HPV (human papillomavirus) is a group of viruses that cause pathological changes in the skin and mucous membranes. To identify it, laboratory diagnostics is required. You can undergo it at our medical center. We use all modern methods for diagnosing this infection.
There are a huge number of types of HPV. They cause the appearance of various pathological formations on the skin and mucous membranes.
It can be:
- warts
- condylomas
- cervical dysplasia
The greatest danger is represented by dysplastic changes in the cervix. Because they can transform into cancer. It is for the prevention of this malignant oncopathology that HPV tests are mainly performed. They are most often taken from women.
But the virus can also cause unpleasant or dangerous changes in other organs.
Warts on the skin can develop into squamous cell carcinoma. HPV also rarely causes other cancers.
In addition, condylomas can be located in unfortunate places and reach large sizes.
They are most unpleasant in:
- urethra
- bladder
- larynx
Appearing in the respiratory system of children, papillomas can lead to suffocation.
In the urethra of adults, especially men, condylomas can cause urinary retention. When localized in the bladder, frequent urination is often observed. Possible urinary retention. When it moves, the jet damages the papilloma. She can come off. As a result, bleeding occurs. Blood appears in the urine.
As you can see, HPV cannot be called a harmless virus. Therefore, it needs to be detected and treated promptly.
For this purpose tests are taken. Basically, smears from the genitourinary tract are used as clinical material. Blood tests are not so informative and therefore are practically not used.
The simplest, fastest and most inexpensive method for detecting papillomavirus is PCR. To carry it out, a scraping of the epithelium of the urethra, cervical canal, and vagina is taken.
Sometimes smears are taken from other areas of the body if papillomas are located on them.
There are two types of tests:
Let's discuss how they differ.
HPV is not just one virus. There can be many types. They differ in genetic structure and pathogenic properties.
Some viruses cause warts on the feet, others cause dysplasia and cervical cancer. Typically, diagnosis is carried out simultaneously for several types. Their number is determined by the doctor and agreed upon by the patient. The more types that are tested, the more accurate the analysis. But the cost of diagnostics may be higher.
Let's say you are tested for 15 types of papillomavirus. Whether it is general or differentiated will determine the form in which you will receive results.
In general analysis, the term “detected” means that one of the 15 types of HPV for which you were tested was detected. However, it is unknown which type persists in your body.
If a differentiated analysis is carried out, then you receive more detailed information. You will also learn which specific types of HPV are found in clinical material.
This type of research is more expensive. But it is more preferable. Because it is important to determine not only the presence of the virus in the body.
Typing is necessary for risk assessment. If they are high, treatment or more active monitoring of the patient will be required.
There are also qualitative and quantitative diagnostic methods. Qualitative tests only show the presence of the virus in the body.
The concentration of HPV in clinical material is determined quantitatively.
Sometimes diagnostics are performed with a CVM. Many patients do not know what CME is. This abbreviation stands for “material intake control.” That is, specialists check whether the smear was taken correctly.
If clinical material is collected correctly, its quantity should be sufficient to carry out a full diagnosis. A sufficient number is considered to be 10 thousand epithelial cells. If there are fewer of them, the result is considered unreliable.
Incorrect collection of clinical material is the main cause of false negative PCR results.
In our clinic, swabs are taken by experienced medical staff. Therefore, such problems do not arise. In order for the results to be reliable, it is necessary to properly prepare for the test. The doctor will inform you about the preparation rules.
Sometimes PCR also gives false positive results. This means that there is no infection in the human body, but the analysis shows that there is one.
The reason is usually a violation of the rules for collecting or transporting material. Contamination will lead to false test results.
Main indications for examination:
- presence of signs of human papillomavirus infection (the appearance of condylomas and warts)
- dysplastic changes in the cervix in women
- unsatisfactory cytology smear result
- preventive examination (screening) of women
- monitoring the effectiveness of papillomavirus treatment
How long the test takes depends on where you took it. In our center you can find out the results the very next day. Reference values are when the virus is not detected. If a pathogen is identified, additional examination or treatment is required.
Very often, HPV testing is done in gynecology. Because it is for women that the virus is most dangerous.
How long it takes for this infection to appear depends on many factors. First of all, it depends on the type of HPV and the characteristics of the immune system.
With reduced immune defense, pathological processes in the cervix develop faster. Typically, the persistence of the virus for 8-10 years is required for cancer to occur. Sometimes less time passes.
You can catch the virus when you are young. This is how it passes from person to person during an intimate relationship. Therefore, cervical cancer is the most common malignant tumor among young women.
Outcomes of HPV can vary. Sometimes spontaneous recovery is observed within a few months. In other cases, the number of viruses in the genitourinary system increases, and pathological changes in the epithelial tissue progress.
Decoding the HPV analysis
To decipher the research results, you need to seek the help of a doctor. Although interpretation is sometimes not difficult for people without medical education. Especially if the test is high quality. In this case, it will indicate whether the virus was detected or not.
When performing PCR, quantitative results are usually not provided. They are high quality. Therefore, it is impossible to understand what concentration of the virus is contained in clinical material. Accordingly, with such a diagnosis it can be difficult to assess the prognosis of the disease.
With a differentiated test, the result can be displayed in the form of a table. It indicates which types of HPV DNA are in the body, and which types of papillomaviruses have not been identified.
Quantitative HPV analysis
It is not always enough to know whether HPV is present in the structures of the genitourinary system. Even typing does not provide complete information about the state of his health.
Normally, there should be no papillomavirus in the urogenital tract at all. But a lot also depends on quantitative indicators. The virus may be inactive.
If the viral load is minimal, then condylomas do not appear, and cervical dysplasia does not progress. But with an increase in the number of viruses, pathological changes occur in epithelial cells.
A qualitative test does not show the number of viruses. To obtain more accurate results, the Digene test is used. It is used all over the world.
A smear is taken as the material. Results are given in relative units. One unit is 100 thousand copies of DNA per ml.
The test transcript is as follows:
- if the result is below 1.0, it indicates that the virus was not detected
- if the result is higher, a numerical value is indicated
If the viral load is greater than one, this means that the concentration of the virus is clinically significant. And the higher this number, the higher the health risks. During successful treatment, quantitative indicators may decrease.
The quantitative Digene test is often used to assess the effectiveness of drug therapy. It is more accurate compared to high-quality PCR. Because the very fact of detection of papillomavirus does not always indicate illness and a possible unfavorable outcome of virus carriage.
Quantitative research is often used to evaluate the results of therapy. If successful, the number of viruses should decrease. The result is designated as negative. Or a number is indicated that is less than what it was at the time of diagnosis. But there are cases when the virus did not disappear, but on the contrary, it got worse after treatment.
Why is this happening?
The probable cause is immunodeficiency. The patient may also have HIV infection.
A decrease in immunity is not always due to an infectious factor.
The immune system suffers from serious illnesses, previous surgeries, and an unhealthy lifestyle. It is suppressed by certain drugs: immunosuppressants, cytostatics, glucocorticoids.
The treatment itself is difficult due to the fact that specific drugs against HPV have not been developed. Doctors have to use general antiviral agents and immunomodulators. Therefore, treatment is not always effective.
But in most cases, with the right approach to treatment, it is possible to reduce the viral load. After this, pathological processes in the genitourinary system cease.
Dysplasia no longer progresses. It can also regress. This is highly likely to happen if the pathological changes are assessed as stage 1 or 2 of dysplasia.
HPV smear test
To diagnose human papillomavirus infection, they generally take smears rather than a blood test.
HPV can be detected in epithelial cells. Preparation is required before taking smears. It is necessary for both men and women.
For male patients, preparation includes:
- abstinence from sex for 1-2 days
- absence of urination 2 hours before taking a smear from the urethra
- not using topical antiseptics or other medications
For women, the study can be carried out both in the first and second half of the cycle.
In the follicular phase, smears are taken no earlier than day 5.
In the luteal phase, tests can be taken later than 5 days before the expected start date of the next menstrual cycle. That is, 5 days before menstrual bleeding.
Here's what you shouldn't do two days before your smear test:
- be sexually active
- use tampons
- do a transvaginal ultrasound
- perform colposcopy
Failure to follow these guidelines may result in a false test result.
When using antiseptics or douching, or urinating immediately before taking a smear, the risk of a false negative result increases. Sexual intercourse or the use of tampons, on the contrary, increases the likelihood of a false positive result.
HPV 16 18 analysis what is it
The greatest threat to females is posed by highly oncogenic types of papillomavirus. They first cause cervical dysplasia and then cancer. Dysplasia develops first in the first degree, then in the second, and then in the third.
The third degree in most patients turns into cancer. Therefore, it is subject to mandatory surgical treatment.
For grade 1-2 dysplasia, conservative therapy can be performed.
To determine the prognosis of the disease (whether dysplastic processes will progress), an analysis for HPV of a highly oncogenic type is required. You can only take classes 16 and 18. These types of the virus are the most common. They cause 70% of all cases of cervical carcinoma.
Another 20% of cases occur from all other types of viruses combined.
In 10% of women with cervical cancer, this pathology develops without the participation of papillomavirus.
Testing for HPV types 16 and 18 is inexpensive. Its price is 500-600 rubles. Plus you need to pay for the collection of clinical material.
Additionally, a cytological examination of a smear from the cervix is required. This is necessary for the timely detection of signs of epithelial atypia.
If HPV is detected and the cytology result is unsatisfactory, the doctor will prescribe a colposcopy. This is an instrumental study. The doctor will examine the cervix using a special device under magnification. It will reveal whether there are areas of dysplasia.
Finally, if the colposcopy results are unfavorable, a biopsy will be performed. It will help determine whether the patient has developed cancer and whether she requires surgical treatment.
Sometimes patients ask: why get tested for HPV if changes in the epithelium are detected using a smear for oncocytology. Because this test is not 100% sensitive. Approximately 15% of women with a good oncocytology result actually have severe cervical epithelial dysplasia. There are even more patients with missed mild or moderate dysplasia.
A cytological smear is a screening test. It is indicative only. While an HPV test allows you to accurately determine whether the body has a highly oncogenic type of papillomavirus.
If detected, control over a woman’s reproductive health will be strengthened. She will undergo preventive diagnostics more often. This will help to identify pathological changes in the epithelium in time and prevent the development of cancer.
Research shows that HPV tests increase the likelihood of detecting dysplasia by 28% compared to using a smear alone.
You can take any tests for papillomavirus in our clinic. We take smears carefully and painlessly. Clinical material is sent to the best laboratories in Moscow, so you can be confident in the accuracy of the results obtained.
We can do:
- PCR for HPV
- typing
- Digene test
Here, if necessary, you can take a cytological smear. If indicated, a colposcopy will be performed. Almost all cases of cervical cancer can be prevented with timely screening.
Source: https://onvenerolog.ru/zppp/analiz-na-vpch.html
Quantitative HPV analysis: interpretation of results and meaning of positive indicators
Decoding the HPV analysis is an integral part of the diagnostic study. Based on the data obtained, the doctor makes a decision on the necessary therapeutic tactics. Correctly conducted analysis and reliably deciphered results allow you to choose the right treatment.
HPV diagnostic methods
Human papillomavirus is an infectious disease that cannot be completely cured. Some people experience recurring infections that negatively impact their health and quality of life. Such patients are recommended to undergo periodic examination to detect the type of HPV, the nature of its severity and oncogenic degree.
Modern medicine uses several diagnostic methods for quantitative control of papillomavirus:
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Study of the presence of antibodies in the body. Antibodies are specific proteins that are produced as an immune response to pathogen activity. Immunoglobulins are unique to each specific infection.
- The Digene test (Hibrit Capture hybrid capture method) is designed to determine the 18 most dangerous types of HPV. The essence of the method is to stain the biopsy material with special fluorescent substances. When a virus is detected in the materials being examined, a highlight occurs.
- PCR is one of the most informative methods for diagnosing HPV. The analysis is based on artificially increasing copies of the pathogen's DNA. It is possible to identify even single viruses with the highest accuracy.
After conducting a laboratory study, specialists begin to decipher the results obtained.
Results table
When conducting an HPV analysis, the results are summarized in a table, which includes information about quantitative and qualitative indicators.
This table provides general information about possible indicators based on PCR analysis.
| Expected result | HPV viral load | Decoding of indicators. |
| Negative reaction. Clinically insignificant. | less than 3 Lg | The virus was not detected in the body. Refers to the norm of indicators. |
| Doubtful information. Clinically significant indicators. | 3 – 5 Lg | The concentration of the virus is at the limit values (slightly exceeds the normal limit). Additional research, including screening, is required. |
| Positive | more than 5 Lg | The viral concentration is at a high level. |
The laboratory sheet indicates all types of HPV for the presence of which the test was carried out. In most cases, these are 12 types - 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59 of medium and high oncogenic degree.
The mark “absence of DNA” and a viral load of less than 3 Lg indicates the complete absence of the virus or its insignificant amount. No treatment required. The infection may be present in the human body, but does not produce any effect. No growths are observed.
A concentration of 3–5 indicates the presence of a small amount of the virus. Women in whose body papillomavirus is detected must undergo additional examination to exclude the presence of cervical dysplasia. Patients receive general immune-strengthening treatment. If condylomas are present, removal is performed.
A positive test result at a concentration above 5 indicates a danger to humans. The body is infected with a virus. The likelihood of developing cervical dysplasia in women is increased. Additional analyzes are being carried out. Treatment consists of removal of growths, large-scale antiviral and immunostimulating therapy. You may need to consult an oncologist.
What does the result mean?
During research, qualitative and quantitative analysis is taken into account. The first may indicate the presence or absence of a virus. The second is about the concentration of the pathogenic agent in the human body. Only an experienced specialist can decipher the information received, taking into account all the surrounding circumstances.
There is no need to take a positive test result as a death sentence. Often during research, errors are made that affect the indicators and make it impossible to determine the correct data. In most cases, mistakes are made by patients while preparing for an upcoming test. Reference values must be taken into account.
False positive HPV
False-positive HPV test results are common. This happens if:
- the bio sample was contaminated;
- there was an incorrect collection of materials;
- the patient was treated before the analysis;
- the person did not comply with the standards of preparation for diagnosis.
To avoid getting distorted results, you need to take into account some rules. Within 12 hours before submitting biological material, it is prohibited to take antiviral, antibacterial and antimicrobial drugs. You should shower on the day of the smear test.
Over the next 2-3 days, it is better to refuse sexual intercourse. A smear test is not required during menstruation. People often encounter false test results if they tried to treat the infection with antiviral drugs the day before.
The virus itself is neutralized, but antibodies remain in the body.
Referential meaning
Reference values of an indicator (another name is reference) imply general values obtained during laboratory research on a specific category of the population. These can be young people aged 20-30 years, women during pregnancy, those who have given birth, those who have not given birth, etc. Such indicators are necessary to obtain the average total indicator of the relative norm.
This is how a quantitative HPV test is determined. The average value of 3-5 Lg, which implies a questionable result, was collected based on the assessment of a certain category of carriers of the papilloma virus. Therefore, reference values cannot be assessed as the only correct indicator. The concept of normal may differ depending on the characteristics of the body, age, and the presence of concomitant diseases.
In most cases, only the qualitative result of the study is important, which indicates the presence of the virus. In cases of detection of a non-oncogenic type of HPV, its concentration is insignificant.
If the test is positive
A positive HPV test indicates the presence of the virus in the body. There is no need to worry, according to statistics, 7 out of 10 people are carriers of the papilloma virus. Most people can go through life without knowing they have HPV. Activation of the symptoms of the disease occurs during a period of weakened immunity.
Depending on the identified type of pathogen and the general picture of the disease, the doctor selects treatment tactics. In most cases, it includes antiviral and immunostimulating therapy, methods of tumor destruction.
At 56, 16, 31, 18 and other cancer-dangerous strains
Detection of carcinogenic strains of the papilloma virus requires immediate treatment aimed at restoring the body's immune defense and eliminating formations.
Highly oncogenic HPV types are especially dangerous for women, as they cause the development of cervical cancer. The patient needs to undergo additional testing for the presence of erosion or dysplasia.
Histological examination of tissues will help identify malignant changes in cells.
Detection of such strains in the body will not indicate the presence of cancer. People with this diagnosis need to be attentive to their own health. Get examined regularly and get tested.
There are cases when self-healing from the virus occurs. Young people with strong immune defenses are most likely to be cured.
Timely removal of condylomas will help prevent the risk of developing dangerous consequences. All patients with identified strains need to do is follow the doctor’s recommendations, get treatment, monitor their immune system, attend routine examinations, and try not to infect others.
For benign strains
Benign strains of HPV are not dangerous to humans. All the patient will encounter is the appearance of unpleasant formations on the body. Depending on the quantitative indicator of the virus in the body, the doctor will recommend drug therapy.
More often, healthy young people with a small number of warts on the body are prescribed removal. A strong immune system is able to cope with the infection, and no auxiliary agents are required. Removal can be done using pharmaceutical drugs or going to the clinic and undergoing a hardware procedure.
If growths occur frequently or papillomatosis is diagnosed, antiviral treatment is required. It involves taking medications that suppress the activity of the infection and the ability to reproduce. Immunostimulants help the immune system suppress the virus.
It happens that the HPV test is positive, but there are no warts on the body. This indicates carriage, but lack of infectious activity.
A negative analysis can also be detected in the presence of papillomas on the body. It happens when the immune system is able to independently reduce the activity of the infection.
In this case, the concentration of the virus in the blood is constantly changing and may be low at the time of the study.
Regardless of what type of HPV is detected, the patient must discuss all necessary actions with a doctor. Self-treatment can lead to the development of the disease and increase the risk of undesirable consequences.
Deciphering the HPV test is an informative and important procedure, on which subsequent actions in terms of therapy depend.
You should not try to decipher the meanings on your own or with the help of people who lack the necessary qualifications.
Only experienced specialists can correctly explain the examination data, who will be based on the numbers and characteristics of the individual patient’s body.
Source: https://VashaDerma.ru/rasshifrovka-analizov-vpch
HPV PCR with typing and viral load
- 01 August
- 0 views
- 0 rating
| Deadline: | 5 workers days |
| Delivery time: | All day according to the medical center's work schedule |
| Preparing for the study: | Rules for taking tests |
| Research method: | Real-time PCR |
| Standards: | |
| Material: | urogenital scraping |
Human papillomavirus, HPV, human papillomavirus, HPV
HPV is the most common sexually transmitted infection. It mainly affects the epithelium, stimulates its growth and leads to the formation of condylomas, warts, and erosions. More than 100 types of papillomavirus are known. It is possible for one person to carry several types of the virus at the same time.
Some types of virus (oncogenic), when integrated into the genome of epithelial cells (integration), can cause their malignant degeneration, leading to cancer. Carriage of HPV types 16 and 18 is considered the most dangerous, since it is highly likely to lead to the development of cervical cancer in women.
- Contact (for genital-genital, genital-oral, genital-anal contacts), vertical (from mother to child), household.
- Ranges from several weeks to several years.
- Analysis of HPV integration using the real-time polymerase chain reaction (Real-time PCR) method allows for a sensitive and specific determination of the presence of HPV with an assessment of its normalized amount (viral load), types of virus, as well as determination of the presence of integrated and episomal forms of the virus 16 and 18 types.
Diagnosing HPV is complicated by the sluggish development of processes in a young body, which often do not give specific symptoms. To detect the disease at an early stage and preventive disease control, centralized screening for HPV HPV is used .
What is HPV screening
Screening is a targeted examination of certain groups of the population in order to identify a disease. Screening is carried out using a specially developed method by trained personnel.
HPV is an infectious strain of DNA containing papillomavirus.
All papillomaviruses (and there are more than a hundred of them) are divided into:
- highly oncogenic strains - viruses that can cause dysplasia of human skin or mucous tissues, followed by their malignant degeneration;
- low-oncogenic - a group of viruses whose activity causes benign formations (papillomas, warts).
Note! The abbreviation VKR means high carcinogenic risk. HPV HCR is the name given to the strains of the virus that cause cancer. In women it is cervical cancer, in men it is penile cancer. For European residents and the population of Russia, these are 18, 16, 31 and 45 genotypes of papillomavirus.
- When HPV type HPV is activated, tissue changes and degeneration occur, which ends in a malignant process .
- Screening for highly oncogenic papillomaviruses is carried out step by step, according to a specially developed scheme:
- Conducting a cervical smear analysis to determine the presence or absence of altered cells (dysplasia) in the patient’s body (PAP test).
- If the reaction to the PAP test is positive, a quantitative determination of the virus and its identification are carried out (advanced screening).
Antifungal shampoos for people
The recommended frequency of the event is once every 3 years.
Note! Screening can reduce the incidence of genital cancer by hundreds of times, which is important given the growing trend of infection.
Indications for testing
Indications for testing are:
- the appearance of condylomas (other neoplasms) on the genitals, anal area or oral cavity;
- discharge from the genitals of unknown etiology;
- a person’s personal concern about possible infection after unprotected contact;
- preventive control.
Importance of examination
Important! Detection of tissue dysplasia of the genital mucosa at an early stage is crucial in predicting the effectiveness of therapy. Early detection of HCR HPV in the body allows one to take preventive therapeutic measures to destroy it.
It takes 5 to 15 years from infection to the development of cancer. Detection of the latent form of the presence of the virus in the body gives:
- the possibility of dynamic monitoring of the condition of the genital organs and the activity of the virus (virus carriers are examined annually);
- the possibility of early treatment when the prognosis is most favorable.
Statistics show that cervical cancer ranks 3rd among cancers of the female genital organs . Studies of the causes of the development of uterine cancer confirm a direct link between infection with HPV HCR and the subsequent development of cancer.
Types of screening for HPV HCR
The most informative and inexpensive is the screening method that is used in Russia - a cytology test allows at the first stage to “weed out” healthy subjects, and further research is carried out only on patients with identified tissue dysplasia.
Cytology analysis (PAP test)
The PAP test is an analysis using the Papanicolaou method.
This type of testing is distinguished by high accuracy of analysis.
To carry out the analysis, material is taken from the cervical canal of the cervix in women or the urethra in men. The procedure is painless and is carried out under normal examination conditions.
The material is placed either on glass (a common practice) or in a special liquid medium, which is more convenient for research.
A liquid PAP test is taken with a special brush, which is placed in a prepared liquid medium for transportation and storage. This method of collecting and storing biomaterial allows you to preserve and analyze all the cells of the collected epithelium.
How to prepare for the procedure
In order for the Pap test to be as reliable as possible, several conditions must be met:
- 2 days before visiting the doctor, refrain from sexual intercourse, douching, and the introduction of vaginal medications;
- women should plan a visit in the first half of the menstrual cycle, but after the complete end of monthly bleeding;
- the study is not carried out during periods of exacerbation of chronic infections or acute diseases;
- the study is not carried out immediately after a course of antibacterial or anti-inflammatory drug therapy.
Herpes on the body what the symptoms look like
Advanced Screening
Note! Advanced screening is a controlled collection of biomaterial for real-time analysis to determine not only the presence or absence of HPV, but also the type and quantity of human papillomavirus of the oncogenic group.
The analysis is carried out using a qualitative PCR method based on RT-PCR.
This technique allows you to interpret the results of analyzes for decoding using the Daijin test. And adjust further tactics of working with the patient.
The collection of biomaterial does not differ from the usual taking of a smear. The requirements for preparing for advanced testing are the same as for the PAP test:
- Abstain from using vaginal medications 2 days before;
- Abstinence from sexual intercourse for the same period;
- Lack of menstrual bleeding.
PCR analysis
Analysis of HPV detection using a polymer chain reaction (PCR test) on its DNA has a high degree of reliability . With its help you can determine:
- fact of infection;
- papillomavirus genotype;
- extent of distribution (quantitative analysis).
Analysis is possible on any fluid from the patient’s body: blood, mucous discharge, urine.
Preparation
- Women should not donate vaginal biomaterial during menstruation;
- Men are prohibited from urinating 1.5 hours before the procedure;
- Blood is donated on an empty stomach;
- When collecting material from the genitals, women are prohibited from douching the night before;
- Any medications are excluded 2 days before the collection of biomaterial.
Test results
- The Papanicolaou test (Pap test) can be negative (no altered cells were detected) or positive (cancer cells were found in the sample taken);
- The PCR test shows the presence or absence of HPV;
- Advanced screening determines the type of virus and its quantity.
The quantitative result of the Daijin test is interpreted:
- less than 3 Lg – the concentration of the virus is insignificant;
- from 3 Lg to 5 Lg – average degree of presence;
- more than 5 Lg – high concentration of HPV.
Papillomas in pregnant women and children
Human papillomavirus (HPV) and papillomatosis in women
Papillomatosis – all the most important things about the disease
Why do papillomas appear?
Consequences of HPV: what else happens besides papillomas
The diagnosis of HPV infection can only be made by a doctor - a gynecologist, urologist or dermatovenerologist. The first examination by a doctor is a gynecological examination (for women) or a urological examination (for men).
During the examination, the doctor takes material for a variety of tests to examine it for the presence of the virus. Also, at a follow-up appointment, the doctor may prescribe additional examinations.
So, in addition to a smear for HPV, a woman may additionally be prescribed a biopsy and colposcopy. Let's look at each procedure in more detail.
A visit to a gynecologist or urologist on any issue begins with a simple examination. The doctor tries to find papillomas or condylomas on the human body.
However, examining the cervix or penis alone is usually not enough to make confident conclusions about HPV.
The fact is that at the initial stage, precancerous processes or incipient cancer are not easy to notice, and the presence of HPV may not be visible in any way if a person does not have papillomas.
Scraping for HPV
Removal of moles by electrocoagulation after care
As a rule, it is taken with a special brush from the cervix (in women) or from the urethra (in men). Further, the material can be examined for HPV in different ways, which we will discuss below. This type of examination is necessary to confirm the presence of the virus and predict the development of the disease. Having a scraping can be a little unpleasant, but it is tolerable.
Scraping from the cervix
For example, a cytological examination, or Pap test (Papanicolaou smear), is often performed on the scraping material.
This is a study in which the type, number and condition of mucosal cells are determined in a scraping. Depending on the picture, the type of scraping is determined (doctors often say “smear type”).
There are: normal smear type, inflammatory type, dysplastic (precancerous) type and oncological (cancerous) type.
In all cases of “abnormality” it is necessary to be tested for HPV infection.
Cytological examination is preventive. Every woman should have a smear for cytology at least once every 2-3 years.
Colposcopy (additional procedure based on test results)
This is an examination of the cervix using a special magnifying device - a colposcope. The purpose of the procedure is to carefully examine the cervix through the device to find areas infected with the papilloma virus or mutating cells.
Colposcopy can be simple or extended . Simple is a regular colposcopic examination, extended is an examination with preliminary treatment of the cervix with special solutions.
With conventional colposcopy you can see: papillomas, areas of keratinization (induration), changes in the mucosa, and oncological formations.
With extended colposcopy you can see: areas changed at the cellular level that are not visible during a normal examination. During extended colposcopy, the cervix is treated with acetic acid and Lugol. Normally, it is colored evenly. In dysplastic, oncological and other pathological processes, areas of uneven staining appear.
At the same time, a woman may not have full-fledged papillomas on the cervix. That is why special devices and solutions are required, with the help of which a doctor can distinguish healthy cells from infected ones.
Biopsy (additional procedure based on test results)
A biopsy is the procedure of removing a small piece of tissue for further examination of the tissue under a microscope. This test is necessary to monitor the condition of the cervix or penis and detect HPV or its complications in the early stages.
Cervical biopsy procedure
The biopsy is performed during colposcopy using a special needle. This procedure may be slightly painful.
Using a biopsy, you can accurately determine the nature of the pathological process: from benign minor changes to serious malignant degeneration of tissue.
Depending on the results of the biopsy, the doctor decides what to prescribe for the person - surgery or further observation.
A biopsy is not always a mandatory procedure. Whether to prescribe it or not depends on previous tests. Women are much more likely to undergo biopsies than men because men have a much lower risk of cancer due to HPV.
Only a comprehensive examination: gynecological examination + scraping for HPV + further examination of the scraping with various tests can give a correct idea of the presence of HPV and the danger it poses.
Source: https://papillomnet.ru/papillomy/pcr-na-vpch-s-tipirovaniem-i-virusnoj-nagruzkoj.html
Differential determination of HPV DNA (Human papillomavirus, HPV) of 21 types (6, 11, 16, 18, 26, 31, 33, 35, 39, 44, 45, 51, 52, 53, 56, 58, 59, 66, 68, 73, 82) + KVM - find out prices for analysis and take it in Moscow
PCR determination method with real-time detection.
Test material Scraping of epithelial cells of the urogenital tract
Home visit available
Quantitative determination of HPV DNA type 21 (6, 11, 16, 18, 26, 31, 33, 35, 39, 44, 45, 51, 52, 53, 56, 58, 59, 66, 68, 73, 82) in scraping of epithelial cells of the urogenital tract using PCR with real-time detection.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a small DNA virus that infects epithelial cells and induces proliferative lesions of the skin and mucous membranes.
Currently, about one hundred types of HPV with different oncogenic potential are known, which are conventionally grouped into groups of high and low oncogenic risk. More than 90% of all cervical carcinomas are positive for the presence of HPV. Types 16 and 18 are most often found in biomaterial from cervical tumors.
Detection of HPV DNA does not confirm the presence of a malignant process; in most (up to 90%) cases, the virus is eliminated and self-healing within 12-36 months. With long-term chronic persistence of the virus and depending on its type, the risk of developing an oncological process increases.
Diagnosis of the disease requires additional cytological, histological examination and dynamic observation.
Infection with HPV types 6, 11, 44 can lead to the development of genital warts (anogenital warts).
The pathogen is transmitted through sexual contact, and can also pass from mother to fetus, causing laryngeal papillomatosis in the child. The incubation period ranges from several weeks to several months.
The nature of the growths and the volume of the affected areas vary from almost imperceptible to extensive. Malignant transformation of infected cells is possible.
Quantitative determination of HPV DNA allows the clinician to select the optimal treatment regimen for each patient and, if necessary, monitor the effectiveness of therapy.
Since HPV infects epithelial cells, a necessary condition for obtaining a reliable result is compliance with the scraping technique.
A special parameter has been introduced into the tests for diagnosing and monitoring HPV – material sampling control (MCM).
KVM is a test to determine the amount of human genomic DNA in a biomaterial, the source of which is epithelial cells included in the sample.
Analytical indicators:
- detectable fragment – unique DNA sequence of HPV types 6, 11, 16, 18, 26, 31, 33, 35, 39, 44, 45, 51, 52, 53, 56, 58, 59, 66, 68, 73, 82;
- specificity of determination – 100%;
- detection sensitivity – 100 copies of HPV DNA in the sample.
- Prevention of cervical cancer: A guide for doctors. - M.: Publishing house. "MEDpress-inform". 2008:41.
- Cervical diseases and genital infections. Ed. prof. V.N. Prilepskaya. - M.: Publishing house. "GEOTAR-Media". 2016:384.
- Human papillomavirus infection. A manual for doctors. Ed. prof. Doctor of Biological Sciences V.M. Talker. 2009:55.
- Bekkers R., Meijer C., et al. Effects of HPV detection in population-based screening programmers for cervical cancer: a Dutch moment. Gynecologic oncology. 2006;100(3):451-454.
- Khan M. et al. The elevated 10-year risk of cervical precancer and cancer in women with human papillomavirus (HPV) type 16 or 18 and the possible utility of type specific HPV testing in clinical practice. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 2005; 97:1072–1079.
- Snijders J., Meijer C. The value of viral load in HPV detection in screening. HPV today. 2006;8:8-9.
Source: https://www.invitro.ru/analizes/for-doctors/1156/8004/
How to take an HPV test in women: description of the procedure, features and reviews
An HPV smear is a test of biological material to determine a viral infection. The procedure for identifying the human papillomavirus is carried out for women and men to determine the type of pathogen and the degree of oncogenic danger. When diagnosing HPV, a smear procedure is required; the indicators affect the examination result and further treatment tactics.
What is HPV and why is it dangerous?
- Papillomaviruses have a spherical shape.
- They tend to affect dividing epithelial cells at the base of the top layer of skin.
- And the formation of new viral particles occurs in the upper epithelial layers.
- In addition to the sexual route of infection, the virus can be transmitted to a newborn by the mother during childbirth.
- Also contact for microdamages of the skin.
- (The virus persists for some time in epithelial cells after they are peeled off).
- A person can be infected with several types at once.
Types of HPV and their danger
There are several classifications of HPV. For the average person, the division into classes according to the level of oncogenicity is of greatest importance. The following classes of HPV are distinguished:
- non-oncogenic strains;
- low oncogenic strains;
- strains of average oncogenicity;
- strains with a high level of oncogenic risk.
Viruses with a low probability of malignant degeneration include types 6, 11, 13, 32, 34, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 51, 72.
The highest risk of cancer formation is when infected with HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, 39, 45, 50, 59, 61, 62, 64, 68, 70, 73. Previously, HPV strain 58 belonged to a class with a high level of oncogenicity .
More detailed studies made it possible to identify him as a type with an average probability of developing cancer.
In an infected skin cell, HPV can exist in two forms:
- separate from the cell's chromosomes;
- inside chromosomes (the genome of the virus is integrated into the genome of the cell).
In the first case, there is no risk of developing cancer. If the HPV genome merges with the genome of a skin cell, the risk of cancer increases.
The virus can live both in the body of the chromosome and outside it
How long does it take for the disease to appear?
- The virus often remains in the body for a long time asymptomatically and then spontaneously eliminates itself.
- But in a number of situations, in the presence of favorable factors, the development of infectious pathology is possible.
- The latter happens both a couple of weeks after infection and several months later.
- Papillomaviruses are the cause of a number of diseases, including cervical cancer (cervical cancer).
- Every year, up to half a million new episodes of this terrible disease caused by exposure to this particular microorganism are recorded worldwide.
- And almost a quarter of a million deaths from cervical cancer.
Forms and treatment of hyperplastic gastritis of the stomach
In general, 93% of cases of cervical cancer are caused by HPV.
According to the risk of cancer, all types are divided into three groups:
- high oncogenic risk (18.16, 35, 33, 31, etc.) – with the participation of provoking factors, viruses of this group can lead to malignant changes;
- low (8, 6, 14, 12, etc.) – viruses cause cancer pathology only under certain conditions and very rarely;
- non-oncogenic (1,2,3, etc.) – not capable of causing cancer.
Representatives of the first of these groups cause diseases such as:
- neoplasia (otherwise dysplasia) of the uterine cervix - the appearance of atypically changed cells, the severity of the process varies from mild (precancer) to cancer;
- bowenoid papulosis (caused mainly by HPV type 16) - manifests itself as dense red-brown formations (papules) on the skin of the genital organs, has a generally benign course, but in 3% of cases leads to malignancy.
Representatives of the second of these groups can cause:
- genital warts (otherwise known as anogenital warts) – formations of a lobular structure in the genital area, anus;
- verrucous epidermoplasia – flat papular warty growths, which in turn can have a high and low oncogenic risk;
- laryngeal papillomatosis (usually caused by type 11 virus) - papillomas of the larynx, most often formed in children due to infection from the mother during childbirth.
Viruses of the third group can lead to the development of warts:
- vulgar (type 2) – self-healing papillary keratinized growths that usually appear in children on the back of the hands;
- flat (types 3 and 5) – small nodules on the face and hands, self-healing and characteristic of adolescence;
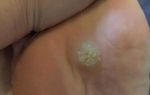
- plantar (type 1, less commonly type 2) - thickenings up to 100 mm in diameter that form at the sites where shoes are compressed, painful, and can be eliminated surgically.
Doctors' opinions on the most effective methods of treating warts and papillomas
The chief physician of Moscow City Hospital No. 62 describes his vision on this matter. Anatoly Nakhimovich Makhson Medical practice: more than 40 years.
“I have been treating people’s papillomas and warts for many years. I’m telling you as a doctor, papillomas along with HPV and warts can really lead to serious consequences if they are not dealt with.
The human papillomavirus is present in everyone on whose body there are papillomas, moles, warts and other pigmented formations. According to rough estimates, 80-85% of the planet's population has it. By themselves they are not dangerous. The problem is that an ordinary papilloma can become melanoma at any time.
These are incurable malignant tumors that kill a person in just a few months and from which there is no salvation.
Unfortunately, in Russia and the CIS countries, pharmaceutical corporations sell expensive medications that only relieve symptoms, thereby hooking people on one drug or another. That is why in these countries there is such a high percentage of cancer diseases and so many people suffer from “non-working” drugs.
The only drug that I want to recommend, and it is also officially recommended by WHO for the treatment of papillomas and warts, is Papinol.
This drug is the only remedy that has an effect not only on external factors (that is, it removes papillomas), but also acts on the virus itself.
At the moment, the manufacturer has managed not only to create a highly effective product, but also to make it accessible to everyone. In addition, within the framework of the federal program, every resident of the Russian Federation and the CIS can receive it for 149 rubles.”
To find out more, read this article.
Papillomavirus can be studied using several methods with the following goals:
- Determine the presence or absence of the strain in the body.
- Assess the activity of the virus and the damage it causes.
- Find out what nature the neoplasms have (malignant or benign).
Conducted:
- Colposcopic examination. Prescribed to women to identify possible growths on the cervix. The examination is performed using a colposcope. The doctor examines the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix. Thanks to magnification, you can see the tiniest papillomas.
- Cytological examination. How is it carried out, and what material is taken for study? To study, you will need a smear containing skin epithelial cells. The material is studied under a microscope. It is used to determine whether there are viral modifications in cells and determine the presence of infection. The method is not highly accurate. Often the result is wrong. The final conclusion is received in your hands after 7 days. Indicated on a five-point scale: 1 – no viral activity, 2 – cells with traces of inflammation are present, 3 – additional studies need to be carried out to establish the exact result, 4 – 5, pathogens are present.
- Histological examination. Usually prescribed as an addition to cytological examination. How is it surrendered? A small fragment of the epithelium is taken for the sample. The doctor examines the drug under a microscope and determines the condition of the cells. Histological analysis allows us to understand the nature of the formations present (condylomas, papillomas or tumor). The result can be obtained in 3 days. Usually, after histology, the doctor prescribes PCR diagnostics.
- PCR analysis is the most reliable research method. It can be used to detect various viruses and bacteria. The PCR research method allows you to determine the DNA of a pathogen, even when the virus is in the body in extremely small quantities and no external manifestations are observed. The method allows diagnostics to be carried out with almost 100% reliability, provided that all the requirements for such analyzes are met.
The material for PCR diagnostics is a smear, but blood, urine or amniotic fluid can be studied. Analysis results can be ready on the same day of treatment. The PCR diagnostic method allows you to most accurately determine the amount of virus in tissues. If a virus is detected, its concentration will be indicated on the form:
- Lg < 3 - papillomavirus is present in negligible or small quantities.
- Lg in the range of 3–5 indicates the presence of virus in an average amount.
- Lg > 5 - indicates a high concentration of the virus in the body.
If any of the studies performed has a positive result, the specialist will send you for a repeat analysis. The reliability of the diagnosis depends on how a person prepares for it. All hygiene standards and rules must be observed.
Important! Modern diagnostic laboratories make it possible to reduce the possibility of errors as a result of research, but do not completely eliminate it. An unreliable result is obtained when the research technique is violated and the biological material is contaminated!
The quality of the study is affected by the wrong timing for conducting it. This happens when a person has undergone treatment and the pathogen has been destroyed, but traces of it are partially observed in tissue samples that have been studied. A false positive result occurs when preparation for the study was carried out incorrectly.
It happens that there are flat warty growths on the patient’s skin, but the papillomavirus itself cannot be detected.
This happens when the virus was active in the past and its activity led to the formation of growths, but the person's immunity was strengthened as a result of drug therapy, which ultimately led to the suppression of its activity. The best solution would be to remove such tumors.
What is the main method for diagnosing the corresponding neoplastic changes?
Cytological examination by Papanicolaou of a scraping (smear) from the cervical canal (the so-called PAP test, PAP).
This is one of the fundamental screening measures in gynecology.
Cytological signs of HPV infection:
- koilocytosis - the appearance of koilocyte cells characteristically changed under the influence of the virus, having one/several dark volumetric nuclei of irregular shape and with a perinuclear light zone, vacuoles;
- dyskeratosis - the appearance of small superficial keratocyte cells with dark nuclei and specific cytoplasm.
When identifying cellular changes, the following are indicated:
- colposcopy with simultaneous implementation of tests with acetic acid and Lugol's solution;
- histological examination - examination of a tissue sample under a microscope.
Signs of HPV during colposcopy are:
- uneven absorption of Lugol's solution;
- pearly surface, white staining of the epithelium in a test with acetic acid (acetowhite epithelium);
- outgrowths, etc.
PCR typing is used to determine the specific type of virus.
Diagnosis of papillomavirus tests to identify the pathogen in the body
Source: https://medlazaret.ru/ginekologiya/vpch-analiz-kak-beretsya-u-zhenshchin.html
63-93-078. HPV typing (21 types +KVM*) HPV 6/11/16/18/31/33/35/39/45/52/58/59/26/51/53/56/66/68/73/82/ 44 (urethral scraping)
- 61-93-150 HPV screening, extended (15 types, individual/group result, + KVM*) HPV 6.11/ HPV 16, 31, 33, 35, 52, 58/ HPV 18, 39, 45, 59/ HPV 51/ HPV 56/ HPV 68 (URETHRA SCRAPPING)Biomaterial: Urethral scraping Duration: from 1 day. *Quantitative determination of 14 types of HPV of high carcinogenic risk. It is important to know the amount of detected virus: - to determine the risk of developing cervical cancer, - to monitor the dynamics of HPV carriage. Control of the collection of biomaterial allows you to exclude a false negative result (i.e. the absence of HPV due to insufficient number of epithelial cells taken). The amount of detected virus is recalculated into the units of measurement of the Digging test (for observationGo to research
- 61-93-601 Pathogens-6 (6 pathogens): Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma hominis, Mycoplasma genitalium, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Ureaplasma parvum, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Trichomonas vaginalis Biomaterial: Scraping from the urethra Duration: from 1 day. *The complex includes the main infections associated with inflammatory changes in the urogenital tract, it is recommended to study as a wholeGo to the study
- 61-94-150HPV screening, extended (15 types, individual/group result, + KVM*) HPV 6.11/ HPV 16, 31, 33, 35, 52, 58/ HPV 18, 39, 45, 59/ HPV 51/ HPV 56/ HPV 68 (SCRAPING FROM THE CERVICAL CANAL)Biomaterial: Scraping from the cervical canal Duration: from 1 day. *Quantitative determination of 14 types of HPV of high carcinogenic risk. It is important to know the amount of detected virus: - to determine the risk of developing cervical cancer, - to monitor the dynamics of HPV carriage. Control of the collection of biomaterial allows you to exclude a false negative result (i.e. the absence of HPV due to insufficient number of epithelial cells taken). The amount of detected virus is recalculated into the units of measurement of the Digging test (for observationGo to research
- 61-94-601 Pathogens-6 (6 pathogens): Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma hominis, Mycoplasma genitalium, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Ureaplasma parvum, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Trichomonas vaginalis Biomaterial: Scraping from the cervical canal Duration: from 1 day. *The complex includes the main infections associated with inflammatory changes in the urogenital tract, it is recommended to study as a wholeGo to the study
- 61-95-150HPV screening, extended (15 types, individual/group result, + KVM*) HPV 6.11/ HPV 16, 31, 33, 35, 52, 58/ HPV 18, 39, 45, 59/ HPV 51/ HPV 56/ HPV 68Biomaterial: vaginal smear Duration: from 1 weekday *Quantitative determination of 14 types of HPV of high carcinogenic risk. It is important to know the amount of detected virus: - to determine the risk of developing cervical cancer, - to monitor the dynamics of HPV carriage. Control of the collection of biomaterial allows you to exclude a false negative result (i.e. the absence of HPV due to insufficient number of epithelial cells taken). The amount of detected virus is recalculated into the units of measurement of the Digging test (for observationGo to research
- 61-95-601 Pathogens-6 (6 pathogens): Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma hominis, Mycoplasma genitalium, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Ureaplasma parvum, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Trichomonas vaginalisBiomaterial: Scraping from the vagina Duration: from 1 day. *The complex includes the main infections associated with inflammatory changes in the urogenital tract, it is recommended to study as a wholeGo to the study
- 90-69-502 Cytological examination of smears (scrapings) from the surface of the cervix (external uterine pharynx) and cervical canal using liquid cytology - Papanicolaou staining (Pap test) (material taken in a liquid transport medium) Biomaterial: Mixed scraping from the cervical canal ( endo + exocervix) Duration: from 3 days. *The “gold standard” for diagnosing cervical cancer. The sensitivity of the liquid cytology method is two times higher than that of traditional cytological research.Go to study
Source: https://citilab.ru/labs/119/services/63/63-93-078/34398.aspx