Mastopathy is the most common disease affecting the mammary glands. The pathology is characterized by an abnormal proliferation of fibrous or connective tissue in the structure of the glands. Diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy is considered one of the most specific forms of the disease.
Reasons for the development of pathology
Diffuse fibrous mastopathy, according to most experts, is an extremely unfavorable background for a woman’s health, since it creates all the conditions for the development of cancer. Often degeneration depends on what specific proliferative processes occur in each specific case.
For example, mild proliferation of breast tissue gives only a small percentage (no more than 1%) of the likelihood of developing cancer. Strong proliferative changes result in cancer pathology in 35–40% of all cases.
Hormonal problems
Diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrinous component is always associated with hormonal imbalance. Insufficiency of estrogen and progesterone against the background of increased prolactin has a specific effect on the glandular structures of the breast.
In the second half of the menstrual cycle, most women normally note the following phenomena:
- Swelling of the mammary glands;
- Swelling of the breast;
- Increased tissue sensitivity;
- Soreness of the mammary glands.
Such symptoms are usually accompanied by a vivid picture of autonomic disorders. Women complain of headaches, mood swings, emotional lability, sleep problems, and general malaise. The galaxy of these complaints was combined into one term - PMS (premenstrual symptom).
Moderate manifestation of all signs is considered normal. However, if specific sensations bring severe discomfort, sharply reducing the level of work ability, there is reason to think about a possible hormonal imbalance. Concerns should also arise if symptoms occur at different periods, without reference to menstruation.
Factors leading to hormonal imbalance
Diffuse cystic mastopathy can form against the background of unstable hormonal levels that arise due to the following circumstances:
- Pathologies of the reproductive system (frequent inflammatory processes, infections);
- Abortions or miscarriages (a woman’s body, immediately after conception, begins to actively prepare for upcoming motherhood, changing the structure and functional potential of the mammary gland);
- Pathologies of the endocrine system (obesity, thyroid problems, diabetes mellitus);
- Individual (and especially abrupt) interruption of the natural process of feeding a child with breast milk;
- Stressful situations, often repeated over a short period of time;
- Long exposure to the sun, as well as abuse of solariums (especially topless);
- Complicated family history;
- Pathologies of the uterus (endometriosis, fibroids);
- Liver diseases (cholecystitis, cirrhosis, hepatitis);
- Late childbirth;
- Breast injuries;
- Bad habits;
- Lack of a full sex life.
We also recommend viewing: Symptoms and treatment of diffuse mastopathy
Main dangers
Diffuse fibrous (cystic) mastopathy is considered a benign phenomenon. The processes of proliferation (active cell division) are combined with regression (some cells disappear). This process leads to changes in the ratio of connective tissue formations and secretory tissue.
The relationship between active proliferation and the risk of malignant neoplasms has already been mentioned. It just so happens that many patients perceive unpleasant symptoms that arise from time to time as a temporary inconvenience. Having lost precious time, women are forced to confront breast cancer.
Treatment of oncological pathologies is always a difficult, exhausting, and not always effective process of getting rid of the problem. It is much easier to work with patients, guaranteeing them a positive result, when tissue diffusion and fibrocystic mastopathy itself have just begun to form.
Types of pathology
Experts classify fibrocystic pathology of the mammary glands as follows:
- The disease is non-proliferative;
- A disease with pronounced proliferation.
According to morphological characteristics, taking into account the dominance of components, they are distinguished:
- Cystic form. The gland is filled with multiple or single cystic formations, consisting of a membrane and a liquid filler substance. A cyst occurs due to the active proliferation of epithelial tissue;
- Fibrous form. The structures of the connective tissue component are prone to growth;
- Glandular form. The development of the disease is associated with the proliferation of secretory elements;
- Mixed form. Cystic mastopathy of the mammary glands can be supplemented by fibrous components. This phenomenon is very common.
Onset of the disease
Initially, signs of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy may be absent. The clinical picture always develops from a diffuse form. The connective tissue begins to grow. Small nodules are formed, as well as a galaxy of strands in the glandular structure.
Gradually they increase in size. The disease becomes nodular in nature. Diffuse fibrinous or cystic changes in the mammary glands become more pronounced and dangerous.
Symptoms
Depending on the form (cysts, fibrous fractions) and the degree of pathology (moderate, minor or severe), the nature of the complaints will depend. The following types of symptoms are distinguished:
- Pain. With cystic mastopathy, pain is localized only in the area of pathological cell growth. FCM is manifested by pain radiating to the collarbone, neck, and arm. Increased discomfort before menstruation;
- Pathological enlargement of the mammary glands, a tendency to constant painful swelling. The symptom appears especially intensely if diffuse cystic or fibrinous mastopathy is severely advanced;
- Discharge from the nipples is an extremely dangerous sign. Clear discharge is relatively harmless. But abundant blood elements indicate that diffuse or cystic mastopathy is not far from malignant degeneration.
Diagnostic measures
If any symptoms or conditions that are of concern occur, a woman should contact her doctor immediately. To prescribe the most correct treatment, the specialist must thoroughly examine the patient.
The most necessary research:
- Palpation of the mammary glands. A mammologist will be able to detect lumps in the gland that are characteristic of cystic mastopathy. It is advisable to carry out the examination on days 6–10 from the beginning of menstruation;
- A mammogram is an X-ray of the mammary glands, which allows one to identify the form of pathology, taking into account the size, location and number of nodes. The best period for carrying out diagnostic activities is the 10th day of the cycle;
- Breast ultrasound is an informative and safe technique that allows you to accurately record all echo signs and detect cysts of the smallest sizes;
- A nipple smear allows you to more clearly determine the nature of fibrocystic mastopathy;
- Blood test for hormones;
- Tumor markers;
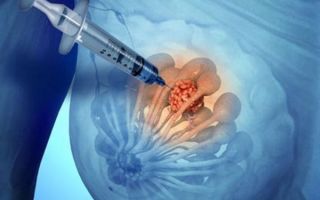
- Puncture of compactions followed by histological examination. Most often, the removal of the substance leads to the walls of the cyst sticking together, and then the seal disappears.
Conservative therapy
The doctor selects the treatment for mastopathy, taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient. For conservative therapy, the following therapeutic “tools” are used:
- Taking vitamins A, E, C and B. These biologically active substances significantly improve the immune response and create a favorable environment for normalizing hormonal levels;
- Diuretics allow effective treatment by eliminating breast swelling, thereby reducing breast tenderness;
- Use of anti-inflammatory drugs. The prerogative is non-steroidal medications such as Diclofenac or Dicloberl. It is not advisable to take such medications for a long time;
- Sedatives help you cope with stress and survive shocks associated with the disease itself. Usually, treatment based on natural ingredients is prescribed (combined herbal teas, motherwort decoctions, tinctures of valerian, lemon balm, mint).
Hormone therapy
Hormonal treatment is aimed at correcting cyclic algorithms in the “hypothalamus-pituitary-ovarian” formation. To normalize hormonal levels, as well as stabilize all processes occurring at the cellular level of the mammary glands, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Gestagens;
- Prolactin inhibitors
If mixed type mastopathy is diagnosed in women after 40 years of age, doctors prescribe contraceptives of the “Janine” type (estrogen-gestagen). Diffuse fibrotic phenomena are cured with the help of androgens. It is advisable to prescribe any hormonal drugs only after a thorough study of the general hormonal background.
Surgical intervention
The fibrous type of pathology is almost never eliminated surgically. Some cases of FCM require radical measures.
There are two options for surgical intervention: sectoral resection and enucleation. The tumor is either cut out along with the lobe of the mammary gland, or the so-called “husking” of the cyst is performed.
Source: https://myzhelezy.ru/ekzokrinnye/molochnye-zhelezy/diffuznaya-fibrozno-kistoznaya-mastopatiya-osobennosti-techeniya-i-spetsifika-lecheniya.html
Diffuse cystic mastopathy: what is dangerous, treatment and symptoms
Diffuse cystic mastopathy, or Reclus' disease (marked No. 60.1 in the medical reference book) is a process of compaction and disruption of the histological structure of the mammary gland due to the growth of fibrous tissue, displacement of the glandular component.
During this process, benign tumors are formed in the mammary gland - cystic formations ranging in size from 0.01 mm to 6-8 cm and of all possible densities. Due to the abundance of cysts, cavities are formed in which fluid accumulates and stagnates - secretion, subsequently the cysts begin to expand.
Small cysts can unite to form multi-chamber cysts. According to medical statistics, 60% of women are affected by the disease.
Classifications:
- Cystic - the development of cysts in the mammary gland.
- Fibrosis of the mammary glands is an increase in connective tissue.
- Diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component - mixed - enlargement of connective tissue and mammary glands with the presence of compactions.
- Nodular mastopathy – Reclus disease.
Fibrofatty mastopathy is distinguished when glandular tissue is replaced by fatty and connective tissue. A disease that develops in both breasts is called bilateral diffuse fibrous cystic mastopathy. The risk of developing it is 40% high among representatives of the fair sex under 35 years of age. A woman over 40 years old is prone to developing a nodular type of unilateral mastopathy.
The disease belongs to the ICD-10 classification (international classification of diseases), adopted in January 2007.
Reasons for development
Reclus' disease has not been fully studied, and its causes are unclear. But more often the diagnosis is made to women suffering from prolonged hormonal disorders with excess estrogen.
Factors associated with the development of mastopathy:
- venereal diseases;
- menstrual irregularities;
- many abortions, miscarriages;
- a sharp decrease or increase in intimate activity, its absence;
- infertility;
- childbirth in women over 45 years of age;
- hereditary factor;
- breast insolation (direct exposure to sunlight);
- liver diseases;
- incorrect use of contraceptives.
According to observations, the most significant factor in the occurrence of fibrosis is considered to be a deficiency of the hormone progesterone with a large amount of estrogens at the same time. Increased production of prolactin is also a possible beginning of the development of mastopathy.
Sometimes the cure for diffuse mastopathy is pregnancy. Once you become pregnant, you can stabilize your hormonal status and health. In isolated cases, women with many children are exposed to the described disease.
Symptoms
One of the common symptoms is the detection of lumps in the mammary gland. And the first alarm bell may be chest discomfort during PMS. Gradually, pain spreads to the armpits and shoulder blades. Additionally, similar symptoms are noted:
- Heaviness, pain and other unpleasant sensations in the breasts.
- Swelling, disproportionate change in breast size.
- Growth of lymph nodes in the armpit area.
- Fluid released from the nipples (in the form of mucus, bloody fluid, lactose).
Almost all symptoms of mastopathy directly interact with PMS and worsen on the eve of menstruation. 13% of women do not feel pain or discomfort from the disease at all.
In addition, symptoms that indicate the occurrence of cancer are called: a change in the condition of the skin in the area of the gland in the form of a “lemon peel” and excessive enlargement of the lymph nodes in the armpits.
Possible complications
The only serious complication that occurs as a consequence of mastopathy is breast cancer: the transformation of a benign tumor into a malignant one. This happens when the disease is ignored.
There are two types of breast cancer – invasive and non-invasive.
Non-invasive type - the first stage of cancer, characterized by the complete absence of atypical cells in the mammary gland and nearby. At this stage, the goal of pathology is to affect tissue locally, most often in the mammary duct. Almost always successfully removed by a surgeon without other complications or relapses.
The invasive form is the case when cancer affects nearby tissues and manifests itself as the most dangerous oncological pathology. Kinds:
- Ductal, or ductal - the development of cancer in the walls of the milk flows themselves. Over time, it spreads to nearby tissues.
- Inflammatory - develops similar to mastitis. It is extremely rare. Manifests itself in painful redness on the chest and fever.
- Paget's disease is an oncological disease associated with the appearance of ulcers and changes in the shape of the areola and nipples.
The most common solution to breast cancer is surgery, which has two options: lumpectomy, which is the removal of specific areas of the breast, and mastectomy, which is the removal of entire breasts.
Mastectomy is performed if:
- the patient has small breast size;
- the tumor has spread to the chest wall;
- the tumor is too large.
When the tumors are removed and the chance of their reappearing is low, doctors continue to operate to restore the shape and volume of the breast. If this is not possible, the patient is offered a range of options to improve the appearance of the breast based on personal preference.
Breast reconstruction is divided into two options:
- one-stage – performed simultaneously with surgery to remove the tumor;
- delayed – carried out if it is not possible to qualitatively restore the breast or there is a possibility of complications. Performed after the entire healing process.
Reconstructive surgeries vary depending on the type of tissue used to reconstruct the breast. Autologous tissue (taken from one’s own body) or allotissue (implants) is suitable for this purpose.
Chemotherapy can be prescribed before, instead of, or after surgery. In the first case, this is to reduce the primary tumor so that lumpectomy becomes possible, in the third, to resolve metastases and reduce the chance of their possible appearance in the future.
Radiation therapy is prescribed to prevent relapses, remove tumors that cannot be manually removed, and treat symptoms.
Diagnosis
The initial examination begins with the collection of information about the disease.
Recognition of the root causes of mastopathy depends on the nature of PMS; number of fetal removals, miscarriages; hereditary disposition and other risk factors that only the patient knows about. Afterwards, specific complaints are specified, the moment of their occurrence, frequency, and relationship with PMS. There are two types of palpation.
Breast self-examination
Breast condition assessment consists of:
- Ultrasound (to find out if there are echo signs of mastopathy);
- electrical impedance and biocontrast mammography;
- pneumocystographic examination;
- blood test;
- blood test for thyroxine, prolactin and thyroid-stimulating hormone;
- palpation;
- MRI of the breast;
- diaphanoscopy;
- general inspection.
If signs of nodules are found, a biopsy of the gland is performed (a tissue sample is removed from the breasts with a needle).
An essential and obligatory part of the examination is the study of a woman’s personal hormonal background, especially the level of estrogen and prolactin. In case of mastopathy, the patient should be under the supervision of a doctor at all times.
The difficulty of diagnosis is understandable. Clinical, radiological, sonographic and sometimes cytological examinations provide information that nodular mastopathy is both benign and malignant. And this calls into question what course of treatment should be used.
It is impossible to spread fibrosis; it is a non-contagious disease. The chance of its occurrence depends on the woman’s personal factors.
Treatment of mastopathy
The most accessible and simple cure is to correct the hormonal levels of the entire body. When choosing a method to treat fibrosis, you need to consult with other doctors. For complete hormonal treatment, the conclusions of three specialists are necessary - a mammologist, a gynecologist, and an endocrinologist. Hormonal medications are rarely prescribed with the approval of only one doctor.
With severe estrogenism, the main goal is to reduce the level of estrogen influence on the breasts. To correct this, tamoxifen and toremifene citrate are prescribed.
To correct and normalize PMS, birth control pills are used, which are selected according to the hormonal situation.
When the reason is the functionality of the thyroid gland, drugs are used that regulate the production of thyroid hormones.
It is difficult to completely cure benign fibrosis - there is always a percentage chance of relapse. But many women live with this disease without even noticing the discomfort. You can live 50 or 5 years with mastopathy; this is a pure lottery with the risk of developing cancer.
Traditional treatment
The main folk remedies for the treatment of cystic mastopathy are St. John's wort and valerian, and tea based on them.
Ingredients:
- crushed dry valerian root (1 tsp);
- caraway seeds (1.5 tsp);
- fennel seeds (1.5 tsp);
- St. John's wort (3 tsp);
- table soda (0.5 tsp).
Preparation and use process:
- Mix the ingredients dry and store in an airtight container.
- To prepare tea, mix with hot water in a ratio of 1 to 6 and let steep for 30-40 minutes. It is important to cover with a lid while steeping.
- Take 3 times before meals.
Such remedies act like homeopathy; using them as the main treatment is dangerous!
Prevention
Mastopathy is a common disease. The chances of avoiding it are close to the chances of getting sick. However, these chances can be increased.
It is worth paying special attention to diseases associated with the mammary gland and hormonal levels, and these specifically include:
- ovarian diseases;
- pathology of the uterus;
- diseases of the endocrine glands;
- liver failure;
- venereal problems.
Also, do not neglect mechanical injuries to the breasts (cuts, bruises, injections).
You should pay attention to the bra, and specifically the size. A bra that is too small can lead to breast stretching or deformation. Long-term exposure to sunlight on the chest is highly discouraged.
The main principle of preventing mastopathy and other diseases is a healthy lifestyle.
Source: https://onko.guru/dobro/diffuznaya-kistoznaya-mastopatiya.html
What is diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy and how to treat it
Lumps in the chest
23.03.2018
8.2 thousand
5.5 thousand
6 min.
Diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy is a common pathology of the mammary glands, which occurs due to various factors in women of different age categories.
The disease can cause the degeneration of neoplasms into malignant tumors. Therefore, it is very important to consult a doctor promptly.
Treatment depends on the cause of the pathology and includes the use of drugs, folk remedies, and in some cases surgery.
The number of representatives of the fair sex with the presence of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy is growing every year. Occurs in 35-70% of cases in girls of childbearing age. If there are concomitant gynecological diseases, the frequency increases to 98%. In rare cases, benign neoplasms occur in adolescents and girls during menarche.
During premenopause, pathology is found in 20% of women. During menopause, the appearance of new cysts and nodes was not detected. This proves that ovarian hormones are involved in the occurrence of the disease. At the age of 30-40 years, a large number of small cysts are most often detected; large size of neoplasms is typical for patients over 35 years of age.
Signs of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy can be confused with similar diseases in the field of mammology. Most often, the patient notes the following symptoms:
| Symptom | Description |
| Pain syndrome | It has a pressing, aching, burning or stabbing character. May radiate to the armpit or neck area. Most often appears in the second half of the cycle, before the onset of menstruation. Moderate pain is noted during palpation |
| Nipple discharge | The consistency of the liquid is similar to colostrum, has a white or yellowish color, the appearance of a greenish tint indicates the presence of an infectious process |
| The appearance of lumps in the mammary gland | In the diffuse fibrous form, the formations have a round or oval appearance; they usually disappear after menstruation. They appear again in the next cycle. Fibrocystic mastopathy is characterized by the appearance of movable seals that are filled with fluid. Cysts in different phases of the menstrual cycle can change their size, position and shape |
| Condition of the lymph nodes | Some patients experience enlargement and pain, while others have subtle changes. |
| Breast swelling | Most noticeable in the luteal phase. There is an increase in the volume of the mammary gland, nodes and cyst-like compactions. There is a feeling of heaviness and burning, sometimes redness of the skin |
The symptoms are quite varied. And in each individual woman they manifest themselves differently depending on the course of the disease, age and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
In addition to the listed signs, there is a deterioration in the general condition, an increase in temperature, nausea, headaches, and changes in the menstrual cycle.
Based on the structure and characteristic tissue damage, diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy comes in the following forms:
- With a predominance of the ferrous component . Lobules of glandular tissue grow. Seals can be felt throughout the mammary gland or in certain areas. As the disease progresses, neoplasms lose clear boundaries and spread into surrounding tissues.
- With a predominance of the fibrous component . A seal forms in the connective tissue. The epithelium actively grows, narrowing the milk ducts. Fibrosis predominantly occurs during premenopause. During the examination, specific lumps are felt in the upper parts of the chest. The pain intensifies before the onset of menstruation.
- With a predominance of the cystic component . The formations are filled with fluid and covered with connective tissue. The contents come in different colors and consistencies. In some cases, during the opening of the cysts, an admixture of blood and the deposition of calcium salts are discovered. These signs indicate the development of a malignant process. Cysts develop in the body if estrogen levels are elevated.
Sometimes a mixed type of mastopathy occurs. It has all the features inherent in each form. Without proper treatment, tumors fill the entire mammary gland.
Depending on the number of detected disorders, the disease occurs in minor, moderate and severe forms. Based on the location, mastopathy can be unilateral or bilateral.
The main reason provoking the development of pathology is a hormonal imbalance.
Progesterone, estrogen, insulin, corticosteroids, androgens, thyroid-stimulating hormone, human chorionic gonadotropin and prolactin influence the development of the mammary gland, constant changes in them during puberty and during pregnancy and lactation. Any hormonal imbalance leads to dysplastic changes in breast tissue.
Blood prolactin has an important influence on the development of the disease; it stimulates the metabolic processes of the mammary gland epithelium throughout life. The occurrence of hyperprolactinemia causes swelling, engorgement, pain and swelling of the breast.
There are also a large number of causes of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy, among them:
- heredity;
- early puberty;
- late onset of menopause;
- abortions and miscarriages;
- problems with conception or complete absence of pregnancy;
- absence or short period of breastfeeding;
- the presence of frequent stressful situations;
- age over 40 years;
- metabolic disorder - diabetes mellitus, obesity, dystrophy, enlarged thyroid gland;
- liver pathologies;
- diseases of the genitourinary system;
- uncontrolled treatment with hormonal drugs.
The lack of regular sex life has a bad effect on the reproductive system, provoking changes in the mammary glands.
Treatment of DFCM is carried out using conservative methods, folk remedies and surgery. Therapy is selected individually. Conservative methods include hormonal and non-hormonal treatment.
It is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination to identify and eliminate the possible cause of the disease.
Non-hormonal therapy includes:
- Nutrition adjustments . Eliminate foods containing methylxanthine from your diet: spicy foods, chocolate, caffeine. This component causes the proliferation of fibrous tissue. The menu must include food enriched with fiber (fresh vegetables and fruits).
- Healthy lifestyle . This includes not only quitting smoking, alcohol and drugs. It is necessary to exercise, get enough sleep, avoid stressful situations, and observe personal hygiene rules.
- Taking vitamin complexes . Vitamins of groups A, B, C, E help normalize the metabolic process in breast tissue.
- Use of immunomodulators. The drugs help increase the body's defenses and its overall resistance.
Other means:
| Group | Description | Drugs |
| Hepatoprotectors | Helps normalize liver function | Legalon, Karsil, Hofitol, etc. |
| Sedatives | Necessary to improve psycho-emotional state. The most popular are products based on motherwort, valerian and hops | Valerian extract, Motherwort, Persen, etc. |
| Diuretics | Diuretic medications to reduce severe swelling of the breast | Amiloride, Metolazone, Furosemide, etc. |
| Anti-inflammatory drugs | Eliminate pain, slow down the production of substances that disrupt blood flow | Mulimen, Wobenzym |
An important point in treatment is the normalization of hormonal levels. For this purpose, the following are prescribed: inhibitors of prolactin synthesis (Caberlin, Bromocriptine, Dostinex), gestagens (Duphaston, Primolut, Utrozhestan). Girls under the age of 35 are prescribed estrogen-progestogen COCs (Marvelon, Janine). They help normalize the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle.
Treatment with traditional medicine occurs in the early stages of the disease and only after the approval of the attending physician. Well proven:
- Burdock. It has absorbable properties. Fresh and well-washed leaves are applied to the chest at night.
- Cabbage. Compresses made from leaves are especially effective. To do this, mix the ground leaves with sour milk. The porridge is applied to the mammary gland pre-lubricated with butter. After which it must be wrapped in cellophane.
- Honey _ To prepare the mixture you need 2 tbsp. l. honey Add 100 ml of castor oil, juice of 2 lemons and ground burdock root. The consistency of the product is similar to sour cream. Apply to a cloth and apply to the chest.
Surgical treatment is necessary if the following indications exist:
- intraductal adenoma;
- breast fibroadenoma;
- active cyst growth.
During surgery the following is used:
- Sclerosis. A special substance is injected into the neoplasm, causing the defect to heal.
- Resection. The affected area is excised. After which the tissue is sent for histological examination.
The pathology responds well to treatment and has positive dynamics. DFCM itself does not pose a threat to a woman’s life, which allows her to live a long life.
Like any other disease, it is better to prevent mastopathy. To do this, it is necessary to follow preventive measures:
- undergo regular examinations with a mammologist, gynecologist and other doctors, this will identify the presence of abnormalities;
- completely cure existing diseases of the genitourinary system;
- avoid stress, lead a healthy lifestyle;
- do not perform abortions or other actions leading to hormonal imbalance;
- perform breast self-examination;
- choose a bra based on size and from high-quality fabrics to prevent disruption of blood flow in the chest.
A timely visit to the doctor will allow you to recognize the disease in time and prevent the development of complications.
Source: https://pokrasote.com/breast/lump/diffuznaya-fibrozno-kistoznaya-mastopatiya.html
Diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy
Diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy (FCM) is a benign process accompanied by abnormal development of mammary gland tissue.
This pathology is a type of mastopathy and differs from its other types by the appearance of cysts, papillomas in the milk ducts, and tumors from glandular tissue cells.
Currently, more than 50% of women suffer from diffuse FCM. As a rule, it is detected between the ages of 30 and 50 years.
Causes
The main cause of the disease is hormonal disorders. Women with diffuse FCM have increased levels of estrogen in the blood. This occurs against the background of progesterone deficiency, which provokes the proliferation of gland tissue (connective tissue framework, alveolar epithelium). There is also an increased production of prolactin, a pregnancy hormone involved in lactation processes.
There are other provoking factors:
- injuries to the mammary glands due to prolonged wearing of uncomfortable underwear and compressive clothing, as well as blows;
- genetically determined predisposition, burdened heredity, the presence in the family branch of cases of breast cancer, mastopathy;
- treatment with hormonal drugs, use of hormonal contraceptives;
- diabetes mellitus, obesity;
- functional disorders of the endocrine system, thyroid diseases;
- sexual disorders, poor quality and irregular sex life;
- diseases of the reproductive system, diagnosed infertility, miscarriages, abortions, late pregnancy terminations.
It has also been established that diffuse FCM can occur during late pregnancy (after 35 years), short-term breastfeeding (less than 3 months) and complete refusal of breastfeeding. A woman’s lifestyle is also important: exposure to stress, drinking alcohol and smoking increase the risk of developing the disease.
Classification
The diffuse form of the disease is divided into:
- adenosis – mastopathy with a predominance of the glandular component;
- fibrocystic – mastopathy with a predominance of the cystic component;
- fibroadenosis – mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component;
- sclerosing adenosis;
- mixed form.
In terms of localization, diffuse FCM can be unilateral or bilateral (affecting one or both mammary glands). According to the severity of clinical manifestations, moderate, minor and severe forms are distinguished.
Symptoms
The main symptom of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy of the mammary glands is a large number of small cavities and seals. Often the tumors are mobile and affect both breasts. Most of them are difficult to detect by palpation. During the menstrual cycle they change size, shape and location.
Possible enlarged lymph nodes. This may occur unnoticeably or be accompanied by severe pain (depending on the characteristics of the body).
Nipple discharge is another symptom characteristic of diffuse FCM. The secretion looks like a milky white, pale yellow or clear liquid. Sometimes there is blood present - a signal indicating a rupture of a small blood vessel. The discharge is irregular and appears in the second phase of the menstrual cycle.
Pain in the mammary gland can be burning, stabbing, or pressing.
Some women complain of constant pain, which subsides after local therapeutic procedures (wraps, compresses, lotions).
Sometimes it spreads to the back, shoulder or armpit area. At the same time, pronounced swelling of the breast is observed, accompanied by an increase in cysts and nodes, a feeling of fullness and heaviness.
Often with the disease, there is an increase in body temperature, headache, dizziness, nausea, general malaise, weakness, bloating and even fainting. The woman experiences mood swings, is irritated, and has trouble sleeping.
In the early stages, these symptoms may subside after the start of menstruation. The patient feels a reduction in the size of the pathological nodules and a significant improvement in well-being. However, this is a temporary phenomenon. The disease does not disappear, but only reacts to changes in hormonal levels.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy of the mammary glands is based on the patient’s sensations and medical imaging methods.
First of all, the mammologist palpates the glands, studies the patient’s history and complaints. Then he orders additional examinations. One of them is ultrasound diagnostics.
It reveals formed cysts and pathological changes in breast tissue.
Non-contact mammography (breast x-ray) is considered more informative. It accurately determines the type of mastopathy, micro- and macrocalcifications (fibrous nodes and cysts). The study is carried out on the sixth or seventh day of the menstrual cycle, in frontal and lateral projections. Contraindications to the study are pregnancy, breastfeeding and age under 35 years.
Breast thermography is sometimes used. The purpose of this diagnosis is to identify areas of increased thermal activity. If necessary, suspicious formations are punctured. Cells are removed from the formed node under ultrasound control and using a syringe to examine them under a microscope, determine the structure of the cysts and rule out breast cancer.
If there is discharge from the nipple, a swab is taken. The material taken is sent for cytological examination. The patient should also consult an endocrinologist. The doctor will order a blood test for liver enzymes and thyroid hormones. A biochemical blood test is needed to rule out diabetes.
Differential diagnosis of diffuse FCM is necessary, since its symptoms are similar to those of breast cancer, fibroadenoma, hyperprolactinemia and premenstrual syndrome.
Treatment
The doctor decides what method will be used to treat diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy, taking into account the form, stage and characteristics of the course of the disease.
Only an integrated approach is effective, including the elimination of provoking and concomitant diseases, medicinal effects on pathological processes, adherence to diet and contraindications.
It is extremely important to make sure that the tumors are not malignant.
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating hormonal imbalances and restoring the full functioning of all organs. For this purpose, physiotherapy (laser treatment and electrophoresis) and various medications are used:
- iodine preparations;
- sedatives - to stabilize the psycho-emotional background;
- analgesics – to eliminate pain;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – relieve swelling and inflammation;
- diuretics - to maintain kidney and liver function.
The complex effects of these medications are systemic in nature, so only a doctor should prescribe them.
Vitamin therapy provides good results. To strengthen the vascular wall and reduce swelling, taking vitamins A, C and P is recommended. B vitamins stimulate metabolism. Vitamin E is a natural antioxidant and affects hormonal and fat metabolism.
Hormonal therapy is selected according to the woman’s age. Patients in the reproductive period are prescribed oral hormonal contraceptives.
Progestogens that are taken in the second phase of the menstrual cycle (Duphaston, Utrozhestan) are also effective. In perimenopausal age, antiestrogens (Tamoxifen) and androgens (Testobromlecid, Methyltestosterone) are recommended.
In case of pronounced cyclicality of the pathology, drugs that block the production of prolactin and homeopathic remedies are used.
Diet plays an important role in the treatment of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy. You should reduce your salt intake, give up fatty foods, chocolate and fast food. It is recommended to replace strong coffee and black tea with herbal or green tea.
The diet should be dominated by foods rich in fiber - cereals, fresh vegetables and fruits. It is advisable to eat fish and lean meats twice a week.
By adhering to these rules, you can not only speed up recovery, but also reduce the risk of developing the disease.
Surgical treatment is performed in very rare cases.
The form of surgical intervention is selected based on the indications: if breast cancer is suspected, rapid tumor growth (within 3 months), complications (suppuration), recurrence of cysts after a recent puncture.
The nodes are removed through sectoral resection. During surgery, the tumor is excised along with a healthy part of the breast. It lasts only 30–40 minutes. After a few hours, the patient can leave the clinic.
If a cyst is detected, it is punctured, removing the cystic fluid. Sclerosing agents are injected into the resulting cavity. They promote fusion of the walls of the cystic membrane.
It is also possible to remove the cyst with suturing of the mammary gland. During the operation, an urgent histological examination of the excised material is performed.
If the results confirm cancer, the scope of surgery is expanded to include removal of the entire mammary gland.
During the treatment of diffuse FCM, it is prohibited to drink alcohol and smoke. Strong thermal effects can activate the pathological process, so you should limit visits to solariums and baths, sunbathe moderately and in a swimsuit. The bra should not put pressure on the breasts.
Pregnancy and illness
With diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy of the mammary glands, pregnancy and a successful birth are possible. If conception occurs, it is important to inform your doctor. Mammography, examination of the milk ducts by injecting dyes, and other complex procedures are not recommended for pregnant women. It is recommended to be careful when treating with herbs.
Typically, expectant mothers are prescribed light maintenance therapy with hormonal correction. The doctor can prescribe safe herbal medicines that have a calming, decongestant and analgesic effect.
Breastfeeding is also allowed with diffuse FCM. Often it helps to correct the patient’s condition. Cysts may decrease in size or disappear altogether. The only thing is that it is important not to feed the baby for too long (no more than 12 months). Otherwise, the risk of tumors increases.
Prevention and possible complications
Compliance with preventive measures reduces the risk of the disease and promotes a speedy recovery if it occurs. These include: giving up bad habits, avoiding stressful situations, choosing the right underwear, maintaining an active lifestyle, reducing salt consumption, timely treatment of diseases of the pelvic organs.
It is important to competently select hormonal contraceptives and regularly visit an oncologist and mammologist (at least once a year). Breastfeeding a child for more than 6 months reduces the risk of developing cancer by 2 times.
All women, including healthy ones, need to learn how to check their mammary glands on their own. This advice is especially relevant in the periclimacteric period (after the age of 45). This is done by visually examining the breast in the mirror and feeling it while lying down and standing. If any abnormal lump is detected, you should consult a doctor.
Despite the benign course, fibrocystic changes are a favorable background for the development of malignant diseases. With active proliferation (growth) of affected cells, the risk of cancer is 32%. With less activity of the pathological process, the risk decreases to 1%.
Source: https://dolgojit.net/diffuznaia-fibrozno-kistoznaia-mastopatiia.php
What is diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy: diagnosis and treatment
- Mastopathy is a multifaceted disease that can be expressed in different forms.
- Depending on the nature, size and number of neoplasms, it is divided into several categories.
- Each treatment has its own nuances, without which complete recovery is impossible.
What is fibrocystic mastopathy, why is it dangerous and how to treat it.
Find out below.
Mastopathy is a disease of the mammary gland, characterized by the appearance of benign neoplasms against the background of altered hormonal levels. The proliferation of glandular or connective tissue forms compactions or cavities of various sizes.
It comes in different forms. It is the nature of the formations that gives the name mastopathy. It can be fibrous, cystic or mixed. With diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy of mixed form, a predominance of the fibrous or cystic component is possible.
Another gradation of the disease concerns the size and location of the tumor.
Large single formations cause a nodular form, small and numerous formations are characteristic of a diffuse form.
Diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy: what is it? Diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy is the formation of various small compactions and cavities filled with fluid (cysts). They usually affect both breasts.
A diffuse form of fibrocystic mastopathy, expressed more often in women of childbearing age (up to 40 years). Nodular forms are characteristic of the period of menopause and premenopause.
Diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy - photo:
The main cause of mastopathy is severe hormonal imbalance. Due to various factors, the ovaries begin to produce an increased amount of estrogen, while the level of progesterone drops.
Fibrocystic mastopathy - causes:
- hereditary predisposition;
- the onset of menarche in adolescence;
- the onset of premenopause;
- ovarian or thyroid dysfunction;
- termination of pregnancy;
- childbirth;
- long-term breastfeeding;
- refusal of breastfeeding;
- treatment with hormonal drugs.
Almost all women are at risk, from adolescence until the onset of climate change. Benign breast tumors are found in younger girls, infants and even men. However, according to statistics, the disease most often occurs in women of childbearing age or those who have entered premenopause.
Main symptoms
Diffuse fibrocystic breast disease has the following symptoms:
- A large number of small lumps and cavities in the chest . Typically, neoplasms affect both mammary glands, and during the menstrual cycle they can change shape, size and location. The seals are mobile, most of them are difficult to detect by palpation.
- Enlarged lymph nodes . Depends on the characteristics of the body. In some cases, the node swells and becomes painful, in others the increase is barely noticeable.
- Nipple discharge . More often they appear as a clear, pale yellow or milky white liquid. They usually appear in the second half of the menstrual cycle and are irregular. Sometimes blood appears in the discharge - a signal that a small blood vessel has burst under pressure.
- Severe swelling of the chest . It occurs in the second half of the cycle and is accompanied by an increase in nodes and cysts. Accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and fullness, sometimes a burning sensation occurs.
- Pain in the mammary gland . It can be pressing, stabbing, burning. It usually comes in the second half of the cycle, but some patients complain of constant pain. It occurs after local therapeutic procedures (lotions, compresses, wraps).
- Temperature increase . Often accompanied by swelling and pain. Depends on the individual characteristics of the body. Sometimes accompanied by dizziness, headache, nausea and even fainting.
The symptoms of mastopathy are very diverse and can masquerade as any disease. If you notice the presence of at least two of them, contact your doctor immediately to confirm the diagnosis and develop an individual treatment regimen.
Diagnostic options
The diffuse form of mastopathy with a large number of small lumps and cysts is difficult to detect during self-examination, especially in the initial stage. Women may go to the doctor with complaints of chest pain, nipple discharge, or changes in the menstrual cycle.
To clarify the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed an ultrasound examination. Ultrasound of fibrocystic mastopathy in women under 35-40 years old gives especially good results.
For older patients, mammography is recommended, which gives more accurate results. Non-contact mammography of fibrocystic mastopathy is contraindicated in women under 35 years of age, pregnant and lactating women.
To clarify the diagnosis, a biochemical blood test may be prescribed; to identify pathologies of other reproductive organs, a referral to a gynecologist is issued to examine the condition of the uterus and ovaries.
When tumors and cysts are detected, a puncture is performed, and the tissue taken is sent for cytological examination . The purpose of the operation is to exclude the appearance of malignant tumors.
If the benign nature of the tumors is confirmed, the patient is prescribed appropriate therapeutic treatment. If malignant cells are detected, chemotherapy, mastectomy or partial resection of the breast is recommended.
Treatment
Even in the initial stages of mastopathy, treatment is prescribed only by a mammologist. What is not allowed for fibrocystic mastopathy? You should not self-medicate, trying on yourself one by one all available drugs and traditional recipes.
The reason for the appearance of advanced fibrocystic disease is a late visit to the doctor. Only a specialist can correctly assess the nature of neoplasms, the state of hormonal levels, and select drugs that will not contradict each other and cause side effects.
In the initial stages, phytotherapeutic and homeopathic preparations are offered:
- pills;
- ointments;
- infusions;
- teas
- Mastodinon in the form of an alcoholic herbal infusion, Phytolon containing brown algae extract have proven themselves well.
- For diffuse forms, Klamin is used, which contains an increased proportion of iodine and has a pronounced antitumor effect.
- To relieve pain symptoms are prescribed:
- For severe tumors and cysts, hormonal treatment is recommended using:
- tablets;
- injections;
- subcutaneous implantations.
The latest generation of contraceptives have proven themselves well and do not cause side effects. The drugs increase the amount of prolactin and suppress the formation of estrogen, inhibiting the development of tumors and reducing existing ones. In this phase, Utrogestan is effective in the form of tablets or vaginal suppositories, containing natural prolactin.
If the development of formations continues, patients receive stronger therapy in the form of testosterone injections or steroids . They are usually carried out in courses, alternating with lighter maintenance medications.
During hormonal treatment, you should be careful with herbal preparations; many plants inhibit the effectiveness of hormonal drugs.
Among folk remedies, they are especially effective:
- soothing herbal mixtures;
- homemade balms;
- tinctures;
- ointments.
To resolve tumors and alleviate the general condition they use:
- burdock;
- plantain;
- red brush;
- celandine;
- hop cones;
- yarrow;
- St. John's wort;
- calendula.
Read about the correct use of burdock, cabbage leaves and red brush for mastopathy on our website.
Used to relieve pain and severity:
- honey or clay applications;
- compresses made from cabbage leaves or burdock.
All methods of traditional therapy should be discussed with your doctor and included in the overall treatment regimen.
Diet is very important for the treatment of mastopathy. Getting rid of obesity, which contributes to increased estrogen production, will help improve your condition.
The diet should be nutritious, varied and not too high in calories.
Be sure to include at least 500 g of vegetables and fruits in your daily menu, preferably fresh, stewed or steamed. The diet is varied with low-fat dairy products, lean poultry, sea and freshwater fish, cereals, legumes and soybeans.
IMPORTANT ! Avoid caffeinated drinks, alcohol of any kind, fatty and fried foods, red meat and hydrogenated oil.
The cystic form requires moderate fluid intake. Eliminate from the menu foods with a lot of salt that cause swelling, and carbonated drinks. Drink clean bottled water, green and herbal tea, homemade berry fruit drinks, compotes and freshly squeezed juices diluted with water.
Illness and pregnancy
With any form of fibrocystic mastopathy of the breast, pregnancy and a successful birth are possible. Since the diffuse form is more common in young women, pregnancy often occurs against the background of the disease.
When it occurs, it is important to inform your doctor. Mammography, examination of the milk ducts by injecting a dye, and some other procedures are not recommended for pregnant women.
You should also be careful when using herbs. Even harmless plants can cause problems in the fetus, including miscarriage.
Typically, pregnant women are prescribed light maintenance therapy with hormonal correction.
Safe remedies from the arsenal of herbalists are prescribed that have a calming, analgesic, and decongestant effect.
Is it possible to breastfeed with fibrocystic mastopathy? Often pregnancy itself and subsequent breastfeeding help correct the condition. Doctors note cases when, during breastfeeding, fibroids and cysts decreased in size or completely resolved.
It is important not to feed your baby for too long . Breastfeeding for more than 12 months is a risk factor that can cause not only benign, but also malignant tumors.
Find out about fibrocystic mastopathy during pregnancy in the article.
Fibroids and cysts themselves do not degenerate into cancerous tumors. However, an increased amount of estrogen is a favorable background for the development of malignant neoplasms.
Can fibrocystic mastopathy develop into cancer? Fibrocystic mastopathy cancer can arise next to harmless cysts; in conditions of hormonal imbalance and reduced immunity, they are guaranteed successful and rapid growth. There is a high risk of not noticing a new seal next to a large number of existing ones .
To avoid the occurrence of cancerous tumors, it is necessary not to delay the correction of hormonal levels. Usually, the doctor prescribes light hormonal therapy at the initial stage of the disease; in more advanced cases, injections of testosterone, which blocks estrogens, are used.
Diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy in women is not a death sentence, but a reason to take your health seriously. The treatment will be long, but if you scrupulously follow the doctor’s recommendations, recovery will occur. It is important not to interrupt the course and not try questionable and even harmful recipes on yourself at the expense of proven schemes.
You can find more information on this topic in the Diffuse mastopathy section.
Source: https://nesekret.net/mastopatiya/raznovidnosti/diffuznaya/d-fibrozno-kistoznaya