- September 12, 2018
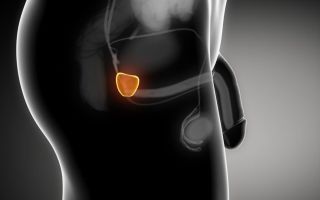
- Prostate
- Sofia Andreeva
The prostate is one of the most important organs in a man’s body. A comprehensive examination is required to study her condition. For these purposes, doctors often resort to prostate puncture. How is this procedure done? What are its indications and contraindications? These issues will be covered in detail in this article.
general information
Puncture is a method of studying organ tissue taken for research. This procedure allows you to assess your current condition and the success of the therapy. With its help you can determine the following parameters:
- composition of cellular elements;
- state of the epithelium;
- functioning of the prostatic glands.
The characteristics of the patient’s body, his age and the results of a previous examination - these factors determine how the prostate puncture will be done. In modern medical practice, one of three variants of the procedure is used: transrectal, transurethral or transperial. Each of them will be discussed in detail below.
The manipulation itself is quite painful. Therefore, before it is performed, the patient is given anesthesia. The type of anesthesia is also determined individually. In some cases, special anesthetic gels are used. Other patients are offered local anesthesia and sedatives to relieve nervous tension.
Indications for use
Most often, a puncture is prescribed to patients who told a doctor about pain in the pelvic area, a feeling of constriction and difficulty urinating. The listed symptoms are quite understandable. With a pathological enlargement of the gland, the urinary flow is compressed. You should also consult a doctor if the following disorders occur:
- discomfort in the pelvic area after physical activity;
- problems with proper emptying of the bladder (pain, feeling of heaviness, burning);
- temporary or permanent erectile dysfunction;
- causeless weight changes, constant drowsiness, hair loss.
The listed symptoms are direct indications for prostate puncture. Other reasons for prescribing the study are:
- detection of echogenic foci on ultrasound;
- diagnostics of a neoplasm to assess its nature and growth rate;
- determination of malignancy or benignity of a tumor.
Before the puncture, the man must undergo blood and urine tests.
Possible contraindications
The standard puncture procedure has some limitations. They are associated with the risk of complications both during and after manipulations.
The following violations are contraindications to the examination:
- cracks and other damage to the rectum (transrectal puncture of the prostate gland is prohibited);
- acute prostatitis (high probability of infection);
- bleeding disorders (there is a risk of affecting blood vessels);
- inflammatory bowel diseases, urinary system organs.
If there are contraindications, prostate tissue examination is carried out in other ways. As a rule, the choice falls on computer or ultrasound testing.
Preparatory stage
Before carrying out the manipulations, the doctor must inform the patient about the chosen puncture technique and possible complications.
Standard preparation for the procedure includes the following steps:
- You must stop taking blood thinning medications 7 days before the test date. We are talking about medications such as Heparin, Aspirin, Warfarin.
- 3 days before the puncture, it is forbidden to take anti-inflammatory drugs.
- The day before the procedure, the doctor prescribes an antibiotic. The choice of drug is carried out on an individual basis.
- On the morning of the procedure, the patient is given a cleansing enema.
It is worth noting that diagnostics are always performed on an empty stomach. It is even forbidden to drink sweet tea or fruit juice.
Transrectal puncture
This option is used in practice more often than others, since it is considered non-traumatic. All manipulations are carried out by introducing the device through the anus. Below is their detailed diagram:
- The patient lies on the couch on his left side and pulls his knees to his chest.
- An anesthetic is injected into the gland, which begins to act in 5-15 minutes.
- The doctor inserts a structure equipped with puncture needles and a probe for examination into the rectum.
- Then the material is directly collected. A hollow needle enters the fabric and plucks off a piece of tissue. In this case, several punctures are made (from 6 to 18). Biological material is necessarily collected from pathological and healthy areas.
If the manipulations are accompanied by pain, you should not endure it. You should immediately report any discomfort to your doctor.
Transurethral puncture
For some reasons, approaching the prostate through the anus is contraindicated. In this case, all manipulations are carried out through the urethra. This is also an informative option for the procedure, which allows the doctor to constantly monitor the progress of actions. It consists of the following stages:
- The patient lies on his back on the couch, and his legs are placed in special supports. The doctor gives anesthesia.
- The specialist inserts a cystoscope through the urethra and begins manipulation.
- The device itself is equipped with a wire loop, which is used to collect material for research. In one approach, it is possible to collect about a dozen tissue samples.
The urethral method is practically not accompanied by complications and is well tolerated by men.
Transperial puncture
This technique is recognized as the most informative, but is rarely used due to its high morbidity. It is used for diseases of the rectum or a high risk of blood poisoning.
How is prostate puncture done using the transperial method? The material is collected through an incision in the perineum. This area is first disinfected and anesthetized. All manipulations are carried out under ultrasound control. After the procedure is completed, the wounds must be treated.
Recovery period
The recovery period requires compliance with some recommendations. Prostate puncture is a complex procedure. For a week after it, doctors advise all patients to take antibiotics.
The risk of infection exists even if all sterility rules are observed. In addition, you need to avoid spicy and fried foods. In this case, tissue restoration will occur faster.
Alcoholic drinks are also prohibited.
During the day after the puncture, you need to drink a lot of water. The very next day you can return to your usual pace of life, but it is better to limit physical activity and intimacy.
Negative consequences
Prostate puncture is an invasive procedure. Therefore, after it the development of complications cannot be ruled out. If you detect a problem in a timely manner and report it to your doctor, the negative consequences will be minimal. It is necessary to monitor your health and not take spontaneous actions to eliminate the disorder.
Most often, patients complain of discomfort in the area where the manipulations were performed. Usually this symptom goes away on its own. Bleeding may also occur after prostate puncture for 3-5 days.
If the discharge is not abundant and its duration does not exceed the specified period, there is no reason to worry. Otherwise, you will need the help of a doctor. Many men do not pass urine during the first eight hours.
This is a short-term phenomenon that goes away on its own.
Infection is observed only in 2% of cases. The disorder is characterized by fever, pain in the perineal area, and lack of urination. Its main reason in most cases is neglect of prophylactic antibiotics in the postoperative period. Treatment of the infectious process requires complex therapy.
Decoding the results
After the prostate is punctured, tissue samples are sent for histological examination. The interpretation of the results is carried out by the doctor who performed the procedure. Typically, the study contains the following information:
- PIN Detection of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia indicates a high risk of developing cancer. With a low PIN, the appearance of a cancerous tumor is predicted within 5 years.
- The presence of a malignant neoplasm. The accuracy of the result is 80%.
- The presence of a benign neoplasm. In this case, additional or clarifying tests are not required.
The results of histological examination are usually ready within 14 days.
Repeated puncture
The absence of cancer cells in the tissues of the prostate gland during the initial examination does not always indicate the absence of pathology in the organ. Constant monitoring of men's health is important. Therefore, many patients are prescribed a repeat puncture. The reasons for the new study are:
- increase in PSA levels in relation to the parameters of the primary analysis;
- a digital examination reveals neoplasms that raise suspicion among the doctor;
- During an ultrasound examination, changes are observed that were not previously diagnosed.
Repeated ultrasound-guided puncture of the prostate gland is permitted 4-6 months after the initial procedure. During this period, damaged tissues heal completely. Therefore, the risk of complications is reduced to zero. An exception is the detection of malignant tissue. In this case, a repeat procedure is allowed 45 days after the first time.
Conclusion
Prostate puncture is a diagnostic procedure. With its help, you can not only identify malignant elements, but also monitor the treatment being carried out. During the procedure, using special equipment, the doctor collects material.
Then it is sent for histological examination in a laboratory. Based on the results obtained, the preliminary diagnosis is confirmed or refuted, and therapy is selected. This procedure does not exclude the development of complications.
Therefore, preliminary preparation and observation in the postoperative period are required.
Source: https://cureprostate.ru/418952a-punktsiya-predstatelnoy-jelezyi-kak-delayut-podgotovka-sposobyi-provedeniya-protseduryi-vozmojnyie-oslojneniya
Why is a needle biopsy of the prostate gland performed?
Prostate biopsy is one of the most reliable methods for identifying a pathological neoplasm in the prostate.
It detects the disease with a probability close to 98%, even in cases where there are no symptoms. The procedure does not require abdominal intervention and can be performed on an outpatient basis.
The collected material is sent to the laboratory and examined using modern equipment.
The essence of manipulation
This procedure involves taking samples of prostate tissue using a puncture needle and syringe to further examine them for the presence of abnormally developing cells. This analysis allows us to detect the formation of a malignant tumor in the early stages, as well as the rate and nature of cancer progression.
If the puncture results are normal, this means that the structure of the gland cells is not disturbed. If the results showed the presence of cancer cells, then the degree of damage is assessed using the Gleason scale, consisting of the following gradations:
- Group 1 - single tumor cells with nuclei that are not subject to change;
- Group 2 - a small number of tumor cells, collected in clusters; the cell nuclei are still separated from healthy ones by membranes;
- Group 3 - the number of tumor cells is significant; germination into healthy cells has begun;
- Group 4 - tumor cells change and grow into healthy cells everywhere;
- Group 5 - the tumor has turned into many layers of atypical cells that have grown into healthy tissue.
When is a biopsy necessary?
Most often, prostate puncture is prescribed to patients who have consulted a doctor with complaints of prolonged discomfort in the pelvic area, a feeling of tightness and problems with urination.
Similar difficulties are caused by chronic prostatitis, inflammation of the organ as a result of previous illnesses, injuries, surgical interventions or age-related changes.
The pathologically enlarged gland begins to compress the urinary duct of the urethra, as well as put pressure on the bladder.
Symptoms for which you should definitely consult a urologist:
- a feeling of discomfort and pressure, as well as pain in the pelvic area, lower back, groin just below the navel, which occurs during active actions and physical stress. Similar phenomena are usually observed during running and other sports, during sexual intercourse or straining during bowel movements;
- problems with emptying the bladder, inability to start or complete urination, pain, spasms and burning during this action;
- the occurrence of periodic or constant erectile dysfunction, difficulties in satisfactory initiation and completion of sexual intercourse associated with pain and discomfort;
- a general state of malaise, lethargy, drowsiness, signs of hormonal changes in the body, for example, sharp fluctuations in weight, hair loss, etc.;
- previously suffered sexually transmitted infections, as well as inflammation of the urinary organs and surgical interventions in the pelvic area;
- The man is over 60 years old.
All these signs should alert you and become a reason to visit a urologist, andrologist, or consult a general surgeon or therapist for a prostate examination.
The most common and painless examination today is ultrasound. It can show changes in the prostate, such as a tumor. But only a prostate biopsy can determine whether this tumor is benign or malignant.
The doctor prescribes this procedure in two cases: when a lump is detected during palpation of the prostate gland and an increase in PSA (prostate-specific antigen) - a protein substance formed in the prostate, identified through a blood test. PSA levels should remain unchanged throughout a man's life. Exceeding the norm of 2.5 ng/ml after 40 years, 4 ng/ml after 60 years and 4.5 ng/ml after 70 years should cause concern to the doctor and serve as a reason to prescribe a biopsy to the patient.
In addition, the following reasons may be indications for a prostate biopsy:
- detection of echogenic foci during transrectal ultrasound examination of the prostate, which may be sites for the development of a cancerous tumor;
- a previously diagnosed malignant neoplasm, the nature and rate of spread of which must be assessed in order to prescribe appropriate treatment;
- conducting control diagnostics to determine the effectiveness of treatment of an existing cancer tumor for possible adjustment of therapy;
- the need to distinguish benign hyperplasia (adenoma) of the prostate from an oncological neoplasm.
Before performing a prostate puncture, you must undergo a full medical examination, take blood and urine tests, and stop taking all medications, except for vital ones, 7 days before the procedure.
Contraindications
Prostate biopsy, like any organ tissue sampling, is a procedure involving surgery, albeit minimal. It carries the risk of injury and is fraught with subsequent micro- or macro-inflammation. Therefore, it has a number of contraindications:
- general serious condition of the body, severe weakened immunity, caused by various reasons;
- inflammatory disease of the pelvic organs, which accompanies prostatitis or enlarged glands;
- acute infectious disease of bacterial or viral etiology in any part of the body;
- patient age over 75 years;
- disease of the hematopoietic organs, accompanied by poor coagulation, since biopsy is a traumatic action;
- the presence of pathological processes in the rectum and anus that do not allow transrectal analysis. But it is possible to insert the manipulator through the urethra.
Repeated puncture
Sometimes it becomes necessary to perform a second puncture. Such situations include the following conditions:
- During the operation, an insufficient amount of material was allocated for research;
- PSA value exceeds 15%;
- in the blood test there is a constant increase in the level of antigens;
- the ratio of free to total antigens is less than or equal to 10%;
- Any abnormalities in the prostate were identified during an ultrasound examination.
Repeated prostate puncture can be performed no earlier than 3 months after the first attempt. To ensure the reliability of the analysis, samples are taken from a larger number of areas. If precancerous changes in prostate tissue are detected in a patient, it is advisable to carry out the procedure every year in order to track the dynamics of the development of the disease.
Preparing for a biopsy
In order to avoid unpleasant phenomena for the patient and minimize the risk of developing any complications, several basic rules must be followed:
- if a man is taking medications that impair blood clotting, be sure to temporarily stop using them about a week before tissue sampling;
- a few days before the prostate biopsy, the doctor usually prescribes a course of broad-spectrum antibiotics to prevent infection;
- if the analysis is carried out transrectally, then the patient must the day before undergo procedures to cleanse the rectum using an enema and taking special medications that promote the removal of feces. Immediately before the biopsy, preliminary cleaning is also done. This is necessary to eliminate contaminants that interfere with the ultrasound view and reduce the risk of infection;
- On the day of the test, the patient is strictly not recommended to eat.
Methods of carrying out
The method of carrying out the procedure is determined by the doctor based on the individual characteristics of the patient, his age, general health, and test results:
- ischiorectal;
- urethral;
- perineal (transperineal);
- transvesical;
- transrectal.
Prostate biopsy is a painful examination, so it is performed under anesthesia, local or general, depending on the condition and sensitivity of the patient to anesthesia. Pain relief is carried out with special anesthetic gels. Local anesthesia and sedative medications may be used to reduce the patient's anxiety.
The procedure is performed with a special hollow needle. Visually, the syringe looks like a huge paperclip with a needle several centimeters long. There are vacuum devices and needles with a spring.
For greater accuracy, the entire process of collecting material is monitored on the monitor of the ultrasound machine. This allows you to insert a needle into the prostate in precisely specified places and without causing pain to the patient or harm to the gland itself. The needle is inserted to a depth of 1 to 2 cm.
In order for the analysis results to be reliable, material is taken from different parts of the prostate. Depending on the number of samples taken for analysis, the puncture can be:
- sextant - samples are taken from 6 points;
- extended, most often used in medical practice - from 10–13 points;
- saturation, used for repeated biopsy - from 20 or more points.
Transrectal form
The needle is inserted through the anus. Body position - on the right side on the couch, legs pressed to the stomach. The doctor controls the position of the needle with his fingers. A gauze swab is applied to the injection site and glued with a bandage for a day.
Crotch shape
In this case, a specialist approaches the prostate through a transverse incision in the perineal area. The patient is positioned on the couch on his back with his legs wide apart. The puncture and tissue collection are carried out under ultrasound supervision using local anesthesia.
Urethral form
This is a rather painful procedure that causes dizziness or even fainting in some patients, so it is performed using local anesthesia. The needle is inserted into the prostate through the urethra.
Usually the manipulation time takes no more than half an hour.
Recovery after biopsy
Prostate puncture is a complex procedure that requires rehabilitation treatment after its implementation.
To avoid postoperative complications, you must not engage in sports or perform heavy physical work for at least 4 hours, and you must abstain from sexual intercourse and food. Bleeding, slight pain in the surgical area, and a slight increase in temperature are possible for some time.
After a biopsy, to stop the possible development of inflammation in the prostate, doctors recommend taking an antibiotic for at least 5 days.
Possible complications after a biopsy:
- damage to the urethra;
- prolonged bleeding from the anus;
- a significant amount of blood in the urine and stool;
- pain in the rectal area when sitting;
- exacerbation of prostatitis and even gland abscess;
- severe deterioration in the patient’s general condition;
- weakness and fainting;
- development of infectious infection as a result of insufficient cleansing procedures and lack of necessary antibacterial therapy;
- In some cases, an allergic reaction to the anesthetic drug is possible.
If at least one of these signs appears, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Prostate biopsy. Consequences
Prostate puncture is a very informative method for diagnosing prostate cancer, so it should not be avoided, but, on the contrary, used as early as possible in order to begin treatment in a timely manner and increase the chances of recovery.
Source: https://MedExpert.guru/prostata/biopsiya-predstatelnoj-zhelezy.html
What is a prostate biopsy and how is a prostate puncture taken?
Oncological diseases pose a threat to the lives of men. Therefore, it is very important to identify the initial stage of the disease in time and carry out appropriate treatment.
In the article you will learn about prostate biopsy, what it is, how the procedure is performed and what the consequences of prostate biopsy are.
Hide content
Prostate: biopsy
What is a prostate biopsy? This is the most common way to detect tissue changes at the cellular level.
This procedure is the most reliable method of research, which with 100% probability allows you to judge the cellular composition of a particular formation.
Using a special prostate biopsy needle, the doctor takes living tissue from the patient, which is then examined under a microscope.
The method will accurately confirm whether the patient has cancer.
A biopsy is prescribed if any tissue changes were detected during the study or if there was a high PSA value during a blood test.
The patient must understand the need for this procedure. Delayed examination may have dangerous health consequences in the future.
To avoid infection, a course of antibiotics is prescribed in advance.
Does a prostate biopsy hurt? The procedure for taking prostate tissue is quite painful.
Therefore, before the biopsy begins, the patient is given local anesthesia. Most often, a special gel with lidocaine is administered.
Sometimes, in agreement with the doctor, the patient drinks a painkiller for greater effect.
How is a prostate biopsy done? There are several methods for performing a biopsy:
- transrectal;
- transureal;
- transperineal.
Transrectal prostate biopsy is performed in the following steps:
- It is necessary to lie with your legs pulled up to your chest on your left side or stand on your elbows and knees.
- To relieve pain, the doctor injects lidocaine gel into the prostate through the anus.
- Allow 10 minutes for the drug to dissolve properly and begin to act.
- Next, a sensor is inserted, which has attachments and disposable needles for prostate biopsy.
- Using a sensor, areas of the prostate are examined.
- To collect living tissue, the doctor immediately marks from 6 to 18 places in the prostate, not only from the diseased area, but also from other areas of healthy tissue according to a special scheme.
- How is prostate puncture performed? The doctor performs a puncture of the prostate gland using a biopsy gun, which shoots a hollow needle into the tissue, removing a column about 17 mm long from each targeted point.
Transperial
How is a prostate biopsy taken? Due to the complexity of the procedure, this method is not very popular.
- The man lies down in the fetal position and the doctor injects him with an anesthetic injection.
- The doctor treats the area between the testicles and the rectal sphincter with an antiseptic drug.
- Next, an incision is made in this area and an ultrasound probe or finger is inserted. After examining the collection site, a biopsy needle is inserted.
- By moving the needle over the tumor using special manipulations, they take the piece of tissue required for the sample.
- The nodule is fixed using a finger located in the anus.
- After the cells are collected, the wound is treated.
- The procedure takes about 30 minutes.
Transurethral
How is a prostate biopsy (transurethal) performed?
- When collecting using this method, the patient can be in different positions. In the more common method, the patient is placed on his back and his legs are placed on supports. He can also lie in the fetal position or be in a knee-elbow position.
- The doctor applies anesthesia around the perimeter of the prostate.
- To accurately place the needle into the prostate, a cystoscope is used, which is inserted into the rectum. It has a flexible probe, and at its end there is a small video camera, a light bulb and a device for collecting tissue in the form of a cutting loop.
- The collection takes place instantly. In this case, from 6 to 12 tissue samples are taken.
- In some cases, the urologist uses a finger to palpate the prostate.
- The entire procedure lasts approximately 30 minutes.
Cells extracted from the prostate are sent to the laboratory for examination as soon as possible.
The procedure is prohibited if:
- infectious diseases;
- if complications of hemorrhoids are identified;
- in case of serious condition of the patient;
- in the presence of an inflammatory process in the large intestine;
- in acute form of prostatitis;
- with blood incoagulability.
Preparation
How to prepare for a prostate biopsy? Regardless of the type of biopsy, the patient should prepare for the procedure in accordance with the precise recommendations of the doctor. Having determined and examined the patient’s condition, the urologist prescribes measures to prepare for a prostate biopsy.
Preparing for a prostate biopsy:
- In the presence of inflammatory processes and infections, the patient is recommended to take a course of antibiotics.
- A week before the biopsy, you must stop taking medications that affect blood clotting.
- 3 days before the procedure you should not take anti-inflammatory drugs.
- The day before the procedure, the patient does a cleansing enema in the evening, and then again in the morning.
- It is necessary to avoid any physical activity the day before the biopsy.
- The biopsy is performed strictly on an empty stomach.
- The patient changes into special clothes.
- If the transrectal method is performed, the entire tissue sampling session will be carried out under continuous ultrasound control.
- It is mandatory to treat the needle insertion site with an antiseptic.
- Depending on the method chosen, a prostate biopsy may be performed under general anesthesia.
- If the patient is excited or very nervous, sedatives are prescribed.
IMPORTANT: Only a doctor determines the need and frequency of a prostate biopsy and decides which method is most appropriate.
After 10 days, the results of the prostate biopsy will be ready. The degree of presence of cancer cells is determined by Gleason scores. They are assessed by a pathologist, who makes the necessary conclusions.
Biopsy indicators for prostate cancer:
- If the indicator is 2-4 units, then the risk of developing a tumor is insignificant. Cells taken for prostate biopsy analysis are similar in structure to healthy ones.
- If the results of the prostate biopsy analysis are from 5 units to 7, we can talk about an average risk of cancer.
- A reading of 8 to 10 units indicates the presence of aggressive cancer cells.
If there have been cases of prostate cancer in your family tree, it is important to consult a urologist and take PSA tests from the age of 45.
Code of Conduct
A biopsy is equivalent to minimal surgery. Therefore, it is very important to follow the necessary recommendations after the procedure.
- Antibiotics may be prescribed for 6-7 days, as there is a risk of infection during manipulation.
- During the week, you should exclude fatty and spicy foods from the menu.
- You should not drink alcoholic beverages for 10-14 days.
- It is recommended to drink 2 to 4 liters of liquid during the day.
- If after the biopsy a tampon was inserted into the rectum, you can remove it yourself in the evening.
- For the next day, you can lead a normal lifestyle: go to work, do morning exercises, take a shower, go for walks, and preferably stick to a diet after a prostate biopsy.
- You should not have sex for a week after a prostate biopsy.
IMPORTANT: It is necessary to strictly follow all the urologist’s prescriptions.
Consequences of prostate biopsy:
- The appearance of discomfort in the rectum.
This is a fairly common complaint that will go away on its own over time. If the discomfort is quite severe, the doctor may prescribe therapy with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Blood mixed.
In 74% of cases after a prostate biopsy, men have blood in their urine, 14% have blood coming out of the rectum, and 1% have blood in their semen.
If blood is released for 3-5 days, this is normal. It goes away on its own, but if there is prolonged discharge, you need to contact a urologist.
In such cases, bed rest, therapy selected by a specialist, and drinking plenty of fluids are indicated.
- Presence of infection.
Approximately 2% of patients experience infection of the prostate and genitourinary system. The doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics. Pain in the perineum, fever, dysuria or polyuria are also observed. If the patient's condition persists for a long time or worsens over time, hospitalization is necessary.
Urinary retention when urinating
This is a temporary phenomenon that goes away on its own without medical intervention.
If after a prostate biopsy there is blood in the urine or stool for more than 8 hours, if there is no urination during this time, if the temperature persists for a long time, you must urgently seek medical help.
Conclusion
Now you know how a prostate biopsy is performed. Many men are afraid to have a biopsy because of the pain. But it is this research method that makes it possible to detect the presence of cancer cells and begin timely treatment.
Therefore, it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations and, if in any doubt, undergo this type of examination.
Source: https://samec.guru/zabolevaniya/onkologiya/rak-predstatelnoj-zhelezy/diagnostika/biopsiya.html
How to do prostate puncture, it hurts
Few people know what prostate puncture is or how this procedure is performed.
The prostate is one of the important organs of a man, which is no larger than the size of a nut, and in order to diagnose diseases, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination.
Diagnostic methods are ultrasound examination and puncture, which should not be confused with a biopsy of prostate tissue.
What it is
- cell composition;
- state of the epithelium;
- condition of the prostatic glands.
This procedure can be performed under general anesthesia or anesthesia. If the procedure is performed under anesthesia, it is recommended to refrain from eating and drinking 6 hours before the procedure. General anesthesia is necessary for patients with high excitability. It is carried out under ultrasound control in order to avoid complications. In some cases, the doctor prescribes antibiotics to avoid complications. But you should not take any medications on your own.
Fact! When receiving material for examination, the patient will experience short-term pain. If a man is very sensitive to pain, then before the procedure, you can take sedatives.
Most often, prostate puncture is prescribed if there is a suspicion of cancer after other examinations. This diagnostic method is relevant if the PSA level is more than 4 ng/ml.
If a severe course of the disease is observed, then puncture of the gland cannot be performed. The procedure is also contraindicated in case of inflammation of the rectum and if residual feces are detected in it. Other contraindications include the following:
- haemorrhoids;
- acute prostatitis;
- poor blood clotting;
- inflammatory processes in the intestines;
- diseases of the genitourinary system.
When is an examination indicated?
Prostate puncture is prescribed for various diseases of the genital organs. Indications for the examination include the following:
- inflammatory processes that occur constantly and severely;
- cancer;
- determination of cancer resistance to hubbub;
- determining the extent of cancer.
In some cases, re-examination of the prostate gland is required, since an unchanged part of the prostate may enter the needle, which complicates the results of the study. A secondary puncture should be performed in the following cases:
- when palpating formations that can be felt during a digital examination;
- if PSA increases after the first study:
- when detecting changes in prostate tissue that can be noticed after exposure to ultrasound.
It is recommended to repeat the procedure no earlier than three months later. In order to obtain reliable data, it is necessary to take material from a larger area of the prostate.
Through such an examination, you can not only diagnose cancer, but also find out the following indicators:
- size;
- progression stage;
- effective treatment.
As a rule, the doctor gives a referral for a puncture if the PSA value is elevated, which most often indicates cancer at an early stage.
Analysis methods
There are several ways to take an analysis, which you can choose based on the patient’s age, tests obtained, general health and individual characteristics of the patient. The most common of them are the following:
- transrectal;
- urethral;
- transvesical;
- perineal (transperineal);
- ischiorectal.
To remove prostate tissue, a special needle is required, the inside of which is empty. Its length is several centimeters, and the diameter of the syringe itself is similar to a large paper clip.
In some cases, a needle with a spring or a device with a vacuum is used. Depending on the method of sampling, preparation is necessary in some cases.
For example, with the transrectal method, it is necessary to perform a cleansing enema in the evening before the procedure and in the morning on the day of the procedure.
Most often, a transrectal procedure is performed to diagnose diseases. The patient lies on the right side on the couch and presses his legs to his stomach. The doctor inserts a needle through the anus into the prostate.
To avoid discomfort, it is recommended to use pain-relieving gels.
The placement of the needle is controlled with a finger and several punctures are performed. After the procedure, a gauze pad is left on for 24 hours.
For the perineal type of procedure, it is necessary to make a transverse incision of no more than 3 cm. Having reached the prostate gland, a puncture is made, prostate tissue is taken for analysis and the instrument is removed. To do this, the patient must lie on his back and spread his legs. This method of puncture biopsy of the prostate is painful and the examination is carried out under anesthesia.
Material for analysis is collected from the entire prostate. To do this, it is enough to take material from 6 points of the prostate gland. In some cases, up to 10 of these points may be required.
Thanks to such an accurate study, it is possible to diagnose cancer at an early stage and you can see its location.
Some men may experience dizziness or loss of consciousness during the test.
Regardless of the method of collecting gland tissue, you need to donate blood and urine for analysis. The procedure lasts no more than half an hour, the resulting tissue is sent to the laboratory for examination, and the result can be obtained in a week.
Most often, a week before the procedure you need to stop taking any medications.
But if without treatment the patient’s life is in danger, then he can continue health therapy, but the recovery period will be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
Recovery after puncture
Prostate puncture is a serious procedure that requires special preparation. After it is carried out, it is recommended to refrain from physical exercise and sexual intercourse for 4 hours, so as not to provoke complications. You are also not allowed to eat for several hours after the procedure.
If the transrectal method was chosen, bleeding, fever and soreness in the rectal area may be observed for some time.
But if the puncture procedure was performed incorrectly or carelessly, complications may follow. The most common ones include:
- prolonged bleeding from the anus;
- prostatitis in acute form;
- painful sensations in the anus;
- streaks of blood in semen or urine;
- damage to the urethra;
- gland abscess.
After detecting one of these complications, you need to consult a doctor. In some cases, an allergy to anesthesia occurs. In order to avoid this, before the procedure you need to tell the doctor about the presence of an allergic reaction to medications.
It is worth noting that prostate puncture is one of the safe and effective procedures for humans. But in some cases complications and contraindications may appear.
Source: http://proprostatu.ru/diagnostika/punktsiya-predstatelnoj-zhelezy-kak-delayut.html
Puncture of the prostate gland: does it need to be done under ultrasound control and what the consequences may be?
The prostate is an important organ in the male body, but it is small in size. Due to this, a comprehensive examination is required to study her condition. For these purposes, puncture is often used.
A similar procedure is a method of studying organ tissue taken for research, which makes it possible to assess its current condition, as well as the success of the treatment. Let us consider in detail: what prostate puncture is, how the procedure is done, and what complications are possible.
Indications
Often, puncture of the prostate gland in men is performed on patients who indicate at a doctor's appointment the presence of pain, discomfort in the pelvic area, as well as feelings of tightness or difficulty urinating.
This is due to the fact that with a pathological enlargement of the gland, the urinary duct is compressed, and pressure is also exerted on the bladder itself. Symptoms for which you should contact a urologist:
- The appearance of discomfort, as well as a feeling of pressure or pain in the pelvic area, which appears after physical activity. Such manifestations often occur while running.
- Difficulty emptying the bladder. It manifests itself in the inability to start or finish urination, which is accompanied by pain, spasms or burning.
- The appearance of temporary or permanent erectile dysfunction associated with discomfort or pain.
- The presence of general malaise, drowsiness, sudden changes in weight, hair loss, as well as obvious signs of hormonal imbalance in the body.
- Previous presence of sexually transmitted diseases, or an inflammatory process that occurs due to surgical intervention in this part of the body.
The listed symptoms are indications for which a puncture is taken.
Important! The cause of discomfort may be the development of a tumor in the prostate gland.
It is for its study that a similar diagnostic method is prescribed. During the examination, the doctor can also identify pathology either by palpation of the pelvic area or by increased PSA values in a blood test.
The latter are protein substances produced by the organ. Other reasons for prescribing the study are:
- detection of echogenic foci by ultrasound, the presence of which may indicate the occurrence of prostate adenoma;
- the need to diagnose the identified formation in order to determine its nature and growth rate;
- carrying out control diagnostics to identify the effectiveness of ongoing treatment and its correction;
- the need to determine what kind of tumor it is: benign or malignant.
Before puncture of the prostate gland in men, additional examination is prescribed in the form of blood and urine tests.
Preparation
To prevent complications, as well as minimize the risk of deterioration of the condition, preparation for puncture is carried out:
- Before the procedure, it is important to avoid taking medications that thin the blood, otherwise it will be difficult for doctors to stop the bleeding.
- When carrying out the transrectal option, the rectum is first washed, and medications are taken to remove feces.
- Immediately before the study, local bowel cleansing is done to remove all contaminants that interfere with ultrasound monitoring and reduce the possibility of infection.
- You cannot eat food on the day of the procedure.
Procedure options
How a puncture of the male prostate gland is taken depends on the characteristics of the patient’s body, his age, as well as the results of previous tests.
The procedure itself is quite painful, which is why prostate puncture is performed under anesthesia. Its type is determined based on the patient's current condition, as well as his sensitivity to anesthesia.
Often, special anesthetic gels are used for this. Local anesthesia is often used and sedatives are given to reduce nervous tension in a person before surgery. It is not recommended for patients with unstable mental health to look at thematic photos on the eve of the procedure.
The procedure itself is carried out with a hollow needle; the syringe is similar in appearance to a large paper clip, having a needle several centimeters long. There are vacuum options, as well as needles with a spring. To increase the accuracy of the manipulations, a puncture of the prostate gland is performed under ultrasound guidance.
Due to this, the needle is inserted exactly in the required places, which reduces pain, as well as damage to the gland itself. The depth of insertion is several centimeters, and for a more accurate result, material is collected from several parts of the organ.
Based on the number of samples, the procedure is divided into:
- sextant, when no more than 6 fences are taken;
- extended, if the number of sampling points is up to 13;
- saturation, in which sampling is carried out from more than 20 places on the organ.
There are three methods used in practice today:
- Transrectal form, when the needle is inserted into the prostate through the anus. The patient's body is on the right side, and the legs should be pressed against the stomach. The angle of inclination and movement of the game is adjusted by the doctor with his fingers. After the procedure, a gauze swab is placed at the puncture site and a bandage is glued.
- An intermediate form, in which the specialist gets to the organ through an incision in the perineum. To do this, the patient is placed on his back and his legs are spread apart. A puncture of the prostate gland is performed under ultrasound guidance and local anesthesia.
- Urethral form. The most painful method, sometimes leading to dizziness and fainting, which is why it is used with local anesthesia. The needle is inserted into the organ through the urethra.
The duration of such procedures takes no more than 30 minutes.
Stages of implementation
The most common method is transrective, and is carried out as follows:
- The patient is given a local anesthetic (usually lidocaine) or general anesthesia.
- As soon as the anesthesia begins to take effect, under ultrasound guidance, a doctor inserts a disposable needle into the prostate by puncturing the walls of the rectum. A puncture of the adenoma is performed (tissue collection of the required amount from different parts of the organ).
- Upon completion of the study, the needle is removed, a gauze swab is applied to the puncture site to stop the bleeding, and a patch is glued.
- Then the patient is placed in the recovery room, where he is monitored. If his condition remains stable, he is discharged.
- The material is sent to the laboratory, where it is studied, and the results are sent to the attending physician.
When prostate puncture is performed under the control of an ultrasound machine, it is usually tolerated very well by patients, and only in rare cases is mild discomfort possible.
Complications
Possible complications during prostate puncture:
- discomfort at the needle insertion site;
- disturbance of the urination process;
- blood begins to appear in the urine;
- blood is released with the family fluid;
- prolonged bleeding occurs in the puncture area;
- inflammation of the prostate gland begins.
It is normal for bleeding to occur within 2-3 days after puncture of the prostate gland. This is considered a pathology only when the duration of this exceeds the specified time.
There may be slight discomfort in the area of the puncture or incision. But the use of painkillers must be agreed with the attending physician.
If you have an elevated temperature, fever or chills, you need to go to the hospital immediately.
Decoding the results
Tissue samples taken at punctures are sent for cytological and histological examination. It usually takes up to 14 days to receive a report from the laboratory. The interpretation of the results is carried out directly by the doctor who performed the procedure. Such studies can provide the following information:
- PIN is the detection of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, which indicates a high probability of oncology. With a low PIN, the appearance of cancer is predicted within 5 years.
- Detection of malignant formation. To clarify them, additional research will be required using the Gleason score, which determines the level of cancer development, as well as the prognosis of its treatment. The accuracy of the result is 80%.
- Detection of a benign neoplasm, the identification of which does not require additional clarifying tests or repeated samples. Moreover, its elimination may not be required in the case when it does not cause the patient discomfort, pain, or does not lead to a deterioration in the functioning of the gland.
The duration of the study of the material depends on the number of tissue samples taken for this purpose, which will be simultaneously studied. Results often reach your doctor within 1-2 weeks. This is due to the lack of priority for histological and cytological examination.
A repeat biopsy is allowed only after 4-6 months. During this time, the damaged tissues heal completely, so the likelihood of complications after this procedure is minimized. Exceptions are situations if a malignant tumor is detected, when repeated tissue sampling can be carried out 45 days after the previous time.
Source: https://prostatu.guru/diagnostika/punktsiya-predstatelnoj-zhelezy-kak-ee-delayut.html