A correct diagnosis is the key to successful treatment, but the doctor is not always able to identify the disease based on an examination of the patient and the collected medical history, especially when there are suspicions of diseases of the abdominal organs, which have a complex structure and often have similar symptoms when pathologies develop.
In the modern world of technology, not a single area of medicine can do without informative and high-quality equipment that allows us to identify the slightest disorders and diseases inside our body.
One of the most common and accessible diagnostic methods is ultrasound examination, which helps to make the correct diagnosis for many diseases, especially when it comes to possible disorders in the functioning of the abdominal organs.
In order for an ultrasound examination to provide maximum information to the doctor, special preparation for an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is required, which consists of several stages, which the doctor must inform about on the eve of the examination.
How does ultrasound work?
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) is a modern non-invasive diagnostic method that is widely prescribed to patients in various fields of medicine. Ultrasound examinations use high-frequency sound waves to produce 2D or 3D images of internal organs in real time.
The special ultrasound sensor of the device has the ability to record all changes, sending their results to the monitor screen.
When ultrasound scanning the abdominal organs, a frequency of ultrasonic waves of at least 2.5-3.5 MHz is used, this makes it possible to accurately determine the size, position, structure, deviations and other characteristics of the abdominal organs.
What organs does an abdominal ultrasound examine?
Using ultrasound, you can examine parenchymal organs, as well as those filled with fluid. Basically, using ultrasound, the ultrasound specialist examines the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, and bile ducts.
At the same time, with the help of this examination, it is possible to examine the kidneys, which are located in the retroperitoneal space, but are clearly visible along with other organs.
The intestines and stomach can also be examined using ultrasound, but given that there is air in these organs, it is difficult to examine them, and the results obtained may be distorted and not true. Therefore, to examine the stomach and intestines, it is better to undergo a colonoscopy.
When should you do an abdominal ultrasound?
Modern ultrasound examination is carried out using the latest equipment, which makes it possible to accurately identify the slightest pathological processes in the abdominal cavity. The great advantage of this study is its low cost, as well as accessibility and high information content.
In addition, an undeniable advantage of ultrasound diagnostics is the absence of contraindications. Both pregnant women and young children can undergo this examination as many times as required by the doctor to make a correct diagnosis or to monitor the development of the disease.
You can undergo an abdominal ultrasound with the direction of your attending physician or independently if you have the following symptoms:
- bitterness in the mouth;
- periodic or constant heaviness in the stomach;
- vomiting, nausea;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- pain in the abdomen, lower back, under the chest and hypochondrium;
- increased gas formation;
- frequent urination, burning, pain during urination;
- suspicion of oncological, infectious, inflammatory diseases.
If a person has a history of chronic diseases of the abdominal organs, then it is recommended to undergo an ultrasound scan at least once every 6 months.
As a preventative measure, this examination should be completed once a year.
The results of an abdominal ultrasound allow the doctor to draw up a complete picture of the disease, determine the extent of damage to the diseased organ, and identify functional or pathological processes in the abdominal cavity.
Ultrasound examination can detect the following diseases or disorders:
- gallstones;
- changes in the structure of the liver: fatty liver, hepatitis of various etiologies, cirrhosis or other pathological neoplasms of benign or malignant origin;
- enlargement or changes in the lymph nodes of the abdominal cavity, which often react to pathogenic bacteria or viruses;
- thickening of the walls of the gallbladder;
- disturbances in the structure of the abdominal organs that occurred as a result of mechanical damage;
- inflammation of the pancreas: pancreatitis;
- enlarged spleen.
In addition to the above pathologies, ultrasound can identify other disorders and diseases of the abdominal organs. In order for the examination results to be reliable, and for the doctor to be able to properly assess the condition of the internal organs, a person needs proper preparation for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, which consists of simple but very important recommendations.
How to prepare for an abdominal ultrasound?
As mentioned above, ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity has no contraindications, and the high efficiency of the examination allows us to identify the slightest disturbances in the functioning of the internal organs of the peritoneum.
However, as with any medical procedure, preparation for an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity is necessary.
The doctor should tell you how to properly prepare for this procedure, but many patients are interested in the question of whether it is possible to drink water before an ultrasound or whether it is possible to eat before an ultrasound of the abdominal organs?
Before undergoing an ultrasound, you need to stop eating and drinking water 4-5 hours. The only exception is that if the doctor needs to examine the kidneys or bladder, then you need to drink at least 1 liter of water before the procedure.
Also, if the patient has had his gallbladder removed, then drinking water is not prohibited. Equally important in preparing for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs is the condition of the intestines, which should be empty; this will help the doctor more accurately assess the condition of the internal organs.
Therefore, the patient may often be prescribed an enema or bowel cleansing with special medications. Before the study, it is prohibited to drink any alcoholic beverages, and you should also stop smoking.
If a person does not adhere to the correct preparation for an ultrasound, this may negatively affect the quality of the examination.
An ultrasound of the abdominal organs is performed in the supine position. For a more accurate examination, the doctor may ask you to turn on your right or left side, take a deep breath and hold your breath.
The doctor applies a small amount of contrast agent to the abdominal area and begins to move the sensor.
In this way, the internal organs are scanned, and the results of the examination are recorded on the monitor screen.
Many modern clinics perform ultrasound in 3D or 4D images, which allows the examination results to be more accurate and of higher quality. After the ultrasound procedure, the doctor makes a conclusion (transcript) on this examination, which is handed over to the attending physician.
Diet before abdominal ultrasound
An important step in preparing for an abdominal ultrasound is nutrition, which can affect the results of the examination. So, on the eve of an ultrasound diagnosis, a person needs to exclude the following foods from his diet for 2-3 days:
- black bread;
- milk;
- carbonated drinks;
- raw vegetables, fruits, and juices;
- confectionery;
- fried, fatty, spicy foods;
- fatty meats;
- alcohol.
Following a diet will reduce the amount of gases formed in the intestines, thereby allowing the doctor to thoroughly examine the internal organs of the abdomen. It is recommended to consume the following products:
- boiled, baked or steamed beef, chicken or fish meat;
- no more than 1 hard-boiled chicken egg;
- porridge with water: pearl barley, buckwheat, oatmeal;
- hard cheeses;
- light and non-greasy soups.
Meals should be fractional, every 3 hours. As drinks, you can drink weak and not sweet tea or still water. However, before performing an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, you need to refuse food for 3 to 5 hours.
If there is a need or a person has diabetes, then you can drink not too sweet tea or eat 1 lollipop.
If the study is scheduled for the afternoon, then a light breakfast is recommended.
It is important to note that if preparation is being made for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys, then it should be done in the morning and only on an empty stomach.
Colon cleansing before abdominal ultrasound
To obtain reliable ultrasound results, doctors often recommend bowel cleansing on the eve of the procedure.
This procedure can be carried out using an enema, but recently most people prefer an alternative method of cleansing the intestines - taking laxative medications: Senade, Senadexin or the drug Fortrans, which must be taken depending on body weight. 1 tablet or one sachet of laxative is designed for 20 kg of human body weight.
As a laxative, you can also take drugs such as: “Normaze”, “Dufalak”, “Prelaxan”. Before using any laxative, you should read the instructions for use or consult your doctor.
Factors that distort abdominal ultrasound
In order for preparation for an abdominal ultrasound to be successful and not affect the results of the examination, a person must strictly adhere to the above recommendations.
If all the recommendations were followed correctly, but the doctor has suspicions that the results are not entirely reliable, you may not have taken into account some points that may lead to distortion of the diagnostic results:
- Smoking is prohibited 2 hours before the ultrasound examination.
- You should not chew lollipops or gum 2 hours before the procedure.
- If an X-ray examination was carried out the day before, you need to inform the doctor and wait 2-3 days, and only then do an ultrasound examination of the abdominal area.
- There is no need to take antispasmodics on the eve of the procedure: “No-shpa”, “Spazmalgon”, “Papaverine”, “Dibazol”, “Papazol”. If there is a need to take them, be sure to inform your doctor.
- If there is a desire or need to examine the kidneys, then the bladder should be full.
- Obesity makes diagnosis difficult.
Failure to comply with the above points may lead to distorted results.
Therefore, if you want to get accurate diagnostic results and not go through the examination procedure again, you must prepare properly for the procedure, and if you have questions, you should definitely ask your doctor, who will give useful recommendations and help you prepare for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Source: https://antirodinka.ru/podgotovka-k-uzi-briushnoy-polosti
Abdominal cavity, ultrasound: what is included? What organs? :
A non-invasive examination method that allows you to observe organs in real time is called ultrasound, or ultrasound for short.
The main goal of this method is to identify pathology and determine future patient management tactics.
Not only the symptoms of the disease are considered indications for examination using abdominal ultrasound, but also their early detection and prevention. What is included in an ultrasound of the abdominal organs will be discussed below.
Advantages and disadvantages of ultrasound examination
The advantages of this method include the following points:
- Painless, i.e. this manipulation will not cause any discomfort.
- Information content and sensitivity. This diagnostic method makes it possible to assess the structure of tissues and organs and is considered one of the most sensitive.
- Safety. The method is absolutely safe, including for the fetus and the expectant mother.
- Availability. You can undergo the procedure at any clinic near your place of residence.
Among the disadvantages it should be noted:
- The reliability and quality of the examination directly depends on proper preparation.
- The interpretation of the results is influenced by the competence and literacy of the medical worker. Sometimes doctors invite their colleagues to help.
- This is a dynamic type of examination, i.e. the picture of the internal organs is assessed only at the time of the procedure.
Abdominal ultrasound: what is included in the examination?
This type of hardware examination examines the condition of the lymph nodes and the following organs:
- stomach;
- spleen;
- gallbladder;
- pancreatic glands;
- liver.
In some cases, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. What does this concept include? When conducting such a study, in addition to the above, the reproductive organs are checked. In women - the uterus, in men - the prostate gland. In addition, the doctor can check the intestines, organs located in the pre- and retroperitoneal region. In cases where the diagnosis has been established, modern technology allows ultrasound scanning of just one organ. In other situations, for example, before surgery, it is possible to examine the abdominal cavity in an expanded form and examine all organs, i.e., it is possible to conduct exactly the type of examination that is necessary for the treating doctor.
Preparing for an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity
It is necessary to carefully prepare for the examination. The following activities are not difficult to carry out, and they are accessible to everyone:
- Three days before the procedure, slightly change your usual diet and give up foods that cause fermentation processes.
- The following are excluded: legumes, red vegetables, all milk-based products, fresh and sauerkraut, carbonated drinks, fatty foods, and fried foods.
- On the eve of the examination, it is not recommended to smoke, suck sweets or chew gum.
What organs are included in an abdominal ultrasound?
Organs that are completely or partially covered by the membrane of the abdominal cavity and located in the preperitoneal and retroperitoneal space (layer of fatty tissue) are subject to examination using ultrasound:
- bladder;
- liver;
- gall bladder;
- spleen;
- pancreatic gland (pancreas);
- epigastrium (stomach);
- prostate;
- uterus;
- ureters;
- kidneys;
- adrenal glands;
- abdominal aorta;
- the inferior vena cava (greater) and its tributaries;
- duodenum;
- the intestines are both small and large.
Many representatives of the stronger sex are interested in what is included in an abdominal ultrasound in men? When prescribing a medical professional, in addition to the organs located in the abdominal cavity, the condition of the prostate gland is also checked.
Indications for ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity
This type of examination is prescribed by medical workers of various specialties. The indications are quite extensive:
- suspicion of ascites;
- abdominal trauma;
- pain in the abdominal area of unknown etiology;
- suspicion of the presence of tumors, cysts or other formations;
- prolonged fever for no apparent reason;
- skin itching that lasts for a long time;
- the sclera of the eyes is yellowish in color;
- constant thirst and therefore uncontrolled consumption of water;
- dull pain not associated with eating;
- constant bitterness in the mouth;
- paroxysmal pain in the right half after eating spicy or fried foods.
In addition, a comprehensive ultrasound of the abdominal cavity (which is included - described above) is indicated for patients with pathologies of the liver, digestive tract, pancreas, a history of abdominal trauma, malignant or benign tumors.
Features of ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity in pregnant women
The effectiveness and quality of this type of study depends on the stage of pregnancy. The larger it is, the more difficult it is to examine the internal organs. At a period of 36 to 40 weeks, it is pointless to carry out this procedure, since the uterus fills almost the entire abdominal cavity. Routine examination is recommended when planning conception and for short periods up to approximately 16 weeks.
Preparation for ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity for pregnant women
How to properly prepare a pregnant woman for an abdominal ultrasound and what is included in this procedure is outlined below. For this category of patients, preparation is necessary only in the first trimester. However, there are situations when the doctor recommends preparing for the examination at other times. Therefore, this issue should be clarified in advance. Preparatory procedures include:
- refusal of food and water at least five hours before the test;
- per day, exclude the consumption of foods that increase gas formation, namely cabbage, milk, fresh fruits, legumes, sweets, dough products;
- the day before, eat a light dinner and take five to ten tablets of activated carbon to adsorb gases.
What does an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity show during pregnancy?
This type of examination helps to identify the pathology of internal organs and check their condition for the presence of various seals, tumor nodes, changes in cellular tissue, etc. What is included in the examination: Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity
- kidneys;
- liver;
- spleen;
- gall bladder;
- duodenum;
- pancreatic gland (pancreas);
- epigastrium (stomach).
The doctor ordered an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. What is included in the examination, besides what is stated above? Using ultrasound, you can see large vascular trunks, lymph nodes of the abdominal cavity, and large vessels of the liver.
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs during pregnancy
The doctor prescribes a diagnosis if a woman, regardless of the stage of pregnancy, has the following symptoms and complaints:
- pain in the location of the kidneys, liver or other internal organs;
- constant gas formation;
- the appearance of bitterness and unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- in the upper abdomen, causing inconvenience and pain;
- presence of heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- bad test results.
Deviations that are most often detected during pregnancy
In case of an acute abdomen, the following pathologies are suspected: gastric ulcer, acute appendicitis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, intestinal obstruction.
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, which is included in this type of examination as described above, in this case provides invaluable assistance in the primary diagnosis of the pathological condition, since X-rays or computed tomography are extremely undesirable for a pregnant woman and such types of examinations are prescribed in extreme cases.
Based on the results of the ultrasound, the medical worker makes a decision on the need for surgical intervention. In addition, almost all changes in the pancreas are visible on ultrasound.
If urine tests are unsatisfactory, kidney ultrasound is prescribed several times in a row. This organ can be clearly seen in later stages from the back. Ultrasound is used to detect a pathology that often occurs in late stages of pregnant women - ureteral obstruction. This condition manifests itself as follows. The uterus, which has reached a large size, compresses the ureter and prevents urine from entering the bladder. Thus, the urine outflow pathways from the kidney are blocked. The same picture is observed when the lumen of the ureter is closed by a tumor or kidney stone. An ultrasound of the liver can detect obstructive jaundice, i.e. blockage of the main bile duct by a tumor or stone. In this case, immediate surgery is required. The most dangerous, and unfortunately, recently the most common condition in expectant mothers is considered to be aortic aneurysm. They can be either congenital or acquired, due to high blood pressure and various anomalies of the vascular walls. The most dangerous are unstable aneurysms, which rupture and lead to enormous bleeding and it is not possible to save the patient in such cases. The next most common pathology in a pregnant woman is the syndrome of portal hypertension and compression of the inferior vena cava. The first is found in pregnant women with a history of liver cirrhosis or chronic hepatitis. Due to the increase in consumption of alcoholic beverages and infection with chronic viral hepatitis, portal hypertension is quite often diagnosed in expectant mothers. Rarely, but malignant tumors also occur in pregnant women. Using ultrasound, both primary lesions are detected in the following organs: liver, kidneys, pancreas, spleen, and metastases, and their size and distribution are also assessed.
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs in a child
The organs located in the baby’s peritoneum are responsible for the removal of harmful substances and the absorption of beneficial substances, as well as for maintaining immunity. Indications for examination of the abdominal cavity (which is included in the ultrasound - described above):
- intense gas formation and girdling pain in the abdominal area;
- bowel disorders for a long period;
- discomfort when palpating some areas of the peritoneum;
- suspicion of pathology of internal organs located in the peritoneum;
- abdominal trauma;
- yellow sclera;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- nausea and feeling of heaviness in the abdomen.
What is included in an abdominal ultrasound for a child? Ultrasound is used to study: pancreas, gallbladder, kidneys, spleen, liver. Additionally, it is possible to diagnose the adrenal glands and bladder.
Preparing a child for an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity
Parents play an important role in this process. It is very important to conduct psychological preparation with the baby. Explain that you will be nearby, that the procedure is completely painless, etc. The next stage is the immediate preparation of the body, which includes:
- Three or five days before the examination, a special diet is required. The attending doctor will give recommendations.
- For children from one to three years old, exclude food four hours before the test and fluid intake one hour before. If the baby is capricious, you can give a little sweet water.
- For children over three years of age, exclude food eight hours before the procedure.
- If the reason for the ultrasound was increased gas formation, the doctor will recommend a medicine that reduces this process or a cleansing enema, which should be done 12 hours before the diagnosis.
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity. What diseases are diagnosed in children?
Using an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity (which is included in this manipulation - described above), anomalies that are of a congenital nature and pathological conditions are identified:
- reactive pancreatitis;
- internal bleeding;
- blood diseases;
- mononucleosis;
- tumors, cysts, kidney stones;
- pyelonephritis;
- neoplasms;
- liver diseases;
- gallstones;
- dropsy;
- cholecystitis;
- gallbladder motility disorders;
- anomalies of the renal vessels.
One of the informative and simple methods of obtaining information about the condition of the abdominal organs is ultrasound, which is included in the study described above. Safety for the patient makes it quite popular and affordable. Interpretation of the examination results is carried out immediately after the end of the procedure, following which the doctor will prescribe the necessary course of therapy.
Source: https://www.syl.ru/article/364575/bryushnaya-polost-uzi-chto-vhodit-kakie-organyi
What is included in an abdominal ultrasound: indications, preparation, results and cost
Ultrasound allows you to look inside the human body. This diagnostic method has been used relatively recently, but has already become a favorite of doctors in many specialties. Abdominal ultrasound (AUS) is used by gastroenterologists, infectious disease specialists, internists and pediatricians.
What organs can be checked with an ultrasound?
Ultrasound is very high frequency waves that the human ear cannot detect. It passes through some soft tissues - skin, muscles. Ultrasound is reflected from other tissues - internal organs, connective tissue, bones. Ultrasonic waves are absorbed by air and liquid.
It is thanks to the property of reflection that this diagnostic method became possible. The reflected waves are captured by a sensor, which transfers them to a computer. There, the sound signal is converted into a graphic signal - an image appears on the screen.
Dense tissues reflect ultrasound at a higher rate and appear white or gray in photographs. This is typical for the liver and kidneys. The bones are very dense, so they cannot be distinguished in the picture.
Softer tissues block ultrasound and appear dark gray or almost black. Air and liquid do not reflect waves at all; they appear as dark spots in the photographs.
These properties explain what an ultrasound of the abdominal organs shows:
- liver;
- gallbladder;
- pancreas;
- spleen;
- large vessels.
The stomach is a hollow organ, so it is not visible on an ultrasound; only the wall can be detected. The kidneys are also not normally visible; there is an ultrasound method for them.
The abbreviated designation OBP has a decoding - in medicine these are the abdominal organs. Therefore, when a doctor prescribes an ultrasound scan of the abdominal cavity, he assumes a disease of one of the above organs.
The types of ultrasound scans depend on what is included in the abdominal examination. All organs are rarely examined at once - this is a complex method, prescribed for serious diseases.
Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system is most often used. It includes the liver, gall bladder and ducts. All types of examination are called abdominal - from the Latin word “abdominum”, which means stomach.
Watch a video about OBP research:
Indications for use
Which doctor prescribes an examination of the abdominal cavity depends on who the person contacted and with what complaints. Usually the first specialist is a therapist.
He can independently prescribe an ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys, or immediately send the patient to a specialist.
Among them, ultrasound diagnostics are most often prescribed by gastroenterologists who deal with diseases of the abdominal cavity.
Ultrasound of any abdominal organs is prescribed if there are indications:
- prolonged discomfort or abdominal pain;
- feeling of nausea, periodic vomiting;
- yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes;
- brown urine or yellow stool;
- persistent skin rashes;
- changes in blood biochemistry;
- abdominal organ injury with risk of internal bleeding.
In such situations, ultrasound of PD is a primary diagnostic method, that is, it helps the doctor to identify a disease that the person did not have before. They do examinations for adults and children from birth.
Ultrasound examination is also used as a monitoring method in people with chronic diseases:
- hepatitis of various origins;
- cholecystitis;
- pancreatitis;
- cirrhosis of the liver.
Ultrasound is performed annually and serves to prevent complications that may arise from irregular monitoring.
How often a person can have an ultrasound depends on the disease they have. There are no strict restrictions on this procedure, as it is safe for health. It is done as many times and as often as once a year, five years, ten years it is necessary to examine a person in order to control his disease.
Additionally, we invite you to read the article about ultrasound of the abdominal organs in children.
Preparation rules
The preparatory stage is prescribed during a routine examination. It is needed to ensure that the result is as accurate as possible. If the procedure is performed urgently, preparation is excluded. A nurse or doctor explains to the patient how to prepare properly. So that he does not forget the important points of this stage, he is given a memo where all the methods are described in detail.
Standard training lasts three days. It includes following a diet that eliminates flatulence and constipation. Medications are prescribed for the same purpose. You need to take a disposable sheet and towel with you for the procedure.
Watch the video with the rules for preparing for an ultrasound examination of the OBP:
Several examination techniques
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs is carried out in several ways:
- transabdominal - through the abdominal wall;
- endousis - endoscopic access through the esophagus;
- with contrast agent;
- with trial breakfast;
- with water-siphon sample.
The choice of technique depends on the disease and the characteristics of the human body. Ultrasound is an overview, assessing the condition of the entire abdominal cavity. In case of disease of a specific organ, a targeted study is carried out. How long the procedure lasts depends on the type of technique and the characteristics of the person being examined. The average manipulation time is 20-30 minutes.
Transabdominal method
A classic method that appeared before others. Inspection of the abdominal organs is carried out through the anterior wall of the abdomen. The doctor asks the patient to lie down on the couch and expose his stomach. The skin is lubricated with sound-conducting gel. Next, using the sensor, all organs or only the required ones are examined sequentially.
Endoscopic method
Used less frequently than classic. The endoscopic method has the advantage that changes in organs are more accurately determined and an examination can be carried out if the abdominal wall is damaged. Typically, this method is used to examine the pancreas.
A thin probe is passed through the nasopharynx into the esophagus and stomach. There is a sensor at the end of the probe. The pancreas is examined through the wall of the stomach.
With contrast
Ultrasound with contrast is a new examination method. It is performed using a contrast agent administered intravenously. It is a powder that, when diluted with sodium chloride solution, forms tiny bubbles. These bubbles are accessible to ultrasound, which makes it possible to study the condition of the vessels. Contrast studies improve diagnostic accuracy.
Since contrast is administered intravenously, the question naturally arises: is it harmful to frequently do such an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity? This contrast is harmless to the body and is excreted through the lungs and kidneys within 24 hours. Therefore, contrast examinations are done as often as required.
With trial breakfast
An abdominal ultrasound is sometimes done with a test breakfast. The method allows you to assess the functional state of the gallbladder. First, the examination is carried out on an empty stomach in the usual way.
The gallbladder is measured and the person is given to eat 2-3 egg yolks or drink a glass of cream. Half an hour later the examination is done again.
During a stress ultrasound, the gallbladder, its fullness, and the activity of contractions are measured.
With water-siphon sample
This method allows you to examine the stomach. The person is placed on the couch and asked to drink 100-1000 ml of water or juice in this position. After 10-15 minutes, bubbles form in the stomach, which can be visualized by ultrasound. The doctor can see the peristalsis of the stomach and understand whether there is a reverse reflux of food.
Research video
Watch a forty-minute video where the doctor demonstrates OBP on the monitor and describes his actions:
Possible results
The purpose of examining the abdominal organs with ultrasound is to determine their health status. The examination may show a normal result - if there are no abnormalities in the organs. But since an ultrasound of the abdominal organs is prescribed when a person has complaints, various changes are usually detected - signs of disease.
The doctor who conducts the examination gives only a description of what he saw. The final interpretation of the abdominal ultrasound results is made by the attending physician. He also makes a diagnosis, taking into account other studies.
Normal indicators
When describing the condition of the abdominal organs, the doctor follows a certain algorithm:
- size;
- outlines and contours;
- homogeneity of structure;
- fabric density;
- diameter of vessels and ducts.
The sizes of the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas depend on the age of the subject, gender, height and body weight. Therefore, there is no strict number that the normal sizes must correspond to. Use an approximate range.
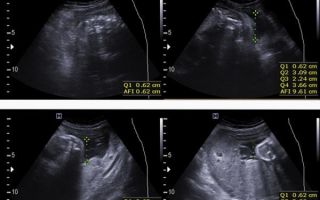
Table of normal sizes of abdominal organs:
| Organ | Dimensions |
| Liver | Length up to 18 cm, width up to 12 cm |
| Gallbladder | Length up to 10 cm, width up to 5 cm |
| Pancreas | Length up to 12 cm, width up to 6 cm |
| Spleen | Length up to 12 cm, width up to 8 cm |
Size indicators for men are 5-10 mm larger than for women - this is the norm. The contours should be clear and even. The normal structure of the tissue is homogeneous and fine-grained. Density is determined by the color of the organ in the image. The liver is taken as a reference point - it is gray in color. The pancreas and spleen should have the same color.
Defined diseases
Ultrasound reveals even minimal changes in the abdominal organs. This is especially important if you suspect cancer. Each disease has a specific set of ultrasound signs.
- Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver. The color becomes darker, the uniformity of the structure is preserved. The size increases, the contours are clear.
- Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. The color becomes darker, the uniformity of the structure is preserved. The size increases, the contours are clear.
- Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder. It increases in size and the wall thickens. With calculous cholecystitis, stones are visible in the cavity of the bladder - round white spots.
- Cirrhosis - normal liver tissue turns into scar tissue. In the picture the dimensions are reduced, the color changes to light gray or white. The structure is heterogeneous, lighter nodes are visible.
- Ascites on ultrasound is free fluid in the abdominal cavity. In the lower abdomen, dark areas are visible that change their position.
- With the help of ultrasound you can see cancer of any organs. The tumor has unclear contours; a white spot with uneven borders is visible in the middle of the gray tissue. Metastases also look the same - smaller, almost always round in shape.
- Cysts are cavities with air and fluid inside. The photo shows round dark spots with a white border.
- If an ultrasound shows enlarged lymph nodes of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space, this is a sign of a cancerous tumor or tuberculosis of the spleen.
Since hollow organs, such as the intestines, are not accessible to ultrasound, not all diseases are detected. An abdominal ultrasound will not show appendicitis, colitis - inflammation of the intestines. Umbilical or inguinal hernias are not accessible to ultrasound waves.
Read more about pathologies of the abdominal organs in articles on the website dedicated to a specific organ.
Contraindications for examination
Ultrasound examination is the safest of all instrumental diagnostic methods. The procedure can be performed on newborns, pregnant women, and the elderly. Contraindications are those conditions that can distort the result:
- pronounced flatulence;
- damage or inflammation of the skin of the abdominal wall;
- psychosis;
- alcohol or drug intoxication.
Contraindications are relative - after the patient’s condition has normalized, the examination can be carried out.
Cost of the procedure
An ultrasound can be performed at any medical institution. In public hospitals free of charge if indicated. The cost in private centers depends on the region of residence and the scope of the study.
Price table for abdominal ultrasound.
| City | Cost, rubles |
| Moscow | 500-2000 |
| Saint Petersburg | 450-1800 |
| Ekaterinburg | 500-1800 |
| Novosibirsk | 500-2000 |
| average cost | 487-1400 |
Modern portable devices make it possible to perform ultrasound at home . The cost of examining the abdominal cavity in this case will be much higher.
Additionally, we invite you to watch an interesting video report on the anatomy of the abdominal cavity:
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is a simple and effective method for detecting hepatitis, pancreatitis, cirrhosis, and cancer. The procedure is prescribed if there are indications - a person’s health complaints, changes in blood tests. There are several techniques that allow you to examine the patient as accurately as possible. The attending physician makes a diagnosis based on the ultrasound findings.
Share your opinion in x. Share the information you read with your friends on social networks; they may find it useful. All the best.
Source: https://uziman.ru/bryushnaya-polost/uzi-bryushnoj-polosti
How to prepare for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs and what is the procedure?
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs is a comprehensive examination that should preferably be performed at least once a year.
This diagnostic procedure includes examination of the gallbladder, liver, retroperitoneum, spleen, pancreas, kidneys and adrenal glands.
It makes it possible to assess the condition of internal organs and timely identify pathologies or consequences of sports injuries.
Using an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, you can determine the cause of pain and discomfort in the abdomen, identify inflammatory processes, the presence of stones in the gall bladder and kidneys, tumors and cysts, and determine the cause of obstructed urine outflow. Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is also indicated after injuries, including sports ones - sometimes injuries do not cause any pain at first and can only be noticed on an ultrasound or MRI.
In addition, indications for an abdominal ultrasound may include symptoms such as constant bitterness in the mouth and unreasonable heaviness in the stomach, nausea, fever, increased gas formation, as well as suspicion of oncological, infectious, inflammatory and functional diseases.
Preparation for ultrasound of the abdominal organs
In order for the examination results to be accurate and correct, preparation for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs is necessary. The method of preparation depends on which organs the doctor’s attention will be directed to.
If you are having an ultrasound of the liver, gallbladder, spleen and pancreas, try not to eat anything for 8-12 hours before the examination. Dinner on the eve of the procedure should be light and not too rich - for example, low-fat fish with vegetables or chicken breast.
Before an ultrasound scan of the kidneys, you need to drink 1-1.5 liters of water or juice an hour and a half before the examination so that the bladder is full during the procedure. It is also advisable not to eat anything for 8-12 hours before the ultrasound to avoid gas formation in the intestines. The presence of gases distorts the picture, since the kidneys are located immediately behind the stomach and intestines.
Before an ultrasound of the abdominal aorta, you should also abstain from food for 8-12 hours before the procedure.
Whatever organs are examined, the patient must warn the doctor if, within two days before the ultrasound, he had an irrigoscopy or x-ray of the upper gastrointestinal tract with contrast. The fact is that barium, which is used in these examinations, can distort the results of ultrasound. After gastro- and colonoscopy, ultrasound is also not performed; you should wait a few days.
To achieve the best results, 3 days before the scheduled examination, it is advisable to follow a diet that will reduce gas formation in the intestines, otherwise the air will distort the image.
You can eat cereal porridges, lean meat and fish (it is advisable to cook them without oil - boil or bake), soft-boiled eggs (but no more than 1 per day), low-fat cheese. It is better to exclude beer, carbonated drinks, white bread, sweets, apples, cabbage, corn and milk from the diet.
You should also not chew gum - this provokes uncontrolled swallowing of air. Meals should be small, 4-5 times a day every 3-4 hours. If you have difficulties with digestion, you should also take anti-flatulence medications.
Preparation for abdominal ultrasound in children has its own characteristics.
Before examining babies under one year old, it is advisable to skip one feeding immediately before the procedure, and you should also refrain from drinking.
Children 1 to 3 years old should not eat for 4 hours or drink 1 hour before the ultrasound. Children over 3 years of age should refrain from eating for 6-8 hours before the ultrasound and should not drink for 1 hour before the examination.
How is the research conducted?
The operation of the ultrasound machine is based on the use of high-frequency ultrasonic waves.
The device emits sound pulses, some of which are reflected from tissues with different acoustic resistance and are perceived by the sensor.
This effect allows you to obtain both two-dimensional and three-dimensional images of organs in real time. Modern devices can even show a moving three-dimensional picture.
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs is a harmless, simple and painless examination for the patient. You simply undress to the waist and lie down on the couch on your side or back. To perform an ultrasound of the kidneys, you need to roll over onto your stomach.
The doctor applies a water-based gel to the skin, which fills the air gap between the sensor and the skin so that ultrasound can better penetrate deep into the tissue.
From time to time you may need to hold your breath for a few seconds - this will allow you to better see the internal organs. The examination usually lasts 20-60 minutes.
The timing of the procedure does not affect the results - ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is performed both in the morning and in the afternoon. If the ultrasound is scheduled for the evening, you can allow yourself a light breakfast no later than 11 a.m., but after that it is not advisable to have a snack.
This is important. Smoking is not recommended before an abdominal ultrasound. Smoking causes stomach spasms, and this can lead to incorrect interpretation of the results.
What does an abdominal ultrasound show and how are the results interpreted?
Based on the results of the ultrasound, the doctor draws up a research protocol with a conclusion. This takes from several hours to several days, depending on the doctor’s workload. In good private clinics, results are given out on the day of the examination. If desired, the results are written to disk. Perhaps, after the procedure, the doctor will prescribe an additional examination of some organ.
Ultrasound is a modern and highly informative diagnostic method that allows you to see even the most minor changes.
It makes it possible to notice inflammatory processes, changes in the shape and size of organs, their displacement due to the proliferation of adjacent tissues, neoplasms and cysts, expansion of the aorta and the presence of an aneurysm, hardening of the walls of the gallbladder and dilation of the bile ducts, stones in the kidneys and gall bladder, as well as any damage to internal organs caused by mechanical trauma.
It is almost impossible for a person without special medical education to understand what is recorded in the image; most of us cannot even distinguish the image of a healthy organ from a diseased one, so there is no point in trying to decipher the results on your own; this requires knowledge and experience that only doctors have. The image quality produced by the latest generation of ultrasound machines is very high, although incorrect patient behavior can spoil the result. In order for all organs and systems to be clearly visible, you need to remain completely still during the examination and not neglect preparation for an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. It should also be taken into account that extreme obesity also interferes with obtaining a clear picture, since fat cells distort ultrasonic waves. An obstacle to performing an ultrasound may be the presence of an open wound or bandage in the area being examined. Perhaps in this case, in addition to the ultrasound, an additional examination will be prescribed.
It is advisable to bring the results of previous examinations to the ultrasound - this will help the doctor assess the dynamics of changes.
Source: https://www.eg.ru/digest/kak-delajut-uzi-brjushnoi-polosti.html
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity: what organs are checked, what is included, what is shown?
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) is an examination procedure without internal intervention, which includes the diagnosis of internal organs and tissues of the human body. During the study, the condition of the organs, their structure, placement, as well as the presence of pathologies and abnormalities are checked.
What organs are checked on an abdominal ultrasound?
The abdominal cavity is the internal space in the body below the diaphragm that includes organs called the abdominal organs.
During ultrasound, the presence of tumors, defects, diseases and consequences of injuries is clarified. What pathologies can be identified during diagnosis:
- An ultrasound of the liver can determine: acute and chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, fatty hepatosis, transformations (which may relate to abnormalities in the functioning of the heart) and benign formations of a local location: cyst, hemangioma, adenoma, hyperplasia. Malignant formations: primary and metastatic cancer.
- Diagnostics allows us to identify abnormalities in the formation of the bile ducts and gallbladder on ultrasound, the formation of stones (stones) and complications of cholelithiasis, forms of cholecystitis (acute and chronic), polyps and tumor formations of varying quality.
- An ultrasound scan of the pancreas reveals disturbances in its formation, as well as inflammation of the organ, pancreatitis (acute and chronic), cysts, pseudocysts, abscesses, and fatty infiltration. In the retroperitoneal space, benign and cancerous tumors, consequences caused by aging, are visualized.
- Ultrasound diagnostics of the spleen will show whether there are developmental problems, injuries received from physical bruises, inflammatory processes, formations, heart attacks, abscesses, modifications of the spleen due to diseases of the circulatory system.
- Vascular ultrasound will show the main and intraorgan parts of the circulatory system, visualize their condition, and detect blood clots.
Using an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, the doctor identifies the characteristics of organs, the presence of changes or neoplasms in them, checks the correct location of the organs and compliance of their sizes with established standards
An ultrasound of the abdominal organs is performed if the following indicators are present:
- bloating and lack of lightness in the stomach after eating;
- heaviness under the right hypochondrium;
- feeling of pain in the upper abdomen;
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen;
- bitter taste;
- strong formation of gases.
A timely examination of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space, which should be done once a year for prevention, makes it possible to prevent or diagnose the disease at the initial stage.
Carrying out diagnostics
To diagnose the peritoneal cavity, the patient must lie on his back.
Sometimes, to get a clear image, a person needs to lie on his side, then take a deep breath or not breathe for several seconds.
In some cases, for example, with an unusual arrangement of organs, the examination must be done in a sitting or standing position. The work of a sonologist during an ultrasound of the abdominal organs has the following tasks:
- establish, clarify and determine the nature of development of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space;
- detect deviations and disturbances in the functioning of the spleen, assess the density and possible damage to tissues, the size of the organ;
- find out the reason for the unexpected appearance of pain with cramps in the abdominal area;
- check for the presence of cysts, hemangiomas, deposits of calcium salts in tissues and other formations;
- document the data in the diagnostic report.
The study is carried out using a special ultrasonic sensor working with a conductor gel. The patient usually lies on his back, but the position can be changed at the request of the doctor. This is usually necessary when there is an abnormal location of organs or poor visibility of one of them
Research Opportunities
Ultrasound, as a diagnostic method, has a number of advantages and capabilities and allows you to eliminate or confirm suspicions of hypertension and identify various disorders. Ultrasound is also performed to monitor paracentesis and biopsy.
Abdominal surgical operations are necessarily preceded by echographic diagnostics. Inflammatory processes, various types of formations and neoplasms, types of disorders in diseases are determined.
Deviations in organ development are also easily determined using ultrasound.
Often, in addition to ultrasound of the abdominal cavity in women, an ultrasound procedure of the uterus and appendages is included. The examination includes purposes such as establishing pregnancy, detecting uterine polyps, ovarian cysts and tumors. Diagnostics can also be done during pregnancy: an ultrasound performed in advance allows you to see disturbances even in the intrauterine development of the fetus.
Ultrasound of the OBP is considered to be most effective and does not require other types of examinations and tests. After the examination and conclusion, you can immediately begin treatment. Another positive aspect of ultrasound is its affordability.
Often patients have a question about where it is better to have an ultrasound scan: in a public hospital or in a private medical institution. In reality, there is no difference.
The main thing to pay attention to is the availability of a modern ultrasound machine and the experience of the doctors who perform the procedure.
If the patient feels acute pain, then diagnosis using ultrasound is not the cause of its occurrence. In this case, the patient needs to be examined by a surgeon. The procedure generally lasts no more than twenty minutes. It will take much longer to prepare for the inspection.
Preparing for an ultrasound
First of all, you need to follow a diet - eat:
- boiled chicken or veal;
- steamed or baked fish;
- oatmeal, buckwheat or pearl barley porridge;
- hard cheese;
- The liquid should be consumed at least one and a half liters per day.
Prohibited:
- eat legumes;
- It is not recommended to drink carbonated and alcoholic drinks;
- Rye bread;
- milk and fermented milk products;
- sweet products;
- raw fruits and vegetables.
In order for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs to be performed correctly, the patient must follow a special diet for three days. It is necessary to reduce gas formation and empty the intestines
You must stop smoking a couple of hours before visiting the clinic. Excessive air makes it much more difficult to scan the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space.
An important nuance during preparation is the elimination of air from the intestines.
Overweight people should prepare especially carefully for the examination, since excessive thickness of the fat layer prevents ultrasound from reaching the insides.
Carrying out an ultrasound of the abdominal organs also requires mandatory bowel cleansing, which is performed in the evening before the procedure.
It can be done by washing with an enema or an Esmarch mug with 1 - 2 liters of not very cold, but not too hot, unboiled water.
After the procedure, you need to take medications with sorbent properties or Simethicone, you need to take them the required number of times.
At the patient's request, an additional ultrasound of the kidneys is performed. In this case, the patient should prepare as follows: drink at least a liter of water or unsweetened tea an hour before the ultrasound examination, and then go to the procedure with a full bladder.
Source: https://vedmed-expert.ru/brushina/uzi-organov-bryushnoj-polosti.html