Papillomas in intimate places are external manifestations of papillomatosis, which is of viral origin and is caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They appear on any part of the body, including mucous membranes. Papillomas appear very often in intimate places and are always transmitted sexually. Papillomatosis can occur regardless of a person’s age and gender.
PVI, or human papillomavirus infection, is widespread, and today 300 million people in the world suffer from it; in Russia - a third of the population.
The rates are especially high among active young people aged 18–19 years.
Most often, papilloma is known as a wart, which protrudes slightly above the skin level and which can easily be accidentally injured by clothing, nails, or shoes. Then it becomes inflamed and bleeds.
Most papillomas are benign formations, but some of them are dangerous. On the genitals they are pinkish-flesh in color, and their shapes may vary.
To date, more than 100 types of virus have been identified, 40 of which are associated with damage to the urogenital organs. Only 5 of them have a low oncogenic risk, which means that the risk of degeneration of formations in intimate places is quite high.
Therefore, it is necessary to know more about them.
Is it possible and how to get rid of papillomas? Unfortunately, when the papillomavirus is introduced into the body, it remains there forever, despite any treatment, and the person becomes its carrier for life. But the manifestations of PVI largely depend on the person himself.
Causes
The reasons for the appearance of PVI, of course, are the entry and development of the virus. Factors provoking its appearance:
- STIs, frequent changes of partners and promiscuity;
- violations of the vaginal microflora;
- pregnancy;
- hypovitaminosis;
- unprotected sexual contact - even 1 contact with a virus carrier gives a 60% risk of infection (with unprotected sex, the risk of a woman getting infected from a man is much higher);
- the risk of infection increases in the presence of chronic inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
- chronic stress;
- hormonal imbalances;
- chemotherapy;
- immunodeficiency states;
- poor nutrition;
- overwork;
- diets;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- basic lack of intimate hygiene.
The human papillomavirus, when it enters the intimate zone, causes the epithelial cells of the basal layer of the skin to actively divide and grow, resulting in the appearance of growths. Gradually they increase in size. Papillomavirus can infect partners during any form of intercourse. Among them are oral and anal sex, friction of the genitals against the partner’s organs.
Infection occurs in the presence of any microtraumas on the surface of the skin or mucous membranes, and almost any person always has them, for example, after shaving. Without an entry gate, HPV cannot penetrate the skin, and the skin in the bikini area is very vulnerable due to its thinness.
The most common viral strains among anogenital warts are 6, 11, 16, 18. The last 2 types have a high oncogenic risk, and they cause cervical cancer. Condoms do not protect you completely from the risk of infection, but only by 50%.
Therefore, you need to take care of strengthening your immunity.
Classification of formations
Since we are talking only about the intimate area, the types of papillomas will be described only from this area. Papillomas on the genitals are soft, located in groups, and are rarely isolated. Types of urogenital papillomas:
- Condylomas acuminata are flesh-colored tubercles, formations on legs, have a cone-shaped shape, which is why they got their name. What do papillomas look like? They are flesh-colored or pinkish in color, rise above the skin in the form of a cockscomb or grow like a head of cauliflower. Usually localized on mucous membranes and transmitted only through sexual contact.
- Lesions in the form of papules are round in shape and can be up to 1 cm in size. They are located on the skin of the genitals.
- In the form of spots - they can be of different colors: from pink and gray to red and brown. Also found on the mucous membranes of the genitals.
- Bowenoid papulosis - may appear as macules and papules, ranging in color from gray to brownish-black. It can grow both on the skin and on mucous membranes, in women - on the clitoris and labia, in men - on the penis. Has a high oncogenic risk.
- Giant condyloma is a wart that resembles a head of cauliflower. It consists of many papules and nodules connected to each other.
The virus can exist inside a cell, infecting its nucleus - the introsomal form. Then it integrates into its genome and acts on the chromosomes; this form of morphology is malignant. In the episomal form, the virus does not invade chromosomes; this type is benign.
Symptomatic manifestations
The incubation period of a viral infection with HPV ranges from several weeks to several years. Everything is determined by the strength of the immune system. Anogenital warts occur most often in the groin and perineum.
In women, genital papillomas occur on the labia, vagina, clitoris, cervix, external opening of the urethra and even on the hymen, perineum, their color is flesh-colored or light brown, on the labia they are covered with a stratum corneum.
In men - on any part of the penis: head, frenulum, shaft, scrotum, foreskin. There are usually no symptoms. When papillomas grow in these places, women often experience constant sensations of moisture in the intimate area (due to humidity, a persistent foul odor appears), an increase in vaginal discharge, itching, and general discomfort - but these are indirect signs that may not exist.
Cervical condylomas have no symptoms and are detected only during examination by a gynecologist. They can be determined by treating the area with 5% vinegar. After or during sex, you may experience some spotting. In men, papillomas on the shaft of the penis and scrotum are also covered with a stratum corneum and are called keratotic. When immunity decreases, the rashes merge into plaques.
Some types of HPV in men can cause Bowen's disease, which is manifested by the appearance of a red, velvety plaque on the penis. This pathology is more common on the scalp. First, a dark spot with jagged edges appears, then it transforms into a scaly plaque with raised edges. May be single or multiple. It is dangerous due to its degeneration into squamous cell carcinoma.
Bowenoid papulosis is caused by HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33. It is considered a precancerous skin condition. The head of the penis is covered with plaques of different colors: pink, yellowish and white, most often red. They are smooth and doughy in consistency. Unpleasant sensations from papillomas in an intimate place can be expressed in itching, burning and pain.
Diagnostic measures
A colposcopy and acetic acid test are performed. When applied, the papilloma turns gray-white in a few minutes.
If cancer is suspected, a cytological examination of a smear from the cervix is mandatory. PCR analysis is the most informative; it determines the presence of the virus and its type.
Treatment methods
Treatment of genital papillomas should be carried out by a doctor. There is no need to try to remove them yourself by tying their bases, cutting, cauterizing, etc., this is always fraught and unpredictable.
Treatment methods for male and female papillomatosis are similar. Treatment of PVI is medicinal and hardware. In this case, the principle is observed: if it cannot be cured, then it can be controlled.
It is necessary to begin treating papillomas by strengthening the immune system, and then acting on the virus.
List of medications
Among the medications, cauterizing substances are used, while ointment, gel, cream is applied to the papilloma once a day or every other day for a week or a month - according to the instructions. Sometimes injectable forms are used. Substances for cauterization on mucous membranes are not used. For papillomas in intimate places, namely mucous membranes, the following is used:
- Oxolinic ointment, Sanfenzhong - a Chinese remedy, Stefalin, Riodoxol, Bonafton, Solkovagin.
- Vartek, Fluorouracil, Condiline Nycomed, Condilin - solutions and creams with a cytotoxic effect. After the disappearance of papillomas, treatment continues with the use of antiviral drugs, cytostatics that suppress the division of papillomas cells and their growth (they are not prescribed to pregnant women), immunomodulators with local treatment to prevent relapses.
- Keravort cream, Ferezol, Verrukacid, Epigen Intim spray, immunomodulators and immunostimulants orally - Cycloferon, Galavit, Viferon, Isoprinosine, Genferon, Imiquimod, Keravort - are used topically.
- Polyoxidonium, intramuscular administration of interferon drugs Roferon-A, Altevir, Allokin Alpha, Alfaferon.
- Solcoderm - causes destruction of affected cells; used in hospital. Contains acid concentrate.
- Condilin - often used in the treatment of genital warts.
- Trichloroacetic acid - cauterization is carried out in the form of a spot application on papillomas, together with soda; stationary use only.
- Vartek and Podophyllin, Podophyllotoxin - preventing papilloma cells from dividing, suppressing their reproduction, applied topically, especially on the pubis and groin.
- Antipapillom gel - smearing papillomas with it leads to their darkening and peeling; the skin is cleansed in 5 procedures.
- Cryopharma spray - you can also remove papillomas with this cryotherapy product; has a freezing effect on papillomas. Leaves no scars. It is used at home, in clinics and beauty salons. Suitable even for children.
- Epigen Intim - gel relieves inflammation and itching. Inhibits cell growth, preventing them from dividing. Suitable for mucous membranes.
- SuperClandestine (contains alkalis), Panavir, Groprinosin - antiviral drugs.
Surgical methods
Hardware treatment - removal of flat papillomas on the perineum is carried out in this way:
- Cryotherapy is the effect of liquid nitrogen on papilloma tissue, which causes their destruction and death. A crust appears at the site of exposure, which then disappears. Nitrogen is not used in the vagina and cervix, only on skin areas. Healing takes 2 weeks. If papillomas reappear, a different method is used.
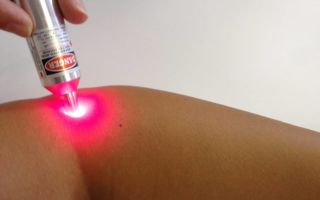
- The laser method also causes the destruction of papilloma; this method does not leave scars. The healing process takes about a month. Today it is the most popular and is performed under local anesthesia.
- Surgical removal - removal of papillomas in intimate places with a scalpel, eliminates the secondary appearance of papillomas. Local anesthesia.
- Radio wave method - destruction of affected tissues is caused by radio waves, for this a special device “Surgitron” is used. Its advantage is that it acts only on warts, healthy tissue is not affected. Has no side effects. Any of the above methods are combined with immunomodulators.
- Electrocoagulation - excision of the papilloma is carried out with an electric knife, while at the same time the vessels are sealed to exclude nutrition of the papilloma. With this method, it is possible to conduct a histological examination of papilloma tissue. Healing is fast, without scars.
- Electrotherapy - burning out the papilloma with an electric current, followed by smearing the crust with an antiseptic until it falls off.
Preventive measures
HPV is transmitted sexually, so contraception becomes the main method of prevention. You must use only your own care products, only your own towels, washcloths, and razors. You should also maintain intimate hygiene and improve your immunity.
Source: https://venerologia03.ru/papillomavirus/genitalnye-papillomy.html
Papillomas in the intimate places of women: causes and treatment methods - Derma
Papillomas in intimate places cause a lot of inconvenience, which affects a person’s quality of life. What causes growths, and how to deal with them using medications and folk remedies, modern methods of removal.
Papillomas in the intimate area cause great discomfort
Causes of papillomas in intimate places
Papillomatosis or human papillomavirus can be hidden for a long time. The main impetus for its development can be a significant decrease in the body’s immune forces.
The following reasons influence the awakening of the virus:
- hormonal disruptions in the body in women after pregnancy or as a result of long-term use of hormonal contraceptives;
- bad habits – smoking, alcohol abuse, drug addiction;
- colds of an infectious nature;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics, immunosuppressants, corticosteroids;
- venereal pathologies, herpes infection, inflammation in the genitourinary system;
- constant stress, emotional tension, chronic fatigue;
- disruptions in metabolic processes.
A long-term cold can awaken HPV
The listed factors lead to immunodeficiency, which is a favorable environment for the awakening of papillomavirus.
Are papillomas in intimate places contagious?
The main feature of papillomas on the genitals is their high level of variability. You can catch the disease, which will later manifest itself on the genitals, through sex with an infected partner, as well as through contact and household contact (through bed linen, towels).
Symptoms in women and men
The main symptom of papillomatosis is the appearance of growths in the groin, which look like loose lobules collected in piles, reminiscent of a broccoli inflorescence or a rooster's comb.
Locations:
- in men - on the scrotum, around the head of the penis, near the urination channel, in the folds between the legs;
- in women - on the vulva (on the labia majora and minora, in the vagina, on the pubic part), in the cervix;
- independence from gender - on the skin in the perineum between the genitals and anus, around the anus and inside the anus (rarely).
The glans penis affected by papillomas
Types of papillomas in the intimate area
Inguinal growths have their own differences and types:
- Filiform papillomas. At the beginning of development, small yellowish bumps appear, which over time develop into elastic thread-like formations.
- Flat papillomas. Rounded small bumps that blend in color with the skin. They are rare, but can cause inflammation in the genitals, itching, burning, and pain.
- Condylomas (pointed). Elastic growths look like a large number of small lobules fused together.
- Papillomas of the bladder and urethra. It mainly affects men.
On the female organs, or rather inside them, genital warts most often develop. You can see them during a gynecological examination.
What types of papillomas there are in intimate places and what they look like is shown in the photo.
Papillomas of the filamentous variety
Flat type of papilloma
Acute condylomas
Are papillomas dangerous?
Papillomas of any type can pose a hidden danger.
- If the growth is injured, it begins to spread to healthy areas, which leads to the growth of unpleasant formations.
- Infection can penetrate into damaged papilloma tissue, which threatens the development of inflammation of the groin area.
- There is a high tendency of papilloma to enter the oncogenic stage, especially those that affect the woman’s cervix.
Papillomas in the intimate area can develop into cancer
Very rarely, papillomas develop into cancer among males, but they can provoke other serious pathologies of the genitourinary system (phimosis, paraphimosis).
Treatment methods
Papillomavirus cannot be removed from the body, but it is quite possible to put it into a dormant state.
The following methods allow you to do this:
- removal of papilloma;
- drug treatment;
- use of folk remedies.
Therapy for papillomatosis should be comprehensive and combine several methods at once.
Removal of papilloma on the genitals
Timely detected papillomas respond well to treatment and do not have time to harm a person. You cannot try to eliminate such a problem on your own, otherwise you can provoke serious complications.
Which doctor removes it?
If you identify suspicious formations on the genitals, you should contact a dermatologist or venereologist. In situations where the warts have become large and darkened, it makes sense to consult an oncologist.
A venereologist will help you get rid of papillomas in an intimate place
The specialist helps get rid of unwanted growths and provides special treatment aimed at preventing relapses.
Should I delete it?
In the early stages of papillomatosis, warts do not cause any discomfort, so doctors may prescribe drug treatment. When the growths are large, often injured, bleed and hurt, and inflammation develops in the genitals due to the addition of other infections, the papillomas must be removed. This will help prevent cancer.
Does it hurt to remove?
Excision of warts occurs under anesthetic. Depending on the procedure, unpleasant sensations are possible: burning, tingling, tingling, slight pain. Most often, papillomas are removed painlessly.
Modern removal methods and their costs
Elimination of papillomas in intimate places can be carried out using several methods. How much removal costs depends on the size of the warts and the type of procedure.
- Surgical method - the growths are excised with a scalpel, and the area is treated with a special solution and tightly bandaged. The manipulation takes place under local anesthesia. Price – from 450 to 1500 rubles.
- Electrocoagulation. Papillomas are cauterized with high-frequency current. As a result of this procedure, irreversible processes occur inside the growths and they disappear. Price – from 400 to 800 rubles.
- Cryodestruction - removal with liquid nitrogen - allows you to painlessly eliminate the tumor. The affected areas are treated with liquid nitrogen, which provokes darkening, drying and death of papillomas. Cost – from 300 to 600 rubles.
- Radio wave removal. Warts are cut off using a radio wave scalpel, which acts exclusively on the affected tissue, does not affect the healthy epidermis and does not leave scars. Price – from 500 to 1000 rubles.
- Laser treatment is the most popular and effective way to combat papillomas. In addition to cutting off the growth, the laser beam gently cauterizes capillaries and injured areas, which helps prevent inflammatory processes, bleeding, and scars. Price – from 650 to 1600 rubles.
- Cauterization with chemicals. To remove flat growths and condylomas, the drugs podofilin and podofilox are used. After treating the affected areas, crusts remain, which disappear on their own after 2-3 days.
Laser removal is the easiest and most popular method
Drug treatment
Doctors try to treat minor lesions of the genitals by papillomas with pharmaceutical preparations for internal and external use.
The medicine Panavir helps remove growths and prevent relapses of human papillomavirus infection. The product is available in the form of an injection solution and gel, which allows it to act on the virus from the inside and outside.
A good antiviral drug is Viferon (suppositories, gel, ointment). The medicine not only suppresses the development of infection, but also stimulates the body's immune forces.
Viferon is an effective antiviral drug
Another effective remedy against papillomas is Oxolinic ointment. The substance has a detrimental effect on the infection, inhibiting its reproduction.
Acyclovir tablets and cream have a high antiviral effect. The product stimulates the body's protective barrier well and suppresses infection.
To achieve the maximum therapeutic effect, the doctor can prescribe several drugs for local and systemic use. Your approach allows you to achieve long-term remissions of the disease.
How to get rid of it using folk remedies
How to treat papillomavirus infection at home? For this purpose, folk medicine has effective and proven recipes.
Castor oil
For 2-3 weeks, injured areas must be treated with castor oil. For best results, the oil should be gently rubbed into the growths for 7–10 minutes. The frequency of procedures is several manipulations per week.
Castor oil is a good remedy for getting rid of papillomas at home
Celandine juice
It is recommended to wipe viral growths on the genitals with a small amount of the substance. Manipulations are done up to 4–5 times a day. Duration of treatment is 1–1.5 months. It is important not to touch healthy areas so as not to provoke a burn.
When applying the juice, it is important not to touch healthy areas of the skin.
Iodine for papillomas on the genitals
Wipe the benign tumor daily with iodine solution. The antiseptic substance not only dries, but also disinfects, which stops the development of infection.
Iodine stops the development of infection
Treatment during pregnancy
Papillomas in the intimate area can grow greatly during pregnancy and subsequently interfere with childbirth. To avoid this, doctors prescribe laser excision of growths and treatment with antiviral substances. During pregnancy, Viferon and Betadine are allowed to be used.
Papillomavirus detected during pregnancy must be treated without fail, as it threatens to infect the fetus (most often during the child’s passage through the birth canal) and cause the baby’s nasopharynx and larynx to be affected by condylomas.
Papillomas on the genitals are an unpleasant and very dangerous phenomenon, since if left untreated for a long time, there is a high probability of developing cancer. Therefore, it is important not to hesitate to consult a doctor if suspicious growths are found in the groin.
Reviews
Black_cat.
“I didn’t pay any attention when I discovered a small lump in my vagina that looked like a wart. A few months later, several more growths appeared. I don't understand where they come from. After the examination, I was prescribed injections and Panavir ointment. Education is gradually decreasing.”
Nika_gda.
“Warts suddenly began to appear in my pubic area, and later near my anus. I underwent an examination, after which the doctors prescribed laser removal. I was worried, but everything went painlessly. I took Acyclovir tablets for some time to consolidate the effect, as the doctor said.”
Krasav4ik.
“I treated papillomas in the groin (in the crease between the legs) with celandine for a long time, but they did not disappear. After consulting with a doctor, it turned out that complex therapy was needed. They cut off the growths and sent me for analysis. Thank God, the formations turned out to be benign. I continue treatment with immunomodulators.”
Infections
Source:
Papilloma on the genitals
Content
Source: https://nuzubbelovo.ru/papillomy/papillomy-na-intimnyh-mestah-zhenshhin-prichiny-i-metody-lecheniya.html
Genital papillomas: causes and treatment methods
The human papillomavirus is one of the most common today. And if about five years ago the diagnosis was not made so often, now about 50 percent of patients are diagnosed with it. Moreover, the virus can manifest itself in absolutely any part of the body. One of the vulnerable places is the genitals.
Causes of papillomas
The main causes of papillomas
As mentioned above, one of the main reasons why papillomas may appear in a person’s intimate places is the penetration of the human papilloma virus itself into the body. Moreover, infection can occur at any time.
The main reasons include:
- Sexual infections that significantly weaken the entire immune system. That is why it is necessary to treat and identify them as soon as possible.
- Frequent change of sexual partners, when it is unclear whether a person is sick or not.
- Unprotected sexual intercourse, especially when the couple does not use condoms, since they are one of the most reliable ways to protect your body from the penetration of bacteria, germs and viruses.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, namely using someone else’s towel, underwear, etc.
- Failure to maintain cleanliness during childbirth, when the virus can pass from mother to child.
- Smoking, which significantly weakens the human body.
- Poor nutrition, as a result of which the body does not receive enough essential nutrients (vitamins and microelements).
- Problems with hormones, which may result in disruption.
Due to the fact that the disease is most often asymptomatic, that is, the emerging papillomas may not bother you for the first few days, the moment during which you need to start treatment is always missed. But by leading the healthiest possible lifestyle, you can protect yourself from the virus, and, accordingly, from the appearance of papillomas on the genitals.
Where are papillomas located?
As a rule, the human papillomavirus behaves very aggressively, and after some time (the longest period is three months) the disease begins to manifest itself.
Approximately 70 percent of people who have had contact with a sick person will become infected, and only 30 percent, thanks to good immunity and a quick reaction of the body, will avoid it.
If we talk about papillomas specifically on the genitals, then they are small growths or, conversely, large growths that are very similar to “cauliflower”.
In women, papillomas are most often located in the following places:
- On the labia. In this place, women most often see the growths themselves, since they can interfere with the “morning and evening toilet”.
- In the vulva area, it is quite difficult to notice papillomas in this place on your own.
- In the vagina, and in this place they can be either single or multiple. And only a specialist can see them.
- Also, growths in women can be found on the cervix, which is very dangerous and can interfere with the normal process of conception, as well as around the anus. Papillomas that appear inside the vagina can also begin to interfere with normal urination. And only with this option, the woman herself will pay attention to the discomfort.
If we talk about men, then they may develop papillomas:
- On the foreskin of the penis, what occurs most often is one of the most vulnerable places.
- On the skin around the penis, and they can be single, or they can grow in large groups.
- In the scrotum area.
- In the anus area.
Usually, every person is attentive to their health, and sometimes even examines their genitals for prevention. With this approach, you can independently notice the changes that appear. Moreover, papillomas can appear in just a few hours, that is, in the morning a person woke up absolutely healthy, and in the evening he already discovered warts.
Incubation period and routes of infection
Papilloma cannot just appear on the genitals. This will be preceded by infection, which can occur in one of the following ways:
- During sexual intercourse when people do not use condoms.
- In everyday conditions, when people living together use the same glasses, spoons, and towels.
- During tests and other medical procedures, during which doctors and nurses do not follow the rules for disinfecting instruments and using disposable syringes.
- During childbirth, namely at the moment when the baby passes through the birth canal.
There are even cases where hospital and clinic staff became infected with the human papillomavirus during some kind of manipulation on a patient.
Many people are mistaken and think that not everyone can be infected. In fact, with unprotected sexual intercourse, as well as with failure to observe personal hygiene and basic rules, absolutely everyone is at risk, that is, they can become infected.
As for the incubation period, it is 12 months.
But most often, the first symptoms begin to appear after three or six months from the moment of infection.
Diagnosis of genital papillomas
Testing for papilloma virus
Diagnosing papilloma on the genitals is very simple. Sometimes you don’t even need to contact a specialist to understand what it is. But in most cases, people still resort to the help of doctors and make an appointment.
During your appointment, your doctor will conduct a thorough examination of your genitals. During the examination, he may even find more papillomas than a person expects, since there are simply places that cannot be examined by oneself. Once the growths have been detected, the doctor can take a smear as well as a tissue sample to determine for sure that it is a papilloma and not any other neoplasm.
If papillomas are found inside the vagina, a Pap test may be needed, which will give an accurate result. Sometimes warts are discovered by chance, and they do not cause any discomfort to the person.
In this case, the doctor will prescribe a PCR test, which will accurately determine the type of virus, as well as determine the degree of oncogenicity.
The degree of oncogenicity is determined only because the presence of papillomas in the vagina can be associated with both early and later stages of cervical cancer. When the diagnosis has been made, the doctor will prescribe special treatment, which is aimed at reducing the overall activity of the virus in the body, as well as eliminating growths.
Treatment of papillomas
Treatment methods for papillomas
Genital warts, unlike their appearance elsewhere, very rarely disappear on their own, and besides, they are highly contagious. Therefore, upon detection (which is actually not a big deal), you need to immediately begin treatment.
The treatment itself will include the following:
- Restoration and adjustment of the body's protective properties.
- Removal of papillomas.
All these actions are carried out simultaneously, since when using certain medications to remove papillomas, the immune system may weaken even more, and accordingly, the treatment will be ineffective.
Strengthening the immune system
A special role during the treatment of warts on the genitals is played by strengthening the body’s protective properties, because otherwise, after removal of papillomas, they will soon appear again.
First of all, in order to strengthen the immune system, you need to start eating right, namely, eat more fruits, vegetables and meat, which contain all the vitamins and minerals necessary for the human body.
And it is known that if the body has enough of these elements (there is no deficiency), then the immunity is good.
In addition to proper nutrition, you need to start taking certain medications.
Among them you can often find:
- Echinacea tincture, which naturally boosts immunity. However, some people may experience an allergic reaction while taking it.
- Probiotics. Most doctors believe that if the intestinal microflora is good, then the body is protected. And in fact it is. From the studies conducted, we can conclude that people with dysbiosis get sick much more often than those who have everything in order with their intestines.
- Preparations based on interferon, which activates the body's immune forces.
- Sometimes the doctor may prescribe special injections to boost immunity. But for this there must be serious reasons and precise purposes.
Video. Treatment of papillomas.
Read: Gynecological tests for infections: types and proper preparation
Removal of papillomas
Today, doctors use several methods to remove papillomas on the genitals.
These methods include:
- Exposure to drugs. The most commonly used products are Verrumal (which contains salicylic acid, which has drying properties). It must be used two or three times a day. Podofilox (due to the presence of podophyllotoxin, prevents cell division), which should be used very carefully and applied only to damaged areas to avoid damage to healthy tissue. Imiquimod, which helps improve immune function.
- Surgical removal. You can remove warts in one of the salons using a laser or nitrogen. But such removal costs a fair amount, and they charge money mainly per papilloma. It makes sense to go to salons when there are several papillomas. But it also happens that it’s about 10-20.
- More recently, a method has emerged for removing warts using the Surgitron device. With its help, you can carefully remove warts on the genitals, and in addition to cutting the tissue, it will also be disinfected, which eliminates the possibility of new papillomas appearing as a result of the virus spreading across the skin.
In fact, despite the large number of methods for removing papillomas, none of them can be called one hundred percent. Sometimes it happens that after surgical removal of a papilloma in one place, a person literally the next day discovers it in another. The same applies to the use of chemicals, each of which is also not universal.
Prevention of papillomas
Disease prevention
In order not to think about what needs to be done to get rid of papillomas on the genitals, you just need to adhere to the following rules:
- Always use condoms during sexual intercourse, especially if it is not a regular or trusted partner.
- Try to avoid casual connections.
- Start treating papillomas at the earliest stage of their appearance, that is, immediately after detection, and not wait for them to go away on their own.
- Always start treatment only after visiting a doctor.
- Use only your own towel.
If you follow the above rules, you can protect yourself from infection with the human papillomavirus.
Genital papillomas are very dangerous, because if treated incorrectly (or not treated at all), they can not only grow, but also degenerate into malignant tumors.
Therefore, if there is any suspicion of papilloma formation, you should immediately see a doctor who will accurately diagnose and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
Source: https://DiagnozLab.com/analysis/infectious/urogenital/genitalnye-papillomy-prichiny-poyavleniya-i-metody-lecheniya.html
Papillomas on the genitals: dangerous or not?
Unexpectedly appearing papillomas on the genitals can greatly frighten their owner. In fact, these growths are external manifestations of a fairly common virus called HPV. Despite the fact that it can provoke the development of cancer, in the vast majority of cases it is still benign.
Routes of infection
Genital papillomas are no exception to the rule. They, like any other types of similar formations, arise due to a virus occurring in the body.
Human papillomavirus is very common. According to various sources, from 60 to 80% of the world's population are infected with it. Most of these people are only carriers of the virus, and it does not manifest itself in any way.
HPV infection is caused by direct contact with an already infected person. This can happen in various ways:
- Sexual. This is the most common option. The risk of infection is very high. It is possible to reduce the risk only by resorting to barrier contraceptives, namely condoms;
- Intrauterine. Indeed, a woman during pregnancy can transmit the virus to her unborn child. This does not always happen, since the placenta firmly protects the fetus, but if there is damage on it in the form of microcracks, then the virus cells can overcome the barrier. In addition, there is an increased risk of infection of the baby during its passage through the birth canal, when it directly comes into contact with the mucous membranes of the mother;
- Domestic. This option involves the transmission of HPV through household items, clothing, and personal hygiene items. The likelihood of infection by this method is especially high in conditions of high humidity, since this is an ideal environment for the virus, which prolongs its viability. For example, in a bathhouse, swimming pool, by sharing a wet towel.
The rarest route of HPV infection is so-called self-infection. This is possible if the virus was on a person’s hands and entered his body through open wounds during combing, shaving, or hair removal.
Risk factors
Since genital papillomas are most often transmitted sexually, risk factors for infection include:
- Adolescence. Most people first become sexually active between the ages of 16 and 19, so this is when the risk of infection is greatest;
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- Lack of a condom during sexual intercourse. Although it does not provide a 100% guarantee, it significantly reduces the risk of infection;
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- Presence of sexually transmitted infections.
Promiscuous sexual intercourse is a risk factor for the appearance of papillomas on the genitals
In fact, anyone can become infected with HPV, regardless of age and gender. But how the virus manifests itself inside the body will depend on the person’s immune system.
Reasons for development
As mentioned earlier, the papilloma virus can be in a “dormant” state in the body. In this case, it does not manifest itself in any way and most people do not even suspect its presence.
The virus is activated when the immune system is weakened, which ceases to protect the body from its effects. The reasons for this may be:
- Acute course of various diseases, including those that have passed into the chronic stage;
- Abuse of bad habits;
- Intoxication of the body;
- Pregnancy;
- Severe stress;
- Long-term lack of proper sleep and rest;
- Unfavorable environmental conditions;
- Disturbed hormonal levels.
Regardless of what exactly triggered the development of the papilloma virus, a person needs to see a doctor for diagnosis, since it is important to make sure that the growths that appear on the body are not oncogenic.
Types of papillomas on the genitals
Papillomas on the genitals can be divided into types according to several classifications.
Depending on the nature they can be:
- Low oncogenic. Such formations undergo malignancy in extremely rare cases. They may be a consequence of certain types of viruses occurring in the body. As a rule, these are types 6 and 11;
- Highly oncogenic. These are growths that have an increased risk of malignancy. For example, in women, highly oncogenic genital papillomas can lead to the development of cervical cancer. In this case, the formations are also associated with certain types of virus. Usually these are types 16 and 18.
Depending on the form, there may be:
- Flat papillomas;
- Filiform papillomas;
- Simple. They have a round shape.
The exact type of formations, as well as their nature, can only be determined during diagnostic procedures.
Symptoms of manifestation
Papillomas are not always accompanied by pronounced symptoms. Single small formations quite often do not cause any discomfort for a long time. But if, under the influence of certain reasons, they begin to manifest themselves, then the following signs indicate this:
- Increase in the number of growths;
- Their increase in size;
- Severe discomfort in the perineum;
- Itching, burning, and sometimes a feeling of pain;
- The occurrence of an inflammatory process;
- Unnatural discharge from the genitals;
- Bloody discharge after sex. This symptom is typical for women;
- Change in color of papillomas. They may become darker or uneven in color.
Itching is one of the symptoms of papillomas on the genitals
Not all of the listed signs must be present. In each individual case, HPV, accompanied by genital papillomas, can manifest itself differently.
Locations
Genital papillomas can occur both outside and inside the genital organs.
In women, such papillomas can be located:
- On the labia;
- Inside the vagina;
- On the cervix;
- In the anus area
For men, the following places of their localization are typical:
- The male penis, namely the head of the penis and the foreskin;
- Urethra;
- Anus area.
Papillomas that occur on the external genitalia, as a rule, do not go unnoticed. As for internal warts, sometimes a person is not even aware of their presence if they are not visible to the naked eye and they are small in size. But during sexual intercourse, the fragile growths are injured, which can lead to inflammation, pain, and bleeding.
Diagnostics
HPV itself is diagnosed using a blood test. But examination of growths in the genital area will require additional measures.
Papillomas on the genital organs in women are subject to:
- A full gynecological examination;
- Cytological examination if they have a risk of malignancy.
Men may be prescribed procedures such as:
- Urethroscopy;
- Anoscopy;
- Similarly, as in the first case, a cytological examination of a sample of papilloma tissue.
Urethroscopy is a method for diagnosing papillomas on the genital organs
After an accurate diagnosis is established, the doctor prescribes treatment.
Therapy methods
It is advisable to treat HPV in the genital area immediately after the first signs appear. This will not only get rid of discomfort, but also prevent the possible development of an inflammatory process and an even more serious phenomenon - oncology.
Medication
Treatment of papillomas, including those located in the genital area, necessarily involves taking medications, since it is not enough to remove formations from the skin; it is necessary to prevent their reappearance.
As part of drug treatment for HPV, a doctor may prescribe medications from the following groups:
- Antiviral drugs. Their main task is to suppress the activity of the virus and, accordingly, stop the appearance and growth of papillomas;
- Immunomodulators. Their action is aimed at strengthening the immune system, which will allow the body to independently resist viral cells in the future;
- Vitamin complexes. They complement the action of immunomodulators and help saturate the body with missing vitamins and minerals.
Antiviral drugs and immunomodulators can be produced both as medications for oral administration and in the form of various ointments and solutions.
Removing formations
In fact, many people live with single papillomas on the body and are in no hurry to remove them if the risk of their oncogenicity is low. But if the growths do not appear on the arms, legs or back, but in the genital area, the question of getting rid of them is usually more pressing.
The reasons for this are that the genitals have thinner, sensitive skin, and since the mucous membranes are still located nearby, the risk of inflammation is high.
In addition, papillomas in this area, especially large ones or in large quantities, almost always create discomfort and, of course, an aesthetically unpleasant appearance.
You can remove growths yourself, using special pharmaceutical products, as well as in medical and cosmetology institutions.
In the first case, it is necessary to obtain mandatory approval from a doctor, since you can burn the delicate skin and mucous membranes in this area. Examples of such drugs are Superchistotel or Solcoderm.
But at home you can only get rid of small formations. In addition, there are no guarantees that there will definitely be a result.
If you resort to papillomas removal services, then you can choose the most suitable method for yourself. Possible options:
- Surgical removal. Despite the fact that such an operation is considered quite simple, in the case of genital papillomas, this is the most unpreferred method, since there is a risk of long healing;
- Cryodestruction. A very popular procedure that allows you to remove formations from the skin by freezing them with liquid nitrogen. But if there are too many papillomas, then the service can be very expensive;
- Laser removal. Painless and very effective method. There is no risk of bleeding;
- Electrocoagulation. The procedure is based on the use of high-frequency currents;
- Radiosurgery. In this case, the role of the knife is played by radio waves.
Laser removal is one of the methods for treating papillomas on the genitals
Unfortunately, the choice of method is not always based solely on personal preference. The nature of the papillomas, their size and number, and, of course, the individual characteristics of the patient’s body will also play a role in this issue.
Removing papillomas on the penis, labia or other intimate areas in Moscow is not difficult. This can be done not only in hospitals, but also in certified cosmetology centers.
Traditional methods
Not only traditional, but also traditional medicine can help answer the question of how to get rid of papillomas. There are many ways to get rid of growths using herbal infusions, alcohol tinctures and various mixtures based on natural ingredients.
But when it comes to removing papillomas on the genitals, then it is better to leave traditional methods aside. The fact is that, trying to independently remove a growth in such a vulnerable place, you can damage the delicate integument.
But the main reason that the removal of genital papillomas should be carried out by a qualified specialist is that the risk of their malignancy is usually higher than that of those that are localized in other parts of the body.
Preventive measures
Papillomas on the genitals are a very unpleasant phenomenon, but, unfortunately, it is practically impossible to protect yourself from them 100%. A special vaccine can reduce the risk as much as possible. According to studies, it gives results in 98-99 cases.
But it is important to note that getting vaccinated only makes sense for those people who have not yet encountered HPV. Otherwise, it has no effect.
In general, you can reduce the risk of infection by following simple recommendations:
- Avoidance of promiscuity;
- Condom use;
- Maintaining a healthy immune system;
- Timely treatment of diseases;
- Rejection of bad habits;
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- Avoiding stress and overexertion.
Compliance with all of the above measures will help not only reduce the risk of HPV infection, but also a number of other diseases.
Source: https://health-post.ru/papillomy-na-polovyh-organah-01/