The structure of a man's reproductive system undergoes certain changes with age, and sometimes not the best.
Age-related changes, infections, hypothermia, injuries, heredity, bad habits and other factors do not have the best effect on the condition of the organs.
And, as a rule, the prostate suffers the greatest impact. One of the most common ailments that can bring a lot of inconvenience to a representative of the stronger sex is diffuse changes in the prostate gland.
Diffuse changes in the prostate gland: what does it mean?
As a rule, diffuse processes develop in the tissues of the gland as a result of inflammation, abscess or the appearance of various neoplasms.
According to research results obtained by the European Association of Urology, diffuse changes appear in approximately 25% of men. As a rule, diffuse changes are asymptomatic, and a man cannot detect any abnormalities in the structure of organ tissues just like that.
To identify pathology, an ultrasound scan is necessary. In most cases, diffuse changes in prostate tissue are only a consequence of a serious disease. Therefore, in order to prevent irreversible processes, it is necessary to regularly contact specialists for routine examinations.
Timely medication measures will guarantee protection against the development of pathology.
Causes
Various factors can cause such changes in organ tissues. These include fungus, chlamydia, bacterial infections and many others.
The following diagnoses can provoke the spread of a diffuse process:
In addition to the ailments listed above, the development of pathology can also be caused by bad habits (alcohol abuse or smoking), a passive lifestyle, poor nutrition, poor heredity, irregular sex life and many other points.
Types of diffuse focal changes in the prostate parenchyma
Diffuse changes in prostate tissue can occur in different ways. In this regard, doctors have identified a separate classification of diffuse changes, each of which has its own characteristics. Modern experts identify the following types of changes.
Atrophy (wasting)
The reason for the development of such changes is hormonal imbalance.
Since the man’s body produces insufficient amounts of hormones responsible for the growth and formation of the reproductive system, the prostate gland becomes unnecessary and therefore begins to gradually die.
If measures are not taken in a timely manner, the development of pathology can provoke the onset of testicular orchitis. In such a situation, the only option would be complete resection.
Dysplasia (pathology in tissue development)
This is the most common type of pathology. Dysplasia is characterized by the growth of tissue on the walls of the organ, the presence of which is not intended by nature in the gland.
Depending on the degree of growth, the pathology can be mild, moderate or severe.
At the initial stage, cells that are atypical for this organ appear on the walls of the prostate. If you do not pay attention to their appearance and do not take urgent measures, they can develop into cancer.
Hypoplasia (developmental defect)
As a result, the prostate gland begins to develop as a “eunuch”. Such abnormalities can only be detected using an ultrasound procedure or an advanced blood test.
Hyperplasia (structural enlargement of tissue)
Such changes usually occur due to an inflammatory process that is chronic in nature. The epithelial cells of the organ begin to grow abnormally, resulting in nodules in the prostate tissue.
Normal prostate and hyperplasia
Over time, these nodules increase in size and unite into one, forming a benign neoplasm. Hyperplasia does not metastasize, but it negatively affects all organs located in the pelvis.
The sooner pathological changes are detected, the higher the likelihood of excluding the development of complications.
What does the heterogeneous structure of the prostate in men indicate?
- The heterogeneous structure of the prostate tissue says only one thing: destructive processes are occurring in the man’s body that require urgent elimination.
- To identify their nature, a comprehensive examination is required.
- Also, research activities will make it possible to determine what type of therapy the patient needs to restore health.
- Since the disease occurs without any symptoms, it is impossible to determine exactly what changes are occurring in the organ without using methods that allow visualization of gland tissue.
Characteristic symptoms
As a rule, the development of pathology is indicated by manifestations characteristic of many other diseases of the male genitourinary system.
This may be a frequent need to urinate and chills that occur simultaneously. In severe stages, the patient may experience pain, itching or stinging during urination. Over time, the pain is localized in the pubic area, groin and lower back.
In addition, a man may also have joint pain, increased fatigue and a constant feeling of weakness. In addition to the symptoms listed above, the patient may also develop uncontrolled urine output. We are talking about enuresis. This manifestation often occurs against the background of an adenoma.
UV signs of pathology
During an ultrasound, the doctor uses a transducer to direct ultrasonic waves into the examination area.
Depending on how high the signal reflection intensity is, the specialist will be able to draw objective conclusions about the presence or absence of diffuse changes in the tissues.
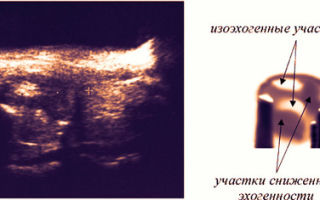
The absence of diffuse changes is called “isoechoicity” and is indicated in gray on the image. Read below about the meaning of other parameters.
Increased echogenicity
Stones or chronic prostatitis usually have high echogenicity. In the photographs, such areas are painted white.
Reduced echogenicity
Hypoechogenicity is evidence of the course of inflammatory processes. In addition, swollen areas, tissues affected by calcification, or places where glandular cells have been replaced by fibrous cells also have reduced echogenicity.
Echogenicity of the prostate gland
Anechoic areas
These are areas that are unable to reflect ultrasound. As a rule, such a manifestation is inherent in various cavity formations (for example, cysts). In this case, there will be a black spot on the image.
If an abscess is detected in the patient, the ultrasound will be weakly reflected, indicating its presence with a dark gray tint.
Treatment approaches
There is no specific treatment for diffuse changes.
- But this manifestation requires careful monitoring by specialists, since serious complications can develop at the site of formed compactions.
- The essence of therapy for diffuse changes is aimed at eliminating the root cause that provoked the appearance of compaction.
- In most cases, the patient is prescribed a complex of medications that help improve blood circulation and metabolism in the prostate tissues.
- If the medication course does not give the desired result, the patient may be prescribed physiotherapy (ozone therapy, laser therapy, therapeutic fasting and many others).
Video on the topic
About the echosemiotics of structural changes in the prostate gland in the video:
Since diffuse changes occur without significant symptoms, men are recommended to regularly visit a doctor for preventive purposes. The sooner neoplasms in the prostate tissue are detected, the longer you can maintain the health and youth of your body.
Source: https://prostata.guru/prostata/diffuznye-izmeneniya.html
Diffuse changes in the prostate gland - what it is and signs
With an ultrasound examination of the prostate, a specialist can detect diffuse changes in the prostate gland. This means that the structure of the organ parenchyma has changed under the influence of certain provoking factors.
These transformations are not an independent disease, but a sign of the presence of a particular disease. The changes are caused by various pathological processes - abscess, inflammation, tumors and diseases - prostatitis, adenoma, etc.
Let's consider the symptoms of diffuse changes in the prostate gland and treatment methods.
How can the structure of the gland change?
Focal transformations in the male prostate can only be determined through ultrasound examination. Since each disease has different diagnostic features, it is ultrasound that makes it possible to differentiate an adenoma from prostatitis, a cyst from an oncological neoplasm, etc.
What are diffuse changes in the prostate gland? This diagnosis is made on the basis of ultrasound, when a medical specialist notes changes in the organ, in other words, deviations from normal indicators.
Almost all pathologies of the genitourinary system lead to “restructuring” of the prostate:
- Metabolic transformations in organ cells;
- Expansion of connective tissues;
- Poor blood circulation in the prostate;
- Inflammation that causes rapid tissue proliferation;
- The presence of a neoplasm located in the prostate.
For your information, in medical practice there are various types of negative transformations of the prostate. These include atrophy (organ depletion), dysplasia (pathological tissue development), hypoplasia (developmental defect) and hyperplasia (structural transformation of soft tissue).
In most clinical pictures, a man is diagnosed with hyperplasia or dysplasia. These terms are not a disease in the truest sense of the word. They appear as signs indicating an abnormal process in the glandular organ.
Against the background of dysplasia, areas of normal cells are modified, transforming into abnormal cells. There are three types of pathological process - mild, moderate, severe. Moreover, if the first two options indicate the development of inflammatory processes, then the last type may signal a pre-cancer condition.
Sooner or later, dysplasia should level out on its own. However, the lack of necessary treatment is always a fairly high risk of developing a malignant neoplasm.
Diseases indicated by diffuse changes
Diffuse changes in the prostate gland mean that the structure and parameters of the organ deviate from the norm accepted in medical practice. Based on the characteristic signs and changes on the ultrasound machine monitor, a definite conclusion can be made that helps prescribe surgical or conservative treatment.
Diffuse changes in the prostate may indicate the following diseases:
- “Diffusion” of the glandular organ as a sign of prostatitis. This means that the prostate gland is affected by an inflammatory process, and the patient experiences other symptoms. Most often she complains of problems with urination, burning and itching in the urethra. Also with prostatitis, there are difficulties in achieving an erection and pain during sexual intercourse. With this picture, the organ is pathologically enlarged, but the structure remains the same. Additionally, other tests are required - examination of prostatic juice, blood/urine tests, CT scan, etc.;
- Cyst or cysts. This means that a cavity is localized in the area of the glandular organ, which is filled with exudate. Cysts are characterized by a benign nature. An ultrasound can determine the size and location of the tumor. Treatment is required, since there is a possibility of the cyst transforming into a malignant course;
- Adenoma. The tumor is benign in nature, but tends to grow rapidly. To exclude an increase in formation and possible complications of nearby organs, mechanical removal is necessary. The symptoms can be compared to the clinic of chronic prostatitis, but the complications are much more serious;
- A tumor of a malignant nature. If diffuse changes are detected in a tumor, they speak of an advanced stage of the disease.
It is worth knowing: tumors, as the cause of diffuse changes, most often develop in men after 50 years of age. Therefore, men over this threshold are recommended to undergo a prostate ultrasound every six months.
Should we be concerned about diffuse changes?
When a man receives the results of an ultrasound examination, the form of which contains a line about diffuse changes in the glandular organ, the question immediately arises - how dangerous is this? After all, any changes in the prostate gland can affect your sex life.
Medical experts suggest not to panic, because if the doctor said everything is fine, then it really is. Conclusion Ultrasound provides only the parameters of the organ being described. For example, the abbreviation OOM is sometimes indicated - it stands for residual urine in the bladder. This is the norm, as it is never dry.
In some cases, if you ask a doctor what diffuse changes in the prostate are, he will say - a normal variant. Provided that the man is not bothered by alarming symptoms, there are no deviations in laboratory tests.
If changes in the glandular organ are caused by prostatitis, adenoma, calcifications, then in the absence of treatment the danger is as follows:
- Chronic form of ischuria (urinary retention).
- Development of cystitis, pyelonephritis.
- Abscess with a high probability of sepsis.
- Formation of fistulas.
- Urolithiasis.
- Erectile dysfunction.
In any case, you need to rely on the doctor's opinion. If he says everything is fine, then it is. When prescribing treatment, you must strictly adhere to all recommendations in order to exclude further complications.
Symptoms of diffuse changes in the prostate gland
Diffuse transformations in the tissues of the parenchyma of the glandular organ may not manifest themselves for a long period of time. Clinical manifestations are determined by the specific disease, severity, and general condition of the man. As the pathological process progresses, symptoms appear.
Signs of diffuse changes in the prostate gland are as follows:
- Violation of the urination process;
- Frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- Pain during bowel movements;
- Painful sensations during sex;
- Pain in the perineum;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Weakening of erection, decreased potency;
- Decreased sexual desire;
- General deterioration in health.
If such symptoms are detected, you should visit a doctor and have an ultrasound done. Criteria for changes according to ultrasound – increase/decrease in echogenicity; formation of fibrous areas; unclear contours of the organ and heterogeneous structure; the presence of swelling, calcifications, purulent processes, etc.
Important: normally the prostate gland is characterized by a homogeneous structure, acceptable density, symmetry, and has clearly defined boundaries. The size of the organ is no more than 25 centimeters; seminal vesicles are easily visualized on ultrasound.
Treatment of diffuse changes in the prostate gland
Diffuse changes do not always need to be treated, since in some cases the transformations are a variant of the norm, for example, in men of the elderly age group. If a patient has been diagnosed with prostatitis, adenoma, cancer, cyst, then treatment is required. The tactics of the therapeutic course and its duration depend on the specific diagnosis.
Surgery
Against the background of prostate pathologies, surgical treatment is a last resort when other methods of conservative therapy do not help improve the clinical picture. If the patient has a history of a large cyst, the doctor may recommend a mini-surgery.
During the procedure, the doctor pumps out the accumulated exudate in the cyst. The manipulation is carried out under the control of an ultrasound machine.
Then, after pumping out the fluid, the walls of the cyst are glued together - for this, a small amount of antiseptic medicine or an alcohol-containing solution is injected into it.
Surgical removal of a cyst using an open method is performed quite rarely. The indication is the presence of complications, rapid growth of the cyst, impossibility of puncture.
For gland cancer, surgery may be recommended before the tumor has spread beyond the walls of the organ. Mechanical excision is carried out in one of two ways:
- Prostatectomy involves partial or complete removal of an organ. For cancer, the entire gland is often removed. It is considered the most traumatic method.
- Transurethral resection is partial removal through the urethral canal.
It is worth knowing: with a large adenoma, they resort to a surgical solution to the problem. Transurethral resection (TUR), transurethral incision (TUI) and open adenomectomy are used.
Traditional treatment
Perhaps the most common non-traditional method of treating prostate pathologies is the consumption of pumpkin seeds. They contain an increased amount of antioxidants, vitamins and minerals, fatty acids, which significantly improves the condition of the organ and normalizes the hormonal balance in the body.
In case of diffuse changes in the prostate, the diet should be enriched with the following foods:
- Turmeric;
- Green tea;
- Tomatoes;
- Watermelon.
To reduce the severity of anxiety symptoms, folk remedies are used - decoctions and infusions based on medicinal herbs. The following plants have analgesic, anti-inflammatory and regenerating properties: stinging nettle, chamomile inflorescences, calendula, yarrow and fireweed.
Drug treatment
Conservative treatment is determined by the specific disease. With prostatitis, it is necessary to eliminate the source. If the cause of the development of pathology is an infection, then the use of antibacterial drugs (Ofloxacin) is recommended. To relieve pain, analgesics are prescribed - Ketanov or Ketorolac.
Treatment tactics involve the use of multivitamin complexes and immunostimulants to increase the body's barrier functions. Additionally, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed - Ketoprofen.
The following drugs are used in the treatment of adenoma:
- Alpha blockers help remove urine by relaxing the muscles of the urethra.
- Antibiotics are recommended for bacterial infections. The most commonly used drug is Gentamicin.
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors help reduce anxiety symptoms.
- Hormonal medications.
Note: treatment of cysts with medications is allowed only at the very beginning of the development of the tumor. The choice of drugs is determined by a specific reason.
Which doctor should I contact?
At the first symptoms of problems with the prostate gland - pain during urination, frequent trips to the toilet, erectile dysfunction, etc., it is recommended to consult a medical specialist, in particular a urologist.
This is the doctor who deals with diseases of the genital organs in men. The doctor interviews the patient, collects anamnesis, conducts a visual examination of the penis, and a rectal examination of the prostate. If any pathology is suspected, additional tests are prescribed.
If a man has an adenoma, then a surgeon’s consultation is necessary, since the neoplasm tends to increase in size, which leads to compression of the surrounding tissues. It is he who makes the decision on the advisability of surgical therapy.
To summarize, we note that diffuse changes in the prostate are not an independent disease, but a sign of another disease. And in some cases, such changes are completely normal, and therefore no treatment is required.
Source: https://ManExpert.ru/prostata/diffuznoe-izmenenie-predstatelnoj-zhelezy.html
What do diffuse changes in the prostate indicate?
- Recently, diffuse changes in the prostate .
- These changes are not a separate disease.
- But they indicate the presence of certain pathologies.
- To examine the prostate gland, you must consult a doctor for an ultrasound examination.
- This method will detect changes in the prostate and prescribe appropriate treatment.
What are diffuse changes in the prostate?
Diffuse changes in the prostate gland are called dystrophic disorders of the structure of the parenchyma caused by an abscess, inflammation or neoplasm. Ultrasound allows you to evaluate the structure of the prostate, its density, size and, based on these data, give the patient an accurate diagnosis.
- During the study, it is possible to detect the majority of “male” diseases: cysts and oncology, abscess and adenoma, chronic and acute forms of prostatitis.
- The ease of diagnosis is explained by the fact that each disease has its own characteristics, which can be detected using an ultrasound scanner.
- Urologists call these features pathognomonic changes and include them among the criteria for ultrasound diagnostics.
- Diffuse changes in the prostate often occur, since most men have problems in the intimate area.
- The main risk factors include:
- promiscuous sexual intercourse (without protection), during which you can catch a sexually transmitted infection;
- the habit of dressing lightly (especially in damp and cold weather);
- unrealized erections, irregular sex life;
- stress, nervous tension;
- frequent colds that reduce immunity;
- sedentary work, sedentary lifestyle;
- having anal sex without a condom;
- bad habits (smoking, frequent drinking of alcohol).
Causes and consequences
Almost all pathologies of the genitourinary system cause disruption of tissue structure.
The reasons for this restructuring include:
- metabolic changes at the cellular level;
- impaired blood supply to the prostate;
- proliferation of connective tissue;
- tumor growth into healthy tissue;
- an inflammatory process leading to tissue compaction.
Typically, a change in the structure of the prostate indicates the presence of:
- Prostate adenomas . The disease is characterized by an increase in the size of the gland and a violation of the outflow of urine. Typical symptoms of the disease are: urinary retention, decreased flow pressure, frequent urge to urinate, and a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. On ultrasound, prostatic hyperplasia is noted by an increase in the size of the prostate and individual adenomatous nodes.
- Prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate gland) . Symptoms of the disease include: burning/discomfort during ejaculation and urination, frequent urge to urinate, and sexual dysfunction. On ultrasound, prostatitis looks like a characteristic enlargement of the prostate gland.
- Oncology . In most cases, prostate cancer is asymptomatic. To detect cancer in a timely manner, it is necessary to undergo an annual ultrasound of the prostate gland.
- Prostate cysts . The disease is characterized by the formation of a fluid-filled cavity in the gland.
- Lack of timely treatment of the listed ailments is fraught with serious consequences:
- Video: “Report on the structure of the prostate”
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
Symptoms of diseases indicated by diffuse changes include:
- urge to urinate (intolerant and frequent);
- pain in the pelvis, lower back, groin;
- pain/burning when urinating;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- difficulty urinating, etc.
To date, the only reliable method to detect the presence of pathological foci in prostate tissue is ultrasound.
During ultrasound, it is possible to identify diffuse changes such as dysplasia, hyperplasia, atrophy, and hypoplasia.
Most often in conclusions the concepts “hyperplasia” and “dysplasia” are found. They are not independent diseases, but indicate the presence of one or another pathology.
Prostate dysplasia refers to the process of restructuring healthy tissue into atypical tissue that is not characteristic of this organ. This process occurs at the cellular level. According to the degree of change, dysplasia is divided into severe, moderate and mild.
The first type reports the presence of a precancerous condition of the prostate, and the last two indicate a long-term inflammatory process. Dysplasia may regress over time, but in the absence of proper treatment there is a possibility of developing oncology.
The criteria for healthy tissue are:
- symmetry;
- clear contours;
- homogeneous structure;
- division into five zones;
- volume up to 25 cmᶟ;
- visualization of seminal vesicles;
- density is within normal limits;
- transverse section 30-45 cm, anteroposterior – 13-25 cm.
- If any of the listed criteria changes, the presence of diffuse-focal changes in the prostate is indicated.
- Echo signs of diffuse changes are also used to assess the condition of the tissue.
- Each disease is characterized by the presence of echo signs:
- in the presence of an abscess, anechoic zones are combined with hypoechoic ones;
- Acute prostatitis is characterized by significantly reduced echogenicity;
- with chronic prostatitis, increased echogenicity is observed;
- in the presence of cysts, anechoic zones are identified;
- Oncology is characterized by the presence of a hypoechoic zone on the periphery (at an early stage, echogenicity may remain unchanged).
- Also, ultrasound shows a disturbed tissue structure, which indicates the presence of edema, fibrosis, pus, infiltration, and calcifications.
- Video: “Male inflammatory prostate diseases”
Treatment
It is pointless to talk about the treatment of diffuse changes in the prostate, since they are signs of certain ailments. The treatment that a doctor prescribes for a person with such changes depends on the diagnosis, the patient’s condition, and the general clinical picture.
The use of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs is often practiced. In some cases, when drug therapy is ineffective, surgery is performed.
If there are diffuse changes in the prostate, it is recommended to follow a certain diet based on:
- Limiting fat intake . To make food less high in calories and fat, it is enough to include as many plant foods as possible in your diet. Vegetables, fruits, and whole grain products contain nutritional components necessary for the normal functioning of the body: minerals, vitamins, amino acids, plant fibers, enzymes. At the same time, you should include in your diet a sufficient amount of unsaturated fats, found in fatty sea fish, flaxseed and olive oils. As for the carbohydrate part of the diet, it includes pasta, bread, cereal, porridge and rice.
- Consumption of protein products of animal and plant origin . Foods high in protein include legumes (lentils, peas, beans), dairy products (yogurt, milk), meat products (chicken), etc.
- Avoid foods that cause kidney irritation (salty and spicy foods, coffee, alcohol, chocolate, coffee).
Prevention
The high prevalence of prostate diseases dictates the need for frequent preventive examinations, the purpose of which is to identify the disease and timely treatment. Regular visits to a urologist allow you to identify the disease in time and select the optimal treatment regimen.
Typically a preventive examination includes:
- conversation with a specialist;
- blood donation for PSA;
- digital rectal examination;
- Ultrasound of the prostate.
You can complete the listed procedures in 1 hour.
To maintain the health of the prostate gland and the body as a whole, you need to follow three simple principles:
- physical activity;
- proper nutrition;
- regular visits to the doctor.
Proper nutrition can reduce the risk of developing diseases (especially cancer and adenoma).
Products that help prevent the development of these ailments include:
- cruciferous vegetables;
- soy products;
- green tea;
- garlic;
- tomatoes.
As for physical activity, preference should be given to any general strengthening procedures that can restore the functioning of the immune system and other protective systems of the body. Hiking, hardening, water treatments, and regular sexual activity are of great benefit. Heavy physical activity is prohibited.
Forecast
With timely consultation with a doctor, prostate diseases can be cured in most cases. In developed countries, regular visits to a urologist are an element of culture. This approach makes it possible to reduce mortality rates from prostate diseases several times.
Conclusion
Thus, diffuse changes in the prostate are signs that indicate the presence of a pathological process in the tissues of the organ.
These changes can be detected using ultrasound. The treatment regimen is prescribed by the doctor based on the diagnosis.
To avoid unpleasant consequences and complications, you must regularly visit a urologist (at least once a year).
Source: https://kakbyk.com/bolezni/opukholi/adenoma/o-chem-svidetelstvuyut-diffuznye-izmeneniya-prostaty.html
What are diffuse changes in the prostate
The prostate gland is popularly called the second heart of men, and this is not surprising, because the prostate has a significant impact on reproductive function. Any disturbances in the functioning of the prostate gland lead to infertility and impotence, problems with the urinary system, which undoubtedly worsens the quality of life of a man.
Diffuse changes in the prostate are several pathologies in which dystrophic changes occur in the gland. Such disorders occur as a result of inflammatory processes and poor lifestyle. It is very important to promptly identify signs of diffuse changes in the prostate and begin treatment in order to maintain organ function and normal potency.
Causes of prostate pathologies
Diffuse changes in the prostate do not occur without a reason. The tissues of the organ begin to degrade as a result of the following pathologies of the prostate gland:
Chronic prostatitis
One of the most common male diseases, which affects every second elderly patient. For the first time, acute prostatitis can occur at a young age due to infection of the organ, for example, during promiscuous sexual intercourse, or during anal sex without protection.
The inflammatory process injures the tissue of the prostate gland, leading to disruption of blood circulation and organ function. If treatment is carried out comprehensively and in a timely manner, diffuse changes can be avoided. But with a long uncontrolled course of the disease, changes occur in the area of the parenchyma, and foci of a dystrophic nature appear.
Prostate stones
The formation of stones in the prostate occurs against the background of chronic prostatitis. In a healthy man, the process of urination is adjusted, as well as the secretion of prostatic juice.
With chronic prostatitis, urine does not come out completely, and stagnation of prostatic fluid also occurs.
As a result of such a violation, salts, phosphates, and epithelial particles accumulate in the organ and become denser, which is how stones form in the prostate.
In turn, calcifications in the prostate put pressure on its tissues and injure the organ, causing pain. Large stones necessarily provoke poor circulation in the tissues of the gland, and as a result, diffuse changes occur.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
Patients are more familiar with this pathology under the term prostate adenoma. With this pathology, hypertrophic changes in the gland are observed, that is, the tissues of the organ begin to grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor.
Although prostate adenoma is not cancer, it does pose some health risks. The growing tumor puts pressure on surrounding tissues, in particular the blood vessels that supply the prostate and nerves. As a result of malnutrition, diffuse focal changes in the prostate are formed against the background of hyperplasia. Also, a large adenoma puts pressure on the urethra, disrupting the process of urination.
Prostate sclerosis
Fibrosis or sclerosis of the prostate is a pathology in which healthy prostate cells are replaced by dense connective tissue. Adhesions lead to the fact that the prostate tissue shrinks, compresses the urethra and blood vessels, thereby disrupting the nutrition of the gland, the process of urination, and impotence occurs.
Prostate fibrosis is most often a consequence of an advanced process. Also, the cause of the pathology can be hormonal disorders, vascular atherosclerosis, congenital anomalies of the genital organs, as well as mechanical injuries.
As a result of the negative influence, ulcers, or wounds and microcracks form in the gland, which are healed by connective tissue, forming dense cords. In this case, the pathology occurs asymptomatically for a long time and is usually detected when the patient consults a doctor with severe genitourinary dysfunction.
Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is the most dangerous gland disease that threatens the patient's life. A growing tumor causes diffuse changes in the prostate, but this is not the worst thing.
A malignant neoplasm once begins to metastasize, that is, spread its cells throughout the body.
This stage of cancer is incurable in most cases and leads to the death of the patient within several years or even months.
It is important to note that moderately diffuse changes in the prostate can occur in the absence of organ pathology. In this case, the provoking factors become:
- smoking and alcoholism, as a result of which malnutrition of the gland occurs and its degenerative changes;
- metabolic disorders, obesity, endocrine pathologies;
- lack of sex and a passive lifestyle, resulting in stagnation in the organ.
Thus, the list of causes of diffuse changes in the prostate is quite wide. In each case, treatment will correspond to the cause of the disease and the stage of the pathology. Therefore, therapy should be carried out under the supervision of a competent specialist.
Signs of diffuse changes in the prostate
Symptoms of diffuse changes are quite nonspecific, the patient is concerned about:
- pain in the groin that radiates to the perineum and rectum;
- urinary disturbances, in particular incontinence, frequent urge, weak urine stream;
- erectile dysfunction, pain during ejaculation.
It is important to understand that such symptoms occur with prostatitis, adenoma and even prostate cancer, so they should not be ignored under any circumstances.
Signs of diffuse changes in the prostate parenchyma can be seen on ultrasound. Normally, the parenchyma should be symmetrical, homogeneous and with clear contours, normal density, with a size of 30-45 mm.
An echographic sign of diffuse changes can manifest itself in a decrease or increase in echogenicity and the appearance of anechoic zones. In most cases, the sonologist notes that the structure of the parenchyma is heterogeneous.
Ultrasound helps to quickly detect that there are diffuse changes in the prostate based on characteristic signs, but this examination method will not accurately answer the question about the nature of the pathology. Therefore, the doctor will prescribe additional diagnostic methods:
- biopsy;
- TRUS;
- prostate secretion analysis;
- spermogram.
A comprehensive examination will help to accurately identify the cause of diffuse changes and prescribe adequate treatment.
Diffuse nodular hyperplasia
Diffuse prostate hyperplasia is the proliferation of organ tissue and the formation of nodules and tumors. Neoplasms are benign and do not metastasize, but in rare cases they can become malignant, that is, transform into cancer.
Focal or diffuse nodular changes in the prostate occur slowly and are practically asymptomatic. A large number of small nodules are formed in the organ, which are interconnected. Over time, problems with urination and urinary incontinence arise.
Treatment of focal hyperplasia can be conservative or surgical. Conservative therapy is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease and reducing the likelihood of tumor transformation, but the patient will not be able to recover completely in this way. The following drugs are prescribed:
- Alpha blockers, for example, Omnic. They help improve the urination process by relaxing smooth muscles.
- Anticancer hormonal drugs, in particular Finasteride. The drug helps reduce the growth of formation.
Surgical treatment is prescribed in the following cases:
- with urinary retention, if it is not possible to install a catheter;
- against the background of renal failure;
- with severe infection against the background of a tumor;
- if it is not possible to be treated with drugs;
- with the threat of cancer.
Unfortunately, not every patient with diffuse focal changes can undergo surgery, because due to advanced age there are contraindications to surgery and general anesthesia.
Prostate dysplasia
Dysplasia is the most common form of diffuse changes in the prostate. Pathology is the degeneration of healthy prostate tissue into atypical one. Dysplasia is not cancer, but the disease is rightfully classified as a precancerous condition, since if left untreated, dysplasia often transforms into oncology.
Dysplasia is widespread among men over the age of 70, and after 45 years the disorder is diagnosed in approximately 20% of patients who seek help with characteristic symptoms of diffuse changes.
Treatment of dysplasia is complex. Drugs are prescribed that help stop the growth of atypical cells, as well as symptomatic drugs: alpha-blockers to normalize the outflow of urine, painkillers. If urination is impaired, the catheter is removed.
If indicated, surgical treatment is prescribed. As a rule, surgery is indicated in severe cases when the outflow of urine is disrupted and there is a risk of cancer. Various techniques are used, for example, in less advanced cases, a TUR of the prostate is prescribed. And if the tumor begins to transform, the gland and inguinal lymph nodes are completely removed.
Prostate hypoplasia is a disease in which there is underdevelopment of the organ. The pathology is usually diagnosed in boys during puberty, when the organ ceases to develop normally due to hormonal imbalance.
Hypoplasia is a very serious disorder that leads to infertility. The prostate secretes bad prostatic juice, which causes the quality of sperm to suffer greatly. In addition, hormonal disorders that accompany this kind of diffuse changes in the prostate often affect the appearance and character of the patient, and also provoke impotence.
Congenital hypoplasia has a significant impact on a man’s life. If the problem is detected in a timely manner, hormonal correction helps alleviate the condition. In the future, patients with hypoplasia often encounter problems in sexual life, and changes in the prostate greatly increase the risk of inflammatory processes, the appearance of tumors and atrophy of the gland.
Prostate atrophy
Another type of diffuse changes in the prostate is prostate atrophy. The pathology is the degeneration of an organ as a result of a decrease in the synthesis of sex hormones, and it occurs against the background of age-related changes and a passive lifestyle in men over 50-60 years old.
It is possible to develop atrophy at a young age, for example, against the background of congenital hypoplasia, as well as as a result of mechanical injuries, benign and malignant tumors and exposure to other negative factors.
Treatment of prostate atrophy in older men is aimed at stopping the pathological process and improving the patient’s quality of life. Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely reverse age-related changes.
In young men, atrophy requires timely and comprehensive treatment, otherwise the pathology will lead to impotence and urinary incontinence. For sexually active patients, this is a serious problem; in addition, impaired urination greatly impairs the quality of life, preventing a man from working normally and leading a personal life.
Atrophy therapy consists of the following activities:
- for stones and tumors, surgical treatment is prescribed;
- for inflammation, anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed;
- In case of hormonal imbalance, hormone replacement therapy is indicated.
For diffuse changes against the background of age-related changes, symptomatic therapy is prescribed. If the outflow of urine is impaired, a catheter is installed. If there is a threat of cancer, the prostate is removed surgically, unless surgery is contraindicated.
Prevention of prostate pathologies
Diffuse changes in the prostate parenchyma in most cases occur as a result of an advanced pathological process in the organ. To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary:
- At the first signs of prostatitis, you need to go to the doctor, even if the patient is 25-30 years old. The sooner the disease is diagnosed and treatment is started, the greater the chances of avoiding diffuse disorders in the future.
- You need to lead a healthy lifestyle. Alcohol abuse, drug addiction, smoking, unhealthy diet - these are factors that significantly increase the likelihood of developing oncology, including prostate cancer.
- It is very important to avoid promiscuity from a young age. Infection with an STI greatly increases the risk of developing prostatitis and its complications. When having sex with a stranger, you must protect yourself with a condom.
- A man after 40 years of age should be examined annually by an andrologist and urologist. Boys and young men should be examined at least once every 2 years.
- After 60 years, you need to lead an active lifestyle and move more. It is also advisable to have regular sex life if you have an erection. Such prevention will help improve blood circulation in the pelvis and prevent the development of diffuse changes in the organ.
Conclusion
Degenerative disorders of the prostate are serious pathologies that can be avoided by following preventive measures. A correct attitude towards your health and life in general will help you avoid not only diffuse changes in the prostate, but also many other serious diseases.
You might be interested
Source: https://prostatits.ru/oslozhneniya/diffuznye-izmeneniya-prostaty.html
Diffuse changes in the prostate how to treat
Diffuse changes are changes in the entire organ. Most often, diffuse changes are a consequence of the disease. Changes can be detected using digital examination, ultrasound
examination, magnetic resonance or computed tomography. Changes can be of two types:
- Reducing volume;
- Increase in volume.
1. Prostate is smaller than standard. It is quite rare and is associated with disturbances in the development of the body. It is quite difficult to cure such changes. Treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a physician.
2. Hyperplasia occurs much more often, since there are more opportunities for the development of this process. The most common pathology is prostate adenoma, a benign tumor. Part of the prostate gland begins to grow and increase in volume.
Less commonly, prostate adenoma develops in different directions or all at once. Prostate carcinoma also occurs - prostate cancer spreads very quickly and significantly increases the size of the organ.
Also, diffuse changes in carcinoma cause swelling and damage nearby organs.
There are also changes associated with bacterial or infectious damage to prostate tissue. Chronic prostate diseases cause the development of prostate stones, as well as calcifications and adhesions. All these changes can be diffuse.
To prevent chronic prostatitis, you should take natural preparations consisting of extracts of plant and animal origin. The main difference between such drugs and synthetic analogues of Viagra is the absence of side effects and the presence of a large volume of essential microelements.
That is, natural drugs give a stable erection, like Viagra, but at the same time nourish the body and stimulate the production of its own hormones. Our specialists are always ready to help you choose the optimal drug for your health.
Symptoms of diffuse change
The prostate gland does not contain nerve cells. In this regard, many changes in the prostate do not cause pain or other external manifestations.
The asymptomatic course of the disease often complicates its diagnosis and treatment. Such a pathology can only be identified by passing tests.
After 45 years of age, men are recommended to be examined by a urologist twice a year, and from the age of 35, at least one visit to the doctor per year is recommended.
How can changes in the prostate be detected?
Most often, prostate pathologies are accompanied by:
- Pain during ejaculation and defecation;
- Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- Decreased sexual desire;
- Poor erection.
If you notice any of the above symptoms, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Tests for diffuse changes in the prostate gland
Initially, the doctor performs a digital examination. This type of examination helps identify changes in the structure of the prostate. If changes are detected in the shape or density of an organ, the doctor prescribes a series of examinations:
- Blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine;
- Analysis of prostate secretions;
- Prostate specific antigen (PSA) test;
- Ultrasonography;
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography.
Tests of blood, urine, and secretions will help specialists understand whether there are inflammations or infections, as well as identify ways to treat the pathology.
PSA is used to detect prostate carcinoma. In other words, a specific antigen helps detect prostate cancer.
It is often necessary to do an ultrasound or MRI to obtain a complete picture of the disease. Based on the collected data, doctors choose the optimal treatment program.
Treatment methods for diffuse changes in the prostate
Treatment methods for this pathology vary depending on the causes and extent of the damage.
Prostatitis in the early stages is treated with anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics, restorative therapy and pain relief are also carried out. Later stages of prostatitis require surgery. During surgical treatment of prostatitis, part of the organ is removed, or in extreme cases the entire prostate gland.
Any congenital changes, cysts, as well as adenoma are not subject to drug treatment. In such cases, partial removal of prostate tissue is performed. After the operation, the man takes various maintenance medications for a long time. It is also worth using complexes of minerals and amino acids - this will speed up recovery and reduce the likelihood of relapses.
For stone disease, treatment depends on the size of the stones. Small stones can be removed with medication, but large formations can only be removed surgically. You can read more in our article about stones in the prostate gland.
Prostate cancer. Carcinoma is a very serious disease, self-medication in this case is deadly! First of all, it is vital to remember that cancer cannot be treated with soda, holy water and grandmothers. A malignant tumor is treated only in an oncology clinic under the supervision of an oncologist. Typically, several courses of chemotherapy, surgery and radiation therapy are used.
All of these abnormalities can be the cause of diffuse prostate disease. Also, diffuse changes in the prostate are a common symptom of pathologies.
Surgical methods
If it is necessary to perform an operation, a tour resectoscope is used - this device allows you to remove the necessary parts of the prostate gland through the urethra. It is possible to additionally use a laser to evaporate tissue. In case of carcinoma, the entire prostate is removed - this is due to the possibility of tumor metastasis and damage to neighboring tissues.
Traditional methods of treating diffuse changes in the prostate
In this case, traditional medicine acts only in addition to official medicine.
When treating diffuse changes in the prostate gland, medication or surgical treatment is carried out; in addition, decoctions of various herbs or herbal preparations based on ginseng, Rhodiola rosea, deer root, extracts from deer antlers and other components can be used.
In this case, there is a simpler way - you need to select a natural preparation containing all the microelements you need and drink it in a course. Foods rich in iron, nuts, and honey also significantly improve recovery. It is necessary to reduce the amount of fatty and fried foods. The consumption of white meat and fish is recommended.
Particular attention should be paid to proper rehabilitation therapy, and for this you can use a call back. Our specialists will select individual medications for the speedy restoration of sexual functions in the body.
Source: https://manzdrav.com/vse-novosti/diffuznye-izmeneniya-predstatelnoj-zhelezy