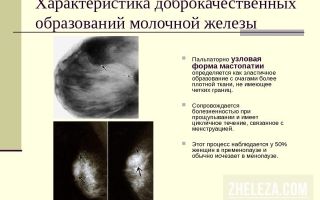
- Mastopathy is a change in the tissue of the mammary gland, which develops as a result of a violation of neurohumoral regulation.
- According to statistics, the risk of developing mastopathy increases after 35 years of age; women who have a history of endocrine disorders, as well as gynecological ailments, are at risk.
- Mastopathy is a collective term that unites a large group of pathologies associated with an imbalance in the ratio of connective and epithelial tissue.
- Mastopathy is a benign disease, but with a combination of certain factors it can give impetus to the development of cancer.
The essence of pathology
Pathology code according to ICD-10 is 60.1.
- Nodular mastopathy is a dishormonal change in the mammary gland of a benign nature, in which nodes and cysts form in the tissues .
- The disease manifests itself as the appearance of lumps in the breasts, increased sensitivity before menstruation, and discharge from the nipples.
- Another name for nodular mastopathy is localized adenomatosis.
- Nodules can be single or multiple, form only in one or in both mammary glands.
- In oncology, nodular mastopathy is considered a precancerous condition in which the risk of malignant disease increases.
- Essentially, nodular mastopathy is a focal variant of fibrocystic pathology of the mammary gland, but signs of diffuse changes in the organ are not excluded.
The peak incidence occurs at the age of 35-45 years. During reproductive age, the female body is subject to two main hormones - progesterone and estrogen. During normal functioning of the body, in the first half of the menstrual cycle, estrogens provoke cell division in the mammary gland in order to prepare it for the period of childbearing and lactation.
In the second phase, progesterone inhibits cell proliferation. Under conditions of increased concentration of estrogen and progesterone deficiency, glandular cells begin to divide uncontrollably, which leads to diffuse, and subsequently, nodular mastopathy.
In some cases, nodular mastopathy can be triggered by an increase in prolactin concentration outside the period of breastfeeding.
First signs
The insidiousness of nodular mastopathy is that the clinical picture is not always expressed, and in some cases it is completely absent.
Therefore, it is so important to undergo preventive examinations with a mammologist, as well as regularly independently examine the mammary gland.
The first signs of the disease may be :
- soreness and increased sensitivity of the mammary gland;
- change in breast volume;
- the presence of compactions in the tissues;
- nipple discharge;
- pain and tingling, which can radiate to surrounding tissues.
Symptoms of the disease
As the disease progresses, the clinical picture becomes more pronounced:
- chest pain may become constant;
- when palpating the breast, you can feel not only lumps, but also nodular formations with clear boundaries;
- the mammary glands swell, which leads to an increase in breast volume
- the nipple retracts;
- when pressing on the nipple, yellow, brown or colorless discharge is released;
- the lymph nodes in the armpit become inflamed.
- It must be said that the intensity of the clinical picture increases before the onset of the menstrual cycle.
- During menstruation or immediately after its end, nodular neoplasms may decrease or even disappear completely, but after some time they appear again.
- It is this feature of nodular mastopathy that leads to the fact that the diagnosis of the disease is not carried out in a timely manner, and, therefore, there is no earlier treatment of the pathology.
Causes
The main reason for the development of mastopathy is a hormone imbalance.
Such situations can be provoked by the following factors:
- chronic and acute diseases of the reproductive organs;
- menstrual irregularities;
- early or late onset of menstruation;
- abortions;
- uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs;
- obesity;
- endocrine pathologies;
- absence of pregnancy and childbirth before age 30;
- refusal to breastfeed;
- lack of regular sex life;
- stress;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- bad habits – smoking, alcoholism;
- chest injuries;
- hereditary predisposition to formations in the mammary gland.
Is it cancer or not?
- Of course, nodular mastopathy is not oncology.
- Any type of mastopathy is exclusively benign in nature.
- However, it is the nodular form that is considered the most dangerous from the point of view of transformation into a cancerous process.
- If the disease is not diagnosed on time and not treated under the supervision of a competent specialist, nodular mastopathy can cause breast cancer.
Classification of nodular mastopathy
According to histological characteristics, the following forms of the disease are distinguished::
- fibrous;
- cystic;
- fibrocystic.
- According to the course of the disease, nodular mastopathy can be:
- The profiling type of pathology is more dangerous, since in this case the risk of a malignant process increases.
- The exact form and type of nodular mastopathy can only be determined by a competent specialist after all the necessary diagnostic measures, therefore, in case of any lump in the breast, in no case should you carry out independent treatment, but you must contact a competent mammologist.
What tests are needed?
- Laboratory tests when diagnosing nodular mastopathy mainly concern the assessment of hormonal status.
- The level of estrogen, progesterone and prolactin is determined in the patient’s blood.
- It is also necessary to donate blood to test thyroid hormones.
- In some cases, especially if a malignant process is suspected, a biopsy and subsequent histological analysis are necessary.
- Biological material from the mammary gland tissue is taken from the woman by puncture, which is subjected to microscopic examination.
Diagnostic methods
In addition to laboratory tests, the following diagnostic measures are necessary::
- Mammography is an x-ray examination of the mammary glands, during which nodes are visualized and their location and size are assessed.
- Ultrasound also helps in determining the size and localization of tumors, but unlike mammography, this study can be performed as often as the situation requires.
- Ductography - a contrast agent is injected into the milk ducts, after which an X-ray examination is performed. Such a study is most often prescribed in the presence of discharge from the nipples.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs - often mastopathy develops against the background of abnormal processes in the reproductive organs, and this study allows us to identify pathology.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment of nodular mastopathy is aimed at restoring immune defense and suppressing the influence of hormones on the glandular tissue of the mammary gland.
Appointed:
- antiestrogens – Tamoxifen, Toremifene;
- oral contraceptives – Diane-35, Ovidon, Regulon;
- gestagens - Duphaston, Utrozhestan, Progesterone;
- gonadotropin antagonists – Zoladex, Buserein, Diferelin;
- thyroid hormones – L-thyroxine, Euthyrox;
- iodine-containing preparations – Klamin, Iodomarin;
- homeopathic remedies – Mastodinon, Mastopol;
- herbal preparations – Mammoleptin;
- vitamins – Triovit, Aevit;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Diclofenac, Indomethacin.
Surgical intervention
To eliminate nodular mastopathy surgically, there must be certain indications:
- suspicion of an oncological process;
- the size of the nodes exceeds 2 cm;
- active growth of nodular neoplasms;
- lack of effect of conservative therapy.
The following methods are used:
- Puncture. Prescribed for cysts with liquid contents. The essence of the procedure is to extract fluid from the cavity and subsequent sclerosis of the capsule.
- Sectoral resection. Part of the affected gland is removed.
- Radical resection. The mammary gland is completely removed.
The type of surgical intervention is selected on an individual basis, taking into account a large number of factors - the patient’s age, stage of pathology, underlying diseases, etc.
After the operation, the patient must spend several days in the hospital and take antibacterial and painkillers that will prevent possible complications.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods of treatment can only be used as additional therapy, and only with the permission of the attending physician .
Decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs can stop the progression of the disease, relieve negative symptoms and speed up recovery.
Are used:
- sagebrush;
- burdock;
- celandine;
- hemlock;
- red brush;
- Echinacea.
In addition, to reduce pain and resolve knots, compresses are recommended,:
Possible consequences
- The most dangerous consequence of nodular mastopathy is its transformation into an oncological process.
- The nodular form of the disease is considered the most dangerous in this regard, in the risk group of women over 40 years of age.
- Most often, this phenomenon is observed in women with undetected hormonal imbalances.
Disease prevention
To reduce the possible risks of nodular mastopathy it is necessary:
- Carry out regular breast self-examination, and if there is the slightest lump, seek help from a mammologist. Nodular mastopathy is preceded by diffuse pathology, which can be cured in the most gentle ways possible.
- Regularly undergo preventive examinations with a mammologist and gynecologist.
- Timely treat all gynecological diseases, as well as endocrine ailments;
- Don't allow abortions.
- Select the optimal means of contraception together with a qualified doctor.
- Do not take hormonal medications unless necessary.
- Don't give up breastfeeding your baby.
- Have regular sex life with one partner.
- Get rid of bad habits.
- Minimize the number of stressful situations.
- Watch your weight.
- Avoid chest injury.
Effect on pregnancy
- Nodular mastopathy does not pose any danger to the development and gestation of the fetus; breastfeeding will only benefit the woman.
- Nodules may significantly decrease or disappear when the baby is breastfed.
- However, given the fact that nodular mastopathy is a hormonal pathology, how exactly the nodes will behave during pregnancy is unknown, so a woman with mastopathy should be under special supervision from a specialist.
Reviews from women
Conclusion and conclusions
With timely access to a doctor, a responsible approach to treatment and the patient’s discipline, treatment of nodular mastopathy has a favorable prognosis.
In this case, it is possible to avoid complications of the disease and stop the pathology at the very beginning of its development.
Source: https://zhenskoe-zdorovye.com/mammologija/mastopatiya/vidy-mas/uzlovaya-u-zhenshchin.html
Nodular mastopathy: treatment, symptoms, types and diagnosis
The female reproductive system is a complex mechanism. The mammary gland is an important organ of the system. Trauma and other internal factors cause a number of diseases that can provoke serious complications in women's health. Mastopathy in medical practice ranks first in detection.
Previously, oncologists were involved in diagnosing and treating the disease. To prevent the disease and early detection, a preliminary examination of the mammary gland is carried out by gynecologists during a routine examination. Nodular mastopathy is a benign pathology. But atypical mastopathy cells degenerate into cancer cells, so early detection with timely treatment is recommended.
This prevents the development of possible serious consequences.
General characteristics of the disease
Nodular mastopathy is a disease of the mammary gland, which is considered a precancerous tumor. The disease is characterized by the formation of various lumps in the breast tissue.
The formation has the shape of a node with the accumulation of microcalcifications in its cells. The node can occur in a single form or in the form of several formations.
It is possible to damage the tissue of one breast or develop a bilateral tumor.
Nodular mastopathy of the mammary gland is a change in the internal structure of tissues with the subsequent formation of pathological neoplasms associated with hormonal imbalances in the body. The development of a tumor is associated with disturbances in the structural relationship of the glandular, connective tissue and fatty layers.
The disease is benign in nature, but after a certain time it can degenerate into cancer. Fibrous nodules require urgent treatment - this will prevent the development of a dangerous oncological formation. Doctors advise regular examinations to detect the disease in the early stages.
The woman feels pain when pressing or palpating the lump. Similar signs appear when the nodules are quite large. During the menstrual cycle, unpleasant symptoms worsen. In the initial stages of formation, the disease develops secretly. In this regard, pathology is detected at later stages.
The ICD-10 code for the disease is N60 “Benign breast dysplasia.”
Classification of pathology
Mastopathy is classified depending on the cellular content and the principle of development:
- The fibronodular form is characterized by a benign formation. Most of the node is occupied by connective tissue. During development, external asymmetry of the mammary glands appears with signs of constant or periodic pain.
- Diffuse nodular mastopathy is characterized by a cystic formation with fluid filling. New growths are elongated or oval in shape. A characteristic symptom is pain radiating to the shoulder or arm and armpit.
- The cystic nodular appearance is distinguished by clear boundaries of the tumor. The node grows, gradually filling healthy breast tissue. A large seal compresses the ducts of the mammary gland, causing venous stagnation and swelling of the soft tissues with pain when touched.
The nodular form of mastopathy, depending on the growth and degree of malignancy, is divided into:
- the non-proliferative type is characterized by the development of nodes without active growth;
- the proliferative form without atypicality increases slowly and is not prone to transforming cells into cancer;
- proliferative mastopathy with the presence of atypical cells is a precancerous type that affects women after 45 years.
There are types of pathology: cyst, fibroadenoma, hamartoma, angioma, lipoma and cystosarcoma. Additionally, dishormonal, focal and fibroadenomatous types of mastopathy are indicated.
Depending on the location and number of nodes, single and bilateral lesions of the body are distinguished. A single formation can be localized in the right or left breast. In the bilateral variant, tumors form in both mammary glands.
The relationship of mastopathy to oncology
The disease is considered a benign formation with slow growth. Doctors classify mastopathy as oncology due to the high risk of cells degenerating into cancer. Therefore, the pathology is dangerous for women's health.
Medicine takes all measures for early detection of the disease. If you have suspicious lumps in the breast, you should contact a gynecologist or mammologist and undergo a full examination. Modern types of diagnostics make it possible to detect small nodules.
Treatment in the early stages of the disease increases a favorable prognosis for a woman and helps prevent relapse. Lack of treatment is dangerous due to the malignant development of pathology, which is complicated by serious consequences.
Reasons for the development of the disease
The disease is diagnosed more often in women after 40 years of age; many doctors associate what is happening with hormonal changes in the body. Reasons for the development of mastopathy:
- hereditary predisposition to breast pathologies;
- chronic gynecological diseases;
- disorders of the central nervous system and stressful situations;
- injury to breast tissue;
- repeated artificial termination of pregnancy;
- during pregnancy after 30 years;
- alcohol and nicotine abuse;
- excess body weight;
- lack of intimate life for a long time;
- hormone-based drugs for contraception;
- inability to breastfeed a child;
- increased levels of estrogen and prolactin;
- wearing tight underwear;
- deficiency in the diet of foods with iodine;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands;
- disease of the endocrine system – diabetes mellitus.
It has been proven that childbirth before age 30 and breastfeeding children prevent the formation of mastopathy in the mammary glands. Therefore, doctors recommend not postponing the birth of a child until a later age.
Signs of mastopathy
The first symptom of the presence of the disease is a suspicious lump in the chest. It can be detected by self-palpation. Often there is pain on palpation, which intensifies during menstruation.
The presence of pathology will be characterized by the following signs:
- Painful sensations in the breast area radiate to the scapular area or shoulder;
- There are foreign nodules and seals;
- Increase in breast size and swelling of soft tissues;
- Congenital pathology – inverted nipple;
- A colorless or yellow-brown fluid is discharged from the nipple;
- Inflammatory processes in the axillary lymph nodes.
The presence of blood in nipple discharge indicates the presence of a malignant process that requires urgent treatment. Women often write off the presenting symptoms as manifestations of the premenstrual cycle and do not consult a doctor. This leads to late detection of the disease and serious consequences.
Diagnosis of pathology
If there are unpleasant symptoms, the patient will be referred for an extensive examination to confirm or refute the preliminary diagnosis. Diagnostics includes the following procedures:
- The doctor conducts a physical examination with palpation of the diseased area.
- Mammography will show the presence of formations - the picture is taken in a direct and oblique projection.
- A puncture is made to collect biological material and subsequent histological examination for malignancy.
- Using ductography, the internal structure of the mammary gland ducts is studied for deformation and expansion.
- Ultrasound determines the location, structure, boundaries and shape of the tumor.
- The pneumocystography procedure reveals large cyst-like formations.
- The blood is examined for the nature of changes in the main elements and hormonal imbalance.
- A test for tumor markers is also prescribed.
After receiving the test results, the doctor will prescribe treatment and rehabilitation process for the patient. Proper therapy will help you recover quickly and prevent the development of serious consequences.
Treatment of mastopathy
Mastopathy with prolonged development is dangerous due to transformation into oncology, so the disease must be treated. The choice of therapy depends on the size of the tumor and the extent of organ damage. The doctor assesses the patient’s condition, the form of the disease and age, as well as general changes in the breast tissue.
In the early stages of the disease, drug treatment is used. They use medications that stabilize hormonal levels.
Restoring the balance of hormones eliminates diseases of the nervous and endocrine systems. In the presence of gynecological diseases, doctors prescribe a course of therapy aimed at treating pathologies.
To restore nervous disorders, sedative drugs are used.
Formations of small size and without oncology can be cured with drug therapy. For a positive effect, it is necessary to suppress the activity of the ovaries in the active production of estrogen with prolactin. This helps to reduce the size of the nodes and lead to gradual resorption. The course of therapy is selected individually in each case.
But more often, doctors resort to surgical treatment of pathology. The operation to excise the node is carried out using the following methods:
- enucleation - used to directly remove a cyst with a tumor without capturing healthy tissue;
- sectoral resection removes large nodes with areas of healthy cells;
- Radical resection is used when cancer is suspected; the tumor is removed along with the mammary gland.
The procedure for excision of mastopathy is performed using general or local anesthesia. The operation lasts from 40 minutes. up to 1.5 hours – depends on the degree of organ damage. The recovery period is individual, depending on the surgical method and the general physical condition of the patient. On average it can last from 2 months to 1 year.
If the disease is detected early, it is allowed to use traditional medicine recipes. In the later stages, this treatment has no effect, so it’s not worth wasting your time.
For therapy, burdock root, calendula, elderberry berries and leaves, knotweed and red brush are used. Before using alternative medicine recipes, you need to consult a gynecologist with a mammologist.
You cannot treat the pathology yourself - this can harm your health and provoke serious consequences.
Consequences of untreated mastopathy
Disease prevention
Women over 30 years of age are at risk for developing mastopathy. Therefore, during this period it is worth undergoing regular medical examinations with ultrasound and mammography procedures.
To prevent the development of pathology, doctors advise following a number of simple preventive measures:
- exclude heavy physical activity;
- avoid stressful situations;
- balance your diet - increase foods with plant fiber, vitamins and microelements;
- prevent injury to mammary gland tissue;
- plan the birth of your first child before the age of 30;
- do not give up breastfeeding your newborn;
- if possible, refuse artificial termination of pregnancy.
When the first signs of a foreign lump appear in your chest, do not delay going to the doctor. This will allow you to identify the disease early and provide adequate treatment.
A timely detected tumor in the mammary gland will prevent the transformation of atypical cells into cancer and cure the disease in a short time. A malignant neoplasm develops faster and threatens serious consequences for a woman.
To avoid such developments, you need to undergo systematic examinations with a gynecologist and other necessary procedures.
During the treatment process, you must strictly follow the recommendations of your doctor - this will speed up the healing process and preserve your breasts and health.
Source: https://onko.guru/dobro/uzlovaya-mastopatiya.html
Nodular mastopathy of the mammary gland: forms and causes, prognosis
Any changes in the mammary gland should be a reason to consult a doctor.
If there are lumps when palpating the breast, then you should not engage in self-diagnosis, but immediately seek medical attention.
Nodular mastopathy, which forms in the mammary gland, has various forms and reasons for its development. We will talk about all the features of this disease on the website zheleza.com.
Nodular mastopathy is classified as one of the forms of fibrocystic mastopathy. This is adenomatosis of a localized type. This form is malignant. If, with nodular mastopathy, a woman is still in a precancerous state, which can be treated, then in the absence of qualified help, the disease intensifies and turns into cancer.
Nodular mastopathy manifests itself in the form of compactions and lumps that can be felt in the armpit. Lymph nodes also enlarge. There can be many of these bumps, or maybe just one. If there are similar seals in the armpit, pain and discomfort in these areas, single fibrocystic nodular mastopathy is diagnosed.
With multiple nodular mastopathy, no discomfort is felt, but excessive swelling, secretion, and high temperature occur.
Types and forms of nodular mastopathy
Nodular mastopathy is diffuse in nature, in which healthy breast tissue is damaged. Here are the different forms and types of the disease that you should know about.
Shapes:
- Nodular is a dangerous disease that occurs in multiple or single nodes in one or both breasts. This form can cause cancer.
- Diffuse - a harmless form, in which granular compactions are noted throughout the breast and swelling of the mammary glands.
Nodular mastopathy is observed in women from 35 to 45 years old. It is a precancerous condition, which increases the risk of developing cancer by up to 32%.
Since the nodular form can be a consequence of the diffuse form, the following symptoms of their manifestation are distinguished:
- Temperatures over 37.5°C.
- Graininess in the chest.
- Flaky skin.
- Pronounced lobular division.
- Pain in the chest outside the glands.
- Secret extraction.
- Feeling of heaviness in the mammary gland.
- Chills and fever.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Unusual breast shape.
Forms of fibrocystic mastopathy are distinguished by severity:
- Leaf-shaped tumors are a fibro-epithelial malignancy.
- Cyst simple - formation of a cavity nature with liquid contents.
- Lipogranulomas are small necrosis of the fatty tissue of the breast.
- Clinical fibroadenoma is a benign formation formed from breast tissue.
- Lipomas are benign formations from the fatty tissue of the breast.
- Intraductal.
- Hamartomas are a consequence of disturbances in processes in the embryonic membranes, which provokes benign formations.
- Clinical papillomas are benign formations on the skin in the form of a nipple-shaped growth.
- Angiomas are benign forms on the surface of the breast in the form of nodules.
The types that are divided depending on the amount of predominant tissue in one form or another of mastopathy are considered separately:
- Lobular.
- Fibrocystic.
- Cystic.
- Cystic proliferating.
- Fibrous-nodular (glandular).
- Cystic papillary.
go to top
Causes of nodular mastopathy of the mammary gland
Nodular mastopathy, which is observed in the mammary gland, is a precancerous stage. Not every patient would like to hear such a diagnosis. The causes of cancer development are always varied. Common causes include various disorders in the formation of tissues or the functioning of organs, as well as hormonal disorders.
Nodular mastopathy most often affects women aged 35-50 years, but there are cases of development in younger representatives. The size and shape of the breast gradually change, which indicates pathological formations.
Cancer is often a consequence of the development of fibrocystic mastopathy in the mammary gland. It does not matter here whether the woman gave birth or breastfed. Damage to breast cells by fibrocystic disease becomes the first stage towards the appearance of cancer.
The monthly cycle is gradually disrupted, due to which an uneven amount of hormones necessary for reproductive age is released into the body.
If a woman ignores treatment, the lymph nodes will gradually enlarge, destroying healthy tissue.
An insufficient amount of estrogen in the blood shifts monthly cycles, days of ovulation and possible pregnancy. The blood in the body is not renewed, which leads to the need for “nutrition” from the existing blood elements.
The causes of nodular mastopathy are:
- Depression.
- Abortion.
- Dysfunction of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands.
- Liver diseases.
- Fatigue.
- Hysteria.
- Diabetes.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Obesity.
- Intestinal dysbiosis.
- Smoking.
- Absent or irregular sex.
- Chest injuries.
- Lack of breastfeeding.
- Tight underwear.
- Late menopause.
- Inflammation of the ovaries.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Lack of iodine.
- High levels of estrogen.
- Hormonal contraception.
- Chronic hepatitis.
- Early onset of menstruation.
- Progesterone deficiency.
- No pregnancy before age 30.
Treatment for nodular mastopathy that does not rupture includes herbal medicines, where the dosage of hormonal drugs is gradually reduced.
go to top
To avoid any talk about the possible development of cancer, timely and correct treatment is prescribed after diagnosis. Women who are not diagnosed by doctors and do not identify their illnesses are at risk. Other categories of women at risk are those who have:
- Neurosis.
- Stress.
- Early abortion.
- Hormonal imbalance as a consequence of a cold.
- Diabetes.
Diagnostic measures make it possible to find out the nature of the disease and determine the correct treatment. So, a woman must visit a mammologist, who palpates her and prescribes a mammogram. Other types of diagnostics are:
- Breast ultrasound.
- X-ray.
- Examination of the lymph nodes under the arms.
- Echography.
- Cytological analysis.
- Blood analysis.
The main direction of treatment is surgery to remove the affected tissue for nodular mastopathy. This prevents cancer from developing further. At the same time, the woman is periodically examined by a doctor to determine the course of the disease after the procedures. This allows you to adjust treatment in time if it does not help.
Surgery is not prescribed if the formation does not exceed 20 mm. In this case, the woman simply undergoes periodic examination by a doctor.
There are two types of surgical intervention for nodular mastopathy:
- Sectoral - removal of the part of the breast where the tumor and affected tissue are found.
- Enucleation is the removal of only the tumor/cyst without affecting surrounding tissue.
go to top
In what cases is surgery performed?
- Rapid development of nodules: in 90 days they increased 2-3 times.
- Formations of a malignant nature or hazardous to health were discovered.
- Cyst recurrence.
The operation is performed for at least 30 minutes under local or general anesthesia. The patient can be discharged either on the day of surgery or 24 hours later. Sutures are removed 7-10 days after surgery.
If changes inside the ducts are observed, chemotherapy is prescribed.
go to top
Forecast
A doctor cannot make an accurate prognosis for the disease, even with an existing diagnosis. How long a patient with nodular mastopathy, which will soon turn into cancer, will live depends on many physiological factors. There are people who live with benign tumors for years. And there are people who, in a matter of days, observe the transformation of mastopathy into cancer.
In any case, you should seek help from doctors who will diagnose the disease and begin treatment. Today, there are many methods for treating various forms of fibrocystic mastopathy. In the early stages, many patients recover. Already in the later stages, the prognosis worsens and is insignificant.
Source: http://zheleza.com/uzlovaya-mastopatiya-molochnoj-zhelezy
Nodular mastopathy
Nodular mastopathy is a benign dishormonal change in the mammary glands, characterized by the formation of nodes and cysts in the tissues. Nodular mastopathy is manifested by the presence of lumps in the breasts, mastalgia, swelling and tenderness of the breasts before menstruation, and discharge from the nipples. Nodular mastopathy can be diagnosed using ultrasound, mammography, examination of the gland ducts, and biopsy. Treatment of nodular mastopathy includes correction of background disorders (inflammatory, endocrine, neurohumoral), sectoral resection or enucleation of the breast cyst.
Nodular mastopathy (localized adenomatosis) is a focal form of fibrocystic disease of the mammary glands. Oncology and mammology consider this type of mastopathy as a precancerous process, which increases the risk of developing breast cancer.
Nodular seals can be single or multiple in nature, detected in one or both mammary glands.
Nodules are determined, as a rule, against the background of signs of diffuse mastopathy - rough lobulation, heaviness, granularity, pain outside the nodes and discharge from the nipples.
Nodular mastopathy
Clinical forms of nodular mastopathy can include fibroadenomas, cysts, intraductal papillomas, leaf-shaped tumors, lipomas, lipogranulomas, angiomas, hamartomas.
Taking into account the prevailing changes in connective tissue, fibrocystic, fibrous and lobular (glandular) forms of nodular mastopathy are histologically distinguished.
Morphological changes in nodular mastopathy are represented by large cystic cavities, papillary growths, pronounced proliferation of the epithelium (multilayered, polymorphic, enlarged nuclei, increased number of mitoses, etc.).
According to the severity of the proliferative processes of the epithelium, the form of nodular mastopathy can be simple or proliferative. Proliferating nodular mastopathy is considered a precancer, since it most often undergoes malignancy.
The peak incidence of nodular mastopathy occurs at 35-45 years, which is understandable from the point of view of the characteristics of female physiology.
Monthly cyclical changes in the body of a woman during the reproductive period occur under the influence of two main hormones - progesterone and estrogen, which ensure the biphasic nature of the menstrual cycle and cause certain processes in the tissues of the mammary glands.
Normally, in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, estrogens stimulate proliferative changes in the glands; in the second phase, under the influence of the antagonist hormone progesterone, proliferation processes are inhibited.
Against the background of an imbalance of these hormones (excess estrogen and lack of progesterone), excessive uncontrolled proliferation of breast tissue occurs, which leads to the development of first diffuse and then nodular mastopathy.
Sometimes the development of nodular mastopathy may be based on excessive production of the pituitary hormone, prolactin. Typically, an increase in prolactin secretion occurs during pregnancy and lactation, promoting milk production. However, with excessive secretion of prolactin outside of pregnancy, nodular mastopathy can also develop.
Hormonal imbalance leading to the development of nodular mastopathy can be provoked by frequent induced abortions, prolonged stress, neuroses, metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, obesity, chronic hepatitis), gynecological diseases (adnexitis, endometritis) and other reasons.
Nodular mastopathy is predisposed by heredity, early onset of menstruation or late onset of menopause, absence of pregnancy and childbirth by the age of 30, short or long lactation period, breast trauma (for example, mammary gland bruise), bad habits, uncontrolled hormonal contraception, intestinal dysbiosis.
Manifestations of nodular mastopathy are characterized by tumor-like compactions in the breast tissue, which have clear boundaries and are not fused to the nipple and skin. Such lumps can be detected by the woman herself during a self-examination of the glands.
During the premenstrual period, the lumps and the entire mammary gland become painful, tense, and increase in size due to swelling. The pain may radiate to the shoulder or shoulder blade. After the premenstrual edema subsides, the nodes become painless. Sometimes with nodular mastopathy no pain occurs, and then the glandular nodule becomes an accidental finding.
Nodular mastopathy is characterized by a negative Koenig symptom - the inability to palpate breast nodes in a lying position. Regional lymph nodes are not enlarged in nodular mastopathy. In the nodular form of mastopathy, individual drops may be discharged from the nipples when pressed, or quite abundant transparent, yellowish-brown or bloody contents may be observed.
The similarity of the manifestations of nodular mastopathy and breast cancer dictates the need for a thorough examination by a mammologist using clinical, radiological, echographic, cytological, and morphological methods.
With nodular mastopathy, palpation in the mammary gland reveals one or several foci of compaction with clear boundaries. The seals may have a granular, lobulated or smooth surface (with a breast cyst).
In the latter case, when pressing on the nodule, a ripple is felt, characteristic of a liquid formation.
With intraductal localization of changes, pressure on the isola is accompanied by the release of liquid of varying consistency and color.
During plain mammography, radiographs may reveal areas of intense uniform darkening, oval shadows of cysts, calcifications, and fibrous strands.
The combination of various forms of nodular mastopathy gives a motley radiological picture (“lunar relief”), characterized by restructuring of the gland structure, multiple areas of darkening and clearing of various sizes and shapes, the presence of strands of connective tissue, individual shadows of fibroadenomas and cysts.
When a breast cyst is detected, a puncture is performed with a cytological examination of the contents, then pneumocystography. Using pneumocystography, the completeness of emptying of the formation is monitored, and intracystic hyperplastic and tumor formations are detected.
If intraductal changes are suspected, ductography is indicated. When contrasting the ducts, their deformation and expansion, deposits of calcium salts, and cystic cavities are determined.
Ultrasound of the mammary glands with Dopplerography allows one to judge the localization, size, vascularization of the formation in the mammary gland, as well as its structure (nodular, cystic).
Carrying out a puncture biopsy of the mammary gland with a cytological examination of cellular material is necessary to exclude oncopathology and choose treatment tactics for nodular mastopathy.
Additionally, for nodular mastopathy, a study of the level of progesterone and estrogens, thyroid hormones, liver enzymes, a pelvic ultrasound and consultation with a gynecologist-endocrinologist are indicated.
Detection of fibroadenoma requires consultation with an oncologist-mammologist.
Conservative treatment for nodular mastopathy is used only to eliminate hormonal imbalance, background gynecological, endocrine and other diseases.
The main treatment method for nodular mastopathy is surgery, the nature and extent of which depends on the form of the disease. For breast cysts, the contents are removed by puncture and sclerosis of the cyst is performed.
In case of relapse, enucleation of the breast cyst is performed.
Detection of fibroadenoma is the basis for sectoral resection of the mammary gland - removal of the tumor and part of the gland.
Absolute indications for surgical treatment are biopsy data that are controversial regarding the benign quality, and a rapid increase in size of the nodes.
In case of multiple cysts or nodes, radical resection of the mammary gland or subcutaneous mastectomy followed by mammoplasty may be required.
- In the matter of preventing nodular mastopathy, it is fundamental to understand the importance of self-examination and preventive examinations by a mammologist, timely treatment of endocrine and inflammatory diseases, and undergoing screening tests (mammography, ultrasound of the mammary glands).
- Important points are the exclusion of provoking factors, diet (limiting caffeine-containing products, increasing the consumption of plant fiber), and physical activity.
- Since the development of nodular mastopathy is preceded by diffuse changes in the gland, early and complete therapy of the initial forms of mastopathy is necessary.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_mammology/nodal-mastopathy
What is nodular mastopathy of the mammary gland: treatment methods and is there a threat?
A woman's mammary glands are important organs of the reproductive system. Due to many reasons, they are exposed to various diseases, the leading one of which is mastopathy.
And if earlier this problem was dealt with by oncologists, now, in order to prevent the onset of the disease and begin timely treatment, regular breast examinations are carried out by gynecologists. It is early diagnosis that allows you to avoid serious consequences.
In the article we will talk about nodular mastopathy of the mammary gland, what it is and what treatment options are available.
What is nodular mastopathy of the mammary gland? Nodular mastopathy includes benign changes in the mammary glands, which are characterized by the formation of nodules and cysts in the tissues.
- Nodular mastopathy is a type of disease that mammologists and oncologists consider as a precancerous stage, with subsequent development of cancer if not treated in a timely manner.
- Seals in the form of nodes can be single or multiple, formed in one breast or in both at once.
- Lumps in the chest (nodes) have clearly defined contours.
- Characteristic features of nodular mastopathy are microcalcifications, induration, breast swelling, pain before the menstrual cycle, and discharge from the nipples.
- Fibrous nodular . It is characterized by a benign course. The connective tissue grows, forming dense nodular formations. The mammary glands become asymmetrical. The pain may be constant or episodic.
- Diffuse nodular . Cysts filled with fluid appear in the glands. They can have different shapes and sizes with a limited outline. Most often, cysts have an oblong or round shape. This type of disease is characterized by pain that radiates to the shoulder, arm or armpit.
- Cystic nodular . Nodes in the mammary gland have clear boundaries and vary in size. The seals gradually increase in size, capturing adjacent tissue. They are especially noticeable before the menstrual cycle. Due to the formation and growth of cysts, compression of the mammary gland ducts occurs, which leads to venous stagnation and edema. Painful sensations appear, the chest becomes sensitive.
The nodular form of mastopathy is divided into simple or proliferating according to the severity of the processes. The latter is considered a precancerous condition.
Is it a precancerous disease?
This type of disease poses a threat to women's health. Therefore, when a diagnosis is made, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment for nodular mastopathy of the mammary gland.
Even minor pain in the chest should be the first sign to visit a gynecologist or mammologist.
Modern diagnostic equipment makes it possible to detect the disease at the earliest stages. This will prevent further complications, since nodular mastopathy is characterized by a transition to the cancer stage .
- With timely and correct treatment, the prognosis can be favorable and there is a high probability that there will be no recurrence of the disease or relapses in the future.
- IMPORTANT The course of the disease may be irreversible if a woman does not visit a specialist at the slightest sign of detection of nodules in the mammary gland.
- The appearance of nodular mastopathy of the mammary gland is typical for women aged 30-45 years. The development of this pathology is caused by factors such as:
- Various types of gynecological diseases.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Nervous system disorders and stressful situations.
- Chest injuries.
- Frequent abortions.
- Smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Long breaks in the intimate sphere.
- Presence of hepatitis, diabetes.
- Any degree of obesity.
- Regular use of hormonal drugs and contraceptives.
- Refusal to breastfeed after childbirth.
But first of all, nodular mastopathy manifests itself with high prolactin and hormonal imbalance, when the amount of estrogen increases. Frequent childbirth and breastfeeding increases the chances of protection against this disease.
Nodular mastopathy of the mammary gland - photo:
Symptoms and manifestations
- The most important symptom is the presence of round or oblong lumps in the mammary gland with clear contours.
- When palpating these places, severe pain appears. The pain may be dull and aching. They appear especially often during menstruation.
- Due to swelling of the connective tissue, breast enlargement occurs.
- Pressing on the nipple of a sore breast causes discharge, which can be clear, white or yellowish.
- With mastopathy, nodules and lumps cannot be felt in a lying position.
IMPORTANT If there is blood in the discharge, you must see a doctor.
This symptom may indicate the onset of a cancer process.
Those who have had nodular mastopathy experience all these symptoms during PMS. That is why they do not attach importance to them and often treatment of the disease begins late. Also, seals may decrease or disappear during critical days.
Diagnostics
- If there are symptoms indicating mastopathy, the doctor prescribes diagnostic procedures for the woman to make an accurate diagnosis.
- This is due to the fact that many types of the disease have similar symptoms and manifestations.
- First of all, palpation is performed to establish the presence of nodes, to determine what surface the seals have: lobulated, smooth or granular.
- They also apply pressure on the nipples to determine whether there is discharge and what color it is.
- If nodular mastopathy of the breast is suspected, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive examination to the patient.
- This includes:
- Mammography . It allows you to see the shadows of cysts, uniform darkening, fibrous cords and other pathological changes in the breast in the pictures. The picture is taken in 2 projections: direct and oblique. The method allows you to identify the disease at very early stages and provide the doctor with complete information about the condition of the mammary glands. Women should undergo this procedure every two years.
- Puncture . If cysts are detected, a puncture is performed followed by a cytological examination of the material. It allows you to accurately determine whether benign or malignant tumors have formed in the mammary gland.
- Ductography . It is carried out if changes within the ducts are suspected. Using this method, you can determine whether they are deformed or expanded, whether there are cysts or salt deposits.
- Ultrasound . The method allows you to see whether there are cystic formations, their location, shape and size. Also, using ultrasound, you can determine their structure and assess the condition of the surrounding tissues.
- Pneumocystography . Helps diagnose the presence of large cyst capsules.
If a woman is diagnosed with nodular mastopathy, it is necessary to undergo such types of examination as: taking hormone tests, pelvic ultrasound, visiting an oncologist and endocrinologist.
Read more about what tests you need to take for mastopathy here.
Treatment methods
For each case of the disease, the doctor prescribes individual treatment. Since in this case it is necessary to take into account what form of the disease is, whether the case is advanced or mastopathy is still at an early stage, whether there are pathological changes, what are the sizes of the nodes.
Conservative method
- It consists of using medications that will help stabilize hormonal levels and help treat gynecological problems and the endocrine system.
- In some cases, the use of sedatives to ensure the proper functioning of the nervous system is indicated.
- The doctor may prescribe a puncture, during which the fluid will be sucked out and the walls of the formations will be further sclerotized.
If this method does not help, enucleation is indicated to remove the cyst. At the same time, surrounding tissues are preserved.
If the case is advanced, surgical intervention is indicated.
Surgery
REFERENCE: If within three months there is an increase in the nodes by more than 2 times, the woman is sent for surgery.
During surgery, complete excision of nodes, cysts or tumors is performed. Also, depending on the severity of the disease, a certain section of tissue may be removed to avoid further spread or growth of the tumor. The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia for 40-50 minutes.
Operation of nodular mastopathy of the mammary gland can be performed in one of the following ways:
- Enucleation method , when only a tumor or cyst is removed.
- Sectoral resection , when not only the tumor is removed, but also nearby tissue.
In most cases, the patient is discharged the next day. The excised node is sent to the laboratory for cytological examination. Next, conservative treatment is prescribed.
Traditional medicine methods
- Folk remedies can give a positive result if you start using recipes at the initial stage of the disease.
- If the disease is advanced, there will be no effect from treatment with folk remedies for nodular mastopathy.
- Here it is important not to self-medicate, but to visit a gynecologist or mammologist without fail.
- The most effective in treating this disease are recipes using:
- red brush;
- burdock root;
- calendula;
- elderberries;
- knotweed.
It is recommended to use traditional medicine in consultation with your doctor.
Prevention
A woman over 30 years old should visit a gynecologist at least 2 times a year. From this age, it is also necessary to independently monitor the condition of the breast by regularly palpating it to identify lumps and other formations.
It is necessary to exclude physical activity, avoid stress and overwork, and monitor your diet. Any chest injury can lead to negative consequences. Therefore, in this situation, visiting a doctor is mandatory.
It is advisable that the first birth be no later than 30 years of age. Minimize abortions, as they are an impetus for the development of mastopathy. Breastfeeding should not be avoided. The duration of breastfeeding should be as long as possible.
If you notice any changes in your breasts, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Is cancer always nodular mastopathy? In 10% of cases the disease can develop into breast cancer. Therefore, it is important not to miss the initial stage of the disease and begin timely treatment under the supervision of a doctor.
Now you know everything about nodular mastopathy, what it is and how to treat it. The disease in its early stages has a positive prognosis for cure. The main thing is to identify the pathology in time and, when prescribing proper treatment, strictly adhere to all the recommendations of the attending physician.
You can find more information on this topic in the Varieties section.
Source: https://nesekret.net/mastopatiya/raznovidnosti/uzlovaya