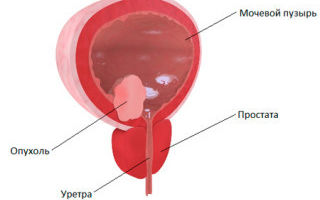
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the urogenital tract is a type of functional diagnostics, the advantage of which is that it is informative and safe due to the lack of radiation exposure.
- The data obtained help to visually assess pathological changes in the bladder, surrounding tissues, organs and vascular structures in three planes.
- Accurate determination of the nature of the disease and the spread of the process in the genitourinary system influences the choice of treatment tactics, on which the patient’s health and life depend.
Diseases that are detected using tomography
MRI diagnoses pathologies of the genitourinary system of an inflammatory, destructive nature, developmental anomalies leading to dysfunction of organs.
Used to identify changes resulting from trauma and tumor processes. List of bladder diseases:
- benign neoplasms (papilloma, polyp, endometriosis);
- malignant neoplasia (transitional cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma);
- invasion of the bladder neck by tumor cells in men with prostate cancer;
- organ duplication, diverticulum, cervical contracture;
- traumatic rupture;
- urolithiasis disease;
- cystitis.
Muscle-invasive bladder tumor
When to choose MRI as an examination method
If, in the presence of complaints and clinical symptoms of diseases of the genitourinary organs, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods have not yielded results to establish a diagnosis, an MRI is prescribed.
Tomography is indicated for enlarged and painful inguinal lymph nodes, suspicion of a tumor process, as a dynamic monitoring of inoperable formations and for deciding on treatment methods (conservative or surgical).
Indications for the use of contrast agents
MRI of the bladder using contrast based on gadolinium chelates helps to obtain images where contrast differences between normal and pathologically altered structures and tissues are clearly visible.
The standard dose of paramagnetic for an adult is 14-20 ml. Administration of the drug is indicated:
- if a tumor disease of malignant origin is suspected;
- for differential diagnosis with benign processes;
- to detect metastases and tumor growth from the bladder into surrounding tissues.
Preparation and completion of the study
- Before examining the genitourinary system, patients undergo preparation to improve visualization of the organs.
- To do this, 2 days before the procedure, a diet is prescribed, the purpose of which is to reduce gas formation and intestinal peristaltic activity.
- Legumes, cabbage, baked goods, milk, and carbonated drinks are excluded from food products.
It is recommended to perform a cleansing enema the day before. 2 hours before the procedure, the patient drinks 1.5 liters of water and comes to the diagnosis with a full bladder.
Children under 7 years of age are given sedatives after consulting an anesthesiologist.
To undergo an MRI with contrast, the patient provides blood biochemistry results with determination of creatinine levels 3-7 days ago.
How does the procedure work?
In the MRI room, an informed consent form is filled out before the examination. Then the x-ray technician removes metal objects (hearing aids, dentures, earrings) from the patient and helps him change into special disposable clothing.
- The patient lies down on a movable table and a surface coil is applied to the area being examined.
- An emergency bulb is placed in the hand in case the patient feels unwell and wants to interrupt the procedure.
- Headphones are placed on the ears for sound insulation, since the operation of the device is accompanied by noise effects.
- The study is consistently carried out in three projections: axial, sagittal, coronal.
- If there are indications for the use of a contrast agent, catheters and infusion tubes are installed.
- After contrast is administered, a series of scans are performed over 25-30 minutes, then the patient is removed from the table.
- The doctor processes the data obtained, documents the images and draws up a conclusion.
In what cases is MRI contraindicated?
Patients whose bodies contain ferrimagnetic metal structures (prostheses, pins, wires, pacemakers, staples) are not allowed for diagnosis.
For women up to 20 weeks of pregnancy, MRI is performed strictly according to indications. Weight restrictions are provided for patients weighing 120-150 kg.
The procedure is not performed on patients in an excited state or under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Patients suffering from claustrophobia are not allowed to study in closed-type devices.
Alternative diagnostic methods
If it is impossible to perform MRI, methods that have diagnostic value are used. These include:
- CT scan of the bladder provides a layer-by-layer picture of the walls of the organ and surrounding tissues. Detects formations and foreign bodies (instrumental diagnostics with increased radiation exposure).
- Ultrasound - evaluates the shape, thickness and contour of the walls, the presence of sand in the cavity and the level of residual urine.
- Cystoscopy - the internal surface and contents of the organ are examined using an endoscopic apparatus. It is performed by introducing a catheter with a camera and a lighting system into the cavity of the bladder through the urethra.
- Cystography is the production of images on X-rays using contrast agents injected into the circulatory system or directly into an organ. Diagnoses stones, wall damage due to tuberculosis, and tumor process.
CT
How much does an MRI cost?
The price for MRI diagnostics of the bladder depends on the power of the machine used for the study, the qualifications of doctors and the use of contrast agent. The cost of the procedure is 4000-6000 rubles.
The contrast agent is paid separately, on average 2000 rubles for 1 bottle (10 ml).
The reliability of MRI in diagnosing bladder diseases is 85%, which shows its advantage compared to other types of research. The disadvantage of the technique is the duration of the procedure and high cost.
Diagnosis of cancer (video)
Source: https://osnimke.ru/bryushnaya-polost/mrt-mochevogo-puzyrya.html
Computed tomography of the bladder
In the process of diagnosing diseases of the pelvic organs, modern techniques are used, including computed tomography of the bladder. CT and magnetic resonance imaging allows you to obtain the most accurate information about the condition of the organ being examined and any abnormalities. The procedure is often performed when indicated, but can also be used during a preventive examination.
Bladder CT
Computed tomography allows you to obtain a high-quality multi-layer image of the examined organ. The image is subjected to computer processing and recorded on digital media. The results obtained are examined by a doctor.
For the procedure, the patient is sent to the radiology room. There he lies down in a special machine - a tomograph, in a supine position and remains motionless. During the scan, the doctor monitors the process in the next room through the window.
The duration of the procedure is no more than 20 minutes.
Examinations may also be performed using a contrast agent. It is given intravenously, but is scanned without it first.
Research may show:
- formation in the bladder or urinary canal of a benign or malignant nature;
- metastases in the urinary system from tumors in other parts of the body;
- the presence of an inflammatory process, such as cystitis. The disease is more common in women due to the anatomical features of the body;
- ruptures, hematomas and bleeding in the bladder;
- renal colic with urinary obstruction;
- congenital anomalies in the development of the urinary system;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- stretching of the walls of the bladder and other degenerative changes.
The image will show the exact location of the source of the problem, the degree of its development and spread, as well as the severity of damage to the bladder and nearby organs.
Indications
Tomography of the bladder is performed if the patient has certain symptoms indicating the development of a pathological process in the area of the bladder or urethra.
The procedure is prescribed:
- With frequent or difficult urination.
- For urinary incontinence.
- If the patient empties his bladder frequently at night.
- For pain and discomfort during urination.
- If you have pain in the lower abdomen.
- When the color, smell and consistency of urine changes, and blood appears in it.
Most often, urological or nephrological disorders manifest as blood in the urine. This symptom indicates dangerous diseases.
It appears when:
- infectious processes in the urinary tract;
- cystitis;
- pathologies that are transmitted during sexual intercourse;
- jade;
- glomerulonephritis;
- stones in the ureter. They injure and damage the mucous membrane of the organ, which is accompanied by the appearance of blood in the urine. The disease can cause blockage of the urinary tract or enlargement of the tract. The ureter suffers from spasms, which is why the patient feels renal colic.
- neoplasms. If tumors are suspected, magnetic resonance imaging is usually performed. The procedure allows you to see all the structural changes that other methods have not helped to identify. MRI helps differentiate benign lesions from cancer.
The most dangerous pathology that is an indication for CT or MRI is cancer. In this case, a tumor forms in the organs of the excretory system, which can spread to other organs. If you notice the pathology in the initial stages of development, this will significantly increase the chances of survival, provided that the correct treatment is selected.
Optical coherence tomography may be needed to confirm the diagnosis. With its help, thin layers of mucous membranes are examined using optical infrared radiation.
Contraindications
If there is a need to conduct a CT scan with a contrast agent, then you should take into account that such examinations are contraindicated:
- for pathologies of the endocrine system;
- in case of renal failure;
- in case of intolerance to the components included in the contrast agent.
There may also be difficulties in examining overweight people, as there are restrictions on the use of the device. It cannot support weight more than 140 kg.
Preparing and using contrast
The device will show a more accurate result if you properly prepare for the procedure. It is important that at the time of the examination the patient has an empty bowel and a full bladder.
For this:
- the day before the procedure, it is advisable to eat light soups or cereals and avoid foods that cause gas;
- in the evening you need to drink a laxative or cleanse the intestines with an enema;
- on the day when the tomography will be performed, the patient cannot eat or drink anything;
- if the examination is carried out with contrast, then the ampoule of the substance is dissolved in water and consumed before the procedure. Sometimes the drug is administered intravenously.
Contrast enhancement is used if there is a suspicion that the patient has cancer or if the diagnosis is controversial. Contrast allows you to get photos with maximum clarity.
Iodine-based preparations are commonly used and are used in two ways:
- injected into a vein. This procedure is called a pyelogram and allows you to identify stones and tumors;
- used internally. One ampoule is diluted in a liter of water, if there are no other instructions, and drunk 5 hours before tomography.
The method of administering contrast enhancement is chosen by the doctor.
Advantage of the method
To conduct the study, a magnetic resonance or multislice tomograph is used. The procedures for CT and MRI are almost identical. The advantage of the second method is that the images of soft tissues are more detailed.
CT also has many advantages, including:
- The ability to obtain high-precision images and detect even minor changes in the structure of organs. Thanks to this, it is possible to identify a dangerous pathology in the early stages of formation.
- Safety and complete absence of adverse reactions.
- Speed of the procedure. It does not cause any discomfort and takes no more than 20 minutes.
- Non-invasive. There is no need to cause trauma to soft tissues during the examination.
- Minimum radiation dose.
- Availability and relatively low price.
The cost of the procedure may vary in different clinics. A procedure with a magnetic resonance imaging scanner will cost more than a CT scan.
Transcript and doctor's report
The examination results are deciphered by the doctor. You can find out the final diagnosis within half an hour after the procedure. A radiologist examines layer-by-layer images. He identifies the presence of pathological changes and draws up a final conclusion.
The specialist determines:
- the nature of the pathological process;
- malignant changes, if any;
- the degree of damage to the organ and nearby tissues;
- focus of the disease.
After completing the diagnosis, the doctor tells the patient where he should go with the existing disorders. The final diagnosis is made by the attending physician.
Source: http://BolezniKrovi.com/kt/mochevogo-puzyrja.html
CT scan of the bladder - examination with and without contrast
It is very important to constantly monitor your health, paying attention to all changes in your well-being and general condition, because there are a huge number of different diseases, so making a correct diagnosis quickly and accurately is not possible in all situations.
If you control your well-being, you will be able to contact a qualified specialist in time, who will not only examine you, but also prescribe the necessary diagnostic procedures that will help you start therapy in a timely manner and get rid of the problem without any complications or dangerous consequences. Let's take a closer look at such a diagnostic procedure as a CT scan of the bladder with contrast, because it is used extremely often and allows us to identify almost any disease related to the urinary tract.
Computed tomography of the bladder can be performed with or without the introduction of a contrast agent.
Indications for use
CT and MRI of the bladder are quite expensive procedures, but if you need a quick and high-quality diagnosis, you definitely shouldn’t neglect them.
A similar study of the kidneys and bladder will provide the specialist with detailed information regarding this organ.
CT scan of the kidneys, as well as the bladder, is a procedure that can be performed with or even without contrast, it makes it possible to visualize the area in question layer by layer.
Here are the main situations when a specialist prescribes a CT or MRI (there is no point in arguing which is better, since magnetic resonance imaging is, of course, safer and more informative than a computed tomograph, but in some cases it is impossible due to the presence of metal implants in the body or what -or other contraindications):
- the presence of severe and acute pain that occurs during urination, which is also sometimes replaced by a burning sensation;
- a condition in which there is causeless urinary incontinence, that is, when this does not occur in an elderly person or in a pregnant woman;
- the presence of periodic pain in the lower abdomen;
- visiting the toilet at night, especially if this happens constantly and several times;
- the appearance of any impurities in the urine without obvious reasons for this;
- the presence of suspicions of the development of a neoplasm of a benign or even malignant nature that has affected the urinary system;
- Magnetic resonance or computed tomography is also prescribed in situations where there is a sharp change in the shade of urine (we are, of course, talking about those situations when this is not associated with obvious reasons, for example, with the use of coloring products);
- change in the consistency of urine without obvious reasons;
- the acquisition of an unpleasant odor in urine that you have not observed before;
- presence of suspicion of cystitis or the need to confirm renal failure;
- The tomograph will also allow you to find out the consequences of a bladder injury.
Note! Under no circumstances should you try to choose a diagnostic procedure on your own, or engage in self-medication, as you will only waste precious time that could be spent on starting competent therapy. Self-medication almost always leads to the development of complications for the same reason - due to loss of time.
A computed tomography scan will allow timely diagnosis of the development of bladder pathologies.
What does the examination show?
We are often asked the question of what MSCT shows when examining the bladder.
Let us immediately mention that the study in question can be quite effectively used both for primary diagnosis and for monitoring various chronic diseases.
Computed tomography is important where the urethra cannot be examined by taking various tests and using other laboratory methods. The research in question will be effective in identifying the following problems:
- cystitis, regardless of the form of the disease;
- pyelonephritis or simple nephritis, regardless of stage;
- some diseases of a sexually transmitted nature (it is important to understand that to identify them it is best to contact the appropriate specialists, since this method is not informative enough for this);
- the presence of various infectious processes developing in any part of the urinary system;
- glomerulonephritis and other serious diseases.
Note! Do not think that the possibilities of computed tomography aimed at diagnosing diseases related to the bladder end there, because there are still a lot of problems that can be identified in this way. At the moment, CT is one of the most progressive and accurate procedures.
CT radiograph of the bladder using a contrast agent.
Contraindications
In fact, computed tomography is very often prescribed by urologists, as it has a relatively small number of contraindications; in any case, when performing a procedure in the presence of contraindications, everything can end in extremely unpleasant consequences, even causing serious danger to health or even life.
There are both absolute and relative contraindications.
In the case of the first of these, it is strictly forbidden to conduct research, and in the case of the second, a specialist must analyze the situation and identify in which case the risks will be more serious, because sometimes such a risk is justified, since in the absence of diagnosis a threat to life may arise.
The study is prohibited during pregnancy or breastfeeding, since the process uses dangerous ionizing radiation that can have a negative effect on the baby or accumulate in breast milk. As for relative contraindications, these include the patient’s young age.
Note! The use of a contrast agent is associated with additional contraindications.
Firstly, the patient must undergo a special examination in advance to determine the presence of individual intolerance to any contrast components, since an allergic reaction may occur after administration of the drug.
Secondly, the procedure with contrast is prohibited for people who suffer from kidney failure, liver failure, diabetes mellitus and many other dangerous diseases, the list of which can be checked with your doctor.
Carrying out the procedure
Pay special attention to preparing for the procedure, the specifics of which will be communicated to you by a qualified specialist.
It is necessary to prepare for it carefully, since the accuracy and information content of the following itself depends on this.
For example, preparation for a CT scan with contrast will necessarily include the fact that you must come for the examination on an empty stomach, otherwise the scan will not be possible.
Before you enter the room where a CT scan will be performed, be sure to remove all jewelry and other metal accessories, and do not forget about piercings, as this may harm the results.
Note! It is important to lie as still as possible throughout the procedure. Most likely, you will be secured using special belts and pillows, which you should not refuse. The fact is that even the slightest movements can negatively affect the results, which may necessitate a repeat examination.
Diagnosis of bladder pathologies using CT
Link to main publication
Source: https://tomografa.net/kt/organov-malogo-taza/puzyrya-mochevogo.html
CT scan of the bladder: indications, contraindications
Computed tomography has established itself as a highly accurate diagnostic technique, and therefore has become widespread in almost all areas of medicine, including in urological practice.
CT scan of the bladder is used for early recognition of pathology in this area and timely initiation of treatment.
What is computed tomography
CT is an x-ray examination method that can provide an accurate and three-dimensional image of internal organs. The device consists of a gantry ring and a couch moving in it.
Over the entire surface of the ring there are more than 1000 sensors that detect what has passed through organs and systems.
Indications
A wide range of indications determines the need to consult a specialist before conducting the study.
After an examination and laboratory diagnostics, as well as, most often, an ultrasound examination, the doctor makes a diagnosis and decides on the need for additional clarifying techniques.
If the following diseases are suspected and the results of mandatory methods are inconsistent, the doctor will prescribe a CT scan of the bladder:
- tumor process in the wall of the bladder;
- cystitis;
- inflammatory changes in the kidneys (glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis);
- the presence of stones in the renal pelvis or their release into the ureter;
- infectious processes in the urinary tract;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- injury or strain to the bladder or kidneys.
Additionally, a CT scan of the bladder can be performed before surgical interventions or before the start of conservative therapy with subsequent correction, if necessary, of the chosen tactics.
Contraindications
The main share of contraindications is for CT with contrast and is associated with its intolerance:
- due to the fact that iodine-containing contrasts are used, their use is prohibited in the presence of endocrine pathology, especially from the thyroid gland;
- allergic reactions to contrast or its components;
- Since the contrast is excreted in the urine, restrictions are imposed on patients with severe and decompensated renal failure.
However, in life-threatening conditions, it can also be used in these population groups using drug sedation for research.
A special group consists of patients with metabolic syndrome. If your body weight exceeds 150 kilograms, the study is impossible, as this exceeds the load-carrying capacity of the table.
Preparing for the examination
Before the examination, the patient must undergo general clinical laboratory tests and visit the attending physician. He will give you a referral for testing and instructions on how to prepare for a CT scan.
- Preparatory measures for the examination include limiting food consumption the day before the examination.
- The day before the examination, you should limit the intake of foods that increase gas formation: dairy, flour, legumes, some vegetables (asparagus, cabbage, potatoes, onions), fruits, chewing gum and carbonated drinks.
- For main meals, it is better to prepare porridges and light soups; for drinks, opt for tea.
In the morning before the tomography, you should avoid food altogether, limiting yourself to colorless, clear liquids. During a contrast study, the last meal should be eaten at least 6 hours before.
If a CT scan of the bladder with contrast is performed, it may be necessary to drink an ampoule of the solution 5 hours before the examination, or it will be administered intravenously immediately before the procedure, or it will be administered in the middle of the procedure with a special device after performing the diagnosis without it.
Methodology
The examination is carried out with an empty intestine and a full bladder. Immediately before the CT scan, the bladder is emptied using a disposable catheter and filled with air.
When entering the CT scan room, you must remove metal jewelry and watches. After this, having undressed to underwear, the patient takes a position on his back. It should be noted that it should be comfortable, since it is necessary to remain motionless for at least 15 minutes.
The procedure is completely painless, however, if any unpleasant sensations or discomfort occur, you must inform the diagnostician through the microphone built into the device.
Contrast
The contrast agent is an aqueous solution of iodine, administered to improve the diagnostic capabilities of CT. After injection into a vein, it is distributed into the soft tissues and allows them to be visualized with greater accuracy.
This substance is eliminated from the body on its own within a couple of days and most often does not cause complications.
Benefits of CT
Examination using computed tomography has a number of advantages over other diagnostic techniques, which is why it has become widespread.
- The accuracy of the result, which allows you to determine the presence of pathology in the early stages of development.
- The method is completely painless.
- Relative safety and rare development of complications.
- Quick examination without severe discomfort.
- Non-invasive.
- Minimizing radiation exposure.
- Availability to people due to relatively low price.
Possible complications
Complications most often occur when contrast is used. They manifest themselves in the form of allergic reactions of varying degrees of severity. The most severe of these, anaphylactic shock, can be fatal.
- However, do not forget that you are in a medical center and if an allergy develops, you will receive emergency medical care.
- Also, the incidence of this complication is extremely low, and before the examination, the doctor who referred for the examination is required to collect an allergy history.
- Quite rare, but with frequent use of CT, the risk of developing a malignant neoplasm may increase.
This may be due to the accumulation of mutations in cells as a result of exposure to X-ray radiation on genetic material. This can be avoided if there are breaks between exposures of more than two weeks.
Other examination options
If there are contraindications, you can resort to other methods.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs is an accessible and non-invasive technique without radiation exposure, available in almost any clinic.
- Cystography is a study of the anatomical features of the bladder using an X-ray apparatus and radiopaque substances.
- Cystoscopy is an invasive technique performed using a catheter and microcamera. Its main advantage is the possibility of simultaneously taking a biopsy from the most changed and suspicious areas.
Magnetic resonance imaging is a non-invasive and radiation-free technique that has the same accuracy of the resulting image. However, it requires more time of immobility, as well as a number of contraindications associated with the presence of metal implants and the mental state of the patient (claustrophobia).
Doctor's report
The radiologist makes a conclusion about the results based on the image on the screen. Using it, he judges the existing pathology or its absence: inflammation, stones or a tumor process.
He also judges the size of the bladder, the tissues surrounding the bladder and the condition of the prostate gland.
He writes all this in his conclusion and makes a presumptive diagnosis, which can later be confirmed or refuted by the attending physician. The image is recorded on disk so that changes in the genitourinary system can be compared over time.
| 486 views
Source: https://bolimed.ru/mochevoj-puzyr/kak-provoditsja-kompjuternaja-tomografija-mochevogo-puzyrja
CT and MRI of the bladder
MRI of the bladder is usually performed during a general MR examination of the pelvic organs. This is a very informative, painless and non-invasive way to diagnose diseases, which also does not harm the body.
Doctors usually prescribe MRI after undergoing an ultrasound or CT scan. Therefore, this procedure is part of the research in this area. For example, if bladder cancer is suspected, in addition to tomography, a general, cytological and bacteriological urine test is taken.
Types of bladder examination:
- Laboratory tests (including urine and blood tests)
- Instrumental.
As a rule, to diagnose bladder diseases, blood and urine tests, ultrasound, X-ray, CT, and MRI are first prescribed.
However, unfortunately, in some cases these studies cannot provide a complete picture for diagnosis. Based on the results of a general and biochemical blood test, the performance of the kidneys is assessed and the presence of inflammation can be detected.
More information will be provided by the results of a urine test, which show the presence of infections and urolithiasis.
Afterwards you will be required to undergo an ultrasound. The examination can detect dysfunctions of the organs of the genitourinary system in case of inflammation, developmental disorders or structural anomalies, stones and their size and location. The value of this examination lies in its low cost, simplicity and non-invasiveness.
Instrumental research plays a huge role. A catheter with an endoscope is inserted into the bladder into the urethra. It will show abnormalities in the structure of the inner wall of the bladder, and it can also be used to remove a small stone from the lumen of the urethra and remove urine.
MRI image with a full bladder
For the purpose of diagnosing urological diseases, X-ray examination is widely used. X-rays using contrast agents will help detect: kidney and bladder stones, urinary tract obstruction, tumors, infections, etc.
To obtain complete data, the patient may be referred to a CT or MRI.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are very similar. They make it possible to obtain high-quality multilayer images in different projections and high resolution.
- CT, as the most informative x-ray method, allows you to diagnose structural and pathological changes and see the disease in the early stages.
- CT is performed with the introduction of contrast agents to increase tissue density.
- CT results will help doctors identify:
- cysts
- neoplasms of the bladder and other organs
- stones, their sizes
- anomalies in anatomy
- consequences of kidney and bladder injuries.
The big disadvantage of CT is the x-ray exposure of the human body. In addition, contrast cannot be used if the patient has impaired renal function.
What does an MRI of the bladder show?
Indications and symptoms for a doctor to refer you for a CT or MRI:
- possible tumor formations (malignant and benign)
- anomalies of various types
- enlarged lymph nodes
- congenital anomalies of the genitourinary system
- preparation for surgery
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment, preventing relapse.
Blood in the urine may indicate the consequences of an infection in the genitourinary system.
The urologist will refer you for the most accurate and informative MRI examination to confirm or refute various possible diseases:
- urinary tract infection
- cystitis
- venereal diseases
- nephritis
- glomerulonephritis.
MRI is most often ordered to confirm bladder cancer.
Procedure and preparation for MRI of the bladder
The examination is carried out using a 1.5 Tesla high-field tomograph. Typically, a contrast agent is injected into the blood to obtain accurate results. After its administration, the liquid concentrates in the tumor. This allows you to see its location and size.
The examination should be performed when the bladder is low or moderately full. Two hours before the examination, you should not empty it, and it is also recommended to drink at least a liter of plain water. You should also abstain a few days before the procedure from eating fruits, bread and other confectionery products, legumes, fermented milk and carbonated drinks.
SHARE WITH YOUR FRIENDS AND VOTE
(2
Source: https://tomografpro.ru/mrt-malogo-taza/tomografyia-mochevogo-puzyrya.html
Computed tomography of the urinary system: how to do it
Diagnosis of diseases using CT and MRI of the urinary system is an important procedure that allows us to identify all hidden pathologies of organs, especially when using advanced equipment of modern medicine. Many leading clinics use the latest computer tomography and magnetic resonance imaging machines to examine the bladder.
Indications for diagnosis
Nowadays, a fairly large number of diseases require thorough diagnosis and the use of computed tomography.
The 6 main symptoms indicating the use of CT of the urinary system are:
- Disturbance in the outflow of urine or too frequent urge.
- Bladder muscle dysfunction (incontinence), especially at night.
- The occurrence of painful sensations during the process of emptying the bladder.
- Pain syndrome in the groin area.
- Visual changes in urine.
- Presence of blood cells in the urine.
Diseases for which CT and MRI are used
Hematuria (the presence of blood in the urine) is especially dangerous, so it is important to find out the nature and area of the disease. MRI of the urinary system allows you to obtain the most accurate image of the patient’s organs affected by the anomaly. Diseases such as urinary tract infections, nephritis, sexually transmitted diseases, and cystitis require highly accurate images.
Urolithiasis is most often diagnosed through a comprehensive examination using CT and MRI tomography. If a stone is found in the urinary system, a bladder examination is prescribed to identify the cause of its appearance. The progression of the disease carries dangerous complications and causes not just discomfort, but also prevents the patient from living normally.
Blockage of the ureter can cause acute renal failure and painful renal colic in the patient. In this case, the specialist chooses CT tomography without contrast enhancement. This diagnostic method is also used in cases of controversial situations, when the cause of the appearance of some symptoms has not been identified, and before surgery to clarify the location of the stone.
It is important to remember that if any of the symptoms described above appear, you should contact your doctor; diseases of the urinary system are extremely dangerous if they occur chronically.
If the doctor suspects the presence of tumors in the patient’s organs, an MRI of the bladder using contrast is prescribed.
This method is highly accurate and allows you to show the entire area affected by kidney cancer; formations over 1 mm are scanned, but it turns out that the most accurate way is to visualize formations over 3 mm.
This advantage is used by the world's leading oncologists for early diagnosis of cancer, which increases the positive prognosis tenfold.
Many formations are not amenable to conventional ultrasound examination due to their anechoicity (inability to reflect sound).
With the use of contrast, the introduction of a special substance that paints the affected areas a certain color, and MRI of the bladder, it is possible to obtain not only a section of the kidney, but also strictly defined edges of the tumor.
The introduction of contrast helps to check the complete blood flow in the patient’s urinary system and to diagnose the appearance of metastasis in the area located next to the neoplasm.
Preparing for tomography
CT and MRI scanning methods do not require special preparation; you just need to follow some recommendations. For several days before the procedure, you should not consume various foods that can lead to increased gas formation. Immediately before the examination, an enema is given to cleanse the intestines, but it is not recommended to completely empty the bladder.
Mskt kidneys
If the clinical picture is unclear, and the most complex and severe cases of disease, the patient is prescribed multislice computed tomography (MSCT of the bladder).
This method is based on a spiral examination of the patient. Scanning is carried out in 3D mode. A large number of sensors transmit a series of signals and build several hundred pictures, which are then combined into a small clip. Pictures are made in layers with a step of 1 mm. The procedure is performed both with and without contrast.
The duration of the procedure using MSCT depends on the complexity of the case, but takes up to half an hour. At the same time, the patient's exposure to harmful radiation is minimized as much as possible, compared to other tomography methods.
The MSCT scanning method is often used to diagnose kidneys:
- Neoplasms in the kidneys of various nature.
- Study of the occurrence of renal colic.
- Diagnosis of the organ after surgery.
- Examination of congenital pathologies of the bladder.
- Study of the size and density of kidney stones.
- Diagnostics of blood circulation in the genitourinary system.
The MSCT method has its contraindications and permissions:
- The patient's weight should not exceed 120 kg.
- The patient cannot sit still due to various disorders.
- Pregnancy.
- The course of diseases in an acute form.
- Age less than 14 years.
- Contrast is not allowed in case of renal failure, since the yield of the dye is impaired.
- Allergic reactions to contrast components.
The method of examining the bladder does not require special preparation. It is recommended not to eat a couple of hours before the procedure and to wear loose clothing. The tomograph consists of a table (mobile) and a tomograph ring. The procedure is performed lying down, in a supine position, with your arms above your head. You need to lie flat and motionless, and follow the doctor’s commands. The specialist is constantly in touch with the patient.
The methods of computed tomography, MRI, MSCT are interchangeable and equivalent, the only differences are in the intensity of radiation and the accuracy of image acquisition. But in modern diagnostics of the kidneys and the entire genitourinary system, they have become an integral part.
Source: https://pochkam.ru/diagnostika/kt-mochevydelitelnoj-sistemy.html
MRI of the bladder, urethra, kidneys and CT of the urinary system
MRI and CT of the genitourinary system are very informative, and therefore in demand diagnostic methods. With their help, doctors identify a large number of pathologies at the initial stage of development.
How does a CT scan of the bladder differ from an MRI? What are the indications and contraindications for these procedures? How does the diagnostic process take place? Which research method is better for women and men? The answers to these questions will be discussed in the article below.
Indications for MRI and CT of the urinary system
In most cases, an MRI or CT scan of the bladder is prescribed after detecting abnormalities that were identified on an ultrasound. Often these procedures are used to confirm or refute the diagnosis, as well as as a differential diagnosis. In most cases, CT or MRI of the genitourinary system is prescribed:
- with enlarged lymph nodes in the groin area;
- if a tumor is suspected;
- for congenital and acquired anomalies of the kidneys, bladder and urethra;
- to control tumor growth;
- in order to establish the most effective method of treatment or monitor the effectiveness of the course being used;
- in order to establish the current condition after surgery;
- as an assessment of the size and location of internal organs before surgery.
Contraindications for each procedure
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging studies are safe diagnostic procedures for the patient, but still have limitations. Doctors include general contraindications:
- pregnancy and lactation;
- diabetes;
- severe diseases of the cardiovascular system, liver and kidneys;
- allergic reaction to iodine.
Patients with ferromagnetic prostheses and implants, persons under 14 years of age, and those with a large body weight (more than 120 kg) should not undergo MRI of the urinary system. The risk group for CT examinations includes people with high concentrations of creatine in the blood, those suffering from theriotoxicosis and experiencing problems with blood clotting.
MRI diagnostics of the bladder, kidneys and urethra
MRI of the bladder, urethral canal and kidneys allows you to obtain the maximum amount of information about the current state of these organs. The procedure is carried out non-invasively and is completely safe for the body of the person being examined. In most cases, diagnosis is part of a general examination, which consists of a complex of different techniques.
Preparation for the study and its stages
In order for the bladder to be displayed as clearly as possible on an MRI, bowel activity should be minimal. To do this, at least 24 hours before the examination, the patient must stop eating foods that can increase peristalsis and cause gas formation. In addition, on the eve of the study, the patient should undergo a cleansing enema.
If an MRI of the bladder is performed, it should be full. To do this, 1 hour before the start of the procedure, the subject needs to drink 1-1.5 liters of still water and not urinate.
Before an MRI, the patient must remove all metal jewelry and lie down on a retractable couch. The procedure itself will begin after the table moves into the tomograph, which resembles a large tube. During the examination, you must lie still so that the image is clear. During tomography, the machine makes noise, so the patient is given earplugs.
In most cases, MRI of the bladder with contrast lasts about 30 minutes, and without the injection of a contrast agent - no more than 15 minutes. The decrypted results will be ready a few hours after the end of the examination.
What does a tomogram show?
The attending physician will see in the resulting images:
- benign formations with a diameter of 1 mm;
- malignant tumors and the degree of involvement of nearby tissues;
- the presence of a hernia in the bladder;
- the presence of stones in the genitourinary system, as well as their size and location;
- diverticulum formation;
- other pathologies of the bladder and pelvic organs of the subject.
CT scan of the urinary system
For these purposes, an X-ray scanner and powerful computer equipment are used to process the resulting images and create a single picture of the area under study.
How do they do it?
A CT scan of the bladder also requires simple preparation. The only thing that is required from the patient is to drink 10 ml of UROGRAFINE, diluted with 200-250 ml of water, first 12 and then 2 hours before the study and completely refuse food 3 hours before the start of the procedure.
Before lying back on a special table, the patient must remove clothing and accessories with metal fasteners. This is done to prevent shadows from appearing that degrade the image quality.
If necessary, the subject is given a certain body position using special bolsters and straps.
The table with the patient slides into the equipment so that the area being examined is flush with the scanner.
Before the machine begins scanning, medical personnel leave the room to avoid exposure to x-rays. The procedure itself lasts 5-15 minutes, and the results will be ready a few hours after the end of the examination.
CT with contrast
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography is an improved examination method that produces more detailed and accurate images. The use of contrast is necessary in cases where, after a conventional tomography, the doctor still has questions.
When it enters the blood, the contrast agent “tints” the tissue, thereby highlighting it in the image. It is this enhancement that allows you to clearly visualize internal organs and tissues, examine their boundaries, and see the features of the blood supply.
Due to the fact that the contrast accumulates in the area under study, it perfectly shows areas of increased blood supply, which are characteristic of cancerous tumors.
By introducing contrast, the location and size of formations can be clearly recorded, their growth and the degree of involvement of neighboring pelvic tissues can be determined.
Computed tomography is performed first without contrast agent. Its results will be the “starting point”. Then a catheter is inserted into the patient’s vein and connected to an injection syringe with a contrast agent.
Almost simultaneously with the administration of contrast, another scan is performed. As the amplifier moves from the artery to the vein, a series of more pictures are taken, and after this comes a final examination, which doctors call the “excretory phase.”
In total, when examining the urinary organs using CT with the introduction of contrast, 4 scans are performed.
Decoding the results
The conclusion describes the pathologies identified during the examination and their characteristics. It is on the basis of the deciphered results that the attending physician makes a decision on the further course of treatment.
Pros and cons of MRI and CT: which method is better?
This kind of research of the urinary organs is very reliable and safe for humans.
Both procedures make it possible within a few hours to obtain a multi-layer image of pathologies at the initial stage of development with high resolution.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging do not cause discomfort to the subjects, do not require special preparation and last no more than 30 minutes.
Magnetic resonance imaging does not expose the patient’s body to ionizing radiation, which is typical for CT, and therefore can be performed frequently. This is a very significant factor in the control of malignant tumors.
In this regard, it is preferable to study the urinary system using MRI, but do not forget that each case is individual. The final decision when choosing a diagnostic method is always made by the attending physician.
Source: https://vedmed-expert.ru/mrt/maliy-taz/mrt-mochevogo-puzyrya.html