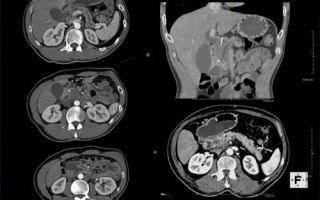
What does MRI show - diagnostics of the abdominal cavity
MRI of the abdominal cavity is a safe, non-invasive and highly informative method for studying internal organs. It is based on the effects of radio frequency pulses and a magnetic field.
In some particularly complex cases, MRI allows accurate diagnoses to be made with high accuracy.
This study is used to monitor treatment and as a diagnostic method without the use of more complex and painful procedures, such as puncture or colonoscopy.
What organs are examined?
Computed tomography is prescribed for examining the following abdominal organs in men and women:
- pancreas;
- intestines;
- liver;
- stomach;
- spleen;
- kidney;
- gallbladder.
Results, pathologies
Magnetic resonance imaging allows us to identify the following pathologies in men and women:
- presence of neoplasms (benign and malignant);
- congenital anomalies of organs and blood vessels;
- size, structure, location of organs;
- pathological processes (inflammation, obstruction);
- deformations of blood vessels and organs (thrombosis, ruptures, deformations, aneurysms);
- circulatory disorders.
After the examination, about an hour later, a person receives photographs of the tissues and organs of the abdominal cavity, as well as a conclusion from a doctor - a specialist in radiological diagnostics. With these results, you need to contact your doctor, who will make a diagnosis and prescribe therapy if necessary.
MRI procedure of the abdomen
The research includes several steps:
- The patient enters the office, where he is met by a doctor or nurse, who tells him the algorithm of his actions during the procedure and the order of its implementation.
- A person changes into loose disposable clothing.
- If necessary, a contrast agent is injected into the vein.
- The person being examined is placed on a retractable table, the limbs are fixed to avoid involuntary movements, and earplugs or headphones are offered so as not to hear the noise that the device makes (this is mandatory for children). The table is pushed into the tomograph opening.
- The doctor goes into a room with monitors on which he will see the scan results. He can communicate with the patient through a microphone.
- The procedure lasts from half an hour to an hour. During this time, the patient must remain completely still. If you feel discomfort or your health begins to deteriorate, you must press a special button and the doctor will stop the procedure.
- After the examination is completed, the doctor informs the patient about this, pulls out the table, removes the fixing elements and helps the person get up.
- The patient gets dressed, and the doctor processes the received images and draws up a conclusion. In particularly complicated and complex cases, he may involve other specialists.
The examination procedure does not cause any significant side effects. But sometimes, when a contrast agent is administered, a person experiences mild nausea, dizziness, and skin reactions are possible. This should be reported to your doctor immediately. Such symptoms are quickly eliminated.
ADVICE! Do not be afraid if during the procedure you experience a feeling of heat spreading throughout your body. When contrast is administered, some patients feel a cold sensation, while others feel a warm feeling. There is also an iron taste in the mouth. This is all completely normal.
Processing the results takes from one to two hours. After this, the results are handed over to the person being examined, and he goes with them to the treating doctor. If you don't have time to wait, you can come back the next day for results. Modern paid clinics send results by email, and images can be received on a disk or flash drive.
Research methods
- Abdominal MRI has several types. These include:
- Using this method, pathologies are determined as blood passes through vessels through tissues and organs.
- Detects metabolic diseases.
- Allows you to see changes in the walls of blood vessels and the vascular bed without the use of contrast.
The most extensive study is a survey MRI of the abdominal organs, which evaluates the size, structure, shape of organs, their blood supply, and the impact of pathological processes.
Survey magnetic resonance imaging allows you to examine the condition of the intestines, stomach, spleen, liver, kidneys, adrenal glands, biliary tract and gallbladder, pancreas, soft tissues of the abdominal cavity, lymph nodes, veins and arteries.
Indications
Abdominal MRI is not used for screening due to the cost of the procedure.
Typically, such a study is prescribed in cases where other research methods do not allow an accurate diagnosis or when the disease occurs with significant complications.
Scanning is also used to study the development of certain dangerous diseases (for example, tumors) and monitor the effectiveness of therapy.
Clinical cases in which the doctor prescribes magnetic resonance imaging are:
- Accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites).
- Questionable results of other diagnostic procedures (CT, X-ray).
- Enlargement of the spleen, liver, pathological changes in their tissues.
- Detection of inflammatory processes (with identification of foci), internal bleeding, ischemic changes in tissues and abdominal organs.
- Pancreatitis.
- Stones in the kidneys, gall bladder, urinary and biliary tract.
- Postoperative complications, the need to evaluate the operation performed.
- Congenital anomalies of the structure of the abdominal organs.
- Detection of benign and malignant tumors, spread of metastases, control of their spread and evaluation of treatment results.
- Contraindications to other diagnostic procedures.
Indications for MRI of the abdominal cavity with the introduction of a contrast agent based on the metal gadolinium are the identification of circulatory disorders of blood vessels and organs, tissue ischemia.
You can undergo an MRI not only as prescribed by a doctor, but also at your own request. This should be done in the following cases:
- frequent cases of nausea, vomiting;
- regular feeling of heaviness or pain in the area of the liver, pancreas, stomach, kidneys;
- yellowing of the skin;
- change in color of stool and urine;
- checking your condition after operations, abdominal injuries.
If you apply for an MRI procedure on your own, you must first study the reputation of the clinic where the examination is planned and look at reviews of the doctors. The procedure is quite expensive, so you need to be sure that the results will be accurate.
Contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging is considered a painless and safe research method. The World Health Organization states that the use of magnetic fields up to 1.5 Tesla does not harm the human body. X-rays are not used during the examination. Gadolinium-based contrast is also not harmful to health.
There are a number of cases in which magnetic resonance therapy is prohibited. But the prohibitions can be absolute, when it is categorically impossible to carry out such diagnostics.
These include:
- Electronic and ferromagnetic structures in the human body (insulin pumps, pacemakers, defibrillators). A powerful magnetic field can cause them to malfunction or move, leading to damage to surrounding tissue and internal bleeding.
- Children's age up to 5 years.
- Diseases in which the patient cannot remain still.
- The patient's weight is more than 150 -180 kg (depending on the specific MRI machine). It makes it difficult for a person to find himself inside the capsule.
MRI with contrast is not performed in the presence of renal failure (gadolinium is excreted by the kidneys, loading them, this can provoke an exacerbation), allergic reactions to a contrast agent, or undergoing hemodialysis.
There are relative contraindications:
- tattoos that use metal-based paint. The patient may experience a burning sensation and itching at the site where the drawing was applied;
- pregnancy in the 1st trimester. MRI can negatively affect embryo development;
- fear of closed spaces;
- lactation (with MRI with contrast). Gadolinium penetrates into all body fluids, including breast milk;
- mental illness. A person cannot behave adequately in a capsule.
Relative contraindications differ from absolute contraindications in that they can be overcome at the discretion of the doctor. Problems with claustrophobia are solved by using an open-circuit MRI machine. For a person with mental illness, the procedure is carried out in remission and before the examination they are given sedatives.
In cases where MRI with contrast is the only diagnostic technique that allows you to determine the health status of a nursing woman, it is allowed to be performed. But the woman will need to express milk or temporarily transfer the baby to artificial feeding, since breastfeeding the baby is prohibited for 2 days after the procedure.
Preparation
It is necessary to prepare in advance for an MRI of the abdominal organs in order for the results to be reliable; first of all, preparation includes following a diet. Foods that can cause increased gas formation are excluded from the diet 2-3 days before the prescribed procedure.
This includes black bread, carbonated drinks, alcohol, legumes, fermented milk products, spices, and a large number of fruits and vegetables that have not undergone heat treatment. If an examination of the liver or pancreas is prescribed, then it is necessary to reduce the consumption of carbohydrates to a minimum, or even give them up for a while.
This will relieve the stress on the organs.
If there is constipation or flatulence, the patient is prescribed an enema, laxatives, carminatives (Sorbex, Espumisan).
If an MRI with contrast is planned, an allergy test to the injected substance is performed. If you have kidney disease, urine and blood tests should be performed, since the contrast puts a strong strain on the urinary organs.
Women should make sure they are not pregnant. In case of hypermobility, the procedure is performed under local anesthesia. For overly restless patients, the doctor will prescribe mild sedatives.
The last time a person should eat a light meal is 7 hours before the scheduled procedure. And within 4 hours any liquid is excluded. You should not use cosmetics on the day of the test, as they may affect the results.
The person comes with the results of the previous MRI, if available. Take any antispasmodic (Papaverine, Spazmalgon) within 40 minutes and visit the toilet. All jewelry, dentures, and wig should be removed. Leave keys, bank cards, gadgets.
Prices
Abdominal MRI is an expensive procedure. In general, prices in Russia range from 4,000 to 10,000 rubles. The cost is influenced by the rating of the medical institution, the purchase of a contrast agent, pricing in the region, the time it takes to decipher the results, and their recording on a storage medium.
MRI is one of the best diagnostic methods with which you can see the slightest damage to organs, tissues, and cell membranes. Any qualified medical specialist who suspects a serious illness in a patient prescribes an MRI. This allows you to identify pathology in the early stages and begin timely treatment.
Source: https://mrtu.ru/organy/mrt-organov-bryushnoj-polosti-chto-pokazyvaet-delayut.html
Abdominal MRI with contrast
Magnetic resonance imaging is one of the most informative diagnostic methods, allowing you to give the most accurate assessment of the state of internal organs and soft tissues of the area under study, as well as identify the pathological process at different stages of its development. This type of examination is carried out through the influence of strong electromagnetic waves on the body, which are generated by a tomograph and are absolutely harmless to the human body.
MRI of the abdominal organs helps to examine in detail such anatomical structures as the kidneys and adrenal glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, as well as muscles, lymph nodes and subcutaneous fat. The study is widely used by specialists in various fields (therapists, nephrologists, oncologists, etc.). The procedure can be carried out either as prescribed by the attending physician or independently, if desired.
There are several options for performing an MRI of the abdominal cavity: with and without contrast. Dyes are used to enhance the visualization of certain structures. Of the contrast agents, preference is most often given to Omniscan and Gadovist, which contain gadolinium.
After intravenous administration, the active substance penetrates the tissues affected by the disease and makes them brighter in the picture. The dosage of the drug used is directly proportional to the patient’s weight. The contrast used during the procedure is practically harmless to the body and quite rarely causes allergic reactions.
Intravenous administration of gadolinium helps facilitate the diagnosis of severe clinical cases
Indications for the study
The attending physician may issue a referral for magnetic resonance imaging of the abdominal organs if pathologies such as:
- Anomalies in the development of internal organs.
- Benign and malignant tumors and their metastases.
- Vascular pathologies (aneurysms, stenoses, thromboembolism, impaired blood outflow in the vena cava or portal vein, etc.).
- Portal and biliary hypertension.
- Internal bleeding of unknown location.
- Post-traumatic pathologies.
- Foreign bodies in the area being examined.
- Inflammatory, ischemic or destructive changes in internal organs (empyema of the gallbladder, kidney carbuncle, cirrhosis of the liver, etc.).
Contraindications for the study
This type of diagnosis is prohibited in the following situations. The presence of metal foreign bodies inside the body (insulin pump, pacemaker, vascular clips, trauma pins, etc.).
Full body MRI
A tomograph is inherently a strong magnet that can displace objects that are not fixed in hard tissues and cause harm to the body, as well as disrupt the operation of electrical appliances and distort the quality of the resulting image.
Significant increase in the patient’s body weight (this value is individual for each device). Claustrophobia: an alternative is to conduct the study in open-type tomographs.
MRI of the abdominal cavity with contrast has additional limitations: pregnancy and breastfeeding, a burdened allergic history, severe renal and liver failure (the time it takes to remove the drug from the body is prolonged, which can lead to the development of complications).
Preparation and methodology for the procedure
To prepare for the study, just follow a few simple rules:
- A couple of days before the procedure, avoid foods that increase intestinal motility and promote increased gas formation (legumes, fermented milk products, carbonated drinks).
- Do not eat for at least 9 hours before diagnosis.
- If you have flatulence, take Espumisan or Motilium.
- Half an hour before the study, take an antispasmodic (No-shpa, Spazmalgon, etc.).
- Immediately before the procedure, remove all metal products, lay out mobile phones and magnetic cards.
Following the instructions will help you get a quality image.
Preparing for an abdominal MRI with contrast also includes consulting with your attending physician and obtaining approval for the procedure. When a contrast agent is introduced into the circulatory system, the vessels become stained and accumulate in the tissues, while the degree of accumulation and the rate of elimination of the substance are affected by the blood supply and metabolic rate.
Thanks to this, the resulting sections show in detail the foci of pathological neoplasms, areas of ischemia, sclerosis and inflammation in the organs.
The study begins with the person being placed on a special mobile table, which drives into the tomograph.
The magnetic field generated by the equipment excites hydrogen atoms in the human body, after which radio waves are emitted by the cell nuclei and project an image onto the monitor screen.
At the end of this process, the cells return to their original state without any changes. The computer processes the information received from organs and vessels and creates a high-quality three-dimensional image.
During the examination, you must lie still so as not to reduce the quality of the resulting image and not to complicate further diagnosis. The procedure lasts from 30 to 60 minutes.
After completion of the diagnosis, patients are given the results on film, disk or other electronic storage medium.
To obtain a specialist’s opinion, you must wait some time until the radiologist describes the detected changes and makes his verdict.
Pros and cons of magnetic resonance imaging
The advantages of this type of diagnosis include:
- Non-invasive and painless. During the study, the skin is not damaged, so the procedure does not cause discomfort to the patient.
- There is a low likelihood of developing an allergy to contrast. Gadolinium is hypoallergenic, unlike iodine, which can be used for CT and X-rays.
- High information content. While scanning the body, the tomograph performs many slices with high frequency and in different planes, which makes it possible to study the image in detail and form a model of the area under study in 3D mode.
- Harmless to the body. During an MRI, a person is exposed to magnetic waves rather than harsh X-rays. Thanks to this, the study can be carried out an unlimited number of times, for example, to assess the degree of disease progression or the effectiveness of the therapy received.
MRI slices can be displayed in multiple views
The disadvantages of performing an MRI of the abdominal organs are much smaller. Firstly, it is impossible to study bone structures in detail. This study is good at visualizing exclusively soft tissues. Secondly, it is impossible to carry out the procedure if there are metal devices in the body. Thirdly, there are some restrictions on the use of contrast agents.
Abdominal MRI with contrast is undoubtedly one of the most reliable diagnostic methods. The procedure can be performed both routinely and in urgent cases. The enormous capabilities of modern tomographs help to detect a problem at the earliest stages, which helps to begin timely measures to eliminate it, thereby increasing the likelihood of a positive outcome.
Source: https://apkhleb.ru/mrt/organov-bryushnoy-polosti-kontrastirovaniem
What is an abdominal MRI? What does it show?
But before we start, please like and subscribe to the channel. Thank you!
What organs are checked using the diagnostic method of MRI of the abdominal cavity?
This question is asked by most people who have ever heard of this research method. Before answering the question, let’s figure out what this research method is and what organs are located in the peritoneal cavity
MRI of the abdominal cavity is an effective diagnostic method that allows you to monitor changes in organs during therapy and in the postoperative period. An MRI study allows you to monitor the condition of the organ under study and obtain a clear image of it in deep sections and in different planes.
Difference between MRI and CT
Both methods of examining the abdominal organs are widely used to diagnose a wide variety of diseases. Each type of tomography has its pros and cons.
In a computed tomography scan, the human body is exposed to x-rays. Also, in most cases, there is a need to inject a contrast agent containing iodine into a vein. From the above, it can be determined that CT is contraindicated for persons with pathologies of the thyroid gland, kidneys and a tendency to allergic reactions.
Due to the fact that the CT method involves x-ray radiation, it is often not recommended.
The advantage of the method is its high speed - the picture is taken within a few minutes.
MRI is a study using the influence of electromagnetic waves in the pole of a high-intensity magnetic field.
Compared to other methods , MRI has virtually no radiation exposure to the human body , and high-contrast soft tissue allows one to obtain a good image of tissue without the use of contrast agents that must be injected into the body (in some cases, MRI is performed with contrast).
Disadvantages of MRI testing include the need to remain motionless in a confined space for long periods of time. Also, this method is not suitable for examining very large people.
Important: the advisability of MRI and CT is determined only by the attending physician.
What does an abdominal MRI show?
The image obtained during the study shows cellular disorders, damage to cell membranes, and determines the state of the intercellular space. MRI also makes it possible to determine the correct functioning of the cells of a particular internal organ .
In the diagnosis of oncological pathologies at an early stage, MRI is an indispensable research method.
Angiographic examination , which is done with an MRI machine, can show any abnormalities in the vascular bed and vascular walls.
What does an abdominal MRI diagnose?
Magnetic tomography of the OBP helps diagnosticians obtain the most accurate results when identifying various diseases in organs, including malignant neoplasms at an early stage . In addition, with the help of tomography it is possible to distinguish the process of metastasis.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
The NetGastritu project was created with the goal of providing people with accurate and up-to-date information on medical topics. Articles are written by professionals and, unfortunately, development costs slow down the development of the project. If you want to support us, use the form below.
Let's make the world a better place together. Thank you for your attention.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
By performing an MRI, a specialist can see the condition of a particular organ and determine the following pathological processes:
- pathologies of the hepatic ducts;
- gallbladder disease;
- spleen diseases;
- pathological changes in the pancreas;
- neoplasms of a malignant or benign nature, their exact location, extent of spread and severity of pathology;
- metabolic disorders;
- disturbances in portal vein pressure;
- dysfunction of the biliary system;
- pathological changes in the stomach, the level of damage to the organ mucosa, the presence of tumor processes, erosions and ulcers;
- intestinal lesions, the presence of the formation of tumors and ulcers;
- vascular abnormalities, vascular spasms, circulatory pathologies
- disorders in the circulatory and lymphatic systems;
- lymphomas with determination of their characteristics.
The specialist will refer the patient for an MRI if he suspects the development of any pathologies, especially with regard to cancer.
Indications for magnetic resonance imaging are:
- suspicion of the development of a tumor process;
- suspicion of the formation of ulcers in the digestive organs (intestines, stomach);
- suspicion of an increase in the volume of the spleen and liver;
- abdominal injuries;
- recurrent or constant abdominal pain;
- jaundice (yellow coloration of the skin and sclera of the eyes);
- inflammatory processes in the pancreas;
- the presence of fluid in the peritoneal cavity;
- suspicion of cyst formation in organs;
- thrombosis of large and small veins;
- increase in the volume of lymph nodes.
MRI is also performed before various operations, which allows us to determine:
- anomalies in the development of systems and organs;
- presence of foreign bodies;
- blood flow disorders;
- localization of inflammation;
- possible dystrophies of internal organs.
What an MRI will NOT show
Since magnetic resonance imaging is intended only for examining soft tissues, the method is not used to determine stones in the kidneys, gall bladder and ureters, as well as deposits of calcium salts.
Contraindications for abdominal MRI
Although the method is the most informative and safe, there are a number of contraindications to its implementation.
You should absolutely not use this research method in the following cases:
- the patient has a pacemaker;
- the patient has any implant in the form of a programmable device;
- presence of metal in the area of the brain or eyes.
Tomography is performed with extreme caution on patients who have the following in their body:
- bullet fragments or bullets in body tissues;
- endoprosthesis;
- metal plates, knitting needles;
- vascular clips;
- insulin pumps;
- any metal implants;
- piercing
Women are strongly advised to notify a specialist about pregnancy, especially in the first trimester and lactation.
The doctor should also be aware of the patient’s possible psycho-emotional disorders, epilepsy, and history of seizures.
How to prepare for research
No specific preparation measures for the study are required.
Shortly before checking a person's internal organs using MRI, he is examined and, if necessary, treated for parasites.
Before an MRI, a person must adhere to a certain diet for at least 24 hours , which includes avoiding eating any vegetables and fruits, raw or boiled, black bread, carbonated drinks and fermented milk products. You can eat before the study no later than 4-5 hours before the start of the test.
People prone to constipation and flatulence are advised to perform a cleansing enema 2-3 hours before the tomography or take a mild laxative.
Before the procedure, a person must take Espumisan or activated charcoal (at a dosage of 1 tablet per 10 kg of weight).
30-60 minutes before the patient is examined, he should take 1-2 antispasmodic tablets.
How the research is carried out
For the test, the patient is placed inside an MRI machine, which is a tube that is open at both ends.
The magnetic field created inside the device promotes the excitation of hydrogen atoms in the human body, after which radio waves emitted by cell nuclei form a picture on the instrument monitor. After this process, the cells return to their original state without any structural changes.
The computer processes information received from an internal organ or vessel and converts it into a three-dimensional image.
The duration of the procedure depends on how many organs are being examined. It takes about half an hour to test one organ.
Video - MRI of the abdominal cavity
Abdominal MRI with contrast - what is it?
Sometimes the patient is prescribed an MRI using contrast agents . Such an examination is necessary to determine the type of neoplasm on the internal organs of a person, the process of metastasis in the abdomen, disorders of the structure and function of blood vessels, and to diagnose minor formations on small organs (bile ducts, adrenal glands, etc.).
The duration of the contrast study is twice as long.
The doctor takes a picture of the organ being examined, injects a contrast agent into the vein, and then takes another (repeated) picture. Next, the specialist compares the results “before” and “after” and, based on the resulting picture, gives a conclusion.
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5a7bf2178139baa694016d48/5aa812df48c85ef92bf8877d
Preparing for an abdominal MRI: what can you eat and drink before the contrast study?
Magnetic resonance imaging is one of the most popular types of examination. This is a painless, non-invasive procedure that is informative and accurate. MRI allows you to detect the slightest changes or pathologies in the body that could not be detected using other types of diagnostics.
This accuracy is achieved by layer-by-layer scanning of organs, soft and hard tissues, and blood vessels. Doctors have the opportunity to study images of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space from all angles.
What are the indications for the procedure? Why do you need mandatory preparation for an MRI of the abdominal cavity? How to prepare properly? Can tomography harm the patient's health?
Indications for MRI of the abdominal cavity
Using the procedure, all organs and structures of the abdominal cavity are examined:
- stomach and pancreas;
- liver and biliary system;
- spleen;
- kidneys, adrenal glands and other urinary organs;
- intestines;
- The lymph nodes;
- blood vessel system (veins, arteries, capillaries);
- surrounding soft tissues;
- retroperitoneal space, including the spine.
When scanning, doctors diagnose:
- damage to internal organs, blood vessels and tissues;
- congenital and acquired anomalies;
- position of organs;
- benign and malignant neoplasms, metastases;
- inflammatory, obstructive or degenerative processes;
- the effectiveness of the operation and the presence of complications (adhesions, scars, abscesses);
- blood flow disorders;
- pathologies of blood vessels;
- disturbances in nerve endings and trunks;
- stones in the biliary and urinary systems (gallbladder and kidneys);
- spinal injury in this area.
The information content, accuracy and harmlessness of diagnostics makes it increasingly popular. Some people get MRIs as a precaution. Indications for mandatory procedure:
- when other types of research (ultrasound, x-ray) did not produce results;
- suspicions of malignant formations and metastases on internal organs and the spine;
- acute or chronic inflammatory processes, fluid accumulation;
- enlarged spleen or kidneys;
- injuries that could lead to organ damage and internal bleeding;
- abnormalities in the development or structure of body structures;
- benign formations (cysts, adenomas);
- pathologies of the biliary tract;
- deterioration of blood supply (ischemia);
- kidney or gallstones;
- pancreatitis;
- after surgery to assess the patient’s condition or when complications occur;
- when it is impossible to conduct another type of examination.
Why is it important to prepare for the procedure?
The abdominal cavity is a fairly large area of the body in which various inflammatory or destructive processes can occur. That is why there are several subtypes of MRI that allow you to study a specific pathology.
Survey tomography is the most comprehensive; it makes it possible to study the abdominal cavity as a whole (the position and condition of organs, vessels, soft tissues). In case of blood flow disturbances, MR angiography or tomography of the venous sinuses is indicated. The study can be performed with or without the introduction of a contrast agent.
It is important to properly prepare for any type of diagnosis. This will allow you to obtain the most accurate and correct results, taking into account the specific structure and functioning of the area under study (it is important that the intestines are as empty as possible). Preparing for an MRI is simple.
The patient is required to follow simple rules and regulations for several days. At home, following a simple diet is indicated, the essence of which will be described below. Preparatory activities do not require additional monetary or physical costs.
Immediately before the procedure, the patient changes into a medical disposable shirt. Almost all clinics provide them free of charge, sometimes they are purchased by the patient at the pharmacy.
The main thing is to remove all metal objects (jewelry, piercings, watches, hair clips, dentures, etc.). Any metal will be attracted by a huge magnet, as a result of which an expensive device may fail.
The procedure is contraindicated for people with fixed metal-containing prostheses, plates, as well as pacemakers and insulin pumps.
What can you eat and drink before the test?
During the initial consultation, the doctor explains the importance of diet and develops a diet. You need to follow it for several days. A diet before an abdominal MRI is necessary to prevent gas formation and cleanse the intestines. The basis of the diet should be natural and light foods low in carbohydrates.
What to give up:
- sugar;
- processed cereals in large quantities (semolina);
- dried fruits (raisins, dates, dried apricots);
- baked goods;
- sweets;
- semi-finished products;
- carbonated and sweet drinks;
- alcohol;
- legumes (beans, peas, lentils);
- fresh cabbage;
- raw vegetables;
- fruits in large quantities (especially apples);
- milk;
- Rye bread.
The diet includes stewed or baked vegetables, lean fish, meat or seafood, greens, some berries, and eggs. A small amount of fermented milk products is allowed, for example, low-fat cottage cheese, natural yogurt.
You can eat low-carb cereals - buckwheat, brown rice, whole grain oatmeal, barley and wheat groats. You need to drink water or unsweetened tea.
The doctor develops the menu individually. Nutrition depends on the health status and other characteristics of the patient. It is forbidden to eat 6-8 hours before the procedure (food is completely excluded). Drinking is also limited. You can drink a glass of clean water no later than 4 hours before the MRI.
Features of preparation for MRI with contrast
The procedure can be performed without contrast or with the introduction of a contrast agent. In most cases, the first type of procedure is performed, as it provides all the necessary information. Contrast is used when benign or malignant formations or various pathological processes are suspected.
The essence of the method is simple. The patient is injected intravenously with a special drug (contrast), which is quickly distributed throughout the bloodstream. When scanning, the substance in the vessels is highlighted, which is visible on the monitor. Tumors, metastases, and foci of inflammation are penetrated by a greater number of vessels than healthy tissues.
That is, they begin to glow brightly on the screen. Using this method, doctors are able to determine the nature of the tumor (benign or malignant), its exact size and location, structure and shape, and the presence of metastases.
This allows cancer to be diagnosed at the earliest stages, which gives a greater chance of recovery.
Preparing for the procedure is not much different from a regular MRI. Doctors should rule out an allergic reaction to the contrast and, if necessary, replace it with another drug.
The patient must report allergies to medications, provide the results of necessary laboratory tests, and report previous illnesses or surgeries.
The doctor should know about the medications you are currently taking (sometimes the contrast agent is incompatible with some medications).
Be sure to follow a diet. The diet includes healthy natural foods low in carbohydrates that do not cause flatulence (gas formation). People prone to digestive disorders and chronic constipation are recommended to undergo a cleansing enema. During the tomography, the intestines must be empty. This will provide accurate and undistorted data.
Before diagnosis, it is recommended to take an antispasmodic (No-Shpa, Spazmolgon). For some mental disorders, excessive excitability or fear of confined spaces, the use of sedatives or relaxants is indicated.
Negative impact of abdominal MRI on the condition of human organs and systems
MRI is one of the safest research techniques. Ionizing radiation is completely excluded, that is, the person is not exposed to radiation. The effect of the magnet does not affect the body and internal processes.
The body may react negatively to the contrast agent, but this does not happen often. It is important to inform your doctor about your health status and allergies. The contrast itself is harmless. It does not affect the functioning of organs, is not absorbed into the bloodstream and tissues, and is quickly eliminated from the body. We are talking about individual intolerance to the drug. In this case, it can be replaced.
To avoid adverse reactions and health problems, you need to highlight a list of conditions for which the procedure is contraindicated:
- pregnancy period (the first trimester is considered the most dangerous; examination is possible if absolutely necessary);
- MRI with contrast during breastfeeding (the substance can get into the milk and harm the baby);
- renal and heart failure;
- mental disorders, since patients are given sedatives before the examination;
- implanted metal prostheses, plates, implants, as well as permanent braces;
- an implanted pacemaker or insulin pump (the electronics will immediately malfunction and break, and the tomograph may also be damaged);
- large dimensions and patient weight more than 150 kg.
To ensure that the MRI does not cause harm, and its results are as informative and accurate as possible, it is necessary to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations and prescriptions. It is important to properly prepare for the procedure and lie still during the scan (up to 1 hour - depending on the type of study).
Source: https://vedmed-expert.ru/mrt/brushnaya-polost/podgotovka-k-mrt-bryushnoj-polosti.html
Medscan network of medical centers
- the presence of cardiac pathologies, both congenital and acquired;
- acute inflammatory process of the respiratory system;
- the presence of signs indicating various liver pathologies, including neoplasms;
- pathological conditions of the urinary system;
- problems with reproductive function;
- pathologies of large vessels (for example, aortic aneurysm);
- inflammatory and/or ulcerative processes of the gastrointestinal tract.
- pregnancy (first trimester), the use of contrast is prohibited;
- the presence of electronic devices to support the functioning of organs (pacemaker, etc.);
- implanted joint endoprostheses, titanium plates and pins;
- claustrophobia - fear of being in confined spaces;
- psychomotor agitation, mental disorders;
- renal failure.
- Ultrasound;
- CT scan;
- PET-CT;
- MSCT.
During magnetic resonance imaging, in most cases, contrast injection is not required. However, on the recommendation of a doctor, a contrast solution can be used to improve the visualization of the image.
No special preparation is required for MRI of internal organs. It is recommended to follow a diet that excludes foods that increase gas formation.
The patient must sit comfortably on the tomograph table in a position that will allow the examination to be carried out. The patient's head, arms and legs can be secured with special straps.
This is necessary to maintain complete stillness, which should be maintained during the scanning process. For better visualization, intravenous contrast may be administered before the procedure, after which the table is directed into the tunnel.
Next, the rotation of the tomograph ring begins.
The patient will not experience any discomfort or pain during the scan. Clicking or cracking sounds may be heard when the scanner is rotated. The doctor will be in the next room, separated from the scanning area by glass. To communicate with medical staff, communication via a microphone is provided.
20-30 minutes, with contrast - 60 minutes.
In our diagnostic center, it is possible to conduct MRI of internal organs in infants using safe anesthesia and mild sedation under the supervision of an anesthesiologist.
Two hours after the scan, the results of the study will be known with a detailed description compiled by the diagnostician. You can get a conclusion both in the center and in your personal account on the website.
Source: https://medscannet.ru/mrt/vnutrennih-organov/
Scandinavian Health Center
| Service | Price |
| MRI of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneum | 8000a |
| MRI of the abdominal organs (liver, pancreas, spleen, gall bladder) | 7000a |
| MRI of the abdominal organs (liver, pancreas, spleen, gallbladder) and cholangiography | 9000a |
| Administering a contrast agent without an automatic injector | 5000a |
| Bolus contrast using an auto-injector | 6000a |
| Issuance of a duplicate of the study on film | 1000a |
| Issuing a duplicate of the study on CD or DVD | 500a |
At the Scandinavian Health Center, diagnostics are carried out using a high-field expert-class tomograph from Siemens “MagnetomAera”, equipped with 64 radio frequency channels, which allows obtaining high-quality images of the examined organs. Thanks to the spacious tunnel (diameter 70 cm), the procedure will not cause discomfort.
Diagnostics allows not only to identify pathology at the earliest stage, but also to evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy itself. For each patient, the Center’s specialists, based on the results obtained, draw up a comprehensive treatment program. Doctors can quickly make changes to the treatment process, which significantly reduces the time of treatment and further recovery.
The professionalism of the Center’s staff, the most modern medical equipment, care and attention to each patient, timely diagnosis are a guarantee of successful recovery.
Why MRI? Advantages of the method.
In the world of rapidly developing modern medical imaging technologies, there are a large number of different methods for examining the human body, among which magnetic resonance imaging, due to its non-invasiveness, safety, accuracy and information content, holds one of the leading positions. The main advantages of this method are:
- safety - X-rays are not used. Diagnostics is based on the action of a magnetic field, which is harmless to humans. This makes it possible, if necessary, to repeat the examination regardless of the time of its last conduct, as well as prescribe this procedure to children and pregnant women after the first trimester;
- painlessness due to the fact that the method does not require surgical interventions;
- detection of difficult-to-diagnose pathologies even at the earliest stages.
What types of abdominal MRI exist, and what organs are included in the scope of the study?
MRI scanning can be performed without the use of contrast agents (native tomography) and with contrast - drugs based on gadolinium salts are administered intravenously (so-called.
paramagnetic substances), which accumulate differently in affected (tumor) and healthy tissues; make them more contrasting, thanks to which it is possible to clearly determine pathological zones (foci, formations), their boundaries and extent.
The organs and tissues of the abdominal cavity examined by magnetic resonance imaging include:
- liver - in order to determine its structure, size and nature of formations, altered parenchyma; traumatic liver, hematomas;
- gallbladder and bile ducts - a specialized study is performed - cholangiography; this method is unique and provides answers to the most difficult questions when confirming or refuting rare or questionable diagnoses made through other less accurate studies. The technique allows you to accurately determine the diameter of the lumen of the bile ducts, the presence of stones or tumors of the ducts; allows you to identify the smallest polyps of the gallbladder;
- spleen - to identify cystic and tumor formations, foci of infarction, traumatic injuries - primarily hematomas;
- pancreas and its ducts - allows you to identify inflammatory changes in the gland, neoplasms, dilation of the pancreas ducts;
- kidneys, adrenal glands - thanks to images of this organ obtained using MRI diagnostics, tumors are detected in the early stages of development (less than 10 mm in size), difficult to diagnose in other ways, stones, developmental anomalies, the condition of the vessels and the renal collecting system;
- stomach and intestines - diagnostics allows us to identify the presence of foreign objects, inflammatory processes, structural pathologies, tumors in the intestinal walls;
- abdominal vessels - using magnetic resonance scanning it is possible to detect blood clots, aneurysms, developmental anomalies, traumatic injuries;
- lymph nodes of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space - the study reveals the size and number of nodes, their increase in inflammatory processes of the abdominal organs; their metastatic damage during tumor processes in the abdominal cavity; lymphogenous tumors and lymphoproliferative processes.
In what cases is an MRI of the abdominal cavity indicated?
Magnetic resonance imaging of this anatomical area is used as an additional study when the nature of the clinical picture makes it difficult to make an accurate diagnosis or requires confirmation of an existing one. Diagnostics using MR scanning is a highly informative and accurate research method and is prescribed to patients when:
- suspicion of neoplasms of various types and metastases in organs of a given anatomical region;
- suspected acute pancreatitis, liver cirrhosis, cholecystitis and other inflammatory processes;
- aneurysms of the aorta and its branches;
- various pathologies and developmental anomalies of the abdominal organs;
- injuries to the abdominal area;
- suspected internal bleeding;
- the presence of stones in the kidneys and gall bladder, urinary and biliary tracts.
Contraindications for MRI.
MRI is based on the use of a high-power magnetic field, although it has a minimal number of contraindications; it cannot be performed in patients with pacemakers, implants, insulin pumps and other metal (magnetic) objects in the body, or in early pregnancy.
In the case of a contrast study - in case of an allergy to gadolinium-based drugs and severe renal failure.
How to properly prepare for an abdominal MRI?
The requirements for the patient before undergoing MRI diagnostics of the abdominal cavity are minimal: so that the contents of the stomach and the peristalsis of the walls of the stomach and intestines do not affect the quality of visualization, one should refrain from eating 6-8 hours before the scheduled procedure, and 4 hours from liquids. In addition, the day before the examination, it is not recommended to consume foods that cause gas formation in the intestines (baked goods, cabbage, legumes, milk).
How is diagnosis done using MRI?
The procedure is absolutely painless and does not cause side effects. Some discomfort in patients is caused by the need to lie motionless for 20-30 minutes in the tomograph.
If an MRI with contrast is performed, the drug (paramagnetic) is administered intravenously.
The patient is placed on a mobile tomograph table, which slides into a tunnel (tunnel diameter 70 cm). To ensure clear images, it is important to remain completely still during the examination.
Modern diagnostic equipment plays an important role, but the qualifications of the doctor who conducts and describes the results of the study are no less important. At the Scandinavian Health Center, abdominal MRI and patient consultations are carried out by experienced and certified radiologists, many of whom are candidates of medical sciences, doctors of the highest qualification category.
Source: https://www.SCZ.ru/diagnostics/magnitno-rezonansnaya-tomografiya/mrt-bryushnoy-polosti/