- vulgar (ordinary);
- flat;
- plantar;
- threadlike;
- genital warts.
As a rule, these neoplasms are benign and the immune system of young people copes with them in a few months or years. Infection with HPV a7, as with other genotypes, is possible when the body’s support capacity decreases through microtraumas of the skin and mucous membranes. Transmission often occurs through sexual contact. Strains of group a7 are highly likely to lead to cancer.
The virus penetrates the cell nucleus of the epithelium of the skin and mucous membranes.
By rearranging the enzyme systems involved in the division of host cells, it begins to copy its own DNA, using the affected structures as building material for virions.
The higher the number of virions, the more undifferentiated host cells are required, and the process of uncontrolled division of epithelial cells begins.
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE RF: Papillomavirus is one of the most oncogenic viruses. Papilloma can become melanoma - skin cancer!
Read more >>
According to various sources, some genotypes of group 7 virus (HPV 16, 18, 31 and 45) are found in 70-100% of cases of cervical cancer.
Clinic and treatment of HPV type 7
Diagnosis of human papillomavirus a7 involves visual detection of growths. HPV group a7 DNA is determined by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). In addition, a Digene test is prescribed, which shows the viral load. All diagnostic methods are called molecular genetic and morphological and are carried out in specialized laboratories.
Destructive treatment is carried out using the following methods:
- cryotherapy;
- laser removal;
- radio wave excision;
- electrocoagulation;
- chemical method.
The medications prescribed are immunomodulatory (Likopid, Isoprinosine), antiviral (Viferon, Panavir, Epigen-intim). Sometimes cytostatics (5-fluorouracil) are used.
- The appearance of visible changes on the body in the form of growths and warts should serve as a signal to immediately contact a dermatovenerologist.
- THE MINISTRY OF HEALTH WARNS: “Papillomas and warts can become melanoma at any time...”
- Read more >>
Interesting materials on this topic!
How can you become infected with papillomavirus? Infection with HPV means that one or more of 100 different types of viruses enter the human body, causing the development of warts in different parts of the body. Because of…
HPV type 52 A person who is faced with the problem of infection with human papillomavirus type 52 needs to take his or her health seriously, because the symptoms of the disease can be...
Why does HPV and papillomas appear? It is known that the appearance of papillomas (small growths on the skin and...
Medical indications
There are several ways to detect infection in the body. A referral for quantitative HPV analysis is issued by a gynecologist, urologist, or dermatologist if there is any suspicion during the examination. The specialist himself chooses the examination method.
Among the most common ways to detect and identify a virus are:
- Colposcopy is the simplest method for visually identifying papillomas. The cervix is examined using a special device - a colposcope. This allows you to examine the mucous membranes in detail, enlarge the image if necessary, and identify neoplasms if they are present.
- Cytology is a microscopic examination of smears for HPV. There are 5 classes of results from such an analysis: class 1–2 results indicate normal, class 3 is doubtful and requires additional research (usually histology). Identification of 4–5 classes of results indicates the presence of malignant elements. Confirmation of the presence of papillomatous infection is the identification of special modified elements in HPV smears - koilocytes or dyskeratocytes.
- Histology - This HPV test requires tissue collection from the patient. This small sample is examined under a microscope for the presence of modified elements affected by the virus.
- Detection of antibodies - the test is considered one of the earliest ways to detect the virus. The immune system reacts to infection with lightning speed, long before the clinical manifestations of the disease appear. This is a qualitative technique; it does not show the concentration of the virus and is not able to determine the type of pathogen. For the study, venous blood is taken.
The Digene test (amplification technique) is a relatively new but accurate method of testing the body for papillomavirus. Shows all research parameters: virus concentration, type and degree of oncogenicity.
The material for testing is a scraping from the urethra or vagina. It is not difficult to decipher the tests; the test results are ready within 24 hours.
The technique is often used in conjunction with other studies to clarify or confirm the diagnosis.
Important addition: Ointment for skin fungus
Non-amplification technique
The most common way to identify highly oncogenic virus subtypes. Any material is suitable for PCR. Often this is blood, urine, amniotic fluid, or mucosal smears. The study is based on identifying the DNA of the virus in the material.
It has been proven that there is a connection between the papilloma virus and cervical cancer. All cancer patients are infected with highly oncogenic strains. Almost all HPV tests are usually simple, painless and low-impact. The duration and scope of preparation completely depend on the method of research. To collect material from the vagina or urethra, preparation is minimal.
A few days before the test, it is important to stop taking all antibacterial and antiviral medications.
On the day of taking the test for papillomas, you should not carry out hygiene procedures. It is recommended not to urinate 2 hours before sampling (this is especially true for men). It is impossible to collect material during menstruation and for several days after its end.
At least 3 days before the test, it is important to stop using contraceptives, as they can distort test results
All studies should be performed on an empty stomach. The last meal should be 10–12 hours before the test. You can only drink water. It is recommended to avoid the consumption of alcohol and junk food. You must abstain from sexual intercourse for at least 2 days before taking HPV tests.
Endoscopic diagnosis of HPV type 16 in women
Extended colposcopy - examination of the membranes of the vagina and cervix using an optical colposcope after they have been treated with chemicals (test with acetic or salicylic acid, test with Lugol's solution).
When areas of altered epithelium are visualized, the patient is sent for a targeted biopsy of the cervix. The final diagnosis and treatment tactics are established on the basis of histological examination of a sample of pathological tissue (biopsy).
If a woman is diagnosed with HPV type 16, what should she do?
It has been established that the presence of above-threshold levels of HPV DNA in 99% of women is accompanied by cervical epithelial dysplasia (CIN) of varying severity.
Procedure for HPV test “+” (positive):
Infection with HPV type 16
The prevalence of human papillomavirus infection is extremely high: DNA of one or another (sometimes several) types of HPV is found in more than 80% of the adult population.
Mucosotropic HPVs, including serotype 16, are classified as sexually transmitted infections (STIs). The likelihood of infection through blood, household items, especially by airborne droplets is negligible.
Routes of infection with HPV type 16:
- Sexual route: traditional, oral, non-traditional sexual contact with an infected partner.
- In utero: infection of the fetus from an infected mother through the placenta or amniotic fluid.
- During childbirth: infection of the newborn when passing through the mother’s birth canal affected by condylomas.
What does the result mean?
During research, qualitative and quantitative analysis is taken into account. The first may indicate the presence or absence of a virus. The second is about the concentration of the pathogenic agent in the human body. Only an experienced specialist can decipher the information received, taking into account all the surrounding circumstances.
There is no need to take a positive test result as a death sentence. Often during research, errors are made that affect the indicators and make it impossible to determine the correct data. In most cases, mistakes are made by patients while preparing for an upcoming test. Reference values must be taken into account.
False positive HPV
False-positive HPV test results are common. This happens if:
- the bio sample was contaminated;
- there was an incorrect collection of materials;
- the patient was treated before the analysis;
- the person did not comply with the standards of preparation for diagnosis.
To avoid getting distorted results, you need to take into account some rules. Within 12 hours before submitting biological material, it is prohibited to take antiviral, antibacterial and antimicrobial drugs. You should shower on the day of the smear test.
Over the next 2-3 days, it is better to refuse sexual intercourse. A smear test is not required during menstruation. People often encounter false test results if they tried to treat the infection with antiviral drugs the day before.
The virus itself is neutralized, but antibodies remain in the body.
Referential meaning
Reference values of an indicator (another name is reference) imply general values obtained during laboratory research on a specific category of the population. These can be young people aged 20-30 years, women during pregnancy, those who have given birth, those who have not given birth, etc. Such indicators are necessary to obtain the average total indicator of the relative norm.
Important addition: Causes of cracks between toes and their treatment
This is how a quantitative HPV test is determined. The average value of 3-5 Lg, which implies a questionable result, was collected based on the assessment of a certain category of carriers of the papilloma virus. Therefore, reference values cannot be assessed as the only correct indicator. The concept of normal may differ depending on the characteristics of the body, age, and the presence of concomitant diseases.
In most cases, only the qualitative result of the study is important, which indicates the presence of the virus. In cases of detection of a non-oncogenic type of HPV, its concentration is insignificant.
Data decryption
Only a doctor can evaluate the test results. The most confusing and incomprehensible interpretation of the results of the Digene test. The result “No DNA detected” indicates the complete absence of the virus. A value of up to 3 Lg is an insignificant concentration of the pathogen, 3–5 Lg is a clinically significant concentration, more than 5 is very high.
Papillomas can grow rapidly in the structures of the urethra. In this case, its lumen is completely blocked, which provokes serious disorders in the body. In severe cases, impotence, infertility and cancer are observed.
Normally, all quantitative tests for HPV titers should be negative. When oncogenic strains increase, the body begins to hurt. At first, the clinical picture of the disease may be hidden, since the pathology is latent.
In later stages, the patient’s condition deteriorates sharply: the correct and proper functioning of many organs is disrupted. In addition, the risk of degeneration of the affected elements increases many times over.
To prevent this from happening, experts recommend that everyone get vaccinated and constantly monitor the dynamics of the lesion. This will prevent the appearance of tumors or allow them to be detected in the early stages.
Negative result
A negative result for HPV does not always indicate the absence of the disease. Often a similar phenomenon is observed at low concentrations of the pathogen. It's all about the immune dependence of the virus.
During periods of strong immunity, the body is independently able to suppress the activity of the virus.
Treatment at this time includes only surgical removal of papillomas followed by histological and cytological analysis.
In the future, monitoring of the cure is necessary. To do this, all patients must be tested for HPV twice a year. Repeated examinations often give positive answers.
If the result is positive, then only the attending physician determines further tactics for patient management. Therapy is selected individually.
This takes into account the type of virus, its concentration, prevalence and general condition of the patient.
Modern medicine is not yet able to defeat the virus. Almost all measures are aimed at eliminating the manifestations of the virus, and not at eliminating it. The effectiveness of such products is sometimes up to 70%.
Sometimes patients undergo destructive procedures. All tumors are removed in various ways (laser, radio waves, cryodestruction). In other cases, complex treatment regimens are used: they combine destruction, medications, and immunology. Immunological treatment refers to therapy with special interferon proteins.
- Pregnant women are a special category of patients with HPV. The decision on the need for therapy is made individually by the treating doctor.
- The feasibility of therapy and the clinical picture of the disease are taken into account. Treatment generally begins with modification of lifestyle
- All pregnant women are advised to get proper rest, limit stress and chronic fatigue, and eliminate vitamin deficiency.
- Medicines are prescribed as a last resort, since they have a very adverse effect on the baby’s health.
What is HPV viral load
The term viral load is most often used in the diagnosis of hepatitis, HIV and cetomegalovirus. But this indicator is also applicable to determine the concentration of papillomaviruses in the human body.
HPV viral load 100 cells is a measure of disease severity, calculated by assessing units of virus per specific volume of biological material for analysis.
The measurement of this indicator is used to monitor the patient’s dynamics, predict the course of the disease and the quality of the body’s response to antiviral drugs.
To determine which group the identified virus strain belongs to, an indicator such as the total HPV viral load is used. This makes it possible to determine the oncogenicity of the strain and more selectively select drugs to treat the disease.
DNA diagnosis of HPV type 16 in women
The material for this study is a vaginal smear or cervical scraping.
There are two main molecular methods for detecting and verifying HPV serotypes:
1. PCR is a polymerase chain reaction method.
Allows you to find DNA of a certain type of HPV in the material being studied.
The PCR test is highly sensitive. It detects even minimal amounts of viral genetic material. But!
Based on its results, it is difficult to distinguish an active infectious process from a safe latent HPV carriage.
Source: https://gribkam.net/newest/vpc-a9-norma.html
Determination of papillomavirus viral load
In the process of diagnosing diseases caused by papillomavirus, not only the presence of the virus is important, but also its quantity - the HPV viral load. This parameter allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment and determine the correct medical tactics.
To diagnose diseases, an analysis is performed to detect the HPV viral load.
What is viral load
This is the amount of HPV per unit volume of blood. This term is used in relation to more dangerous pathogens, for example, HIV or hepatitis. The viral load is directly related to the severity of the disease and the risk of complications. It also shows how effectively medications fight papillomavirus.
There are groups of patients for whom quantitative analysis is extremely important. These include:
- married couples planning pregnancy;
- women with a burdened gynecological history;
- people with weakened immune systems;
- patients suffering from multiple papillomatosis of the skin and mucous membranes;
- children born from infected mothers.
The analysis is carried out for patients planning pregnancy
In all cases, there is a high risk of HPV complications and determining the viral load allows you to avoid serious pathologies.
The examination is not mandatory, but patients who have received a referral for it should not ignore the doctor’s instructions.
In some cases, the alarm turns out to be false and the test shows a negative result. We can only rejoice at this, but it is advisable to take another blood test.
How is the analysis carried out?
The viral load for HPV is determined by two methods. Their combination makes it possible to detect the DNA of the pathogen with a 100% probability; false-positive and false-negative results are excluded. The technique determines the presence, quantity and type of virus. Using the transcript of the analysis, the doctor will be able to decide which treatment will be most effective.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique based on detecting the genotype of viruses.
The peculiarity of the procedure allows you to artificially increase the amount of DNA, which makes the accuracy of the analysis extremely high.
This test can be qualitative (detects the fact of infection) and quantitative (viral load). Another analysis method, the Digene test, is even more accurate because it detects not only whole DNA, but also its fragments.
Viral load can be determined by PCR
To determine the degree of risk of complications, biological material is needed:
- blood;
- scraping from the skin or mucous membrane;
- a smear from the cervix or urinary tract;
- sample of neoplasm tissue (warts, condylomas).
To prevent the HPV test from giving a false negative result, you should not use local antiseptics for a week before collecting the material. If we are talking about the epithelium of the uterus, penis or urinary system, you cannot have sex.
Normal value and deviations
Only one indicator is considered the norm - there should be no viruses in the material being tested. For greater accuracy, the results of both tests are compared; if necessary, they can be repeated at intervals of 2-3 weeks. Both qualitative and quantitative tests will show a negative result. The sensitivity of qualitative analysis is higher, so its results are primarily important.
Normally there should be no virus in the blood
If you end up with an elevated HPV level, you should pay attention to the type of virus (the method allows you to determine it). For this purpose, there are several columns in the result form - general HPV and individual types. If the permissible level of total viral load is exceeded (it is greater than 0), this indicates the presence of a pathogen, but does not indicate possible health risks.
Individual types of HPV are reflected in the form of a table, where the quantitative parameters of each are indicated. Typically, an examination is performed for 15 common and dangerous variants (there are more than 50 in total). The form indicates genotypes of high oncogenic risk.
During treatment, the viral load decreases, and the speed of this process is an indicator of the effectiveness of therapy. The concept of a low number of pathogens does not exist, since the normal value is 0. If the concentration of the virus decreases slowly, it is necessary to change medical tactics.
If treatment does not produce results, it is necessary to change its tactics
What kind of load is called indeterminable?
The sensitivity of a quantitative analysis is lower than a qualitative one, so a situation is possible when the test shows a positive result, but the viral load is not determined.
This means that the pathogen is present in the human body, but it is not enough to accurately determine its quantity.
This condition is called undetectable viral load and requires confirmation by repeated tests.
Does a person who has so little HPV need treatment? Yes. Any amount of the virus is a potential threat of complications, and the patient can infect loved ones.
If there are papillomas on the skin - clear signs of damage, and the test is negative, this can mean several situations:
- the virus was destroyed by the immune system, but traces of exposure remained on the epidermis;
- the formations on the skin were not papillomas; they were a sign of another disease.
The test result may be negative even if skin papillomas are present
A conclusion about the absence of a pathogen can only be made based on the results of two tests with an interval of 2-3 weeks.
Erroneous data is possible if the patient violated the rules for taking the test - used local antiseptics, took antibiotics, or was sexually active.
Why do you need to treat HPV?
Papillomavirus is quite widespread, but most often its negative impact is limited to unsightly growths on the skin.
It multiplies rather slowly in the cells of the epidermis and mucous membranes, causing minor changes in their metabolism.
But under unfavorable circumstances - high virus activity, low immunity, hereditary predisposition - malignant degeneration of epithelial tissues is possible.
Patients may have a hereditary predisposition to developing HPV
According to the degree of danger, viruses of high (cause cancer with proven frequency) and low oncogenic risk are distinguished. Most types of the virus belong to the second group, but for them the danger of a tumor cannot be excluded. Highly oncogenic species are designated by numbers 16, 18, 33, 45, 66 and about 20 more options. The first two are the most famous and dangerous among them - they cause cervical dysplasia.
Conditions in which the risk of a malignant tumor is greatest:
- warts on areas of the body that are often injured;
- genital warts on the genital tract;
- manifestation of papillomatosis in newborns;
- cervical erosion (precancerous condition).
Cervical erosion often develops into cancer
In such cases, you need to start treatment as soon as possible - this will reduce the risk of dangerous complications and prolong the patient’s life. Antiviral therapy is important, and removal of warts is of secondary importance.
Another reason to treat HPV is that the disease is contagious, and even if the patient does not experience discomfort, it is a source of infection for those with whom the patient lives in the same apartment and for sexual partners. A pregnant woman can transmit the infection to her child, and for him this is fraught with condylomas, including in the respiratory tract.
How to treat HPV
Once the virus is identified in vitro (i.e., by PCR), it must be eliminated from the body. To do this, an integrated approach is used - you need to destroy the pathogen and increase immunity. As a rule, interferon drugs are prescribed in tablets, as well as immunostimulants. The dosage of medications depends on the patient's condition, viral load and the effectiveness of its reduction.
Walking in the fresh air will help strengthen your immune system
As additional measures of non-drug support, the doctor recommends walking in the fresh air, healthy eating and taking vitamins, and physical activity. These measures strengthen the immune system and harden the body, which helps it cope with the infection on its own, and makes treatment more effective.
The combined effect of the drugs and strengthening the immune system leads to the disappearance of most papillomas on the body. Removal of formations is necessary in cases where large warts appear on the face, neck and hands. For this purpose, laser, cryodestruction, radiosurgical methods are used, and for large papillomas - a scalpel. Before undergoing them, a consultation with an oncologist may be required.
Why viral load tracking is carried out, see below:
Source: http://bolezni.com/stati-o-boleznyah/papilloma/virusnaya-nagruzka-vpch.html
HPV analysis: deciphering the results
The human papillomavirus (HPV) can exist in the body for a long time, manifesting itself only when the immune defense is weakened. To detect infection, various types of tests are used to detect the disease at an early stage and provide effective treatment.
Types of analyzes and techniques
Referrals for testing if HPV is suspected are issued by dermatologists, gynecologists or urologists. Modern medicine can not only detect the presence of a virus in the human body, but also determine whether it belongs to a certain type of strain (dangerous or harmless).
For these purposes, experts resort to the following methods:
- Quantitative analysis.
- PCR (polymer chain reaction).
- Cytology.
- ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay).
- Histology.
Digene test
Quantitative analysis , or Digene test, is based on the principle of hybrid DNA capture. To carry out the analysis, biological material is collected from the affected area (using the scraping or smear method). The technique makes it possible to determine the stage of development of the pathology and the type of strain. Results are provided within 7-10 days.
PCR research
PCR is a widely used type of test for detecting papillomavirus and other common infections.
This type of research involves working with liquid media - urine, blood, saliva, amniotic fluid, and discharge from the genital tract. This test is highly accurate and expensive.
Determines the presence of HPV by the presence of viral DNA in the body within 24 hours.
To learn how PCR analysis is carried out in men, watch our video:
Linked immunosorbent assay
Enzyme immunoassay allows us to identify the quantitative and qualitative content of antibodies in the biomaterial. Traditionally, venous blood donation is prescribed for ELISA. Other environments of the body can also be studied:
- cerebrospinal fluid;
- urethral discharge;
- cervical mucus.
A response with the examination results is prepared and given to the patient within 3 days.
HPV Digene test (Digene test) - “hybrid capture” method Cytological examination
Cytology , also called a Pap test or Pap smear, is the study of body cells using a microscope. The material used for analysis is urethral secretions in men and the contents of the urogenital canal in women. To obtain highly accurate results, material must be taken simultaneously from several sections of tissue. How to perform a PAP test in women:
The method allows you to determine the presence of benign and malignant strains of the papilloma virus. The reliability of the results is 95%. You can receive them in 1-2 days, in urgent situations - within one hour.
Results of histological examination
Histology - taking a scraping from the site of papilloma formation for further microscopic examination. This informative diagnostic method allows you to detect the presence of cancer cells with 100% certainty and prevent the development of oncology. The analysis is recommended for patients with papillomas that have changed shape, color, or size.
To conduct a histological examination, a biopsy is performed - tissue is taken, which is subsequently treated with medical solutions and studied under a microscope. The answer is issued after 1-2 weeks from the day the biomaterial was taken.
How to prepare for the procedure
To get the most accurate HPV test results, patients will be required to follow certain guidelines. It is recommended for both women and men:
- Do not take antibiotics or antibacterial drugs at least 2 weeks before the test.
- On the eve of handing over the biomaterial, do not use antiseptic personal hygiene products.
- 2 days before the study, refrain from sexual intercourse.
- Do not drink alcoholic beverages for 3 days before handing over the biological media.
- Do not urinate 3 hours before the procedure.
Women should not be examined 5 days before and for the same period after their period. On the eve of the examination, douching is not recommended. Blood donation should be done in the morning on an empty stomach.
Decoding - what the results mean
Interpretation of HPV tests is traditionally carried out by a specialist who has the necessary medical knowledge. Simplified, they can be interpreted as follows:
What is an HPV test and how to take it?
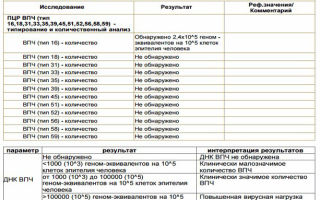
| Results of quantitative analysis | Less than 3 units of virus per 10⁵ cells is a safe concentration (norm). |
| 3-5 units per 10⁵ cells is a significant concentration (there is a possibility of the appearance of neoplasms). | |
| More than 5 units per 10⁵ cells - high concentration (increased risk of developing a malignant process). | |
| PCR results | No DNA was detected – there is no papillomavirus in the patient’s blood. |
| Lg less than 3 – insignificant presence (within normal limits). | |
| Lg 3-5 is a significant amount. | |
| Lg 5 or more is an indicator of a high concentration of the virus in the blood. | |
| Cytology | Numbers from 1 to 2 are acceptable. |
| Number 3 – additional tests are required. | |
| From 4 to 5 – the presence of malignant cells. |
After testing for human papillomavirus using ELISA, the following results can be obtained:
- IgA – presence of fresh infection;
- IgM – recent infection;
- IgG – long-term presence of the pathogen in the body.
The results of the histology study are provided in the form of a written report. In the form you can find an explanation of whether there are or are not abnormalities in cells and tissues. Information about the results of the examination is provided in Latin using special medical terminology.
It is important to remember the possibility of receiving erroneous test results. The reasons may be the use of dirty test tubes, improper collection of biomaterial, or improper preparation of the patient for the procedure.
A negative answer after testing does not guarantee the complete absence of the virus. This result can be obtained with a low concentration of the pathogen, which the body manages to cope with on its own.
If incorrect data is received, in most cases, specialists prescribe a repeat examination.
Source: https://papillomus.ru/analizy/analiz-na-vpch-rasshifrovka-rezultatov/
HPV clinically significant viral load
To conduct a histological examination, a biopsy is performed - tissue is taken, which is subsequently treated with medical solutions and studied under a microscope. And another question: how to determine uterine erosion? I was diagnosed with HPV 16,31,33,35,52,58 Tell me what to do, what to do. It is also necessary to take into account the list of DNA-detectable HPVs, since the patient may have a type of pathogen present in the body that is not included in this list. I wanted to inquire about the results of the analysis. HPV type 58 detected.
Quantitative analysis for HPV
A clinically significant amount of HPV implies a concentration of the virus sufficient to cause external symptoms of the disease to manifest in the form of cutaneous or anogenital neoplasms. Read moreA clinically significant amount of HPV implies a concentration of the virus sufficient to cause external symptoms of the disease to manifest in the form of cutaneous or anogenital neoplasms. This will require further regular monitoring and prevention. If with HPV, a clinically insignificant concentration of the virus cannot be a precursor to oncology, then an increased concentration in most cases is observed in severe forms of dysplasia. In this condition, atypical cells multiply - there is a high probability of their malignancy. Hide. The amount is clinically significant. Human papillomavirus (HPV, human papillomavirus infection) is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. Read moreThe amount is clinically significant. Human papillomavirus (HPV, human papillomavirus infection) is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. This virus infects most adults under the age of Hide. Ref. interval interpretation clinically significant, what type is it and what does it even mean? The analysis showed that HPV types 16 and 18 were not detected in you. Reference values indicate the amount of blood taken at which Read moreRef. interval interpretation clinically significant, what type is it and what does it even mean? Answer. Fedor Nekiporenko. The analysis showed that HPV types 16 and 18 were not detected in you. Reference values indicate the amount of blood taken at which the results will be reliable. Your indicator is above 4, which means the result can be considered reliable. Alesya. Hide.
Types of HPV tests
It is also necessary to take into account the list of DNA-detectable HPVs, since the patient may have a type of pathogen present in the body that is not included in this list. It also happens that a positive HPV test does not guarantee the presence of the disease. During an HPV test, a false positive result is possible if:. The test to determine HPV and its type is simple to perform and does not require special efforts from the patient to prepare for it.
When examining for human papillomavirus, the test results are known already the day after the test. Normally, quantitative determination of HPV gives a negative result.
An increased content of oncogenic strains of the human papillomavirus in the body for a long time can provoke the development of cancer processes in epithelial cells.
In this case, experts recommend vaccination and constant monitoring of the dynamics of the life processes of the pathogen.
This is interesting: HPV types 51 and 56. What is this? How to live and what to do?
This will prevent the development of malignant neoplasms or at least carry out their early diagnosis and prescribe timely therapy.
A similar picture can be observed when there are no high concentrations of the pathogen in the human body at the time of examination. The fact is that the papilloma virus is immune-dependent.
That is, if the body’s immune forces are in good condition, it can independently suppress the activation of the pathogen’s vital processes.
In this case, treatment simply comes down to removing papillomas using any of the known methods, followed by histological and cytological examination. After removal of tumors, it is recommended to undergo HPV testing 2 times a year to monitor the cure.
Upon repeated examination, deciphering the results of the analysis for papillomavirus may give a positive answer. There are many factors that influence specific treatment.
If papillomavirus is diagnosed for the first time in a young patient, it is very likely that the doctor will not prescribe drug therapy.
This is due to the fact that in the initial stages of infection, provided the human immune system is functioning normally, the body is able to cope with the pathogen itself.
As a result, this ends with the patient’s self-healing. In some cases, patients are shown only destructive methods of treatment, that is, removal of tumors on the skin and mucous membranes using various methods: laser, radio waves, cryodestruction and others.
In other clinical situations, an integrated approach to the patient’s rehabilitation is required—a combination of destructive, medicinal and immunological therapies.
The immunological method involves the use of specific proteins - interferons.
A special category of patients are pregnant women. The decision on the advisability of treatment is made for each woman individually, taking into account the pattern of manifestations.
General recommendations during pregnancy are to avoid exposure of a woman’s body to factors that lead to a deterioration of immunity.
These include increased emotional stress, the presence of chronic fatigue, the development of vitamin deficiency, and hypothermia.
Drug treatment is in most cases contraindicated for pregnant women, as this can negatively affect the development of the fetus.
No less important are further prevention and periodic examination by a specialist, including testing. Deciphering the analysis for papillomavirus is an important step in diagnosing the disease.
Based on the indicators obtained as a result of the study of biological material, the attending physician prescribes antiviral therapy and the most appropriate method for removing pathological growths.
A general blood or urine test cannot determine the presence of HPV in the body.
This research method is used to identify concomitant sexually transmitted diseases, because in almost all cases several pathogens are identified.
In case of HPV, a general DNA analysis of this pathogen will not determine the pathogen, but it will identify concomitant infections, which allows the specialist to adjust the therapy.
If the general test for HPV is negative for concomitant sexually transmitted infections, therapy is directed only at the treatment of this virus.
Diagnostic methods should be aimed at qualitative and quantitative determination of the pathogen, as well as a detailed study of the affected surface.
This is interesting: Laser wart removal: prices
The Digen test is considered quantitative; it is a diagnostic method based on hybrid DNA capture. To carry out the analysis, it is necessary to take a smear or scraping of biological material.
Using this study, both the viral load, HPV titers, and the strain type are determined. Only an experienced doctor can interpret the results. The following indicators are for informational purposes only:.
In the first case, there are very few papillomavirus DNA particles even to cause the appearance of body growths.
Most often, such indicators are accompanied by independent elimination of the pathogen from the body. A clinically significant amount of HPV implies a concentration of the virus sufficient to cause external symptoms of the disease to manifest in the form of cutaneous or anogenital neoplasms. This will require further regular monitoring and prevention.
If with HPV, a clinically insignificant concentration of the virus cannot be a precursor to oncology, then an increased concentration in most cases is observed in severe forms of dysplasia. In this condition, atypical cells multiply and there is a high probability of their malignancy.
If a patient, for the purpose of prevention, decided to be tested for the presence of a pathogen and several non-oncogenic strains of HPV were identified, this is the norm.
If the doctor has not identified external symptoms, this condition does not require therapy only if there is a small concentration of non-oncogenic strains.
Papillomavirus is one of the most oncogenic viruses. Papilloma can become melanoma - skin cancer! This research method is carried out using a special device - an amplifier.
To obtain results, it is necessary to load pre-prepared samples into the device, which are examined for 4 hours.
Using the polymerase chain reaction method, you can determine the number of pathogen particles for HPV, as well as perform DNA typing, which will provide information about the presence of one or more strains of the virus.
The test is able to detect HPV, even if the sample contains several particles of viral DNA, or it is in the incubation period of development.
Automation of the process eliminates the situation when HPV is negative, but papillomas are present. Collecting biological material is no less important stage of the procedure than deciphering the analysis.
The material used is scraping from the mucous membrane of the vagina or urethra. The Digene test is often ordered in conjunction with a cytology test to obtain specific results.
This is a widely used test for oncogenic HPV types. The material for analysis is a smear from the mucous membrane, sometimes blood, urine, amniotic fluid.
The method is based on the detection of viral DNA and allows one to determine with great accuracy whether a patient is infected or not.
This study must be carried out by an experienced and responsible specialist, since if the technology is not followed, the result may be false negative or false positive. For the patient, almost all HPV tests are simple, painless and non-traumatic.
If material is taken from the vagina or urethra for analysis, minimal preparation is required.
3 days before donating the biomaterial, you must stop using any antibacterial and antiviral agents, as well as antibacterial products for intimate hygiene.
This is interesting: Laser removal of condylomas: features, reviews, price
On the day of the test, it is not recommended to carry out hygienic procedures; it is also advisable not to urinate 2 hours before collecting the material, especially for men.
It is recommended to take a blood test on an empty stomach - this means that for 10-12 hours before visiting the doctor it is better not to eat anything and drink only water. It would also be good to eliminate alcohol and junk food for 2-3 days.
Both men and women must abstain from sexual intercourse for two days before sampling.
Only a doctor can decipher the results of HPV tests. The patient should have some idea of the form of the results and the rules of interpretation.
However, remember that everything found on the Internet is intended for informational purposes only, and not for making an independent diagnosis. The results of the Digene test raise the most questions. Less than 3 Lg indicates an insignificant concentration of the virus, 3-5 Lg indicates a clinically significant concentration, and more than 5 Lg indicates a very high concentration.
The human papillomavirus is especially dangerous for women; it can cause cervical cancer and other cancers. And with age, this risk only becomes higher.
However, at older ages, lesions regress much less frequently. However, the human papillomavirus is also dangerous for men.
Growing in the urethra, papillomas can completely block its lumen and cause serious problems, including impotence, infertility and cancer.
Tests to detect HPV and its subtype are simple to perform and do not require complex preparation from the patient or long wait for results. Meanwhile, the importance of early diagnosis of HPV lesions is difficult to overestimate.
Correctly chosen therapy will significantly reduce the risk of developing cancer.
Since a complete cure for human papillomavirus infection is currently impossible to achieve, along with this, spontaneous, spontaneous recovery is often observed, the manifestations of HPV are treated, and not the presence of the virus in the body.
In this case, it is necessary to avoid factors that reduce immunity: hypothermia, severe emotional stress, chronic fatigue, vitamin deficiency.
There are studies that indicate the preventive effect of retinoids beta-carotene and vitamin A, vitamin C and microelements such as folate against diseases caused by HPV.
Among the treatment methods for genital warts, the most commonly used are:. Destructive methods are local treatment aimed at removing condylomas. There are physical cryodestruction, laser therapy, diathermocoagulation, electrosurgical excision and chemical destructive methods (trichloroacetic acid, Feresol, Solcoderm), as well as surgical removal of condylomas.
The article was written based on materials from the sites: www.jks-k.ru.
»
Source: https://womens-life.ru/drugoe/vpch-klinicheski-znachimaja-virusnaja-nagruzka.html