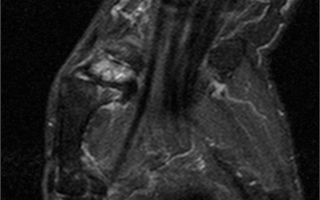
The wrist is considered the most vulnerable place to injury.
Moreover, it is not at all necessary that an injury to this area of the hand can occur as a result of a careless blow or fall: to damage the wrist, an awkward movement while performing usual everyday activities, constant work at the computer or rest is enough. Therefore, if pain or aching sensations occur in this area of the arm, you should immediately do an MRI of the wrist joint and hand, and consult a specialist.
What does magnetic resonance imaging of the hand show?
MRI of the hand is a completely safe and painless procedure. However, it is very important when it comes to diagnosing the causes of the painful syndrome. Tomography allows you to identify inflammatory processes in tissues and blood vessels, check the patency of the circulatory system and its condition, detect neoplasms, assess the condition of nerve endings, tendons, muscles, and small joints.
Diagnosis of the hand using magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed if the patient has suffered an injury or feels causeless but constant pain in the wrist.
In this case, MRI provides the most accurate research results that cannot be obtained with conventional visual examination, palpation or other alternative methods.
So what does an MRI of the wrist joint show? Tomography is capable of visualizing absolutely all the smallest structures of the area under study and their pathologies.
Tomography of the wrist joint and hand reveals:
- injuries: sprains, fractures, bruises, ligament ruptures;
- inflammatory diseases: arthritis and osteoarthritis, synovitis;
- degeneration of joint tissues - arthrosis and osteoarthritis;
- carpal tunnel syndrome;
- anomalies in the development of intra-articular elements;
- cysts, malignant and benign formations;
- blood flow disorders.
When is tomography of the hand necessary?
An MRI of the hand can be done if the attending physician sees the need for this procedure. In fact, tomography of the wrist joint is an additional study that helps clarify the data obtained after radiography, ultrasound or CT. Indications for the procedure may be:
- preoperative and postoperative period to check the condition of joints, tissues and other structures, as well as the speed of their regeneration;
- hand injury;
- pinched nerves and tendons;
- diseases of the ligamentous-muscular system of the wrist (phlegmon - purulent inflammation, and hygroma - benign formation);
- joint diseases - arthrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, osteomyelitis and gout);
- presence of tumor formations;
- study of the presence of metastases after removal of a malignant tumor;
- constant pain in the wrist joint, the cause of which is unknown;
- tunnel syndrome, which is often observed in patients who work at a computer.
However, before deciding to undergo a tomography of the hand, it is recommended to consult with a specialist and also make sure that there are no contraindications to the procedure. So in what cases is it prohibited to do an MRI of the wrist?
- During pregnancy, lactation and children under 7 years of age.
- If metal devices are installed in the patient's body: hearing aids, insulin pumps, metal prostheses and implants, vascular clips, pacemakers, neuro- and cardiac pacemakers. Titanium plates, as well as plastic and ceramic prostheses do not interfere with the procedure, since this material is not attracted by a magnet.
- If a person cannot control the movements of his body (hyperkinesis or epilepsy), he also cannot undergo an MRI procedure.
- Fear of closed spaces (claustrophobia) may be a reason for refusal to undergo tomography of the hand. However, if the tomograph is an open type, the procedure can be performed.
- Contraindications include renal and heart failure, and an allergic reaction to contrast.
If the patient is unable to hold his hand in one position due to severe pain, he may be given an anesthetic injection to help him keep his wrist motionless.
Features of preparation for the procedure
There is no special preparation for an MRI of the wrist. But still, experts recommend following some rules:
- If diagnostics with contrast are used, then the patient should not eat food 5 hours before the procedure - MRI is done on an empty stomach.
- The patient should not be wearing metal objects - jewelry, accessories.
- The doctor must have a conversation with the patient about the presence of contraindications to MRI.
- Make sure that the patient is not allergic to gadolinium (contrast).
- Patients suffering from claustrophobia may be given sedation or anesthesia.
- If the patient is allergic to iodine, the doctor should be warned about this in advance, since markers for MRI of the hand contain a large dose of this substance.
You should be prepared to change into a sterile, disposable hospital kit.
How is tomography of the hand performed?
A tomograph is a medical device with a retractable table where the patient lies down. The patient's head, legs, body and arms are fixed with special straps, since any, even minor, movement negatively affects the results of the study.
When the table slides inside the tomograph, the tomograph ring rotates around the part of the body being examined (in our case, around the hand). Its movement is accompanied by a faint crackling sound. During the procedure, the patient does not feel any discomfort.
If we talk about how long the procedure takes, then if contrast is not used, the patient spends about half an hour in the machine. With markers, the duration of the procedure increases significantly and is 40-60 minutes.
The apparatus tunnel has light and ventilation, and the patient can communicate with the radiologist through an intercom. If the clicks produced by the tomograph bother or irritate the patient, you can use headphones (earplugs).
It should also be remembered that the patient must lie as still as possible throughout the procedure in order to obtain correct MRI results.
The radiologist evaluates the resulting images and compiles a three-dimensional picture from them, which allows you to understand how healthy the elements of the hand are.
If MRI is performed using markers, then the patient is prescribed a preliminary allergy test. If, as a result, there are no contraindications to the procedure, the patient is given a catheter into which contrast is injected intravenously. The marker instantly colors the vascular system of the hand, allowing the most accurate visualization of pathological foci.
After the MRI procedure, the patient can return to their usual daily routine. After some time, the patient receives the result of the study, with which he needs to contact a doctor, who sent him for a tomography. The same specialist, based on the MRI results, will decide what therapeutic measures need to be taken.
Cost of tomography of the hand
Magnetic resonance imaging of the hand costs differently in different clinics. Depending on which clinic the patient went to (private or public), the price of the study can range from 3,000 to 20,000 rubles. The cost of the study also depends on the quality of the device and its condition, and on the location of the clinic.
MRI is the single most accurate way to diagnose pathologies, injuries, inflammatory processes and cancer of the wrist joint and hand.
This diagnostic method allows you to prevent serious diseases and monitor the rehabilitation process after surgery or injury.
It must be remembered that it is better to prevent any disease, therefore, if you have pain in the hand, the origin of which is unclear, you should consult a specialist.
Source: https://DiagnostLab.ru/mrt/sustavy/mrt-kisti-ruki.html
MRI of the wrist joint: features of the procedure and limitations
Hands and wrists are quite often exposed to various diseases and injuries. Moreover, pain can arise not only from mechanical damage (impact, compression, etc.), but also from any constant load on the hands. As soon as pain and discomfort appear, you should definitely consult a specialist and get an MRI of the wrist joint.
Indications for diagnosis
Scanning hands and joints using MRI is considered an effective non-invasive method, which is also absolutely harmless and painless. Most often, this procedure is prescribed to patients who have already undergone X-rays, ultrasound of joints, and computed tomography, but it was not possible to accurately determine the diagnosis.
MRI of the wrist and hand is prescribed in the following cases:
- Before and after surgery. The need for the procedure is due to the fact that the doctor evaluates the condition of the bones before the intervention and the result after the operation.
- For limb injuries (fractures, cracks, dislocations).
- For inflammatory joint diseases - arthritis, arthrosis, osteomyelitis and gout.
- If there is a suspicion of a tumor process. The specialist evaluates the development of metastases.
- Pinched tendons and nerves, including carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Pain of unknown origin with limited mobility of the limb.
Currently, the MRI procedure is becoming the most popular, as it differs significantly from other types of diagnostics.
For example, a computed tomography scan shows all the small bones in the hand, but does not evaluate the ligamentous-tendon system.
Detectable diseases
Magnetic resonance imaging is a universal scanning method that allows you to study in detail all the elements of the part of the arm and hand being examined. These are bone tissue, cartilage, joints, ligaments, muscles and blood vessels.
Diseases that can be detected using MRI:
- congenital joint abnormalities;
- injuries received at home and at work (dislocations, fractures, sprains, ruptures);
- inflammatory diseases (arthritis, arthrosis, osteomyelitis);
- polyosteoarthrosis at an early stage, when there are no clinical manifestations yet;
- tumors of various etiologies;
- tunnel syndrome;
- tenosynovitis and Kienböck's disease.
Most often, this examination is carried out to identify the cause of pain.
MRI has a number of advantages and limitations that every subject needs to know.
Advantages of the procedure:
- you can see the entire structure of the hand down to small vessels;
- identifies diseases that cannot be detected by other means, including muscle, vascular and nervous pathologies;
- determines the severity of the disease and establishes the exact location of the inflammation;
- diagnoses small cracks and fractures that cannot be seen on a regular x-ray;
- the procedure does not cause any side effects and is absolutely safe.
- the examination takes place without the risk of radiation.
When carrying out the procedure, you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations, then the examination will be safe and easy. But in some cases MRI is contraindicated or has special limitations. It is prohibited to conduct research in the following cases:
- Pregnancy at any stage and lactation. When breastfeeding, when a decision has been made to undergo an MRI, milk should not be given to the baby for 24 hours.
- Children's age up to 6 years. The examination requires complete immobility during the examination, and children cannot lie still. In rare cases, when there is an urgent need, an MRI is performed on children under general anesthesia.
- People with metal objects in the body - pacemakers, metal valves, prostheses, vascular clips, platinum prostheses, hearing aids, etc. Insert implants made of ceramics and plastic are not contraindications for examination.
- Patients who do not control their body movements (hyperkinesis).
- People whose weight exceeds 120 kg.
- For claustrophobia (exception: MRI in an open tomograph).
- In case of an allergic reaction to a contrast agent, heart or kidney failure.
- Mentally unbalanced people. In severe cases, patients are given sedatives.
Before agreeing to a magnetic resonance imaging scan, you should tell your doctor about all your features.
Details
The scan is carried out using a tomograph. This is a device that consists of two main parts - a retractable table and a camera. The person being examined carefully lies down on the table, and the doctor ties his head, arms and legs. This is necessary, since even the slightest movement of the body will distort the image. Then the patient slowly moves inside the device.
A small camera begins to rotate around the area under study and runs for 30 to 50 minutes. When introducing contrast, the procedure will take more time. As the tomograph ring rotates, it makes a faint squeaking sound, but the patient does not feel pain or discomfort.
After completing the MRI examination of the wrist and hand, the patient is asked to wait. After 20-30 minutes, the radiologist issues a sheet with a full description of the study results.
The objectivity of scanning is achieved by many detailed images of the area under study.
Preparing for the study
Long-term preparation for MRI of the hands with joint disease is not required. Nevertheless, these tips will help you approach this important procedure correctly:
- You need to choose the right clothes. It should not restrict movement and there should be metal parts (buttons, rivets, fasteners, etc.).
- Remove decorations. Gold, silver and other metal products should not interfere with the event.
- Inform the radiologist about any allergic reactions to medications so that the doctor is alerted.
- If you have claustrophobia, you need to take a calming medicine.
If you follow the basic rules for conducting MRI, you can be confident in the complete safety of this study.
Using Contrast
The most commonly used contrast agent in medicine is gadolinium. It is completely harmless; only 1% of those studied had an allergic reaction to the drug. Before its administration, the patient is tested for sensitivity to the drug. If no reactions are detected, contrast is injected into a vein using a catheter.
All vessels are immediately stained, allowing you to see the slightest pathology. This method is most effective in detecting tumors. Using magnetic tomography, you can see the size of the formations and establish precise localization.
Commonly detected tumors:
- hygroma is a benign tumor that develops from the periarticular bursae on the hand or forearm;
- lipoma appears from adipose tissue and is dangerous because it compresses nearby vessels, tendons and nerve trunks;
- Giant cell xanthoma (synovioma) occurs on the tendons of the palm; with intensive development, pain appears in the fingers;
- hemangioma, forming from vessels, poses less danger since it does not grow;
- neurofibroma, schwannoma, neurinoma - tumors of the nerve sheaths;
- glomus neoplasm manifests itself in the form of pain at low temperature.
There are many more diseases that are detected by magnetic resonance imaging.
Patient actions after MRI
After completing the procedure, the radiologist issues a description with which you need to go to a specialist. Which one exactly - you can see in the conclusion. This could be a surgeon, oncologist or rheumatologist.
If necessary, the attending physician will prescribe additional tests, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment. If the patient is a candidate for surgery, an MRI will help track the recovery period.
The procedure for tomography of the wrist and hand is widespread in Western countries. Basically, the procedure is carried out in open machines so as not to expose patients to stress. In Russia, this examination is carried out both in public and private clinics.
Source: https://Artroz.guru/mrt-luchezapyastnogo-sustava.html
MRI of hands
Today in the medical industry, among non-invasive methods for assessing the condition of bone and soft tissues, there is no equal to magnetic resonance imaging. Using this diagnostic procedure, practicing doctors diagnose various pathologies - from injuries to malignant processes. MRI is most often used in traumatology.
The wrist is considered one of the most susceptible parts of the human body to injury. The occurrence of problems with the wrist joint may be preceded by bruises, injuries, prolonged work while driving a car or a computer - carpal tunnel syndrome develops, which is characterized by pain and numbness of the fingers.
If you experience pain in the wrist area, you should immediately get an MRI of your hand! In terms of the quality of the final data, the magnetic resonance technique is second only to arthroscopy, a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed for the purpose of diagnosing and treating joint injuries. However, this method requires violating the integrity of the skin.
In our article we will provide information about the indications for MRI of the wrist and hand, the stages of preparation and diagnostics, and the use of contrast media.
We will also answer questions that often arise in patients undergoing the procedure - what diseases can be identified through examination, are there any contraindications to scanning, how often are MRIs of the hand done and what do the results mean?
What is the purpose of magnetic tomography?
First of all, diagnosis is prescribed after injury to the wrist joint, as well as in cases where the patient complains of pain and impaired functional activity of the wrist.
Using scanning, you can detect various pathological processes:
- infectious lesions;
- impaired blood circulation;
- foci of inflammatory reaction;
- tumor-like formations.
MRI of the hands is the most universal and informative study that allows you to make a competent diagnosis. This method provides visualization of vessels, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, bone formations, and soft tissues. No other method of examining organs can provide a clear picture of all its structures.
Most often, the doctor prescribes a scan not as a method of primary diagnosis, but to clarify the data obtained from radiography, CT or ultrasound
The main indications for prescribing this diagnostic procedure are:
- the patient has prolonged pain;
- blocking of the wrist joint;
- muscle damage;
- diagnosing arthritis, osteomyelitis, gout, arthrosis;
- pinched tendons and nerve endings;
- suspicion of the development of phlegmon (purulent inflammation of the connective tissue) or hygroma (synovial cyst) of the wrist;
- tumor-like formations;
- lack of effective results from the previous course of treatment and rehabilitation measures.
An MRI of the hand is mandatory during the period of preparation for surgery and after the operation to evaluate its results and the rate of tissue regeneration.
Very often, magnetic resonance scanning is performed to clarify the results of x-rays, ultrasound diagnostics or computed tomography.
The main difference between these research methods and MRI is the greater degree of information content of the data - the ability to assess the condition of the soft tissues and skeletal system of the hand.
There is no alternative to this method of diagnosing pathological processes in modern medicine!
MRI allows you to visualize all structures of the wrist joint - its result shows:
- circulatory disorders;
- congenital pathologies of joint structure;
- damage resulting from injury, sprain or rupture of tendons and ligaments;
- osteonecrosis of the lunate (Kienbock disease);
- neoplasms of various origins;
- damage to adjacent tissues.
Using MRI of the hand, you can find out the exact causes of pain and dysfunction of the hand.
During the diagnosis, the doctor can detect whether the patient has:
- injuries to the hand and forearm that were received at home, at work and during sports;
- rupture of finger tendons;
- tenosynovitis - inflammation of the connective tissue membranes that surround the tendon;
- arthritic and rheumatoid processes;
- osteoporosis and gout – pathological conditions of tissues and joints caused by metabolic disorders in the body;
- carpal tumors;
- neoplasms that affect nearby tissues.
Rules for preparing for the diagnostic procedure
No complicated preparation is required for an MRI of the hand. A few simple recommendations will help the patient prepare properly for the examination.
How many times can an MRI be done?
It is important to choose the right clothes - the main thing is that they do not restrict movement and do not have metal elements (buttons, fasteners, rivets). In the event that a patient who comes for a diagnosis has inappropriate items in his wardrobe, medical workers provide him with disposable underwear.
If a contrast agent will be used during MRI, the patient should worry about his diet. You should not eat food 8-10 hours before the test - the active component of the contrast agent may cause nausea or vomiting. It is necessary to warn the diagnostician about the presence of diseases of the urinary system or increased sensitivity of the body before the procedure begins.
If the patient suffers from claustrophobia, he is prescribed sedatives. Diagnosis of a child’s hand is also accompanied by taking sedatives - during the examination the patient must be completely relaxed.
Procedure for conducting the examination
To scan the wrist, a special medical device is used - a tomograph.
Medical staff place the patient on a retractable table, fix his head and limbs - this is necessary to prevent the slightest distortion of the image, which can appear even with slight movement. Then the table slides inside the tomograph and the ring of the device begins to rotate, producing a faint crackling sound.
The scan lasts about half an hour and does not cause any discomfort to the patient.
Obtaining several detailed high-quality images of individual areas and sections of the wrist allows for an objective study of its condition
When using a contrast agent, diagnosis will take a little longer. Before the procedure begins, the patient is given an allergic skin test.
The drug gadolinium, which is considered absolutely safe for humans, is administered intravenously through a catheter.
The component quickly stains the vascular system - this increases its visualization and allows you to see even minor pathological elements.
This technique is used to identify tumor-like formations, assess the area of affected tissue and study their nature. If there are oncological tumors in the scanned area, the network of vessels stands out most strongly - this is immediately noted by the diagnostician.
In what cases is MRI contraindicated?
It is better to refuse the diagnostic procedure:
- pregnant women;
- children under 7 years old;
- patients with implanted metal devices - hearing aids, insulin pumps, cardiac and neurostimulators, dental crowns, prosthetic limbs;
- persons suffering from hyperkinesis, a pathology in which it is difficult to control the movements of one’s own body.
What the patient should do after receiving the test result
After the tomography is completed, the patient is asked to wait a certain time - the doctor begins to interpret the resulting image of the joint.
Upon completion of the decoding process, the patient receives images with a detailed description, conclusion and preliminary diagnosis.
After this, he goes to the treating specialist, who, based on clinical symptoms, medical history, laboratory tests and MRI, will make a competent diagnosis and develop rational treatment tactics.
Ceramic or plastic dentures and titanium plates do not interfere with the full operation of the magnetic scanner - patients with such foreign bodies can be examined
The most important role in drawing up a clinical picture of the pathological process is played by the ability to represent the wrist joint in a three-dimensional image. This technique helps to identify pathology in the most inaccessible parts of the hand structure in the early stages of its formation.
After the necessary surgical correction, magnetic resonance scanning allows you to track the progress of the rehabilitation process.
This diagnostic procedure does not have a harmful effect on the human body, therefore it can be performed as many times as required by the ongoing course of treatment and preventive measures.
In modern medicine, scanning of hands in open tomographs is increasingly being used - this makes it possible not to subject the patient to psychological stress during the examination.
Source: https://apkhleb.ru/mrt/kistey-ruk
CT or MRI of the hand: which method to choose
Recently, a large number of visits to a traumatologist are associated with diseases of the wrist joint. For severe pain of unknown etiology, carpal tunnel syndrome, or serious injury, a CT scan of the hand is recommended. The procedure allows you to detect any pathologies of bone and muscle tissue, helps to quickly make the correct diagnosis and begin treatment.
Main indications for undergoing MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging in the medical environment is deservedly considered the most high-quality and accurate diagnostic method. Among its advantages are absolute painlessness for the patient, ease of implementation, and does not require lengthy preparation.
It helps make a diagnosis in situations where standard ultrasound or x-rays do not provide the correct information.
There are many medical conditions for which a CT scan of the wrist and hand is recommended:
- preparation for surgery for traumatic amputation;
- preoperative preparation if it is necessary to restore the nerve plexuses;
- with spasms or pain of unknown origin;
- if it is impossible to use other diagnostic methods for various reasons (presence of metal staples in the bone, pregnancy);
- diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome, which occurs during prolonged work at the computer;
- establishing the stage of arthrosis or arthritis of the hand joint;
- confirmation of osteoporosis of bone tissue;
- suspicion of the development of bone marrow cancer, bone metastases;
- diagnosis of skin melanoma;
- developmental anomalies of the wrist joint;
- the need to determine the cause of inflammation in the arm joint.
When conducting an MRI of the hand, the diagnostician has the opportunity to obtain a high-quality image. Cartilage and bone tissue, nerve endings, and blood vessels are simultaneously visible on it.
Which is better: CT or MRI of the wrist?
Depending on the cause of the disease, the traumatologist recommends a CT or MRI of the hand. But for most patients there is virtually no difference between the methods.
In fact, they differ significantly in many respects: information content, impact on the patient’s body, methods of visualizing bone or soft tissue.
Therefore, it is necessary to understand the diagnostic features of each method.
CT or computed tomography involves exposure to high-power X-rays. It is generated using a variety of sensors and is well concentrated in the bones and cartilage of the patient.
It highlights injured and damaged areas, shows small cracks, growths and calluses.
This is a good way to carry out urgent diagnostics after surgery to implant an artificial joint in the hand.
Among the disadvantages of the CT technique is that radiation is considered dangerous, so the procedure can be used no more than 1-2 times a year. It is less informative for vascular abnormalities and does not provide a complete picture when searching for the cause of inflammation or acute pain. According to the methodology, computed tomography of the hand is compared with radiography, which does not have a high degree of information content.
MRI of the wrist joint and examination of the hand are safer for patients of any age. The operating principle is based on creating a resonance of hydrogen molecules using an electromagnetic field. They actively move in certain trajectories, leaving information on the sensors about the shape, appearance and structure of internal organs.
What can be detected with an MRI of the hands?
When performing an MRI of the hands, the tomograph takes the thinnest sections with a thickness of no more than 0.1–1 mm. They form a complete image, which the diagnostician examines in different planes. This allows you to detect serious diseases and complex pathologies:
- inflammatory foci that disrupt the functioning of tendons;
- household or work injuries, sprains, punctures;
- improper healing of bone tissue after a fracture;
- rupture of nerve endings or death of tendon;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- arthrosis;
- salt deposits;
- calluses and spines in the joint capsule of the hand;
- tissue osteoporosis;
- cysts or malignant neoplasms;
- Kienbock's disease (necrosis of the lunate bone);
- Tenosynovitis.
When discussing what an MRI of the hand shows, the possibility of diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome should be mentioned. This is a common disease among office workers that occurs due to prolonged use of a computer keyboard or mouse. Patients complain of severe pain in the wrist, radiating to the elbow. It interferes with full work, eating and resting, and is difficult to detect using ultrasound.
How to properly prepare for the research procedure
The lack of special training can be attributed to the advantages of the examination method. But before visiting the tomography, the diagnostician gives several recommendations that you should pay attention to:
- Before scanning, it is better to change into comfortable, non-tight cotton clothing. Synthetics often provoke skin irritation and make it difficult to remain still.
- The MRI scanner reacts to metal objects, so you should remove jewelry, clothes with a zipper or hairpins, and leave your mobile phone outside the tomography room.
- If the procedure is performed urgently due to severe injury, the patient is asked to change into a special disposable gown.
In some cases, patients are recommended to have an MRI of the joint and hands with the addition of a contrast agent.
This is the only way to diagnose the cause of blood flow disturbances and detect tumors and hygromas of synovial cysts of the wrist.
To do this, the patient is first given a drug containing metal particles that react to an electromagnetic field. They highlight hidden areas in sections and show vessels clogged with blood clots.
When prescribing contrast, the patient is advised to stop drinking 4–6 hours before. This helps the drug to distribute quickly through the blood vessels, which reduces diagnostic time. Radiologists advise undergoing the examination on an empty stomach: the substance sometimes provokes nausea and discomfort, which makes it difficult to remain motionless on the MRI scanner table.
Contraindications to undergoing MRI of the wrist
Magnetic resonance imaging is based on the physical properties of the electromagnetic field. It is safe for adults and children and does not provoke the development of cancer. But there are contraindications under which MRI of the wrist should not be performed:
- Psychological fear of closed spaces. Patients with claustrophobia or neurosis cannot remain motionless in a narrow tunnel for a long time. For them, the diagnostic option remains an open type device or the introduction of anesthesia while the scanner is closed.
- Excess body weight. Many tomograph models are designed for a specific patient's waist diameter. Therefore, if you weigh more than 120–130 kg, you should look for medical centers where the examination is carried out using an open-type scanner.
- Presence of implanted pacemakers and other electronic devices. The magnetic field disrupts their operation and provokes life-threatening failures. Such patients undergo hand diagnostics using ultrasound, CT or conventional x-ray.
- Implanted metal alloy joints, vascular clips or staples. They create serious interference with the operation of scanning sensors and prevent a correct diagnosis.
- Tattoos on the body made in an “artisanal” way. Often the design is applied with paints containing metal particles. When scanning, this not only disrupts the clarity of the images: the person experiences discomfort, burning and itching on the skin.
One of the contraindications to MRI of the hand is pregnancy. Numerous practical studies have not proven any dangerous effects on the growing embryo. But doctors try to eliminate any danger and early intervention. In case of urgent need, the examination is carried out in the last trimester without a contrast agent.
How is an MRI examination performed?
Most medical institutions have closed-type tomographs. Therefore, during scanning, the patient is completely placed in the tunnel on a retractable table. The person arrives for the procedure in advance and changes into prepared clothes. The diagnostician helps you take the necessary position, fixes the hand using a special device, and determines the main parameters on the device.
Video: Carrying out an MRI of the wrist and hand
When scanning a limb, you must remain still and relax as much as possible. The examination takes no more than 30 minutes. Among the unpleasant moments are loud sounds when magnetic coils operate, sharp knocks or blinking sensors. After completing the MRI procedure of the hand, the patient goes home without hospitalization.
If the procedure is carried out with the addition of a contrast agent, it is recommended to additionally undergo a test for possible allergies. It takes a few minutes, but helps get rid of dangerous complications.
Advantages of hand tomography
The MRI procedure is the most modern way to diagnose serious diseases at an early stage.
It has a number of advantages for the patient and doctors: irradiation is safe for humans;
- slices allow you to visualize the smallest details as small as 1 mm;
- from the sections you can trace the cause of the development of the pathology;
- after the examination, it becomes possible to create a three-dimensional image of a tumor or a deformed joint;
- the scanner detects the slightest defects in bone tissue or cracks in areas that are not visualized on x-rays;
- allows you to accurately determine the type of tumor without a preliminary biopsy;
- determines osteoporosis, its stages and the degree of bone tissue destruction.
The contrast agent used for MRI or MSCT of the hand does not contain iodine particles. It rarely causes an allergic reaction and is well tolerated by patients.
Possible risks of an MRI scan
If you follow all the recommendations of radiologists, the examination is absolutely safe for humans. It can be carried out several times a year, monitoring the consequences of the operation or the disease over time. But we should not forget that any medical procedure carries certain risks for the patient.
When performing MRI of the hand, in rare cases the following is observed:
- distortion of images and information when small metal implants are in the body;
- 1–2% of people remain at risk of allergy to gadolinium, which is part of the contrast agent;
- When breastfeeding, the drug is transferred to the newborn, so the woman needs to pump for 1–2 days.
Many contraindications when undergoing MRI of the hand are conditional. Small compact tomographs are already in use in large clinics. They can scan only the hand and carry out the procedure in a sitting position.
What to do after receiving answers
After scanning, the first results can be obtained within 1–2 hours. The diagnostician carefully examines numerous sections, analyzes the differences and identified anomalies. But the final diagnosis is made by a specialized doctor: traumatologist, neurologist, oncologist.
Source: https://mrtdom.ru/diagnostika-mrt/obshhee-ob-mrt/kt-ili-mrt-kisti-ruki
MRI of the wrist and hand
Up to 25% discount on all types of MRI!
In the recent past, information about morphological changes in the wrist and hand was only available using radiography, CT or scintigraphy.
MRI of the wrist and hand has significantly increased the ability to visualize these parts of the upper limb, making it possible to diagnose even small changes in both bone tissue and soft tissue, including blood vessels and nerves.
MRI is often prescribed after injuries, especially in cases of falls on an outstretched arm. In addition, an MRI examination is required to clarify the scope of the planned operation.
It is preferable to carry out MRI of the wrist joint and hand using high-field devices, since anatomically this part of the upper limb requires high resolution, which will allow visualization of small changes.
Indications for MRI of the wrist and hand:
- Acute trauma (fractures)
- Acute soft tissue injuries
- Chronic pain
- Damage to the bones of the hand
- Ligament damage
- Presence of nerve compression
- Pain in the joint or hand of unknown origin
- Swelling in the wrist or hand
- Suspicion of the presence of pus or blood in the joint area
MRI examination allows diagnosing the following diseases:
- Congenital defects of the wrist and hand
- Injuries and damage (ruptured ligaments, tendons)
- Arthritis of various origins (for example, gout or rheumatological diseases)
- Osteoarthritis
- Impaired blood supply to the hand
- Tumors of the joint and hand and nearby tissues (for example, hygroma or lipoma)
- Tunnel syndromes (eg, carpal tunnel syndrome or Guyon's tunnel syndrome)
- Dupuytren's contracture
- Tenosynovitis
- Kienböck's disease
- Habitual dislocation
- Osteomyelitis
- Tendinopathy
- Instability of the wrist joint
No special preparation is required for MRI of the wrist and hand Before the examination, patients must get rid of any metal products, since MRI examinations are carried out using a powerful magnetic field. If you are pregnant, you must inform the doctor conducting the study. In addition, it is necessary to inform the doctor about the presence of somatic pathology, since in some cases the use of contrast is possible, and its administration has certain contraindications.
Also, the patient’s body should not contain metal or electronic products, which is a contraindication for MRI.
An MRI scan takes on average 30 minutes. MRI results are interpreted in conjunction with the results of other studies, which allows the attending physician to choose the correct treatment tactics.
Source: https://www.dikul.net/units/diagnostic/mrt/kist/
MRI of the hand and wrist joint during illness - what will the examination show?
According to medical statistics, the hands and wrists are more likely than other parts of the hand to suffer from injuries and various diseases. If you complain of pain and discomfort, you should consult a doctor and undergo a diagnostic examination.
MRI of the hand and wrist joint is considered a universal diagnostic method, as it can detect pathologies in hard and soft tissues, tendons, and blood vessels.
How to do an MRI, and what will the tomography results show? What is the difference between magnetic and computed tomography? Let's take a closer look.
Indications for MRI diagnostics of the hand
Typically, the procedure is prescribed when other types of examination (ultrasound, radiography, CT scan of bones and joints of the hands) have not yielded results or their indications are ambiguous. It is worth noting that MRI has now become popular, so many patients with wrist injuries immediately undergo the procedure, knowing its benefits. Main indications:
- fractures (cracks) of the bones of the hand;
- joint dislocations;
- arthritis or arthrosis;
- planning of surgical intervention (for precise planning of the course of the operation), postoperative control over tissue restoration and healing;
- diseases of a rheumatic nature;
- osteomyelitis of bones and joints;
- sprained or torn muscles and tendons;
- pinched nerve endings (tunnel syndrome);
- inflammatory process occurring in joints and soft tissues;
- disruption of the circulatory process in this area;
- chronic pain and swelling for no apparent reason;
- deterioration in wrist motor function and decreased range of motion;
- various diseases of joints and tendons;
- congenital anomalies of structural units;
- the presence of tumors (benign or malignant) or suspicion of them.
In what cases is it necessary to examine the wrist joint?
The wrist joint is part of the wrist joint, it is located between the forearm and the first row of carpal bones. It stands out from the general structure, since it is especially susceptible to injuries and pathologies of various origins, and requires comprehensive diagnostics.
Indications for MRI of the wrist joint:
- sports injuries and accidents;
- inflammatory processes;
- pain syndrome of unexplained origin;
- pathologies and abnormalities of the joint structure;
- arthritis and arthrosis;
- rheumatic ailments;
- examination before and after surgery;
- search for malignant or benign neoplasms (MRI on the wrist joint will determine the presence of tumors of any size or metastases);
- suspicion of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Preparing and conducting a contrast study
MRI of the hand does not require complex and lengthy preparation. The procedure is completely painless and does not cause discomfort.
Preparatory activities:
- The doctor collects the necessary medical history. The patient must report any surgeries, illnesses, psychological disorders, medications taken, or the presence of metal plates, staples, wires, or implants in the body that will react to the magnet.
- If MRI of the arm is performed using contrast, you must abstain from food for 5 hours before the procedure. You need to inform your doctor about any allergies to medications to avoid a reaction to the contrast agent.
- Immediately before the procedure, you need to remove metal jewelry, clothing with rivets or buckles. Typically, the medical facility provides disposable shirts for MRI exams.
The contrast is administered intravenously, after which it quickly spreads throughout the body. The substance is brightly illuminated on the monitors of the device.
Malignant tumors and some pathological lesions have a larger number of blood vessels, so they glow especially brightly. Areas with impaired blood flow will be less illuminated, signaling a problem.
Stages of an MRI of the hand:
- the patient changes into a disposable shirt, removes jewelry and piercings, then lies down on the moving table of the tomograph;
- the table slides into the apparatus tunnel, after which the scanning process begins;
- during operation of the tomograph, the patient hears characteristic clicks or squeaks without feeling pain or discomfort;
- after the end of the examination (30-60 minutes), the table moves back;
- The patient receives the results with a full description in about an hour.
Diseases detected by magnetic resonance imaging
MRI of the hand can detect many diseases:
- fractures, bone cracks;
- dislocations, tears or strains of muscles and tendons;
- arthritis and arthrosis;
- congenital or acquired anomalies in the structure of the hand and wrist;
- benign and malignant tumors;
- tunnel syndrome;
- blood flow disturbance;
- diseases of the joints and tendons (tenosynovitis, Kienböck’s disease).
Which is better - CT or MRI?
There is no big difference between MRI and CT (computed tomography). Both diagnostic methods are completely safe, painless and maximally informative.
Computed tomography of the hand is prescribed for injuries, fractures or serious dislocations. With the help of CT, doctors obtain accurate data about bones and joints; it works using x-rays.
However, in case of blood flow disorders and soft tissue pathologies, CT scan of the hand is not informative.
What is best for diagnosis is decided by the attending physician, based on the patient’s complaints or diagnosis.
Possible risks of the procedure
If you strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations, the procedure is completely safe and cannot cause harm to health, otherwise some unpleasant consequences are possible:
- metal objects entering the MRI machine distort its readings and can damage the equipment;
- a mild allergic reaction to the contrast agent is possible;
- contrast administered to a woman during breastfeeding ends up in the milk (it is recommended to stop feeding for a day).
Contraindications for examination
Contraindications for MRI of the hands:
- the presence of metal elements in the body or body, including tattoos made with metal-containing ink;
- heart or kidney failure;
- pregnancy and lactation (with doctor's permission);
- psychological disorders (in this case, relaxants or sedatives are often administered);
- presence of insulin pumps or pacemakers (the devices will fail).
Source: https://vedmed-expert.ru/mrt/sustavi/mrt-kisti-ruki.html