One of the main indicators of women's health is the body's menstrual function. Its disturbances can manifest themselves in the form of oligomenorrhea, which is one of the types of hypomenstrual (weakened menstruation) syndrome and occurs in 2-3% of women.
Oligomenorrhea is a menstrual cycle disorder (IMC) in the form of short, less than 2 days, regular spontaneous menstruation with an interval between them from 36 days to six months. Understanding the causes of this syndrome is impossible without a general understanding of the physiological processes of regulation of menstrual cycles.
Physiology of regulation of menstrual cycles
Menstrual cycles are repeated cyclical changes in the female body, especially in various parts of the reproductive system. Its culminating external manifestation is menstruation, which repeats at a certain interval throughout the entire reproductive period, except for periods of pregnancy and lactation. Failure of these processes leads to the development of disorders, including oligomenorrhea. After the first menstruation (menarche), which usually appears at 10-12 years of age, the regularity of the cycles can be established over the course of 1-1.5 years.
The normal course and cyclicity of these processes, accompanied by changes throughout the body, is ensured by a single neurohormonal system, consisting of central (unifying) and peripheral effector (executive) structures, as well as intermediate links. In the mechanism of reproductive regulation, 5 levels are conventionally distinguished, which interact with each other in accordance with the principles of positive and negative direct and feedback connections.
Highest or first level
Represented by the cerebral cortex and some other structures of the brain. They participate in the perception and corresponding influence on other parts of the reproductive system, depending on the frequency, severity and duration of exposure to external (severe stress, instability of the psycho-emotional sphere, etc.) and internal stimuli.
In the latter case, this occurs with the help of specific receptors for estrogens, androgens and progesterone.
In response to the action of stimuli, biologically active substances are synthesized, released and undergo biochemical transformations in these brain structures, affecting the corresponding function of another brain formation - the hypothalamus.
Second level
The hypothalamus, as a neuroendocrine structure, is the second level of regulation.
It has the properties of both neurons that reproduce electrical impulses and cells that secrete the hormonal substances liberins (stimulating) and statins (blocking).
The activity of the hypothalamus depends both on the regulatory influence of the first level structures and on the content of sex hormones in the blood. Gonadotropic liberins of the hypothalamus are collectively called gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
Its secretion is programmed genetically and is circoral (pulsating) in nature. The maximum activity of the hypothalamus lasts several minutes, activity intervals range from 1 to 3 hours, which is also influenced by the concentration of estradiol in the blood during the luteal or follicular phase of the menstrual cycle.
Third level
The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland is the third level of neuroendocrine regulation. This part of the brain secretes hormones:
- FSH (follicle-stimulating), stimulating the growth and maturation of follicles in the ovaries;
- LH (luteinizing hormone), which together with the first one promotes the production of progesterone;
- prolactin, which controls the release of progesterone by the corpus luteum into the blood, as well as stimulating the growth of the mammary glands and regulating lactation;
- TSH (thyroid-stimulating), STH (somatotropic) and ACTH (adrenocorticotropic).
Only with a balanced secretion of these hormones is it possible for adequate functioning of the reproductive system, the establishment of a regular menstrual cycle and the absence of such disorders as oligomenorrhea, amenorrhea, hypomenorrhea, etc.
Fourth level
Consists of peripheral endocrine organs, which include the ovaries, thyroid gland and adrenal glands. The ovaries, in which follicles grow and mature, sex hormones are synthesized, and the corpus luteum is formed, play a major role.
Hormones synthesized in the ovaries are decisive not only in the functional changes of the reproductive system itself, but they also have an active influence on metabolic processes in tissues and organs that have receptors for sex hormones, aminopeptides, insulin and glucagon.
Fifth level
It consists of the mucous membrane of the vagina, the uterus, especially its mucous membrane (endometrium), in which cyclic processes are most expressed, fallopian tubes and mammary glands.
Cyclic changes in the endometrium, consisting of cell proliferation, secretion and menstruation itself, depend both on the concentration of sex hormones in the blood and on the state of the tissue receptor apparatus for sex hormones.
These levels form the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis. The principles of direct and reverse interaction through specific hormone receptors at all levels ensure cyclicality and adequate functioning of the reproductive system.
By “direct” connection we mean the stimulating effect of the hypothalamic region of the brain on the pituitary gland with the subsequent synthesis of sex hormones in the ovaries, by “reverse” - the influence of the level of concentration of sex hormones on the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
One of the main general indicators, which reflects the interaction of different levels of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis and the possibility of implementing the main function of the body's reproductive system, is the menstrual cycle. Its character makes it possible to clinically determine the level of condition of the reproductive system, due to the correct relationships in the hypothalamus-pituitary-ovarian system.
Thus, NMCs of the oligomenorrhea type, like other types of these disorders, can be provoked by factors that cause disturbances in the interaction of parts of the neuroendocrine system at one or several levels.
Reasons for the development of oligomenorrhea
Oligomenorrhea can be physiological or pathological. Physiological oligomenorrhea is a disorder that accompanies physiological conditions. It occurs in adolescence, when the formation of the menstrual cycle occurs, and during premenopause, that is, the decline of the functions of the reproductive system (read what the menopause period is and when it occurs in our article). In the latter case, it precedes menopausal amenorrhea.
The pathological syndrome differs as:
- Primary oligomenorrhea - occurs during the formation of the menstrual cycle. In this case, it represents an external sign of the beginning of the development of a process that, in the fertile period, determines the violation of the neuroendocrine function of the reproductive system of the body. By the end of adolescence, disorders in the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian system, which initially have a functional nature, acquire relative stability and retain their main features already in childbearing age.
- Secondary oligomenorrhea - develops after an established normal regular menstrual cycle.
Having an idea of the levels of physiological regulation of the menstrual cycle, it becomes clear that the cause of oligomenorrhea can be any organic or functional disorder at one of the levels. These reasons may be:
- Anatomical changes in the brain due to trauma, pituitary and other tumors of various types, Itsenko-Cushing’s disease and syndrome.
- Chronic negative psychogenic stress or severe stress conditions.
- Excessive prolonged physical activity and sudden changes in climate or time zone.
- Acute infectious diseases complicated by neuroinfection, as well as previous meningitis or encephalitis.
- Diseases of the endocrine organs (hypothyroidism, pancreatic diseases, adrenal tumors, some forms of menopausal and premenstrual syndromes).
- Family predisposition to reproductive disorders (read more about female infertility here).
- Congenital anomalies of the development of the genital organs.
- Metabolic disorders in obesity, rapid weight loss, unbalanced diet, underweight for a long time.
- Long-term use of oral contraceptives containing estrogens, opioid drugs, metoclopramide (an antiemetic), hallucinogens and some narcotics, long-term or inadequate treatment with hormonal (glucocorticosteroid) drugs.
- Ovarian diseases (cysts, polycystic ovary syndrome, tumors).
- The cause of oligomenorrhea can be frequent infectious diseases in childhood and adulthood, including chronic inflammatory processes and post-inflammatory changes in the endometrium, as well as tumors, endometriosis, surgical interventions on the uterus and ovaries, trauma (abortion).
- Diseases of the liver and cardiovascular system (rare).
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) also introduced a category such as “oligomenorrhea, unspecified.” It belongs to the class of diseases of the genitourinary system, the block “Non-inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs”.
This category includes oligomenorrhea, which may be caused by exhaustion syndromes, dysgenesis, ovarian hyperinhibition, or immune disorders that cover the humoral and cellular components of immunity and may manifest themselves as autoimmune oophoritis or other disorders in the ovaries of unknown cause.
Symptoms of oligomenorrhea
Changes in the nature of bleeding during menstruation and the interval between them are often accompanied by disorders of fat metabolism in the form of excess body weight (in 80%), the appearance of acne on the face, on the skin of the anterior and posterior surface of the chest, the development of acne, increased greasiness, porosity and scarring. (striae) of the skin. 25% of women with this syndrome have symptoms of hirsutism, that is, excessive development of hair in the face, abdomen, mammary glands, and chest.
Some women experience the development of a male-type physique and a decrease in libido, headaches and dizziness, deviations from normal blood pressure readings, asymmetrical blood pressure readings, numbness of the fingers, vegetative disorders, sleep and appetite disorders, tearfulness, irritability, and emotional instability.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of a disease that causes menstrual irregularities is established on the basis of complaints and anamnesis, general objective and gynecological examinations, as well as an assessment of the state of the psycho-emotional sphere and neurological condition.
Additional methods for diagnosing oligomenorrhea include determining basal temperature with plotting a graph, ultrasound and MRI examination of the pelvis using a vaginal sensor, and magnetic resonance imaging of the skull.
In addition, laboratory studies of the content of pituitary hormones (prolactin, follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones) and sex hormones (progesterone, estradiol, testosterone), as well as glucose and cholesterol in the blood serum are carried out, the content of 17-ketosteroids in the urine is determined (to assess adrenal function) .
Treatment
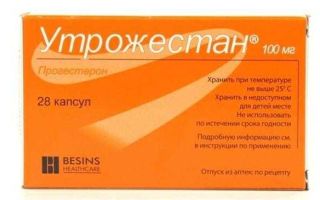
Treatment of oligomenorrhea consists of treating diseases and correcting pathological conditions that result from it. In order to stimulate ovulation, clomiphene or gonadotropic drugs according to certain regimens, oral combined contraceptives, utrozhestan, parlodel, etc. are prescribed.
Recommendations are given regarding proper nutrition, drugs with a sedative and, if necessary, antidepressant effect, and physiotherapeutic treatment are prescribed. If brain tumors, pituitary adenomas and some ovarian diseases are detected, surgical treatment may be recommended.
Timely correction of functional disorders of neuroendocrine regulation can slow down their development or lead to complete recovery. In the case of late diagnosis and treatment, functional disorders become irreversible and lead to organic changes in the reproductive organs.
Is it possible to get pregnant with oligomenorrhea?
This largely depends on the reasons that led to the development of the syndrome. If hormonal disorders occur, there is no ovulation, there is no rejection and restoration of the uterine mucosa, then naturally, pregnancy becomes impossible. In cases of infantilism, the possibility of pregnancy depends on the degree of uterine hypoplasia, the degree of hormonal functioning of the ovaries, and the presence of concomitant pathological conditions.
According to the World Health Organization data for 1985, of all causes of infertility, 14.7% are accompanied by this type of pathology. Among all infertile women suffering from any menstrual irregularities, the frequency of oligomenorrhea is 41.6%. Spontaneous pregnancy occurs in only about 20% of women with this syndrome.
Source: https://ginekolog-i-ya.ru/oligomenoreya.html
Oligomenorrhea in women: symptoms, causes of development and treatment
Menstruation cycle
11.05.2018
16.6 thousand
11.1 thousand
7 min.
The regularity and duration of menstruation are the main indicators indicating the state of the reproductive system of the female body. Menstrual dysfunction is often manifested by oligomenorrhea, which is a hypomenstrual syndrome, or rather, one of its types, which occurs in 2.5% of women.
Oligomenorrhea is characterized by weakening of menstruation, disruption of their regularity and reduction in duration. The duration of the cycle is about 2 days, and the interval between them varies from 36 days to six months. The causes of this syndrome are associated with the physiological mechanism responsible for the regulation of menstrual cycles.
Correction of the condition is prescribed by a doctor.
Each menstrual cycle is accompanied by physiological changes occurring in the female body. In this case, various parts of the reproductive system are involved in the process. Its external manifestation is considered to be periodically recurring menstruation, which continues in women of reproductive age, with the exception of the period of pregnancy and lactation.
Violation of these processes entails the development of oligomenorrhea. Sometimes the pathology is combined with other forms of hypomenstrual syndrome:
- hypomenorrhea - a decrease in the amount of discharge during menstruation;
- spaniomenorrhea, or opsomenorea - rare menstrual cycles.
The disorder, manifested in the form of oligomenorrhea, is caused by both physiological and pathological processes occurring in the body.
Physiological oligomenorrhea is characterized by disruptions that can occur during the formation of the menstrual cycle in girls during adolescence, as well as in women during the period of decline of the functions of the reproductive system, called premenopause.
- The main cause of this pathology is insufficient synthesis of sex hormones, which are responsible for regulating the menstrual cycle.
- The primary form of oligomenorrhea most often occurs against the background of congenital, genetically determined malformations of the female reproductive system, for example, with infantilism of the uterus.
- The secondary form develops as a consequence of previously suffered gynecological diseases of an infectious and non-infectious nature. Their list includes:
- ovarian cysts, polycystic disease;
- uterine hyperplasia;
- endometriosis;
- endometritis.
The causes of the development of the disease can be tumors of the pituitary gland or surgical operations (endometrial curettage, abortion), pathologies of the endocrine system (functional disorders of the thyroid gland, pancreas or adrenal glands).
Oligomenorrhea can be caused by: disruption of the hematopoietic process, cardiovascular pathologies and liver disease. The risk group includes women with mental disorders (anorexia, bulimia) and professional athletes.
The functional features of the reproductive system have a direct relationship with a woman’s weight category. The accumulation of female sex hormones occurs in fatty tissue, which should be sufficient. An underdeveloped fat layer is often the cause of serious disorders of the female reproductive system, including the disappearance of menstruation and infertility.
Oligomenorrhea has a number of symptoms, characterized by obvious and hidden manifestations. The main ones:
| Symptoms of the disease | Character of manifestations |
| Shortened periods of menstruation | The symptom occurs at the very beginning of the disease. The duration of normal bleeding varies from 4 to 6 days. With the development of oligomenorrhea, this period is 2-3 days. Sometimes the discharge may stop after a few hours. This change indicates poor growth of the endometrium - the inner uterine layer, on which the egg after fertilization will not be able to attach. As a result, a woman is at risk of developing infertility |
| Extended cycles | Long female period, the duration of which ranges from 40 days to 6 months |
| Infertility in women | In the presence of the above-described signs, it is a pronounced symptom of a pathological process. With such disorders, normal ovulation does not occur. Preservation of egg maturation is observed in only 20% of women suffering from this disease |
| Hormonal disorders | Women experience a decrease in the number of estrogens in the body. Hormonal imbalance in almost every case accompanies secondary oligomenorrhea. Deviations can be identified using a blood test to determine the levels of FSH and LH. In some female representatives, manifestations may be accompanied by an increase in body weight, lipid metabolism disorders and the appearance of masculine signs: changes in the bone skeleton, the appearance of hair in certain areas of the body, increased oiliness of the skin on the face as a result of enlarged pores |
With oligomenorrhea in women, sexual desire decreases. The consequences of the disease can be the development of uterine carcinoma and endometrial hyperplasia.
The diagnosis and treatment of the disease is carried out by a gynecologist and an endocrinologist. Diagnostic measures are aimed at identifying the causes of oligomenorrhea and assessing the condition of the female body. In addition to the patient’s complaints, the results of instrumental and laboratory tests are taken into account. A gynecological examination is mandatory for diagnosis.
The choice of therapeutic tactics is made depending on the form of the disease and the degree of neglect of the process.
In case of primary oligomenorrhea, which most often occurs in girls during adolescence, treatment comes down to nutritional correction, elimination of stress factors, vitamin therapy and other measures aimed at increasing immunity. In the secondary form of oligomenorrhea, therapy is supplemented with drug treatment and physiotherapeutic procedures.
For oligomenorrhea, it is strongly recommended to change the daily routine to include walks in the fresh air and exercise therapy. According to most experts, women with this diagnosis should avoid overwork and stressful situations.
It is mandatory to prescribe immunostimulants (vitamins B, A and E), as well as bimanual gynecological massage aimed at improving blood circulation, strengthening muscles and eliminating congestion in the pelvis. Using these methods, it is possible to prevent the formation of adhesions and even achieve their resorption.
Massaging the uterus is carried out with both hands with simultaneous impact on the organ from the rectum or vagina and abdomen.
Correction of nutrition for oligomenorrhea comes down to limiting salt, excluding animal fats and carbohydrates. It is recommended to drink teas made from medicinal herbs.
The main role in the treatment of secondary oligomenorrhea is given to hormone therapy. It allows you to regulate the menstrual cycle and ovulation.
If the cause of the disease is ovarian cystosis, then the patient is prescribed progesterone drugs: Utrozhestan, Pover, Duphaston. The duration of the course varies from 10 to 12 days. Such treatment is carried out once a month or quarter and lasts until the frequency and duration of the menstrual cycle is completely restored.
In most cases, taking medications with progesterone is combined with contraceptives. Their introduction speeds up the healing process and helps avoid the development of hirsutism and acne.
In order to restore ovulation, women are prescribed hormonal drugs: Pergonal, Clomid, Clomiphene.
In parallel with drug treatment, patients are prescribed the following procedures:
- magnetic therapy;
- ultrasound treatment;
- phototherapy;
- electrophoresis with the addition of copper;
- paraffin applications;
- acupuncture.
Physiotherapy is carried out for the purpose of:
- improving blood supply to the pelvic organs;
- relief of inflammatory processes;
- relieving spasms in the internal genital organs;
- stimulation of the production of female sex hormones;
- restoration of the functioning of the genital organs.
The use of these methods is contraindicated for cancer, endometriosis, liver failure, liver disease and severe circulatory disorders.
Sometimes surgical treatment is advisable for oligomenorrhea. In case of polycystic ovary syndrome, precise cauterization of neoplasms is carried out with high-frequency current - diathermocoagulation. Manipulation is contraindicated for women who have not given birth. Girls planning a pregnancy in the future may be prescribed radio wave coagulation. This method is more gentle.
Traditional methods for oligomenorrhea can be used as a supplement to the main treatment and only after consultation with your doctor. There are several proven remedies aimed at relieving inflammation, improving the general condition of the body and restoring the functionality of the genital organs:
| Means | Recipe and application |
| Herbal tea |
|
| Alcohol tincture of cypress cones |
|
| Decoction of cherry leaves |
|
| Wine decoction |
|
With timely treatment, the prognosis for oligomenorrhea of both primary and secondary types is favorable. Otherwise, this disease can lead to irreversible changes in the reproductive system, which often result in amenorrhea and infertility.
If primary amenorrhea develops against the background of uterine infantilism, the prognosis depends on the degree of hypoplasia of this organ and the functional capacity of the ovaries. At the same time, the probability of conceiving a child for women is 40% of the total number of cases.
Serious consequences of the pathology are: endometrial hyperplasia and uterine cancer. In this case, a separate treatment is assumed.
To prevent the development of complications, women are recommended to follow the following rules:
- regular examinations by a gynecologist;
- balanced diet;
- body weight control;
- proper organization of work and rest;
- timely detection of pathology and treatment in compliance with medical recommendations.
Source: https://fraumed.net/menstruation/cycle-of-monthly/oligomenoreya.html
Oligomenorrhea
A disease in which the intervals between menstruation last more than forty days is called oligomenorrhea.
It is characterized by short-term, scanty bleeding during the critical period, usually with a short duration - about two to three days. The intervals between menstruation in this pathological condition last up to six months.
Its symptoms are most often found in young girls and women before menopause. In general, this disorder affects up to 3% of women of reproductive age.
Causes of pathology
A condition in the female body in which there is no normal menstrual cycle is caused by improper functioning of the endocrine system or diseases of the genitourinary system.
Rare menstruation indicates delayed maturation of follicles, which is associated with the presence of polycystic disease, malignant tumors, and disruption of the glands that produce sex hormones.
If such a picture is observed with menarche, then this is called primary oligomenorrhea, but if at first menstruation occurred regularly, and the cycle was disrupted over time, then we are talking about secondary oligomenorrhea. Ovarian dysfunction, leading to rare menstruation, is caused by the following factors:
- endocrine diseases;
- experienced severe stress;
- physical fatigue;
- weight loss diets;
- cancellation of hormonal contraceptives after a long period of use;
- poor acclimatization during contrasting changes in climate zone.
Prolongation of the cycle with signs of oligomenorrhea may be a transitional condition leading to a complete absence of menstruation (amenorrhea). Repeated long periods between menstruation more than once signal problems in the body.
For timely treatment, as well as to exclude such consequences as uterine cancer and endometrial hyperplasia, at the first signs of menstrual disorder, you must consult a gynecologist.
Symptoms
In addition to the main symptom of rare menstruation, this pathological condition may be accompanied by:
- decreased libido;
- male pattern hair growth (hirsutism);
- obesity;
- acne.
Often, menstrual irregularities characteristic of oligomenorrhea occur in women whose physique is similar to a man’s (narrow hips and broad shoulders). But all of these symptoms can exist separately or in combination, without causing the effect of cycle disruption. The main symptom remains prolongation of periods over 40 days with a tendency to increase.
Oligomenorrhea in adolescence
Among menstrual disorders in teenage girls, oligomenorrhea ranks first.
The puberty period is characterized by the rapid development of the reproductive system, as well as the launch of hormonal regulatory mechanisms, where the pituitary gland and hypothalamus are involved.
Against the background of hormonal changes in the body, adolescents may experience symptoms of oligomenorrhea. They occur on average in every tenth girl after menarche.
The course of oligomenorrhea in adolescents may be accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen, resulting from spasms of the uterine wall. The cause of such spasms most often lies in an insufficient luteal phase. But pain can also occur with congenital connective tissue dysplasia.
Painful menstruation during teenage oligomenorrhea can last up to 2.5 years from menarche, and then gradually disappear against the background of the formation of a normal cycle. Such pain usually lasts 1-2 days from the beginning of menstruation. If they are protracted and continue for more than 2 years after menarche, then the cause may be endometriosis.
Primary and secondary oligomenorrhea
Primary oligomenorrhea means the presence of symptoms of the disorder at the very beginning of menstruation. Signs of pathology may persist for a long time. Its cause is most often congenital pathologies of the reproductive organs, disruption of the endocrine functions of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, as well as a hereditary factor.
Secondary oligomenorrhea occurs in women whose menstrual cycle was normal before the disease. Very often, pathology occurs due to diseases of the ovaries and other internal organs that can affect the functioning of the reproductive system.
Pregnancy and oligomenorrhea
Significant menstrual irregularities sharply reduce the chances of natural conception. Rare menstruation means rare ovulation, or its absence, and without it, pregnancy is impossible. With symptoms of oligomenorrhea, it is necessary to establish the exact cause of the pathological condition.
Women suffering from this disorder cannot conceive a child and, unfortunately, it is this fact that often forces them to consult a gynecologist. The prognosis will depend on the cause of infrequent menstruation.
If the issue is the incorrect functioning of the endocrine system, then hormonal therapy is prescribed, which gives a good effect.
Treatment
Restoring the normal menstrual cycle is necessary not only for reproductive function, but also for the general health of a woman. Symptoms of oligomenorrhea are manifestations of a complex of problems, if the pathology is not caused by congenital anomalies of the genital organs.
Therefore, treatment is prescribed individually, taking into account the patient’s medical history, lifestyle and other characteristics.
Hormonal therapy, pharmacological stimulation of ovulation, physiotherapy, exclusion of infectious diseases of the reproductive system - together they give a positive effect.
Surgical treatment is prescribed as a measure to overcome diseases that cause menstrual irregularities. These include polycystic ovary syndrome, endometriosis, benign and malignant formations of the internal genital organs, requiring surgical intervention.
Physiotherapeutic procedures have a beneficial effect on overall well-being, strengthen the immune system, and help normalize the menstrual cycle. Procedures that do not have a proliferative effect give good results during the rehabilitation period after ovarian surgery.
Traditional medicine uses herbal medicine to normalize the menstrual cycle. A decoction of chamomile, lemon balm, birch leaves and buds, peppermint tincture, wormwood, elecampane root, and St. John's wort have a beneficial effect.
- To prevent oligomenorrhea, doctors recommend avoiding excessive physical activity, taking oral contraceptives with caution (only after consulting a gynecologist), and regularly undergoing routine gynecological examinations.
- Opsomenorrhea
- Treatment for ovarian cysts
- Follicles and their maturation processes
- Reasons for lack of ovulation
Source: https://KRMed.ru/articles/oligomenoreya.html
Oligomenorrhea
Oligomenorrhea is one of the types of menstrual irregularities, characterized by signs of hypomenstrual syndrome.
It manifests itself in the form of an increase in the intervals between menstruation or a reduction in the duration of menstruation. In the first case, the cycle length exceeds 40 days, and the woman has less than eight menstruation per year.
In the second case, bleeding continues for no more than two days.
The content of the article:
In some cases, oligomenorrhea is accompanied by diseases such as:
- polycystic ovary syndrome - a condition in which the size of the ovaries increases, and they themselves fill with many bubbles with fluid;
- endometritis - inflammation of the uterine mucosa (endometrium);
- endometriosis is the growth of fragments of the uterine mucosa outside of it.
According to statistics, oligomenorrhea occurs in two to three percent of women.
Causes of oligomenorrhea
Oligomenorrhea can be primary or secondary. This depends on the age of the patient and whether she had a normal menstrual cycle before the onset of the pathology. Primary oligomenorrhea occurs in teenage girls. In the first years after menarche (the arrival of the first menstruation), the formation of the menstrual cycle occurs, and bleeding may be irregular and rare.
In addition, if oligomenorrhea is primary, it may be caused by hypoplasia (infantilism) of the uterus. Hypothalamic dysfunction of puberty often contributes to oligomenorrhea. Finally, hereditary factors may play a role.
Secondary oligomenorrhea is undoubtedly a deviation. Before her appearance, the girl had stably regular menstruation, but some disease caused a malfunction. Most often, the development of oligomenorrhea is promoted by ovarian dysfunction. This, in turn, is due to the following reasons:
- hormonal disorder;
- physical activity;
- stress;
- exhausting diets;
- climate change;
- taking certain medications;
- the beginning of menopause;
- neoplasms in the pelvic organs.
If oligomenorrhea is secondary, the doctor will certainly ask whether the patient has had an abortion. Such interventions often cause menstrual irregularities.
Symptoms of oligomenorrhea
The main manifestation of oligomenorrhea is the intervals between menstruation.
And if oligomenorrhea in adolescents can go unnoticed, then an adult woman can notice a lot of unpleasant signs that accompany it. First of all, this is hirsutism - excessive male-type hair growth.
Vegetation appears on the face, chest, stomach, inner thighs - that is, in places where the fair sex should not have it.
Hirsutism is usually caused by an excess of male sex hormones in the blood, which also causes:
- change in physique: a woman’s figure becomes similar to a man’s;
- overweight;
- acne;
- decreased libido;
- problems with conception.
In most cases, it is the latter factor that forces women to start treatment.
Diagnosis and treatment of oligomenorrhea
The first thing you need to realize before starting to fight a condition such as primary or secondary oligomenorrhea is that this is not a disease, but an indicator of some kind of malfunction in the body. Therefore, it is not enough to simply make an appropriate diagnosis: you need to find out what caused the oligomenorrhea.
Diagnostic measures include:
- Anamnesis collection. The doctor asks the patient about:
- age of first menstruation;
- the period during which the cycle stabilized (if we are talking about secondary oligomenorrhea);
- past diseases;
- the presence of similar problems among relatives;
- other related complaints.
- Gynecological examination:
- functional;
- instrumental;
- laboratory
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs. In case of oligomenorrhea, it is recommended to conduct research using the transvaginal method to increase information content.
- Blood test for sex hormones:
- progesterone;
- FSH;
- LH;
- prolactin;
- estradiol
- Hysterosalpingoscopy is a study of the patency of the fallopian tubes.
It is advisable to take your menstruation calendar with you when going to your appointment.
For oligomenorrhea, consultation with a psychologist or psychotherapist is not necessary, but is still advisable. It is obvious that this pathology with all its manifestations has an extremely negative effect on the moral state of the patient.
On the other hand, mental well-being is the key to the normal functioning of the reproductive system. Among women with oligomenorrhea, less than 29 percent can boast of the absence of any nervous system disorders.
Patients admit that with the appearance of the problem, their quality of life decreases according to the following indicators:
- health;
- sexual activity;
- material well-being;
- peace of mind;
- good rest.
Depending on the identified picture of oligomenorrhea, the doctor selects an adequate treatment method. It’s worth noting right away that oligomenorrhea is a dangerous pathology, and delaying treatment here is unacceptable. Otherwise, you can lose the chance for the greatest happiness in life - motherhood.
So, if a gynecologist-endocrinologist has determined that the patient has oligomenorrhea, treatment will most likely be medicinal.
This refers to hormonal therapy aimed at eliminating the signs of hypomenstrual syndrome by stimulating ovulation. If the eggs are actively maturing, the cycle length will be shortened.
The course of taking appropriate medications lasts from 10 to 12 days and is repeated every month. Thus, an artificial imitation of the follicular phase is obtained.
For some patients, lifestyle adjustments are sufficient:
- choosing a proper nutrition plan;
- reducing loads;
- limiting salt intake;
- inclusion of vitamins in the diet.
As a rule, this works when it comes to primary oligomenorrhea. Secondary may require more complex treatment, including surgery.
A common surgical method is spot diathermocoagulation of the ovaries, but it is contraindicated for nulliparous girls. The scar tissue that forms after such cauterization can subsequently interfere with the normal birth process.
An alternative to this procedure can be radio wave coagulation, which is more gentle.
After completing a course of treatment, some patients are prescribed a course of physiotherapy, gynecological massage or physical therapy. Such procedures help improve blood circulation in the pelvic organs.
A patient whose menstruation has become regular and the intervals between them does not exceed 40 days will be considered completely cured. In order to draw such a conclusion, a woman will need to keep a calendar, which will take into account the following indicators:
- start date of menstruation;
- their duration.
In addition, visits to the gynecologist every three months are required to monitor the patient’s condition. In conclusion, we note that the recovery statistics are quite favorable.
Source: https://www.mosmedportal.ru/illness/oligomenoreya/
Treatment of oligomenorrhea, signs and causes of rare periods
Oligomenorrhea is caused by unbalanced functioning of the endocrine system. The body sometimes experiences a strong lack of female hormones or, conversely, an excess of male hormones. As a result of these problems, the girl’s physique becomes more like a man’s.
It is also possible to develop profuse acne, excess body weight, and hirsutism—male-type hairiness of the skin. Oligomenorrhea is a quite serious disease that can lead to infertility and even cancer.
Causes
There are 2 types of oligomenorrhea: primary and secondary. The main cause of primary oligomenorrhea is ovarian dysfunction: hormones are not produced in sufficient quantities for the reproductive system to function properly. Most often, this problem is of hereditary origin.
The causes of secondary (acquired) oligomenorrhea are abortion, hormonal disorders, anorexia, exhaustion, severe stress, sudden and contrasting climate change.
Diagnosis of oligomenorrhea
The disease is diagnosed using hormonal testing and gynecological examination. If related problems are identified, additional diagnostics are prescribed.
Treatment
If oligomenorrhea occurs against a background of obesity, a balanced diet and moderate physical activity play a major role in the treatment of the disease. Sometimes weight loss can restore normal ovulation without complex interventions. But in most cases, painstaking and complex treatment is necessary.
The DaliMed clinic has developed a whole range of methods to solve this problem: Hormone therapy All menstrual cycle disorders are associated primarily with hormonal imbalance. Often this is either a lack of female or an excess of male hormones. To return them to normal, hormonal therapy is prescribed. It restores the amount of hormones and the functioning of the glands.
Homeosiniatry A unique treatment method that combines homeopathy and traditional Chinese medicine. It is remarkable because it covers the entire body in treatment.
Hirudotherapy (including intravaginal placement) Leech enzymes normalize hormonal levels. Stimulates the body's strength.
Plasmolifting The method is based on the use of the patient’s own blood plasma. Raises local immunity. Stimulates the restoration of the pelvic organs, normalizing their functioning.
Physiotherapy Complements basic treatment methods. They relieve pain, stimulate the functioning of organs, and help in the fight against inflammatory processes.
- Laser therapy
- Magnetic laser therapy
- Electrophoresis
Mud therapy A method that “starts” the work of the pelvic organs. Used in sanatoriums to restore normal functioning of the body and immune system
Ozone therapy A method of treatment with an ozonized solution. Can be used both locally and intravenously. Relieves inflammation and swelling. Stimulates adequate functioning of the immune system.
All methods are designed to normalize hormonal levels and stimulate the immune system.
In order to prevent oligomenorrhea, you should adhere to a nutritious diet, avoid stress, emotional and physical overload. And be sure to use only those contraceptives prescribed by your doctor. Taking these medications on your own is dangerous to your health.
Remember that most problems affecting hormonal levels and reproductive function can be solved. Don't delay treatment - make an appointment.
Source: https://www.dali-med.ru/ginekologiya/narusheniya-menstrualnogo-tsikla/oligomenoreya/
Oligomenorrhea secondary
Volkova A.A., endocrinologist, practical experience since 2015.
May, 2019.
Synonyms: rare periods, a variant of hypomenstrual syndrome.
ICD-10 code: N91.4
Secondary oligomenorrhea is an increase in the interval between menstrual bleeding, often in combination with a shortening of the bleeding period itself.
It develops after the establishment of a normal menstrual cycle. Occurs on average in 2.5-3% of women. In addition to menstrual irregularities, it can be characterized by obesity, the development of male pattern hair, and mood instability.
It is treated both medically (COC) and surgically, depending on the cause.
Classification
Secondary oligomenorrhea differs from primary in that the secondary form occurs against the background of an established cycle, and the primary form is observed in girls with a not yet established cycle.
There are different forms of secondary oligomenorrhea:
- shortened menstruation (duration of bleeding from several hours to 1-2 days);
- extended interval between menstruation (from 40 days to six months)
- mixed variant, in which shortened bleeding is combined with a large gap between them (most common).
Additionally, secondary oligomenorrhea is divided into physiological and pathological.
Important! Physiological oligomenorrhea can be considered during lactation, at the onset of menopause. In all other cases, the symptom is pathological.
Causes and risk factors
Secondary oligomenorrhea in most cases develops as a result of exposure to various negative factors on the female body. The most common reasons are:
- acute and chronic infectious processes affecting the uterus and ovaries (gonorrhea, chlamydia, candidiasis, ureaplasmosis, genital herpes);
- diseases of the reproductive system of an inflammatory or traumatic nature (salpingitis, endometritis, oophoritis, myometritis);
- various stressful effects, nervous shock, the presence of certain mental disorders (bulimia, anorexia);
- the influence of negative environmental factors (living in an environmentally unfavorable area, working in hazardous industries, etc.);
- decompensated (untreated) diseases of the pancreas, adrenal glands, thyroid gland (diabetes mellitus, adrenal insufficiency, hypo- and hyperthyroidism, etc.);
- surgical interventions on the uterus and ovaries, including abortions;
- disturbances in the functioning of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, due to which the hormonal regulation of the body generally suffers;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels (with diseases of the cardiovascular system, the blood supply to the genital organs may be disrupted, which leads to a disorder in their functioning, and the body as a whole is weakened).
Doctors also identify risk factors that increase the risk of developing oligomenorrhea, but do not lead to it in 100% of cases. Among these factors:
- unfavorable environmental influences;
- regular stress;
- habit of eating poorly, going on irrational diets;
- taking hormonal medications without a doctor’s recommendation or neglecting the doctor’s recommendations;
- lack of vitamins;
- being overweight;
- sudden climate changes.
Professional female athletes are also at risk, as they constantly experience not only severe stress, but also have to cope with high physical activity.
Symptoms
The main symptom of secondary oligomenorrhea is short periods or a long interval between menstrual bleeding. A significant number of women ignore this symptom for a long time, not realizing that this is not a normal option, but a pathology.
After all, the rarity or short duration of menstrual bleeding indicates that the uterine endometrium is renewed slowly and does not grow intensively enough. Such a change in the organ threatens infertility.
Often a woman thinks about the need to visit a doctor for oligomenorrhea only after unsuccessful attempts to become pregnant and carry a child to term.
In addition to problems with pregnancy, the following symptoms may occur due to hormonal imbalance:
- disturbances in fat metabolism develop, which leads to the development of obesity;
- when there is an excess of testosterone in the female body, the figure changes to a male type (broad shoulders, narrow hips);
- acne appears on the skin, acne develops;
- hirsurtism develops (hair on the face, neck, back, abdomen according to the male type of hair growth), observed in 20% of patients;
- Libido decreases, sexual desire becomes less pronounced;
- There are sudden mood swings, increased nervousness and irritability.
In case of secondary oligomenorrhea, the symptoms may not cause significant discomfort to the woman for a long time, which is why she postpones seeing a doctor.
Diagnosis of secondary oligomenorrhea
Secondary oligomenorrhea is diagnosed based on a combination of medical history, symptoms, results of laboratory and instrumental studies.
During a conversation with the patient, the doctor clarifies when the first menstruation (menarche) occurred, how quickly the menstrual cycle became regular, whether the woman suffers from symptoms of premenstrual syndrome, whether she has a history of diseases of the reproductive organs or abortions. An examination in a gynecological chair is required.
From the studies applied:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (can be performed both transabdominally and transvaginally, the second option is preferable due to its greater information content) - pay attention to the size of the uterus and its appendages, their shape, structure;
- analysis of sex hormones - assess the level of progesterone, prolactin, estradiol, LH, FSH (an LH level of more than 15 mE should alert you outside the peak of ovulation, on days 1-14 of the cycle, as well as at the beginning of menstruation);
- hysterosalpingography is a method that allows you to assess the patency of the fallopian tubes;
- a group of tests to detect sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, etc.).
If a tumor of the pituitary gland is suspected, a woman may be recommended to have an MRI of the brain. If a disease of the adrenal glands is suspected, a urine test for 17-ketosteroids is taken, and if a pathology of the thyroid gland is suspected, a blood test is taken for thyroid hormones.
Treatment
Treatment of secondary oligomenorrhea should be comprehensive and selected depending on the cause of the disease. Therapy is jointly selected by a gynecologist and an endocrinologist. Treatment is possible with conservative and surgical methods.
Conservative therapy
Based mainly on the use of hormonal drugs. The purpose of the medications is to normalize the ratio of hormones and start the ovulation process. For this purpose, progesterone preparations are prescribed (Duphaston, Inzhesta, Utrozhestan, etc.
) or combined oral contraceptives. They are suitable for women who do not plan to become pregnant or give birth in the near future. Progesterone preparations are taken in a course of 10-12 days a month until menstruation returns to normal.
Combined oral contraceptives are taken according to standard regimens selected by doctors.
If a woman wants to get pregnant, she undergoes drug stimulation of ovulation under the supervision of a doctor.
In addition to drug treatment, it is necessary to eat well and rest, give up bad habits, and monitor your weight.
If it is determined that the cause of oligomenorrhea is an infectious disease, an antiviral, antifungal or antibacterial drug is selected with the help of a doctor, depending on the specific causative agent of the disease. In addition to the treatment of infection, drugs that stimulate the immune system, anti-inflammatory drugs, and physiotherapeutic procedures are used.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment of secondary oligomenorrhea is indicated for women in whom drug therapy does not produce results.
The operation is performed for polycystic ovary syndrome. Today, doctors mainly perform sectoral resection of the ovary with cauterization, removing the part on which the largest number of cysts are found. The operation is performed laparoscopically. The recovery period takes 4-6 weeks.
Complications, prognosis and prevention
The main complication of secondary oligomenorrhea, which is most feared, is infertility.
According to statistics, in approximately 40% of cases a woman is not able to conceive or bear a child precisely because of the presence of secondary type oligomenorrhea.
Also, hormonal imbalance in general negatively affects the body, increasing the likelihood of developing cancer of the reproductive system.
With timely initiation of treatment, the prognosis for secondary oligomenorrhea is favorable. A significant number of women, under the supervision of a doctor, manage to normalize hormone levels and regulate the menstrual cycle.
Prevention of the secondary form of oligomenorrhea is based on maintaining a healthy lifestyle, timely treatment of identified diseases, and regular preventive examinations with a gynecologist.
Source: https://www.diagnos.ru/diseases/ginec/endocrinologiya_v_ginekologii/oligomenorea-vtorichnaya