- Endocrinologist of the highest category Anna Valerievna
- 47373
- Update date: December 2019
Mastopathy is a disease of the mammary glands in which their tissue grows.
This is a fairly common pathology that many women face. Lymph nodes with mastopathy can become enlarged and inflamed, which is caused by the pathological process occurring in the chest.
Why pathology affects the lymph nodes and how to deal with it - more on this.
Lymph nodes and mastopathy
One of the causes of mastopathy is a hormonal imbalance that occurs in the body, including due to a woman delaying childbearing or even refusing to have children.
Mastopathy in ICD-10 is designated by code N60.1. This disease is the most common form of mammary gland pathology. Mastopathy is a disease of a hormonal nature and develops due to low levels of progesterone and increased estrogen in the female body.
With mastopathy, there is a proliferation of glandular tissue in the breast with the formation of numerous nodules. This pathology is accompanied by engorgement of the mammary glands, tissue swelling and pain.
Mastopathy is a dangerous disease that requires timely and adequate treatment. Untreated breast pathology increases the risk of developing breast cancer.
Lymph nodes with mastopathy in the vast majority of cases enlarge. Mammologists and therapists do not consider moderate enlargement of lymph nodes in mastopathy to be a pathology. Lymphadenopathy (the so-called enlargement of nodes) is a natural reaction to a pathological process occurring in a woman’s body.
Mastopathy and armpit lymph nodes are closely related. It is the axillary nodes that are the first to respond to pathology of the mammary glands. Nevertheless, enlarged lymph nodes cannot be ignored, because in some cases such a symptom can signal a malignant process.
If, with a slight enlargement of the axillary lymph nodes with diagnosed mastopathy, there is no reason for concern, then inflammation of the nodes and their noticeable increase are dangerous symptoms, the presence of which requires you to urgently consult a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination. Lymphadenitis (inflammation of the nodes of the lymphatic system) with mastopathy indicates the penetration of infection into the tissue of the mammary glands.
Causes of lymph node pathologies
The main reason for enlarged lymph nodes in mastopathy is a natural immune reaction. Lymph nodes are an important element of the immune system, so they are the first to respond to disturbances in the body. Moreover, with mastopathy, predominantly the lymph nodes in the armpits enlarge, which is due to the peculiarities of their location near the pathological focus (breast glands).
Mastopathy in severe cases can develop into a malignant form. With breast cancer, the lymph nodes in the armpits enlarge in response to the process of malignant cell degeneration.
In this case, enlargement of lymph nodes can be both the body’s reaction to cancer pathology and the result of the spread of metastases to the lymphatic system.
The second case is the most dangerous and requires radical treatment measures.
Inflammation of the axillary lymph nodes during mastopathy is observed only in the case of mastitis, which is often observed in nursing women. This pathology is characterized by infectious inflammation of the mammary gland.
Infection through the lymphatic vessels can penetrate the lymph nodes, causing them to enlarge and develop an inflammatory process. Mastitis is designated by code N61.
The pathology is manifested by acute chest pain, fever, purulent discharge from the nipples, and symptoms of intoxication.
Typical symptoms
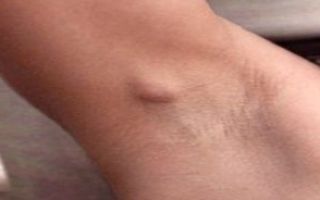
Feeling the armpit can be painful if the lymph nodes are enlarged due to mastopathy
There are two main pathologies of lymph nodes against the background of mastopathy - lymphadenopathy (enlargement of nodes) and lymphadenitis (inflammation of nodes).
Lymphadenopathy according to ICD-10 is designated by code R59. Enlarged lymph nodes in the armpits with mastopathy are manifested by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of noticeable tubercles in the armpits;
- discomfort when pressing;
- night sweats;
- general weakness.
Such symptoms are characteristic only of pathological enlargement of the lymph nodes, when their sizes become twice as large as the original ones. If, with mastopathy, only one lymph node in the armpit is slightly enlarged, only a small tubercle appears, which can only be detected by palpation.
With significant enlargement of the lymph nodes, redness of the skin of the armpits is also possible. Palpation usually does not cause discomfort, but in cases of severe lymphadenopathy, pressing on an enlarged lymph node may cause a dull pain.
Lymphadenopathy in breast pathologies is bilateral, that is, the lymph nodes of the left and right armpits are enlarged. With lymphadenitis, unilateral lesions are more often observed.
Lymphadenitis of the axillary nodes according to ICD-10 is designated by code L04.2. This pathology is characterized by an acute course and more vivid symptoms. Manifestations of lymphadenitis in mastopathy and mastitis include the following signs:
- severe enlargement of the lymph node;
- pain syndrome;
- local redness of the skin;
- increased body temperature;
- symptoms of intoxication;
- headache;
- enlarged liver and spleen;
- night sweats;
- general weakness and loss of strength.
With infection of the lymph nodes, body temperature can increase to 40 degrees. This is accompanied by symptoms of intoxication: nausea, vomiting, weakness, dizziness, loss of strength. The pain syndrome due to inflammation of the lymph nodes intensifies with sharp turns of the body, as well as when wearing too tight clothes.
In the case of purulent inflammation, the size of the lymph nodes increases by 3 or more times. The presence of an infectious process is noticeable to the naked eye.
What are the dangers of lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis?
Lymphadenitis poses a danger to the entire body as a whole
With mastopathy, axillary (axillary) lymph nodes enlarge in response to the presence of a pathological process. With moderate mastopathy, the lymph nodes increase slightly. In general, this condition is not dangerous and is a natural reaction of the body. Timely detection and adequate treatment of mastopathy can completely avoid any complications.
Significant enlargement of the lymph nodes, when tubercles or lumps in the armpits are clearly visible, may indicate a malignant pathology.
In addition, a long course of lymphadenopathy (a chronic form of the disorder) threatens irreversible changes in the lymph nodes, as a result of which their size will not return to normal even after eliminating the cause of this disorder.
Severely enlarged lymph nodes interfere with everyday life, as they hurt noticeably, so in such cases, surgery to remove the nodes may be prescribed.
Another risk of chronic lymphadenopathy is the degeneration of the tissue of the affected lymph node into a malignant tumor. Despite the fact that such a complication is extremely rare, the risk of its development cannot be completely excluded.
Lymphadenitis poses a danger to the entire body as a whole. The presence of an infectious focus weakens the immune system. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, there is a risk of infection spreading throughout the body through the blood or lymph, as a result of which the disease will affect more and more organs and systems.
Purulent lymphadenitis, in which suppuration of the lymph node occurs, is doubly dangerous, since the entry of purulent contents into the blood can cause infection (sepsis). In advanced cases, sepsis can lead to death.
It is important to understand that mastopathy itself is also dangerous, since in advanced forms it is potentially dangerous for the development of breast cancer due to the degeneration of fibrocystic foci in the mammary gland into a malignant tumor.
Thus, having figured out whether lymph nodes can enlarge with mastopathy, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis of mastopathy, a woman needs to visit a gynecologist or mammologist. A gynecologist will be able to make a preliminary diagnosis and exclude some pathologies of the reproductive system that can lead to the development of mastopathy, but then will still refer you to a mammologist.
Diagnostics includes the following examinations:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands;
- Ultrasound of lymph nodes.
It is important to exclude the infectious nature of the disease, so an additional test for hidden infections may be prescribed. In addition to mastopathy, the doctor determines the nature of the changes in the lymph nodes.
Therapy
Take half an hour before meals (can be 50-60 minutes after meals)
With mastopathy, either one lymph node or several nodes at once can enlarge. In severe cases, an increase in all regional lymph nodes is observed. With lymphadenitis, as a rule, 1 or 2 nodes in one area become inflamed.
Enlarged lymph nodes with mastopathy do not require separate treatment. To eliminate the disorder in the lymph nodes, the cause of lymphadenopathy – mastopathy – must be eliminated.
For this use:
- hormonal drugs;
- homeopathic remedies;
- diet;
- rejection of bad habits;
- compliance with the daily routine.
Hormonal drugs are prescribed depending on the state of the woman’s hormonal levels. There is no universal treatment regimen for such medications; medications are selected individually for each patient. Doctors often order a blood test to measure hormone levels before prescribing medications.
Homeopathic medicines stop the process of changes in glandular tissue. For mastopathy, Remens drops or their analogues are often prescribed. In case of enlargement and inflammation of the lymph nodes against the background of mastopathy, as well as disturbances of lymph flow in the area of the mammary glands, the homeopathic remedy Lymphomyosot is prescribed.
The treatment process for mastopathy is lengthy and often lasts for many years. In fact, treatment of mastopathy is not a special drug regimen, but a way of life.
It is important for a woman to give up bad habits and addictions (nicotine, alcohol), learn to deal with stress, follow a special diet, and normalize her daily routine.
At least 8 hours should be allocated for sleep, while overstrain, both physical and emotional, should be avoided during the day.
For lymphadenitis due to mastopathy or mastitis, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. In case of suppuration of the lymph node or mammary gland, surgical emptying of the abscess contents is practiced.
Prevention
Having figured out why there is an enlargement of the lymph node during mastopathy, you should know how to prevent this disorder. There is no specific prevention; it comes down to being attentive to your own health. To prevent the lymph nodes from enlarging or becoming inflamed again, you should strengthen your immune system and follow your doctor’s recommendations for the treatment of mastopathy.
Source: https://limfouzel.ru/limfouzly/limfouzly-pri-mastopatii/
Enlarged lymph nodes under the arms: classification, causes of development, treatment measures
Enlarged lymph nodes under the arms are observed in a large number of diseases. Most often we are talking about bacterial or viral infections, cancer and autoimmune processes. The lymphatic system is the most important component of the body's protective functions, so it is necessary to pay special attention to its condition.
What are lymph nodes for and how do they work? They represent a “biological filter” of our body. Lymph flows through these structures, carrying immune cells from internal organs and tissues. With them, viruses and bacteria that have somehow entered the body penetrate into the lymphatic structures. In the lymph nodes, they are disinfected and destroyed.
If we talk about the axillary lymph nodes, then these structures are responsible for the condition of the mammary glands, upper limbs and chest. That is why, when they increase, we are talking about the development of a pathological process in this area.
Differentiation
Enlarged lymph nodes under the armpit can occur due to the following diseases:
- Lipoma. A benign formation that consists of adipose tissue. The tumor is mobile and soft. It is not fused to the skin and is not painful when pressed.
- Hidradenitis. Inflammatory process in the area of the sweat glands. In this case, severe pain and inflammation are observed.
- Atheroma. Intradermal formation is benign and has nothing to do with damage to the lymphatic system.
Only a medical specialist can make an accurate diagnosis after a comprehensive examination. It is difficult to independently determine what kind of disease we are talking about.
Classification
Lymphadenopathy (lymph nodes under the armpits) is more often diagnosed in women than in men. Such processes in the body can be inflammatory or non-inflammatory in nature. Depending on this, treatment is prescribed.
If the lymph nodes are enlarged, then we can talk about a specific or nonspecific process. In the second case, the pathogens are similar to those with streptococcal, staphylococcal and viral infections. A specific process occurs when pathological microorganisms that cause plague, tuberculosis and syphilis enter the body.
Lymphadenitis in the armpits can occur in acute and chronic forms. In the first case, we are talking about a pronounced clinical picture. When the skin over the formation becomes redder and the local temperature rises. In this case, there is pain syndrome. In the chronic form, the symptoms are hidden.
Reasons for development
Enlargement of the axillary lymph nodes is not the main disease, but a manifestation of the pathology existing in the body. Treatment in this case is aimed primarily at eliminating the underlying cause. The size of healthy lymph nodes is 0.5-1.0 cm. They are painless, mobile and not fused to each other.
The causes of enlarged lymph nodes are divided into two main groups.
1. Inflammatory:
- General viral infection (varicella, infectious mononucleosis, cytomegalovirus, etc.). The changes are insignificant: the pain is not pronounced, adhesions are not observed. After eliminating the viral infection, after a certain period of time (1-2 weeks), recovery occurs on its own. No additional measures need to be taken.
- Infectious process in the area of the upper extremities (wounds, cat scratch disease, panaritium, etc.). In this case, the lymph nodes perform a barrier function, preventing infection from entering the general bloodstream. The increase is observed only on the side on which the lesion is located. Pathological disorders in the body are accompanied by inflammation of the vascular structures in the area of the lymph nodes - lymphangitis. Treatment consists of surgery to cleanse the infected soft tissue of the upper limb. Antibiotics are mandatory.
- Carbuncle or boil. Characterized by the presence of inflammation in the area of the hair follicles. From the source, bacteria penetrate into the lymph flow and are retained by “filters,” which is accompanied by their increase. Treatment is carried out by opening the abscess and carrying out sanitation. After eliminating the main cause, the general condition of the body returns to normal.
2. Non-inflammatory:
- Sarkaidosis. A systemic disease is accompanied by damage to the lymphatic system in several areas simultaneously. In this case, dysfunction of the liver and lungs is observed. In rare cases, the skin and eyes are affected. The patient suffers from general weakness, dry cough and pain in the chest area. The clinical picture resembles pulmonary tuberculosis.
- Lymphoma. A malignant disease that can affect not only lymph nodes, but also internal organs. The body experiences uncontrolled production of lymphocytes, which have a degenerated form.
- Mastopathy and breast cancer. When tumors appear in the chest area, consisting of glandular tissue, in 10% of cases an increase in lymphatic capsules occurs. Distinctive features are a low pain threshold and the absence of adhesions.
If the lymph node under the arm is enlarged, you should immediately visit a specialist who will conduct a comprehensive examination and prescribe effective treatment for the underlying disease. Symptomatic adjustments will be made if necessary.
Is self-examination possible?
How to understand that the lymph nodes in the armpit area are enlarged? To do this, you need to raise your hand to the side and press with your free hand to the entire depth of the armpit. Next, using soft and sliding movements, perform an examination, supposedly scooping out the lymph nodes.
If there are no pathologies, then, as a rule, nothing can be felt. There will be no pain or discomfort.
If there is a small compaction that is loose or fused with surrounding tissues, then in this case it is recommended to consult a doctor to find out the cause of the development of disorders in the body. Timely diagnosis is the key to successful treatment of life-threatening diseases and is a guarantee of the absence of complications.
Therapeutic measures
If the lymph nodes in the armpit are enlarged, then you need to go to see a doctor who will conduct a comprehensive examination. The specialist will prescribe laboratory and instrumental diagnostics and determine the true cause of the changes occurring in the body.
If there is a purulent process in the body, surgical correction is mandatory in order to cleanse the source of inflammation. Next, antibacterial therapy is prescribed, which continues for quite a long time.
In the presence of viral agents, immunomodulatory therapy with Eleutherococcus and Echinacea is prescribed. You can also use sunflower oil or Immunal.
Ultrasound and electrophoresis are prescribed as auxiliary measures. In order to eliminate the inflammatory process in the foci of infection, ointment and cream, such as Heparin or Troxevasin, are used. For oncological processes, chemotherapy is prescribed. In this case, only temporary improvements can be achieved.
Please note that there are no preventive measures for pathological disorders associated with inflammation and enlargement of lymph nodes. As a preventive measure, you can use universal tips that involve maintaining a healthy lifestyle and timely treatment of dysfunctions of internal organs and systems. Exercise and proper nutrition play a big role.
Do not try to self-medicate if the lymph nodes in the armpits are enlarged.
You may be able to deal with the formation by reducing its size, but remember that the underlying cause will not be eliminated. After some time, relapses will occur.
Don't waste time on ineffective treatment. Contact a doctor who will carry out complex therapy, which will eliminate the likelihood of complications.
Source: https://ProLimfo.ru/bolezni/uvelichenie/pod-myshkami
Solving the problem of enlarged lymph nodes in mastopathy
The disease mastopathy is characterized as a benign formation in the mammary glands, the proliferation of connective structures and tissues of the glands, which leads to the appearance of compactions and cyst-like outgrowths. A fairly common disease in women of reproductive age.
Can a lymph node become enlarged with mastopathy? We will talk about this in the article.
Can lymph nodes become enlarged with mastopathy? When a woman is diagnosed with diffuse type mastopathy, it will not be accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes.
- If the diagnosis is fibrocystic dysplasia, then in this case mastopathy and the lymph nodes under the arm are interconnected.
- That is, it can cause complications in the form of lymphadenopathy.
- An increase in axillary lymph nodes is especially observed with mastopathy shortly before the start of the menstrual cycle.
- Because at this time the woman’s hormonal state changes, which also affects the disease.
- After the menstrual cycle ends, the acute symptoms of the disease also disappear.
- There are several stages in which the disease develops. With mastopathy, hyperplasia of the lymph nodes is observed, and the disease is accompanied by pain of varying degrees or without it:
- Stage one is characterized by the fact that before the menstrual cycle, 7-9 days before the menstrual cycle, the internal structures of the mammary glands begin to coarse. These manifestations begin to be noticeable during self-examination. Inflammation of the lymph nodes in mastopathy may not be observed, or they will not have painful manifestations. The age at which this phase of the disease usually manifests is from 20 to 30 years.
The menstrual cycle does not change in any way in terms of regularity, but becomes short up to 21 days.
- In the second stage, one can note the presence of cysts and the onset of symptoms 2-3 weeks before the start of the menstrual cycle. The age group in which this phase of mastopathy occurs is from 30 to 40 years. The lymphatic system becomes inflamed more often and is accompanied by aching pain, sometimes the pain can be stabbing in nature and manifest itself in the area of the diaphragm and heart.
- At the third stage development, which in most cases affects the age after 40 years, the pain of the mammary glands themselves is of low intensity, but there is a large accumulation of cysts. Additionally, there is a brown-green discharge that can be observed by pressing on the nipples.
At the same time, the lymph node is enlarged due to mastopathy. There is also acute pain of a shooting nature, which can manifest itself in the cervical spine, collarbone or stomach.
- Enlarged lymph nodes may not always be accompanied by a disease such as mastopathy, no matter what type it is.
- If the lymph nodes change their normal state and become enlarged, then this is a signal that pathological changes are beginning to occur in the body.
- If we consider inflammation and enlargement of the lymph nodes, starting from the fact that mastopathy has been diagnosed, then the following nodes are more susceptible to this:
- axipilar (those located under the armpit);
- clavicular and subclavian.
- Inflammation of these particular lymph nodes occurs due to the fact that blockage (formation of cysts and nodes) in the chest and mammary glands affects the normal movement of lymph through the woman’s body system.
- The lymphatic system in this area is designed in such a way that the outflow of lymph goes directly to the armpit area and the supraclavicular region.
- It is impossible to say with certainty where exactly the inflammatory process will manifest itself in the lymph nodes.
- With mastopathy, the supraclavicular lymph nodes may also enlarge.
If you observe enlargement of the lymph nodes under the arms with mastopathy, then pain may appear only during menstruation or shortly before its onset. In some cases, pain with mastopathy in the armpit is constantly present, but it is not as severe as during an exacerbation.
IMPORTANT If swollen lymph nodes are detected, you should immediately consult a specialist, because self-medication in this case is unacceptable, because the lymph nodes can be enlarged for more serious reasons.
An enlarged and swollen lymph node indicates that the body is fighting some kind of infection that has entered the body. With the help of the lymphatic system, the body gets rid of foreign objects.
Reasons why lymph nodes may be enlarged:
- The simplest reason lies in non-compliance with hygiene rules or incorrect selection of cosmetic care products. For example, deodorant clogs the sweat glands or lack of self-care due to excessive sweating.
- Sometimes pregnancy and lactation cause enlarged lymph nodes, but this manifestation does not require treatment, because in fact it is not a disease.
- The cause may be boils or suppuration on the shoulders, arms or chest.
- In childhood, inflammatory lymph nodes may occur if chickenpox, measles or monoculosis are present. In this case, you should treat the underlying disease.
Considering the swelling of the lymph nodes, we can name the following diseases that provoke this process:
- tuberculosis;
- brucellosis;
- tularemia;
- syphilis;
- plague;
- some systemic diseases, such as rheumatism;
- oncological diseases: breast cancer, lymphogranulomatosis, lymphoma.
Swelling may also occur in the lymph nodes in the event of a disease such as axillary lymphadenitis.
It can be recognized by symptoms of fever, chills and malaise. Several nodes can be inflamed at once, which either retain their mobility or become fused with nearby tissues.
Pain syndrome is not always accompanied by such diseases. If acute lymphadenitis is caused by tuberculosis infection or syphilis, then pain may not be observed. There is also no pain with cancer or blood diseases.
Help with armpit pain
When mastopathy hurts under the armpit, what should I do? When the pain from an inflamed lymph node becomes very severe, then initially it is worth eliminating the pain with any medication with painkillers and anti-inflammatory effects.
- But you need to do this only in order to be able to get to the doctor and undergo an examination.
- Self-diagnosis and self-treatment will not lead to the desired results, because it is not possible to understand the cause on your own.
- The following measures may be prescribed by a doctor for enlarged lymph nodes:
- If the lymph node does not stop showing pain within 21 days and the causes have not been identified, a puncture and even a biopsy are prescribed.
- When a cause is discovered, all efforts are directed toward treating the disease that caused the inflammatory process in the lymphatic system.
- If the cause is mastopathy, then treatment methods will depend on the type of disease. Basically, the examination is carried out by doing a mammogram, ultrasound, taking a course of medications and contraceptives containing hormones in order to equalize the hormonal level in a woman’s blood.
- In some cases, inflammation can only be eliminated through surgery.
Who should I contact if symptoms appear?
- If the pain syndrome is so severe that it is not possible to get to the hospital on your own, you should call an ambulance, which, after a superficial examination, will refer you to the right department in the hospital to a specialist.
- If swelling of the lymph nodes is detected that is not accompanied by severe pain, you should contact your doctor, who will give you a referral to the right specialist.
- This should be done when the patient has no idea why the lymph node is inflamed.
- If you have previously been diagnosed with one of the types of mastopathy or such symptoms were discovered during breast self-examination, then you need to contact a mammologist.
- If for some reason there is no such specialist in the clinic or hospital, you can contact a gynecologist, or better yet, an oncologist.
- To avoid such a disease, it is better to take preventive measures and monitor your health.
- You should also undergo regular checkups to ensure that your breasts remain in stable, normal functioning and healthy condition.
- When implementing preventive measures, there is a chance to detect the disease and get rid of it in the early stages, which is much easier and less painful.
- You can find more information on this topic in the Diagnosis and Symptoms section.
Source: https://nesekret.net/mastopatiya/diagnostika-i-simptomatika/limfouzly
Lymph nodes with mastopathy: does enlargement occur under the arms, what to do, what is dangerous
Enlarged and painful lymph nodes with mastopathy are a common symptom caused by the progression of the pathological process in the mammary gland.
Delayed diagnosis or lack of treatment can lead to dangerous complications such as degeneration into a malignant form and the formation of purulent lymphadenitis.
You can cope with the problem with the help of medication, following a special diet and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
How mastopathy affects the lymph nodes
Mastopathy is one of the most common forms of breast disease.
The pathology is considered hormone-dependent, and its cause is low concentrations of progesterone and high levels of estrogen.
Mastopathy is accompanied by the proliferation of glandular tissue in the mammary glands, which leads to the formation of multiple nodules. Pathology is indicated by swelling of the tissues, engorgement of the glands and the appearance of pain in the affected area.
Enlarged lymph nodes under the arms during mastopathy are one of the most common signs of the development of the disease. Experts note a close relationship between the disease and the lymph nodes. It is in the armpits that the body’s reaction to the pathological process occurring in the chest is primarily observed.
Despite the fact that many experts do not consider enlarged lymph nodes due to mastopathy to be a pathology, it is not recommended to ignore this condition, since this sign in certain situations may indicate the onset of the development of an oncological process.
If the lymph nodes are slightly enlarged, then there is nothing to worry about. In the presence of inflammation and severe enlargement, this condition can pose a danger to women's health. Lymphadenitis is a sign of infection of breast tissue.
Why is swollen lymph nodes dangerous?
If mastopathy occurs in a mild form, then the enlargement of the lymph nodes is insignificant. This condition is considered not dangerous to the body and manifests itself as a reaction to a disorder in the body.
With significant damage, when the formed bumps become visible to the naked eye, there is a threat of the development of an oncological process.
In the chronic form of lymphadenitis, the likelihood of irreversible changes in the lymphatic system increases. Against this background, the lymph nodes will no longer be the same size even after therapeutic measures are carried out and the main provoking factor is eliminated.
In addition, the pronounced course of the pathological process creates certain difficulties in everyday life, since the pathology is accompanied by severe painful sensations. In such a situation, surgical intervention may be prescribed in which the inflamed nodes must be removed.
An infectious focus with lymphadenitis helps to weaken the immune system. If you do not begin to treat the pathology, the infection begins to spread throughout the body, which entails damage to new systems and anatomical structures.
One of the most dangerous is considered to be the degeneration of a tumor into an oncological neoplasm.
A clear threat is observed in the purulent form of lymphadenitis, since the entry of pus into the blood can trigger the occurrence of sepsis. If left untreated, this condition can be fatal.
You also need to understand how dangerous mastopathy itself can be. An advanced form of the disease can trigger the development of breast cancer, since fibrocystic lesions can begin to degenerate into a malignant neoplasm.
What to do
To eliminate pathological changes in the lymph nodes, all therapeutic measures must be aimed at eliminating the root cause, that is, mastopathy. Treatment is carried out using several methods.
Drugs
For this purpose, the doctor may prescribe drugs from the following groups.
Hormonal
The decision to choose a medication in this category is made depending on the hormonal state of the patient. Medicines are selected individually.
Homeopathic
The use of drugs in this group is aimed at eliminating changes in glandular tissue. Remens in drops, as well as its analogues, have good effectiveness. In addition, for the inflammatory process in the lymph nodes, Lymphomyosot can be used.
Lifestyle
When diagnosing mastopathy, which is accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes, you should immediately get rid of bad habits. In addition, it is necessary to monitor nutrition and not expose the body to stressful situations.
It is recommended to sleep at least 8 hours a day. Throughout the day, emotional and physical stress does not subside.
If you suspect mastopathy, which is characterized by inflammation and enlargement of the lymph nodes, you should immediately visit a specialist. Untimely treatment can lead to irreversible processes.
Source: https://onkologia.ru/dobrokachestvennyie-opuholi/molochnaya-zheleza/uvelichivayutsya-li-limfouzly-pri-mastopatii/
What will inflamed lymph nodes tell you about mastopathy?
According to WHO data, every fourth woman under 30 years of age shows signs of mastopathy, and after 40 years, 60% of those examined show signs of mastopathy. The disease itself rarely degenerates into a malignant oncological pathology, but serves as a background for cancer.
So, in 60 - 70% of women with this disappointing diagnosis, certain signs of mastopathy were found. Self-examination of the mammary glands, regular preventive examinations and extended examinations when indicated are the key to breast health.
Can lymph nodes be enlarged with mastopathy? When should you sound the alarm and run to the doctor? To answer, you need to understand the causes and symptoms of the disease.
What is mastopathy
Mastopathy includes a large group of benign breast diseases. All of them are united by uneven tissue growth - glandular, epithelial, stromal components. As a result, cysts of various sizes and even groups of them, compactions of various types, etc. can form. All this is accompanied by certain clinical symptoms.
The basis of such disorders is an imbalance of sex hormones: estrogens, progesterone and prolactin. Each of them affects the breast tissue in a certain way, and their non-physiological fluctuations during the cycle cause the clinic of mastopathy.
Prolactin stimulates the growth of the mammary glands and their special transformation, aimed at further preparation for lactation. It increases the sensitivity of organ tissue to the effects of the main female sex hormone - estradiol.
It is this one from the group of estrogens that is responsible for the increased formation of ducts, cell division and the appearance of new acini - lobules, increases the blood supply to the breast and its ability to accumulate fluid.
Progesterone inhibits these processes to some extent, thereby establishing balance and ensuring the health of the mammary gland.
Reasons for the development of pathology
An increase in the amount of estradiol and a decrease in progesterone - this is the ratio that is most often observed in women suffering from mastopathy. And with elevated prolactin values, breast tissue becomes even more sensitive to the action of estrogens.
It is also possible to identify a number of reasons that lead to an imbalance of sex hormones, and therefore to the appearance of mastopathy. These include:
- Psycho-emotional overload, stress, dissatisfaction with one’s own family and social situation. This leads to disruption of the cyclic functioning of the endocrine organs and nervous system, and there is a breakdown in the connections between systems.
- Features of a reproductive nature. This includes early puberty (before 10 - 11 years), late menopause (after 50 - 55 years), onset of sexual activity after 30 years, termination of pregnancies, especially the first, a small number of children and absence or insufficient breastfeeding (less than a year), and also some others.
- Inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs also contribute to the development of mastopathy.
- Hormonal imbalance due to gynecological pathology. For example, with endometriosis, endometrial hyperplasia, uterine fibroids, polycystic ovary syndrome, etc. All these conditions are associated with an increase in the level of estrogens in the blood, which stimulate tissue proliferation and the formation of nodules, cystic changes, etc.
- Problems in the sexual sphere (dissatisfaction, discomfort, decreased libido) are also a sign of both hormonal imbalance and some other pathology. As a result of all this, mastopathy develops.
- All endocrine disorders lead to changes in the functioning of the ovaries. Mastopathy develops against the background of diabetes mellitus, thyroid pathology, metabolic syndrome, and others. Most often, this pathology is associated with hypo- and hyperthyroidism. This happens due to the fact that the regulation of the functions of the thyroid gland and ovaries occurs in similar areas of the pituitary gland. It also affects the fact that thyroid hormones play an important role in the metabolic functions of the body, including the metabolism of estrogens and gestagens.
- Disruption of the liver and bile ducts. The fact is that the production and level of estrogen largely depend on this. This is due to the fact that the liver is a “factory” for processing and releasing steroid (sex) hormones.
- Hereditary predisposition to mastopathy.
All of the above shows that pathology develops under a combination of causes. Today you can rarely find a woman who would not check several of the listed points for herself.
We recommend reading the article on the prevention of mastopathy. From it you will learn about the causes of the development of the disease, the influence of hormones on the condition of the mammary gland, examination and treatment, as well as measures to prevent the development of mastopathy.
Characteristic signs and symptoms
Each form of mastopathy has its own characteristics of manifestation. But it is possible to identify common features for all.
Pain (mastalgia)
As a rule, at the initial stage of development of mastalgia, women either do not worry about it, or they do not pay attention to minor discomfort in the mammary glands. In the future, the pain has a brighter color and its appearance is clearly visible 7 - 10 days before the next menstruation.
The character can be aching, stabbing, sharp, pulling and others. Sometimes it is impossible to touch the breast due to discomfort. On days 1 - 2 of the cycle, the pain usually gradually disappears.
Mammalgia
In addition to mastalgia, mastodynia is characteristic - enlargement and swelling of both mammary glands. Sometimes women identify axillary lymph nodes with mastopathy. In most cases, these are not them, but additional slices.
Such formations undergo the same cyclic changes as the mammary glands.
Therefore, additional lobules are easy to distinguish from lymph nodes: the first ones always appear on the eve of menstruation, bring pain and discomfort, and disappear in the first days of the cycle.
Both processes, mastalgia and matodynia, are associated with excessive accumulation of liquid blood in the breast tissue. This happens due to excess estrogen.
Nipple discharge
Normally, discharge from the mammary glands can be present during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as for two years after the end of lactation. Everything else is signs of mastopathy.
As a rule, discharge appears only when pressure is applied to the nipple. They can be transparent, milky, with a greenish or yellowish tint. The presence of blood in the discharge is an alarming signal, and if detected, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Definition of formations
Often with mastopathy, during palpation of the mammary glands, compactions of different shapes and sizes will be determined. They are painless, immobile, and not fused to the surrounding tissues. If any lumps are detected, you should consult a doctor for examination and further examination, as it may be a malignant tumor.
Can lymph nodes become enlarged with mastopathy? If the pathology occurs without any complications, then there should be no temperature or any formations in the armpit. The exception is the additional lobe of the mammary gland; with mastopathy, it sometimes looks like an enlarged and painful “lymph node”.
Diagnostics
Identifying mastopathy is not difficult if you carefully question the woman. Complaints of pain, swelling and enlargement of the mammary glands on the eve of menstruation are the main signs of pathology.
Also, upon palpation, heterogeneity of tissue structure and compaction can be determined.
As a rule, they are small in size, sometimes resemble “grains” in the breast, are not fused with the surrounding tissues, and are often irregular in shape.
To clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary in all cases to conduct an additional examination, primarily to completely exclude a malignant process. For this purpose, the following is carried out:
- Ultrasound examination of the mammary glands. This is the most informative procedure for girls of reproductive age. An ultrasound should be performed on days 5 - 7 of the menstrual cycle, at this time the mammary glands are “calm” and the result will be the most reliable.
- Mammography. This test is more often used for menopausal women. It is when the mammary glands are in the stage of involuting changes that mammography shows the true picture.
- Biopsy of breast tissue. This procedure is not always used, but when a malignant process is suspected or to clarify the diagnosis. It is performed both on an outpatient and inpatient basis, usually under local anesthesia.
- Contrast ductography is used to diagnose intraductal papillomas. As a result of the study, it is possible to clarify any formation located inside and confirm the diagnosis.
Often several techniques are used simultaneously, for example, biopsy under ultrasound guidance of the mammary glands, etc.
If a woman has mastopathy and the lymph nodes under the armpit have been identified for some time, then an ultrasound examination is also performed after examination. It helps differentiate education. This can be either a lymph node or an additional lobule of the mammary gland.
What do swollen lymph nodes indicate?
Identification of round formations in the armpit does not always indicate that these are lymph nodes. These changes can be detected under the following conditions:
| Inflammation in the mammary gland | Infectious pathology can develop both during and outside of lactation. Sometimes suppuration of a cyst or hematoma occurs in the mammary gland. In such situations, round formations in the armpit area will be painful; several are identified. Also, in most cases, general well-being suffers: body temperature rises, pain in the affected mammary gland, the skin over the pathological area on the chest becomes red. The fact that the lymph nodes are enlarged, including mastopathy, in such situations indicates inflammation in nearby structures. |
| Inflammation in the upper limb | Any infection of the hand or other part of the arm can lead to enlargement of the lymph nodes in the armpit. This is due to the fact that blood from the fingertips flows through the veins into the subclavian vein and further into the superior vena cava. |
| Oncological pathology with damage to the lymph nodes. In this case, often the first manifestations of the disease can be detected in the armpit. As a rule, a group of lymph nodes immediately increases and then “clusters” are determined. | |
| Malignant neoplasms | If during an oncological process something similar is found in the armpit, then most likely these are metastases. Including breast cancer located in the upper outer part of the organ, it is this group that primarily increases. |
| Additional lobule of mammary gland | It is found in 5 - 10% of women, and they often believe that it is the lymph nodes that hurt due to mastopathy. If such round formations appear on the eve of menstruation, their pain appears, then first of all it is necessary to exclude the variant of the anatomical norm - an additional lobe of the mammary gland. |
Treatment of pathology
Therapy for mastopathy depends on its form. For diffuse cases, conservative, including hormonal, treatment methods are used. For nodular cases, preference is given to surgical intervention.
Conservative therapy
The basis of treatment in this case is based on the supposed theory of the development of pathology. The essence of the method is to use various methods to increase the level of gestagens in breast tissue.
Vitamin therapy is always prescribed - group A and E, B6, P, C. They can be used in the form of complexes or separately. Vitamin A reduces the effect of estrogen on breast tissue, and Vitamin E enhances the effect of progesterone.
Groups P and C improve blood supply and fluid outflow during the premenstrual period. Vitamin B6 reduces prolactin levels in the blood to some extent. It is also useful to use iodine. This microelement regulates the formation of estrogens and gestagens in the body.
But iodine should be prescribed with caution in cases of thyroid pathology.
- If a woman has liver and biliary tract diseases, complex therapy includes hepatoprotectors.
- It is useful to prescribe herbal preparations to increase the adaptive properties of the body, for example, tincture of Eleutherococcus, rosea radiola and the like.
- If there is severe engorgement of the mammary glands on the eve of menstruation, it is recommended to use mild diuretics, including herbal ones.
Progestin drugs are also used, most often in the form of gels and ointments for topical use. The advantage of this form of drugs is that they enter the systemic bloodstream in minimal quantities, acting at the level of the mammary glands.
Hormonal medications are also used in tablet forms. These can be drugs of different groups: antiestrogens, oral contraceptives, gestagens, androgens, drugs to reduce the amount of prolactin and others. But their purpose is determined only by the doctor.
It is also possible to use various methods of traditional medicine: decoctions, infusions, etc. They are also available in tablet form, for example, the drug “Mastodinon” and others.
Surgical treatment
Surgical intervention is preferable for all nodular forms. This is due to the fact that often in such situations an unfavorable tumor is hidden behind a benign process.
There are often cases when in such situations mastopathy and enlarged lymph nodes are detected, which is another proof of the possibility of a malignant formation.
The scope of surgical intervention is determined after further examination. In most cases, this is a sectoral resection or even simply removal of the tumor with urgent histological examination, after which the operation can either be completed or its course can be changed.
When to sound the alarm
Sometimes the line between benign and malignant is very thin. But there are clear signs of cancer, if detected, you should immediately contact a specialist. These include:
- asymmetry of the mammary glands, which did not exist before;
- symptom of nipple retraction;
- determination of tumor formation;
- symptom of “orange peel” on the skin of the chest due to its swelling;
- discharge from the nipples, especially bloody in nature;
- change in skin color and pain in the mammary gland.
But you should know that breast cancer is often asymptomatic, especially in the initial stages. Therefore, regular examination is extremely important, especially for women at risk.
Mastopathy is a dishormonal disease of the mammary glands.
The prevalence of the pathology, the discomfort it brings, as well as the latent course of cancer against its background obliges doctors of all specialties to conduct a breast examination at every appointment.
If mastopathy is detected or the lymph nodes are inflamed, you should immediately consult a doctor. Only he will be able to establish the cause and prescribe effective treatment.
Source: http://GrudInfo.ru/limfouzly-pri-mastopatii/