During pregnancy, a rather dangerous pathology can develop due to disruption of the normal location of the placenta. In this case, bearing a baby may be complicated by the development of certain unfavorable symptoms. It is necessary to consider in more detail what marginal placenta previa means, as well as how it can be dangerous and what it affects during pregnancy.
Doctors consider placenta previa to be a pathology in which the place of initial attachment of placental tissue is in close proximity to the internal uterine os. Normally, a fertilized egg attaches during implantation in an area of the top of the uterus called the fundus.
The location of the future chorion largely determines the initial location of the placental tissue. It is formed from fetal components, therefore it is in close proximity to it.
If for some reason the fertilized egg moves to the internal uterine os, then placental tissue subsequently begins to form in this area.
This leads to the development of pathology - placenta previa.
Doctors identify several clinical variants of this pathological condition. They determine them by how much the placental tissue is in contact with the internal uterine os. One of these clinical variants is marginal presentation. In this case, not the entire surface of the placental tissue, but only its individual sections are in contact with the uterine os with their edges.
A variety of causative factors can lead to the development of this pathology. Quite often, this pathological condition is preceded by chronic diseases of the reproductive organs. Women who suffer from endometriosis, adnexitis, cervicitis and other diseases of the genital organs even before pregnancy are at increased risk for the development of this pathology.
The risk of developing marginal presentation is also quite high in women who have undergone surgery on the uterus or its appendages. Doctors note that the development of marginal presentation can also be facilitated by scars on the uterus, which appeared as a result of a previous cesarean section.
The consequences of past infectious diseases can also lead to the development of marginal placenta previa. Thus, the coccal flora, which affects the internal uterine walls, leads to changes in the mucous membranes, which contributes to the disruption of implantation. In this case, usually the fertilized egg descends to the lower parts of the uterus, where the endometrium is more functional.
Congenital anomalies of the female genital organs can also lead to the development of this pathology. Thus, with a bicornuate uterus, the risk of developing placenta previa increases slightly. The presence of polyps and myomatous nodes that are located in the uterine fundus area can also become a certain obstacle to the implantation of a fertilized egg in this area.
Not only pathologies on the part of the woman can lead to placenta previa. Some anomalies in the development of the chorion can also cause the development of this pathology.
With some genetic pathologies, the trophoblast lacks certain enzymes necessary for implantation into the uterine wall.
In this case, attachment to the uterus does not occur; as a result, the pregnancy is terminated on its own almost at the very beginning of its development.
Doctors note that the risk of developing marginal placenta previa is slightly higher in women who give birth to their second and subsequent babies. If the previous pregnancy ended in a cesarean section, then the likelihood of developing marginal presentation increases.
Regional placenta previa can significantly complicate the process of bearing a baby.
Such a pregnancy is usually characterized by a turbulent course, as well as the periodic appearance of unfavorable symptoms.
It is worth noting that with extreme presentation, gestation is still somewhat calmer than with complete presentation. In this case, the prognosis for the course of pregnancy is more favorable.
Adverse symptoms for this pathology usually appear after 16–20 weeks of pregnancy. By the third trimester they may increase. In the very first weeks after fertilization, the expectant mother may not experience any significant discomfort symptoms.
The location of the placental tissue is now quite easy to determine. To do this, doctors resort to ultrasound examinations. In case of marginal placenta previa, it is not advisable to perform a transvaginal ultrasound. In this case, the possibility of damage to low-lying placental tissue is quite high. In this situation, it is better to choose a transabdominal ultrasound.
The location of the placenta can also be determined through a routine vaginal examination. However, with marginal placenta previa, it is often not worth resorting to this technique. If such an examination is carried out carelessly, the delicate tissue of the placenta can be damaged. That is why doctors give more preference to ultrasound techniques.
If during the diagnosis a marginal presentation was determined, then the expectant mother is prescribed the following additional studies. They are necessary in order to assess the dynamics of the course of this pathology.
If the pathology was detected quite early - at 12–16 weeks of pregnancy, then in such a situation the localization of the placental tissue may still change. Doctors call the upward displacement of the placenta migration.
It proceeds rather slowly and ends only by the 3rd trimester of pregnancy. That is why the localization of the placenta during its presentation is determined several times during the entire period of gestation.
Unfortunately, placental migration does not occur in all cases.
The most striking sign that usually forces a pregnant woman with marginal placenta previa to seek advice from an obstetrician-gynecologist is the appearance of blood from the genital tract.
With this pathology, blood usually appears after lifting heavy objects or after intense physical exercise. The appearance of blood on underwear can only be an isolated symptom.
In some cases, it is combined with the appearance of pain in the abdomen.
If a pregnant woman sees bleeding from the genital tract and has severe stomach pain, this means that she should not hesitate to seek medical help.
Bleeding from the genital tract with a very low position of the placenta can also develop after sex. The possibility of sexual activity in the presence of such a pathology must be discussed with an obstetrician-gynecologist. Usually, however, doctors recommend their patients with marginal placenta previa to limit sex and prescribe sexual rest.
Many pregnant women confuse the pathologies of the placenta and umbilical cord. Thus, the marginal presentation of the placental tissue has nothing to do with the marginal origin of the umbilical cord. Placenta previa is a pathology, and marginal departure of the umbilical cord is only a physiological feature of the course of a particular pregnancy.
An equally dangerous complication that can develop during pregnancy complicated by marginal placenta previa is the development of detachment of placental tissue from the walls of the uterus. This pathology usually occurs as a consequence of traumatic influences. The more the placental tissue detaches from the uterine wall, the less favorable the pregnancy prognosis.
To avoid the development of possible placental abruption, doctors make a whole range of different recommendations. So, contraindications include intense sports, as well as running. A pregnant woman whose pregnancy progresses with the development of marginal presentation is prohibited from lifting objects that are too heavy. It is very important that the expectant mother gets more rest.
In addition to playing sports, a pregnant woman with marginal placenta previa may be prohibited by her doctor from visiting the pool. Reviews from many women who had this pathology during pregnancy confirm this. In case of extremely severe presentation, any physical activity may be limited, and in some cases even bed rest may be prescribed.
Severe stress can also make the situation worse. The expectant mother should strictly follow these recommendations.
Preventing infection of the low lying placenta is another challenge during a complicated pregnancy. In this case, pathogenic organisms most often enter the uterine cavity from the external genitalia.
In order to prevent such infection, a pregnant woman should carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene.
The extreme position of the placenta relative to the uterine os can also be dangerous for the fetus developing in the mother’s womb.
Violation of uteroplacental blood flow can lead to the development of fetoplacental insufficiency. In such a situation, the intensity of intrauterine development of the fetus is significantly reduced.
Pregnancy occurring with marginal placenta previa can have an extremely unpredictable prognosis.
At any stage of bearing a baby, dangerous complications can arise that contribute to a change in the tactics initially chosen by doctors.
So, if severe bleeding occurs or the life of the fetus is threatened, the doctor will be forced to resort to emergency surgical obstetrics.
Pregnant women with marginal placenta previa usually undergo a cesarean section. In this case, you can minimize the risk of developing dangerous complications that arise during spontaneous childbirth.
If, before childbirth, a woman was diagnosed with severe anemia due to frequent previous bleeding from the genital tract, then in such a situation she will be prescribed iron-containing medications.
To quickly compensate for the general condition, such medications are administered by injection. Even during a cesarean section during a pregnancy accompanied by marginal placenta previa, there is a high risk of severe bleeding.
During the operation, doctors must monitor the woman’s pulse and blood pressure.
With the development of severe bleeding and massive blood loss, these indicators begin to decrease critically. In this situation, doctors usually resort to parenteral administration of oxytocin or hemostatic agents. The main goal in carrying out such drug therapy is to preserve the life of the mother and her baby.
After the baby is born, doctors must evaluate his general condition. If necessary, the child is given a set of resuscitation measures.
Usually they are required if the baby was born much earlier than expected. Such medical manipulations are carried out by a neonatologist who is in the delivery room during the birth.
After the birth, doctors must monitor the condition of the woman in labor.
With placenta previa, it often happens that during the birth of the baby, the woman loses quite a lot of blood. In order to quickly restore her condition, doctors resort to administering medicinal solutions and, if necessary, hemostatic drugs.
To learn about the dangers of marginal placenta previa, see the following video.
Source: https://o-krohe.ru/placenta/kraevoe-predlezhanie/
Types of placenta previa during pregnancy and their danger to the child and mother: risks of lateral, inferior, posterior complete or partial presentation
During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes numerous changes. Sometimes during this period problems that were not there before or chronic diseases worsen, which provokes some pathologies during pregnancy.
Placenta previa during pregnancy
Placenta previa is a serious problem that poses a high risk for the mother and the child. But, if you take all the necessary measures in time, the situation can be corrected. What kind of pathology is this? What nuances do you need to know?
What is placenta previa: how dangerous is it?
The placenta is a temporary organ that forms in the uterus during pregnancy to nourish and provide the baby with the necessary substances. Simultaneously with the development of the embryo, the placenta also grows. After delivery, she comes out after the fetus. It has two sides, on one side there is an umbilical cord, through which nutritional components are transferred to the baby.
The normal location of the placenta is at the bottom of the uterus or on the sides. It is these parts of the uterus that are the thickest and have a rich blood supply, which allows the fetus to receive nutrition, oxygen and develop properly.
Sometimes the embryo is located closer to the cervix, in the area of the lower segment; accordingly, the placenta is formed there and blocks the exit from the uterus - this is called presentation.
Incorrect fastening causes many problems:
- the fetus does not receive enough nutrients;
- the child will not be able to be born naturally;
- when the placenta separates, there is a risk of bleeding and death of the mother and baby.
Initial risks
In the first trimester, the incorrect position of the placenta poses a danger to the embryo; it receives insufficient nutrients, vitamins and oxygen. Accordingly, it develops more slowly.
Incorrect position is observed in 60% of pregnant women; by the twentieth week it falls or, conversely, rises, thereby becoming in the correct position. In recent weeks, the percentage of women with breech presentation has almost halved.
Dangers in the last trimester
In the last weeks of pregnancy, pathology of the placenta carries a great risk for the baby and mother. The chance of a child being born naturally drops sharply because it blocks the exit from the uterus. Physiologically, the placenta cannot come out before the fetus.
Detachment of the organ is possible, which can cause severe bleeding and death of the woman and child.
It is possible to give birth with a presentation, but only under regular medical supervision.
Causes of incorrect localization of the baby's place in the uterus
The “baby place” is formed in the uterus, in the area where the fertilized egg is implanted. It is this that chooses the location where there are no scars or other defects. Sometimes it is located at the bottom of the uterus, which provokes placenta previa. There are several reasons.
- inflammatory diseases can be provoked by changes in the endometrium in the uterus;
- abdominal operations, curettage, abortions;
- hormonal imbalance;
- active inflammatory infections, tumors.
- several fetuses in the uterus;
- diseases: fibroids, endometriosis;
- congenital pathologies of the uterus, abnormal structure or insufficient development.
Types of placenta previa
There are several types of placenta position:
- Lateral (edge).
- Rear.
- Inferior placental presentation.
- Along the front wall.
Lateral or edge
The placenta is positioned abnormally, covering some part of the internal os of the uterus. In the first trimester, such fastening does not pose a great danger, because the placenta can shift and take the correct position. But you should not treat this negligently, because if this process is not controlled, the organ can crush the nutritional vessels and cut off oxygen, which leads to antenatal death of the fetus.
In the later stages, such presentation is dangerous for the mother and the child. The placenta can detach and cause bleeding, which is fatal for both.
Causes:
- sexual infections;
- abnormal structure of the uterus;
- abdominal operations, scars;
- myometrial depletion;
- pathologies of the uterus and tumors;
- problems with the cardiovascular system;
- abnormal development of the embryo.
Symptoms and dangers
The pathology is accompanied by blood, but the general condition is stable. More often appears during the rest period. It is more convenient to determine the marginal position at 28–32 weeks. At this time, the uterus is most active and preparing for delivery. Much less often, marginal attachment is detected at the beginning of the second trimester.
In the last stages, this position of the organ often causes bleeding as a result of physical exertion, sexual intercourse, and even sudden movements of the fetus, which can provoke a violation of the integrity of the blood vessels.
Regional placement can cause miscarriage. Accompanied by hypertonicity of the uterus and pain in the abdomen. Iron deficiency anemia is often observed.
The embryo receives less nutrients and oxygen, and in general, develops slowly. Often, marginal attachment is caused by an abnormal position of the embryo itself; it can be oblique or transverse.
Treatment
Treatment is prescribed based on the general condition of the mother and fetus. If you feel stable and have no bleeding, outpatient monitoring is possible.
In case of sudden and severe bleeding, urgent hospitalization, rest and lack of stress are needed. It is recommended to wear a special bandage. Drug therapy is used.
In general, if the pathology is detected in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable and the woman can carry the fetus up to 38 weeks and give birth safely.
Rear
With this attachment, the placenta is adjacent to the back of the uterus and closes the exit, thereby making natural delivery impossible.
The reasons are the same as for other incorrect placement. Prevention and treatment measures are similar.
Inferior placental presentation
This pathology is characterized by the location of the reproductive organ six centimeters from the internal pharynx. It is detected in the middle of pregnancy by ultrasound. Often the placenta has migrated to the correct location by the time of delivery.
With the lower location of the organ, minor bleeding occurs, starting from the twelfth week. In the second trimester, exacerbation occurs and partial peeling is possible.
Danger of pathology
The embryo has limited access to oxygen, which negatively affects overall development. For a woman in labor, it causes discomfort in general, causes anemia and a high risk of intravascular coagulation disorders. With the latter, there is a high risk of miscarriage.
Treatment
Complex treatment with drugs is used; if the woman’s health worsens, the woman is sent to the hospital. With this pathology, you need to exclude any stress, sex, visiting baths and saunas.
Along the front wall
The placenta is located on the anterior wall of the uterus. Often observed with low and incomplete presentation. This arrangement is not considered anomalous. It can be detected before the twenty-sixth week of pregnancy. More often, the placenta migrates to the correct place and delivery occurs naturally.
Is the central attachment of the placenta normal?
When the placenta is centrally attached, it completely covers the entrance to the cervical canal. With this pathology, natural delivery is impossible and they resort to caesarean section.
Symptoms and possible dangers are similar to other abnormal attachments.
What are the consequences of breech presentation for the baby?
Incorrect attachment of the placenta causes inconvenience to the woman and the embryo.
Main consequences:
- placental abruption;
- bleeding;
- gestosis;
- anemia;
- fetal hypoxia;
- slow embryo development;
- abnormal position of the fetus;
- miscarriage;
- premature birth;
- stillbirth.
Degrees of presentation
Presentation has several degrees:
Partial
Partial or incomplete fastening is characterized by the fact that the organ partially covers only the internal canal of the cervix, leaving a small hole. With this arrangement, the baby's head cannot pass through the birth canal.
Complete
The placenta completely covers the entrance to the uterus. Childbirth is carried out by caesarean section. Often with this arrangement, complications arise during natural childbirth, and there remains a high probability of mortality.
What are the signs of previa
The main sign of abnormal attachment of the placenta is bleeding. At the beginning and end of the term it means incomplete presentation, and in the second - complete.
How is it determined: at what time is the diagnosis made?
The position of the placenta and the degree of anomaly are determined by ultrasound. During an obstetric examination, the gynecologist can identify the location of the embryo and determine the incorrect position, and detect the absence of uterine hypertonicity.
The attachment of the placenta can be detected already in the first trimester.
When can the placenta change position?
The placenta has the ability to migrate, i.e. move during pregnancy. Most often, she changes position in the last trimester.
Is it possible to cure
Placenta previa can be corrected with medication. The pregnancy is monitored carefully. If necessary, the woman can be hospitalized.
Drug prevention includes the use of drugs (usually Drotaverine, Fenoterol, Dipyridamole, and others). Take measures to prevent anemia.
If the condition is stable and does not require hospital treatment, then the expectant mother is prescribed bed rest, sexual rest, and lack of physical activity and stress.
Prevention of placenta previa: how effective is it?
To prevent improper attachment of the placenta, it is necessary to carefully monitor your health, especially in gynecology: no abortions, curettage, mandatory timely treatment of inflammations and infections.
The most effective way is to plan pregnancy and prevent possible risks. To do this, you need to check the condition of the body in a year or two; it is best to lead a correct lifestyle so that pregnancy does not become a strong burden.
In general, presentation of one degree or another occurs in most women. Also in half of them it migrates to delivery.
How doctors recommend giving birth: cesarean section or natural birth
If the placenta is abnormally attached, the method of birth of the child depends on the general condition of the expectant mother. Complete presentation excludes natural childbirth. With partial, if the woman has no complications and the pregnancy is proceeding normally, spontaneous childbirth is possible. In any case, the risk remains, and therefore the doctor monitors the process, sometimes emergency intervention is required.
If you want to give birth to a child, it is better to carefully plan your pregnancy and get checked for all diseases and abnormalities. Placenta previa without medical supervision poses a great danger to the woman and child.
Source: https://bestmama.guru/zabolevaniya/predlezhanie-platsenty-pri-beremennosti.html
Placenta previa and natural delivery: chances
How dangerous is placenta previa, is natural childbirth possible, and is long-term observation in a hospital always necessary? Read our article.
General information about the placenta
The afterbirth (baby place), as the placenta is also called by old-school obstetricians, is necessary to supply the fetus with nutrients and oxygen. Normally, it is located in the fundus of the uterus, mainly along the posterior wall. But it can also be located in the front.
The principle by which the fertilized egg is “attached” has not yet been fully studied. Doctors say that the future embryo does not attach to problem areas of the uterine epithelium.
But according to statistics, 1% of pregnancies are complicated by placenta previa. In this case, it is attached to the lower part of the uterus. In this case, the pharynx is partially or completely blocked. The danger to the fetus in this arrangement is a lack of nutrition and oxygen due to poorer blood supply.
Classification of presentation
- Full presentation – when the baby’s place completely covers the exit to the cervix. It is also called central. Pathology occurs in 20% of all anomalies. In most such cases, one cannot count on upward migration of the placenta. If the pharynx is partially blocked, they speak of incomplete presentation.
Statistically, it occurs more often. In approximately 35-50% of cases. If you were given a similar diagnosis at the beginning of your term, do not panic. Between 10 and 22 weeks of pregnancy, this disorder is common. The placenta moves higher in 90% of cases. By the end of pregnancy, there is no longer any talk of pathology.
- Partial presentation can be marginal or lateral. In the first case, the lower edge of the placenta is located level with the exit from the uterus. In the second, the edge of the child's seat partially covers the pharynx.
Doctors also distinguish the so-called low location of the placenta. This condition is not called previa.
The edge of the placenta in this case is located 5 or less centimeters from the pharynx.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The main manifestation of placental presentation is bleeding. They pass painlessly, the tone of the uterus does not increase. They can often occur at night and stop by the morning.
Bleeding occurs spontaneously and also stops. In the later stages, they can be provoked by physical activity and sexual intercourse.
Even with minor discharge, you should consult a doctor.
He will be able to diagnose presentation:
- Ultrasound with a transvaginal sensor is the most informative method; it provides complete information about the condition and location of the child’s place;
- during a vaginal examination - the method is used less and less, there is a high risk of bleeding;
- Ultrasound through the abdominal wall - the probability of error is 25%.
Why is breech presentation dangerous?
If after 30 weeks the diagnosis of placenta previa has not been changed to a low location, there is a high risk of complications.
It can be:
- accretion of the baby's place - the villi with which it is attached to the uterus grow deeply into it (placental tissue cannot separate; in especially severe cases, removal of the uterus is required);
- high risk of preterm birth – children are born premature;
- placental abruption, leading to oxygen starvation of the baby;
- intrauterine growth retardation.
Pathology can also provoke premature rupture of amniotic fluid. It leads to low or breech presentation of the fetus.
During childbirth, in most cases, heavy bleeding develops. The woman needs a blood transfusion. In the postpartum period, she has a high risk of developing inflammatory diseases of the endometrium of the uterus.
Children are born with low body weight. They are more likely to have pathologies of the respiratory system that require urgent resuscitation. Subsequently, mental and physical developmental delays may occur.
Causes
Pathology is more common in repeat pregnancies. This is due to the depletion of the epithelium of the uterus and the female body in general.
The following diseases lead to low placenta or placenta previa:
- endometritis;
- polyps in the uterine cavity;
- myoma.
Any manipulation that damages the uterine mucosa can cause breech presentation. Abortions, “purges,” cesarean sections, and various types of laparoscopy increase the risk of pathology significantly.
- With some heart or liver diseases, the blood supply to the pelvis deteriorates.
- This leads to the formation of areas on the uterine mucosa that are “unfavorable” for the attachment of a fertilized egg, which can provoke presentation.
In some cases, the problem is associated with abnormalities of the ovum. Due to the incorrect location of the villi, it is attached to the lower part of the uterus.
Features of pregnancy
In the presence of previa, or when we are talking about low placentation, women are recommended to go to bed. You need to give up excessive physical activity and sex. Try to avoid stressful situations.
There is a high risk of developing anemia, so starting from the second trimester, the expectant mother is prescribed iron supplements.
There are no special medications or methods to raise the placenta during pregnancy. At periods up to 30 weeks and a diagnosis of partial (marginal) presentation, there is a higher chance of migration of the placenta.
The greatest danger for a woman and baby is bleeding. Even minor cases require hospitalization. If they occur at the end of the second term, the woman may be in the hospital until delivery. Especially if it is repeated bleeding.
After 33 weeks, there is a high risk of heavy blood loss; the expectant mother is often asked to wait for the birth in a hospital.
In the maternity hospital, in addition to monitoring the condition of the mother and baby, local treatment of symptoms and preparation for childbirth are carried out. The woman is prescribed antispasmodics to reduce the tone of the uterus and drugs that improve blood supply to the fetus.
If blood loss as a result of placental abruption is 250 milliliters or more, pacemaker is prescribed. At the same time, the efforts of doctors are aimed at saving the woman, and the degree of maturity of the fetus is taken into account to a lesser extent.
Childbirth
If the exit from the uterus is completely blocked, a caesarean section is prescribed. It is carried out on a line of 36-38 weeks as planned. The woman is hospitalized a week before the scheduled date of the operation.
CS is also indicated for aggravated incomplete presentation.
When choosing a method of delivery, consider:
- fetal position;
- woman's age;
- presence of scars on the uterus;
- width of the pelvis.
A medical consultation will allow natural childbirth if the cervix is ready and labor is active. At the same time, constant monitoring of the fetal condition is carried out (CTG, auscultation). A gynecological surgeon is called to the woman in labor to perform an emergency CS, and resuscitation is prepared.
Most often, even partial presentation becomes an indication for cesarean section, so great is the risk of heavy bleeding in the mother.
Prevention
The cause of presentation may be a normal abortion. It is better to avoid this method of abortion, when the modern contraceptive market can offer a large selection of safe drugs.
A history of genital pathologies and hormonal dysfunctions can provoke this pregnancy complication.
To protect yourself from the risk of placenta previa, doctors recommend that women undergo gynecological examinations on time. This is done twice a year.
You should consult a doctor if you suspect an STD. Untreated infections most often cause endometritis and other pathologies of the uterine mucosa. Properly selected contraception, which eliminates the risk of abortion, will also protect you.
Conclusion
Presentation is a serious pathology of pregnancy. It can threaten the life of the mother and fetus. In this case, it is more important than ever to follow all the doctor’s instructions.
Natural childbirth with such a diagnosis is rather an exception. The risks are too great for both: mother and child. Presentation is an indication for caesarean section. It is prescribed as planned and the woman is warned about the operation a week before giving birth.
Source: https://its-kids.ru/predlezhanie-platsenty.html
Regional placenta previa along the posterior or anterior wall: prognosis of childbirth with a dangerous diagnosis
The membrane of the fertilized egg provides nutrition and protection to the baby while in the womb. There is a flow of nutrients, vitamins, and oxygen through the vascular bed of the placenta. The membrane is a hemoplacental barrier.
According to statistics, four out of a thousand pregnant women have an abnormal location of the placenta. What does such a diagnosis mean and why is it bad? What factors influence the pathological attachment of a child's seat? How to diagnose marginal displacement of the placenta? Can pathology be prevented or not? What are the consequences of placenta presentation for delivery?
Where and how is the placenta normally located?
The transformation of the chorion into placental tissue occurs by the 3rd month after conception. Final maturation occurs at 16 weeks. It depends on the last ovulation before conception.
The placenta develops along with the growth of the fetus.
How complete the placental exchange between mother and child will be and whether the baby will have enough nutrients and oxygen depends on how the baby’s seat is secured and its growth.
The normal location of the amniotic sac is along the back or front wall of the uterus. Side mounting is also available. By the beginning of the third trimester, the distance from the edge of the fetal place to the exit from the uterus should be at least 7 centimeters.
In most cases, the fertilized egg is attached to the uterine fundus. Other options require constant monitoring by doctors.
Types of abnormal placentation
According to the location of the child's seat, they distinguish full, low, lateral, incomplete, and central presentation. The greatest danger to full pregnancy is complete occlusion of the pharynx. Central presentation is determined during a gynecological examination or ultrasound. With such a presentation, natural childbirth is impossible; a caesarean section is required.
Low presentation means that the exit from the uterus is not blocked. The baby's place does not reach the pharynx, but is located at a distance of less than 7 centimeters from the cervical canal. Such placentation has the most favorable prognosis. Natural childbirth is possible.
Partial marginal attachment means incomplete overlap of the internal canal of the cervix by the placenta. The clearance is too narrow. The newborn's head will not fit through it, which means the baby will not be able to exit through the genital tract.
Lateral and marginal placenta previa are determined during a vaginal examination and confirmed during an ultrasound examination. With lateral presentation, the placenta partially covers the exit from the uterus. When the edge is located next to it, without blocking the entrance. There is also partial attachment along the posterior and anterior wall with incomplete, low presentation.
Is it possible for the placenta to shift as the fetus and uterus grow?
The uterus gradually increases over time, because the child inside the mother’s womb grows and develops. The baby's place moves and may rise a little during pregnancy. Such a process cannot be stimulated from the outside.
The task of doctors in case of abnormal attachment of the placenta is to prevent ruptures and detachment of the fetal membrane, minimize the amount of blood loss during bleeding, and promote delivery naturally or by cesarean section. Treatment tactics for detected presentation include constant monitoring of the well-being of the woman and child.
Diagnostic methods
The main way to diagnose marginal placenta previa is transvaginal ultrasound. The examination is carried out through the vagina. The accuracy of diagnosis is 99–100%. The method has no contraindications. It is also used to determine the length of the cervix and the distance from the placenta to the uterine os.
Transabdominal ultrasound is performed through the anterior abdominal wall. The study has a large error when diagnosing marginal presentation (accuracy - 92%).
An alternative to vaginal insertion of the sensor is transperineal ultrasound, in which the sensor is located in the perineal area.
In addition to the place of attachment of the placenta to the uterine wall, ultrasound examination is used to determine the gestation period, the functionality and structure of the umbilical cord, the weight and size of the fetus, and possible developmental pathologies.
From the 36th week, when the placenta is present, magnetic resonance imaging is indicated. The data is used to identify possible placenta accreta and determine delivery tactics.
Features of marginal presentation
After diagnosis and determination of pathological attachment, presentation is assigned one of the following degrees:
- The edge of the child's seat is located at a distance of more than 3 centimeters from the internal pharynx.
- The placenta reaches, but does not close, the exit from the uterus.
- The internal os is partially blocked. The placenta is located asymmetrically on the anterior or posterior wall.
- The child's seat is located symmetrically in the center above the pharynx, completely covering the exit.
Regional presentation is usually accompanied by bloody discharge. They begin at 28–31 weeks and continue throughout the third trimester, often until delivery. Usually the bleeding is painless and of low intensity. Loss of blood causes a decrease in hemoglobin. To avoid anemia, iron supplements are prescribed.
Causes of pathology
The second group of reasons is related to the characteristics of a woman’s body. These include:
- underdevelopment, abnormal structure or location of the uterus;
- thinning of the endometrium due to abortion, curettage;
- perforation of the uterine walls;
- caesarean section, childbirth with complications in the anamnesis;
- diseases of the genitourinary system.
Congestion and poor circulation in the pelvis also prevent the embryo from fully implanting. Also, the embryo may not attach properly due to excessive physical exertion.
Course of pregnancy
Considering the severity of the consequences of improper attachment of the placenta, the woman should be under constant supervision throughout the entire period of gestation. In the absence of pain and bleeding, routine examinations are carried out in the same order as during pregnancy without pathologies. At 12–20 weeks, one visit to the doctor per month is indicated, from the 20th week – two.
The course of pregnancy depends on the placenta attachment site - along the back or front wall, central or along the edge of the cervical canal. Regular monitoring of the pregnant woman's condition is indicated. Treatment tactics depend on the frequency of bleeding, the volume of blood lost, the presence of anemia and other complications. General recommendations:
- avoid excessive physical activity;
- avoid stress;
- stop sexual activity;
- take multivitamins and supplements containing iron;
- increase the amount of protein in your diet.
From the 24th week of gestation, regardless of the woman’s well-being, hospital stay is indicated. In some cases, medications are prescribed that reduce the contractile activity of the uterine myometrium, sedatives, antispasmodics and tocolytics. To establish placental blood flow between the fetus and mother and strengthen the walls of blood vessels, hormonal drugs are prescribed.
Possible complications of pregnancy
Frequent complications:
- fetoplacental insufficiency caused by circulatory disorders in the lower segment of the uterus;
- early aging of the placenta;
- oxygen starvation of the fetus;
- breech presentation of the fetus due to lack of space in the lower uterus for the head;
- gestosis;
- polyhydramnios;
- ischemia, congenital heart defects.
Hypoxia and bleeding cause a threat of miscarriage. Carrying with placental presentation often ends in premature birth.
Delivery with marginal placenta previa
Partial presentation may result in natural birth. The delivery option is finally determined when the cervix is dilated by 5–6 centimeters. The amniotic sac is opened. As the baby's head descends, it compresses the blood vessels, which stops the bleeding.
The prognosis for natural childbirth is favorable if labor is active, the baby is head down, and the cervix is mature. When passing through the birth canal, a child with a low-fixed placenta can compress the umbilical cord, and this is dangerous: with an acute lack of oxygen, stillbirth is possible. If completion of labor naturally is not possible, a caesarean section is performed.
Natural delivery is impossible with complete presentation. The placenta, which covers the exit from the uterus, completely peels off during childbirth. This causes severe bleeding, which is life-threatening for the woman and child. A planned cesarean section is scheduled.
Is it possible to prevent improper attachment of the placenta?
The risk group for abnormal attachment of the placenta includes women over 35 years of age with a history of abortion, cesarean section, or uterine surgery.
To prevent problems with your child’s place, you need to lead a correct lifestyle.
It is important to monitor the functioning of the reproductive system and use contraception to prevent unwanted pregnancy. It is necessary to promptly identify and treat diseases of the genitourinary system.
If a woman has hormonal dysfunction, pregnancy should be planned and her hormones should be adjusted first. It is impossible to completely avoid the risk of pathology even if the woman’s health is ideal. Abnormal presentation caused by the characteristics of the ovum cannot be prevented.
Source: https://VseProRebenka.ru/beremennost/plod/kraevoe-predlezhanie-placenty.html
Delivery with placenta previa
Placenta previa can be partial (incomplete) or complete. With partial pharynx, the internal pharynx is not completely blocked or the placenta touches it with its lower edge, and with complete pharynx, the internal pharynx is completely blocked.
Placenta previa is dangerous due to complications both during pregnancy and childbirth. Often, when the first contractions appear or during childbirth, bleeding occurs, which is life-threatening for the woman.
Gestation period for delivery with placenta previa
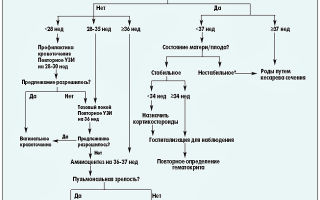
When placenta previa occurs, all possible measures are taken to maintain the pregnancy until 37–38 weeks. When this period is reached, doctors, regardless of the type of placenta previa, insist on delivery by cesarean section. In this case, it is possible to prevent bleeding and large blood losses by the mother in labor.
If partial placenta previa, although it does not cause bleeding, is combined with another complication of pregnancy (breech presentation, polyhydramnios) or the pregnancy is multiple, there are uterine scars in other cases, then a planned cesarean section is performed at 37-38 weeks.
In case of complications of pregnancy with placenta previa, surgical delivery is indicated at any stage of pregnancy . A complication may be the opening of massive bleeding, which threatens the woman’s life, as well as the development of untreatable hypotension or anemia resulting from periodic bleeding and causing deterioration in the condition of the fetus.
Delivery with complete placenta previa
With complete placenta previa, natural childbirth is impossible. The placenta blocks the birth canal through which the baby must pass at birth.
During childbirth, the fetus puts pressure on the placenta and it detaches completely, causing massive bleeding. This is very dangerous for the life of the woman and the fetus. Therefore, with complete placenta previa, a planned caesarean section is performed.
Delivery with incomplete (partial) placenta previa
A woman with incomplete (partial) placenta previa has the opportunity to give birth on her own. Natural birth is permissible in the absence of bleeding during contractions, any indications for cesarean section, good condition of the woman and fetus, and dilatation of the cervix. In other circumstances, a caesarean section is performed.
In the case of natural childbirth, if slight bleeding occurs before the onset of labor, the amniotic sac is opened, the amniotic fluid is poured out, and the descending fetus with its head presses the edge of the placenta, thereby preventing it from exfoliating.
If no further bleeding occurs, labor ends naturally. If the bleeding still does not stop, the birth ends with surgery.
Complications after childbirth
After the birth of a child, bleeding may occur due to weak contractile activity of the uterus at the location of the placenta.
Therefore, in order for the uterus to contract normally, after the second stage of labor (with natural childbirth) or after the baby is removed (with a caesarean section), the woman is given drugs that increase tone and cause contractions of the uterus. For example, oxytocin. If the placenta does not come out well, it is removed manually.
In severe cases, when it is impossible to stop the bleeding after removing the child and the woman’s life is in danger, the uterus is removed.
Tatyana Tereshkova
Source: https://mambest.com/page/rodorazreshenie-pri-predlezhanii-placenty