Ovarian apoplexy (hematoma, heart attack) is a sudden rupture of organ tissue. It is considered an acute condition in which the patient requires hospitalization. It varies in the degree of pain and the amount of bleeding. In some cases, surgery is required.
Description of the disease
With apoplexy, or rupture of the ovary, hemorrhage occurs in the peritoneum - this poses a danger to the patient. This pathology can occur on any day of the menstrual cycle, but most likely during the period of ovulation and immediately after it. This is caused by the dominant follicle reaching its maximum size or the maturation of the corpus luteum after the release of the egg.
Ovarian hematoma most often occurs during the reproductive period, less often before the onset of menopause or before the onset of menstruation in adolescence. Diagnosed in 3% of cases of internal bleeding in women.
What can cause a woman's ovary to burst?
The predisposing factor as a result of which ovarian infarction occurs in the second half of the cycle is associated with the peculiarity of the blood supply to the genital organs. During and after ovulation, the permeability of the vessels intertwining the dominant follicle and the corpus luteum changes - with excessive filling as a result of increased blood flow, the integrity of their walls is disrupted.
Apoplexy can develop as a result of a sharp increase in luteinizing hormone, which stimulates the release of the egg from the follicle.
Internal causes of ovarian rupture:
- an increase in the number of blood vessels in the tissues of the corpus luteum;
- disruption of the ovulation process - damage to the walls of the follicle when the egg is released simultaneously with the ovarian tissue;
- pathological location of the uterus;
- the course of the inflammatory process of the genital organs;
- the appearance of cysts on the ovary or corpus luteum;
- disruption of the pelvic vessels or the entire body as a whole;
- low blood clotting;
- hormonal imbalance;
- rapid growth of tumors of the uterus or neighboring organs;
- adhesions in the pelvis.
External reasons:
- physical overexertion, which contributes to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure - excessive stress, active sexual intercourse;
- inaccurate gynecological examination;
- frequent douching or improper use;
- abdominal trauma;
- excess weight, which causes compression of blood vessels;
- taking anticoagulants.
Typically, several factors contribute simultaneously to ovarian hematoma. Exposure to multiple causes is more likely to result in heavy bleeding or increased pain.
Signs of pathology
Symptoms of ovarian apoplexy appear sharply and may be present temporarily:
- pain in the lower abdomen - are strong, sometimes unbearable, appear suddenly, but the day before the rupture the woman sometimes feels pulling and pressing pain in the ovary area;
- drop in blood pressure - indicators decrease significantly with heavy blood loss;
- rapid pulse;
- general weakness;
- frequent urination - more than 10 times a day.
Changes in the location of female reproductive organs
Detection of long-standing ovarian infarction is determined after the patient complains of irregular menstrual cycles or during a routine medical examination. Apoplexy can go unnoticed with a small hemorrhage that does not cause complications.
With heavy blood loss in women, the following symptoms of ovarian rupture are present:
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- cold sweat;
- fainting state;
- pale skin and mucous membranes;
- dry tongue;
- swollen and tense belly.
When examined on a gynecological chair and palpated through the abdominal wall, the patient feels pain in the left or right lower abdomen.
When examining with a vaginal speculum, the doctor determines the condition of the genital organs - the affected ovary enlarges during apoplexy, the size of the uterus remains within normal limits.
It is quite difficult to detect pathology on an ultrasound - the device only shows fluid with blood clots located in the abdominal cavity.
Forms of the disease
Classification of apoplexy
The types of disease are determined by the nature of the manifestations:
- Painful apoplexy. Absence of hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity against the background of intense pain.
- Anemic or hemorrhagic. Increasing blood loss in the peritoneum with mild pain.
- Mixed. There are signs of the two previous types due to rupture of tissues, blood vessels and capillaries.
The safest type is pain apoplexy. This is explained by the small number of complications of the body and appendage after a hematoma without hemorrhage and the possibility of treating the ovary non-surgically.
Types of hemorrhages due to ovarian rupture
The intensity of bleeding varies from mild to severe. The forms of the disease are determined by the volume of hemorrhage:
- Mild (grade I) – the amount of blood lost does not exceed 150 ml.
- Moderate (II degree) – blood loss can reach half a liter.
- Severe (III degree) – more than 500 ml of blood lost.
The most dangerous to the patient’s health are hemorrhagic and mixed apoplexy with III degree of blood loss - they contribute to the development of severe anemia.
Diagnostic measures
Before conducting laboratory and instrumental examinations, the doctor must collect the patient’s medical history and conduct a physical examination. To do this you need to do the following:
- interviewing the patient to determine the current phase of the menstrual cycle, the nature of menstruation, possible concomitant diseases, and the type of contraceptives used;
- exclusion of pregnancy – uterine and ectopic;
- gynecological examination - determination of the condition of the mucous membranes, uterus and ovary, the rupture of which caused pain;
- palpation of the abdomen - differentiation of pathology from diseases of the pelvic organs and ectopic pregnancy.
Characteristic signs of ovarian endometriosis and ways of treating it
After the initial examination, you must undergo the following types of tests:
- puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix - when the appendage ruptures, light blood is released;
- general blood test - determination of hemoglobin level and leukocyte concentration;
- blood test for hCG - allows you to detect pregnancy;
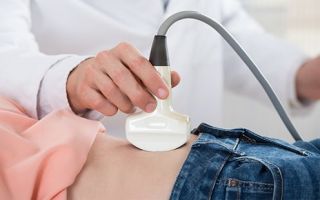
- Pelvic ultrasound - shows the presence of fluid in the abdominal space, an increase in the size of the ovary;
- laparoscopy – examination of the abdominal cavity and treatment of pathology at the same time.
Laparoscopy is considered the most informative diagnostic method and is performed in the absence of results from other studies or in the serious condition of the patient.
Treatment methods
If there is a suspicion that a woman’s ovary has burst, the patient is immediately taken to the hospital for further diagnosis and treatment. If there is little hemorrhage and no severe pain, drug therapy is prescribed, which includes taking the following drugs:
- antispasmodics – eliminate pain;
- vitamins – normalize a woman’s well-being, increase immunity;
- hemostatic drugs;
- vaginal suppositories – eliminate inflammation and pain.
During treatment, a patient with ovarian apoplexy should observe strict bed rest. To relieve pain, it is allowed to apply ice to the aching area.
In more severe cases, surgery is prescribed. This is also necessary if a woman wants to preserve reproductive function. The main indications for surgery are a strong drop in hemoglobin levels, further deterioration of the condition with signs of internal hemorrhage.
Types of surgical intervention for ovarian apoplexy:
- Laparoscopy. It is carried out using surgical instruments and a laparoscope, at the end of which a video camera is installed. It is a minimally invasive type of intervention and there are no scars after it. Recovery of the body occurs much faster than after abdominal surgery. In case of apoplexy, using this method, damaged tissue of the ovary and corpus luteum is sutured, and bleeding is stopped. Removal of an organ rarely occurs - it is only necessary if it is complicated by other diseases, torsion of the tubes or appendage.
- Laparotomy. Abdominal surgery is performed when it is not possible to stop bleeding during laparoscopy. During this procedure, the accumulation of blood is removed and the tissues of the organ are sutured.
For a speedy recovery after surgery, the patient is recommended to follow a diet consisting of liquid light soups, crackers, boiled vegetables, jelly and fruit drinks.
Recovery after surgery
The reason for the decrease in ovarian follicular reserve
Physical activity after treatment
Experts recommend avoiding physical activity, limiting any sports activities and giving up sexual activity for 1-2 months. This time is necessary for complete healing of the ovaries and restoration of the body. It is forbidden to lift weights and, at first, to engage in any physical labor. It is best to stay in bed for a few days immediately after treatment.
Apoplexy and pregnancy
Possible complications and consequences
The prognosis after treatment is most often favorable. However, the occurrence of complications cannot be ruled out - they can be caused by incorrect selection of therapy or individual characteristics of the body.
The most common consequences of any type of ovarian rupture are:
- adhesive process - its formation is possible after surgery;
- infertility – develops due to the formation of adhesions, hormonal imbalance and prolonged inflammation;
- relapse of apoplexy - occurs due to adnexitis or failure of endocrine organs;
- ectopic pregnancy - the chances of pathology increase in the absence of one ovary, the presence of adhesions, bending and torsion of the fallopian tubes.
Preventive measures
Compliance with the following rules reduces the likelihood of ovarian apoplexy:
- limiting physical activity and active sexual intercourse during ovulation;
- prevention of inflammation of the genital organs;
- control of hormonal levels;
- regular checks of the condition of blood vessels;
- visiting a gynecologist every six months.
Advice: if you have previous ovarian ruptures, you should regularly undergo not only a doctor’s examination, but also take all the necessary tests.
Taking these rules into account helps maintain women's health and prevents the development of many gynecological diseases.
Source: https://TvoiYaichniki.ru/narusheniya/apopleksiya
Ovarian rupture: causes, consequences, treatment
Ovarian rupture is a violation of the integrity of the organ, which is accompanied by the release of blood into the abdominal cavity and severe pain. It usually occurs during ovulation or at the stage of formation of the corpus luteum. The disease is not very common, it occurs at a relatively young age, in women under 35 years of age, and occurs extremely rarely at older ages.
Causes and symptoms
During ovulation in women, a follicle with an egg matures on the ovary and the corpus luteum is formed. The unfertilized cell “breaks out” from the follicle, ovulation occurs, then menstruation occurs.
With normal functioning of the blood vessels, this process occurs almost painlessly and is not accompanied by any pathologies.
However, if there is excessive pressure on the blood vessels, their functioning malfunctions and they are easily damaged.
Damaged vessels first form a hematoma on the ovary, where blood flows. Then, when the pressure becomes excessive, it ruptures and releases blood into the abdominal cavity. This situation poses a great danger to the patient’s life and requires emergency hospitalization and surgical intervention.
There may be several causes of ovarian rupture (apoplexy):
- Excessive physical activity, including those associated with lifting weights, jumping, and horse riding.
- Injuries, falls from heights.
- Hormonal imbalance, in which the production of luteinizing hormone is disrupted.
- A bleeding disorder in women caused by certain endocrine diseases or taking anticoagulants.
- Inflammatory diseases of the uterus, its appendages and ovaries, such as adnexitis, salpingitis, etc.
- Varicose veins in the pelvic-abdominal region and other vascular pathologies.
- Anatomically incorrect position of the uterus and its appendages (in some cases, a hereditary predisposition).
- An adhesive process in the pelvis, which was a consequence of infectious and inflammatory diseases and surgical interventions, including abortions.
- Pressure on the ovary caused by a cyst, uterine fibroids or other neoplasms.
- Too intense sexual intercourse, especially in the second half of the cycle.
- The presence of nervous disorders, excessive stress, which lead to hormonal imbalance and, as a consequence, disruption of the ovulatory process.
Unfortunately, there are often cases when the exact cause of ovarian rupture cannot be identified, since the disorder can be caused by a combination of factors, and in some cases it can even occur during sleep.
The symptoms of the disease are pronounced, since apoplexy is characterized by an acute form. Hidden ruptures, accompanied by minor hemorrhages and the absence of pain symptoms, are extremely rare.
During a rupture, a sharp pain occurs in the lower abdomen, on the side where the ovary burst. Due to the spread of internal bleeding, the patient may feel weak, dizzy, and sometimes lose consciousness.
Most often, the rupture occurs in the right ovary. This is due to the number of blood vessels located in it - there are more of them in the right one than in the left one.
Therefore, the disease is often confused with appendicitis, since the appendix is also localized on the right side. Also, rupture can be confused with an ectopic pregnancy and some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
However, qualified diagnostics will easily identify the cause of pain and differentiate between diseases.
Diagnostics
If acute pain occurs in the ovarian area, you should not hesitate. It is necessary to contact a medical facility or call an ambulance as soon as possible.
Diagnosis of the disease begins with an analysis of symptoms and palpation. Patients complain of severe pain in the lower abdomen, dizziness, and nausea. With internal bleeding, the pressure usually drops, the pulse quickens, which is why the skin becomes pale.
Next, a hardware examination is performed - ultrasound. An ultrasound sensor detects the presence of fluid (blood) in the abdominal cavity. In some cases, with mild symptoms, diagnostic laparoscopy is performed - examination of the abdominal cavity from the inside through a puncture in the abdomen.
Treatment methods
After laparoscopy and diagnosis, a treatment methodology is selected. Independent measures in the form of uncontrolled use of painkillers are unacceptable. They may give you a false sense of well-being, but will not stop internal bleeding.
Statistics show that a burst ovary in women must be treated surgically. Conservative treatment can be used, but does not restore tissue completely and often leads to complications.
Thus, the lack of surgical intervention for a rupture in most cases causes the development of extensive adhesions, infertility and possible relapse of the disease.
Therefore, drug therapy should be carried out as a preparatory measure for surgery.
So, the following medications are used:
- drugs that increase the level of hemoglobin in the blood;
- antispasmodics to eliminate vasospasm and reduce pain;
- means to stop bleeding, etc.
Direct surgical intervention involves stopping bleeding, completely removing blood clots and restoring the integrity of the tissue of the damaged ovary.
Bleeding is stopped by coagulation (cauterization) of the rupture site or stitching of the damaged vessel. The tissue is then stitched together in such a way as to preserve the functions of the ovary as much as possible. Complete removal of the organ is performed only in cases where there are other pathologies requiring removal, as well as in the case of extensive damage to the ovary.
A modern method of eliminating pathology is laparoscopy, which is performed through a small puncture in the abdomen. This is not only a method of diagnostic research, but also an opportunity to perform a surgical operation with minimal consequences for the female reproductive system.
Recovery
Rehabilitation after laparoscopy can be divided into an early recovery period (up to two weeks) and a late recovery period (up to three months). On the first day after surgery, the patient is prohibited from excessive movements, and it is not advisable to get out of bed. On the second and subsequent days, on the contrary, it is recommended to walk to avoid congestion in the pelvic organs and possible swelling.
In the early rehabilitation period, it is necessary to follow a special diet. The fact is that the female internal genital organs and the gastrointestinal tract are inextricably linked, so immediately after the operation there may be disturbances in its functioning (constipation, diarrhea, stomach discomfort). The diet should be aimed at eliminating these disorders and facilitating the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. D
For consumption, light vegetable soups or broths, steamed cutlets from lean lean meat (chicken, turkey), mashed potatoes, stewed vegetables, etc. are recommended. It is also necessary to consume a sufficient amount of liquid in the form of plain water or tea. It is advisable to avoid coffee and sugary drinks in the first days after surgery.
The patient spends several days in a hospital setting under the supervision of doctors and monitoring her condition. This is necessary in order to promptly notice possible complications after laparoscopy and eliminate them. Postoperative complications include:
- the presence of an inflammatory process;
- increased body temperature;
- rotting of puncture sites, etc.
In the early surgical period, patients may feel pain in the abdomen that is not associated with the presence of inflammation. These symptoms are a natural reaction of the body to surgery and do not require serious therapy other than taking painkillers in the form of injections and tablets.
A few days after laparoscopy, the patient is discharged, and further rehabilitation is carried out on an outpatient basis, but under the regular supervision of the attending physician.
Sports activities are prohibited for 4-6 weeks after surgery. Also during this period it is forbidden to be sexually active.
You cannot lift weights, touch laparoscopic sutures, or visit baths, saunas, or swimming pools. Doctors do not recommend hot baths; in general, it is not advisable to get puncture sites too wet.
You can only observe partial hygienic procedures with minimal moisture on the seams (at least until they are completely healed).
In the late postoperative period, doctors recommend leisurely walking and following a special diet, which involves avoiding heavy fatty and fried foods, foods containing large amounts of sugar and harmful additives, as well as spices.
After laparoscopy, women may have scanty, bloody discharge from the genital tract. There is no need to be afraid of this, as this is a normal phenomenon. If the discharge becomes profuse, there are blood clots in it, or there is pain, you should consult a doctor.
Pregnancy after apoplexy
Difficulties with conception can arise only if an extensive adhesive process develops against the background of untimely treatment, inflammatory processes, or if adhesions were present before the integrity of the organ was damaged. However, this is not a death sentence; adhesions can be eliminated with the help of medications or, again, laparoscopy.
The main thing is to follow all the doctor’s recommendations and pregnancy will not take long.
Consequences of ovarian apoplexy
The consequences of an ovarian rupture can be divided into early and late.
The first include:
- Hemorrhagic shock is the most dangerous complication, in which there is extensive blood loss, threatening not only the health, but also the life of the patient.
- If the rupture occurs during pregnancy, the situation can lead to miscarriage.
- Already mentioned adhesions that lead to problems with conception and infertility.
- Ectopic pregnancy, which is a consequence of adhesions leading to obstruction of the fallopian tubes (uterine appendages). On the way to the uterus, the fertilized egg encounters an obstacle in the form of adhesions, and the pregnancy begins to develop in the tube. If this process is not stopped in a timely manner, a pipe rupture may occur, which is a threat to the patient’s life.
- Relapse of the disease. Unfortunately, this is a fairly common occurrence, especially if the cause of the primary case was congenital vascular or anatomical pathology of the pelvic organs.
Prevention
Prevention of ovarian rupture and prevention of its recurrence is based on restoring reproductive functions, preventing the development of adhesions, as well as ensuring the correct functioning of the damaged organ.
A course of preventive measures may include:
- physiotherapeutic procedures to improve metabolic processes in the pelvic organs, as well as accelerate the regeneration of damaged ovarian tissue;
- correction of hormonal levels if the root cause of the disease is hormonal imbalance;
- treatment of concomitant gynecological pathologies;
- refusal from sports that are characterized by excessive stress on the abdominal area and a high risk of injury.
Also, until complete recovery is complete, you must refrain from possible pregnancy and use contraception.
Ovarian rupture is a rather dangerous disease. It requires timely diagnosis and emergency medical care. The rehabilitation period can last several months. However, with proper surgery and subsequent rehabilitation therapy, the risk of complications can be minimized.
Source: https://oyaichnikah.ru/zabolevaniya/drugie-narusheniya/razryv.html
Ovarian apoplexy: what it is, causes of rupture, symptoms, treatment options and consequences for reproductive health + reviews
Ovarian rupture in its “pure form” is rare. Most often, this diagnosis is established at the diagnostic stage, and in the case of surgical treatment, rupture of the ovarian cyst is confirmed. The clinical picture, mechanisms of occurrence, surgical technique and consequences for the body are similar for both conditions.
What is ovarian apoplexy
Synonyms of the term are the concepts of rupture, hematoma, infarction, and violation of integrity. The pathology occurs in fertile women and is associated with the characteristics of their body, which prepares for pregnancy every month.
Theoretically, every girl once a month has the risk of ending up under the “surgeon’s knife” due to rupture of ovarian tissue. ICD-10 code for ovarian apoplexy N.83 and pathology refers to non-inflammatory processes of the female reproductive system.
In the ovaries, follicles grow, inside which the egg matures. With the onset of menstruation, it increases to 18-20 mm, after which its shell “bursts,” releasing a full-fledged female reproductive cell and a small amount of fluid.
Instead of a burst follicle, an active corpus luteum is formed, which produces progesterone. The latter is responsible for preparing for pregnancy and if it occurs during the first 12 weeks. This is how monthly ovarian cycles normally proceed.
Due to certain factors, disruptions occur in the process of ovulation and the formation of the corpus luteum. At the site of ovarian rupture, the integrity of the blood vessels is disrupted, which leads to intra-abdominal bleeding. At the same time, due to the fragility of the vessels, a hematoma forms in the already formed corpus luteum. Increasing bleeding can be dangerous not only for a woman’s health, but also for her life.
More often, a rupture of the right appendage is detected.
This is explained by the fact that it is more intensively supplied with blood from the right ovarian artery, which is directly connected to the aorta, while the left one departs from the renal artery and the blood flow to the left appendages is less.
Also, the right ovary is larger in size and weight, and its lymphatic system is more developed. This adds complexity to the diagnosis of pathology: apoplexy is mistaken for acute appendicitis.
Most experts distinguish forms of ovarian rupture depending on the severity and intensity of blood loss. However, this classification is not complete, since there are known cases of ovarian apoplexy without bleeding - painful, not requiring surgical treatment. The table shows the types of pathology.
Table - Separation of types of ovarian rupture by signs and causes
CriteriaTypesCharacteristics| According to complaints | Painful (pseudoappendicular, algid) | — There is no significant bleeding; - severe pain and nausea are observed; - looks like an attack of appendicitis |
| Anemic (hemorrhagic) | — Signs of abdominal bleeding predominate; - pain is mild |
|
| Mixed | Has signs of both forms | |
| According to the degree of blood loss | First | Blood loss no more than 150 ml |
| Second | Blood loss within 150-500 ml | |
| Third | Intra-abdominal effusion exceeds 500 ml | |
| By origin | Caused by external factors | The cause could be sports, sex, injuries |
| Spontaneous | Against the background of the general condition |
About 90-93% of patients experience pathology in the periovulatory period (14+/-3 days), as well as in the luteal phase. This may be caused by the following:
- features of anatomy and blood supply - the blood supply of blood vessels changes and their fragility and permeability increases;
- inflammatory processes - chronic infections worsen in the second phase;
- bleeding disorders - long-term use of coagulants, thrombophilia, taking medications that indirectly affect the properties of blood;
- stimulation of ovulation - taking drugs leads to increased growth of follicles, they are easier to injure and provoke apoplexy.
The table lists the main endogenous and exogenous provoking factors.
Table - Causes of ovarian rupture
Group of factors Provoking factor Dependence on external influences| Exogenous group of factors | Impacts resulting in excessive intra-abdominal pressure | — Physical activity on the abdominal area; - injuries; - rough and intense sex; - improper douching |
| Endogenous group of factors | Do not depend on external circumstances | — Tumors; - adhesions (leads to mechanical compression of blood vessels) |
The clinical picture is always accompanied by abdominal pain and signs of acute anemia.
- Pain. They are concentrated in the lower abdomen, sometimes radiating to the sacrum, perineum, rectum and umbilical area. Pain after ovarian apoplexy occurs suddenly, can be in the form of attacks or constant, “contractions”. The attacks are short-lived or last several hours, disturbing throughout the day.
- Signs of bleeding. The pulse weakens or increases, and the blood pressure drops. Characterized by dizziness, general malaise, and pallor. The condition is also accompanied by nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, frequent urge to go to the toilet, and bloody vaginal discharge similar to menstruation.
The classification by severity is shown in the table.
Table - Degree of severity of the condition
DegreeCharacteristics| I | - Periodic tolerable attacks of pain; — peritoneal phenomena and shock are absent |
| II | - Severe pain, weakness; - nausea and vomiting; - mild peritoneal phenomena; — shock I degree; - fainting; - low-grade fever |
| III | - Acute ongoing pain, vomiting; - bloating, cold sticky sweat; - fainting, tachycardia; — shock II-III degree; - symptoms of peritonitis are pronounced; - decrease in hemoglobin to 60 g/l and below |
Symptoms of ovarian apoplexy are similar to an attack of acute appendicitis. They can also be confused with signs of ectopic pregnancy, torsion of an ovarian cyst, pancreatitis, peritonitis, and renal colic.
But the distinctive feature of ovarian tissue rupture is that a woman can pinpoint the exact time when the pain began. For example, immediately after sexual intercourse, after jogging or jumping rope.
Ovarian apoplexy is not so easy to differentiate due to the clinical picture similar to other acute conditions. But it requires quick recognition, since increasing bleeding poses a real threat to life. Mostly girls complain of an “acute abdomen” and with this preliminary prognosis they are admitted to the hospital.
To make an accurate diagnosis, a gynecologist, urologist, and surgeon are involved in the examination. The sequence of complete diagnosis of ovarian apoplexy is presented in the table.
Table - Tests and examination for apoplexy (rupture) of the ovary
Diagnostic methodFeatures and significance| Blood analysis | — Allows you to detect a decrease in hemoglobin and suggest bleeding; - with apoplexy there are no inflammatory changes in the analysis |
| Blood for hCG | Values above 20 U/ml indicate pregnancy, including ectopic |
| Examination by a gynecologist | - Examination and movements of the cervix are painful; - with heavy blood loss, the posterior fornix “hangs” due to filling with blood; - the abdomen is painful and swollen on palpation; - peritoneal symptoms are determined |
| Pelvic ultrasound | — Signs of fluid (blood) in the abdominal cavity; - excludes pregnancy, ovarian cyst |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys, intestines, abdominal organs | Pathologies of these organs are excluded |
| Culdocentesis | Blood is detected in the abdominal cavity |
| Laparoscopic surgery | Used in unclear cases to clarify the diagnosis |
With apoplexy - normal or subfebrile temperature, in contrast to appendicitis.
The need for culdocentesis
Culdocentesis is a puncture of the abdominal space through the mucous membrane of the posterior vaginal fornix. This is done as follows:
- the cervix is exposed in the speculum and the mucous membrane is processed;
- local anesthesia or intravenous anesthesia is performed;
- A special needle is used to puncture the vaginal mucosa in the area of the posterior fornix.
If there is liquid (blood “in the abdomen”), it flows out in droplets or streams through the needle.
Culdocentesis is the “last resort” before surgery. If the results reveal an accumulation of blood in the abdominal cavity, urgent surgical treatment is necessary.
If serous fluid was obtained during culdocentesis (normally, it may be at the time of ovulation) without any admixture of blood, further treatment tactics are conservative.
A contraindication for performing the manipulation is the patient’s serious condition with obvious symptoms of a “catastrophe” in the abdomen.
Is surgery necessary?
Treatment without surgery is possible only for mild forms of the disease, when there are no obvious signs of bleeding and culdocentesis does not give a positive result.
Emergency care in this case includes the following:
- peace;
- applying cold to the stomach;
- hemostatic drugs;
- antispasmodics;
- antibiotics to prevent infectious complications.
After the end of the acute period, physiotherapy is prescribed: electrophoresis using calcium chloride, diathermy, Bernard currents. If the pain intensifies or signs of intra-abdominal bleeding appear, surgery is performed.
In doubtful cases, diagnostic laparoscopy is performed, and the following facts are also in favor of surgical treatment:
- intense abdominal pain;
- detection of free fluid in the abdominal cavity by ultrasound;
- obtaining blood during culdocentesis.
Laparoscopy is the most preferred type of intervention. This is a minimally invasive operation with a short subsequent postoperative period and rehabilitation.
After two or three punctures, manipulators are inserted into the anterior abdominal wall, with the help of which the injured area on the ovary is cauterized. The bleeding stops. The abdominal cavity is irrigated with saline solution. Blood and clots are removed.
In some cases, sutures may be placed on the ovarian tissue. It is extremely rare that the appendages, part of the ovary or other internal genital organs are removed.
If the medical institution does not have laparoscopic equipment or a trained specialist, a conventional laparotomy is performed. The doctor's further actions are the same - suturing the ovary, removing blood from the abdominal cavity.
Treatment of ovarian apoplexy ends with subsequent recovery of the body after surgery. All appointments are aimed at correcting hormonal levels, maintaining the reproductive system and generally strengthening the body.
It is necessary to eliminate physical activity for two to three weeks. During rehabilitation for a period of three to six months, the woman is prescribed hormonal therapy using combined oral contraceptives (Zhanine, Novinet, Regulon), taking into account the phenotype and concomitant diseases.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are useful: magnetic therapy, laser therapy, ultrasound, electrophoresis with zinc. Their main effect is aimed at preventing the formation of adhesions in the future.
Apoplexy as an acute condition does not affect the reproductive function of a woman. However, problems with conception after ovarian rupture do occur.
- The adhesion process is initiated. The greater the woman's blood loss, the higher the likelihood. This is due to the fact that no matter how carefully the surgeon rinses the abdominal cavity of blood during the operation, part of the fibrin, invisible to the eye, remains. In the future, this provokes the formation of adhesions and tubal obstruction. For prevention, it is recommended to use enzyme suppositories (for example, “Distreptase”) and undergo physical therapy during the rehabilitation period.
- The supply of eggs decreases. Even in the case when the ovarian tissue is only sutured or coagulated at the site of injury, its volume decreases. If this is less important for young girls, then planning a pregnancy after 30 years of age may be problematic due to “ovarian exhaustion.”
- The likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy increases. The adhesive process and previous surgery increase the likelihood of an abnormal location of the fallopian tubes and narrowing of their lumen.
Reviews from women who had to undergo surgery for ovarian rupture prove that in most cases, apoplexy does not tend to recur, and problems with conception and pregnancy do not arise.
To avoid ovarian rupture, inflammatory processes in the genital organs should be treated in a timely manner; they very often provoke changes in ovarian tissue and increase the risk of ovarian rupture.
It is not always possible to avoid relapse of pathology. After apoplexy, it is important to protect yourself from excessive physical activity and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Drug therapy that corrects the activity of certain brain structures is useful.
Nootropics are used to stimulate the metabolic mechanisms of the central nervous system and drugs aimed at improving cerebral perfusion (Tanakan, Cavinton, Vinpocetine), and tranquilizers.
Clinical guidelines for the prevention of ovarian apoplexy recommend long-term use of oral contraceptives. Hormonal drugs contribute to the transition of the ovaries into a “dormant state”, their size and activity decrease. The likelihood of apoplexy is extremely low.
Ovarian apoplexy requires immediate response and treatment, which most often involves surgery.
In many cases, after suffering a rupture of ovarian tissue and timely measures taken, a woman manages to realize her reproductive function without complications.
The consequences of ovarian rupture depend on the type of treatment undertaken and the severity of the woman’s condition at the time of apoplexy.
Reviews
Girls, I have ovarian apoplexy... my stomach hurts so much, especially on the right side, that I called an ambulance, I thought it was appendicitis, the doctor gave an injection for pain and that’s it... I went to the gynecologist, the doctor said that during ovulation, a blood vessel burst and an inflammatory process on the right side began.. The operation was not performed, suppositories were attributed to both anal and vaginal... and also douching..
Yana, http://www.woman.ru/health/woman-health/thread/3944723/
I had this “byak”. The ovary ruptured due to physical impact from the inside. I walked for half a day with pain in my side. Then she began to lose consciousness. They took me by ambulance to the emergency hospital (the one that is currently abandoned in Green Grove). They operated on him and immediately sent him to the intensive care unit due to the large loss of blood - internal bleeding.
In the intensive care unit, when I came to my senses, I immediately asked the nurse what kind of operation was performed. She said that they had repaired a ruptured ovary. It healed like a normal abdominal operation - about a month.
The doctors explained that that day I was ovulating, during which the ovary breaks to release an egg. But since “physical force” was applied, the ovary ruptured very strongly, which caused bleeding.
Now sometimes in the middle of the cycle I feel a little pain. The gynecologist called it ovulatory syndrome.
Trap, https://www.u-mama.ru/forum/family/health/412283/index.html
I have had. My stomach hurt, I thought I had been poisoned, then I fainted late in the evening. I suffered all night, I thought it would pass, in the morning they called an ambulance, it turned out to be apoplexy.
It was painful to breathe, and lying down I couldn’t breathe at all. only sitting. At the hospital they immediately took me for an ultrasound - it turned out that a lot of blood had poured through this ovary into the stomach. Go straight to surgery.
Then they said that there was 330 ml of blood in me, in my stomach.
Well, the operation was quickly done, I was in the hospital for 2 days, and that was because I was pale, so they wanted to let me go the next evening. In general, the operation itself is not difficult. Many are discharged the next day. After 10 days you come back to remove the stitches. Well, have an ultrasound in 3 months to see what’s going on.
Saving, https://www.u-mama.ru/forum/family/health/412283/index.html
In February, I had an ovarian rupture (other names are apoplexy, ovarian infarction). The pain was terrible, there was free fluid in the abdominal cavity, on the third day they made a puncture in the back wall of the vagina, took a puncture... They decided to treat conservatively (a bunch of pills, physiotherapy, injections), they did not do laparoscopy.
They prescribed me to take Novinet for six months, and then get pregnant while withdrawing. I’ve been drinking for a month now, but somehow the bottom still feels suffocating from time to time...
Girls, maybe someone has encountered the same problem? They write that the diagnosis is quite common... I’m very worried
Scarlet OHara, http://forum.forumok.ru/lofiversion/index.php?t30167.html
Source: https://doktor365.ru/apopleksiya-yaichnika/
Symptoms, causes and diagnosis of ovarian apoplexy: treatment without surgery
Ovarian rupture is an emergency condition in gynecology that requires immediate intervention by specialists.
Symptoms of the pathology increase rapidly, and severe pain signals serious damage. If you go to the clinic early with ovarian apoplexy, it is possible to completely preserve the functions of the organ.
What is ovarian apoplexy
When blood vessels, stroma, or corpus luteum rupture, ovarian apoplexy may occur. Apoplexy of an ovarian cyst is characterized by a violation of the integrity of the organ tissue and hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity.
Typically, damage occurs in young women of childbearing age, and half of the patients experience relapses of the disease.
The most vulnerable is the ovulatory opening of the ovary. Scientists who studied this issue noted that rupture of the protein shell does not occur so often.
Histological studies of ruptured appendages show that blood leaks through the stroma gradually, accumulating in the area of the ovulation opening.
This is where the place of least resistance is formed, and therefore the hemorrhage occurs directly from here. If the ovulation opening has already become covered with luteal tissue, then this barrier is easily destroyed and the blood comes out.
The tunica albuginea of the ovary can be damaged by a hematoma of the cystic cavity, as well as due to a true rupture of the tunica albuginea of the epididymis.
As a rule, even in these cases, doctors do not talk about the process of rupture of the hematoma accumulated inside the organ. The mechanism of rupture lies in the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the medulla and cortical layers, the stroma of which is more loose.
When soaked in blood, it increases sharply in volume. And the protein shell, which lacks elasticity, breaks under pressure because it is not prone to stretching.
Right
Apoplexy of the right ovary occurs three times more often than the left. This is explained by the anatomical features of the appendage.
The right ovary has a much more developed network of blood vessels; it is supplied autonomously by the right ovarian artery. The mass and volume of the organ are greater than that of the left one.
Also in the right appendage there is a more active lymph flow. All this creates the preconditions for the threat of organ rupture under the influence of related factors.
Left
Damage to the appendage on the left side is rare. This is also explained by the characteristics of the organ itself.
It has a much smaller size, a less dense network of blood vessels, and the blood supply occurs thanks to the renal artery.
This allows you to avoid reaching high pressure levels, which is why apoplexy of the left ovary does not occur so often.
Causes
The structure of the female genital organs, the histological features of the appendages and their supply with blood form an unfavorable background against which ovarian apoplexy occurs in women.
And when additional factors arise, the threat of rupture increases significantly. It is possible to identify the causes that lead directly to apoplexy:
- an increase in the permeability of ovarian tissue in the second half of the cycle (it is at this time that a greater number of epididymal ruptures occur);
- previous cases of termination of pregnancy;
- inflammatory processes in the ovaries;
- drug stimulation of ovulation;
- neuroendocrine disorders;
- strength training;
- polycystic disease;
- aggressive sexual intercourse;
- abdominal injuries;
- taking anticoagulant drugs.
Popular drugs for the treatment of ovarian cysts
As a result of exposure to these factors, intra-abdominal pressure increases; fragile or damaged ovarian tissues cannot withstand such pressure, which is why the integrity of the tissue is compromised.
Classification
Doctors in practice actively use G. Savelyev’s classification in relation to ovarian ruptures, according to which not only the form of pathology is determined, but also the degree of blood loss.
According to the classification, there are two forms of ruptures:
- Painful form (pseudoappendicular).
- Hemorrhagic form (anemic).
In the hemorrhagic form, the degrees of blood loss are distinguished:
- first degree, in which blood loss is up to 150 ml:
- second degree, hemorrhage volume – from 150 to 500 ml;
- third degree - severe hemorrhage with a volume of lost blood of more than 500 ml.
Symptoms
Signs of ovarian apoplexy in most cases increase rapidly. Apoplexy can happen at any time and anywhere, even at home, while sleeping.
If damage to the appendage occurs, symptoms of ovarian apoplexy appear:
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen on the side of the rupture;
- radiating pain in the back, perineum, lower back or rectum;
- signs of internal bleeding - weak pulse, cold sweat, weakness and dizziness.
Hemorrhage into the ovary can cause not only pain in the area of the appendage itself, but also provoke radiating discomfort.
The nature of the pain is sharp, cramping, stabbing. The attack can last up to several hours, worsening in the next 24 hours after the injury.
Bleeding and hematomas of the appendages provoke typical signs of cavitary hemorrhage. In women, blood pressure decreases, the skin turns pale, and cold sweat appears on the face.
Typically, such signs are characteristic of the first degree of intra-abdominal bleeding.
With the second degree of blood loss of more than 150 ml, vomiting, the urge to defecate or urinate are possible, and patients complain of severe pain. Signs of ovarian apoplexy can progress, and with extensive blood loss, fainting is common.
- The third degree of development of the pathology, when the volume of hemorrhage amounts to more than half a liter of blood, is characterized by signs of collapse - women experience constant sharp pain in the lower abdomen, vomiting, cold sweat, foggy consciousness or loss of consciousness.
- Tachycardia and shock of the second or third degree of severity develop.
- It is important to recognize the symptoms in time, since the pathology is disguised as an ectopic pregnancy, pancreatitis or peritonitis, appendicitis - competent diagnosis will allow you to quickly prescribe medication or surgical treatment.
- The picture of an acute abdomen requires competent differential diagnosis.
Diagnostics
If pain occurs in the lower abdomen, doctors conduct a series of standard gynecological examinations - external examination, two-hand examination.
Note that the external genital organs are not changed - the vagina will have a normal color or a little paler. Examination of the uterus is often impossible, because when pressing on the abdominal cavity, sharp pain occurs and the muscles are tense.
- If it is possible to feel the uterus, then its size will be standard, and the gynecology will not be changed, but one of the ovaries is slightly enlarged and painful.
- A blood test may not give diagnostically correct results: with extensive bleeding, hemoglobin may be low, but if the blood has clotted, then hemoglobin may remain normal or be slightly elevated.
- Diagnosis using ultrasound shows the presence of a certain volume of blood in the abdominal cavity, clots can be seen.
- To confirm the ultrasound results, you can perform a puncture of the posterior vaginal vault, which will show free blood, but the most reliable method - laparoscopy - will help you make a final diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment of ovarian apoplexy can be conservative or surgical. Drug treatment is resorted to in rare cases; laparotomy or laparoscopy is preferably performed.
Therapy is urgent, because blood loss can reach large volumes. In addition, blood released into the abdominal cavity can irritate the peritoneum and cause peritonitis.
The addition of such a complication threatens with serious consequences.
Previously, doctors believed that with minor blood loss and minor pain, the ovaries could be treated conservatively. It was believed that they healed after apoplexy on their own.
But recent studies indicate the need for surgical intervention. At the moment, there is no consensus, because even with conservative methods, competent doctors who know how to assess the situation achieve excellent results and the absence of complications.
Conservative
If doctors decide to treat without surgery, then this is done in a hospital setting, under the supervision of staff.
The main group of drugs prescribed to the patient will be coagulants to stop bleeding, antispasmodics to relieve pain and vitamins for subsequent restoration of the body.
Bed or semi-bed rest is recommended. At first, during bleeding and after it, cold is applied to the stomach.
Patients are primarily concerned about pain. With light bleeding, the pain is not very pronounced, but it is still necessary to relieve it with antispasmodic drugs - Drotaverine, Papaverine, Buscopan.
- To stop bleeding, along with antispasmodics, the drugs Etamzilat (intramuscular), Tranexam (intravenous), Ambien (intravenous) are injected.
- Among the fortified drugs that improve blood counts and help restore a woman’s body after a rupture, doctors prescribe Thiamine, Pyridoxine, Cyanocobalamin.
- Conservative treatment of ovarian apoplexy threatens the formation of adhesions (80% of patients), and infertility occurs in four out of ten women.
The problem with such complications is the remaining blood clots. Conservative treatment at this stage is used extremely rarely.
Surgical
If ovarian apoplexy is aggravated, signs of extensive bleeding are developing, then emergency surgery is necessary. Indications for the operation are as follows:
- a woman’s desire to preserve reproductive function;
- ineffectiveness of conservative therapy;
- increased pain, worsening blood counts;
- sharp deterioration in general condition;
- the presence of fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity, as shown by ultrasound.
Despite the need for surgery, it is not always possible to do it due to contraindications that the patient has.
These include:
- severe hypertension and heart disease;
- acute blood loss;
- severe exhaustion of the body;
- renal or liver failure;
- malignant tumors of the appendages;
- peritonitis;
- pregnancy (over 16 weeks).
In these cases, the operation is postponed until the pathology is eliminated, or the possibility of performing a gentle intervention - laparoscopy - is considered.
Laparoscopy
The operation is one of the most gentle methods of surgical intervention. It is carried out under the control of a videoscope, which takes pictures inside the abdominal cavity and displays it on the screen.
After the operation, there are no traces left, since all the instruments are inserted through small incisions - three or four incisions of one and a half centimeters each. After a few months, the scars disappear completely.
During the operation, damaged tissue of the appendage is sutured. Bleeding areas are cauterized with an electrocoagulator. Usually, during the operation it is possible to save the ovary; resection is resorted to only if there are concomitant pathologies.
In other cases, reproductive function is preserved. If laparoscopy cannot be performed, laparotomy is resorted to.
Laparotomy
During laparotomy, an 8-10 cm incision is made on the abdominal wall in the area above the pubis.
The bleeding is stopped by an electrochemical coagulator. Usually the intervention is performed under endotracheal anesthesia.
During the operation, all the blood that has accumulated during the bleeding is removed from the abdominal cavity, and the abdominal cavity is washed with a special solution.
The ovaries, fallopian tubes, and appendix are examined for the presence of concomitant pathologies. The abdominal cavity is then sutured. In the postoperative period, antibiotic therapy is carried out.
Complications
- The consequences of ovarian apoplexy are adhesions, a high risk of developing peritonitis, and in some cases, adnexal cancer is possible.
- With timely assistance, the patient’s life is not in danger, but if assistance is not provided on time, then extensive bleeding can lead to death.
- In the future, women may lose reproductive function and suffer from an ectopic pregnancy.
Forecast
The prognosis for the treatment of appendage rupture depends mainly on the timing of specialized care and the amount of bleeding that occurred during apoplexy.
In most cases, the prognosis is favorable - patients not only eliminate the consequences of the pathology, but also maintain reproductive function.
Prevention
Prevention of ovarian apoplexy consists of minimizing factors that can provoke epididymal rupture. Women need to undergo gynecological examinations in a timely manner to identify polycystic disease and adnexitis.
You should not engage in strength sports that require heavy lifting; you need to protect yourself from various types of injuries. When prescribing anticoagulants, the dose of the drug should not be exceeded.
Rupture of ovarian corpus luteum cyst
If the corpus luteum has a cyst, then for many years women do not even suspect it, and the first symptoms appear when the cyst ruptures.
The pathology is provoked by an increased load on education - this can be a difficult pregnancy, excessive physical activity, or stress. Since the cyst wall is quite dense, this pathology is rare.
If the cyst ruptures, surgical treatment is not performed at the initial stage. Doctors act on it with electrophoresis and magnetotherapy, which in most cases allows the situation to normalize.
If the situation does not improve several cycles after the examination, surgical treatment of the injury is performed.
Pregnancy after apoplexy
- With timely treatment of the disease, ovarian function can be preserved, which means further pregnancy is quite possible.
- When one damaged ovary is removed, the chances of pregnancy remain high because the paired organ takes on the rest of the job of producing eggs instead of the removed appendage.
- Complications and negative prognoses for pregnancy arise with conservative therapy, since there is a high risk of formation of adhesions and dysfunction of the ovaries, including the cessation of their activity.
- It is to preserve reproductive function that doctors resort to surgery.
Source: https://endometriy.com/yaichniki/apopleksiya