Esophageal papilloma is a neoplasm that appears on its walls due to infection with the HPV virus.
It can develop asymptomatically for years, but then, increasing in size, it begins to cause serious discomfort to the patient, making it difficult to swallow, causing causeless vomiting, excessive salivation, and pain.
To remove the growth, surgical methods are used , which are supplemented by taking medications and vitamin complexes.
Brief information
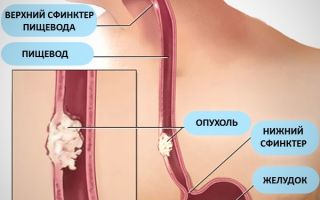
According to statistics, squamous cell papillomas of the esophagus are most often localized in the central or lower part. They are located one at a time, have a nipple-like structure, or in multiple quantities, reminiscent of a bush or polyp. Their color matches the shade of the surrounding fabrics. The surface of the neoplasms is heterogeneous.
The average size of the growth is about 2 mm, but there are specimens with a diameter of up to 2-3 cm, the appearance of which contributes to a significant narrowing of the esophagus and difficulties in swallowing.
The larger the tumor, the higher the risk of injury from solid food. This causes bleeding, and the development of an inflammatory process or infection through an open wound is possible.
Papillomas grow slowly, so the patient may not know for many years that a neoplasm has “settled” in his esophagus. Often pathology is discovered by chance during an examination of the gastrointestinal tract.
Video
Esophageal polyp
Features of the virus
The occurrence of esophageal papilloma is a consequence of infection of the body with HPV. According to statistics, it can be diagnosed in more than 70% of the population. The danger of this situation is that the papillomavirus may not show any manifestations for many years, and then become the cause of the development of a malignant tumor.
There are three ways HPV enters the body:
- sexual intercourse is the most common way;
- household route - involves the use of hygiene items, clothing of an infected person;
- vertical infection (papillomavirus is transmitted from mother to baby during childbirth).
Modern science knows more than 100 varieties of the HPV virus. Two of them are considered the most dangerous: 16 and 18. The remaining strains may never manifest their existence during the patient’s entire life until provoking factors arise.
The problem of HPV infection is potentially dangerous for the patient, so a visit to a doctor and treatment is required.
In the absence of therapy, benign neoplasms may degenerate into malignant ones and the development of cancerous tumors.
Reasons for appearance
The formation of squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus is one of the possible consequences of HPV.
It occurs if there are provoking factors:
- violation of the integrity of the esophageal mucosa;
- neglect of hygiene rules (eating dirty foods, refusing to wash hands before eating);
- smoking – contributes to a decrease in general immunity;
- frequent consumption of strong alcohol - such drinks can burn the walls of the esophagus, which leads to a violation of their integrity;
- passion for excessively hot, spicy food - it depresses the patient’s gastrointestinal tract and becomes an impetus for the development of various pathologies;
- Frequent stress reduces the body's defenses;
- grueling physical activity, constant dieting.
Other provoking factors are hormonal disorders, colds that “hit” the immune system, or exacerbations of chronic ailments. Practice shows that esophageal papillomas are rare phenomena; they are mainly diagnosed in older people, but sometimes they are also found in young people.
Symptoms
At the initial stages, the tumor develops asymptomatically, the patient is unaware of its existence. Gradually, the size of the growths increases, they protrude above the surrounding tissues, which causes a set of unpleasant symptoms when eating.
Doctors identify the following symptoms of papilloma in the esophagus:
- pain when swallowing;
- constant feeling that a foreign object is stuck in the esophagus;
- pain, burning in the chest that occurs immediately after eating food;
- nausea, causeless vomiting;
- belching, intense salivation;
- decreased performance, general weakness.
The first signs of a growth are a good reason to consult a doctor. Without proper treatment, the tumor can increase in size, and in some cases, become the cause of malignant tumors of the esophagus.
Diagnostics
Manifestations of papillomatosis of the skin or mucous membranes require careful medical diagnosis. To do this, the patient needs to contact a therapist or gastroenterologist. The appointment begins with a history taking, during which the nature of the unpleasant sensations, their frequency, intensity, and connection with provoking factors are clarified.
Next, studies are prescribed to help determine the location of the tumor in the esophagus, its size, and other features.
These include:
- radiography;
- CT or MRI
- endoscopy.
Additionally, the patient is prescribed blood and urine tests; if there is a suspicion of tumor malignancy, a blood test for tumor markers.
If the studies indicate that a papilloma has formed in the esophagus, the patient is prescribed a PCR test. To do this, they use sputum, blood or urine; in women, scrapings from the cervix. The test results show whether there is HPV in the body and help determine its type and concentration.
Virus typing is a necessary condition for further effective treatment. HPV is divided into two types: less dangerous and oncogenic, causing precancerous conditions and malignant tumors.
If in the first case you can do without taking medications, then in the second, immediate therapy is required, selected individually.
Treatment methods
Therapeutic methods are selected after consultation with a gastroenterologist.
If a patient is diagnosed with esophageal papilloma, three treatment methods are used:
- drug therapy - aimed at reducing the activity of the HPV virus - the root cause of growths, activating the patient's immunity;
- surgical removal – aims to normalize the patient’s gastrointestinal tract, remove obstacles to the free passage of food through the esophagus;
- traditional therapy - used exclusively as an addition to a complex of medical measures, aimed at increasing the body's defenses.
If there is a tendency towards malignancy of papilloma, i.e. its degeneration into a malignant neoplasm, the patient may be prescribed a course of chemotherapy after resection of the growth.
Stages of therapy
If a papilloma that has affected the mucous membrane of the stomach or esophagus does not produce a set of unpleasant symptoms that reduce the patient’s quality of life, doctors do not prescribe its removal. Observation tactics are used: the patient visits a gastroenterologist approximately once every six months, undergoes tests, and undergoes examinations that allow one to judge the dynamics of the development of the tumor.
At the observation stage, patients are advised to follow a special diet, which involves avoiding the consumption of too spicy and spicy foods and strong alcohol. Quitting smoking is advisable. In addition to these measures, drug therapy is prescribed.
If esophageal papilloma tends to grow, disrupts the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, is often injured or can develop into a malignant form, doctors move on to the second stage of treatment - surgery.
Drug therapy
If a patient is diagnosed with esophageal papilloma, he is prescribed drug therapy, including three groups of drugs:
- antiviral agents - suppress the activity of HPV, used in the form of tablets, injections, rectally, intravaginally. This group of drugs includes Isoprinosine, Panavir, Alpizarin, etc.
- Immunomodulators – increase the patient’s body’s defenses. They are used in the form of tablets or injections. This group includes Lykopid, Polyoxidonium.
- Vitamin complexes help maintain immunity at a high level, which helps suppress the activity of the virus.
Relatively recently, doctors were able to discover the positive properties of ozone to combat HPV. This element is used as one of the components of complex therapy in the form of injections or ozonated oils.
Surgical intervention
If papilloma causes a complex of unpleasant symptoms, the patient requires surgical treatment of the esophagus.
There are the following methods:
This is the least traumatic method of exposure, when the device is inserted into the lumen of the esophagus through an incision with a diameter of several millimeters. The doctor removes the papilloma, tracking his actions on the monitor. For this manipulation, a laser, electrocoagulator or surgical scalpel is used.
The endoscopic method avoids hospitalization of the patient and minimizes the recovery period.
It is used exclusively for benign tumors, for papillomas accompanied by esophagitis of the lower third of the esophagus, and is not prescribed for growths that can become malignant.
This is a low-traumatic operation used to detect large papillomas. It is performed through an incision of up to 15 mm.
This is a classic abdominal operation, which is prescribed for multiple neoplasms. The patient is left with large scars, and the recovery rate may be slow.
If the papillomas are very large or the risk of their development into a malignant form is high, the patient needs partial or complete resection of the esophagus followed by plastic surgery (the removed walls are replaced with colon tissue).
Folk remedies
Traditional methods are part of complex therapy for esophageal papilloma, but not the only way to combat the problem. They can be used after consultation with your doctor.
Doctors “for plow” offer the following ways to increase immunity and fight HPV:
The garlic is twisted through a meat grinder, poured with boiling water, left in a cool and dark place for 2 days, then filtered through cheesecloth. Take 10 g at night.
Potato tubers have proven antiviral properties. Traditional medicine recommends grating them, then squeezing the juice and consuming a tablespoon before breakfast.
One of the effective recipes involves combining nettle, currant and raspberry leaves in equal quantities and pouring boiling water over them. The composition is covered with a lid, wrapped in a towel, and left for half an hour. It should be drunk 1-2 times a day as tea.
Complications
Complications of esophageal papilloma include:
- growth of tissues into malignant ones with subsequent metastasis;
- food injury, subsequent bleeding, infection;
- risk of developing stomach ulcers;
- germination into muscle and bone tissue.
The most common complications of surgical removal of a growth include suture dehiscence, bleeding, and the development of an inflammatory process. If esophageal plastic surgery is performed, the transplanted tissue may be rejected.
Forecast
If the papilloma in the esophagus is benign, the prognosis is completely favorable. Surgical intervention allows you to completely get rid of the pathology, mortality does not exceed 1-2%. The likelihood of relapse is close to zero. The speed of recovery and the presence of scars depend on the surgical method chosen by the doctor.
If the papilloma has degenerated into a cancerous tumor, the patient’s probability of survival is 50%. The recovery course is long because partial or complete resection of the esophagus and chemotherapy are required.
Prevention
Esophageal papilloma is a consequence of the development of the HPV virus in the patient’s body. To prevent infection by it, you should not use clothes and hygiene items of sick people, and walk barefoot in public saunas and baths. Intimate hygiene is of particular importance: avoiding casual relationships, using condoms.
Additionally, prevention methods are used aimed at increasing the body's immune strength.
If symptoms of any disease occur, it is important to undergo medical examinations in a timely manner, follow medical recommendations, avoid hormonal fluctuations, give up bad habits, ensure a balanced and regular diet, sufficient sleep and rest, and moderate physical activity.
Source: https://papilom-net.ru/vpch/ploskokletochnaya-pischevoda
What is squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus and why is it dangerous?
A disease called “squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus” is diagnosed more and more every year. This neoplasm is a benign pathology. A tumor appears on the esophageal mucosa with a structure in the form of papillae, an uneven surface and a diameter of no more than 2 mm.
Among those in whom this disease is most often detected are men aged 40 years and older who have bad habits. This is a rare disease of the esophageal tube, mainly characterized by single growths on its walls.
But there are also several papillomas together, then they grow into a large wart up to 2-3 cm in diameter, with a bumpy surface, causing a narrowing of the esophagus.
Causes of papilloma
It is believed that the appearance of esophageal papilloma is provoked by one of more than 100 varieties of the human papillomavirus (HPV). Many of us are carriers of this virus.
But under normal conditions, it may not appear even once in a person’s entire life. And only with a decrease in immunity and damage to the walls of the esophagus do favorable conditions appear for its awakening.
And the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract is damaged as a result of the lifestyle and nutritional system that a person adheres to.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of papillomas:
- abuse of strong alcohol, smoking;
- advanced gastritis and colitis;
- spicy, salty, fatty foods;
- fast food;
- severe prolonged stress and depression;
- passion for strict diets;
- great physical activity;
- irregular, unhealthy diet.
The virus, once in a wound or erosion on the wall of the esophagus, which is a favorable environment for it, begins its activity. Any virus that has settled in the body is actively fought by the immune system, suppressing it.
When such protection is weakened for any reason, the virus begins to exhibit increased activity. Papillomas can form not only on the neck or body in various places, but also on the esophageal mucosa. These formations are dangerous because there is a high risk of their development and degeneration into malignant ones.
HPV is transmitted from person to person through everyday life - from mother to newborn, through various tools - for manicure or pedicure, for example, during sexual contact, through the skin.
This virus, its behavior and impact are not fully understood. Doctors, for example, do not guarantee that after excision of a papilloma it will not reappear.
Or there are cases when, after removing one such neoplasm, the rest also disappeared.
Main symptoms
As long as the papilloma in the esophagus grows slowly and its size does not exceed 1-2 mm, it does not make itself felt. That is, its development is mostly asymptomatic.
Papilloma of the esophagus is detected by chance, often during an examination for another reason, for example, during endoscopy for esophagitis.
The color of the growth is the same as that of healthy mucous membrane.
And only when its surface, as a result of growth, begins to rise above other tissues, symptoms appear:
- lump in throat or esophagus;
- difficulty swallowing;
- sensation of the presence of a foreign body in the gastrointestinal tract;
- chest pain;
- heartburn;
- belching;
- increased salivation;
- nausea and vomiting;
- general weakness.
The larger the tumor becomes, the greater the risk of it being damaged by solid foods. This is fraught with bleeding and infection in the open wound.
The main danger of such a neoplasm is that under unfavorable conditions it turns into a malignant form and a cancerous tumor develops.
Therefore, when it is detected, the doctor immediately prescribes an operation to excise the papilloma using surgery and complex treatment with medications.
Treatment
If papillomas are detected in the esophagus, additional instrumental studies are prescribed to clarify the diagnosis, location, determine the size, and take biomaterial from the surface for histology.
For this purpose:
- radiography;
- CT scan;
- endoscopy;
- general clinical tests.
Patients undergo specially designed tests to determine the presence of human papillomavirus in the body. At the same time, the female and male tests differ from each other.
Based on the research results, comprehensive treatment is prescribed as the most effective. The therapeutic part of it is the prescription of antiviral drugs that suppress the effect of HPV. Medicines to enhance immunity, so-called immunomodulators, may be prescribed, but their effectiveness has not been proven in practice. The course of treatment also includes vitamins.
Surgical treatment consists of excision, removal of the tumor. The operation is performed, depending on the clinical picture, using several methods:
- endoscopic - with the introduction of an endoscope through the nose or mouth and special instruments for removing or cauterizing the tumor, the technique is used for minor growths;
- laparoscopic - through a 15-mm incision, which ensures the absence of scars on the body, the patient requires almost no postoperative rehabilitation;
- classical surgery to remove tumors that occupy a large area;
- resection of the esophagus followed by plastic surgery – for very large tumors, with a high risk of malignancy (the growth of healthy cells into cancerous ones).
The last two types are rarely used, after which a significant period of rehabilitation of the patient is required. But it is impossible to do without surgical intervention completely with such a diagnosis.
With timely consultation with a doctor and diagnosis of esophageal papilloma in the early stages, successful treatment results in 98% of cases. Recovery after surgery depends on the patient’s condition, the type of surgery, and the development or absence of complications.
In cases of removal of a malignant tumor at an early stage of development, a positive result is observed in 50% of cases.
Experts believe that the malignant tumor into which papilloma develops is less treatable with chemotherapy than with radiation.
Therefore, more often for further treatment after surgery, such cancer patients are prescribed a course of radiation therapy or both. Along with the malignant tumor, nearby tissues and lymph nodes are removed.
After removal of metastases, esophageal plastic surgery may be necessary, when a part of the small, large intestine or stomach is replaced in place of the removed part.
Treatment of papilloma of the esophagus, as well as other diseases of the digestive system, with folk remedies is permissible only on the recommendation of the attending physician. It is auxiliary, providing a general strengthening, restorative effect on the human body after surgery or therapeutic treatment.
Traditional medicine in these cases suggests:
- calamus roots, elecampane, licorice are taken in equal parts, only 30 g of the collection per glass of clean water, a decoction is prepared, infused, you need to take 50 ml 3 times a day;
- salad of boiled beets, carrots with walnuts and lemon, dressed with olive oil;
- infusion of garlic in water, infused for 48 hours, take a tablespoon at night;
- tea made from raspberry, currant and nettle leaves;
- freshly squeezed potato juice on an empty stomach every day for a month;
- Dilute celandine juice in half with water, take 15 drops in tea for no more than 7-10 days. Attention! Take with caution, celandine is poisonous!
Treatment of esophageal papilloma takes a lot of time, but since the condition is considered precancerous, it is important to complete it in order to avoid serious complications that are difficult to treat.
Prevention
You can prevent the development of papillomas in the esophagus, like any other diseases of the digestive tract, using simple, well-known preventive measures:
- rejection of bad habits;
- proper, balanced, nutritious, but moderate nutrition;
- absence of severe prolonged stress, depression;
- strengthening the immune system;
- moderate physical activity;
- regular doctor visits and medical examinations.
We have to admit that theoretically knowing these preventive measures well, in practice, due to the fast pace of life and constant employment, we take care of our health only when serious problems arise.
The information on our website is provided by qualified doctors and is for informational purposes only. Don't self-medicate! Be sure to consult a specialist!
Rumyantsev V. G. Experience 34 years.
Gastroenterologist, professor, doctor of medical sciences. Prescribes diagnostics and carries out treatment. Expert of the group for the study of inflammatory diseases. Author of more than 300 scientific papers.
Ask your doctor a question We recommend: The most effective drugs for the treatment of reflux esophagitis
Source: https://gastrot.ru/pishhevod/ploskokletochnaya-papilloma
Squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus: causes, symptoms, treatment
One of the benign diseases is squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus . What kind of pathology is this, how does it manifest itself? Papilloma is a small, slightly convex formation with an uneven surface, which is localized on the walls of the esophageal tube. It does not differ in color from other fabrics. This pathology is quite rare and in most cases occurs in men who follow an unhealthy lifestyle. Alcohol, cigarettes, and junk food can trigger the development of the disease.
Causes of esophageal papilloma
Human papillomavirus (HPV) type 52 is the primary source of the tumor. But it does not always have its aggressive effect. Patients who are carriers of this disease often do not even know about its presence, since the virus does not manifest itself in any way for a long time.
Many unfavorable conditions contribute to the activation of the virus:
- weakened immune system;
- bad habits (alcohol, smoking);
- problems in the functioning of the gastrointestinal system;
- dietary irregularities;
- heavy physical activity;
- stress.
Symptoms of papilloma in the esophagus
Since the disease is practically asymptomatic, it is discovered mostly by chance. When the esophagus narrows due to the growth of papilloma, the patient begins to feel discomfort. Most often, the neoplasm is localized in the middle or lower part of the esophagus and the following symptoms may develop:
- discomfort when swallowing;
- pain in the solar plexus area;
- belching;
- increased salivation;
- sensation of a foreign object in the throat;
- weakness, increased fatigue.
If the above symptoms appear, you must consult a doctor to establish an accurate diagnosis. Timely treatment will help to avoid serious complications - the degeneration of papilloma from benign to malignant.
Diagnostics
To identify squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus, after examining and analyzing the patient’s complaints, the doctor will prescribe a mandatory examination, including:
- radiography with contrast to determine the size of the pathology and the degree of narrowing of the esophagus;
- endoscopic examination to examine the type of growth and perform a biopsy;
- computed tomography or MRI to clarify the diagnosis;
- laboratory tests to identify concomitant diseases.
The most important thing in the study of papilloma is to determine its malignancy or benignity, therefore the endoscopic research method is the most informative.
Treatment of papilloma of the esophagus
Therapy for such pathologies must be comprehensive. Conservative treatment methods are effectively combined with surgical ones, which makes it possible to cope with the disease much faster and prevent the development of new growths.
Drug treatment
Patients diagnosed with esophageal papilloma are prescribed a course of antiviral drugs. You can reduce the activity of the virus and strengthen the body’s defenses using the following medications:
- "Acyclovir";
- "Viferon";
- "Amiksin";
- "Interferon".
The doctor selects medications on an individual basis. In addition, you will need to take a course of vitamins.
Surgical intervention
To avoid complications, the formation in the esophagus must be removed. Several methods can be used for this:
- Endoscopy. In this case, access to the pathological growth is through the oral or nasal cavity. This method of surgical intervention is used for small papilloma.
- Laparoscopy. The procedure is low-traumatic, since removal occurs through a small two-centimeter incision. Within a day, the patient can return to normal life.
- Esophagotomy. Open abdominal surgery is performed for large tumors.
In some cases, it is necessary to remove a piece of the esophagus, then plastic surgery is required after the procedure. In this case, part of the esophageal tube is replaced with a sample taken from the wall of the colon.
Traditional methods
If papilloma is present, it is absolutely impossible to replace drug therapy with folk remedies. They can only be used as an addition to the main course of treatment. The most effective home methods are:
- An infusion of licorice, calamus and elecampane roots, taken in equal parts. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture into a glass of boiling water and leave until it cools completely. Next, the finished drink is filtered and taken a quarter glass three times a day.
- Instead of tea, you can use an infusion of nettle, raspberry and currant leaves. This excellent tonic can be taken up to several times a day.
- Garlic infusion is no less effective for neoplasms. To do this, crushed cloves are poured with water and left for 48 hours. Take 10 grams of home remedy before bedtime.
Prevention
There are no specific preventive measures to prevent the development of esophageal papilloma. Patients are recommended to have a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition and getting rid of bad habits.
Squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus: causes, symptoms, treatment Link to main publication
Source: https://prorak.info/papillomy/papilloma-pishhevoda/
Squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus – Gastrology
Home — Papillomas
Squamous cell papillomas of the stomach are benign tumors. They are growths of epithelial and connective tissue.
Epithelial cells actively divide, which increases the layer, visually resembling the formation of a growth. It has a developed stroma - a complex of vessels and connective tissue elements.
Detection often occurs during the diagnosis of other organs and systems, because the disease progresses slowly and asymptomatically.
What is and ICD 10 code for squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus
Squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus is a dangerous and insidious disease. It is rare for a patient to seek help from a doctor due to complaints related to this organ.
It is represented by the proliferation of multilayered squamous non-keratinizing epithelium and occupies the surface layers of the organ wall (up to the submucosal layer). The disease is typical for older people. Men are more often affected.
When the growth is small, a person does not feel any symptoms; when it reaches 2-3 cm, serious complaints appear.
In the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), the disease received code D13 - benign neoplasms of other, ill-defined digestive organs.
Causes and symptoms of papilloma in the gastrointestinal tract
The appearance of squamous cell papillomas in the intestine can be caused by several factors:
- hereditary disorders;
- viral infection (HPV);
- systematic damage.
Congenital disorders of cell coordination lead to the appearance of growths on the wall.
There is no consensus on the main cause of the disease. Squamous cell papilloma in the intestine is rare. It is believed that the disease occurs as a result of a person being infected with a virus against the background of damage to the mucous membrane or chronic inflammation.
Human papillomavirus is widespread. Stable in the environment, easily transmitted through contact (handshakes, sharing utensils, things). Places with large crowds of people and high humidity are dangerous.
A person is not susceptible to the influence of the squamous cell papillomavirus agent due to active immunity. Reduced local defense promotes infection.
Reasons for reduced local protection:
- chronic inflammation that develops with esophagitis, frequent reflux of stomach contents;
- secondary and primary immunodeficiencies;
- damage resulting from exposure to ionizing radiation;
- mechanical damage to the mucosa;
- age;
- drinking strong alcohol, spicy or hot food;
- smoking;
- endocrine disorders.
Immunodeficiency develops as a result of the harmful influence of the external environment and internal factors on the body. Main reasons:
- poisoning with heavy metals, drugs;
- nutritional depletion (starvation);
- long-term use of certain medications (for example, immunosuppressants);
- overwork;
- constant stress;
- helminthiases;
- bacterial infections;
- oncology;
- congenital defects in the interaction of cells of the immune system, their differentiation.
Upon transition to the stage of clinical signs, the disease is manifested by the appearance of squamous cell papillomas, warts on the skin of the hands, feet, face, and genital warts on the genitals (depending on the strain). In case of insufficient cleansing, the virus continues to reside in the body. When predisposing factors appear, it can cause the formation of a neoplasm in the wall of the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms of the disease vary depending on the location.
Features of localization and diagnostics
Diagnosis of squamous cell papillomas is carried out using endoscopic and x-ray methods by a gastroenterologist.
The clinic is observed when the size reaches 2-3 cm. Symptoms of localization:
- the lumen of the stomach is blocked, the act of eating is disrupted;
- after swallowing, heaviness and pain are felt;
- feeling of a foreign body;
- bleeding when damaged by rough food;
- vomiting while eating;
- salivation.
Usually the patient is unaware of the disease. The neoplasm can grow asymptomatically for a long period.
During an endoscopic examination, it is possible to visually evaluate squamous cell papilloma: it does not differ in color from healthy mucosa, can be smooth or have multiple growths, be located on a thin or wide stalk, and resemble a mushroom or cauliflower in shape. During the study, it can be removed and the resulting material can be sent for histology. The procedure is diagnostic and therapeutic.
Single growths form in the stomach. But there are also multiple ones, in which case we are talking about papillomatosis.
Rectal papilloma has the following symptoms:
- feeling of discomfort during bowel movements;
- difficulty in defecation;
- the presence of blood, mucus in the stool;
- itching, burning sensation in the anus;
- flatulence;
- abdominal pain.
Formations in the digestive tract reach large sizes - up to 5 cm. Inspection is carried out using endoscopy and sigmoidoscopy.
Manifestations of localization of squamous cell papilloma in the stomach:
- abdominal pain in the epigastric region while eating;
- flatulence due to fermentation of food;
- vomiting during or after eating;
- nausea;
- salivation;
- hemoptysis due to gastric bleeding.
For diagnosis, endoscopic examination, contrast radiography, and ultrasound are used.
Do you need advice from an experienced doctor? Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
In other parts of the stomach, such formations are less common. Symptoms of papilloma in the intestines are similar to other localizations. With massive growth, obstruction develops with acute pain and a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition.
The provoking factor is a chronic inflammatory process (colitis). The disease is easily confused with intestinal polyps, which develop as a result of the inflammatory process. It mainly affects men over 50 years of age.
There is no viral etiology.
Treatment methods for squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus
Treatment is difficult due to the specific location. The program includes medical and surgical methods for the treatment of squamous cell papilloma. The doctor selects treatment options individually, focusing on the course of the patient’s disease and associated health problems.
Drug treatment
Medicines are used for a general effect on the body, restoring defenses. For this purpose, antiviral drugs and immunomodulators (interferons) are prescribed. Medications that suppress the synthesis of hydrochloric acid are prescribed to reduce the damaging effects of reflux. When it reaches medium size, squamous cell papilloma can be removed using hardware.
There are traditional medicine methods that allow you to get rid of squamous cell papilloma at home.
Recipes with the following ingredients are widely used:
- propolis;
- soda;
- nettle;
- currants;
- licorice.
Traditional medicine is useful as an additional condition for strengthening the immune system and relieving inflammation.
It is useful to prepare decoctions from currants, nettles, and licorice, drinking 1 glass a day. It is advisable to use in training camps.
Self-medication can harm your health
Surgical removal
Hardware methods in surgery are widely used. They involve cutting squamous cell papilloma from the surface of the mucosa and excision within healthy tissue. The first option is carried out using endoscopic instruments. Electrocoagulation is used as a method of removal; it prevents the development of bleeding and complications.
The operation is easily tolerated and the recovery period is short.
Complete excision of squamous cell papilloma within healthy tissue is carried out in case of malignant degeneration or a large volume of formation. Carry out classical operational access and reception. The operation is difficult to endure and the recovery period is long. If cancer is confirmed, a further course of chemotherapy and radiation therapy is carried out.
The need for diet and balanced nutrition
After removal or during treatment of squamous cell papilloma, it is necessary to ensure free passage of food and minimal irritation. Excluded:
- hard;
- fried;
- sour;
- acute;
- hot and cold dishes, drinks;
- alcohol;
- smoking.
A diet with well-cooked, steamed food is recommended. Eat in small portions, chewing well. Number of techniques – 5-6. A balanced diet is necessary to maintain immunity and prevent vitamin deficiencies.
While in the hospital, it is forbidden to eat the evening before the operation, then for the first few days.
Possible complications and treatment prognosis
The treatment prognosis is favorable in the case of complex therapy and timely detection of squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus. Otherwise, it will cause discomfort and increase the risk of degeneration into cancer. The papilloma is likely to be damaged by rough food, which will lead to bleeding. This will be indicated by hemoptysis and the presence of blood in the stool.
In case of incomplete removal, a relapse is possible, which will be prevented by instrumental examination, tests, and complex therapy.
If similar neoplasms are located in other areas, there is a risk of developing consequences:
- ulcer formation;
- development of the inflammatory process;
- addition of infection.
- Prevention consists of periodic examinations by a specialist.
- The article has been reviewed by the site's editorsLink to the main publication
- Didn't find suitable advice?
- Ask your doctor a question or see all questions...
- ask a QUESTION to the doctor
- Article rating:
- (1
- Source:
Papilloma in the esophagus: danger and properties
Esophageal papilloma is one of the diseases that are difficult to identify in the early stages. Often, discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract is explained by overeating, undereating or poor-quality products. This situation is dangerous. The international conclusion of scientists indicates that the most terrible blow of the human papillomavirus is esophageal cancer.
Content
Reasons for appearance
Papillomas in the esophagus are viral in nature. The infection enters through the mucous membrane of the esophagus or through the skin. It is not known for certain what is the true cause of papilloma inside the esophagus. Experienced doctors observing patients believe that the tumor may appear due to the following factors.
- If there is damage to the mucous membrane of the esophagus. This is an excellent opportunity for a virus to attack. In such an environment, he feels great and begins a destructive function.
- If a person has problems with personal hygiene. The virus loves dirty hands, unwashed food and careless people who care little about the cleanliness of their bodies.
- If you smoke, the papilloma virus can weaken your health.
- At risk are lovers of strong alcoholic drinks: alcohol, cognac, vodka. Alcohol burns the mucous membrane of the esophagus, provokes inflammation, ulcers and creates favorable conditions for the development of the disease.
- Spicy and spicy foods are another danger factor. Spices consumed in unreasonable quantities can cause a devastating blow to the gastrointestinal tract.
- Other reasons include unfavorable environmental conditions, early onset of sexual activity, and stress.
In addition, the neoplasm can provoke chronic esophagitis.
Main symptoms
Squamous cell papillomas carry out quiet destructive work in the human body. For the time being, they do not show themselves in any way. The painless development of papilloma can last for many years.
Their existence becomes known when diagnosing other diseases during X-ray and endoscopic examinations. One or more neoplasms in the form of bush-like growths may develop in the organ. It happens that papilloma takes the form of a polypoid node.
Symptoms of papilloma that appears in the stomach can manifest themselves as follows:
- There is some kind of weight pressing on the esophagus. It seems to a person that there is a foreign object there.
- Eating food is painful. Even ground light food does not save the situation.
- Swallowing is difficult and painful.
- Regardless of food intake, chest pain may occur.
- Vomiting occurs periodically.
- I suffer from drooling and belching.
Removal of tumors in the esophagus
It is believed that squamous cell papilloma in the esophagus occurs mainly in older people. It used to be like that. But times have changed and international studies show that young people, mainly men, who are prone to bad habits are increasingly at risk.
If you have the above symptoms, you should immediately contact a specialist. The attending physician will prescribe a diagnosis - x-ray photo or endoscopic examination. Complete information about the condition of the esophagus will be obtained using computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. The nature of the formation will become clear with the help of cytological and histological examination.
List of tablets for gastritis and stomach ulcers
After the diagnosis is established, the patient will be prescribed a course of treatment for esophageal papilloma. The source of the disease is a virus, and to suppress it it is necessary to use antiviral drugs. Most often, doctors recommend removal of papilloma. There are two methods of procedure.
Endoscopic surgery. In its process, access to education is gained through the mouth and nose.
Laparoscopic surgery is surgical removal through a small incision. This method leaves virtually no scars on the body.
Both methods allow the operation to be performed as accurately and efficiently as possible. After such intervention in the body, patients quickly recover. Undesirable consequences in the form of various complications are practically zero.
Traditional medicine to get rid of illness
Therapy with folk remedies inspires optimism, but they should be used only after consultation with the attending physician and in parallel with traditional methods of treatment.
Time-tested recipes:
- 25 g of calamus roots, elecampane, licorice, taken in equal proportions, pour 250 ml of boiling water. Infuse, cool, take 50 ml three times a day.
- Nettle, raspberries, currants - ratio 1: 1: 1. Use instead of tea in any quantity.
- Horsetail, plantain, dandelion roots - 50 g, pour 500 ml of water. Boil for 5 minutes, leave. Drink 100 ml 3 times a day.
- Juice fresh potatoes on an empty stomach for 30 days daily.
- Squeezed juice, water - 1: 1. Set aside. For 14 days, take 15 drops as an additive to tea. Course: 7-10 days.
- Chop the garlic and add water. Leave for 2 days. Drink 10 g at night. Can be mixed with freshly squeezed vegetable juices and unsweetened yogurt.
- Salads of chopped nuts with lemon, boiled beets, carrots, olive oil. You can eat salad every day before lunch.
Source: https://gastrologpro.ru/lechenie/ploskokletochnaya-papilloma-pishhevoda.html