- Vesiculitis (spermocystitis) is a disease that affects the seminal vesicles.
- It occurs against the background of other inflammatory processes in the male genitourinary system, congestion in the vesicles.
- Neglecting to treat the symptoms of vesiculitis in men is an inevitable cause of infertility.
- Vesiculitis - what it is and how to treat it, read the article.
Hide content
Description and classification
Vesiculitis is an inflammation of the seminal vesicles, located in men between the bladder and prostate.
The existing classification distinguishes three forms of vesiculitis:
- Spicy. Characterized by bright manifestations. It begins suddenly and symptoms increase rapidly.
- Chronic. Smoothed course of the disease. Symptoms mainly appear during sexual intercourse.
- Prostate vesiculitis. Simultaneous development of inflammation in the prostate gland and vesicles. Occurs with frequent constipation and disrupts blood circulation in the pelvic organs.
- Vesiculitis can be unilateral or bilateral. In the advanced form of the disease, a complication of vesiculitis occurs in the form of suppuration of the seminal vesicles. This form is treated exclusively by surgery.
IMPORTANT! Advanced bilateral vesiculitis means almost one hundred percent infertility in a man. The affected organ cannot fully function and produce seminal secretions.
Vesiculitis is a disease of infectious etiology that occurs due to the entry of staphylococci, streptococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, chlamydia, and ureaplasma into the organ.
The following routes of infection are distinguished:
- Hematogenous - for sore throat, tonsillitis, caries.
- Lymphogenic – through the lymph flow for hemorrhoids, prostatitis.
- Ascending - through the spermatic cord, with urethritis, orchitis.
Factors that provoke vesiculitis are:
- sexual abstinence;
- indiscriminate, frequent sexual intercourse;
- hypothermia;
- sedentary work;
- reduced immunity;
- inflammation in the intestines;
- caries.
In 30% of cases, vesiculitis is a complication of prostatitis, in 5% of cases the root cause is the herpes virus.
Diagnostics
Urologists and andrologists treat all problems in the male genital organs. At the first signs of any inflammation in the genitals, you should contact one of these specialists. A urologist specializes in inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system, and an andrologist treats disorders of the reproductive system.
Only a specialist can make a correct diagnosis. Based on a detailed interview with the patient and a rectal examination, the urologist will determine the problem. For examination, the patient is placed on his side with his knees pressed to his body. Vesicles in advanced forms of the disease are easily palpable. To the touch they have a round or pear-shaped shape.
To confirm the visual inspection, studies are carried out:
The main evidence of vesiculitis is the presence of pathogens in the semen and a sharp decrease in the number of sperm in it. It is also possible to study using transrectal ultrasound and MRI.
The andrologist uses instrumental research methods:
- Catheterization of the urethra and bladder.
- Bougienage (stretching) of the urethra.
- Endoscopic urethroscopy.
- Cytoscopy and pyeloscopy.
Acute and chronic vesiculitis manifest themselves differently:
- Acute form:
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen, aggravated by defecation;
- frequent urination mixed with blood;
- pain during ejaculation, blood in semen;
- involuntary erection at night;
- fever, chills.
- Chronic form:
Sometimes the only symptom when vesiculitis passes into the chronic stage is the admixture of blood in the semen.
Sometimes men feel:
- unexpressed pain in the groin and sacrum;
- painful erection, dim orgasm;
- discomfort when urinating.
When vesiculitis becomes chronic, only signs of a sexual nature appear. As the disease progresses, pus appears in the semen.
Techniques
How to treat vesiculitis in men? The method of treating vesiculitis in men and specific medications are prescribed by the urologist after identifying the specific causative agent of the disease. For infectious etiologies of the disease, antibiotics are prescribed; for congestive forms, angioprotectors are used.
Antibiotics
How to treat vesiculitis? The specific medications prescribed by your doctor depend on the type of pathogen.
For inflammation caused by staphylococcemia and streptococci, the following are prescribed:
- Erythromycin – 200 mg 2-3 times a day.
- Sumammed (azithromycin) – 500 mg once a day.
- Furagin – 50 mg. 3 times a day.
- Metacycline – 300 mg. 2 times a day.
For inflammation caused by chlamydia, ureaplasma, gardinella, the following is prescribed:
- For vesiculitis, Dalfaz, Lincomycin, Dalatsin, Miranem, Macmiror, Lidaprim - the dose and frequency are prescribed strictly individually.
- Immunotherapy with Levamisole, Viferon, Solkourovak is carried out for two days.
- After two days, treatment with antibiotics begins.
- Ten days later - a course of macrolides or tetracycline drugs.
- After the first blow of illness, a break of 5-7 days is taken. Then the course of antibiotics for vesiculitis is repeated, with their change.
If the cause of vesiculitis is gonorrhea or syphilis, benzyl penicillin is prescribed intramuscularly.
When secretion stagnates in the vesicles, the following are prescribed:
- Trental – 400 mg. 2 times a day.
- Obzidan – 1 tablet 3 times a day.
- Aescusan – 1 tablet 3 times a day for two weeks.
IMPORTANT! The treatment regimen is applied to both sexual partners.
During treatment of vesiculitis, the patient must adhere to a special diet.
Products that irritate the genitourinary system are excluded:
- increasing gas formation - cabbage, legumes;
- spices;
- smoked and fried;
- canned food, pickles;
- strong tea, coffee, alcohol;
- The diet should include fermented milk, fish, lean meat, juices, vegetables and fruits.
Candles
As part of the general course of treatment, rectal suppositories are widely used for vesiculitis. This remedy reduces pain and inflammation. As the only therapeutic drug, without the use of antibiotics, suppositories will not work. They are an auxiliary remedy that relieves the symptoms of vesiculitis.
The following drugs are most effective:
- Anestezol. The composition includes benzocaine, a local anesthetic.
- Indomethacin.
- Voltaren. Used for prostatitis and inflammatory diseases of the male reproductive system.
- Rifampicin. Antibacterial candles.
- Prostopin. Promote tissue regeneration and have a general strengthening effect.
In severe forms, vesiculitis can only be cured in a hospital setting. The patient is prescribed semi-bed rest in combination with a laxative diet.
The course of treatment of vesiculitis with antibiotics from the group of penicillins, macrolides, cephalosporins and antibacterial agents is combined with physiotherapeutic procedures:
- Hot baths for the pelvis – 15-20 minutes in the morning and evening. To enhance the therapeutic effect, baths are used with fillers (coniferous, mineral, herbal). They have a relaxing, antispasmodic, analgesic effect.
- A heating pad for the groin area.
- Instillation of silver nitrate into the urethra.
- Microclysters with antipyrine - twice a day.
- UHF, electrophoresis.
- Magnetotherapy.
The newest treatment methods are:
- Laser therapy – transrectal, transurethral. A flexible conductor with an LED is inserted into the organ and the laser is applied.
- Mud therapy - anal tampons or applications to the groin area with special therapeutic mud.
- A good therapeutic effect is achieved by transrectal vesicle massage, which stimulates blood circulation in the organ. Treatment of vesiculitis: how much massage is needed? It is done approximately every two days, and the full course consists of 12-15 procedures.
IMPORTANT! Massage is contraindicated in the acute stage of vesiculitis.
If complications of vesiculitis occur, the presence of edema and purulent discharge, surgery is used to clean out the vesicles.
It consists of the following stages:
- A catheter is inserted into the bladder.
- An arcuate incision is made 2 cm above the anus.
- The incision provides access to the prostate, and from it to the seminal vesicles.
- The pockets of the vesicles are opened and drainage is made in them.
- The operation is completed by layer-by-layer suturing of the wound.
REFERENCE! A gentle type of surgical intervention is puncture of the seminal vesicles.
The doctor makes a puncture and washes the vesicles with saline solution with the addition of anti-inflammatory and antiseptic drugs.
Washing the vesicles is used for purulent forms of the disease and if treatment with antibiotics and antibacterial drugs does not bring the desired result.
Treatment of vesiculitis at home is popular among many patients. And this is not surprising, since in case of inflammation in the early stages, such methods can eliminate the symptoms of damage to the seminal vesicles.
Treatment of vesiculitis with folk remedies in an uncomplicated form:
- Propolis tincture. 20 gr. propolis is poured with 100 ml of alcohol. Take 30-40 drops diluted in 50 ml of water 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
- Suppositories with propolis. 40 gr. propolis is crushed and poured with a glass of alcohol and infused for 12 days. The mixture is boiled until the alcohol has completely evaporated. Then 2 grams are added to it. cocoa, candles are formed. Manufactured candles should be used at night.
- Honey-pollen mixture to strengthen the immune system. The components are mixed and taken 1 teaspoon 3 times a day for a month and a half.
- Parsley seeds. 2 tbsp. l. The seeds are ground in a coffee grinder and poured with 2 cups of hot water. Heat in a steam bath for 15 minutes. Drink half a glass 2 rubles. in a day.
- Herbal mixture. 25 gr. burdock root, 15 g poplar buds, 10 g sage, 5 g. Mix St. John's wort and pour 500 ml of boiling water into a thermos. After 10 hours, filter. Take 50 ml per half hour of meals three times a day. Course – 2 months.
- Microenema with chamomile and calendula. 2 tablespoons of flowers are poured into 500 ml of water and heated in a steam bath for 15 minutes. The enema is done at night, the temperature of the liquid is 40 degrees.
- A mixture of beetroot, cucumber and carrot juices in equal doses. It is recommended to drink 100 ml 4 times a day.
- Decoction of herbal mixture. Nettle (10 gr.), fennel (15 gr.), calendula (25 gr.).
Relapse and prevention
It is almost impossible to cure vesiculitis one hundred percent; the impetus for a new manifestation of the disease can be the presence of any provoking factor. Those who have had spermocystitis are advised to carefully monitor their health and monitor the condition of their own genitourinary system. If relapses of the disease occur, sanatorium-resort treatment is indicated.
One important factor is nutrition. The menu should contain a full range of vitamins and minerals. To prevent constipation, which can become a source of infection, it is necessary to include foods high in fiber in your diet.
The disease can return due to hypothermia, so it is necessary to wear warm underwear in the cold season. Long-term sexual abstinence and sperm stagnation are harmful to the male body.
Prevention of vesiculitis:
- Timely treatment of male diseases: prostatitis, urethritis.
- A healthy lifestyle, sufficient physical activity to prevent stagnation in the pelvic organs. If your occupation requires you to spend a long time sitting, you need to do physical exercises every hour to stimulate blood circulation in the pelvis. Squats, leg swings, and bending are effective.
- Maintaining intimate hygiene.
- Sanitation of all foci of infection in the body: carious teeth, tonsils with sore throat and tonsillitis.
- Inadmissibility of promiscuity.
- Quitting alcohol and smoking.
Vesiculitis is a serious inflammatory and infectious disease leading to disruption of the reproductive function of men. The disease most often occurs against the background of other inflammatory processes, so timely treatment is necessary first of all. The success of vesiculitis treatment depends on timely consultation with a doctor.
Source: https://samec.guru/zabolevaniya/andrologiya/vezikulit/simptomy-i-metody-lecheniya.html
Vesiculitis: 2 groups of causes, symptoms, 4 treatment approaches
The seminal vesicles are two secretory formations of the small pelvis, present only in men. The normal functioning of these formations is necessary to provide sperm with nutrients and, in general, for their normal functioning. Inflammation of the seminal vesicles is fraught with dire consequences, for example, disruption of the reproductive function of men.
These formations are up to 12 cm long and only 0.7 cm thick. They are located relative to other organs as follows: in front is the bladder, behind is the rectum, and below is the prostate.
The structure of the seminal vesicles is divided into:
- base – the widest part;
- body - middle section;
- narrow part - lower section;
- excretory duct.
Departing from each testicle, the vas deferens at the base of the prostate connect with the excretory ducts (those same seminal vesicles) into one duct called the ejaculatory duct.
Inside these formations have cavities lined with secretory epithelium. The wall of the formations also contains a muscular layer.
The bubbles secrete a thick, yellowish-colored secretion, the basis of which is the substances necessary for the viability of sperm and which serve as a nutrient medium for them.
The efferent ducts penetrate the prostate and open into the urethra, where sperm are released along with seminal fluid at the time of ejaculation.
Thus, a group of accessory male sex glands (which include the seminal vesicles, prostate and bulbourethral = Cooper's glands) jointly produces seminal fluid - energy support for sperm.
What is vesiculitis and why does it develop?
So, vesiculitis (also known as spermatocystitis) is called inflammation of the seminal vesicle, one or both at once.
Definition of the concept and mechanism of the inflammatory response
It extremely rarely develops “alone”; most often it becomes inflamed together with the prostate or urethra, together with epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis). This nature of inflammation is explained by the close location and close connection of the duct system.
In addition, the infection can enter the blisters through the blood and lymph flow. Here, existing foci of pathogenic infection in the body as a whole (viral infections, tonsillitis, carious teeth, etc.) will be important.
The following factors can stimulate the onset of the disease:
- smoking;
- consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- disharmonious sex life (in particular, practicing interrupted sexual intercourse);
- hypothermia;
- sedentary lifestyle with poor blood circulation in the pelvic organs.
Causes of vesiculitis
Vesiculitis is caused by infection. Vesiculitis can be caused by gonococci, as well as other pyogenic microbes. They most often penetrate through the inflamed urethra, through the ducts or directly from the prostate. There are 2 significant groups - according to the reasons - vesiculitis caused by infection and non-infectious factors.
Infectious ones, in turn, can be specific and nonspecific.
Specific options:
- gonorrheal;
- tuberculosis;
- Trichomonas.
Among the nonspecific subgroups:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- chlamydial;
- mycotic;
- mixed infection;
- transient.
Non-infectious vesiculitis is caused by allergies, metabolic disorders, injuries, iatrogenics, and psychogenic factors.
Classification of vesiculitis
Vesiculitis in men can be unilateral or bilateral. In 85% of cases this is a two-way process. Along the way, inflammation in the seminal vesicles can be acute and chronic. Chronic vesiculitis occurs due to untreated acute vesiculitis, with improper treatment or its absence.
Symptoms depend on whether it is isolated vesiculitis or combined with prostatitis and urethritis. Patients are bothered by pain in the groin or iliac regions. The pain may radiate to the rectum, there may be pain during bowel movements, and false urges. Ejaculation becomes painful, and there may be some blood in the ejaculate.
Acute vesiculitis
The acute form occurs with a more pronounced clinical picture; these are primarily symptoms of intoxication: the temperature rises to 39 degrees and above; Malaise, pain throughout the body, headache, and chills also occur. Appetite decreases. I am concerned about pain in the lower abdomen, which intensifies when the bladder or intestines are full.
The urge to urinate becomes more frequent, and urine output becomes painful. Traces of blood may be observed in the urine.
Chronic course
The acute form of vesiculitis becomes chronic if not treated correctly. With this course of the disease, the pain becomes dull and aching. They are often not localized and occur in the perineal area and in the pelvic organs.
Pain often occurs after sexual intercourse. Often there is an admixture of blood and pus in the urine and ejaculate, and the structure of the sperm changes.
Urinary disorders and erectile dysfunction become common, and the ejaculation process is disrupted.
In some cases, chronic vesiculitis occurs without pronounced symptoms.
If you notice these complaints, you should immediately consult a doctor. Treatment of this disease is within the competence of a urologist.
The above symptoms will suggest the presence of a disease. If this pathology is suspected, a digital rectal examination is performed. Seminal vesicles are palpated as enlarged, painful formations along the anterior wall of the rectum. When they are located high, it becomes impossible to palpate them, which does not exclude this diagnosis.
Diagnosis is possible using ultrasound. After ejaculation they do not decrease in size.
Discharge from the urethra is also examined. Examine the discharge formed immediately after rectal examination and emptying of the seminal vesicles (massaging them). During inflammation, a large number of leukocytes and red blood cells are found in the fluid. This type of study becomes decisive in the diagnosis of acute vesiculitis.
Also additional diagnostic methods are:
- examination of urine - red blood cells, streaks of blood, leukocytes and bacteria visible to the naked eye are found in it, the urine becomes cloudy;
- general blood test - to assess the degree of the existing inflammatory process;
- bacteriological examination of seminal fluid - to identify the pathogen and identify its vulnerability (sensitivity of the bacterium to certain types of antibiotics);
- testing for infections that are predominantly sexually transmitted.
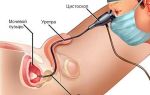
As mentioned above, an ultrasound examination of the seminal vesicles is carried out to determine their size over time. Ultrasound is performed transrectally.
Complications and prognosis of the disease
Since inflammation in most cases is caused by pyogenic microorganisms, one of the complications is empyema of the seminal vesicles - purulent melting of them.
This complication develops in the absence of antibacterial treatment or when treated with drugs to which the pathogen is resistant.
This process threatens sepsis - the spread of infection throughout the body through the bloodstream, the formation of foci of purulent inflammation in other organs. The outcome is fatal.
With long-term chronic untreated vesiculitis, infertility may occur (due to sclerosis of the wall of the vesicles, and, consequently, the lack of release of nutrients for sperm).
Also one of the complications is epididymitis and orchitis - inflammation of the testicle and its epididymis, which can also lead to infertility and sclerosis of testicular tissue if not treated properly.
Sexual life and vesiculitis
In case of acute vesiculitis, the patient is recommended to have sexual rest. Sexual intercourse itself will be accompanied by pain and is also fraught with the risk of pathological secretions flowing through the ducts and their spread (which facilitates the spread of infection to all anatomically related structures).
Approaches to the treatment of vesiculitis
- Acute vesiculitis is treated with the mandatory prescription of antibacterial drugs (ideally, taking into account the sensitivity of the cultured pathogens, which in practice becomes problematic and is not always feasible).
- Also, to eliminate inflammation, a group of NSAIDs is used - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - rectal suppositories, tablets, injections.
- Symptomatically, it is possible to take antipyretic and analgesic drugs, since different representatives of the NSAID group have their own properties to varying degrees, each drug has its own preferential effect.
- In addition to everything, it is necessary to follow a dietary diet with abstinence from alcohol and hot, spicy foods.
- Such auxiliary methods are not prohibited - the use of microenemas with warm chamomile, massage of the seminal vesicles.
- Physiotherapy is applicable - the therapeutic effect of currents, mud applications on the perineal area - but not in the acute period.
- Immunity stimulants can be prescribed for persistent frequent relapses of the disease and at the stage of healing acute forms.
Chronic vesiculitis with suppuration and frequent relapses, lack of effect from conservative treatment, are treated surgically. “Vesiculostomy” is performed by puncture under ultrasound control with washing of the cavity of the vesicles with antiseptic solutions.
The fact is that the space in the middle of the seminal vesicles is filled with loose fiber. Its anterior wall is the bladder, the posterior wall is the aponeurosis, and the upper wall is the peritoneum. On the sides there are thin connective tissue “septa” - fascia; they are pierced by the vas deferens. Pus from this space can easily penetrate into the pelvic space.
In such cases, puncture and drainage are indicated. In some cases, vesiculectomy becomes justified.
Antibiotics, as mentioned above, are prescribed taking into account bacteriological examination of seminal fluid and determination of sensitivity to antibiotics. Preference is given to groups taking into account sensitivity, the ability to specifically destroy the pathogen, and not stop its reproduction and growth, and the effectiveness of the impact specifically on the pelvic organs.
In most cases, these are drugs from the groups of fluoroquinolones and macrolides.
ethnoscience
This method is applicable during the period of attenuation of the inflammatory process, or as an auxiliary method to the main treatment. Warm microenemas with chamomile have an antiseptic, anti-inflammatory effect; its use is justified for the purpose of relieving symptoms from the rectum and bladder - tenesmus and frequent painful urination.
Prevention of vesiculitis
Measures to prevent this disease include timely sanitation of foci of infection in the body (treatment of caries, sinusitis, tonsillitis, etc.). For patients with the chronic form, an important point will be to follow a diet - avoiding spicy, smoked foods, alcoholic beverages, and quitting smoking.
Sports activities are especially recommended: they will improve blood flow in the pelvic organs.
Sex life must be regulated. There should be no long breaks or sexual excesses.
When a disease occurs, it is important to recognize it in time. This pathology is relatively rare, and the doctor can often miss specific signs with these general, non-specific complaints.
Treatment of this pathology must be timely and complete, which depends not only on a specific specialist.
Compliance with the recommendations and regimen is the key to success on the path to getting rid of this dangerous disease with its complications.
Article rating
We have put a lot of effort into making sure you can read this article and would welcome your feedback in the form of a rating. The author will be pleased to see that you were interested in this material. Thank you!
(3
Source: https://UstamiVrachey.ru/urologiya-i-andrologiya/vezikulit
Vesiculitis: main symptoms and treatment
Zakharov Nikolay Viktorovich Updated: December 20, 2018
- If a man develops vesiculitis , the symptoms and treatment of the pathology must be known.
- This is a disease that affects the organs of the urinary and reproductive systems.
- More precisely, the seminal vesicles in men.
- It usually develops in parallel with inflammation in the prostate.
- The disease is characterized by impaired sexual function.
- If the disease is not treated for a long time, it causes infertility .
Reasons for the development of pathology
It is known that inflammatory processes of the seminal vesicle develop not only in older men (after 50 years), but also in representatives of young (25-30 years) and middle (30-45 years) ages. The growth in statistics is due to the deterioration in people’s quality of life.
All causes that provoke inflammatory disorders of the vesicles and duct can be divided into 2 main categories - infections and stagnation.
In turn, infectious factors are divided into typical and nonspecific.
The first include: trichomonas, gonorrheal, tuberculosis and mixed infections. Nonspecific - viruses, bacteria, chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, candida, gardnerella.
If we consider the bacterial microflora, then most often the causative agents of inflammation of the prostate and seminal vesicle are staphylococcal and streptococcal infections. The most common cause is Klebsiella, Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Proteus.
But congestive vesiculitis (also called congestive) is associated with congestion in the prostate , seminal vesicles, as well as the vas deferens, other sex glands and blood vessels in the pelvic organs and scrotum.
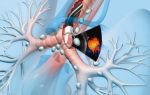
Which part is affected by vesiculitis can be seen in the picture.
There are factors that contribute to the development of stagnant processes in this zone:
- sexual intercourse that was interrupted;
- masturbation;
- a sign of irregularity in sexual life;
- sexual abstinence;
- incomplete ejaculation, which is caused by stress during sexual intercourse;
- inactive lifestyle;
- smoking and frequent drinking of alcoholic beverages;
- severe hypothermia;
- proctitis, hemorrhoids and other inflammatory diseases in the pelvic area.
There are several ways of infection entering the seminal vesicles:
- By the circulatory system. This route is called hematogenous. This usually happens with common diseases of an infectious nature. Pneumonia, tonsillitis, sinusitis, cholecystitis, frontal sinusitis, cholangitis and other diseases also affect.
- Upon contact (contact method). With the urinogenous ascending tract, the infection spreads from the urethra as a consequence of urethritis. With the descending urinogenous route, the infection penetrates the ureters from the kidneys (usually this occurs with pyelonephritis). In addition, it is necessary to take into account the ascending canalicular method, that is, the infection spreads along the vas deferens during defrentitis, funiculitis, epididymitis.
- Through the lymphatic system. In this case, a person is most often pre-treated for proctitis, paraproctitis, prostatitis, thrombophlebitis in hemorrhoidal veins.
In addition, vesiculitis in men can be the result of an allergic reaction, mechanical injury, chemical poisoning (medicines, other chemicals), or a malfunction of the immune system.
What are the symptoms?
If acute inflammation of the seminal vesicles develops, the symptoms will be as follows:
- Sudden development.
- Body temperature rises to 39ºС. The man suffers from headache, fatigue, chills, and weakness. All these signs indicate general intoxication of the body.
- Sharp painful sensations in the pelvic area: pubis, perineum or near the rectum. Sometimes the pain moves to the sacral region or lower back.
- When a person pushes, the pain intensifies. The same applies to defecation, erection, ejaculation, gradual filling of the bladder, or any muscle tension in this area. Because of this, the seminal organs are compressed. If a man has right-sided vesiculitis, then pain will appear on only one side.
- Mucus is released from the urethra during bowel movements. Sometimes you can notice reddish blood clots in it. Due to the fact that the seminal vesicles are located close to the intestines, when feces move, they are compressed, and their contents enter the urethra.
- Urination becomes more frequent. In some patients, this is because the walls of the bladder are irritated. In addition, a man may suffer from spermatocystitis.
- There are traces of blood in the semen. This is because the blood vessels in the seminal vesicles are damaged.
- Erection at night. This quite often happens due to the fact that the nerve fibers are excited. Sometimes an involuntary erection is accompanied by ejaculation, which is called a wet dream.
- The volume of sperm changes, and it can either increase or decrease. This is due to the fact that a large amount of mucus is released or, conversely, there is an outflow of the substance from the organ.
- The quality of sexual life deteriorates significantly. Due to pain and stress, blood flow to the genital organs deteriorates, so that erection decreases, as does the quality of orgasm.
Video: “Vesiculitis: symptoms and treatment”
As for the chronic form, the symptoms of vesiculitis in this case will be the same as in the acute form, but less pronounced. In addition, potency decreases and sexual disorders appear.
If the inflammation of the vesicles is chronic, then disruptions occur in the vascular and neurological mechanisms that are responsible for erection.
This male disease can lead to infertility, since the seminal vesicles protect sperm and are responsible for their nutrition. Due to disturbances in the functioning of organs, the quality of sperm deteriorates greatly.
The acidity level of the substance, its viscosity, and sperm motility change.
To diagnose the disease, the following methods are prescribed:
- rectal examination;
- examination of the contents of the seminal vesicles;
- vesiculography;
- Ultrasound;
- computed tomography;
- semen, blood and urine tests.
- All these techniques will help determine the disease.
- Video: “What you need to know about vesiculitis?”
Drug treatment of vesiculitis
The treatment itself is selected depending on the factors that provoked such an illness. For example, if a patient has vesiculitis of an infectious nature, then antibacterial therapy is prescribed.
For the cognitive form of pathology, medications are used that eliminate congestion in the organs of the reproductive and urinary systems.
If a person has an inflammatory process or signs of spermatocystitis, then symptomatic therapy is used. In any case, treatment must be comprehensive.
Drug treatment of bacterial vesiculitis (infectious) involves the use of antibiotics.
For example, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Drugs that belong to the group of macrolides: Macropen, Sumamed, Erythromycin.
- Tetracycline antibiotics - Metacycline, Doxycycline.
- Drugs with combined effects. For example, Tetraolean or Oletetrin are suitable. Their feature is a selective effect on the tissues of the prostate, urethra and seminal vesicles. They act against mycoplasma and viruses.
- Drugs from the nitrofuran group - Trifurantoin or Furagin. The active components of these medications penetrate the secretions of the prostate and seminal vesicles.
- Drugs from the sulfonamide group. For example, they are used: Trimethoprim, Bactrim.
If the patient’s inflammation of the vesicles is caused by rare pathogens (like Klebsiella or Proteus) or urogenital-type infections, then drugs from the following groups are prescribed:
- tetracyclines;
- macrolides;
- fluoroquinolones;
- sulfonamides with trimethoprim.
In the presence of chlamydia or mycoplasma, Dalacin and Lincomycin are prescribed, and in case of gardnerella, Macmiror and Miranem are prescribed. The peculiarity of the treatment is that it is carried out in parallel not only in the man, but also in his sexual partners.
If the disease is caused by specific infections (such as gonorrhea, syphilis, tuberculosis), then the following are prescribed: Rifampicin, cephalosporins and penicillins.
If inflammation of the seminal vesicles is caused by congestion, then the following methods are used:
- Angioprotectors. For example, the following are suitable: Aescusan, Inderal, Obzidan, Venoruton, Dartilin, Agopurin, Trental.
- Massage of seminal vesicles and prostate.
- Microclysters (volume ranges from 10 to 100 ml, liquid should be warm).
- UHF therapy.
- Physiotherapy with equipment such as Intraton, Yarilo, Intramag.
- Assistive therapy.
If the patient has vesiculitis, treatment also involves the use of anti-inflammatory drugs. For example, Diclofenac or Indomethacin are suitable. They help reduce body temperature, eliminate pain, inflammation, and prevent damage to nearby tissues and organs.
Additionally, immunomodulators are prescribed - these are Levamisole, Pyrogenal, Taktivin, Timalin, Viferon, Soklourovac. They strengthen defense mechanisms, as a result of which the body can fight infections.
Other treatments for vesiculitis
If a man develops inflammation of the seminal vesicles, then therapy should be comprehensive.
In addition to drug treatment, other methods are prescribed:
- Physiotherapy . The use of UHF is very useful. Acupuncture (also called reflexology) is also used. The doctor may prescribe electrotherapy. Sanitary resort treatment with mud rectal suppositories, mineral and mud baths, and applications is necessary. Physical therapy is considered very effective. This will help strengthen both general and local immunity. The process of tissue repair is stimulated. Inflammation gradually goes away and metabolism improves.
- Diet . Treatment of vesiculitis involves proper nutrition. It is aimed at preventing constipation. In addition, the diet will help strengthen the human immune system. You definitely need to eat more fresh fruits and vegetables, fish, lean meat, and dairy products. It is necessary to exclude from the diet sour fruits and berries, canned food, smoked foods, fatty and fried foods, coffee, strong tea, spices and foods that increase the intensity of gas formation in the intestines.
- Surgical intervention . Treatment of vesiculitis in the later stages involves surgery. Typically, this procedure is prescribed when the pathology has complications - for example, empyema. This is a condition where the seminal vesicles are filled with pus. In this case, puncture of the organ is performed with further drainage. In the most severe cases, the seminal vesicles are removed, a procedure called vesicolectomy.
Conclusion
Every man should know what vesiculitis is in order to pay attention to certain symptoms in time and go to the hospital. Treatment is selected by the doctor depending on the diagnostic results.
Vesiculitis develops due to various factors, so therapy is primarily aimed at eliminating their effects. In addition, supportive methods are prescribed.
But it is best to know the essence of this disease and carry out prevention.
Source: https://kakbyk.com/bolezni/invektsionnye-i-vospalitelnye-zabolevaniya/vezikulit-osnovnye-simptomy-i-lechenie.html
Vesiculitis
The pathology is characterized by inflammation of the seminal vesicles.
In the male body, this paired organ is involved in the process of ejaculation and also reproduces fructose, which is necessary to maintain normal motility and viability of germ cells.
This disease appears as a complication of infections already existing in the body, which include prostatitis, urethritis or orchitis.
How does the disease develop?
Vesiculitis is an infectious disease. Pathological microorganisms can reach the seminal vesicles by hematogenous route, this is often observed with influenza, pneumonia or sore throat.
They can also reach this organ through the lymphogenous route or penetrate through the spermatic cord (along the ascending route).
The appearance of this disease can result from the entry into the body of the following microbes that cause infection in the genitourinary system:
- coli;
- staphylococcus;
- gonococcus and other microorganisms.
After reaching the seminal vesicle, they begin their active reproduction on the mucous membranes, thereby provoking the development of the inflammatory process.
The following factors can contribute to the appearance of vesiculitis:
- improper diet, as well as prolonged constipation;
- hypothermia of the body;
- indiscriminate sexual intercourse;
- staying in one position for a long period of action;
- weakened immune system;
- sexual abstinence.
Symptoms of the disease
Vesiculitis can have a chronic and acute form. The chronic stage occurs as a consequence of an untreated acute disease, but can also have a primary chronic development.
The pathology begins to manifest itself as painful sensations in the perineum, which have a pulling nature, frequent urge to urinate, erectile dysfunction and altered sperm composition. In frequent cases, pain radiates to the lumbar region. Erections become painful and orgasms may stop completely.
Patients notice pain and acceleration of ejaculation. This form of the disease requires long-term treatment, after which stable remission can be achieved.
Sometimes patients are not bothered by any symptoms of vesiculitis. They can only find out about its presence after a thorough examination.
The acute form of the disease reveals itself with a sudden increase in temperature, as well as the appearance of painful sensations in the anus, sacrum or groin. This pain increases with bowel movements and also with emptying the bladder. In addition to a high temperature, men may feel chills. Many of them develop headaches and increased fatigue.
Patients complain of frequent urge to urinate at night and the appearance of blood in the semen. In many men, such phenomena occur against the background of existing prostatitis, which is chronic in nature. In this case, patients often confuse these symptoms with an exacerbation of the latter. Experts call this inflammation prostatovesiculitis.
If it spreads to adjacent tissues, then paravesiculitis occurs.
What are the complications?
In the absence or insufficient treatment of acute vesiculitis, suppuration or empyema appears in the seminal vesicles.
If the disease is chronic, then the inflammatory process can affect the epididymis and contribute to the appearance of chronic epididymitis. It is worth noting that bilateral epididymitis in chronic form contributes to the appearance of infertility in men.
Diagnosis of pathology
If an inflammatory process is suspected, specialists prescribe an ultrasound examination, spermogram, bacteriological analysis of vesicular secretions, as well as a rectal examination. A diagnosis can only be made after an examination has been completed.
Therapeutic measures
After confirmation of acute vesiculitis, certain antibacterial drugs are prescribed. Antibiotics in this case are selected depending on their effectiveness in the sexual sphere, bactericidal activity, and price. To eliminate the disease, specialists use not only macrolides, but also a group of fluoroquinolones.
Specialists also prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs and drugs that have an analgesic effect. To reduce pain during bowel movements, it is necessary to take laxatives that will help normalize stool.
When patients' body temperature decreases, it will be necessary to move on to physiotherapeutic procedures, among which are especially effective:
Source: https://yrologiia.ru/vezikulit.html