From this article you will learn:
- how to get rid of caries,
- video of teeth preparation using a drill,
- how to treat caries - standards in dentistry.
Caries is a process of destruction of hard tooth tissues, which occurs with the participation of cariogenic bacteria in the oral cavity (as part of dental plaque), as well as food residues processed by them.
Organic acids produced by bacteria gradually destroy first the tooth enamel and then the underlying dentin.
As a result, a carious cavity is formed in the tooth, the walls of which are filled with the soft decay of rotting dental tissues and a large number of cariogenic bacteria.
Treatment of dental caries is a process that involves removing areas of the tooth affected by caries using a drill, after which the shape of the tooth is restored using filling material.
The latter can be light-curing composites, compomers or glass ionomer filling materials.
Caries therapy largely depends on the depth of damage to the hard tissues of the tooth, as well as on the localization of caries.
How to treat caries will depend on the depth of the lesion (Fig. 1-3).
- Caries in the white spot stage (Fig. 1) is the most initial stage of caries, which is reversible, and the only one that does not require traditional filling. In this case, one or more white spots can be seen on the surface of the tooth crown, which indicate the presence of areas of demineralization of the tooth enamel. There is no actual defect yet, but the white spot has a rough surface and lacks the shine characteristic of healthy enamel. This form of caries is treated by remineralization.
- Superficial form of caries (Fig. 1) - if demineralization of the enamel in the white spot area continues, then the enamel structure is destroyed and a carious defect is formed (so far within the enamel layer). In Fig. 1 you can see that in the center of some white chalky spots there are already small carious defects. This form of caries can be treated with traditional filling.
- Medium caries (Fig. 2) - in this case, caries spreads deeper than the enamel layer, affecting the upper layers of dentin. Enamel has a very high density, and therefore, as soon as the carious process spreads to the softer underlying dentin, the size of the carious cavity begins to increase rapidly. In this article we will talk about the treatment of medium-sized caries, as the most common form with which patients come to the dentist.
- Deep form of caries (Fig. 3) - in this case, caries spreads to the deep layers of dentin, and the dental pulp (neurovascular bundle) is separated from the bottom of the carious cavity only by a narrow strip of healthy dentin. This form is distinguished by a special treatment technique. You can read about how to treat caries with deep carious lesions in the tooth in our review: Treatment of deep caries.
How to treat caries: stages
To get rid of caries, you need to make an effort, because although modern drills do not vibrate like hammer drills, they still make us wait for the sudden appearance of acute pain - while drilling out carious tissues. Fortunately, modern anesthetics allow the dentist to properly numb the teeth during treatment - unlike the ineffective novocaine and lidocaine that were widely used previously.
Proper treatment of dental caries in dentistry consists of a number of successive stages, each of which has a clear goal. But nevertheless, the most important thing is the complete removal of caries, because...
if the removal of tissue affected by caries is incomplete, it will immediately develop under the filling and will certainly lead to the development of pulpitis and the need to remove the nerve from the tooth.
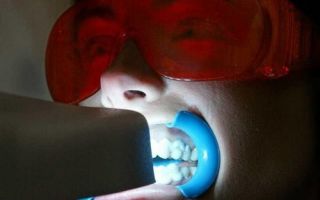
Watch the video below to see how hard tooth tissues affected by caries are removed.
Treatment of dental caries: video 1-2
In detail about the stages of treatment of average caries -
But before we move on to drilling out the carious tissue, which you could see in the video above, you still need to perform a number of procedures to prepare the tooth for treatment, as well as anesthetize it with an injection of a local anesthetic. For those who like stronger anesthesia, there are methods of sedation and general anesthesia.
-
Cleaning the tooth from plaque (Fig. 4) - before starting treatment, it is necessary to hygienically clean the tooth, as well as neighboring teeth, from plaque and tartar. For this purpose, ultrasonic attachments are used to remove massive dental plaque, as well as special brushes and abrasive pastes to remove soft microbial and pigmented plaque.
- Determining the color of the tooth using a special scale (Fig. 5) - hygienic treatment of the tooth also helps the doctor to accurately select the color of the filling material. In this case, the filling will match the color of the tooth, and will not stand out against the background of the tooth’s own tissues. This is especially important for teeth that are visible when you smile.
- Anesthesia (Fig. 6) – is it painful to treat caries: for painless drilling of carious tissues if the tooth is alive, local anesthesia is necessary. Modern painkillers in dentistry, for example, ultracaine or ubistezin, make the intervention absolutely painless. Depending on the amount of anesthetic administered and the method of anesthesia, the anesthesia time can last from 40 minutes to several hours.
The only pain that the patient can feel is the moment the needle is inserted into the gum, as well as the process of removing the anesthetic into the tissue. This process can sometimes be painful, which largely depends on the patient’s level of pain sensitivity, as well as on the speed at which the anesthetic is injected into the soft gum tissue. The faster the solution is administered, the more painful the injection.
- Drilling out carious tissues – As can be seen in Fig. 7, enamel is always destroyed with average caries to a lesser extent than the underlying tissue (dentin). This is due to the fact that enamel is much, much stronger and harder than dentin. Therefore, the carious cavity usually expands in depth, and the entrance hole in the enamel can even be quite small.
The dentist must drill out the edges of the enamel overhanging the carious cavity, and also remove all carious dentin. If you leave even a small amount of dentin affected by caries and put a filling on top of it, then very soon you can expect complications - the rapid development of caries under the filling and destruction of the tooth crown, with the subsequent development of pulpitis and periodontitis (24stoma.ru).
In Fig. 8, the dotted line shows the approximate boundaries of tooth tissue removal. In this way, the cavity is given a relatively correct shape and the next stages of treatment can begin. It should be noted here that recently new methods of tooth preparation have appeared, which help to do without traditional drilling. Recently, it has become possible to remove caries with a laser.
- Isolation of tooth from saliva – this is a very important stage! After the carious tissue is drilled out, and before filling the tooth, the doctor must carefully isolate the tooth from saliva and even the patient’s wet breath. These factors will greatly affect how long the filling will last. Previously, cotton balls and gauze balls were used for insulation, which were used to cover the tooth on all sides. It should be noted that this is a very unreliable and ineffective protection.
For the last 10 years, “cofferdam” has been used for these purposes. The latter is a thin latex “scarf” in which holes are made for the teeth. This scarf is pulled over the teeth (Fig.
9-10), after which 1-2 special metal clasps are installed on the necks of the teeth, which hold the rubber dam against the gums. The edges of such a latex scarf are attached to a special frame (Fig.
11), and we see the result - a group of teeth is completely isolated from the oral cavity.
Installing a rubber dam is quite labor-intensive. Some doctors refuse to use it on principle to save their time. The doctor’s use of a rubber dam in the treatment of caries indicates that the doctor is very attentive to the quality of his work, because the quality of the filling will be affected not only by the accidental contact of saliva on the tooth being filled, but also simply by the moist breath of the patient himself.
- Medical treatment of a carious cavity - a cavity formed in the tooth during the removal of carious tissues - is treated with antiseptics.
- Restoring the contact point between teeth – If caries is treated on the contact (interdental) surface of the tooth, then it is also necessary to restore the side wall of the tooth. This is a rather labor-intensive and complex task than simply treating average caries, for example, on the chewing surface of a tooth. In this case, another stage is added - the installation of special devices to restore the side wall of the tooth. Such devices include wedges (a) and matrix (b) in Fig. 12.
Read more about the treatment of interdental caries in the article:
→ “Treatment of caries between teeth”
→ Cost of treatment of dental caries
Filling a carious defect: video 3-4
Please note that dentists use special metal strips (matrices) and wedges to restore the side walls of teeth. In addition, tooth filling in both cases is carried out using a rubber dam.
Treatment of caries: photo
Treatment of dental caries using a specific example. All main stages of caries treatment are shown in Fig. 15-23. Explanations for each photo appear when you click on it.
- Dental filling: photo
In this article, we tried to answer questions from people interested in caries treatment, such as: how to treat caries, how to remove caries, how to cure caries. We hope that you found this article at least somewhat useful. Read about the average cost of treatment for different types of caries in the article: “Cost of treatment.”
Sources:
1. Higher prof. the author’s education in therapeutic dentistry, 2. Based on personal experience as a dentist, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. “Therapeutic dentistry: Textbook” (Borovsky E.),
5. “Practical therapeutic dentistry” (Nikolaev A.).
dentist Kirill Valerievich Kamenskikh, 19 years of experience. 24stoma® – Dentistry Online LLCLast edition: 11/01/2019
Source: https://24stoma.ru/lechenie-kariesa.html
Superficial caries
Caries is a slow pathological process in dental tissues. With initial (superficial) caries, only the top layer, the enamel, is destroyed. This defect appears at the site of a pigmented or white spot.
If the carious lesion has reached the dentinal layer (bone tissue of the tooth), the next stage develops - medium caries.
Causes
Tooth enamel has a mineral structure; it is the hardest tissue in the body that can withstand increased mechanical loads. However, it is quickly destroyed by acids.
The main cause of initial caries is harmful bacteria (Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus viridans) that live in the oral cavity.
During their life, these microorganisms release toxins and organic acids that damage the enamel layer. Calcium and other valuable minerals are washed out, and a carious lesion is formed.
Factors contributing to the development of caries:
- unbalanced diet, eating foods rich in carbohydrates;
- violation of the rules of oral hygiene - contributes to the accumulation of bacterial plaque on the teeth;
- disturbance of mineral metabolism in the body due to chronic ailments;
- deficiency of calcium, fluorine and other microelements.
Stages
Stages of development of the initial form of caries:
- white spot stage - chalky spots on the enamel - these are areas of demineralization (where a loss of minerals has occurred). They have reduced resistance to negative external influences;
- destruction of the enamel layer is an irreversible process in which the integrity of dental tissues is already compromised. Over time (literally after a few months), the carious process begins to affect deeper and deeper layers of the tooth.
What is superficial caries
Superficial caries can be localized:
- on the front of the teeth,
- in the area of the contact surface,
- as well as near the gingival margin (cervical area).
However, most often the defect is found on the fissures of the lateral teeth. In this case, fissure caries is diagnosed.
Fissures are natural depressions (grooves, pits) on the chewing surface of molars. This anatomical feature contributes to the rapid accumulation of plaque - food particles get into the deep fissures and are difficult to clean with a toothbrush.
As a result, the carious process begins in the central part of the tooth. The defect does not affect the cutting edges or the root zone, so it is quite difficult to diagnose this form, especially at the initial stage.
Fissure caries
Complaints and symptoms
Painful sensations
The main symptom of initial caries is pain. Painful sensations occur only when exposed to chemical irritants (sweet, salty, sour foods) and are short-term in nature. When eating cold or hot, pain usually does not occur.
Enamel defects
On the surface of the tooth you can notice small cavities with uneven edges. Roughness and indentations appear on the enamel. Areas of demineralization become darker.
Discomfort while brushing your teeth
If the carious lesion is located in the cervical zone, then a reaction to mechanical stimuli occurs. And all because the enamel in this area is very thin. Therefore, you may experience increased sensitivity and discomfort while brushing your teeth.
Features of superficial caries of primary teeth
Caries in primary teeth is often detected at the age of 2-3 years. In this case, the disease progresses faster than in adult patients. The reason for this is incomplete mineralization and thin walls of baby teeth.
Typical symptoms of initial caries in children:
- reaction to sweet and sour foods,
- noticeable destruction (destruction) of enamel.
It is recommended to undergo preventive examinations with a pediatric dentist once every six months in order to detect and eliminate carious lesions in time. Baby teeth must be treated!
At a very early stage, the gentle Icon method can be used, which does not require drilling. The procedure consists of the following steps:
- Removing (grinding) the affected enamel with a hand tool.
- Drying the tooth with a stream of warm air.
- Surface treatment with alcohol.
- Application of infiltrate (liquid filling).
- Transillumination of the tooth with a polymerization lamp.
Suitable for both adult patients and children.
Sealing
This method is used in most cases. Includes the following steps:
- Removal of dental plaque – removal of plaque and tartar.
- Preparation (drilling) of a carious cavity is carried out using a drill.
- Isolation of the dental crown - for this purpose an elastic dam is used.
- Antiseptic treatment - rinsing the dental cavity with a chlorhexidine solution.
- Etching the enamel is the treatment of the walls and bottom of the dental cavity with acid, this is necessary for better adhesion of the filling material and dental tissues.
- Application of an adhesive is a special glue that improves the shrinkage of the filling.
- Filling the defect with a filling mass - layer-by-layer application of a photopolymer composite and illumination of each layer with a polymerization lamp.
- Grinding and polishing – the filling is polished to achieve perfect smoothness and shine.
Filling a carious cavity
Prevention
To prevent the development of caries, it is enough to follow simple rules of prevention:
- Maintain good oral hygiene, brush your teeth at least 2 times a day;
- less sweets, carbonated drinks and other unhealthy foods;
- Once every six months, undergo ultrasonic teeth cleaning in the dentist’s office, this is an excellent remedy against bacterial plaque and tartar.
It is also useful to do remineralization, that is, saturation of the enamel with minerals. For this, deep fluoridation (professional method) or homemade fluoride preparations (Rocs, Tooth Mousse, Elmex, etc.) are used.
The initial stage of caries develops into a deep carious “hollow” and subsequently becomes the cause of pulpitis (inflammation of the dental nerve). Therefore, the sooner you contact your dentist, the easier it will be to fix the problem.
If you are looking for a clinic where you can inexpensively cure initial caries or undergo preventative care, we recommend that you look at the list of dentists on our website. All establishments from economy to premium class are collected here.
- Drilling with a drill, ozone therapy, infiltration, abrasive treatment - there is an optimal treatment for each type of caries. Average price in Moscow 2970 ₽
- Solutions and varnishes with fluoride will create a reliable protective film on the enamel of your teeth. Fluoridation is often recommended for children. With deep fluoridation, the result lasts 1-2 years. Average price in Moscow 397 ₽
- Icon method - dental treatment without drilling The use of Icon infiltrate is suitable for the treatment of superficial caries, eliminating the need to treat the affected area with a drill. The procedure takes from 15 minutes to half an hour. Average price in Moscow 2970 ₽
- Fissure sealing is the sealing of the grooves on the chewing part of the tooth with a special filling material to protect against food debris getting into them and the development of caries. Indicated in the presence of underdeveloped enamel or deep fissures. Average price in Moscow 1505 ₽
Source: https://MyDentist.ru/diseases/poverhnostnyi-karies/
Initial caries
Initial caries is the process of demineralization of the surface layer of dental tissues, which is characterized by a change in the color of the enamel in the absence of a carious cavity. The main symptom is the appearance of a practically painless white or brown spot on the enamel, representing an aesthetic defect. Diagnosis is carried out by clinical examination, collection of anamnesis and complaints, probing, vital staining and electroodontometry. Treatment is carried out using remineralizing therapy, deep fluoridation, filling, fissure sealing, and physiotherapy.
Initial caries is called the spot stage, which characterizes the main symptom of the pathological process. The spot is the first phase of a carious lesion, followed by superficial caries.
Pathology is a progressive process of demineralization, softening and destruction of tooth enamel of infectious origin. The disease affects people of different ages, genders and ethnicities.
Caries in the spot stage most often affects children's primary teeth, is localized mainly on the cervical surfaces of the teeth, but can occur in fissures, blind pits and on proximal surfaces.
Initial caries
Many etiological factors play a role in the occurrence of the disease. The main cause of caries is considered to be the presence of cariogenic microorganisms that ferment carbohydrates and produce acids that destroy the surface layer of enamel. There are general and local factors that contribute to the pathological process:
- Low level of oral hygiene . With insufficient hygienic care, soft and hard plaque accumulates on the teeth, plaque and tartar form. Dental plaque contains pathogenic microorganisms, carbohydrates, food debris, epithelial cells, and leukocytes. The unfavorable situation is aggravated by disturbances in the pH and composition of saliva, and malocclusion.
- Poor nutrition . Consumption of large amounts of carbohydrates, namely their prolonged presence in the oral cavity, is accompanied by intense carious lesions. An important cause of the disease is considered to be a deficiency of protein and vitamins in the diet. Multiple caries occurs with a lack of fluoride in drinking water.
- External influences . It has been proven that ionizing radiation has an extremely negative effect on dental tissue. 6-8 months after radiation therapy, multiple white lesions appear in the cervical areas. Radiation causes a decrease in saliva secretion and creates favorable conditions for caries formation.
- Heredity. The presence of an unfavorable genetic background in a person makes him vulnerable to the disease. This is due to the structural features of enamel and dentin, as well as the chemical composition of hard dental tissues. In such individuals, in the presence of local factors, caries develops more often and more intensely.
- General diseases of the body . Some pathologies (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, rheumatism, AIDS, gastrointestinal diseases, rickets) reduce the protective properties of saliva, which contributes to the carious process. There is an opinion that when the human immune system is exposed to severe stress, dental damage is observed.
The trigger for the development of the initial stage of the disease is the presence of a cariogenic situation in the mouth. Dental plaque creates suitable conditions for the proliferation of microorganisms that synthesize carbohydrates and form acids.
As a result, the acidic environment on the tooth surface increases tens of times, dissolution of hydroxyapatite crystals and demineralization occur. When examined using electron microscopy, the acute form of the pathological process on the section looks like a triangle, and the chronic form looks like a trapezoid. The wide base of the lesion is located on the surface of the enamel.
At the spot stage there is no destruction of the organic matrix. Initial caries consists of four zones that are directed towards the dentinoenamel junction.
The first zone is superficial, has a thickness of 20 microns, and is characterized by the dissolution of the pellicle. In this case, the tissue structure is preserved, but has increased permeability.
The subsurface zone is called the “body” of the lesion; demineralization is pronounced in it, the amount of mineral trace elements is reduced by 20%. The third zone is hypomineralization; changes in the structure of microprisms are observed in it, and microhardness is slightly reduced.
The zone of hypermineralization is characterized by transparency and is located on the dentin side. It is expressed during a chronic course of the process.
Clinicians distinguish fissure, approximal and cervical caries in the form of a spot. According to the intensity of damage, caries can be single (on 1 tooth), multiple (on several teeth) and systemic (affects most teeth). According to the sequence of occurrence, primary and secondary (recurrent) initial caries are distinguished. According to the clinical course, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Progressive. It is characterized by the formation of white and light yellow spots on the teeth, which cause soreness and discomfort. The initial carious process is acute and is often not diagnosed in time. The stain stage exists for a short period of time, after 2-3 weeks it turns into superficial caries.
- Intermittent. It is distinguished by the appearance of brown lesions on the enamel without disturbing its structure. The changes do not cause discomfort, so they may be mistaken for pigmentation. The disease is characterized by a chronic course - more than 2-3 months.
- Suspended. With this form, a dark brown or black formation is observed. The disease is preceded by a white spot, which, thanks to the immunity of the oral cavity, does not pass into the next stage of the carious process, but becomes pigmented. The pathology develops over a long period of time (3-4 months) and can exist for years.
Clinical symptoms are mild and are characterized by the formation of a round or oval-shaped spot on the tooth. The focus of demineralization is smooth and can have a different shade from white-yellow to dark brown. First, a light spot appears, painless or somewhat painful, depending on individual sensitivity.
When eating sour and sweet foods, there is a feeling of sore throat and discomfort. After a few months, focal demineralization turns into superficial caries or becomes saturated with oral pigments and turns brown. How the initial process will develop depends on the cariogenic situation, the presence of general and local factors of the disease.
The dark lesion is completely painless; patients complain of an aesthetic defect.
In the absence of timely treatment, the stain stage progresses to the superficial stage of caries. Further progression is characterized by the destruction of dental tissues and the formation of a cavity. Microorganisms spread into the deeper layers of the tooth.
When the focus of demineralization is located between the teeth, soft tissue injury occurs at the edges of the carious cavity, which manifests itself as localized gingivitis. The most unpleasant complications are pulpitis (inflammation of the nerve) and periodontitis (inflammation of the periodontal tissues surrounding the root).
As a result of these diseases, tooth loss occurs sooner or later.
Initial caries is diagnosed using basic and additional research methods. The dentist-therapist carries out differential diagnosis of pathology with hypoplasia, spotted form of fluorosis, and superficial caries. This takes into account the time of appearance of caries, localization, dynamics of development, and staining results. The following methods are used to identify the disease:
- Inspection and probing . During a clinical examination, the doctor assesses the location, size, and color of the lesion. After drying the tooth with a stream of air, a clearly defined spot with dull enamel of a matte white shade or a pigmented brown lesion is determined. Upon probing, dense, smooth and painless enamel is observed.
- EDI . To check the tooth for vitality, electroodontodiagnosis is performed - an assessment of the condition of the nerve elements in the pulp. The results of electroodontometry are in the range of 2-6 μA, which corresponds to a living tooth. EDI is carried out to differentiate from medium and deep caries, periodontitis, and pulpitis.
- Vital coloring . The method is informative for the differential diagnosis of caries from hypoplasia and fluorosis. When 2% methylene blue is applied to the lesion, a blue tint appears in the tissues of the carious area; in other pathologies, the tissues remain unchanged. The stronger the stain, the more intense the demineralization process.
- Luminescent method. It is used to identify pathology on the approximal (contact) surfaces of teeth. If there is a stain, a shadow appears in the area of tissue destruction during candling. The size of the shadow can be used to judge the extent of the carious process. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, healthy tissues luminesce, but in the area of the carious lesion, the luminescence is extinguished.
Therapy for caries in the spot stage includes a set of measures. Patients undergo professional cleaning and sanitation of the oral cavity. Treatment depends on the form of the disease (acute or chronic) and on the location of caries (on a smooth surface or in fissures). In modern dentistry, the initial carious process is eliminated using the following methods:
- Remineralizing therapy. The main method of treating acute forms of the disease, which is based on the restoration of foci of demineralization. This is done through a course of application of medicinal substances to the tooth - 3% Remodent, 10% calcium gluconate solution, 2% sodium fluoride solution, various fluoride varnishes.
- Deep fluoridation . The method is used if remineralization does not bring the desired results. Treatment involves applying a solution of magnesium fluoride silicate and copper-calcium hydroxide to the lesions. In this case, crystals of fluoride silicate are formed, which over a long period (more than a year) release fluoride and strengthen the tooth.
- Invasive sealing . If the initial caries is localized in the fissure area, then sealing is indicated, regardless of the form of the pathology. Treatment involves widening the natural grooves of the tooth with a small bur and filling them with a special sealant. For wide and open fissures, the expansion stage is not carried out.
- Filling. The brown spot cannot be eliminated using therapeutic methods, since pigments and dyes have penetrated into the demineralized area of the enamel. If the lesion is small, grinding is carried out; if it is large, the defect is prepared and filled. The enamel is removed with a diamond bur, treated with an antiseptic and sealed.
- Treatment without drilling - Icon . A modern method of treating the first stage of caries. It is based on the infiltration of affected tissues with a special material that is fluid and penetrates the porous enamel. At the same time, cariogenic microbes are neutralized, and the process of tissue destruction stops.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures . Electrophoresis of medicinal substances is carried out for the treatment of chalky spots. Using direct current, microelements are introduced into the subsurface layer of enamel, thereby restoring its structure. The procedure uses calcium gluconate and sodium fluoride.
With timely treatment, the prognosis of the pathology is favorable. To prevent the disease from progressing, the initial stage of caries must be treated. The chronic form can exist for a long time within the enamel and not cause complications. The acute form spreads to the underlying tissues, causes tooth destruction and threatens complications.
Specific prevention consists of careful dental hygiene, the use of fluoride-containing toothpastes, preventive sealing of fissures, visiting the dentist 2 times a year, and professional hygiene.
General preventive measures include maintaining proper balanced nutrition, treating body diseases, and increasing immunity.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_stomatology/spot-caries
Initial caries - causes, symptoms (photos), treatment
Initial caries is a pathological process that develops as a result of demineralization and softening of hard dental tissues. This is the first stage of this type of damage. Also in medicine it is called the spot stage.
The pathological process almost always progresses unnoticed by a person. It can be detected when visiting the dentist for a routine examination.
With the development of initial caries, the tooth loses its natural shine, which indicates demineralization of the enamel.
Online consultation on the disease “Initial caries”.
Ask a question to the experts for free: Dentist.
Most often, this carious process first affects the neck of the tooth, but gradually it begins to destroy other tooth structures, moving into other stages. The initial stage is the simplest and the lesion is easiest to eliminate. But due to the fact that at this stage few people go to the doctor, caries often develops into the following forms, where more radical treatment (preparation) is already required.
Initial caries can affect people from various age groups, including children and pensioners.
The development of a pathological process in children is most often due to the fact that they consume a lot of sweets and do not take good care of their oral cavity.
In the elderly, the progression of caries is associated more with age-related changes in the body (insufficient amount of calcium and fluoride in the body, etc.).
Causes
The main reason for the formation of initial caries is the occurrence of an acid-base imbalance in the mouth, which occurs with the direct participation of pathogenic microorganisms.
Certain types of bacteria constantly “live” in the mouth and take an active part in the process of decomposition of food that remains on the teeth and between them.
As a result of their vital activity, organic acids are formed that have a detrimental effect on the mineral compounds that make up the enamel. As a result, its destruction occurs.
Factors that contribute to the progression of initial caries:
- poor oral hygiene. As a result of incomplete cleansing of the surface of the teeth, tongue and gums, food residues may remain on them for a long time. Gradually they form a so-called soft coating in which bacteria are concentrated. Microorganisms for their vital functions use carbohydrates that are part of such deposits. As a result, they release acids that destroy enamel. It is poor oral hygiene that is the main cause of caries development in children. In addition, children are very fond of sweets, which contain a lot of carbohydrates;
- genetic predisposition. The quality of enamel in children is determined during their prenatal development. If at this time the mother’s body did not receive a sufficient amount of vitamins, calcium and fluoride, then there is a high probability that her children’s teeth will be more susceptible to the development of caries;
- food preferences. Enamel “loves” fluorine, phosphorus and calcium. But at the same time, carbohydrates have a detrimental effect on it. The initial stage of caries can begin to progress in those who consume insufficient amounts of cottage cheese and protein foods, but at the same time eat a lot of sugar-containing foods (this especially applies to children);
- lack of professional care. Typically, caries in the stain stage is located in the neck of the tooth. This place is very difficult to clean. Therefore, experts recommend that adults and children visit the dentist once every six months for a preventive examination, as well as professional oral hygiene;
- saliva viscosity and changes in its composition. This physiological fluid is necessary for people not only to moisten the food they eat. It is also needed for self-cleaning of the surface of the teeth. If its natural composition is changed under the influence of unfavorable factors, it will become an acid-forming factor that contributes to the destruction of enamel.
Stages
Clinicians divide initial caries into two stages:
- white spot stage;
- dark spot stage.
Initial caries
White spot stage
Caries in the white spot stage is also called white caries. This pathological process is characterized by the formation of matte white spots (chalk-like) on the surface of the enamel.
At the same time, the shine of the enamel is preserved. In places where spots form, massive deposits of soft plaque are noted.
If at this stage you do not notice the appearance of caries and do not begin to treat it, then it will move to the next stage of its development.
But in most cases, patients do not even assume that their pathological process is progressing. Therefore, it is important to constantly visit a specialist for prof. inspection. White caries is a reversible process that does not require serious dental intervention.
Dark spot stage
This stage is a more serious pathological process. It develops if white caries is not cured in a timely manner. Demineralized tooth tissues grow, and the white spots change their color to brown or even black. This is due to the fact that pathological microorganisms penetrate the porous structure of the enamel.
Symptoms
Caries in the spot stage usually occurs without obvious symptoms. That is why it is quite difficult to identify it.
Possible signs of the development of initial caries:
- sometimes there is a feeling of teeth set on edge;
- the tooth does not respond to the influence of irritants - sweet, sour or cold;
- The enamel in certain places changes its shade and also loses its shine.
Diagnostics
Caries in the spot stage can be detected using several diagnostic methods. The most common method is to stain the surface of the teeth. For this purpose, a solution of methylene blue or a caries detector is used, which contains fuchsin (it colors the affected area pink).
Drying the tooth surface is also an important diagnostic method. First, the tooth is treated with hydrogen peroxide (3%), rinsed with water and dried using cotton or gauze swabs.
After this, the surface is repeatedly blotted with napkins and dried with warm air.
These manipulations allow you to completely dry the surface, since white carious spots become most noticeable on dry enamel.
To diagnose caries at this stage of development, the UV-stomatoscopy method is actively used. This manipulation is performed in a dark room with a fluorescent stomatoscope. Before the procedure, the tooth surface is first cleaned of soft plaque. This diagnostic method allows the doctor to clearly determine the localization of the pathological process, as well as its boundaries.
These methods are used to diagnose early caries in adults and children.
UV-stomatoscopy
Treatment
Treatment of initial caries is carried out using several methods. It is worth noting that this process, in essence, is simply the loss of mineral components by the upper layers of enamel. Therefore, the dentist’s task is to compensate for losses.
The most effective treatment methods are:
- remineralization;
- deep fluoridation;
- ozone therapy;
- If a dark spot forms, it is removed by preparation, followed by the application of a filling.
Prevention
- complete and regular oral hygiene with high-quality toothpastes;
- normalization of diet. It is recommended to exclude snacks;
- It is best to brush your teeth after every meal so that no pieces of food remain in your teeth;
- Visit your dentist regularly for examinations and professional oral hygiene;
- It is better to exclude drinks from the diet that can negatively affect the condition of tooth enamel. This includes coffee, carbonated sweet water, etc.
Source: https://SimptoMer.ru/bolezni/zuby-i-rot/1129-nachalnyj-karies-simptomy
Initial and superficial caries: symptoms and treatment methods
In dental practice, it is customary to distinguish 4 forms of dental caries:
- initial caries, caries in the spot stage;
- superficial caries;
- average caries;
- deep caries;
Initial and superficial caries are early forms of caries.
Initial dental caries or caries in the stain stage is the first stage of the carious process on teeth. It is characterized by the presence of white and dark spots on the enamel, under which the structure of hard tissues is disrupted. This form can stop with proper care of the affected tooth.
Superficial dental caries is an intermediate form between initial and intermediate caries. With superficial caries, the integrity of the enamel is violated, that is, the formation of a small cavity within the upper layers of the tooth.
Causes of initial caries and superficial dental caries
- Acid-forming bacteria . A key role in the appearance of initial forms of caries is played by pathogenic microorganisms (microbes) that form acids. Organic acids cause a violation of the permeability of the enamel, useful minerals are washed out of the tooth (primarily calcium, fluorine, phosphorus), because of this the tooth becomes more fragile.
- Poor oral hygiene . In order for bacteria to grow and multiply, carbohydrate residues must remain on the surface of the tooth after eating, which serve as a substrate for the attachment of microbes. It is necessary to brush your teeth 2 times a day for 2-3 minutes and use a floss or irrigator to remove food debris from the surface of the teeth.
- Hereditary factors . Genetics plays an important role in the occurrence of initial dental caries. Teeth are formed during the mother’s pregnancy, so the nature of nutrition and the general condition of the expectant mother’s body affect the health of the child’s teeth.
- Unbalanced diet . The predominance of sweets, flour, carbonated drinks, and fast food in the diet contributes to the development of early forms of caries.
If you visit the dentist on time, that is, at least once every six months, this will significantly reduce the risks of the occurrence and development of initial and superficial dental caries.
Symptoms of initial dental caries
Patients often do not present any complaints, because initial and superficial caries affect only the tooth enamel, and it is not very susceptible to various irritants.
What does initial caries look like?
At the initial stage of caries, stains form on the tooth: from dull white to dark brown colors. In such cases, the patient may complain about aesthetics.
What does superficial caries look like?
With superficial caries, an inconspicuous shallow cavity with rough edges appears on the tooth. The main complaint with superficial caries may be a feeling of soreness when ingested by sweet, sour, and salty foods.
Diagnosis of early forms of caries
The dentist performs various tests to determine the presence of pathology.
- Visual inspection . Any professional examination begins with a visual assessment of all tooth surfaces.
- Probing . The specialist runs an instrument with a sharp end - a probe - along the outer part of the tooth, identifying roughness, irregularities, and carious cavities. With initial caries, the tooth surface is smooth, but with superficial caries, small cavities (chips) of the enamel are identified.
- Drying the tooth . The dentist blows air on the tooth in order to remove moisture from the surface and see foci of demineralization: areas with reduced enamel density.
- Coloring with special dyes . In dental practice, to detect caries, you can use caries indicators - dyes that are used to stain the tooth surface. Absorption of the dye indicates that a carious process is developing there.
- X-ray diagnostics . On a targeted X-ray, a specialist can see early forms of caries.
Treatment of initial and superficial caries
How to treat initial caries?
Initial caries in the white spot stage is considered a reversible form of caries. Treatment consists of saturating the tooth with useful minerals. The process of saturating tooth enamel with necessary substances is called remineralization. Remineralization can be of 2 types:
- Endogenous - when minerals enter the tooth enamel along with water, nutrition, vitamin complexes, that is, “from within” the body.
- Exogenous - when macro- and microelements enter the tooth “from the outside”, that is, when applying special pastes, solutions, gels.
The main elements that strengthen tooth enamel are calcium, fluorine, and phosphorus.
To remineralize teeth, it is recommended to create a diet rich in dairy products, seafood, protein foods, vegetables, grains, legumes, and herbs.
An important point is to take vitamin and mineral complexes, but only after consulting a specialist . It is not recommended to prescribe vitamins for yourself.
In order for pastes, varnishes, and solutions containing important minerals to work, professional oral hygiene must be performed before the course . The dentist will remove all dental deposits (tartar, plaque) from the surface of the tooth, and the substances can be absorbed into the dental tissue.
During the consultation, the dentist will draw up an individual treatment plan and tell you what products should be used in your case.
How to treat superficial caries?
Despite the fact that the cavity with superficial caries is considered shallow, without the intervention of a specialist the process cannot be stopped, it will worsen and can lead to unpleasant complications. Treatment of superficial caries takes place in several stages during one visit:
- Anesthesia . Tooth anesthesia is necessary so that the patient does not feel discomfort during treatment.
- Isolation of the tooth from the oral cavity . This stage involves placing a special rubber scarf (cofferdam, rubber dam) on the tooth in order to isolate the tooth from saliva and the oral cavity from working solutions.
- Using a microscope . Optical magnification will allow you to avoid damaging healthy tissue during treatment and monitor the quality of all stages.
- Removal of carious tissues . To ensure that the infection does not spread deeper and does not provoke the development of more serious forms of caries, it is necessary to thoroughly clean the tooth of the affected tissues. For this, the dentist uses dental handpieces, including those with air-water cooling.
- Modeling of restoration (filling) . The missing tissues are replaced with composite light-curing materials that imitate the density, color, and shine of healthy teeth.
- Polishing the restoration . Using articulating paper (carbon paper), the doctor adjusts the height of the restoration, then uses polishing tools and pastes to finally smooth the entire surface of the filling.
At the Dana clinic, the cost of treating superficial caries using a microscope and imported materials is 2,500 rubles.
What happens if initial and superficial dental caries is not treated?
Most dental diseases are characterized by rapid progression. From initial caries, superficial caries develops, from superficial caries - medium, from medium - deep. After deep caries, the nerve of the tooth is involved in the process, pulpitis begins, and then periodontitis of the tooth, when the inflammation extends beyond the apex of the root, that is, a granuloma or tooth root cyst is formed.
Timely treatment in the early stages of the disease prevents the development of serious complications, so do not delay visiting the dentist if any symptoms characteristic of initial and superficial caries appear.
Prevention of initial and superficial dental caries
- Visit the dentist once every six months . Since often only a professional can detect incipient dental caries, preventive examinations should not be neglected.
- General strengthening of the body . A healthy body not only has a healthy mind, but also healthy teeth.
- Maintaining a rational diet . A balanced diet rich in macroelements, vitamins, and minerals helps strengthen tooth tissue and increase resistance to dental diseases.
- Good oral hygiene . Proper daily brushing of teeth is the first step to healthy teeth and gums. Using dental floss, mouthwash and irrigator helps to better clean plaque from teeth.
https://dana.spb.ru/blog/nachalnyij-i-poverxnostnyij-karies.html
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5c88fb8630651f00b337181a/5c88fdb7d92ee700b306f90b