally, atheroma may resemble a lipoma, but unlike it, it is often inflamed, denser to the touch, cannot appear on internal organs, etc.
It is not easy to distinguish the growths on your own, so to determine the nature of the origin of the tumor, you need to consult a specialist.
The formation is characterized by the accumulation of a sebaceous gland in the capsule; its second name is a skin cyst.
The protrusion can fester and break through after some time. If the atheroma is inflamed, pain occurs. The growths are localized in places with an increased number of sebaceous glands, on the neck, head, groin, and back. The growth can take on a substandard appearance, liposarcoma, so it makes sense to remove it with a laser or surgery.
Subscribe to our Yandex Zen channel!
Lymphangioma
The pathology is congenital; cases of its development in adults are very rare. It consists of lymph nodes. It occurs due to the non-standard location of the lymphatic vessels in the embryo. The tumor tends to grow under the influence of unfavorable factors, in which case immediate surgical removal is required. Growths mainly form on the tongue, neck, face and chest.
Hemangioma
The tumor is formed due to a congenital abnormality of the blood vessels. Formations appear on the skin, internal organs, and in women, growths appear in the vagina.
Hemangiomas do not degenerate into malignant ones, but they grow quickly and often recur after removal. A growing formation leads to atrophy of neighboring tissues and disruption of organ function when localized internally.
On the skin, the formation looks like a burgundy or bluish stain.
Nevi and moles
Nevi and moles in themselves are not dangerous if they are not constantly exposed to external influences. They are a cluster of cells filled with melanin, which is considered a natural coloring pigment. If they are aesthetically unattractive, they can be removed with a laser.
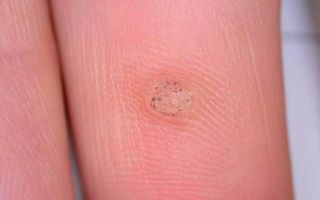
Warts
The cause of warts is the human papillomavirus, which enters the body through damaged skin layers. People with good immunity cope with infection without developing warts. They can be distinguished from moles by their torn edges, itching, and asymmetrical appearance. They can appear on the skin or mucous membranes; growths on the labia are called condylomas or genital warts.
In some cases, the formations disappear on their own, but more often they require treatment, as they pose a danger to the body.
Malignant growths
Unlike the previous ones, malignant tumors progress quickly. Once in the blood, infected cells spread to other areas of the skin or internal organs. The condition is very dangerous and can be fatal.
Melanoma
The disease is often a consequence of severe mechanical damage to a nevus or mole, but it can also form independently. Due to its similarity to moles, it is not easy to diagnose melanoma in the early stages; it is considered a severe type of oncology. It develops rapidly, within 1 year metastases appear in the lymph nodes, and then affect other organs.
Fibrosarcoma
The tumor develops in muscle tissue and may not manifest itself for a long time. Localization is most often in the arms and legs, less often on the jaw and intraperitoneal area. The cause of development in children is a chromosomal mutation, in adults due to ionized radiation, carcinogens, injuries, etc.
Subscribe to our VIBER channel!
Basalioma
This growth is formed from epidermal cells. It often relapses even after proper treatment, affects neighboring areas of the skin, but does not metastasize. The initial form may look like a regular pimple, which begins to grow over time, becoming covered with a gray crust in the center. Germination of basilioma into cartilage or bone tissue causes pain.
Copos' sarcoma
This species mainly affects HIV-infected people and quickly leads to death. The formations are practically never single; initially they look like burgundy or purple spots, later they transform into bluish-tinged nodes.
Liposarcoma
Poor-quality formation of adipose tissue, when it grows into the bones, causes pain. Can cause thrombosis, paralysis, limb ischemia and edema. Externally, it is a single node of a yellow, white or gray hue.
Precancerous growths
Formations whose cells are at the stage of degeneration into cancer are called neoplasia. This group includes the following types of diseases:
Cutaneous horn
It has the shape of a cone with a yellowish or brownish tint. It mainly occurs in old people, as it is formed from spiny layers of skin or warts. The cutaneous horn, a photo of which can be seen below, is considered the initial stage of squamous cell carcinoma.
Xeroderma pigmentosum
The disease is manifested by high sensitivity of the skin to sunlight. Normally, cells damaged by ultraviolet radiation are constantly restored.
Over time, the processes reduce activity, and layers of the epidermis accumulate, from which oncology is formed. Xeroderma pigmentosum is a hereditary disease with a low rate of renewal of destroyed skin layers.
Externally, it is large pigmentation, usually on the neck, face and shoulders, in red or brown shades.
Actinic keratosis
The disease manifests itself exclusively on the skin of older people. Externally, a round, small spot raised above the skin, covered with keratinized skin. Initially, the formation is small in size, from yellow to brown, with growth it becomes plaque-like. Keratoma often degenerates into skin cancer and is located mainly on the face, neck, shoulder area or hands.
Bowen's disease
Initially, the growth looks like a red spot; later, the skin becomes scaly. In appearance, the disease can be confused with psoriasis or eczema. However, if the condition does not improve after using Lorindene, then it is Bowen's disease. When it degenerates into cancer, ulcers appear on the surface of the spots.
What causes growths to appear and how do they manifest themselves?
The causes of formations on the skin are various factors, both external and internal. The nature of the origin of some of them has not yet been established; there are only assumptions about the reasons for the appearance of growths.
The main reasons for the appearance of neoplasms of various types are:
- papilloma virus;
- low immunity;
- the presence of inflamed areas of the skin;
- metabolic disorders;
- irradiation;
- genetic predisposition;
- bright skin;
- many freckles or moles;
- tumors in the past;
- contact with a sick person or object.
When an infection enters the body, it may not manifest itself for a long time and become more active when the immune system is weakened or in the presence of the following conditions:
- chronic diseases;
- long-term use of certain types of medications (antibiotics, hormones, antidepressants);
- nervous system disorders;
- endocrine system and hormonal disruptions.
Almost all types of formations begin with redness on the skin. Then, they rise above the skin and often have a rough surface. Colors can vary, all shades of beige, pink, red, brown, grey, green or yellow. The tumors may be painless or cause pain and itching.
It has been noticed that skin problems more often occur in people with excessive sweating, wearing synthetic underwear and tight and uncomfortable shoes.
Diagnosis and treatment
An initial examination of the patient by a dermatologist, blood and urine tests, histological examination and biopsy help to identify formations. Depending on the origin of the formation, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
If the growth is benign, then it can be left as is, in other cases it is cut out, capturing a small amount of healthy tissue. With this method, relapse often occurs; an alternative to surgical intervention can be electrocoagulation, cutting with a radio wave knife, or cryodestruction (removal with liquid nitrogen).
The next method is a laser procedure, with reduced risks of relapse. I influence the tumor with rays, which lead to its destruction. The method is the safest, painless and effective in the treatment of such diseases.
The approximate cost of removing growths using different methods is from 1000 to 5000 rubles. For cancerous lesions, the patient is observed by an oncologist and a dermato-oncologist; radiation and chemotherapy are used in treatment.
Complications and prevention
The most dangerous consequence of skin growths is the degeneration of formations into cancer. The success of treatment of the disease and the patient’s life expectancy depend on timely diagnosis and elimination of oncology.
Prevention measures include:
- Raising the body's defenses. Preparations and consumption of vegetables, fruits and herbal infusions
- Hygiene rules. Should include not only regular hand washing, but also the use of personal items that should not be given to anyone or taken from others, these can be shoes, clothes, soap, cosmetics, etc.
- Avoid promiscuity and use protective equipment.
- Take care of your skin. In particular, protect moles from damage and promptly treat them with antiseptic agents if necessary. Published by econet.ru.
Ask a question about the topic of the article here
PS And remember, just by changing your consciousness, we are changing the world together! © econet
Source: https://econet.ru/articles/narosty-na-kozhe-kakie-byvayut-i-chto-delat
Warts: what are they and what do they look like?
Most skin growths are benign, however, this does not guarantee their safety and harmlessness.
Such aesthetic problems bring physical discomfort and negatively affect the psychological state of the infected person (a feeling of inferiority arises).
With mechanical damage, the neoplasm can become inflamed and cause discomfort. This article will tell you why warts are dangerous and how to treat them.
Structure of growths
What is a wart? It is a growth on the skin consisting of overgrown skin cells. When examined under a microscope, the structure of the wart is clearly visible - its roots go deep under the epidermis.
The part that protrudes above the skin resembles a small lump or hemispherical lump. Their surface can be hard, elastic, smooth or keratinized. Its structure depends on the location of the growth and its type.
The growths can be light, pale yellow, white, and after a long period of time, gray-black.
The visible part of the tumor is a small part of its body, which goes deep under the skin. It feeds through blood vessels that completely penetrate the wart. In addition to the vessels, the body of the growth consists of small pale or red rods in “live” cases and black in healed cases. These rods are the root.
If it is done incorrectly, you can see black roots that will stick out from the remaining wound. The smaller the growth, the smaller they are. It is not recommended to get rid of the remaining roots yourself; this is best done by a qualified doctor. If they are not completely eliminated, a relapse may occur over time.
If you examine warts under a microscope in section, you can clearly see the following layers:
- growth body;
- superficial layers of the epidermis;
- deep layers of the epidermis;
- wart root;
- subcutaneous fat layer.
Reasons for appearance
One of the causes of human papillomavirus infection is unprotected sexual intercourse.
Many people are interested in whether warts are dangerous and where do they come from? Growths occur when the human body becomes infected with papillomavirus. Strains of the papilloma virus are transmitted in the following ways:
- sexual – during unprotected sex, infection occurs through the mucous membranes of the genitals;
- from mother to child during pregnancy or during childbirth - modern medicine makes it possible to prevent the transmission of the virus to the baby;
- contact and household - shaking hands, wiping with other people's towels, contact with railings, shopping carts and other objects leads to the entry of the papilloma virus into the body.
The virus may not make itself felt for a long time, maintaining its vital activity. The neoplasm may appear many years later, when the conditions for its development become favorable.
How to get rid of warts on the face If treatment for warts and papillomas is not started on time, then in advanced stages they develop into...
Read more
Diagnostic methods
A dermatologist can diagnose this pathology. The picture of the disease is compiled taking into account the specifics of the neoplasms. The specialist must differentiate the wart from other skin growths and make sure that it is benign.
Diagnostic methods include the following:
- polymerase chain reaction - allows you to detect papillomavirus DNA, determine its quantity and degree of oncogenicity;
- biopsy - examination of biomaterial (a small area taken from a growth) makes it possible to determine the benign quality of the wart and the degree of its degeneration;
- Digene HPV test is a study that not only identifies virus cells, but also determines its strain, concentration level and degree of oncogenicity. Thanks to this test, a prognosis for the development of a wart and methods for its treatment can be made.
A dermatologist can combine various diagnostic methods to obtain maximum information about the tumor.
Symptoms
Skin growths rarely show symptoms. You can note a feeling of itching when flat growths appear in adolescents, as well as discomfort when walking caused by plantar growths.
In most cases, warts do not manifest themselves and do not bother the patient. Most people are more concerned about the cosmetic defect caused by the growth. However, there are a number of signs, if they occur, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible:
- sizes are rapidly increasing;
- the growth itches, tingles, slightly hurts;
- the neoplasm suddenly turned black;
- the appearance of droplets of blood;
- Other new growths appear around one growth.
Each of these situations requires medical advice and assistance.
Differences from other growths on the surface of the skin
Treatment of warts (papillomas) differs significantly from the treatment of other neoplasms, so it is important to be able to distinguish them. These neoplasms can be confused with the following growths on the surface of the skin:
- nevi (moles) are accumulations of skin pigment. To distinguish these growths, you need to move the skin around with your finger, the mole will move along with the skin. It is also worth paying attention to the surface of the growth - for a mole it is elastic, but for a wart it is harsh;
- calluses - such neoplasms mainly affect the skin of the feet in those places where the foot is compressed or rubs against shoes. Calluses go away on their own in one to two weeks, but warts rarely go away on their own and require a longer period of time. The surface of a callus is smooth, while that of a wart is rough due to small papillae. The boundaries of the calluses are unclear;
- keratoma - such a neoplasm looks like a plaque, the surface of which is smooth, and the structure of the wart is rough due to small papillae. Keratoma has a significant pigment content, so its color is more saturated;
- hemangioma - the color of this growth ranges from pink to burgundy, due to overgrown vessels. Warts never take on this hue;
- melanoma - this neoplasm is malignant. Initially, melanoma is a nevus or wart, but then it degenerates - it acquires uneven borders, changes its color, and the shade may be uneven. Another sign of melanoma is bleeding from the growth.
If everything is in order with the growth, then it does not change color or shape. In this case, there is no danger to human health. The average person may not know what a wart looks like or where it comes from, so to differentiate it from other skin growths, it is worth contacting a dermatologist.
Types of warts
New growths on the skin appear due to the entry of papillomavirus into the body. This virus has many strains that cause the following types of warts:
- simple - rounded, hard growths of natural color, mainly affecting the fingers, hands, and knees;
- flat - even and smooth growths, slightly raised above the surface of the skin. Most often occur on the face in adolescents;
- plantar - hard warts that form on the skin of the feet, are many small formations (terry warts), since they protrude strongly above the skin, they cause significant discomfort while walking;
- filiform - are a soft, elastic papilla, the length of which rarely exceeds 5 mm. The color of such neoplasms varies from natural to brown. Most often appear on the skin of the face, neck, groin area or under the arms;
- genital warts - can have a cone shape or resemble a rooster's comb, affect the skin in the genital area and tend to grow. In advanced forms, they cause destructive changes in nearby muscle tissue.
Each wart has its own structure and is characterized by certain characteristics, so they are quite easy to distinguish from each other.
Prevention of warts
The main prevention of warts is to maintain a psychologically and physically healthy lifestyle. Following these recommendations will help you avoid warts on your hands, feet, or other parts of the body:
- strict adherence to personal hygiene. Behave carefully in public places - do not touch handrails, do not use shared objects. When you come home, be sure to wash your hands with soap;
- treat any wounds with antiseptics;
- have as little contact as possible with an infected person;
- eat a balanced diet, take vitamins;
- avoid stressful situations and emotional experiences;
- take personal shoes when going to steam rooms, baths, saunas, swimming pools;
- when using household chemicals, wear rubber gloves;
- do not wear shoes made of synthetic materials;
- avoid promiscuous sexual intercourse (by the way, this will help avoid many other dangerous diseases). General principles for treating skin growths
How to get rid of papillomas and warts?
Can a wart go away on its own? In some cases, warts go away on their own, and in others, special treatment is required, which is based on the following principles:
- all methods of eliminating warts are powerless against papillomavirus;
- Regardless of the method of removing the growth, relapse occurs in 30% of cases;
- the effectiveness of any method of removing plantar warts and growths in other parts of the body is no more than 95%;
- After most methods of eliminating tumors, scars remain on the skin. However, there is a tendency for more effective methods to be more likely to leave marks on the surface of the skin;
- growths on the skin are unpredictable - warts go away on their own (20% of cases) or are completely resistant to any treatment methods;
- The initial stage of treatment of skin tumors consists of the use of inexpensive but safest methods. If they do not provide the desired result, then they move on to aggressive and expensive procedures to eliminate warts. This principle is due to the fact that aggressive treatment methods leave scars on the skin. Safe treatment methods (use of medications) do not leave scars if applied directly to the wart.
The problem of warts is relevant today, but not everyone knows what they are, where they come from and why they are dangerous. Such neoplasms are benign, but when injured they can degenerate into other skin growths.
Important!
Many people live with warts and papillomas, not even suspecting that they are already infected with this dangerous...
Read more
on this topic:
- Causes of warts: dispelling myths
- Itchy skin due to liver disease
Source: http://bolezni-kozhi.ru/chto-takoe-borodavka.html
Warts
Warts are flat, keratinized, benign growths caused by the human papillomavirus. This fairly common disease most often occurs in children and adolescents and is an epidermal tumor with a diameter of several millimeters to several centimeters.
The content of the article:
Warts can affect the skin of the hands, feet and face, as well as the mucous membranes and genitals. This disease is very contagious: it spreads quickly and is transmitted from one person to another.
When injured, warts become painful and may change their color and shape. In addition, such neoplasms create a certain psychological discomfort and are a cosmetic defect. Incorrect treatment can lead to the formation of rough scars and scars.
In some cases, warts can develop into malignant tumors.
Cause of warts and pathogenesis
Warts are caused by a filterable virus. It cannot be examined under a microscope or “caught” by bacterial filters. These viruses include the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Anyone can become infected with it, but there are people who are more at risk of infection than others. To date, more than 120 human papillomaviruses have been studied. It is known that the cause of warts is viruses of types 2 and 4.
These types of viruses are especially associated with the appearance of warts on the hands.
Constant use of a sauna, swimming pool, public beach or gym can cause HPV infection. In addition, if a person’s professional activity involves periodic contact with fresh meat or fish, then he cannot feel safe.
You can become infected both through contact with a carrier of the virus, and through household means by sharing household items with an infected person. Warts spread especially quickly in children's groups (kindergartens, schools, sports sections, etc.).
Predisposing factors are considered to be maceration (natural swelling of the epidermis, which occurs in people of certain professions) or minor skin injuries. The incubation period can last from 5-6 to 16 weeks.
As a rule, infection with the human papillomavirus is asymptomatic and often goes unnoticed by the patient.
But what is the common cause of warts appearing on the fingers? Without a doubt, human fingers are the most traumatized area of the body, through which the virus is so quickly and easily transmitted, which causes the appearance of warts.
Contact with a carrier of the virus (essentially the cause of warts) occurs through a handshake or touching handrails or railings in public places. An interesting fact is that a person infected with such a virus may not even be aware of its presence.
He finds out about it when a wart appears. In addition, the cause of warts is often reduced human immunity.
As practice shows, even if a person manages to strengthen his immunity, warts do not disappear anywhere, since the virus continues to live in the blood, causing the reappearance of warts.
Types of warts
In dermatology, it is customary to distinguish between common, plantar, senile and flat (juvenile) warts. Each type of wart has its own characteristic features.
Ordinary type
Common warts externally look like non-inflamed nodules of small size and dense consistency. Common warts are flattened or hemispherical in shape and may be slightly dark or the color of normal skin.
Most often, such warts are localized on the hands, palms, face and other areas of the skin. In most cases, these tumors are painless. The exception is warts located in the nail area. They will be quite painful and difficult to treat.
Typically, the appearance of such warts occurs in childhood.
Causes of common warts
What are the reasons for the appearance of common warts in children? It's simple: the cause of a wart can be an ordinary scratch or abrasion, through which the human papillomavirus (HPV) enters the skin.
Having penetrated the body, the virus begins to actively multiply, concentrating mainly in the basal layer of the skin, which causes the first warts to appear after a month or two. It is important to note that the appearance of a wart may not be a mandatory symptom of the development of this virus in a child’s body.
If a child has a strong immune system, then he may not be able to reach an extremely severe form of the disease, in which warts appear one after another. The virus will simply live in the body, without showing itself in any way outwardly.
If we have found out the reasons for the appearance of common warts, we should now talk about the symptomatic features. As you know, such warts usually appear on the back of the hand or foot.
An ordinary wart has a round shape, the size of which does not exceed 10 mm.
An important feature of this type of wart is its multiple nature: the occurrence of one can affect the formation of a second wart, and in the future their number will only increase.
Another interesting fact is that the causes of the appearance of warts of the vulgar type are the warts themselves. This means that next to one vulgar wart a second one often appears. The latter is popularly called a “kissing” wart.
Plantar type
Plantar warts can appear in both adults and children. Because plantar warts are not immediately detected, they are difficult to treat. Such neoplasms are localized in areas of greatest pressure.
They interfere with a person’s walking, are quite painful and can grow to the size of a chicken egg. Sometimes patients mistake keratinized plantar warts for calluses or skin abrasions.
A wart differs from a callus in the presence of papillary growths.
Type of flat warts
Flat juvenile warts are small epidermal tumors of small size, yellowish or pale pink in color. Most often, such warts appear on the patient’s forehead, chin or cheeks, as well as on the neck and hands (usually on the back). There are two types of juvenile warts - filiform and flat papillomas, localized on the mucous membranes
Type of senile warts
Senile warts affect patients of both sexes over the age of 40 years. Localization of the pathological process occurs in closed areas of the skin: abdomen, back and chest. Senile warts are flat in shape and covered with characteristic scales. If the scales are removed, papillary growths become visible.
Diagnosis of warts
Diagnosing warts is not particularly difficult for an experienced dermatologist. Such tumors have characteristic external signs, so it is difficult to confuse them with something else.
However, the common wart must be differentiated from keratoma, nevus, tuberculous skin lesions, warty basal cell carcinoma, polyps, calluses, skin cancer and other dermatological diseases.
To definitively confirm the differential diagnosis, the patient may be prescribed additional blood tests for human papillomavirus (HPV). This study is carried out using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method.
Treatment of warts
Before starting therapy, you should definitely consult a doctor. Only a specialist can make the correct differential diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
There are many “grandmother’s recipes” for warts, but trying them on yourself is not only not wise, but also very dangerous for your health, because a wart is not just a cosmetic defect, but a very serious disease.
Treatment of various warts is aimed at its removal. The method of wart destruction is chosen individually, taking into account the location and nature of the pathological process.
Often warts are multiple in nature, but it is often enough to remove one “mother” tumor and then all the others disappear on their own over time.
Warts whose treatment with conservative methods has proven ineffective are subject to destruction.
Basic methods of wart destruction
There are a number of progressive methods used to destroy warts. The most effective among them are the following:
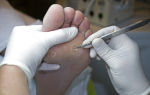
- Cryodestruction. This method is based on applying liquid nitrogen or dry ice directly to the wart. The damaged area of skin is frozen, after which it is rejected. When exposed to extremely low temperatures, the virus completely dies and the wart is destroyed. This method is painless, and postoperative scars are almost invisible. If the wart is large or the patient has a very high sensitivity threshold, then the doctor may decide to use local anesthesia. After the operation, a black crust forms at the site of the wart, which under no circumstances should be removed. After 4-5 weeks it will be rejected on its own. If the wart was very large, then after 3-4 weeks the affected area is re-treated.
- Electrocoagulation. This method involves burning out the tumor with an electric current. Electrocoagulation is used in hard-to-reach areas and can be used to remove warts on mucous membranes. The disadvantages include a relatively large list of contraindications: violation of the general somatic condition, individual intolerance to anesthetics, inflammatory skin diseases, etc.
- Laser destruction of warts. This is the most progressive method of removing warts of any kind. The duration of the operation is only a few minutes. The postoperative wound heals quickly and does not require special care. After the operation, no traces of the wart remain. There are no age restrictions; this method can also be used to treat warts in young children.
- Surgical excision of warts. It is used less and less, only to remove particularly large warts. The method is quite painful, accompanied by heavy bleeding, and the postoperative wound often does not heal well, leaving a scar.
- X-ray irradiation. This method is used to treat plantar warts.
However, treatment of warts can be not only surgical, but also medicinal.
Today, for the treatment of various types of warts, there are a number of topical medications that can destroy the structure of the wart, thereby corresponding to local treatment.
Among the most common and well-known drugs for the treatment of warts are Solcoderm and Collomac. Often, treatment of warts is possible with the help of a special ointment, which will quickly and painlessly eliminate the wart.
Treatment of warts is, first of all, the destruction of the formed growth on the surface of the skin. Drug treatment corresponds to drugs that can be classified into several groups:
- Necrotizing (Vartek, Condyline Nycomed, Solcoderm);
- Keratolytics (a number of drugs that help treat warts by melting them: Collomac, Salipod).
- Components for cryotherapy.
- Various antiviral drugs.
- Drugs that can enhance immunity.
Treatment of warts using the above remedies may not give an immediate effect. Repeated use of medication may be required to eliminate a wart. However, in a number of other cases, treatment of warts is not necessary at all - after a while they go away on their own.
According to statistics, self-healing occurs no later than 2 months after the first wart appears (about 20-22% of all cases) or 3 months (30% of cases).
If we are talking about an older wart, then most likely self-healing will occur after 2 years (and this is 50% of cases). Adults are least likely to respond to self-treatment.
Treatment of warts in adults is facilitated by medications or surgical procedures.
Treating a wart can be complicated by its unpredictable behavior. The reason for such complicated treatment may be a late visit to the doctor, when the wart swelled in size, it changed shape or color. Usually, a second one soon appears near one wart, and then their number increases, which also complicates treatment.
If wart therapy is carried out correctly, this will lead either to the complete disappearance of the wart, or to a gradual disappearance. At the same time, you don’t have to be afraid of a new wart that appears.
Source: https://www.mosmedportal.ru/illness/borodavki/
Warts: symptoms, causes and complications; diagnosis, treatment and prevention
Many people associate the appearance of growths on the skin “in the old fashioned way” with damage or heavenly punishment. In fact, warts are a disease that can be treated conservatively and surgically. Therefore, when they appear, it is best to consult a doctor.
This term refers to a group of neoplasms localized on the skin with a predominantly benign course. They have the form of a growth, papilla or nodule.
Warts are mainly of viral origin and appear as a result of damage by papilloma. This is an RNA virus found in the blood of 80% of the inhabitants of our planet. There are also lesions with other etymologies. For example, senile forms of pathology.
The classification of warts is quite simple. In our state they are usually divided into the following forms:
- Flat or youthful. Neoplasms that do not rise much above the dermis. Typically, such warts are localized on the hands (on the back of the hands) or on the face.
- Vulgar or ordinary. They appear in the form of flesh-colored or grayish-brown growths. They are characterized by the growth and appearance of “daughter” warts next to the main one.
- Filiform or acrochord. Pedicled neoplasms are usually located on the face, neck, armpits and under the breasts.
- Condyloma acuminata. These are growths that resemble the shape of cauliflower. They can be different shades of brown. Localized in the genital area and oral cavity.
- Plantar warts. This type is often classified as a type of vulgar form. The lesion is localized on the foot, appearing in the form of a thorn or growth. The pathology is characterized by a feeling of discomfort and even pain when walking.
- Senile or age-related. The pathology is a consequence of seborrhea in older people. Because of this, the skin grows, forming a growth.
In ICD-10, all types of warts are classified as viral skin pathologies. They were assigned code B-07. But only ordinary warts are equated to this disease. The following types of skin neoplasms are excluded from this group and transferred to other sections:
- Anogenital or venereal. Now this pathology is classified as a disease that is sexually transmitted.
- Papillomas localized in the bladder, cervix and larynx.
Typically, such growths do not pose a significant threat to human life, causing exclusively aesthetic discomfort. But some types of warts can develop into malignant tumors. Therefore, if you notice these growths, it is better to consult a doctor.
Causes of warts
It has been proven that the main source of their appearance is the human papillomavirus. Therefore, the main route of infection is contact. The virus usually enters the body during childhood: 3–5 years. But the first signs (warts) may not appear for several decades.
The following factors provoke the virus to emerge from hibernation:
- Decreased immunity is what causes warts to appear.
- Incorrect selection of shoes (too tight, rubber, does not allow air to pass through, etc.).
- Active sports activities, as a result of which the skin is injured.
- Increased sweating of hands and feet. Because of this, warts may appear on the feet and palms.
- Lack of gloves and winter shoes at sub-zero temperatures outside.
- Dry skin.
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse without condom.
- Insufficiently balanced diet, vitamin deficiency.
- HIV.
- Presence of fungus. This is one of the main causes of warts on the feet.
- Taking medications that suppress the immune system.
- Insufficient genital hygiene.
These factors can lead to activation of the virus and the appearance of warts with different localizations. Please note: such neoplasms are often confused with malignant processes, so if they appear, it is better to consult a dermatologist.
Symptoms of warts
Recognizing these neoplasms is quite simple. They are localized on the skin, mucous membranes and are visible to the naked eye. The symptoms and shape of the growth depend on its type. But there are such general signs of warts:
- The appearance of a growth or elevation above the skin, which was previously healthy.
- There may be no change in color of the growth at all. But brown and red shades are likely to appear.
- The surface of the dermis of condylomas is wrinkled and resembles cauliflower.
- When a wart appears on the legs, in particular on the foot, there is likely to be a feeling of discomfort and slight pain when applying pressure to the defect.
Itching, bleeding or exudate, pain are signs of malignancy or degeneration into cancer. Such symptoms should alert you. If you notice signs of degeneration, consult a doctor immediately.
Diagnosis of warts
Determining the origin of a skin growth is usually not difficult. To do this, the dermatologist performs the following manipulations:
- Initial examination, history taking.
- Carrying out dermatoscopy if there is a suspicion that the doctor is not seeing a wart, but an altered nevus.
- Blood collection for PCR diagnostics.
It is also possible to carry out histological analysis after removal of the wart. In particular, if the tumor has deepened and affected the tissue under the dermis.
How to get rid of a wart
There are many ways to combat the human papillomavirus. Their selection is carried out by a physician, depending on the type of lesion and its size. The following treatment approaches are distinguished:
- Drug therapy.
- Surgical techniques.
- Treating warts at home.
Each direction has its own characteristics and a number of specific techniques. But you should not try to remove the wart on your own. It is important to accurately determine its type by contacting a specialist. After all, independent manipulations can lead to the development of a malignant neoplasm.
Drug therapy or treatments for warts
To combat the human papillomavirus that affects the skin, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Antiviral medications. But they are strictly prohibited to be prescribed if a person suffers from flat warts.
- Destructive chemotherapy. Patients are prescribed ointments containing acids (trichloroacetic, salicylic, retinoic, etc.). For example, Feresol, 5-Fluorouracil.
- Immune therapy. Usually, injections into the affected area with Candida and Trichophytin antigens or innovative agents based on low-molecular-weight derivatives of imiquidazoquinolinamine are prescribed.
- Novocaine injections. They are used only to eliminate formations on the soles.
Drug treatment for warts is not always effective and is used quite rarely. In most cases, more radical methods are recommended. The drugs are prescribed as a supplement.
How to get rid of a wart with surgery
These are the most effective methods of combating pathology. Depending on the extent of damage to the skin, the following manipulations are used:
- Minimally invasive. These are the most modern and safest ways to remove warts. Usually one of the following procedures is prescribed: cryodestruction, electrocoagulation, various methods of electric shock, radio wave techniques, etc.
- Surgical intervention. The operation is performed only when removing genital warts.
- Surgical intervention is the most effective method of eliminating formations on the dermis.
- How to remove warts yourself
- To combat these growths, you can use the following traditional methods:
- Aloe soda. Take a glass of warm water. Thoroughly dissolve 1 tsp in liquid. baking soda. Make a compress from this mixture on the wart. Then, apply the pulp from an aloe leaf that has just been cut to the affected area.
- Celandine for warts. The use of the plant is extremely simple: apply the cut part of the stem with the released juice to the growth.
- Garlic. Peel a segment of this plant and cut it in half. Rub it on the wart. The procedure should be repeated three times a day.
Since it is not always possible to remove a wart at home, it is better to immediately contact a specialist. This is the only way you will get a guaranteed result. Please note: under no circumstances try to remove skin growths on your own! This can lead to the development of a malignant tumor.
Complications of warts
Usually, even without treatment, these neoplasms do not lead to more serious consequences. But if the wart is located in a place that is often injured, then the risk of malignancy is high.
The onset of a malignant process can be recognized by the following signs:
- The appearance of itching, burning.
- Peeling of the neoplasm.
- The appearance of pus, blood or exudate.
- Pain syndrome.
If you notice these symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. This could save your life.
Prevention of warts
It is almost impossible to prevent infection with the human papillomavirus, because often the signs of the disease are not noticeable. But to minimize the risk, follow these recommendations:
- Don't wear other people's things.
- Always wash your hands with soap before eating or upon returning home.
- Do not walk barefoot in swimming pools, baths and saunas.
- Buy exclusively comfortable shoes that fit.
- Get rid of bad habits.
- Eat right.
- Ventilate your apartment or house.
- Walk outdoors every day.
Please note that if strange growths appear on your skin, you should immediately consult a doctor. After all, it is important not to confuse them with malignant neoplasms that have similar symptoms.
Source: https://GoodDoc.ru/diseases/kozhnye-bolezni/borodavki/