Among the many defects of the cervix, erosion occupies a special place. This pathology is very common among representatives of the fair half of humanity who are part of the reproductive group.
Today, unfortunately, there are often cases when advanced erosion is diagnosed.
This pathology is very dangerous, since there is a high probability of its transformation into a malignant form.
Causes of advanced erosion
If a gynecologist detects erosion during a routine examination, the woman should immediately begin to eliminate it. Otherwise, the pathology will transform into such a degree as advanced cervical erosion.
To prevent the development of dangerous complications, you should familiarize yourself with the reasons why the disease develops:
- the main reason is the presence of infection in the reproductive system;
- often such a negative phenomenon is provoked by sexually transmitted diseases;
- less often, but can provoke the development of erosion and pathology of bacterial origin.
In addition, the disease in question can occur after the resolution of childbirth, during an abortion, and as a result of mechanical trauma, after a surgical procedure.
Stages of erosion
Currently, there are 3 stages of cervical erosion:
1st degree: inflammation of cervical erosion. A negative phenomenon is formed as a result of infection entering the cervical epithelium. In turn, this degree is classified into three stages of development:
- attack of pathogenic microorganisms, alteration;
- formation of swelling followed by effusion of serous or purulent exudate into the vaginal lumen, exudation;
- intensive tissue growth with subsequent replacement of the defect, proliferation.
In the absence of adequate treatment, this stage progresses to the next stage;
2nd degree: formation of a wound on the surface of the mucosa. As a result of the destruction of the epithelium and lack of therapy, a wound forms on the surface of the cervix, which does not heal for a long time;
3rd degree: transformation of the wound site into ectopia. With this abnormal process, the wound does not heal properly, causing the surface to become covered with cells from the cervical canal. And the multilayer epithelium is replaced by single-layer cells.
Important: To determine the stage of the defect, the doctor uses a colcoscope. This technique allows you to accurately determine the extent of damage to the mucous membrane of the neck.
Lack of timely therapy leads to the development of dysplasia, which can gradually turn into cancer.
Types of erosion
In addition to the degree of development, the disease in question is also classified by type:
1. Pseudo-erosion, congenital origin. This type is not always considered a pathology. Congenital cervical erosion is often not detected during routine examination. As a rule, the appearance of formation is associated with the peculiarities of the formation of the reproductive system. Moreover, with age, this type of disease can become inflamed, but does not transform into a malignant neoplasm;
2. Pseudo-erosion, acquired nature. Such a pathological process occurs as a result of hormonal imbalance or as a result of injury. This type of erosion is determined by visual inspection and can have several varieties
- follicular, with the presence of cysts;
- papillary with signs of inflammation;
- mixed, having symptoms of follicular and papillary.
Pseudo-erosion can develop over a long period of time and increase in size.
3. True. This type is formed due to injury and subsequent destruction of the epithelium. This type of formation is similar to an ulcer. In addition, when it comes into contact with a gynecological instrument, purulent discharge often comes out of the wound.
Important: If an acquired pseudo-erosion is detected, treatment should begin immediately. Because there is a risk of the defect transforming into uterine fibroids.
Regardless of the type, the pathology in question should be treated immediately and not neglected. Otherwise, negative consequences may develop.
Signs of advanced pathology
The main feature of the uterine cervix is the absence of nerve endings. In view of this, when the damage is formed, the feeling of discomfort does not bother the woman. As a rule, patients more often turn to a gynecologist with complaints about other pathologies of the reproductive system. And during the examination, erosion is revealed.
If the disease in question is diagnosed in a timely manner, there is a chance of defeating the pathology with conservative treatment. It is necessary to take into account the fact that in the initial stage of development, symptoms are practically absent. And often the problem that has arisen can only be determined by inspection. Therefore, a planned visit to the gynecologist should not be ignored.
If a woman develops symptoms such as:
- the appearance of discharge with small fragments of blood on any day of the cycle that is not related to menstruation;
- discomfort felt in the groin area and spreading to the abdomen;
- discomfort that occurs during intimacy;
- Excessive whitish discharge with blood streaks that appears after intimacy.
Important: If a woman is bothered by pain in the abdomen, increased discharge of leucorrhoea and discomfort during intimacy, she should immediately consult a doctor. Since such symptoms signal the formation of many diseases of the reproductive system.
Pain in the lower abdomen, caused by erosion, can occur any day. In this case, discomfort intensifies during menstruation. In addition, inflammation is often associated with erosion, as a result of which the pain intensifies and the discharge becomes more abundant. Moreover, if the inflammation is in an acute stage, the woman’s body temperature often rises.
Consequences of erosion
The main danger of the pathology in question is that it does not disappear, but transforms into a chronic form, which contributes to the manifestation of other, more serious defects. In this case, therapy largely depends on the type and likelihood of complications.
If ectopia progresses, this leads to the formation of cervical dysplasia. In addition, the structure of cells is disrupted and atypical structures appear. Such processes have several types of development:
- first, the changes affect the deepest layer, located next to the muscle wall;
- further, the deformation concerns the layer on the surface;
- if the mucous membrane is affected 1/3 deep, a diagnosis of grade 1 dysplasia is made;
- a lesion affecting 2/3 indicates stage 2 pathology;
- a complete change in the mucosa indicates that grade 3 dysplasia has formed;
- the next stage of change is a malignant neoplasm.
Important: If a woman is a carrier of the papilloma virus, the risk of developing dysplasia, and then a malignant neoplasm, increases several times.
The last stage is characterized by the appearance of metastases. Therefore, urgent surgical intervention is required to remove the uterine organ and appendages.
Complications in adolescents
Often a very pressing question arises: how dangerous is erosion in adolescence? Girls usually reach puberty by age 14.
Changes in hormonal levels in the first years lead to the fact that the menstrual cycle occurs intermittently and often passes with discomfort, behind which it is difficult to recognize the development of pathologies of the reproductive system.
In addition, the discharge between periods is also unstable. Therefore, it is important to promptly recognize the problem and visit a gynecologist.
Most often, the development of a chronic inflammatory process and the formation of erosion is caused by the following factors:
- failure by a teenager to comply with basic hygiene rules;
- hypothermia of the genitals;
- early entry into intimate relationships.
If a girl complains that the menstrual cycle is too painful, bleeding is observed between periods, or pathological discharge is observed, the mother should immediately contact a gynecologist. It is important to understand that if the reproductive system becomes inflamed, ignoring the problem will lead to infertility.
Consequences of menopause
As menopause approaches, estrogen levels gradually decrease. This, in turn, leads to a decrease in mucus production in the cervical canal. This increases the risk of infection in the reproductive system and the manifestation of inflammatory processes.
In addition, surgical interventions, abortions, bearing and giving birth to children, as well as many years of physical labor often provoke such a negative phenomenon as uterine prolapse.
This pathology contributes to the loss of elasticity of the ligaments, a decrease in muscle tone and drying out of the mucous membrane.
As a result, cracks and ulcers form on the surface of the mucous membrane, which causes erosion.
If a woman is bothered by symptoms such as:
- bloody impurities are observed in the discharge;
- sexual intercourse causes pain;
- discomfort occurs in the lower abdomen.
Important: The severity of erosion symptoms largely depends on the presence of concomitant pathologies, the individual characteristics of the female body and the state of the immune system.
You need to immediately visit a gynecologist. Since at this age there is a high probability of degeneration of the pathology in question into a malignant neoplasm.
Complications during pregnancy
Before starting pregnancy planning, it is recommended to visit a doctor and undergo an examination to identify erosion. Since the advanced stage causes the penetration of infections that the child can later become infected with during the passage of the birth canal.
If minor erosion is detected during pregnancy, therapy to eliminate it is not performed. Because there is a risk of cervical dilatation and miscarriage. However, if the pathology is diagnosed in an advanced stage after childbirth, the doctor will recommend not delaying treatment, but resorting to cauterization, which does not leave scars.
Consequences after childbirth
There are several reasons why erosion forms after childbirth:
- ruptures that occurred during labor;
- injury from medical instruments;
- poorly placed sutures;
- infection.
In addition, the formation of pathology often occurs due to hormonal disorders or due to exacerbation of chronic ailments. In this case, the main danger lies in the fact that the manifestation of the defect is often mistaken for a consequence of labor. As a result, the uterus is gradually corroded. And such a condition is fraught with the fact that in the future the woman will not be able to give birth again.
Important: During drug treatment of the disease in question, the doctor prescribes medications aimed at strengthening the immune system and restoring hormonal levels as part of the main therapy.
To prevent dangerous progression of the disease, young mothers must undergo a routine examination of the reproductive system.
Why is neglected erosion dangerous?
In the absence of timely treatment, erosion develops into leukoplakia. Such a defect is a white spot of a dense structure.
In this condition, the uterus is constantly exposed to attacks by various bacteria. Since the damaged mucosa no longer performs its main function of protecting the uterine organ.
In this case, the risk of developing inflammation and infection increases several times.
If cervical erosion is detected and treatment is not started in a timely manner, bilateral inflammation may occur, which in turn leads to an acceleration of epithelial cell division. And this already provokes the transformation of the defect into dysplasia.
In general, gynecologists note that if erosion is not in an advanced stage, there is no obvious threat to women’s health and life. However, if complications are identified, postponing treatment until later is strictly prohibited. Since, as mentioned above, there is a risk of pathology transforming into cancer.
In addition to malignant neoplasms, the defect in question can cause infertility. Since damaged mucous membranes often interfere with the natural process of fertilization. In addition, pathologies of the mucous membrane during pregnancy can provoke miscarriage, the development of colpitis and cervicitis, and also cause premature birth.
How to avoid the advanced stage
Modern medicine has in its arsenal many methods for eliminating the defect in question. Drug therapy is considered one of the most effective; it is indicated only for the initial stage of development of the pathology. In addition, this problem can be eliminated by resorting to cauterization with a laser or radio waves.
Important: If erosion is diagnosed in a timely manner, it can be overcome using a medicinal complex consisting of drugs, vitamin complexes and suppositories.
The choice of the most suitable method is determined only by the doctor based on the examination and taking into account the individual characteristics of the female body.
Prevention of pathology
In order not to look for ways to eliminate uterine lesions in the future, you need to follow some rules of prevention:
- visit a gynecologist 2 times a year for a routine examination;
- observe basic hygiene rules;
- when having intimate contact with a casual partner, use contraceptives;
- to prevent infection, it is recommended to adhere to monogamy and have regular sex life;
- if you are not planning to conceive a child, you should use contraception to avoid abortion;
- if erosion is detected, it is recommended to immediately begin treatment, while at the same time adhering to a healthy lifestyle;
- When menstruation occurs, you need to regularly change your personal hygiene products and take a shower 2 times a day.
Erosion itself is not dangerous for a woman and is a benign process. However, in some cases, a disease not detected in a timely manner at a late stage of development can transform into dysplasia, and then into oncology. Considering this important point, experts recommend regular examinations and, if erosion is detected, immediately begin its treatment.
Source: https://yazvnet.ru/eroziya-matki/zapushhennaya-eroziya-shejki-matki.html
Cervical Erosion: Symptoms and Treatment - Lifestyle for Good Health
Types and description of cervical erosion
The cervix has a conical shape and is a thin canal, which is covered from the inside with a layer of epithelium with cylindrical cells. This part also contains special glands that produce lubricant to moisturize the vaginal area.
The area of the cervix that extends into the vaginal area is called the pharynx and is covered with an epithelial layer with flat-shaped cells. Damage occurs here; outwardly, they appear as damaged structures of the mucous membranes.
It is necessary to know what erosion looks like and how it manifests itself in order to recognize the disease in the early stages.
- Congenital. It is characterized by displacement of the epithelium, which occurs even at the stage of intrauterine formation of the reproductive system.
- Ectoropion. Provoked by abortion or childbirth, in this case, inversion of the mucous membrane in the area of the cervical canal is diagnosed.
- Endometriosis. In this situation, the endometrium leaves the uterine cavity and is deposited on the surface of the cervix.
- Leukoplakia. This type is characterized by keratinization of particles of squamous epithelium.
- Polyps on the cervix and cervical canal.
- Condylomas of the pointed type.
Characteristic signs of cervical erosion
Signs of erosion often do not make themselves felt at the very beginning of the disease. This happens because anatomically the cervix is not too sensitive and does not provoke discomfort even during sexual intercourse.
The presence of blood or ichor is a serious reason to contact a gynecologist. The accuracy of the diagnosis can always be confirmed only during a preventive examination and special diagnostics.
Symptoms of the disease directly depend on its type and can vary markedly.
Symptoms of true erosion
If the disease becomes chronic, the inflammatory process can affect the area of the uterus and appendages. As a result, patients experience a disruption in the menstrual cycle, brown discharge with a spotting consistency, and an increase in temperature. Typical erosive signs, photos of which are presented in the article, sometimes include discharge of a curdled or foamy consistency with pus. The same symptoms occur if a woman is diagnosed with vaginal dysbiosis. A general list of symptoms of this type includes:
- greenish or yellow liquid discharge with a characteristic odor;
- nagging pain in the lumbar region and abdominal area;
- pain during urination.
Cervical erosion is often found in pregnant women; it is worth considering that erosion does not affect the course and process of childbirth, so treatment begins only after the birth of the child.
During pregnancy, the patient's condition is monitored and local anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to treat and eliminate discomfort, since the mucous membrane can cause ruptures during childbirth. In rare situations, signs of infections and inflammatory processes are observed.
The presence is indicated by discharge mixed with blood, itching and burning sensations during sexual intercourse.
Treatment methods for cervical erosion
When prescribing a course, gynecologists take into account the size of the affected area, the age of the patient, as well as the presence of additional diseases. Symptoms and treatment of diagnosed cervical erosion are individual in each case; the results of therapy depend on timely diagnosis and accurate diagnosis.
The goal of the initial course is to eliminate the inflammatory process affecting the cervix and vaginal area.
Sometimes inflammation of the cervix is accompanied by impaired ovarian function, in which case additional measures must be taken.
Modern treatment methods, including laser cauterization or radio wave therapy, are aimed at destroying columnar cells in the layers of the epithelium. Afterwards, the cells are rejected, and a flat epithelial layer is restored in their place.
Laser vaporization, cryodestruction and diathermocoagulation also show good results. The essence of each of these methods is worth considering in more detail:
- Cauterization by radio waves. Therapy with a special device “Surgitron”, with which the procedure is carried out, does not require special preparation and promotes healing in two weeks. Many gynecologists consider this technique to be the most effective.
- Cryodestruction. During this procedure, the damaged area is treated with liquid nitrogen at the lowest possible temperatures. Cold allows you to “freeze out” erosion until healthy tissue forms; according to numerous reviews, this method is also quite effective.
- Laser coagulation. Using a targeted laser beam on the affected area helps treat both superficial and deep erosion. Laser treatment is recognized as one of the safest methods.
- Chemical type coagulation. Ectopic formation on the cervix can also be removed using special chemical solutions. For this purpose, the drug Solkovagin is used, which contains a complex of acids, including oxalic, nitric and acetic.
- Candles. In the early stages, erosive lesions can be treated medicinally with special suppositories for oral administration, which are purchased at the pharmacy or prepared independently. The list of drugs, the names of which should be checked with a doctor, to restore the mucous membrane includes drugs such as Depantol and Hexicon, as well as suppositories based on sea buckthorn oil.
Radio waves
Thanks to this method of removal, scabs do not form on the tissues, and they do not need to be cut off after the procedure is completed. This avoids infections because the uterine tissue will not be scarred.
Before starting, doctors recommend undergoing a full gynecological examination, taking a smear and all necessary tests.
If the patient is diagnosed with fungal or infectious diseases, the gynecologist will prescribe complex therapy, after which radio wave cauterization can begin.
Radio wave destruction is carried out using a colposcope, which provides an accelerated radio wave healing period. During the procedure, the instrument does not come into contact with the cervix, the woman does not feel discomfort, since this area is treated with an anesthetic in advance.
Folk remedies for cervical erosion
Well-known folk methods include a list of the most popular ways to restore eroded tissue using natural remedies.
The appropriate medicine must be selected individually, in consultation with your doctor. It should be remembered that traditional methods cannot replace traditional methods of treatment, including standard cauterization and other procedures.
The list of natural medicines that act quickly and effectively includes the following recipes.
Sea buckthorn oil
Good results are obtained with oil tampons, which must be inserted into the vaginal area at night; the total course lasts at least 3 weeks. The oil can be mixed with grated blue onions or mummy tablets dissolved in water and soak cotton swabs with this mixture. Treatment with oil usually lasts at least two to three weeks.
Honey and aloe
Healing honey in combination with aloe can also give good results in complex therapy for erosive lesions of the uterus. To prepare this medicine, you need to take castor oil, aloe juice and honey in equal proportions, soak a cotton swab with this mixture and leave it in the vagina overnight.
In the mornings, you need to additionally lubricate the cervical area with sea buckthorn oil; to obtain optimal results, the procedure should be repeated every day for 10 days. A mixture of fish oil and natural honey also gives good results, which is also used to make night compresses and suppositories for treatment.
Calendula
Natural calendula flowers help relieve inflammation and have a restorative effect due to their antibacterial properties. The dried flowers of the plant are used to prepare solutions, infusions and compresses.
To prepare the solution, you will need to pour boiling water over 200 g of flowers, leaving for at least a day. The finished medicine is used for daily douching, after which a tampon soaked in hydrocortisone ointment is inserted into the vagina.
Propolis with Vaseline
Thanks to its antibacterial properties, propolis promotes accelerated healing of wounds and damage.
In order to prepare the ointment, you will need 5 tablespoons of Vaseline and ground propolis, which must be heated in a water bath, stirring for at least 10 minutes.
The resulting ointment must be cooled and mixed, then used to prepare compresses that are inserted into the vaginal area for 12 hours. The general course is at least 16 days to obtain optimal results.
Conclusion
After completing the course, you can get rid of even problematic erosive formations. Regardless of the method chosen, you should start as soon as possible to prevent the disease from becoming chronic. A woman’s reproductive health directly depends on the timely treatment of diseases, so if you have this diagnosis, you should agree to the method of therapy offered by the gynecologist.
Cervical erosion: symptoms and treatment - all the details on Pitanie4Zdravie.ru
Source: https://pitanie4zdravie.ru/eroziia-sheiki-matki-simptomy-i-lechenie/
Cervical erosion: treatment, causes, symptoms, signs, photos
Erosion is damage to the mucous membrane of the cervix. A large list of factors can lead to such a pathology, so the problem is becoming more and more popular every year. The danger of erosion lies in the high probability of complications that it leads to in the absence of proper treatment.
Now let's look at this in more detail.
What is “cervical erosion”?
From the vaginal side, a woman’s uterus ends in a narrow pharynx, which is called the cervix. It has a mucous membrane that can become inflamed, injured and become the main site for the development of microbes. When sores and small ulcerations appear on the cervix, this condition is called erosion.
Depending on the severity of the pathology, its symptoms can be quite characteristic or occur in an erased form. Violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane makes the cervix and the reproductive organ itself more vulnerable to infection. Most infectious and inflammatory processes in the female genital organs can lead to infertility, and therefore require timely diagnosis and treatment.
Another danger of cervical erosion is the likelihood of its degeneration into a malignant formation. Against the background of microtraumas and hemorrhages, the nutrition of the tissue in the affected area, its periodic regeneration and new injury are disrupted. According to statistics, women with cervical erosion have a higher risk of acquiring gynecological cancer.
In the initial stages, erosion can cause only mild discomfort, which is why many women delay seeing a doctor. Modern medicine says that you need to visit a gynecologist at least once a year in order to promptly identify pathological processes at an early stage.
Most other gynecological diseases (cervicitis, vaginitis, endometritis) occur against the background of cervical erosion. For a pregnant woman, erosion is dangerous, as it can cause a miscarriage or the spread of infection through the bloodstream of the mother and child.
Doctors distinguish the following types of cervical erosion:
- True erosion. It can be compared to a skin abrasion - the mucous membrane of the neck is damaged, bruising, cracks, and inflammation are visible. After some time, this condition can go away on its own and the tissues regenerate. Another outcome of erosion is the appearance of ectopia (displacement of two types of epithelium relative to their normal position).
- Pseudo-erosion. This condition is also called ectopia. It looks similar in appearance to true erosion, but upon closer examination it becomes noticeable that the red areas are not inflammation, but simply a layer of other epithelial tissue. Ectopia can be either acquired or congenital. In itself, it does not pose a danger to a woman’s health, but under the influence of provoking factors it can turn into true erosion.
- Congenital erosion. This condition is considered physiological until the age of 25 or the first birth. It lies in the fact that the border between the cervical and flat epithelium is displaced, so it looks like erosion.
The greatest danger is true erosion, which is an open source for infection. According to etiology, the following types of true erosion are distinguished:
- Inflammatory. The root cause is a specific or nonspecific infection, which provokes the inflammatory process.
- Traumatic. It is a consequence of abortion, curettage and other gynecological manipulations.
- Chemical. The cervix is damaged by chemicals, for example, during douching or self-medication.
- Burns. Appears after cauterization of the cervix.
- Trophic. Violations of the cervical structure appear when there is insufficient nutrition or blood supply to the tissues.
- Specific. Appears when infected with syphilis or tuberculosis.
- Cancerous. Accompanies the development of malignant processes.
What does cervical erosion look like with a photo
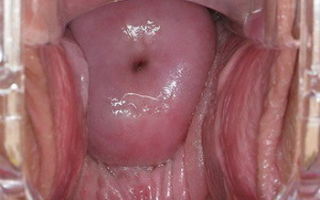
Erosion can affect both a small area of the cervix and its entire surface. Externally, the ulcerations have a more pronounced red color, and when touched with a cotton swab they bleed. What such a mucosal defect looks like is shown in the picture:
The first signs of cervical erosion
The peculiarity of erosion is that it may not manifest itself for a long time. Severe discomfort, for which women go to the doctor, is not always present. This leads to the fact that the pathology remains and progresses for many months and years until it leads to another, more serious disease.
If you pay close attention to your health, a woman may still notice that her daily discharge has become more abundant (due to increased secretion of glandular cells), and mild nagging pain occurs in the lower abdomen. These are the first signs of erosion, which you should pay attention to and make an appointment with a gynecologist for further detailed examination.
Symptoms of cervical erosion
Cervical erosion can manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- daily discharge becomes more abundant;
- bothered by aching pains that periodically appear and disappear;
- urination may cause discomfort;
- daily discharge changes in color and smell;
- During sexual intercourse, unpleasant and painful sensations appear;
- During the intermenstrual period, spotting brown discharge occurs.
Erosion is clearly visible during routine examination using a gynecological speculum. However, more modern diagnostic methods should be used so as not to confuse this condition with ectopia, which in most cases is a physiological norm. Therefore, recently, a routine examination by a gynecologist includes a colposcopic examination.
Causes and prevention of cervical erosion
Various reasons can lead to damage to the mucous membrane. Among the main doctors, the following are distinguished:
- Inflammatory processes in the female genital organs. The root cause may be colpitis or cervicitis, which were not cured in time and sank the cervical mucosa.
- Pathological discharge from the uterus. In some cases, when fibroids or uterine polyps are isolated from the genital organs, these formations damage the epithelium of the cervix and cause true erosion. The injured mucosa becomes a good environment for the development of pathogenic microorganisms, which only worsen the structure and function of tissues.
- Mechanical injuries. Direct damage to the cervix can occur during childbirth, abortion, diagnostic curettage, inaccurate sex, or installation of an intrauterine device. Careless handling can cause erosion or even infection.
- Hormonal imbalances. A sharp disruption of hormonal levels (pregnancy, puberty) or, conversely, a delay in the maturation of genital tissues can lead to cervical erosion, menstrual irregularities, and problems with pregnancy.
- Immune disorders. A decrease in general and local immunity (in gynecological organs) leads to activation of opportunistic flora and inflammatory processes, as a result of which the cervical mucosa is injured.
- Congenital condition or ectopia. Ectopia is pseudo-erosion. In this condition, the epithelial cells of the cervical canal are slightly shifted towards the vagina and may look like an erosive formation. In fact, with ectopia, no inflammatory process is observed, and the cervical tissue remains intact. This feature is considered a physiological norm and does not require treatment if it is present in a girl from birth.
In nulliparous women and those who have not resorted to abortion and diagnostic curettage procedures, erosive changes in the cervix may occur if the following predisposing factors are present:
- hereditary predisposition;
- smoking, poor nutrition, alcohol consumption;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- a large number of sexual partners;
- decreased immunity.
The connection between erosion and changes in the psycho-emotional background (frequent stress) has not been proven. But the number of sexual contacts and the quality of sexual life directly affects a woman’s health. Both frequent changes of sexual partners and a complete lack of intimacy are harmful.
The following recommendations will help prevent the development of erosion:
- Don't skip gynecological examinations, even if you feel healthy. Instrumental and laboratory research methods make it possible to identify the pathological process in the early stages before the appearance of pronounced symptoms.
- Use underwear made from natural fabrics.
- Choose pads over tampons and change them more often.
- Contact with a regular sexual partner reduces the likelihood of developing erosion. Frequent changes of men, as well as aggressive sex, will provoke irritation of the genital mucosa and lead to erosion.
- The preferred method of protection is a condom. It will protect not only from unwanted pregnancy (and abortion), but also from most sexually transmitted diseases.
- Pay attention to the health of the whole body. It is important to maintain general immunity at a high level, as well as promptly treat diseases of other organ systems.
Diagnostics
It is very important to correctly determine the cause of erosion. If it is successfully removed and there are no complications, the cervical mucosa is able to independently recover to a healthy state.
First, the doctor examines the patient using a gynecological speculum. In the presence of erosion, it clearly stands out against the background of the rest of the mucous membrane and has a more pronounced scarlet color. The use of extended colposcopy will allow you to accurately distinguish true erosion from ectopia and see the structure of cells in the lesion.
It is mandatory to interview the patient, as this can reveal the cause of the inflammatory process, especially if it is a consequence of an abortion or recent childbirth.
Additionally, the following must be used in diagnostics:
- Determination of vaginal microflora. Allows you to determine whether there are enough lactobacilli present on the mucous membrane, and how high the level of local immunity is.
- Blood test for dangerous infections (HIV, syphilis, hepatitis).
- PCR is a research method that allows you to identify specific pathogens that are mainly sexually transmitted.
- Colposcopy. A detailed examination of the cervical mucosa under a microscope, which allows you to distinguish true erosion from false, as well as identify atypical cells that are not visible to the naked eye.
- Smear to detect atypical cells. In laboratory conditions, the presence of dysplasia, epithelial proliferation and other atypical processes is determined.
- Biopsy. A cervical sample is taken only if atypia or malignancy is suspected. Isolating a section of tissue makes it possible to examine it in more detail under a microscope and give a more accurate answer.
If the doctor suspects that the cause of erosion is a violation of the woman’s general health, he may additionally prescribe hormone tests or an immunogram.
Treatment of cervical erosion
Treatment tactics will depend on the cause. Which caused erosion. As a rule, treatment has two directions - eliminating the underlying cause and influencing the cervical tissue to restore it.
If a pathogenic infection is detected in the smear, it should be eliminated first. The woman is prescribed a course of antibiotics, after which the smear is repeated. If pathogenic microbes are not identified, you can proceed to the next step - conservative or surgical treatment.
Moxibustion, which is known to many women, is not always carried out using devices. There is also chemical cauterization, which is carried out with drugs. The need for such therapy and the choice of method of exposure are selected by the doctor individually for each patient.
The drug treatment regimen also includes anti-inflammatory drugs and hormonal drugs.
The main methods to get rid of affected areas of tissue on the cervix are:
- Chemical coagulation. The cervix is treated with a special preparation that contains a mixture of acids. After applying the product, a crust forms on the mucous membrane, which disappears after a few days and is naturally replaced by healthy tissue. The procedure is inexpensive, simple and painless.
- Diathermocoagulation. A painful method, after which scars form on the cervix, so at present it is practically not used.
- Laser vaporization. A popular and painless method, which is based on the non-contact action of a laser. As a result, the affected cells lose moisture and are destroyed.
- Cryodestruction. Getting rid of erosive tissue occurs using cold exposure. The method has many advantages, including high efficiency, no pain and no deformation of the cervix.
- Radio wave method. It is considered the most modern and popular. Gives a 100% guarantee of getting rid of erosion. At the same time, a scar does not form on the cervix, due to which it continues to function normally. Three weeks after the procedure, complete tissue restoration occurs and the woman recovers.
For mild erosions, the doctor may prescribe conservative local treatment and not resort to surgical methods. In this case, therapy will be carried out with vaginal suppositories, among which one or more drugs with the required spectrum of action can be selected. The following tools are popular:
- Vagical.
- Livarol.
- Depantol.
- Hexicon.
- Suporon.
Erosion is not always treated. If a woman is diagnosed with pseudo-erosion, which does not bother her, therapy may not be carried out. Treatment is mandatory if pathogenic microflora, atypical cells or an inflammatory process are detected.
Treatment of cervical erosion with folk remedies at home
Treatment with folk remedies can only be effective as an adjuvant therapy. You cannot self-medicate, since you first need to undergo all the necessary examinations and identify the infection that has entered the mucous membrane. Eliminating the infection is the first priority, but it will not be possible to cope with it at home without consulting a doctor.
If antimicrobial therapy has been completed, the doctor may prescribe folk remedies to accelerate mucosal regeneration:
- Sea buckthorn oil. Can be used internally or topically by soaking cotton swabs in it. The product is known for its anti-inflammatory effect, as well as good regenerating ability. Treatment can be done independently at home. The result will be noticeable in approximately 2 weeks.
- Levomekol. A popular remedy that many people have in their home medicine cabinet. It is widely used in gynecology, providing antibacterial and regenerating effects.
- Propolis. A well-known component with strong antibacterial and wound-healing activity. In gynecology, an aqueous solution of propolis is used, soaking cotton swabs in it.
Regardless of the method of therapy, after treatment a woman should adhere to the following recommendations:
- abstain from sexual activity for 6 weeks;
- avoid hot baths and saunas;
- limit physical activity;
- use pads instead of tampons.
Source: https://zdorrov.com/zhenskie-bolezni/eroziya-shejki-matki.html
Cervical erosion: types, causes, symptoms, treatment
Cervical erosion is a pathological, but benign process, manifested in the form of rounded red formations localized in the area of the cervical mucosa; the diameter of such formations can reach about two centimeters. Cervical erosion, the symptoms of which manifest themselves in the form of characteristic formations, can exist in several varieties, being congenital erosion, true erosion or pseudo-erosion.
general description
First of all, it should be noted that cervical erosion is one of the most common diseases of the female genital organs. The course of the pathology is characterized by replacement due to the influence of one or another type of factor of the normal mucous epithelium in the area under consideration by the cervical columnar epithelium.
As a rule, this disease does not pose a significant threat, if only for the reason that erosion itself is a benign process, and accordingly, it can become the cause of serious diseases, including tumor processes, in the rarest cases.
Cervical erosion: type and location
This disease, which is also defined as cervical ectopia, occurs in about half of women of reproductive age, while it does not occur in women who have passed the age of forty.
As for the opinion regarding erosion and its harmfulness in particular, although it is somewhat common, for the most part experts attribute it to a number of normal physiologically variable conditions.
Let us consider the types of erosion we previously noted in more detail.
Types of cervical erosion
Erosion is congenital. The congenital variety of this disease consists of displacement of the cervical columnar epithelium. Congenital erosion is observed in childhood or adolescence, while the symptoms of the disease mostly do not manifest themselves in any way.
Detection of erosion occurs during colposcopy, where the presence of a bright red area that cannot be stained using Lugol's solution is determined.
It is noteworthy that congenital erosion does not predispose in its course to subsequent development into malignant formations, and therefore treatment, as a rule, is not provided.
Erosion is true. With true erosion, its characteristic manifestations are localized in the area of the pharynx (on its outer side, in some cases on the back); localization in the area of the lip of the cervix is much less common. True erosion manifests itself in the form of a small rounded area with pronounced coloring, and sometimes bleeding is noted.
For this type of erosion, a characteristic manifestation is often endocervicitis, as a result of which the damaged part of the mucosa may have purulent discharge. The duration of true erosion is about 10-14 days, then the cervix is covered with epithelial cells belonging to neighboring areas.
Pseudo-erosion is in this case the next stage in the development of the disease.
Pseudo-erosion. It appears in the form of a rounded area of pronounced red color, in some cases it does not have a specific shape; the diameter can range from several millimeters to several centimeters.
The surface of the formation may be characterized by the formation of mucous discharge on it, which in some cases may be purulent. The duration of this type of erosion can be quite a long time, which is determined based on the characteristics of the inflammatory process that provoked it.
The danger of pseudo-erosion lies in the possibility of recurrence; accordingly, in this case there is a high risk of developing cancer, which must be taken into account in treatment.
In addition to the main types of erosion, the following variants are also distinguished:
- Ectropion. In this case, we mean a kind of eversion of the cervical mucosa, which occurs as a result of abortion or after childbirth.
- Endometriosis of the cervix. It is characterized by the process of transplantation of the endometrium of the uterine cavity to the surface of the cervix.
- Leukoplakia. Characterized by keratinization of squamous stratified epithelium.
- Polyps of the cervical canal, polyps of the cervix.
- Genital warts.
Causes of the disease
- Mechanical injuries that occur as a result of rough and frequent sexual intercourse, as well as during abortion and childbirth. With physical impact, the stratified squamous epithelium begins to thicken, which leads to the subsequent formation of an inflammatory process.
- Sexually transmitted infections. Among these are the papilloma virus, genital herpes and other diseases.
- Incorrect and untimely treatment of genital tract infections.
- Early onset of sexual activity, late onset of sexual activity.
- Rare sexual contacts, or, conversely, frequent changes of partners.
- Current disturbances in hormonal status, disturbances in the menstrual cycle.
- Changes in the immunological scale (decrease in immunity).
- The presence of inflammatory diseases relevant to the pelvic organs (oophoritis, salpingitis, endometritis, etc.).
- A combination of some of the above reasons.
The occurrence of the disease in elderly patients is possible due to the pressure exerted by the uterine ring.
In addition, there is also “physiological” erosion, determined in young women (up to 25 years), which has a tendency to heal independently.
Cervical erosion: symptoms
The vast majority of reported cases of the disease in women indicate that it extremely rarely manifests itself in the form of specific clinical symptoms, and therefore in most cases the diagnosis of the disease is made randomly. Meanwhile, it also happens that patients turn to a specialist based on the occurrence of the following symptoms:
- spotting not associated with menstruation, especially often appearing after sexual intercourse;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- purulent-mucosal discharge (whose occurrence is explained by the addition of an inflammatory disease to erosion, as a result of which the disease itself significantly worsens in the peculiarities of its own course), which women often independently confuse with menstrual discharge, thrush or harbingers of miscarriage in the case of pregnancy.
Diagnosis of cervical erosion
The diagnosis can be established already at the first visit to the doctor. Meanwhile, in many cases, visual examination is only half the battle in diagnosing the disease. Therefore, patients will need to undergo the following tests:
- flora smear;
- extended colposcopy;
- cytological examination;
- PCR diagnostics, aimed at identifying the main types of infections (genital herpes, trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis, etc.);
- blood test for hepatitis, HIV, syphilis;
- bacteriological culture;
- biopsy (if the patient is suspected of having a malignant tumor).
Treatment of erosion
The tactics of treatment suitable for each specific case are developed individually, based on the type of erosion and the size characteristic of it, including the presence of concomitant infections.
Thus, congenital erosion requires dynamic observation, as a result of which its independent disappearance can be noted.
In general, treatment can be conservative or surgical, again based on the specific characteristics of the course of the disease.
Conservative treatment involves eliminating the cause that provoked the erosion. Therefore, based on the concomitant disease identified in the patient, antibiotics with a wide spectrum of action can be prescribed. Additionally, anti-inflammatory drugs and immunomodulators may be prescribed.
The cervix is treated locally with drugs that lead to chemical coagulation in the affected area.
These drugs are used only for benign formations; they are more suitable for nulliparous girls, since the treatment does not leave scars in the cervical area, which is a significant advantage of the method.
Its disadvantage is the possible relapse of the disease, but it is applicable to any type of erosion.
If the effect of conservative therapy is insignificant or completely absent, then cauterization is prescribed (which is the surgical method in this case). In addition, any of the following methods can be used:
- electrosurgery;
- cryosurgery;
- laser destruction;
- radiosurgery;
- thermocoagulation.
As for such widespread proposals regarding folk remedies in the treatment of erosion, experts have ambivalent attitudes towards them - the effectiveness of any of the options in the treatment of erosion has not been proven. Among non-traditional methods of treating cervical erosion, some effectiveness is most often observed with the use of acupuncture (acupuncture) and physiotherapy.
If alarming symptoms appear, which is especially important due to the predominantly asymptomatic course of uterine erosion, you should consult a gynecologist.
Source: https://SimptoMer.ru/bolezni/zhenskie-zabolevaniya/158-eroziya-sheyki-matki-simptomy