Home › Papillomas
04.04.2019
What to do with papillomas on the back?
All information on the site was checked by an employee of
the Pervomaisky Branch of the Moscow Scientific and Practical Center for Dermatovenereology and Cosmetology.
The appearance of papillomas on the skin of the back is quite common. Many people do not attach importance to the specific formations that have arisen, mistaking them for moles until the growths begin to cause discomfort.
In fact, papillomas are a sign of the HPV viral infection present in the body , the carriers of which are the majority of the world's population, about 90%. Often, carriers of papillomavirus are unaware of its presence in the body for many years.
Under the influence of unfavorable factors and decreased immunity, the virus is activated and leads to the formation of papillomas, which are not just a cosmetic defect, but can cause serious harm to health.
Reasons for appearance
The papilloma virus can be transmitted both sexually and through household contact.
The method of infection can be:
- touch, handshake;
- unprotected sexual contact;
- using other people's hygiene products and personal belongings;
- visiting public places (toilets, baths);
- infection of a child during childbirth from the mother.
The virus is able to penetrate the human body in the presence of the slightest disturbances of the epithelium: wounds, cuts, microcracks, scratches. But, even if infected, HPV may not manifest itself in any way until its amount in the blood exceeds the norm. In this case, the virus is activated.
The main provoking factors include:
- weakened immune system;
- the presence of chronic infections and hormonal disorders;
- indiscriminate sexual contacts;
- alcohol abuse and smoking;
- stressful situations, depressive states;
- pathologies associated with the gastrointestinal tract;
- long-term use of potent medications;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene standards.
Regardless of the reasons, the appearance of formations cannot be ignored.
What does papilloma look like?
There are many types of tumors associated with HPV.
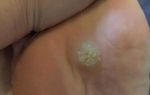
Papillomas on the back are pointed growths, but can also be flat.
- Flat papilloma is similar in appearance to a mole, has a clear border, and is usually darker in color than the epithelium.
- Pointed - resemble keratinized papillae, having thread-like “legs” and protruding above the surface of the skin. The size of the formations often reaches several centimeters.
Papillomas, regardless of the type, can appear either in a single copy or in large numbers.
Papillomas grow in colonies
What is the danger of papillomas on the back?
Due to the absence of painful symptoms, the growths do not cause any discomfort to the infected person, except for their unaesthetic appearance.
- The danger of HPV lies in the fact that it is one of the factors in the appearance of a malignant tumor. With a high oncogenicity of the virus, the likelihood of papilloma degeneration into cancer cells increases significantly.
It is possible to determine what type of oncogenicity the papillomavirus belongs to only through a medical examination . 16 and 18 strains of the virus are the most dangerous. - Papillomas formed on the back are constantly exposed to mechanical stress when changing clothes or coming into contact with clothing, which can lead to injury and sometimes rupture. Infection can penetrate into the resulting wounds, swelling, inflammation, pain, and suppuration appear. Multiple formations may appear at the site of the torn growth .
If the damaged papilloma has increased in size and changed color, you should immediately seek qualified medical help.
Drug treatment
To treat HPV, complex therapy is prescribed, including:
Antiviral drugs:
- Viferon
- Isoprinosine
- Panavir
- Cycloferon
- Allokin-alpha.
Prescribed in the following cases:
- the PCR method confirmed infection with papillomavirus of high and potentially high risk of oncology;
- high activity of the virus (confirmed by multiple papillomas);
- immunodeficiency, in which the body is unable to cope with the virus on its own.
Contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation.
Medicines that help strengthen the immune system:
- Lycopid
- Polyoxidonium
- Ferrovir
- Wobenzym
- Kolpocid
- Laferobion
- Immunomax
The action of the drugs is aimed at strengthening the immune system, which, due to its weakened state, is not able to resist HPV. Medicines in this group are prescribed after consultation with an immunologist. Contraindicated for nursing mothers, pregnant women and those with individual intolerance.
Destructive (burning) agents:
Preparations containing aggressive substances that destroy epithelial cells are used to remove papillomas from the skin.
- Cryopharma;
- Solcoderm;
- Kondilin;
- Verrucacid;
- Papilight;
- Fresol;
- Super clean.
Ointments for papillomas:
- Salicylic;
- Oxolinic;
- Viferon;
- Solcoderm;
- Aldara and others.
To prescribe optimal treatment in each individual case, medical examinations and tests are carried out, depending on the results, the doctor selects medications and the required dosage.
Removal of papillomas
In cases where drug treatment does not produce the desired effect, the papillomas are removed. There are the following methods for getting rid of tumors:
- Liquid nitrogen /cryotherapy/.
The papilloma is instantly frozen. As a result, the growth cells die. - Radio waves /radiosurgery/.
The cutting is done using radio waves. At the same time, healthy skin cells are not injured, burns and the possibility of infection are excluded. - Laser beam /laser therapy/.
It is the most popular and painless method. - Electric current /electrocoagulation/.
Removal is carried out using electric power. If necessary, anesthesia is used. - Surgical method.
Used quite rarely. The growth is cut off with a scalpel using local anesthesia. After the operation, scars and scars remain. - Chemical cauterization.
Removal /burning/ using salicylic acid and cantharidin.
Despite the favorable prognosis, after completing a course of treatment, it is worth considering that even if the papilloma is removed, HPV continues to exist in the body, and relapse is possible at any time.
You cannot get rid of papillomas on your own . Self-medication usually leads to infection and other serious consequences.
A practicing dermatovenerologist will tell you about the intricacies of removing papillomas:
Rehabilitation rules
After the papillomas removal procedure. The next important stage is the rehabilitation period. Both the preservation of the cosmetic effect and the prevention of negative external influences depend on strict adherence to the recommendations.
Basic Rules:
- Do not cover the resulting crust with a band-aid.
- Do not wet the area of the back where the papilloma was removed for several days.
- Do not tear off the crust, which protects against infection.
- Avoid direct exposure to sunlight during the entire recovery period of the skin.
Prevention
HPV vaccine
Compliance with preventive measures will avoid infection and activation of HPV.
- take measures to strengthen the immune system;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- exercise;
- adhere to a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition;
- avoid promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- undergo routine medical examinations;
- timely treatment of infectious diseases;
- Experts recommend getting vaccinated against HPV.
What to do with papillomas on the back? Link to main publication
Source: https://papillomam.ru/papillomi/na-spine
What is the danger of papilloma on the back: what it looks like and whether it needs to be removed
A papilloma found on the back, more popularly known as a wart, leaves some indifferent and causes concern for others.
But is there any reason for it?
First, you need to understand the reasons for the formation of papillomas.
Why do papillomas occur on the back?
Warts of any kind are caused by infection with the widespread filterable human papillomavirus (HPV) through direct, primarily sexual, contact with a carrier or through various objects. The duration of the incubation period is from several weeks to 5 months.
The development of papillomas is promoted by reduced cellular immunity, excessive sebum secretion, and microtrauma of the skin, for example, local irritation, minor abrasions.
As a result, with the development of the clinical form of a viral disease, small tumor-like formations may be found in various areas of the skin: condylomas of the anogenital area, papillomas on the back, face, arms, the causes of which lie in damage to the surface epithelium by the virus. Latent (virus carriage) and subclinical forms are asymptomatic.
Video
Papilloma on the back
Types of papillomas
About a hundred types of papillomavirus can live on the surface of the skin. Each of them has a different degree of risk of malignancy, causes damage to different locations, and affects how the papilloma looks. Warts are distinguished:
- ordinary or simple - rough papules of a yellowish-gray color or matching the color of the skin, of varying sizes (up to 1 cm), sometimes merging into bumpy plaques, localized mainly on the back of the hands, feet, face and scalp;
- flat (youthful), usually occurring in children, youth, young women - flattened, smooth, rounded or polygonal in shape, flesh-colored, yellowish-brown, less often bluish in color and erupting in a short time on the skin of the hands and forehead , chin, knees, often in large quantities;
- filamentous - elongated, oblong formations, most often occurring under the female breast, in the armpits, face, neck and are found mainly in older people;
- plantar - sharply painful elongated papillae surrounded by layers of keratinized yellowish skin up to 2 cm in diameter, which appear on the plantar surface of the feet and resemble a callus;
- genital - condylomas predominantly of the anogenital area in the form of individual papillary formations of a flesh-colored, pink or bright red color on a thin, short stalk, prone to proliferation and the formation of cauliflower-type clusters.
Papillomas prefer moist places with poor air exchange, but they often form over the entire surface of the skin, including on the back. Papillomas are also observed on the mucous membranes of various anatomical systems.
What is the danger of their appearance?
Most warts caused by the human papillomavirus are benign and often regress spontaneously.
There have been cases of spontaneous disappearance of HPV, especially in young people.
If so, the question arises: is it necessary to remove papillomas from the back? The decision must be made by the doctor after examination and diagnostic testing.
It should be remembered that some types of papillomas are prone to malignancy and can lead to the development of squamous cell skin cancer and malignant tumors of the genital organs, especially in women.
In addition, they can be subject to chronic trauma, cause physical and aesthetic discomfort, and lead to the development of complications: itching, bleeding, bacterial or fungal infection.
Large papillomas are also dangerous, because if their legs are twisted, the risk of detachment or necrosis of the formation increases with the development of subsequent inflammation.
Diagnostics
If you find that papillomas have begun to grow on your back or in any other area, you need to contact a dermatologist (dermatovenereologist) for diagnosis and selection of the necessary treatment. The examination can be carried out using:
- PCR diagnostics or Digene test - to detect papillomavirus;
- histological methods - for examining tissue after biopsy for persistent and atypical lesions;
- endonuclease DNA analysis, hybridization method - to determine the type of virus.
In the case where papillomas are visible to the naked eye, in most adult patients the diagnosis can often be established after a visual examination.
If necessary, the doctor carries out differential diagnosis with other skin diseases: molluscum contagiosum, lichen, etc.
, consultations with related specialists are scheduled: immunologist, oncologist, urologist, gynecologist, proctologist.
Treatment methods
There are no drugs for systemic use against the virus, so papillomas on the back, like any others, are treated using a whole range of therapeutic measures. Combined treatment is aimed at the destruction of papillomas and suppression of viral activity by activating the body's immune forces.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment includes antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy; if necessary, cytostatic (antitumor) agents are used. Don't forget about taking vitamins. When treating papillomavirus disease, tocopherol acetate (vitamin E) is often additionally prescribed.
Antiviral and immunostimulating drugs
The main direction in HPV therapy is to strengthen antiviral immunity. This stimulates the body’s fight against the virus, reduces viral activity, and helps get rid of warts as quickly as possible.
Papillomas on the back, face, arms, genital warts are treated with local or systemic (subcutaneous, intramuscular, intravenous, rectal) use of interferons: viferon, genferon, intron A, altevir and others. Preference is given to recombinant interferons.
When prescribing treatment with interferons, the doctor takes into account the patient’s immune status and the possibility of developing side effects (flu-like conditions, decreased synthesis of interferons in the body), therefore their thoughtless independent use is unacceptable.
Immunotropic drugs and antiviral agents with immunomodulatory effects are also prescribed:
- Lycopida;
- Isoprinosine;
- Gepon;
- Panavir;
- Immunomax;
- Allokina-alpha;
- Gronprinosina.
Treatment of papillomavirus in a child with any such drugs is carried out strictly as prescribed by the doctor in an individually selected dosage.
Removal of papillomas
Destructive methods include various methods of physical (surgical) and chemical removal of papillomas. Physical destruction is carried out using:
- electrocoagulation - using high frequency current;
- laser therapy – CO2 laser;
- radio wave surgery - using a radio knife;
- simple excision with a scalpel;
- cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen, nitric oxide and carbon dioxide, which is the safest and most effective way to remove papillomas, regardless of location, which avoids the formation of scars.
Chemically, papillomas are removed using various drugs: solcoderm, feresol, trichloroacetic acid. However, medical removal may lead to scarring of the skin tissue or subsequent pigmentation.
Among the over-the-counter pharmaceutical products used in the home treatment of papillomas, one can note salicylic acid, an alcohol solution of iodine, and a lapis pencil.
The method of destructive therapy is chosen by the attending physician, based on the location of the papillomas, the size of the growths, and the extent of the spread of the rash on the back. The combined use of non-drug methods is possible. During removal, local anesthesia is used.
Folk remedies
The arsenal of traditional medicine has accumulated many recipes for getting rid of warts. Almost all of them are easy to use:
- apply a mixture of Vaseline and fresh garlic gruel to the papilloma overnight, while the surrounding skin must be protected from the aggressive effects of the burning composition with an adhesive plaster;
- twice a day, lubricate the papilloma on the back with juice squeezed out from celandine (preferably orange - from its root part) or milkweed juice, and after its surface turns black, carefully cut off. Continue the procedure until it disappears completely;
- Soak the peels of citrus fruits (tangerine, lemon) in vinegar for three days, then fix them on the papilloma overnight. If the wart is large, the procedure should be repeated;
- regularly apply a mass of raw rowan berries to the papilloma;
- small young warts can be reduced with dandelion juice;
- several times a day, lubricate the rashes on the back with banana peel, potato, egg white;
- Apply artificial ice to children's warts and leave for some time - if possible. To disappear, several treatment sessions are necessary.
Various essential oils have proven themselves to be effective in getting rid of wart rashes: thuja, fir, tea tree, but they cannot be used for papillomas located on the mucous membrane. Oils are added to cosmetics for daily use or applied spot-on in a mixture with any vegetable oil.
Rehabilitation rules
Skin care and the duration of healing after removal of papilloma from the back depend on the type of destruction method used.
Immediately after the procedure, the wound may be sore, there may be slight swelling and redness. The surgical method using a scalpel is the most traumatic.
Healing is easiest after removal with liquid nitrogen. During the postoperative period it is prohibited:
- cover the resulting scab with an adhesive plaster;
- remove the formed crust, rub it, injure the wound;
- apply cosmetics to the surgical site that have a moisturizing and softening effect, as well as those containing alcohol;
- treat the wound with a solution of potassium permanganate or calendula tincture to avoid allergic reactions;
- wet the damaged skin in the first days after surgery.
Compliance with these rules will reduce the risk of complications from the procedure associated with infection, the development of inflammation, and suppuration.
But what needs to be done?
- As prescribed by the doctor, treat the wound with antiseptic agents (for example, fucarcin), and in case of surgical removal, apply a protective bandage with an antibacterial drug (ointment, solution).
- Avoid exposure to sunlight and avoid hypothermia.
- Follow all doctor's orders.
- Avoid deficiency of vitamins E and A, take vitamin and mineral complexes.
- Support immunity by consuming herbal adaptogens, ascorbic acid, ginseng tinctures, and echinacea.
During the course of drug treatment, you need to try to avoid stress, overwork, eat right, and spend enough time in the fresh air.
Prevention
To avoid relapse of the disease, preventive measures aimed at strengthening the immune system are required. You also need:
- use of barrier contraception when changing sexual partners to reduce the likelihood of HPV reinfection;
- maintaining personal hygiene;
- timely completion of medical examinations;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- rejection of bad habits;
- compliance with the rules of a balanced diet high in vitamins and minerals.
It is important to remember that only careful attention to your health and an integrated approach to the treatment of a viral disease will allow you to achieve good results.
Source: https://papilom-net.ru/vpch/papilloma-na-spine
Papilloma on the back photo
The problem of papillomas is familiar to almost everyone. This pathology is a benign formation on the human body. They look different. There are about a hundred types of virus, which provokes their development. Typically, a papilloma on the back (see photo) is a small keratinized tubercle or a soft skin elevation on a thin stalk.
Why is papilloma on the back dangerous?
This disease has no pronounced symptoms. The growths hardly bother the patient, they only cause aesthetic inconvenience.
The danger of pathology is as follows:
- Some of their varieties have a tendency to develop oncology.
- During contact with clothing or friction, the growth becomes inflamed, causing pain and itching.
- It is easy to damage a tumor on the back, then it spreads quickly and a bacterial infection can occur.
Why do papillomas occur on the back?
The main cause of papilloma on the back is a virus. It is dangerous because it remains in the body most of the time without causing symptoms. This infection can persist for years until the immune system weakens. Statistics say that 80% of people are carriers of the pathogen.
The most common ways of transmitting the virus are:
- promiscuous sex life;
- infection by the mother of the child during childbirth;
- visiting public baths, swimming pools, ponds;
- sharing hygiene items.
The infection penetrates through any damage to the skin and mucous membranes. Therefore, you should be careful in matters of hygiene and remember about condoms.
Papilloma on the back: treatment
If papilloma appears on the back, treatment must begin immediately. First of all, you should get tested for the presence of papillomavirus, then go for a consultation with an immunologist. He will prescribe complex therapy to strengthen the immune system.
The largest formations are removed. They are maternal (main), which provoke the growth and emergence of new ones. After their elimination, the spread of shoots is significantly reduced. Fans of traditional medicine should be careful when using burning agents. They leave scars, deep burns, and pigmentation. You can remove tumors using the following methods:
- a liquid nitrogen;
- electrocoagulation;
- radio wave knives;
- laser removal.
The rehabilitation period after removal of growths on the back is very important. It is necessary to take care of the resulting wound after the procedure. It is forbidden:
- to rip off;
- expose to sunlight;
- apply cosmetics to the inflamed areas.
To reduce the likelihood of relapse, your doctor may prescribe a course of medications.
zppp.saharniy-diabet.com
Are there malignant papillomas?
Human papillomavirus is a disease that manifests itself in the form of growths of various shapes.
- They can be small (up to 1 mm) or large (about 2 cm).
- From the very beginning, the papilloma has a flesh-colored tint, and then becomes brown.
- Warts usually form near the eyes, on the head, knees, elbows, groin, armpits and neck.
- In addition, growths can appear in inconspicuous places, for example, in the vagina and on the cervix.
Basically, these formations are benign, but doctors also identify papillomas, which are associated with a precancerous condition.
Reasons for appearance
The occurrence of papillomas is the result of a viral disease.
Its cause is primarily a weakened immune system.
This virus is very insidious. Once in the human body, it is able to hide and wait for several years for the right opportunity to reveal itself in full.
Sometimes a simple nervous disorder is enough to trigger the activation process.
The likelihood of getting sick increases in people who abuse smoking, alcohol, or have multiple sexual partners.
Methods of infection
Papilloma is not a congenital disease, it is acquired.
sexual transmission of HPV
Human papillomavirus infection can be transmitted:
- during self-infection. Autoinoculation is infection of oneself as a result of careless handling of sharp objects (for example, when shaving) and failure to comply with hygiene rules (for example, when epilating);
- by everyday means. Infection through household means is possible due to insufficient hygiene, general use of towels, hygiene items, shoes;
- during sexual intercourse. Sexual transmission is also very common;
- during childbirth. The virus is transmitted during childbirth from mother to newborn (0.1% of cases when the woman has an infection).
Photo
Why is HPV dangerous?
- Can papilloma be dangerous?
- There are over 100 types of papillomavirus, doctors divide them into 2 main groups: non-oncogenic and oncogenic.
- Each type of virus manifests itself differently in the human body.
- To determine whether a papilloma is benign or malignant, it is necessary to conduct a histological analysis after removal.
- If no degenerated cells are found, it does not pose any danger to humans.
- But sometimes a formation on the body can be dangerously degenerate, resulting in a cancerous tumor.
- In some cases, papilloma can cause bleeding.
- And when localized on the mucous membrane of the larynx, it can cause hoarseness or impaired respiratory function.
Malignant papillomas
The most insidious for women are HPV 16 and 18.
- As a result of their activities, there is a risk of developing cervical cancer.
- And in men, malignant papilloma affects the penis.
- Highly oncogenic types of the virus can also cause anal cancer.
- degeneration into cervical cancer
- The disease usually reaches its peak after 50 years.
- Degeneration occurs slowly; first, new infected cells appear inside the papilloma, then they change their function and become malignant.
- Malignant papilloma can become inflamed, turn black, become covered with a dense crust and begin to bleed.
- To prevent the development of an oncological process, people who are found to have oncogenic types of HPV require mandatory vaccination, regular monitoring, and timely treatment.
Diagnosis of HPV
Diagnosing HPV does not cause any difficulties. The virus is detected by a doctor during a medical examination.
- examination of tumors by a doctor
- In the absence of visual manifestations of infection, it can be diagnosed through a more in-depth examination.
- There are 2 main methods for diagnosing papillomavirus.
- PCR. A qualitative analysis that determines the presence or absence of a virus. Thanks to PCR, the type of virus is established and its dangerous types are diagnosed.
- Digene HPV test. It is an effective diagnostic method. DNA analysis makes it possible to determine the concentration of the virus in the body and its type.
In addition to tests for papillomavirus, a cytological examination is also performed. This method detects infection in 80% of cases.
cytological examination
When diagnosing a virus with increased oncogenic risk, the doctor prescribes further examination:
- colposcopy. This test is performed to determine the size and location of the lesion and exclude the possibility of invasive cancer;
- biopsy. Removal of small areas of tissue for examination under a microscope;
- urethroscopy. Detection of the virus in the urinary system.
Blood tests, smears, and scrapings are also needed to establish the nature of the infection in order to correctly prescribe treatment in the future.
Video: “Benign and malignant skin neoplasms”
Papilloma on the oral mucosa
- Oral papilloma is a common manifestation of HPV.
- It is a hyperplastic growth that occurs as a result of accelerated cell division, which is provoked by the papillomavirus.
- The pathogen is activated when immunity decreases or in the absence of antibodies against the virus.
- The main reasons contributing to the occurrence of papillomas in the mouth:
- constant exposure to high temperatures, chemicals, damage;
- disruptions in the endocrine system;
- genetic predisposition;
- weakening of the immune system.
Symptoms
Source: https://rodinkl.ru/papillomy/papilloma-na-spine-foto.html
Papilloma on the back - what it looks like and why it is dangerous
Many people develop papillomas on their back, but most do not pay attention to them. They believe that this is not a wart, but an ordinary mole that does not require treatment.
Some people remove such tumors for the sake of beauty, while others ignore them. But in the growths on the back there is a danger, which we will talk about in the article.
We will also consider the diagnosis, symptoms, types of papilloma on the back and methods of removal.
Diagnosis and symptoms
In order to distinguish a papilloma from a mole, a visual examination is sufficient for an experienced specialist. To consult about unknown tumors on the back, you should visit a dermatologist. He may also refer you to other doctors to rule out the possibility of warts appearing on other parts of the body.
A more accurate diagnosis is given after additional research:
- Cytological. Determines the presence of morphological changes within cells;
- Biopsy. A sample analysis is taken for a more detailed study of the structure of the cells of the growth;
- Histological. Determines the likelihood of papilloma degenerating from a benign to a malignant form;
- Polymerase chain reaction. Allows you to identify the type of pathogen;
- Digene test. Determines the strain of the virus, the degree of concentration in tissues and oncogenicity with high accuracy.
To accurately determine the treatment method, several studies are often performed together.
Once a person is infected, the virus undergoes an incubation period that can last from two weeks to two years. It is only when the immune system weakens that symptoms appear. External factors include the following manifestations:
- in most cases, a painless growth appears on the skin;
- in some situations, tingling or itching may appear near the papilloma;
- a wart that appears at the site of friction between clothing and the body; sometimes inflammation appears;
- sometimes swelling and pain of the formation are added to the symptoms;
- when open wounds appear near the papilloma, there is a possibility of bacterial infection entering, which leads to suppuration of the growth.
Even if there are no acute symptoms, the growth should be shown to specialists.
Methods of infection
The causes of the virus are varied. There are three ways to become a carrier of human papilloma infection:
- household;
- sexual;
- contact
As a rule, if the skin is damaged, scratches or cuts appear, the virus can enter the blood. Small doses of the pathogen are killed by the immune system, but when there is too much of it, the disease becomes more active.
Thus, the appearance of papilloma in men is associated with the widespread tradition of shaking hands. Children can transmit the virus to each other in schools, sections and other public events.
To do this, it is not necessary to touch the carrier; the source can be personal belongings.
Between men and women, HPV is often transmitted through sexual intercourse. However, contraception is not reliable protection.
The greatest risk of infection for both men and women occurs in the following public places:
- toilets;
- saunas;
- swimming pools.
Men are at risk, as many of them do not comply with personal hygiene standards. This may be why men have more growths on their backs. There is a risk of contracting papilloma warts through cuts caused by careless shaving.
Kinds
The international classification of the disease has recorded more than 100 varieties of human papillomavirus. The type of strain affects what the formation looks like and what symptoms it brings.
Thus, the growths vary in color; there are gradations from flesh-colored to dark brown. There are different sizes, in some cases the papilloma grows in diameter up to 20 mm.
Warts have a thin stalk or a wide base.
The most common types of papillomas on the back are:
- Vulgar or simple. These skin growths look like a small bump with a keratinized surface. They can occur not only on the back, but also on other parts of the body;
- Flat. Round formations have clear outlines and most often have the same color as the skin. In some situations, several growths appear in one place, then the papilloma acquires uneven boundaries. Such formations usually cause itching and pain;
- Thread-like. Papillomas often appear in the armpit area. Most of these papillomas are yellow. They appear in mature people over 40 years of age and are not always caused by a virus; sometimes the cause may be age-related changes in metabolism.
Why is papilloma on the back dangerous?
Although most formations are benign and do not manifest themselves in any way, they pose a threat to health. Doctors identify two dangers of papillomas on the back:
- The papilloma virus is an additional factor that encourages the formation of a malignant tumor. Although it is worth noting that growths on the skin are not as dangerous as those on mucous surfaces.
- Warts on the back are more often injured than on the head or arms. Often thread-like growths are torn off while changing clothes. This leads to the appearance of a conglomerate of papillomas in place of the previous one. As a result, you have to spend more time and money to remove the problem.
- If the papilloma on the back has been damaged, a bacterial infection can penetrate through it.
In this regard, it is recommended to get rid of the consequences of HPV from the back, especially if they have a thin leg. Since children are unable to take care of themselves and take care, if a papilloma is found on the child’s back, it must be removed immediately.
Modern removal methods
Modern medicine has developed various methods for treating papilloma on the human back. Each method has its own effectiveness and contraindications, so you should see a specialist. The most advanced procedures for combating warts:
- Laser. Within 15 minutes, a professional can get rid of a medium-sized growth. This will leave no scars and the patient will not experience pain. The laser cauterizes the capillaries, so this method does not cause bleeding;
- A liquid nitrogen. The essence of the procedure is the local application of liquid nitrogen. This leads to instant freezing of damaged tissues and their death. It is not recommended to use if the growth is deep;
- Chemical treatment. Various remedies are used to get rid of the problem: cantharidin, salicylic acid, podofilin or podofilox. Preparations based on celandine juice are often prescribed;
- Surgical intervention. Local anesthesia is administered and the papilloma is excised using a scalpel. This technique is used in extreme cases, for example, when removing large warts. After the procedure, scars remain. There is a risk of incomplete removal of the damaged area, which is why there is a possibility of relapse;
- Electrocoagulation. As with laser burning, this method is bloodless. Using high-frequency current, the tumor is removed. If the wart is large, a local anesthetic is used;
- Radio wave removal. The safest method, since there is no contact with the skin, the penetration of infections into the blood is excluded and no burns remain after the procedure.
Prevention
Like any viral infection, HPV requires preventive action. After all, it is better to avoid infection than to waste time and money on treatment. To protect yourself from papillomas, you must avoid promiscuous sex. It is worth remembering that many can be carriers of the disease without knowing it.
In addition, it is important to follow natural hygiene rules: wash your hands after visiting public places, wash your body regularly, and so on. Always try to have personal protective equipment with you, such as a towel and toothbrush.
Modern medicine helps build an internal barrier to the virus. To do this, vaccination is done, injections are administered into the blood three times after a certain period of time. As a result, the body is able to produce antibodies in advance to fight the threat.
Source: https://IDermatolog.ru/obrazovaniya-na-kozhe/papillomy-i-kondilomy/chem-opasna-papilloma-na-spine-i-kak-ee-udalit.html
Papillomas on the back: causes, dangers, treatment
Papilloma is a benign formation of viral etiology that can appear on almost any part of the body. Often such formations appear on the back, outwardly resembling an ordinary mole or wart. Papillomas on the back are a clear sign of a viral infection in the body.
The presence of the virus often goes unnoticed for many years, but with a decrease in immunity and the presence of provoking factors, HPV can become aggressive and cause the development of formations on the skin, and less often, internal organs.
- Infection with the virus can occur 2-4 or more months before the appearance of papillomas. Routes of transmission of the pathogen:
- - sexual; - contact;
- - household.
HPV often enters through damaged skin: scratches, cuts, microcracks. Activation of the virus occurs when its amount in the blood exceeds the norm. This condition can be provoked by:
- weakened immunity;
- frequent stress, depression, nervous shock;
- smoking, alcohol abuse;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- promiscuous sex life;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- long-term use of potent drugs.
Depending on the strain of the virus, some types of such formations can degenerate into malignant neoplasms. If the pathogen has a low type of oncogenicity, then the risk of developing cancer is minimal. In cases where the virus strain is highly oncogenic, the risk of developing cancer increases significantly. A doctor can determine the type of virus and its oncogenicity after the examination results.
What does papilloma on the back look like?
Both flat and pointed papillomas can appear in the back area. Flat ones resemble an ordinary mole and have clear outlines. Pointed ones develop from a flat layer of epithelium, protrude above the surface of the skin, and outwardly resemble a papilla with a thin stalk. The size of papillomas can be from 0.5 to 3 cm. They have a soft consistency and can be either single or multiple.
Why is papilloma on the back dangerous?
Papilloma on the back does not cause physical or pain, but only until the formation is injured. After an injury, it may bleed and there is a risk of infection. Papilloma is dangerous when it is caused by a highly oncogenic strain of the virus, which greatly increases the risk of its degeneration into malignancy.
Diagnosis and treatment
If a growth appears on the back, you need to consult a doctor who, after examination, will prescribe a series of laboratory and instrumental tests:
- PCR diagnostics - determines the strain of the virus and the degree of its oncogenicity.
- Laboratory blood test.
- MRI of soft tissues.
- Radiography.
The research results will allow us to determine the type of pathogen and prescribe the necessary treatment. Treatment of papilloma is carried out under the supervision of a doctor. Any rash actions or folk methods can increase the growth of the growth and provoke additional complications, so it is not recommended to self-medicate.
- The result will be brought by complex treatment, which consists of taking medications and removing the growth itself.
- Methods to get rid of papilloma on the back:
- — electrocoagulation; — cryodestruction;
- - laser therapy.
- The prognosis after treatment is favorable, but one must remember that even after removal of the papilloma, the virus remains in the body and can relapse at any time.
- Self-medication or removing the growth yourself can aggravate the course of the disease and provoke more serious complications.
Source: http://papillomy-lechenie.ru/papilloma-na-spine-prichiny-simptomy-diagnostika-metody-lecheniya/