The papilloma virus has haunted humans for a very long time. Its connection with the development of some malignant tumors was noticed already in the middle of the last century. In the 70s, a hypothesis was put forward about the role of HPV type 66 as a carcinogen, which provokes the formation of oncological problems. At the end of the 90s of the last century, this theory was confirmed.
HPV type 66 has a high oncogenic potential
The role of the virus in the formation of papillomas and cancer is undeniable today. Infection with HPV from the high-carbon group contributes to the development of oncology. In most cases, this pathology passes through the body's immune system and undergoes regression at another period.
Detailed description of HPV 66
So far, more than 100 types of the virus have been identified, of which about 30-40 are classified by various sources. They are related to the anogenital area.
Representatives were divided into groups according to the level of participation in the morphogenesis of oncology and benign proliferative changes.
Number 66 (HPV type) is a pathology with a high oncogenic potential, which leads to the likelihood of developing cancer of the female and male genitalia.
If HPV type 66 DNA is detected in women, only a doctor will tell you what it is and how to fight it during a consultation. You should not re-read the literature and make lotions with folk remedies, as this will not bring the desired result.
Stress causes the spread of HPV
After entering the body, the virus is not immediately activated, sitting on the epithelial layer of cells for this purpose. In the presence of favorable factors (most often reduced immunity, stress or exacerbation of a chronic disease), HPV begins to penetrate the structure of cells, changing DNA and actively multiplying them. This leads to the formation of papilloma.
Variants of infection
The pathology belongs to the category of common sexually transmitted diseases through direct heterosexual or homosexual contact.
HPV is diagnosed in 10-15% of women examined, while it is believed that about 30-60% of sexually active patients have been exposed to one or more types of the virus.
The highest percentage of infection occurs in people under 30 years of age.
This is not the only route of infection, because transmission of the virus occurs through underwear, the use of shared towels or other personal hygiene items, especially when lesions are diagnosed on the external genitalia. Infection in public toilets is theoretically possible. In the absence of basic hygiene rules, the virus can enter the child’s mucous membranes and skin.
You can get infected by using someone else's towels
To avoid the growth degenerating into oncology, it is important to visit the gynecology or urology office on time.
The detection of HPV type 66 DNA molecules in the genital area of infants at birth indicates that the child could have become infected during childbirth. A case of fully developed condyloma lesions in a newborn is described, and separate studies have been conducted on the presence of this virus in umbilical cord blood. You can infect the fetus during its passage through the birth canal or through placental blood.
The transmission mechanism itself has not been fully studied. Sometimes one of the partners, despite regular sexual intercourse, does not become infected with the virus, or the couple has different types of HPV. Therefore, not all routes and mechanisms of infection have been well studied, which makes it possible to live with the virus and not have any formations.
Sometimes, even through sexual contact with an infected person, the patient does not become infected
Possible threats
Due to the presence of 2 types of papillomas with high (dangerous) and low levels, infection can occur in the following cases:
- infection with one or more low-risk types of viruses;
- infection with highly oncogenic variants;
- mixed infection in which HPV viruses are found from different groups.
The first phase of HPV type 66 is the period from the moment of infection until the appearance of changes on the epithelial surface of the vagina or vulva. This is the latent phase of the process, in which the presence of pathology can only be detected by performing virological tests to determine the DNA molecule.
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by cytological examination
At this stage, both cytological examination and colposcopy give correct results. The latent phase of infection lasts several months or years. The last evolutionary stage of infection is the clinical stage (benign proliferative lesions visible to the naked eye). These could be condylomas or cervical or vaginal formations.
HPV type 66 is a necessary but not sufficient factor for the development of cancer, especially of the cervix.
It is assumed that many systemic and extracorporeal factors have a stimulating effect on the formation of warts and subsequent oncology.
One of these is considered to be the process of reducing cellular immunity, which is influenced by the general state of the defenses and external factors (smoking or vitamin A deficiency).
Tobacco smoke contains various toxic chemicals that damage the epithelial layers, and a deficiency of beneficial elements disrupts the proper course of differentiation and maturation of these cells.
Tobacco smoke can spread infection
Another factor is the high number of pregnancies and long-term use of hormonal contraceptives.
Early sexual activity and contact with several partners leads to re-infection with papillomavirus, but has a high risk of sexually transmitted diseases: HIV, herpes, chlamydia.
Together with nonspecific inflammation, these pathologies are independent factors provoking the development of papillomas and cancer processes.
There is still no information that the HPV virus is a threat to pregnancy and intrauterine fetal formation.
Thus, latent and subclinical infection will not be a contraindication to procreation. The possibility of infection of the fetus is considered an important problem.
This indicates the presence of HPV DNA obtained from the nasopharynx and genital organs of newborns, if his mother has such a pathology.
Some genital types of HPV promote the formation of papilloma and cause laryngeal cancer. However, no studies have shown that the problem can be passed on to children from infected mothers. Children are more likely to have papillomas and genital or laryngeal cancer.
HPV can cause laryngeal cancer
Clinical picture
A characteristic feature of HPV of the cervix, vagina and vulva is the complete absence of subjective symptoms in the latent and subclinical phase of infection. The same applies to men who have a preclinical form (no visible damage). In them, the problem occurs without symptoms, although in both cases the virus is transmitted to a sexual partner.
Purulent discharge and itching are symptoms of other infections, and with HPV they appear if the body of the wart or precancerous changes have already formed.
Such manifestations are considered the result of overlapping secondary bacterial or fungal infections.
The irritating factor in the development of these signs is not the virus itself, but only coexisting inflammation, which further enhances the evolution of HPV-dependent changes.
Symptoms in the form of abnormal bleeding appear in men and women in case of clinical forms of cancer.
The virus causes itching and soreness of the genitals
Diagnostic measures
There are several types of tests based on modern PCR/Polymerase Chain Reaction technology. This is a genetic test that allows you to accurately determine the type of HPV virus and the amount of infected DNA in the body. In cases of the latent phase (inactive form), this is the only way to detect pathology.
A positive DNA test always indicates the presence of the virus. A negative result is not equivalent to the absence of HPV. Current tests find most of the common and dangerous types, but not all of them.
At serious stages of pathology, the genetic material of the virus integrates with the same material of the epithelial cell. Its diagnosis becomes difficult or impossible, which sometimes leads to false negative results.
PCR testing provides the most accurate results
In some cases, HPV infection of the cervix and vagina is located in such a way that the response to the examination of material from the cervical canal will be negative. Only after examining a fragment of infected tissue taken from the site of colposcopically visible changes in the epithelium does it give a positive answer.
In the subclinical phase, if there are lesions in a small area, you need to wait for the appearance of any symptoms or manifestations. The condition for carrying out such a procedure is complete confidence in the nature of the observed changes. Only a physician experienced in colposcopy can observe these phenomena without prior histological examination.
In the case of subclinical infection that persists for more than 12-24 months, or during the progression of papillomas, treatment will be removal of the affected tissue. The method of therapy depends on the result of histological examination of the sites and colposcopy, the degree of epithelial changes and location on the cervix, vagina or vulva.
Tissue affected by papillomas is removed surgically
Course of therapy
What to do in these cases? In the presence of sublated virus and low-grade lesions on the cervix, the following methods can be used:
- cryotherapy (exposure to liquid nitrogen);
- photocoagulation;
- evaporation using a CO2 laser.
Treatment is prescribed if there are strict colposcopic, cytological or histological criteria for changes that must be strictly observed.
Laser techniques can be used to treat papillomas
Surgical removal is done in cases of higher levels of dysplasia or unfavorable location of the lesions. All stages of cervical cancer, as well as early invasive forms, are completely curable, which preserves the woman’s ability to become a mother.
In the case of papillomatosis (especially of the vulva), chemical solvents are used: Condilin and cream with a similar effect (Vartek or Aldar). The effectiveness of these substances varies, but is not always satisfactory. Recurrences of changes often occur.
Other methods of treating condylomas:
- cryostimulation;
- removal with an electrosurgical loop;
- laser evaporation.
Cauterization of papillomas is carried out using Condilin
Surgical removal of lesions gives good results. The choice of method depends on the location, number and size of outbreaks. Changes in genital warts can develop without the involvement of the HPV virus as a result of chronic inflammation caused by chlamydia.
The presence of gonorrhea and fungal infections leads to the same process. They give a picture of microvaginitis of the cervix and vagina. During pregnancy, pathologies take on the distinct form of condylomata acuminata. These changes quickly disappear after using causative therapy. For this type of symptoms, accurate bacteriological and mycological diagnosis is important.
HPV is treated with vitamin A, immunostimulants and complexes of beneficial substances. An attempt to eliminate the pathology with drugs that are used in the treatment of the herpes simplex virus is unjustified.
What tests are taken to identify sexually transmitted diseases, see below:
Source: http://bolezni.com/stati-o-boleznyah/papilloma/vpch-66.html
The danger and features of the manifestation of papillomavirus type 66 in women and men
Home-HPV
HPV type 66 (HPV) is a type of papilloma virus that can cause dangerous degeneration into a malignant tumor. Decoding means strain number. In total, there are over 100 papillomavirus viruses; the incubation period of the disease is on average 6 months.
The DNA of the virus is integrated into the nuclei of cells of the mucous membranes, with further proliferation of parasites and the death of healthy cells. If the pathological condition is not treated, oncogenic papillomavirus leads first to dysplasia, then to cervical cancer.
Features and danger of strain 66
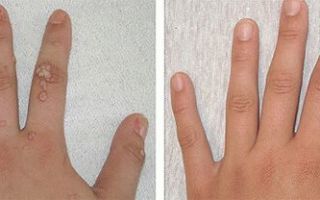
Frequent locations of papillomas with HPV 66 are the mucous membranes of the genital organs, less often the external genitalia.
There are 3 types of papilloma virus
- non-hazardous – do not cause degeneration into a malignant neoplasm;
- conditionally dangerous - degenerate into cancer under certain conditions;
- dangerous - lead to the development of dysplasia and cancer.
HPV 66 strain belongs to the second class.
How is hpv 66 transmitted:
- sexual intercourse is the main route of transmission;
- in everyday life - through the patient’s clothes, things and personal hygiene products;
- when visiting public places (swimming pools, baths) - rarely;
- during childbirth - through the birth canal infected with HPV;
- independent infection - movement of the virus from one part of the body to another (through shaving injury).
The main danger of the strain is the change in HPV 66 DNA cells by type in women, the transition of the neoplasm from benign to the malignant stage.
Symptoms of papillomavirus and diagnosis
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Initially, the disease is asymptomatic. Condylomas are located on the inner surface of the genital organs, so they can only be detected after a medical examination. A visit to the gynecologist is mandatory once a year.
Diagnosis of HPV 66 occurs during a routine gynecological examination. To make an accurate diagnosis, you must do the following:
- PCR research;
- smear, scraping from the cervix;
- colcoscopy after treating the cervix with acetic acid, then with iodonate solution;
- Digene study determines tumorigenic risk;
- targeted biopsy – if cancer is suspected;
- general blood and urine tests.
The research results will help determine the type of virus, the stage of the disease, and the likelihood of degeneration into a malignant tumor.
In men
The disease is often asymptomatic, and the man may not know that he is a carrier of the virus. Condylomas are located on the genitals and anus.
A man may experience pain when urinating, slight itching in the genital area and anus.
Among women
The following symptoms should alert you:
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- highlighting an unknown cause;
- itching when urinating;
- traces of blood after sexual intercourse;
- regular relapses of diseases associated with weakened immunity (thrush, colds, ARVI).
The disease often manifests itself in the presence of concomitant diseases: chlamydia, endocervicitis, AIDS.
Treatment of HPV with 66 drugs
Treatment is carried out by both partners at the same time. It is not recommended to be sexually active during therapy. If the HPV result is positive, no treatment is given during pregnancy.
The table of drugs for the treatment of papillomavirus is provided for information. Medicines for the treatment of HPV type 66 in men are prescribed by a doctor and can be purchased at a pharmacy.
| Group of drugs | pharmachologic effect | Representative drugs |
| Antiviral drugs | Blocking the virus in papillomatosis, suppressing the infectious agent. | Zovirax, acyclovir, panavir. |
| Immunomodulatory drugs | The drugs contain the main component – human interferon in different dosages. Increases antibody production and susceptibility to infections. | Viferon, genferon, interferon, cycloferon, intron a. |
| Antiviral agents | Prescribed for the treatment of HPV type 66 in women with a history of cervical dysplasia. | Allokin-alpha, epigen (spray) |
| Medicines for destructive removal of papillomas | Cauterizing action. Do not use on mucous membranes. | Solcoderm, nitric acid, cryopharma. |
| Homeopathy | Preparations of natural composition. Eliminate the cause of papillomas formation. | Thuja (ointment), hepar sulfur (granules). |
| Vitamin and mineral complexes | Regulation of metabolic processes in the human body, removal of toxic substances. | Alphabet, vitrum, aevit. |
Review of antiviral drugs
| Drug name | Composition, pharmacological action. |
| Panavir (vaginal suppositories, spray, gel) | Inhibition of virus cells. Disinfecting, anti-inflammatory, bactericidal effect. |
| Acyclovir (ointment, tablets) | Blocks virus 66 and does not affect healthy cells. |
| Altevir | Antiviral drug based on human interferon. |
| Amiksin | A drug based on tilorone. Removing waste products of the virus, blocking HPV and transferring it to an inactive state. |
| Isoprinosine | The active ingredient is inosine pranobex. An antiviral immunomodulatory drug that blocks HPV and renders it inactive. |
Review of immunomodulatory drugs
| Drug name | Composition, pharmacological action |
| Intron a, viferon | Preparations based on synthetic human interferon. Depending on the form of release (ointments, gels, suppositories), the dosage of the active component is different. |
| Immunomax | Immunomodulator based on acidic peptidoglycan. Promotes the formation of antibodies, enhances protection against infections caused by viruses. The action of macrophages is activated. |
| Gepon | An immunomodulator, which is produced on the basis of a synthetic peptide of 14 amino acid residues. Suppresses HPV, increases susceptibility to bacteria. |
| Galavit | Immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory effect. |
The treatment prognosis worsens if there is a history of other diseases (gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia, HIV infection).
Modern methods of removing papillomas
It is impossible to completely cure HPV. Therapy is aimed at strengthening the immune system and cauterizing condylomas.
Hardware methods for removing papillomas
| Removal method | Description when used |
| Laser | Removing tumors using a laser is a quick and painless method. The build-up is removed layer by layer. The disadvantage of this method is that it is not possible to take material for a biopsy. |
| Cryotherapy | Use of liquid nitrogen. |
| Chemical cauterization | The drug Solkovagil is used. The method is suitable for nulliparous women. |
| Radio waves | Removal of growth using the Surgitron device. The advantage of the method is the ability to send the papilloma for histological examination to diagnose oncology. |
| Dmatermoelectrocoagulation | Exposure to high frequency electric current. Suitable for formations that are small in size. |
| Operative surgery | The papilloma is removed in an inpatient surgical department of the hospital. The method is used in the presence of large papillomas and severe dysplasia. |
Precautions to take if you have a virus in your body
The papilloma virus cannot be completely removed. By following these precautions, you can reduce the likelihood of relapse to a minimum.
- Avoid casual sex. A condom does not provide any protection against the HPV virus.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Individual products for personal hygiene.
- Moderate physical activity. Strengthening the immune system by any means: hardening, dousing with cold water, eliminating stressful situations, optimal sleep and rest.
- Maintaining hygiene rules.
- When performing cosmetic procedures or visiting tattoo parlors, monitor the sterility of equipment. When performing procedures, the master must wear disposable gloves.
- When visiting public places (swimming pool, sauna, bathhouse), use removable shoes.
HPV 66 is much easier to prevent than to treat. Early diagnosis at the first symptoms guarantees successful treatment. To prevent infection, it is necessary to follow the rules of personal hygiene and not use other people’s clothes or cosmetics.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Link to main publication
Didn't find suitable advice?
Ask your doctor a question or see all questions...
Article rating:
(2
Source: https://VashaDerma.ru/hpv/66-tipa
HPV type 66 in women: what is this disease and how to treat it
Virus type 66 is an extremely dangerous infection that can cause cervical cancer. You need to know the features and symptoms of HPV, since early diagnosis of the presence of the pathogen in the body and timely treatment will help avoid complications.
Characteristics of papilloma, what kind of disease it is
HPV type 66 is a type of human papillomavirus. This disease belongs to a group with a high risk of cancer. Once in the body, this infection causes changes in epithelial tissue.
Today there are more than 100 types of papillomavirus. Most people are carriers of this infection. Some of the existing types of the virus are not dangerous to humans. They appear as skin rashes and do not cause discomfort.
Important!
HPV type 66 is not so harmless: it belongs to the so-called opportunistic viruses. Representatives of this group are capable of causing cancer, but only under unfavorable circumstances (hereditary factor, problems with immunity).
Features of the stamp
When the type 66 virus enters the human body, it begins to change. As a consequence, pathological tissue transformations are observed. The slightest malfunction in the body can provoke the degeneration of neoplasms resulting from mutations into malignant tumors.
HPV 66 may not manifest itself for a long time, especially in healthy women. But against the background of existing diseases, as a rule, active reproduction of the virus occurs and its further transition to oncology.
Probable causes of infection
HPV is one of the diseases that is most easily transmitted through sexual contact. This circumstance is explained by the characteristics of the virus:
- its size;
- the possibility of infection through a kiss or protected sexual intercourse;
- absence of severe symptoms.
In men, the virus may not manifest itself in any way. And it is even more dangerous, since the risk of infection of the partner increases.
It is quite possible to become infected with HPV type 66 by using someone else’s towel or another person’s cosmetics. Therefore, there is a possibility of infection in public places:
- swimming pools;
- gyms;
- saunas and baths.
REFERENCE: Papillomovirus is not destroyed when exposed to high temperatures and retains its activity well in a humid environment. HPV can be passed from mother to child during childbirth.
There are a number of factors that increase the risk of infection with type 66 strain:
- smoking;
- drinking alcohol in large quantities;
- stressful situations;
- constant lack of sleep;
- condition after illness;
- treatment with antibiotics or steroid drugs;
- avitaminosis.
How dangerous is papillomatosis for women and men?
HPV type 66 can be completely asymptomatic in women, provided there are no other concomitant diseases transmitted by PP.
And it can manifest itself in the form of itching sensations in the genital area. Often there is heavy discharge that has nothing to do with the onset of menstruation, pain when urinating, and discomfort during sexual intercourse.
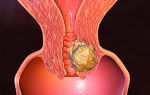
The virus is dangerous because over time it can cause cancer - cervical cancer. The mechanism of development of this disease is as follows.
HPV blocks special cells designed to protect against harmful microorganisms. As a result, the protective function decreases and the epithelium degenerates into precancerous formations - cervical dysplasia. If the necessary treatment is not given, malignant tumors appear.
According to studies, type 66 virus is found in the majority of women with cervical cancer. Patients who have a hereditary predisposition to cancer should be especially attentive in this matter, because their risk of developing the worst-case scenario increases.
Cervical dysplasia (in the presence of HPV type 66) can be provoked by:
- a large number of births;
- hormone therapy;
- long-term use of intrauterine devices;
- hypervitaminosis;
- HIV infection;
- smoking;
- promiscuity;
- early onset of intimate life.
Diagnosis of the virus
For timely detection of HPV type 66, a woman should undergo regular examinations with a gynecologist (at least once every six months). If a doctor diagnoses dysplasia, the following clinical studies are performed:
- take a smear;
- do a scraping from the cervix and a blood test;
- take material for biopsy.
Since a complete examination of the body is carried out, the HPV type is determined with one hundred percent accuracy and the stage of the disease is determined. Next, appropriate treatment is prescribed. With timely detection of cervical dysplasia, the likelihood of a successful outcome is very high.
If a man is suspected of having the HPV virus, the patient must visit a urologist and/or proctologist and get tested.
How does the disease manifest itself?
Since many people do not know how human papillomavirus type 66 manifests itself, this makes it difficult to make a correct diagnosis in a timely manner.
Important!
HPV has the following effects on a woman’s body: skin and mucous membranes are damaged. So-called condylomas form on the genitals.
It is good if, when a neoplasm is detected, a woman immediately consults a doctor and she is found to have type 66 virus. Then there will be a chance to carry out full treatment on time, before changes occur in the uterus and cancer cells appear.
It is almost impossible to diagnose HPV type 66 on your own. This is due to the fact that condylomas are located in the vagina and are difficult to detect. However, there are indirect signs of the presence of infection in the body, if they occur, you should immediately contact a specialist:
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- copious discharge;
- increase in the number of ARVI and other diseases.
During sexual intercourse, condylomas are injured. This causes pain and discomfort. There may even be blood if the affected condyloma is large in size.
The injured neoplasm is attacked by various microbes, as a result of which it becomes inflamed and hurts all the time. As a result of inflammation, the discharge becomes more abundant - this is how the body gets rid of unwanted growth in the vagina.
After a certain time, a decrease in local immunity is observed. A woman begins to suffer more often from diseases caused by the presence of opportunistic bacteria.
Among all microorganisms known to science that cause the formation of papillomas and condylomas, HPV type 66 has the least number of obvious signs of the disease. Visible condylomas on the labia minora are extremely rare. In men, the virus may not manifest itself at all: in rare cases, condylomas form on the head of the penis (then there is a chance to receive timely treatment).
Principles of treatment
Today, it is impossible to completely defeat the papillomavirus, since science does not know effective drugs that can destroy its DNA. During treatment, therapy methods are used aimed at eliminating the unwanted symptoms of the virus and the consequences of its presence in the body. It is imperative to increase immunity to avoid relapses.
The most commonly prescribed drugs are:
- "Isoprinosine."
- "Solcoderm".
- "Podophyllin."
REFERENCE: If the sick person is pregnant, then, as a rule, treatment is postponed, since there is a high risk of harming the child. After childbirth, complex therapy is necessarily prescribed, since changes occurring at this moment in a woman’s body can provoke activation of the virus.
In the case when, in addition to HPV type 66, a diagnosis of cervical dysplasia is also made, antiviral drugs, laser therapy, and electrocoagulation are prescribed.
But such procedures are quite effective only at the early stage of the disease. If dysplasia is in an advanced form, then extreme measures are taken - conization of the cervix or surgical removal of the reproductive organs is prescribed.
If dysplasia is severe, its treatment is not quick and is carried out in most cases in a hospital, with a long recovery. After providing the necessary assistance, a woman should undergo regular examinations with a gynecologist: for 1 year - every 3 months, for 2 years - every 6 months, then - once a year.
Prevention of human papillomavirus infection
To avoid becoming infected with HPV, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle and avoid casual sex. It must be remembered that the use of condoms does not provide 100% guarantee of protection against human papillomavirus infection: it is transmitted through secretions, including kissing.
It is important to have personal hygiene items (cosmetics, washcloth, towel, toothbrush). It is unacceptable to use other people’s things, even in the most extreme situations, because for HPV to enter the body, one close contact with an infected person is enough.
Since it is quite possible to become infected with papillomavirus in a public place (gym, sauna, swimming pool), before visiting such establishments you should inquire in advance about the disinfection methods used.
Important!
Today, a special vaccine has been developed, the use of which can protect future women from the most dangerous types of HPV.
Conclusion
HPV type 66 is very dangerous for women: the virus can lead to cervical cancer. The infection does not die in the external environment and is easily transmitted from person to person. You can become infected even by using someone else's personal hygiene products. Therefore, it is important to follow preventive measures against this virus.
Source: https://vseopapillome.com/papillomy/chto-ehto-vpch-66-tipa-u-zhenshchin.html
HPV 66 treatment
First, some statistics: 7 out of 10 Russians are infected with human papillomaviruses to one degree or another. HPV causes significant harm and deprives us of a full, happy life. And the first signs of the presence of a virus in the body are WARTS and PAPILLOMAS , but first things first.
Hello, my dear!
I have been appearing on your TV screens for many years, and we have repeatedly touched upon the problem of various diseases of our body.
They often talked about serious and not so serious illnesses, as well as about various methods of healing.
Today we will talk about secretive, but very terrible pests with which we have been living for years, without even knowing where all our ailments and diseases come from - these are strains of the papilloma virus .
HPV causes enormous harm to the human body, and our immune system is the first to suffer, which, in turn, must protect the body from various diseases. As a result of a weakened immune system, the body misses the active reproduction of viral cells , and also becomes susceptible to the development of numerous diseases.
The fact is that in our latitudes alone there are more than 70 types of human papillomavirus, not to mention the strains that can be contracted while traveling to exotic countries.
Signals of the appearance of HPV in your body can be: frequent fatigue, drowsiness, lack of interest in life, depression, headaches, as well as various pains and spasms in the internal organs.
Frequent rashes of WARTS and PAPILLOS on the body, especially on the face and hands, also indicate the presence of a virus in the body.
If you feel frequently unwell, you simply need to carry out an antiviral cleansing of the body.
Cleansing the body must be done using effective and modern means. The best and most affordable cleansing product at the moment is the drug “ Papinol ”.
I recommend this remedy to everyone without exception, but especially to those who want to carry out antiviral cleansing of the entire body. Already in the first 3 days of use, you will feel noticeable improvements, a surge of strength, headaches will disappear, and your mood will improve.
At the end of 30 days, the virus will go into deep remission or be destroyed.
The drops have a general strengthening effect and at the same time effectively work to eliminate human papillomavirus, including subtypes 16 and 18, which are markers of cancer diseases.
- The method of application is simple: - take once a day orally - treat twice a day externally
- - after 30 days, HPV is destroyed
Remember, the longer the virus progresses in the human body, the more damage it causes. Get rid of it and you will notice how great life is!
Attention! Cases of selling counterfeit Papinol, which has no medicinal properties, have become more frequent! Therefore, especially for our viewers, we are placing an order button for Papinol from the only official supplier! By placing an order here, you are guaranteed to receive a quality product at the best price!
An additional discount is provided for viewers and readers of Elena Malysheva . To receive it, click on the “Place an order” button below. You will be taken to the official website where you can place an order. The number of discounted packages is limited!
Source: https://womens-life.ru/drugoe/vpch-66-lechenie.html
HPV type 66 in women: what is it and is it dangerous?
Many people are interested in how HPV type 66 appears in women and what it is. This is the name of a virus transmitted from person to person. It is characterized by a high risk of developing cancer.
The human papillomavirus is dangerous for women because it provokes cervical cancer, as well as various pathological conditions that are defined as precancerous: neoplasia, dysplasia, etc.
During the incubation period, it is not always possible to identify an infection in the body by external signs, since there are often no symptoms. If HPV infection is suspected, a diagnosis is carried out, after which a course of treatment is prescribed.
Oncogenic classification of strain 66
If you are interested in the question, human papillomavirus - what is it, you should know that this is the name of the infection that provokes the growth of excess tissue on the skin and mucous membranes: papillomas, condylomas, flat warts.
Growths develop only if suitable conditions for this are created in the human body. At the initial stage, papillomas caused by HPV type 66 are benign formations.
Gradually, the nature of such growths changes, and oncology develops.
Today there are about 100 genotypes of papillomavirus. A significant part of them pose a danger to humans, since these varieties provoke the development of cancer. Oncogenic classification of HPV:
- Genotypes with a low risk of developing malignant tumors. These include 6, 11, 13, 32, 34, 40, etc.
- Strains that differ in their average oncogenic character: 26, 30, 35, 52, 53, 58, etc.
- Genotypes with a high risk of developing cancer: 16, 18, 31, 33, 39, 45, 50, 56, 59, 61, 62, 64, 66, 68, 70, 73. This group also includes a variety of papillomavirus type 66.
- Harmless types of HPV, in most cases they do not lead to the development of a cancerous form of the disease. This includes all remaining genotypes.
To understand which strain has affected the human body (oncogenic or not), diagnostics are carried out.
Papillomas are localized in the perianal area, on the labia. Dangerous consequences arising from infection with HPV genotype 66:
- neoplasia, cervical dysplasia;
- cervical cancer;
- malignant formations in the vagina, on the external genitalia (labia majora and minora, clitoris).
In men, HPV 66 genotype provokes the development of pathological processes that can affect the penis and scrotum.
Routes of transmission of HPV 66
Methods of penetration of the human papillomavirus into the body:
- sexual;
- contact and household;
- vertical.
In the first case, HPV type 66 is transmitted during sexual intercourse. The likelihood of this is present not only during classical, but also during oral and anal sex.
The main condition for the penetration of harmful particles into the human body is the presence of microtraumas. If the integrity of the outer covering is not broken, infection will not occur.
Barrier contraception does not guarantee complete protection. Using a condom only significantly reduces the risk of infection.
The sexual route of infection is the most common. Virus genotype 66 can also enter the body through hygiene items, linen, towels, and razors, but this happens much less frequently.
It must be remembered that harmful particles are capable of maintaining viability outside the human body for a short period. For this reason, infection can also occur through household contact. In this case, there is a risk of infection not only when using other people’s hygiene items, but also when visiting a bathhouse, sauna, or swimming pool.
Much less often, the virus penetrates the body of another host vertically. In this case, HPV is transmitted from mother to child during labor. To find out whether a woman is infected, she undergoes an examination during pregnancy.
Reasons for virus activation
A jump in the development of infection is observed under certain conditions:
- hormonal changes in a woman’s body, for example, during pregnancy, lactation, and menopause;
- excessive physical activity;
- chronic fatigue;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- frequent illnesses;
- chronic diseases;
- STD;
- regular stress;
- lack of vitamins and nutrients;
- taking antibiotics;
- abortions.
With frequent changes of sexual partners or unprotected sexual intercourse, the infection enters the body, but begins to develop if at this stage the person’s immunity is reduced. For this reason, HPV may not manifest itself for a long period.
As soon as immunity is significantly reduced, the virus begins to actively multiply, which provokes the appearance of excess tissue in the genital area.
The above factors contribute to a decrease in immunity. By themselves, they are not the cause of the development of HPV genotype 66.
How does the disease manifest in women?
The main sign of infection is the formation of excess tissue. This occurs as a result of the division of cells containing viral DNA.
This process is not accompanied by visible symptoms until papillomas begin to appear on the mucous membranes of the vagina, cervix or skin.
At this stage, other unpleasant sensations may occur, but they are caused by injury to neoplasms, for example, upon contact with underwear, clothing, or during sexual intercourse.
If the growth is exposed to external factors, intercellular processes accelerate, as a result, excess tissue increases in size and spreads, covering healthy areas of the body. Damaged skin may develop an inflammatory process caused by the addition of other infections.
The signs are as follows:
- redness of the outer skin;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- burning when urinating;
- unpleasant odor from the vagina;
- the presence of uncharacteristic discharge.
In addition, with the gradual development of HPV type 66, the structure of the upper layers of the epithelium changes, so during an external examination by a gynecologist, papillomas, condylomas, and flattened formations may be noticed, which gradually increase in size.
The growths differ in shape. Genital warts most often appear on the genitals. As the virus develops, those excess tissues that are localized close to each other combine into a large growth.
In appearance, it often resembles cauliflower.
Symptoms of HPV in men
When infected with HPV strain 66, papillomas appear on the penis and scrotum. In men, they are more often localized on the body and head of the genital organ. Growths appear on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes. If a papilloma has formed at the opening of the urethra, urination may be difficult.
During sexual intercourse, pain is felt, because the growths are subjected to intense impact. Deformed areas of the skin become inflamed after some time, which is a consequence of the addition of a secondary infection, often of a bacterial nature. In this case, a burning sensation occurs, and redness of the outer integument is noted.
Diagnostic methods
When the body is infected, the values of the main indicators change in the blood test. An external examination of the genital organs is carried out. In this case, the doctor examines the cervix and cervical canal using a colposcope. Effective methods for diagnosing HPV:
- urogenital smear,
- Digene-test – allows you to determine the quantitative component of a viral infection;
- PCR is a polymerase chain reaction method, with its help it will be possible to find out the HPV genotype;
- biopsy followed by histology.
During an external examination, it is not enough to simply find neoplasms on the patient’s body, although their increased number indicates high activity of the virus.
To prescribe treatment, diagnostics are carried out using different methods, and PCR should be performed again, which will increase the chances of obtaining a more accurate research result, since sometimes a combination of strains is found.
Treatment of papillomavirus type 66
When infected with HPV, different means are used to fight the virus:
- Antiviral drugs. Their main task is to stop the development and spread of infection throughout the body. Such medications cannot destroy HPV. However, due to the action of blocking the activity of the virus, drugs in this group help stop the development of excess tissue. The growths stop increasing in size, and other papillomas do not appear on the body.
- Immunostimulants/immunomodulators. With the help of such means, human immunity is increased. In this case, the body’s natural defenses are activated and it begins to have a depressing effect on harmful particles.
Additionally, the growth is removed. The procedure is carried out in different ways, including:
- cryotherapy;
- laser destruction;
- radio wave therapy;
- electrocoagulation;
- excision with a scalpel.
The last option is rarely used due to the pain of the procedure.
The most common methods are laser therapy, radio wave method and electrocoagulation.
If cryodestruction is used, there is a high probability that the growth will appear again after some time. The reason for this is that it is quite difficult to regulate the intensity of pressure on the applicator.
Precautions after treatment
In order to avoid the appearance of a cancerous form of the disease in the future, it is necessary to maintain immunity at a sufficient level. This can be achieved by following the recommendations:
- normalize sleep;
- introduce foods rich in nutrients and vitamins into the diet;
- reduce the intensity of physical activity;
- carry out STD prevention;
- reduce the amount of alcohol consumed;
- Periodically check your hormonal levels.
These measures will help maintain the treatment results. You should know that it is not easy to destroy the virus. However, drug therapy can block its activity.
How to prevent disease
Considering that HPV does not manifest itself at the incubation stage, it will be difficult to detect the virus without additional examination. To avoid infection and the development of the disease, you should follow simple rules:
- casual sex should be avoided;
- It is recommended to use barrier contraception during sex;
- Frequent changes of sexual partners are undesirable.
Intimate hygiene and maintaining a high level of immunity - these factors also help prevent the development of the disease.
Source: https://SkinPerfect.ru/vpch/66-tipa-u-zhenshhin-chto-eto