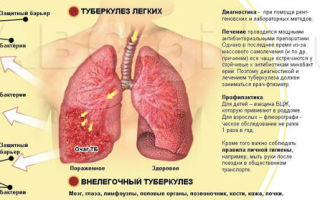
According to statistics from the World Health Organization, about 9 million people fall ill with tuberculosis every year, of which about 3 million die from complications of a general infection of the pulmonary system.
In addition to other dangerous symptomatic signs, the first symptom of the disease is a cough. What kind of cough with tuberculosis occurs at various stages of respiratory diseases is the topic of our conversation.
We visited the Moscow City Scientific and Practical Center for the Fight against Tuberculosis and met with the leading specialist of the medical institution, Lyudmila Mikhailovna Tuktarova, to ask her questions of interest to the readers of our site.
– Hello, Lyudmila Mikhailovna! Before starting our conversation, I would like to know what tuberculosis is and how it is dangerous for humans?
L.M.: – Hello, dear readers! Indeed, tuberculosis is one of the most dangerous diseases of the respiratory system, the infectious agent of which is the Koch bacillus. In 1882, in one of the Berlin clinics, he managed to isolate the bacterium that causes this infection.
Pulmonary tuberculosis or consumption is a very dangerous disease, which until the 20th century was considered incurable. Until now, TB specialists are alarmed by the large number of deaths from this disease. The main reason for this is the late contact with specialists, when infectious damage to the pulmonary system reaches its peak.
The first sign of the disease, which should be an alarming signal for a person, is a constant hacking cough.
Important! It should be remembered that any coughing person poses a potential threat to others.
– Lyudmila Mikhailovna, how to determine the degree of the disease, and what kind of cough occurs with tuberculosis at an early stage?
L.M.: – The person has sweating, a slight fever and a constant cough. In addition, patients at the initial stage of the disease complain of headache, lack of appetite and weight loss. According to initial signs, cough with tuberculosis at the beginning of infection is very similar to the cough reflex with bronchitis.
Primary infection: main symptoms and signs
The primary location of the source of infection is very important. Pulmonary tuberculosis at the early stage of the disease is asymptomatic. The disease disguises itself as various types of diseases of the respiratory and respiratory systems. However, there are special distinctive signs that should alert a sick person and his environment:
- The appearance of low-grade fever, when a person’s body temperature remains within 37-38ºC for a long period. At the same time, the cheeks are covered with a blush, and the eyes shine from the constantly releasing tears.
- A person rapidly loses body weight regardless of appetite.
- Pain in the chest or back, accompanied by a slight tingling sensation when sighing or coughing.
- Night sweats are another feature of pathological damage to the respiratory system infected with bacteria.
- Weakness of the body and constant fatigue even with minimal physical activity.
- Productive cough with little mucus production.
Coughing attacks are becoming more frequent due to impaired gas exchange in the alveoli and accumulating mucus in the bronchi, which impedes ventilation of the lungs.
– Lyudmila Mikhailovna, what cough is the most dangerous for pulmonary tuberculosis? Is it true that the infection process is irreversible?
L.M.: – Naturally, a cough with sputum discharge is not always a clear sign of tuberculosis. It is necessary to diagnose the disease. For this purpose, X-ray scanning of the lungs, microscopic examination of sputum released during coughing and other clinical examinations are used.
Attention! A cough with blood discharge is evidence of a serious pathology, but with timely consultation with a doctor, the risk of further development of the disease can be significantly reduced.
Forms of clinical manifestations of tuberculosis
It is important to know what kind of cough during tuberculosis in adults manifests itself in various forms of damage to the respiratory system, and how it is dangerous for others:
- With latent tuberculosis (latent form), minor changes in the tissue structure of the lungs are characteristic. Cough with mycobacterial infection of this type does not pose a threat to others.
- Infiltrative tuberculosis is expressed in the accumulation of a large number of cellular elements mixed with blood. The accumulated infiltrate in the lungs is partially released with a cough in the form of bloody sputum, which is dangerous for others.
- The cavernous form of pulmonary lesions in tuberculosis is characterized by a number of symptomatic signs (hemoptysis, dull wheeze in the lungs). Damage to large vessels of the pulmonary system leads to internal bleeding, which entails purulent and bloody discharge when coughing.
- Total defeat occurs in cirrhotic tuberculosis, when the lung is completely destroyed. Cough in this form of the disease causes unbearable suffering to the sick person.
Diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis is based on the analysis of sputum produced by coughing. A swab is taken from the oral cavity of a sick person and the degree of concentration of biological material is determined using polymerase chain reaction.
– Lyudmila Mikhailovna, how the symptoms of the disease are determined in the youngest patients, and what kind of cough occurs with tuberculosis in children.
L.M.: – First of all, you should pay attention to the duration of the child’s cough. If the cough lasts more than 3 weeks, there are no concomitant diseases, and the temperature remains stably within subfebrile limits, then this indicates possible pathologies of the pulmonary system. Such a child should be seen immediately by a doctor.
What is tuberculous bronchoadenitis?
Tuberculous lesions of the intrathoracic nodes of the lymphatic system in the root of the lung most often occur in the primary form of tuberculosis.
The difference between tuberculous bronchoadenitis and systemic lesions in the lung tissue during tuberculosis is its minimal pneumonic changes. This form of tuberculosis is most common in school-age children.
The course of the disease is asymptomatic, however, there are various intoxications:
- unproductive paroxysmal cough without sputum;
- body temperature remains within subfebrile limits;
- due to the enlargement of the lymph nodes, compression of the bronchi occurs, causing wheezing in the chest.
Confirmation of the diagnosis occurs through fluorographic and laboratory testing. Tuberculous bronchoadenitis is one of the multiple signs and symptoms of tuberculosis in children.
For this disease of the pulmonary system, treatment is provided with antibacterial drugs and pharmacological combinations that help strengthen the immune system.
In addition to intensive pathological and specific therapy, sanatorium treatment is recommended.
– Lyudmila Mikhailovna, are there any methods of treating cough with tuberculosis using folk remedies?
L.M.: – Since cough in tuberculosis is not the only symptom, the disease must be treated comprehensively. Treatment of tuberculosis with folk remedies at home should not be the determining factor.
Traditional medicine is only an auxiliary method of curing a bacterial infection with various pharmacological drugs over many months. However, such treatment cannot be excluded in complex anti-tuberculosis therapy.
Cough with tuberculosis: treatment with folk remedies
It is known that the causative agents of tuberculosis infection are mycobacteria.
Attention! Airborne droplets of focal infection of the lungs are the main type of transmission of tuberculosis. Therefore, blocking the cough during infection, as the most common route of infection, is of great importance.
Using traditional medicine, you can not only strengthen the body’s immune system, but also significantly reduce the adverse effects of mycobacteria on the pulmonary and respiratory systems.
Treatment of cough due to tuberculosis with garlic
Garlic juice and/or extract has an inhibitory antibacterial effect on Koch's bacillus, stopping its development. For people suffering from infectious lesions of the pulmonary system, garlic must be in their diet. It is recommended to eat 2-3 cloves of garlic every 3-4 hours.
Several recipes for preparing “garlic” medicine:
- Before going to bed, finely chop 2 cloves of garlic and pour a glass of warm boiled water. After 12 hours of infusion, the cough medicine for tuberculosis is ready. Taken daily in the morning throughout the entire treatment.
- Grind 100 g of garlic into a mushy mass with the addition of butter (100 g) and natural bee honey (100 g). The entire healing mixture is infused in a water bath for 10 minutes. Use 50 g daily before meals.
Aloe for tuberculosis
There are many different homemade medicinal recipes that help treat cough due to tuberculosis. In addition to the most important protective properties of this plant for the body, aloe saves tuberculosis patients from rapid exhaustion. Here are some recipes:
- To prepare a healing tincture, you will need the following ingredients: badger fat (150 g), garlic, birch buds (50 g each), 100 ml of cognac and 200 g of aloe. All medicinal components are mixed and infused in a dark, dry place to infuse for 7 days. At the end of the period, all contents are filtered and poured into a clean glass container. Take 2 tbsp. 3 times a day half an hour before meals.
- Mix 200 g of flower honey with a glass of crushed aloe leaves. The healing mixture is heated over low heat until liquid. After cooling, add 1 tbsp to the broth. olive oil, mix everything thoroughly and put it in the refrigerator. Take a tablespoon 30 minutes before meals.
Bear fat for cough in tuberculosis
This medicine for the treatment of tuberculosis has unique natural components and rare biologically active substances. For effective treatment, it is recommended to use natural fat, which is not sold in pharmacies.
Source: https://antirodinka.ru/kakoy-kashel-bivaet-pri-tuberkuleze-priznaki-i-lechenie
Treatment of cough in pulmonary tuberculosis: what happens, features of symptoms in the early stages
Tuberculosis is a serious infectious disease that can affect any segment of the population and age groups.
The danger of this disease lies in the fact that in the initial stages it may not manifest itself at all, or the symptoms may be so minor that they will not cause concern to the patient.
Cough with pulmonary tuberculosis is one of the early signs of this terrible disease.
In addition to a persistent cough, one of the first symptoms may be:
- increased fatigue;
- prolonged low-grade fever;
- night sweats;
- weight loss (without changing diet and physical activity).
What is a cough like with pulmonary tuberculosis?
The nature, severity and frequency of cough in pulmonary tuberculosis can vary greatly depending on the form of the disease and the extent of the pathological process in the pulmonary parenchyma. Therefore, it is not possible to say unequivocally what the cough will be like, but there are some features of this symptom in tuberculosis:
Diagnostics
- in the initial stages of the disease, most patients have a dry cough, but as lung damage progresses, copious sputum production appears (the cough becomes wet);
- the symptom appears in the patient constantly over a long period of time (even if a person has a rare, weak cough that does not bother him, but lasts for a month, then he must seek medical help);
- often the cough is accompanied by hemoptysis (during an attack, sputum with streaks of fresh, uncoagulated blood comes out);
- in children, due to severe bronchoadenitis (enlarged lymph nodes, which leads to compression of the bronchi and trachea), the cough may acquire a bitonic sound;
- the patient also has other symptoms and signs of pulmonary tuberculosis.
The fact that the cough occurs and is most intense in the morning immediately after sleep may also prompt the doctor to think about the tuberculosis process. This feature is due to the fact that during the long stay of the body in a horizontal position, a significant amount of sputum and pathological exudate accumulates in the bronchial tree.
When the patient moves to a vertical position, a cough occurs, which is necessary to cleanse the bronchopulmonary system. Therefore, a morning cough is always accompanied by the discharge of sputum (the amount of sputum depends on the form and stage of the disease).
Do not forget that a morning cough can also occur with a number of other pathologies of the lungs and bronchi, such as smoker’s chronic bronchitis, colds and others.
Treatment of cough due to tuberculosis
The occurrence of a cough attack in pulmonary tuberculosis is provoked by a specific inflammation caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Koch bacillus). Therefore, all treatment methods are aimed at combating this microorganism and suppressing the inflammatory process in the lung tissue.
Treatment of patients with open forms of tuberculosis occurs in specialized medical institutions - anti-tuberculosis dispensaries. This is necessary in order to prevent infection of surrounding people, since with open forms the pathogen is actively released into the external environment.
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a resistant microorganism, therefore, to combat this bacterium, treatment regimens that include several antibiotics simultaneously are used.
- Treatment in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis begins with the prescription of first-line antibacterial drugs. These include:
- Isoniazid;
- Rifampicin;
- Pyrazinamide;
- Ethambutol;
- Streptomycin.
- Depending on the form and severity of the disease, the doctor selects a combination of several drugs for the patient.
- If the process is caused by mycobacteria resistant to first-line antibiotics, then the treatment regimen is drawn up using second-line drugs. These include:
- Capreomycin;
- Ethionamide;
- Rifabutin;
- Fluoroquinolones.
Antimicrobial therapy is supplemented by taking immunostimulating agents, vitamins, and drugs that restore normal intestinal microflora. When taking a large number of potent antibiotics, the normal flora of the gastrointestinal tract is suppressed.
Throughout the entire treatment process, the patient is prescribed a special dietary regimen. Nutrition should be rich in all nutrients (especially proteins) and microelements in order to activate the body's defenses and replenish the body weight deficit that has appeared during the illness.
Treatment of tuberculosis is a long process that requires the patient to strictly adhere to the treatment and protective regime. You should not independently interrupt taking prescribed medications, even for a short period of time, as this may subsequently lead to ineffectiveness of the therapy.
ethnoscience
There are many methods and recipes for traditional treatment to combat tuberculosis. In order to help the body fight the disease, you can use the following medicinal components, available to everyone:
- aloe vera is a medicinal plant, the juice of which will help stimulate and strengthen the immune system, as well as enrich the body with many essential vitamins and microelements;
- garlic is a spicy vegetable with pronounced bactericidal properties and an inhibitory effect on bacteria;
- pine pollen has a varied and balanced composition, which will help strengthen the immune system and suppress the pathological process in the lungs (pine pollen is known to act as a natural antibiotic, so inhaling it is extremely useful for patients with tuberculosis);
- an infusion of dill seeds, when taken long-term and regularly, also helps in the fight against this disease;
- dried mole cricket is an unusual Chinese method of treatment, which, according to those who have tried it, very effectively fights the disease (the healing effect is provided by leukocytes contained in the blood of the insect);
- propolis is a sticky substance produced by bees in the course of their life (has pronounced general strengthening and bactericidal properties);
- alcohol tincture of Icelandic cetraria has an inhibitory effect on microorganisms, increases the body's reactivity and thereby suppresses infection;
- badger or bear fat accelerates the process of cell regeneration, has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, and speeds up metabolism;
- Nettle helps with complications such as hemoptysis and pulmonary hemorrhage.
All methods of alternative medicine can be used only as a complement to therapy prescribed by a phthisiatrician. The use of prescriptions must be discussed with the attending physician, since the substances contained in the medicinal components can affect the effectiveness of drug therapy.
other methods
As an addition to the main course of treatment, the following therapy methods can be used:
Inhalations for tuberculosis
- physical therapy (a physiotherapist individually selects a set of exercises aimed at improving ventilation of the lungs and increasing blood circulation in the pulmonary capillaries);
- inhalations with antibacterial drugs (facilitate the delivery of medicine directly to the pathological focus, ensuring higher efficiency);
- inhalation administration of moisturizing mixtures and mucolytics (to improve sputum discharge);
- electrophoresis with drugs (also improves the effect of drugs);
- high-frequency magnetic therapy, ultra-high-frequency therapy (methods that help suppress the inflammatory process).
Cough is a constant and specific manifestation of pulmonary tuberculosis, but this symptom is not pathognomonic (unambiguously indicating this disease). Therefore, to reliably confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to consult a phthisiatrician and undergo a set of laboratory and instrumental tests.
Source: https://pulmohealth.com/bolezni/kashel/kashel-pri-tuberkuleze-legkih/
What is a cough like with tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis is considered an infectious disease that affects the human respiratory system. Cough in tuberculosis is one of the first and main symptoms. Koch's bacillus causes tuberculosis. Let's look at what kind of cough occurs with tuberculosis and how it differs from other diseases.
What is a cough like with tuberculosis?
As the disease develops, the nature of the cough in tuberculosis is dry or wet with sputum production.
Tuberculosis cough is characterized by sudden attacks:
- at the beginning, damage to the lungs by the causative agent of tuberculosis;
- compression of the airways of the lungs by enlarged lymph nodes;
- with an inflammatory process affecting the bronchial walls of the lungs and provoked by the tuberculosis bacillus;
- protracted non-specific inflammatory process in the bronchi;
- breakthrough of pus from the cavity of the lung membrane.
- An active cough occurs against the background of a protracted inflammatory process in which the bronchi are involved.
- Other symptoms
- Tuberculosis has a variety of symptoms, which depend on the type of disease, location, type of pathogen, and also on the immune system. There are following symptoms when tuberculosis and cough occurs:
- severe coughing that does not stop for more than two weeks;
- there is pain in the chest area;
- when coughing, sputum with blood is released;
- sudden loss of body weight;
- temperature increases rapidly;
- excessive sweating at night;
- loss of appetite;
- lethargy;
- nodules under the skin in the legs that are very painful.
Blood when coughing up is common. Initially, scarlet blood is released, then with clots. When blood enters the lungs, aspiration pneumonia with high fever is likely to occur.
As a result, an emergency condition of the body appears, developing during acute blood loss and requiring immediate medical attention.
Can you have tuberculosis without a cough?
If the lesion is not too large, coughing with tuberculosis does not appear. Just the onset of the disease is characterized by symptoms without fever, without cough, and after a while there are constant coughing attacks.
- The non-contagious form of tuberculosis is most often not characterized by coughing.
- Also, patients with tuberculosis with the following pathologies do not have a cough: bones, joints, kidneys, genitourinary system, intestinal tract, eyes, skin.
- Intoxication syndrome is characterized by:
- powerlessness, nervousness, rapid fatigue;
- reducing body weight up to 20 kg within a month;
- Excessive sweating at night or in the morning is a sign of a “wet pillow,” since the head sweats in particular.
How to distinguish tuberculosis cough from other varieties
Tuberculosis is difficult to recognize, since these symptoms can be traced as manifestations of subsequent diseases:
- pneumonia when taken on an x-ray is visually similar to tuberculosis;
- allergic inflammation of the bronchial mucosa;
- clinical syndrome caused by increased hormonal activity of the thyroid gland;
- a disease caused by insufficiency of insulin in the body;
- an eating disorder characterized by deliberate weight loss;
Tuberculosis can destroy various human organs, but the lungs are most often affected. Consider the symptoms when the body is infected with tuberculosis:
- a feeling of fatigue that occurs constantly;
- general weakness, hyperhidrosis;
- complete indifference, slowness;
- decreased ability to work;
- pallor of the dermatological surfaces;
- poor appetite, weight loss;
- increase in body temperature for a long time in the range of 37.1-38.0 C;
- feverish state with changes in t;
- feeling of cold and chilliness;
- in women – absence of menstruation, menstruation for a long period (about six months).
During the formation of the disease, bronchopulmonary signs are expressed that increase over a long period:
- Cough in tuberculosis is the main expression of the disease. The frequency of cough, the type and amount of sputum depends on the severity of the stage of the disease.
- Hemoptysis occurs after coughing and is considered an indicator of the development of infiltrates.
- Shortness of breath occurs due to a decrease in the respiratory plane of the lung, caused by its damage.
- Chest pain occurs when the pleura is damaged. When exudate accumulates in the pleural cavity, breathing is restricted and the pain disappears; as it dissolves, it reappears.
Tuberculosis in children accompanied by cough
The cough is annoying, dry, worsens in the morning and at night, lasts 20 days. The cough is stable, but sometimes turns into a wet form with purulent discharge and blood.
In this state, a child’s concentration deteriorates and he lags behind in academic development, unlike other children. The main thing is to be able to distinguish cough due to tuberculosis in children from acute respiratory diseases.
During the period of infection caused by viruses, cough is also present, but contains certain characteristic features:
- last no more than a week;
- after a couple of days, a dry cough turns into a wet cough;
- when acute inflammation of the bronchial mucosa of viral etiology is connected to inflammation of the mucous membrane of the larynx, elevated temperature often occurs (at night);
- lacrimation and photophobia due to the inflammatory process in the tissues of the eyes,
- discharge with mucus from the nasal cavity.
Diagnosis of tuberculosis
If similar symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor to rule out cough, which occurs with pulmonary tuberculosis.
Don't expect the symptoms to go away on their own or for the tuberculosis incubation period to pass. The doctor should examine the patient and check the lymph nodes for swelling.
The doctor also observes the coughing process, whether the patient can cough up sputum, to determine whether these could be signs of tuberculosis.
The doctor determines what instrumental methods of study the patient should undergo at the next stage of the examination:
- The most common and accessible method for diagnosing pulmonary tuberculosis is radiography and fluorography. These methods determine the level of lung damage and the spread of the disease.
- Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging provide the most detailed information about the pathology and can help identify non-pulmonary forms of the disease.
- Bronchoscopy is used to obtain a smear from the larynx or perform a biopsy to obtain lung tissue for research.
It is important to get a blood and urine test. The examination is carried out together with other mandatory procedures as prescribed by the doctor. Based on the information, the doctor will make a conclusion, assess the severity of the disease, and compare the data with the characteristics of cough in tuberculosis. Only then can quality therapy be determined.
Cough and tuberculosis treatment principles
The main task of treating cough in tuberculosis is based on the destruction of inflammatory processes, as well as the elimination of pronounced symptoms. Monitor your health, since the chronic form is practically untreatable. Go through a mandatory procedure - examination of the chest organs using X-rays once a year.
The duration of therapy varies, but in most cases it lasts up to a year. Proper treatment is based on medications and physical therapies.
The first stage of treatment is carried out in a tuberculosis clinic. The goal is to stop the release of pathogenic microorganisms. Then therapy is carried out, in which the person regularly visits a therapist, but does not stay in the hospital.
- After treatment, a patient who has had pulmonary tuberculosis must undergo specialized sanatoriums.
- Surgical methods of treatment are intended when treatment has not brought results or complications have occurred.
- Intensive phase
This phase lasts two months. A list of drugs prescribed against tuberculosis (first line drugs - Isoniazid, Rifampicin) is used every day, the person is not dangerous to other people.
Maintenance phase
It is characterized as consolidating, so that the positive result of the treatment remains. Therapy is carried out for about four months. The patient uses two drugs - rifampicin and isoniazid daily or every other day.
As a result of interruption of treatment, an exacerbation will appear in 80% of cases within six months, as the disease becomes persistent. The disease at this stage can be cured over a long period of time (three years), and only with expensive medications. To prevent bacteria from becoming resistant to medications, the following recommendations should be followed:
- correctly calculate the dose of medication;
- do not skip taking the drug;
- adhere to the terms of admission (six months).
Conclusion
Infection often occurs if someone in the family is sick, so it is worth knowing the safety measures, and always wear a mask, ventilate the room and monitor your health by periodically taking tests and conducting x-rays.
Source: https://kashlya-net.ru/kashel/kakoj-kashel-pri-tuberkuleze
Cough during tuberculosis: causes, types, folk remedies
The causative agents of the disease are mycobacteria. These pathogenic microorganisms quickly penetrate tissues saturated with blood and oxygen. It is for this reason that tuberculosis primarily affects the lungs. Currently, the disease is quite common. This is due to the emergence of various strains of tuberculosis that are resistant to antibiotics.
There are two forms of the disease: closed and open. With a closed form of the disease, the patient does not pose a danger to others.
This is due to the fact that the activity of harmful microorganisms is suppressed by the immune system.
In the absence of proper treatment, pathology often develops into an open form, in which a person can transmit the disease to others. In most cases, infection occurs through airborne droplets.
Who is at high risk?
Most often, the disease is diagnosed in the following categories of patients:
- people with weakened immune systems;
- patients with HIV infection;
- medical workers who are in close contact with people infected with tuberculosis;
- persons addicted to nicotine;
- patients with low body weight;
people who are addicted to alcohol or drugs; - patients taking medications to relieve symptoms of depression.
The main cause of cough
When the immune system is weakened, the patient’s body cannot suppress the attack of harmful bacteria. As a result, an inflammatory process occurs in the tissues of the respiratory tract. This is why the patient develops a cough with pulmonary tuberculosis, which is the main symptom of the disease.
Diagnostic measures
If you suspect that cough is the main manifestation of tuberculosis, a variety of diagnostic methods :
- X-ray techniques;
- performing a Mantoux test;
- quantiferon test;
- Diaskintest.
X -ray methods include:
- fluoroscopy;
- tomography;
- radiography.
The Mantoux test involves the introduction of tuberculin into the body to assess the body's reaction. This diagnostic procedure is intended to detect tuberculosis in children.
The accuracy of the test results may be reduced in the following cases:
- there is a violation of the technique of performing the Mantoux test in a medical institution;
- the child has recently suffered from an infectious disease;
- the patient was administered a low-quality drug;
- The child’s body contains harmful organisms similar to tuberculosis pathogens.
One of the most common methods for diagnosing the disease is the quantiferon test. The study allows us to detect various forms of the disease: both open and closed. Recent infectious diseases do not affect the accuracy of the results of the corresponding test.
Types of cough with tuberculosis
The disease may be accompanied by a lingering cough. It is caused by the presence of a constant inflammatory process in the area of the bronchi and their branches, which causes increased sputum production.
As a result, the process of natural ventilation of the lungs is disrupted and the disease steadily progresses. The patient often has breathing problems. Pus often accumulates in the lung area.
With tuberculosis, various types of cough can be observed:
- dry. It is not accompanied by sputum production;
- wet. In the presence of this type of cough, sputum is released, accumulating in the upper respiratory tract;
- mixed. With this type of cough, periodic sputum production is observed.
Other symptoms of the disease
In addition to coughing, the following symptoms may occur in early stages of tuberculosis:
- dizziness;
- lethargy;
- sleep disturbance;
- increased sweating;
- pale skin;
- rapid decrease in body weight;
- loss of appetite;
- slight increase in temperature.
In later stages of the disease, the following unfavorable signs may be observed:
- the appearance of a severe cough: both dry and accompanied by sputum production;
- feeling of lack of air;
- the appearance of wheezing in the throat;
- tachycardia;
- the appearance of bloody spots during expectoration;
- the occurrence of pain in the chest area.
Carrying out a sputum examination
If tuberculosis is present, an analysis of the secretions released when coughing is performed. Laboratory specialists conduct a thorough study of biological material. The study determines:
- composition of secretions released when coughing;
- the presence of bloody impurities or pus in the sputum;
- the number of mycobacteria that provoke the appearance of tuberculosis.
At a late stage of the disease, the sputum may turn scarlet. This is due to the fact that a strong, debilitating cough can provoke the gradual destruction of capillaries located in the lung area.
Traditional methods against cough
Aloe - a folk remedy for the treatment of tuberculosis
There are many effective folk recipes that can improve the patient’s well-being. Effective cough remedies for tuberculosis are presented in the table.
Product nameCooking diagram
Mode of application
| Drinks based on pine pollen | Pine pollen contains a variety of beneficial substances in high concentrations. The drug is actively used in the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. You can make a delicious dessert from pine pollen. To do this, combine 10 grams of plant material and 150 ml of liquid honey in a separate glass container. The resulting mixture is stored in a cool place. The duration of the treatment course in most cases is two months | Take one dessert spoon of the drink three times a day. The mixture is recommended to be consumed before meals |
| To speed up the process of removing phlegm, you can prepare medicinal tea. To prepare the drink you will need the following ingredients: 1 tablespoon each of pine pollen, marshmallow root, cut into neat pieces, pre-dried chamomile. The specified components are poured into 0.2 liters of hot water. The product must be infused for 30 minutes | Drink the drink in small sips throughout the day. | |
| Products with garlic | The vegetable is endowed with pronounced antibacterial properties. To prepare a medicinal infusion, 2 pre-peeled garlic cloves are poured into 0.2 liters of water. The product is infused for 24 hours | A glass of the drink is recommended to be consumed before breakfast. Duration of treatment course - 2 months |
| If the patient has tuberculosis, garlic jam is also prepared. To do this, you need to chop 0.2 kg of horseradish and garlic. The resulting mixture is combined with 0.4 g of butter and 2 kg of honey. The resulting mass is heated in a water bath for 10 minutes. | Spread 50 grams of the mixture on a slice of bread. The product is consumed three times a day, before meals. Duration of treatment course - 2 months | |
| Decoction of aloe and cocoa powder | Aloe contains a large number of biologically active substances. The medicinal plant has antiseptic, regenerating properties, improves the condition of the immune system. Aloe-based products free the lungs from decay products, alleviate cough symptoms, and saturate the body with nutrients. In a separate pan, you need to mix 100 grams of honey, a package of butter and 40 grams of cocoa powder. Place the container on low heat. Add juice squeezed from one aloe leaf to the pan. The mixture is kept on a gas stove until the butter is completely melted. The resulting product is cooled and poured into a glass container and stored in a cool place. |
The product is taken twice a day, 10 grams. Before use, the decoction is dissolved in 200 ml of hot tea. Duration of treatment course - 6 months |
Drugs for the treatment of cough in tuberculosis
In the treatment of tuberculosis, drugs belonging to the class of antibiotics are used. in complex therapy of the disease:
- "Isoniacid";
- "Streptomycin";
- "Rifampicin."
To relieve cough in tuberculosis, the following medications can be used:
drugs belonging to the mucolytics:
- "Bromhexine"
- "Ambroxol";
- expectorants: licorice root;
- medications with a combined effect (expectorant and mucolytic): “Doctor Mom”;
- Centrally acting cough suppressants: Sinekod.
Along with medications, the following are used in complex therapy of the disease:
- breathing exercises;
- physiotherapy sessions;
- diet therapy;
- vitamin and mineral complexes.
Lung complications
With pulmonary tuberculosis, not only a cough is observed, but also other complications:
- hemoptysis. If blood enters the lungs, symptoms of aspiration pneumonia may occur, accompanied by an increase in body temperature;
- pulmonary hemorrhage. It can lead to hemorrhagic shock;
- dyspnea. This pathology often occurs during exhalation. The occurrence of shortness of breath is caused by a decrease in the volume of lung tissue, a decrease in bronchial patency and a deterioration in the functions of the respiratory center located in the brain;
- increase in size of lymph nodes.
Features of cough in the later stages of the disease
At the third stage of tuberculosis, a cough with sputum usually occurs, which contains impurities of pus and bloody spots. At the fourth stage of the disease, death of lung tissue is observed, and the patient may develop meningitis. The patient often complains of hemoptysis and increased body temperature.
So what is a cough with tuberculosis and how to distinguish it from malaise with acute respiratory infection in children?
Malaise due to tuberculosis in children is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- The child usually has a strong dry cough;
- malaise worsens at night;
- cough continues for a long time;
- as the disease progresses, the cough becomes wet with the release of blood or purulent mass;
- malaise is accompanied by absent-mindedness, decreased performance, and weakness.
A cough during an acute respiratory infection usually goes away within 2-5 days. It has a dynamic character: it changes from dry to wet in a short period of time. When taking antiviral medications and drinking plenty of fluids, the child’s condition worsens significantly.
Lung tuberculoma
Tuberculoma is diagnosed in patients who have previously survived tuberculosis. The risk of its occurrence increases with a weakened immune system.
Tuberculoma is a caseous-necrotic formation surrounded by 2 layers:
- tuberculous granulations;
- fibrous fibers.
The pathology is characterized by an asymptomatic course. In some cases, a person experiences the following unfavorable symptoms:
- loss of appetite;
- decreased performance;
- increased sweating;
- the appearance of a dry cough;
- aching pain in the chest area.
When a tumor disintegrates, the following negative consequences may occur:
- intoxication of the body;
- increased body temperature;
- the appearance of a wet cough mixed with blood.
The severity of symptoms largely depends on the state of the patient's immune system. If tuberculoma is present, surgery is usually performed.
There are several types of operations:
- thoracoplasty;
- resection;
- pleurectomy.
Preventive measures
In order to reduce the likelihood of tuberculosis, you must follow the following recommendations:
- it is necessary to strengthen the immune system with the help of vitamin and mineral complexes;
- you should give up bad habits;
- Stress and hypothermia must be avoided;
- if you experience a severe cough that lasts more than two weeks, you should contact a medical facility;
- You should regularly undergo preventive examinations at your place of residence.
Source: http://tuberculosis.su/kashel-pri-tuberkuleze.html
Types of cough with tuberculosis, features of the disease
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease with an inflammatory course in the lungs, damage to the bronchial tree by Koch's bacillus. As inflammation develops, the cellular structures of the bronchi are subject to pathological modifications; as it develops, the respiratory system as a whole is destroyed and begins to malfunction.
Path of transmission of tuberculin bacilli: airborne. Infection can occur through contact with an infected person while talking, sneezing, or coughing. Many patients wonder what cough is like with tuberculosis? After all, it is important to identify the disease at an early stage, while the chances of recovery and a favorable prognosis are much greater.
What is a cough like with tuberculosis?
A cough with tuberculosis does not appear immediately. At the first stage, at the early stage, it is practically absent. By nature it happens:
- dry, paroxysmal, causes: enlarged lymph nodes, compression of the bronchial tree, outpouring of pathological fluid into the bronchial lumen or pleural cavity;
- strengthened, productive against the background of disease progression, the addition of nonspecific bronchitis, severe lung destruction.
The cough begins to clog the bronchi, causing attacks due to the accumulation of pathogenic bacteria, leading to irritation of the respiratory receptors.
The symptoms and urge to cough can be quite long until the accumulated mucus is completely cleared.
As serous fluid accumulates, a paroxysmal cough may appear lasting 3-10 minutes, especially in the morning when taking a horizontal position after sleep.
The mucus stagnates overnight, and in the morning it again spreads through the bronchial cavity, leading to disruption of normal breathing and the urge to wet expectoration due to the body’s rapid reaction to the situation.
The appearance of a cough after sleep or taking an upright position is a clear sign of the development of the disease. During the night, mucus accumulates in the pleural cavity and splashes out in the morning, causing a prolonged cough (up to several hours) until the lungs are completely cleansed.
Source: https://ChahotkiNet.ru/diagnostika/simptomy/vidy-kashlya-pri-tuberkuleze