Intradermal papillomatous nevus is a benign neoplasm that rises above the epidermis and has an uneven surface.
The elevation is observed on the skin of both adults and children, including newborns. The nevus reaches its final size by the age of 30.
What are the external characteristics of the tumor and the reasons for its appearance, as well as the likelihood of degeneration into a cancerous tumor?
Intradermal nevus is a congenital neoplasm of the skin.
What is a growth
Intradermal nevi rarely become malignant in the absence of negative factors. Most often, the formation is localized on the face, neck and head, less often - in the axillary folds, groin, and back. The rarest areas where the formation is located are the arms and legs.
The color of the nevus varies from light brown to black. The growth does not pose a particular threat to health and is only a cosmetic defect. Often people are embarrassed by the appearance of their skin and try to remove the papillomatous elevation on their own. Such measures lead to dangerous consequences.
Varieties
Experts distinguish the following types of intradermal nevus:
- Pigmentary.
The growth is noticeable to others because it forms in open areas, for example, in the neck area. Color varies from brown to black. There is no hair on the surface of the spot. Pigmented nevus appears on exposed skin areas - Hair. The neoplasm has several or many hairs. It is forbidden to get rid of it yourself, since injury to cells leads to their degeneration into oncological structures.
- Verrucous. The external characteristics are similar to the pigmented appearance. The only difference is lighter shades and a rougher surface.
Papillomatous nevus tends to grow slowly in size. In addition to the listed types, neoplasms are also divided into noncellular and disseminated. The first type of elevations is diagnosed more often. They practically do not protrude above the surface of the skin. To the touch, the changed tissues have a dense structure.
Papillomatous nevus tends to grow in size
Disseminated growth is characterized by an uneven structure due to the fact that it is formed by several nevi. Such an elevation can appear on any part of the body. They often have black shades and are large in size.
Causes
There is no consensus on why intradermal papillomatous nevus appears. The mechanism of formation of growths has not been precisely established.
The list of predisposing factors includes several circumstances:
- Heredity.
It is believed that genes are responsible for the location of moles on the body. The fact has also been revealed that in people the nevus is usually located in the same areas as in their closest relatives. The patient may have a hereditary predisposition to the appearance of nevus - Excess melanin in the skin. Pigmentation can be caused by aggressive exposure to sunlight or other negative external factors.
- Disturbances in the body during intrauterine development.
According to statistics, most of the neoplasms of this type appear in people during puberty or at 15-20 years of age.
Symptoms of melanocytic nevus
Intradermal growth differs from a regular mole in its external characteristics.
Normally, a nevus has a uniform shade
It is worth listing its main features:
- soft structure;
- uniform shade;
- minor external changes over time;
- similarity in characteristics to a flat wart, barely rising above the surface of the skin;
- absence of inflammation near the eminence.
There are one or many similar outgrowths on the body. They can be localized in one area or in different places of the human body. The size of the spots ranges from a few millimeters to 2 cm. Depigmented (colorless) elevations are less common.
Biomaterial is studied under a microscope
Over time, the spot changes color and size. In order to determine the type of tumor, it is studied in the laboratory under a microscope. Based on the results of the study, the doctor identifies the need to remove the nevus and the likelihood of its degeneration into a cancerous tumor.
Diagnostics
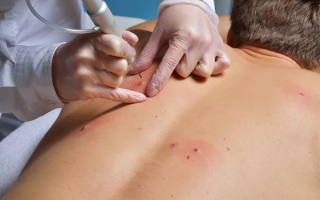
During a visit to a dermatologist, the specialist carefully examines the patient's body. Most often, the neoplasm is studied by fluorescent microscopy using a dermatoscope. The procedure is quick and painless for the patient. The device illuminates the surface of the mole and allows the doctor to better examine its structure.
During luminescence, no material is taken from the suspicious area of the skin. The inspection results are highly accurate. The only drawback of the technique is that few clinics are equipped with a dermatoscope.
Doctor examining patient using dermatoscope
The tumor can also be studied using computed tomography. The advantage of the study is that all inspection data is stored on electronic media. CT scanning is quite expensive, so it is used only in rare cases when diagnosing an intradermal birthmark. Typically, this method is required if there is a suspicion of the degeneration of benign cells into cancerous ones.
Treatment
It is necessary to remove intradermal growth only in special medical institutions that have a license to carry out such procedures. Before removing a birthmark, it is necessary to undergo a diagnostic complex to determine the type of neoplasm and select the optimal treatment option.
The most popular method of therapy is excision of the birthmark with a scalpel. The mole is removed along with the surrounding tissues and sent to the laboratory for histological examination.
This is necessary to identify the nature of the growth. The main disadvantages of this method of treatment are heavy bleeding and a long recovery period.
After the intervention, noticeable scars may remain on the body.
Nevus treatment is performed surgically
An alternative to surgical excision of the nevus is laser therapy. Using a beam, the doctor removes tumor cells layer by layer. After laser cauterization, the wound heals faster, and scars rarely remain on the body. The disadvantage of the technique is its high cost and the impossibility of removing degenerating birthmarks.
Another modern method of dealing with the problem is cryodestruction or burning out the mole at low temperatures. The duration of the procedure is about 1 minute. After it, a light crust appears on the surface of the growth, which peels off a few weeks after treatment. A healthy epidermis remains underneath.
Intradermal nevus can be removed using electrocoagulation. The doctor applies electrodes to the formation, through which high-intensity currents flow.
The cells of the birthmark are evaporated under the influence of electrical energy. During the procedure, as with laser therapy, cauterization of blood vessels occurs.
After electrocoagulation, patients do not require a long recovery period.
A tumor on the body can be removed using electrocoagulation.
One of the most progressive ways to remove birthmarks is to use a radio knife. The pathological elevation is affected by radio waves of a certain frequency. As a result, the growth cells overheat and are destroyed. All that remains of the nevus is a crust, which disappears 5 days after the intervention.
Danger of condition
The main danger of intradermal papillomatous nevus is possible malignancy. The list of factors predisposing to degeneration includes:
- hormonal disbalance;
- excessive sun exposure and frequent visits to solariums;
- genetic predisposition to skin cancer;
- endocrine disorders.
In patients with endocrine disorders, nevi may become malignant
In order to prevent the degeneration of a nevus into a malignant growth, it is necessary to constantly examine it and contact a specialist in the following cases:
- blurring of the boundaries of the neoplasm;
- change in color of the birthmark and the appearance of roughness on its surface;
- bleeding of the growth;
- development on the formation of erosive or ulcerative lesions.
If malignancy is suspected, the specialist will offer the patient a surgical solution to the problem.
Changing the color of a nevus is a dangerous signal
Prevention of nevus
There are no specific measures to prevent the appearance of a growth on the skin. However, persons susceptible to skin cancer should follow some precautions to prevent the degeneration of mole cells into a malignant tumor:
- Protect skin from ultraviolet radiation. In summer, it is advisable to stay indoors from 12 to 4 o'clock. Sunbathing is prohibited at this time.
- Avoid visiting solariums, especially if there are several nevi on the skin.
- Do not try to remove the growth yourself, even if you are completely sure that it is benign.
- Contact a specialist immediately if you accidentally or intentionally damage a mole.
To prevent the development of dangerous complications, it is necessary to avoid contact with ultraviolet radiation on the skin.
A visit to a specialist is also necessary if the growth changes its shape and size or the number of elevations on the body increases. The prognosis for treatment of a cancerous tumor in the initial stages of development is 90% favorable.
The process of removing papillomatous nevus on the scalp, see below:
Source: http://bolezni.com/stati-o-boleznyah/papilloma/vnutridermalnyj-papillomatoznyj-nevus.html
Modern methods of treating papillomatous nevus
Papillomatous nevus is a benign melanocytic neoplasm. Its characteristic feature is its external resemblance to papillomas. The risk of the neoplasm degenerating into a malignant tumor is low, although its condition still needs to be monitored.
What is papillomatous nevus
A papillomatous nevus looks like a bumpy mole protruding above the surface of the skin. This is a soft and elastic neoplasm, sometimes with scales and crusts. In terms of its structure, it belongs to complex or intradermal melanocytic nevi, i.e., it affects not only the superficial, but also the deeper layers of the skin.
Most often, the tumor is located on the scalp or in the neck area, but it can form in the groin area, under the breasts, and in the armpits. There are known cases of moles appearing on the upper and lower extremities, but they are rare.
Causes of occurrence. Characteristic signs
Papillomatous skin nevi can be congenital or acquired. In the first case, they are formed before birth, in the second, they appear throughout life, most often by the age of 20-30. Occasionally, the formation decreases as one gets older or disappears completely. What are nevi (moles) and what do they look like?
The reasons for the formation of neoplasms are not fully understood. From the point of view of official medicine, they are considered a defect of embryonic development, causing the accumulation of pigment cells. It has been established that the likelihood of mole formation is influenced by:
- fluctuations in the level of female sex hormones during pregnancy;
- infectious diseases of the urinary tract;
- maternal toxic poisoning;
- ultraviolet and radiation radiation.
There are other characteristic features:
- Color - flesh or brown. Moles of a black or brown hue are less common.
- Density. The structure of the formation contains dead skin cells, so it feels dense to the touch.
- Convexity and wide leg. Papillomatous moles are never flat; they rise above the surface due to their wide base.
- Clearly defined boundaries. The edges of this type of skin formation are easily distinguishable and are never blurred.
- Lumpy surface. Upon closer examination, it is clear that the mole consists of large segments. If you examine it with a microscope, the surface resembles cauliflower.
- Size. This type of mole is characterized by large size - more than 1 cm in diameter.
Papillomatous nevoid tumors can be either single or multiple. Both options occur with equal frequency. Some experts point out another characteristic sign - the slow growth of the tumor, but in this case the mole needs to be given increased attention.
Main varieties
Based on their appearance, there are three types of nevi:
- Pigmented. They form on open areas of the body, often on the face and neck. Hair does not grow on the surface of the mole. Color - dark brown, even black.
- Verrucous. Similar to pigment ones, but differ in a lighter shade. The formation is divided into several parts, which is why it has a bumpy, rough surface.
- Hairy. On the surface of the mole there are one or more dark-colored hairs. This type has an increased risk of malignancy, so it is strictly forbidden to treat it yourself.
Based on size, moles are divided into 4 groups:
- up to 1.5 cm - small;
- up to 10 cm - medium;
- up to 20 cm - large;
- more than 20 cm in diameter - gigantic.
Based on their location in the skin structure, they are distinguished:
- intradermal papillomatous nevus - localized in the dermis;
- epidermal - located within the epidermis;
- borderline - accumulations of pigment cells between the epidermis and dermis.
According to the form of education they are divided into two groups:
- organic;
- disseminated.
Organic papillomatous nevus is the most common form. It is a single neoplasm with a wide stalk. Color - all shades of brown, including brown and light gray shades. Outwardly it looks like a cluster of small papillary outgrowths covered with a dense keratinized layer.
The disseminated form manifests itself in the form of multiple plaques scattered over the surface of the body. It may be a manifestation of epilepsy and other diseases of the nervous system. The disseminated form is prone to changes in size. Sometimes it disappears on its own as the body ages.
Should I delete
Most papillomatous nevoid tumors are not dangerous. Degeneration into skin cancer is only possible with regular, long-term exposure to provoking factors.
Nevertheless, oncologists recommend monitoring the condition of the tumors - independently or with the help of a specialist.
A complete examination of the whole body should be carried out at least once a year, and if specific changes occur, unscheduled.
A mole is removed if it causes serious discomfort (this is one of the most common reasons for teenagers). The most common location of the tumor is the face, neck, and scalp, so the risk of infection is high. Everyday procedures - combing, washing your hair - become dangerous.
A mole or intradermal papillomatous nevus can also be removed if it creates aesthetic discomfort. A skin formation with a bumpy surface looks unsightly, which is why it can become a significant defect in appearance. Then you can get rid of it.
Another reason why a mole is removed is progressive growth, symptoms of degeneration into a malignant tumor. But the doctor must decide whether to remove the papillomatous nevus. TOP 5 methods for removing moles.
Modern methods of treatment
Papillomatous nevus is removed using the same methods as other types of moles:
- laser;
- radio wave knife;
- electrocoagulation;
- surgical excision.
Cryodestruction is not used in the treatment of papillomatous nevoid tumors. This type of mole is not very susceptible to the effects of liquid nitrogen.
The optimal technique is selected by a dermatologist-oncologist. To do this, he conducts a series of studies - dermatoscopy, biopsy of the affected tissue. Sometimes examining the mole is enough. The biopsy sample is taken using a scalpel or radio wave knife directly during the removal procedure. If other methods are used, the study is performed before the session.
Laser removal is good because it eliminates the risk of complications. This is a painless procedure that guarantees rapid wound healing. The same can be said about the radio wave method: it demonstrates a good rate of tissue regeneration and a low probability of complications.
Electrocoagulation allows for accurate histological analysis. It is used if there are symptoms of mole degeneration. One of the disadvantages of the method is that a scar forms after the procedure.
Surgical excision is used if the mole has reached large or gigantic sizes. The depth of removal is the entire thickness of the skin. With other methods, it is enough to remove the tumor to the upper layers of the dermis - the place where melanocytes accumulate. Wound care is standard for such procedures.
Papillomatous nevus in children
Papillomatous nevoid tumors in children are predominantly a cosmetic defect. They are removed using the same methods as in adults. The exception is cases requiring surgical excision. The operation is postponed until the child is 1.5-2 years old.
If the tumor is small in size, laser removal is recommended. This method is painless and has no age restrictions.
Papillomatous nevus during pregnancy
There are two situations worth highlighting here. The first is when a tumor appears in the expectant mother. The reasons are hormonal fluctuations caused by the restructuring of the female body in preparation for bearing a child, childbirth, and feeding. During this period, moles may appear or disappear. There is nothing abnormal in such changes.
If a new mole causes serious psychological or physical discomfort, you can consult a doctor about removing the papillomatous nevus. But it is better to postpone the procedure until the birth of the child.
During delivery, another dramatic change in hormone levels occurs, which may cause the mole to reappear. The exception is when the formation suddenly changes shape, color, or size: then it must be urgently shown to a doctor.
He will decide whether to remove the papillomatous nevus.
The second situation is when a neoplasm may appear in an unborn baby. To avoid it, a woman must follow a number of rules during pregnancy:
- If the expectant mother works in a workplace with toxic or potentially hazardous substances, she should definitely inform management about her situation. According to current legislation, while carrying a child, she should not have contact with such compounds, even if this is provided for by her position.
- If a woman likes to sunbathe, it is advisable to limit their time: avoid such procedures in the period from 11-00 to 16-00. And you can get a light and beautiful tan in the morning.
- If the expectant mother lives in an environmentally polluted area and near sources of radiation, it is better to move during pregnancy. Otherwise, there is a high risk of not only the formation of nevi, but also other anomalies of intrauterine development.
You can reduce the risk of tumors in your child by giving up bad habits - smoking and drinking alcohol. Doctors also recommend not to come into contact with aggressive household chemicals and to use rubber gloves when cleaning.
The main differences between papilloma and nevus
Papillomatous nevus can be confused with other skin neoplasms:
- seborrheic keratosis;
- epidermal warty nevi;
- melanoma;
- soft fibroma or cutaneous fibrous polyp;
- papilloma.
To differentiate, a thorough examination is required, preferably by a specialist.
Compared to seborrheic keratosis, or static warts, papillomatous nevus is softer to the touch.
It is easy to notice a skin pattern on its surface, which will be slightly deformed when displaced.
Seborrheic keratosis often manifests itself in the form of multiple formations, and papillomatous nevus - single ones. But it is difficult to distinguish them on your own, and even in medical practice, confusion often occurs.
Epidermal warty nevus has a fundamentally different structure. It occurs due to impaired development of the epidermis in the prenatal period, and does not contain melanocytes.
Papillomatous nevus, on the contrary, is a melanocytic tumor consisting of pigmented cells. The appearance of the formations also differs.
The verrucous nevus consists of many hard spines rather than papillae; it is denser to the touch and often takes on a linear shape. This type of tumor is always congenital.
To differentiate melanoma, histological examination is necessary. There are a number of signs by which one can suspect an oncological disease - uneven edges, uneven color, changes in shape - but an accurate diagnosis can only be made after analysis.
Fibrous skin polyp and soft fibroma are similar in appearance to papillomatous nevus. The differences lie in the base of the tumor. The stalk of a fibroma and skin polyp is always narrower than that of a nevus.
Papilloma has an asymmetrical shape and loose structure. Small vessels are visible in its structure, and the color ranges from flesh-colored to dark chocolate. Papilloma grows quickly, reaching 2-15 cm in diameter, often accompanied by itching or exudate.
Another important difference is the localization of education. If moles often appear on the face and neck, then papillomas appear in the folds of the skin or mucous membrane. They can be found under the arms, in the genital area, on the elbows and knees.
Source: https://beznarostov.ru/rodinki/papillomatoznuy-nevus
What is papillomatous nevus and is the formation dangerous?
Home-Papillomas
Papillomatous nevus is a brown mole with a bumpy surface. Outwardly, it vaguely resembles papilloma. The formation is localized mainly on the scalp. The formation of melanomorphic growth occurs in the prenatal period.
What is and ICD 10 code for papillomatous nevus
Papillomatous nevus does not have an ICD-10 code and is a benign skin formation.
It is characterized by an irregular shape and a bumpy surface.
The growths differ in color. Some have a brown or brown tint. There are flesh-colored elements. Pigmented hair may pass inside.
The growths are located singly or in groups. Characteristic features of specific moles include:
- Slowly growing.
- Favorite localizations are armpits, head, neck, groin area.
- Formed in the prenatal period, adolescence.
- They may not be noticeable at first. Gradually increasing. Large formations significantly complicate the patient’s life. The owner of the mark easily injures her. If the growth is located on the scalp, damage occurs with a comb or nails.
- A bumpy mole is inherited.
- The outgrowths rarely become malignant. The main cause of malignancy is damage.
Why is a nevus called intradermal papillomatous?
An intradermal papillomatous nevus is a cellular structure consisting of elongated islands of epidermis. The growth has a dense consistency due to the upper stratum corneum. It contains melanocytes. Pigment cells provide the dark color of the element. The lumpy surface is created by numerous papillae, which can be distinguished under a magnifying glass.
Often there is a black or brown rim around the wart. It does not rise above the skin level.
The name papillomatous is due to the similarity of the growth to papilloma. The two skin formations have nothing in common except their appearance.
According to the international classification, several types of moles are distinguished:
- The verrucous type looks like a regular wart. The formation can be light brown, pink, or flesh-colored. It has a bumpy surface, a lobular structure (2-3 moles that are closely adjacent to each other). The verrucous element rarely bleeds and is not prone to malignancy.
- Melanocytic nevus is a convex growth with intradermal or borderline growth. Localized in the neck and face. The growth poses a serious danger. It can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
- The hair type of a specific mole differs from other formations by the presence of long hair on its surface. Periodic hair pulling leads to traumatization of melanocytes. Damaged cells degenerate into a malignant tumor.
- The mixed or complex type refers to abnormalities in the development of the skin and has a complex structure. The germinal elements are located in two layers of the skin at once: intradermal and border. The growth consists of many papillae of different sizes. The formation grows up to 10 mm. Doctors try not to disturb mixed nevus.
Disseminated growths are brown plaques that are localized near nerve trunks and large vessels. The growths periodically fall off on their own, then grow back. The appearance of disseminated elements indicates a pathology of the nervous system. Patients should be observed by a neurologist.
Separately, it is worth noting the classification according to the risk of malignancy. There are melanoma-hazardous and melanoma-non-hazardous elements. In the first case, the risk of degeneration is high, in the second - minimal.
Is HPV the cause of nevus?
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Intradermal papillomatous nevi resemble papillomas in appearance. The appearance of the melanocytic element is not associated with papillomavirus. Two similar skin growths differ in etiology and structure.
Papillomatosis (code D 23 according to ICD-10) is a chronic infection caused by HPV activity. The pathology affects children and adults. The main route of transmission of the virus is through household contact, sexual contact, and intrapartum.
Melanocytic papillomatous intradermal warty nevus is formed by melanocytes. The reasons for its appearance on the human body are not fully understood. There are several theories of origin:
- According to the first theory, education is transmitted along the family line. Confirms the fact of similar localization in parents and children.
- The second theory is based on excess melanin secretion. Melanocytes accumulate under the skin in one place and begin to intensively secrete coloring pigments. Active production of melanin occurs under the influence of ultraviolet radiation.
- According to the third theory, the formation of an intradermal growth occurs in the prenatal period. The appearance of bumpy formations is provoked by the mother’s addictions, inflammatory diseases, and contact with harmful substances.
- The fourth theory associates the occurrence of growths with hormonal disorders. Melanocyte-stimulating hormone of the pituitary gland activates melanocytes, which begin to synthesize melanin.
Similar and different features of papillomatous nevus and papilloma
The similarities are evident in the following points:
- They have a lumpy surface, are large in size, and are colored brown.
- Refers to benign elements.
- They rarely become malignant.
- They do not show pronounced clinical symptoms.
- Easily injured.
The differences between this type of nevus and papilloma are the following:
- Different structure, causes.
- Papillomas regress under the influence of medications and folk remedies.
- Melanoform moles are most often localized on the scalp and neck. The favorite location of papillomas is the groin area, back, palms, and feet.
The main task of the patient is to seek medical help in a timely manner.
The main task of the doctor is to correctly carry out differential diagnosis.
Is it necessary to treat melanocytic papillomatous intradermal nevus?
Melanocytic skin growths do not require treatment if they are asymptomatic.
It is recommended to consult a dermatologist in the following situations:
- Education has rapidly increased in size.
- Pain, burning, itching appeared.
- The growth is located on a stalk and is often injured.
- Darkening may be associated with its malignant degeneration. A change in the color of a mole is a direct indication for consulting a doctor.
- There is severe peeling and visible erosion.
- Localization on the head increases the risk of mechanical damage to the element. A person breaks the integrity when combing or cutting his hair. Damaged melanocytes can degenerate into atypical cells. Over time, melanoma occurs. Injured growths should be immediately shown to dermatologists.
- The appearance of bleeding or purulent discharge from a mole requires immediate consultation with a doctor.
The dermatologist will examine the papillomatous element and decide on further treatment tactics. The doctor will prescribe general clinical blood tests and the necessary additional studies. After a detailed diagnosis and obtaining examination results, the question is raised about how to get rid of the formations.
There are several removal methods:
- Surgical treatment is used to combat various skin growths. The surgeon removes the moles using a scalpel under local anesthesia. The resulting material is sent for histology. Specialists make a microslide, which is examined in detail under a microscope. After the operation, a small wound remains, which heals quickly. A scar forms at the site of the former nevus. At the present stage of development of medicine, there are non-traumatic methods of treatment.
- Cryodestruction allows you to remove skin growths using liquid nitrogen. The substance freezes cellular elements. Blood circulation and metabolic processes inside the mole stop. It dries up and disappears. The treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. The procedure takes from 5 to 20 minutes. The element disappears after 2-3 days. An important feature of the method is that it does not cause bleeding and does not leave scars.
- Laser removal is a modern way to get rid of papillomatous growths. The laser burns out the formation painlessly. A small depression remains, which quickly heals. Laser destruction is never complicated by bleeding and does not lead to the formation of keloid scars.
- Radio wave surgery is based on the action of a radio wave knife.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Link to main publication
Didn't find suitable advice?
Ask your doctor a question or see all questions...
Article rating:
Loading…
Source: https://VashaDerma.ru/papillomy/papillomatoznyj-nevus
Papillomatous nevus: what is it, removal surgery
In the article we will tell you about papillomatous intradermal melanocytic nevus of the skin and what it is. The name sounds scary. But that's not true. We are accustomed to such small moles that rise above the surface of the skin, and we mistakenly believe that these are papillomas. At first glance, they are very similar, but there is still a difference. People also call them warts. They have a pale color (flesh, light pink), rise high from the dermis on a thin stalk and are soft and plastic to the touch. They do not look aesthetically pleasing, which adds a lot of trouble to the female population. The weaker sex always tries to get rid of such growths and make a huge mistake by removing them themselves. This often leads to sad consequences, and then you still have to turn to specialists.
Features of papillomatous pigmented nevus
Let's look at the difference between it and warts. This is a type of melanocytic condylomas, which means it is also a neoplasm on the surface of the skin. Scientists have concluded that it is congenital and begins to form on the baby’s body in the womb during pregnancy. There are many reasons for the formation of moles:
- Chronic venereal diseases.
- Heredity. Until now, many people believe that if a newborn child has a condyloma in the same place as the father’s, it means that this is his biological baby.
- Finding the expectant mother in an unfavorable radioactive environment.
- Work in hazardous industries (contact with dangerous poisons, household chemicals without special suits).
- Reckless and prolonged use of ultraviolet radiation (tanning in solariums during pregnancy is strictly prohibited).
- Taking hormonal medications before and during pregnancy.
- Diseases of the genitourinary system and kidneys.
- Use of certain medications.
- Alcohol and cigarette abuse.
- Therefore, dear ladies, in order to avoid various pathologies, think not only about yourself, but also about your unborn child.
Papillomatous nevus is also acquired. If in an infant it appears immediately, then in others it appears in the third year of life or later, and ends its progression by the age of thirty.
Symptoms and appearance
As we have already said, this is a mole that rises above the skin on a stalk. This is a benign formation that does not pose a threat to human life. Rather, it causes cosmetic discomfort, especially for people with increased mental excitability, often leading to depression and stress (pubertal youth).
Condyloma grows rather slowly and stops growing by the age of 30. Papillomatous nevus is localized mainly on the scalp and neck.
But there are cases when clothing rubs, knots appear on the collar area, in the armpits, in the groin and under the breasts in women. They are rarely found on the arms and legs.
These spots can become inflamed when scratched, but never actually develop into melanoma (a malignant tumor). Therefore, beauty salons undertake their removal, because there is no need to do a histology analysis.
The shape of the mole has an irregular outline, round, with a bumpy surface, with cracks, similar to a mulberry (berry). Its color is usually light brown, rarely found in black. Often with bristly, pigmented hair. The size is quite large, reaching 2 centimeters, which does not give pleasure to the weaker sex, especially if it jumps up on the face.
Localization on the body can be single or group.
Pathology is divided into several types:
- Mixed papillomatous nevus. It refers to a benign neoplasm. Rarely develops into cancer. But experts try not to remove them, especially on the face. This is a lumpy mole, similar to a wart, attached with a wide base to the dermis. Very dense to the touch, does not sag under your fingers. The size barely reaches 10 mm. It has a wide range of colors: beige, pink, light and dark brown. This depends on the amount of melanin in the cell. Condyloma has a clear border and a varied shape.
- Disseminated species. An extremely rare pathology on the body is located in groups along nerve trunks and large vessels. Throughout life, marks may spontaneously fall off and new ones may grow. Their location tells the doctor about the presence of epilepsy or diseases of the central nervous system. Therefore, the patient is observed by a neurologist for a long time.
- Complex papillomatous nevus - what is it. This is a type of two pathologies: intradermal and melanocytic. It begins its growth in the upper layers of the skin (epidermis) and ends in the dermis. Although it is not a malignant formation, if injured, a mole can degenerate into melanoma. Therefore, at the first suspicion, you should contact an oncologist. The difficulty of removal is that after taking analysis for histological examination, the damaged papule can transform into cancer. To do this, scraping and surgery to destroy it are done on the same day. The papilloma is small in size, brown in color, and has a barely noticeable outline around it. The surface is smooth, glossy. In the photo you can see papillomatous skin nevi with a crust.
- Organic look. A common disease characterized by a single growth. This is a large condyloma, slightly raised above the surface of the dermis, connected to it by a thick stalk. Round in shape, with clear boundaries. The color varies from light brown to dark brown. The growth is keratinized, with protruding papillae and therefore resembles cauliflower.
Another feature of this pathology is that it can be combined on the face with other neoplasms: birthmarks and warts. Only a specialist, with a thorough examination under a microscope, will be able to determine its type.
On the forum on various social networks, people suffering from papillomatous nevus correspond and exchange their photos. This is a relevant topic for them, since no one wants to walk around with ugly growths on their face. The most common question they ask each other is what is the difference between a papillary polyp and moles?
Papillomas are an acquired disease that is viral in nature and transmitted through sexual contact or other contact. Externally, they are completely different from congenital spots:
- The formation always remains the color of a person’s skin, that is, beige or flesh-colored.
- They concentrate in groups on the mucous membranes, neck, genitals, and armpits.
- The shape is different, without clear boundaries. The structure is homogeneous, without cracks, nipples, or dark crusts.
- On palpation they are very soft and subject to compression.
- They are attached to the dermis by a thin stalk.
- The sizes are different. They do not increase with the growth of the owner.
Trying to get rid of them on their own, people make a big mistake by pulling the papillomas with a thread. Only the cap falls off, but the leg remains. This can lead to degeneration into a malignant neoplasm. To treat and eliminate them, you need to consult a dermatologist.
A modern method for removing papillary polyps includes the domestic cream “Vartotsid”. Over the past few years, he has had great success in eliminating small-diameter hanging moles on the genitals.
It was developed by the Russian company Cytomed. The cream contains the active immunomodulator Imiquimod, which helps reduce or disappear condylomas in intimate places or in the perinatal area.
It is prescribed to people who have reached 18 years of age and are sexually active.
Features of its use:
- Apply once a day throughout the night three times a week.
- In the morning, wash off with warm water and soap.
- Use until the viral disease is completely eliminated, but no more than four months.
Removal of papillomatous nevus for medical reasons does not exist. It does not transform into melanoma, so doctors perform surgery for two reasons:
- If during hormonal changes in the body (puberty in boys and girls, pregnancy and menopause in women), there is a strong growth of moles. For cosmetic reasons, they try to remove them, since such growths attract attention.
- Injury. When combing and washing the hair, condylomas are often damaged, and they bleed, become wet, change shape, grow and cause pain.
To make an accurate diagnosis, you should contact an oncologist. As a rule, a doctor will immediately identify a papillomatous nevus by its appearance. But to completely exclude malignancy, additional examination is prescribed using:
- Ultrasound examination of the dermis.
- Biopsy (scraping from the surface of a mole).
- Dermatoscopy. Of course, the doctor visually examines the skin, but with the help of a dermatoscope he will see a 10-fold magnified picture of the color change, shape and borders. Especially after injury, it helps to recognize whether melanoma has already formed. Previously, this procedure was performed using a scalpel, which increased the risk of the spot degenerating into a malignant tumor.
- Siascopy. A modern, painless, non-invasive digital method for examining the dermis using two beams aimed at condyloma to a depth of three millimeters. The oncologist, having applied the device to the papule, can see its structure on the monitor after a few seconds.
Treatment
After a complete diagnosis and collection of information about the cause of the inflammatory process, the oncologist takes an anamnesis of the disease and decides how to eliminate the growth:
- Removal of papillomatous nevus using surgery. This is a proven method, done under local anesthesia. After excision with a surgical scalpel, the doctor removes not only the neoplasm itself deep under the skin, but also captures healthy areas of the dermis. Therefore, after suturing, scars remain that do not completely disappear. This is the only disadvantage of this procedure.
- Radio wave method. A painless and seamless way to remove moles. Destruction occurs using the Surgitron device, which converts electric current into high-frequency radio waves. The operation lasts only two minutes, and after it the patient returns to normal life. Since the area is not injured, the wound does not require special care.
- Electrocoagulation. This is burning out the nevus using chemicals or electric current. This procedure is performed under local anesthesia in one session, with a high degree of effectiveness on any area of the skin. It is also prescribed to people of all ages. It completely eliminates infection of the wound due to bleeding, and with good care, rapid regeneration of the dermis occurs.
- Removal using laser. A modern, affordable and painless method. The operation is quick, an injection for pain relief is given at the patient’s request. Does not affect ability to work, does not require hospitalization. The wound heals quickly. Such destruction of moles does not leave scars or scars.
- Cryodestruction. This is the “freezing” of neoplasm cells at low temperatures using liquid nitrogen or carbonic acid. The peculiarity of this method is that these components reach temperatures down to minus 190 degrees. The operation must be carried out within a few seconds, otherwise, if delayed, tissue necrosis may occur. Therefore, a large mole is removed in several stages. Doctors with great success remove formations in the patient’s intimate places. After “freezing”, condylomas noticeably decrease in size and become lighter in color. The result will be noticeable within five days, and complete restoration of the affected skin occurs in 1-2 weeks.
Preventive measures
In our article, we tried to fully cover the topic: what is melanocytic papillomatous intradermal nevus, the causes of its occurrence, types, appearance and treatment.
If you already have moles, you need to examine them more often. If there is redness, increase in size, bleeding, itching or inflammation, immediately contact a specialist for help.
And to avoid visiting an oncologist, it is necessary to adhere to preventive measures. This is especially true for people who have a family history of melanoma.
Take precautions:
- Stop or reduce your intake of cigarettes and alcohol.
- Sunbathe during the summer season from 7 to 9 am and in the evening when the sun is in its passive phase.
- Use sunscreen and tinted glasses.
- Refuse to work in hazardous industries (chemicals).
- Change your place of residence and climate if you are in an environmentally unfavorable area.
- Do all housework with rubber gloves.
- Avoid solariums.
Our information is for informational purposes only. Do not use folk remedies in the form of compresses and lotions. Contact the oncology clinic, only a specialized doctor can help you. Share on social networks
Source: http://skinproblems.ru/diseases/papillomatoznyy-nevus-chto-eto-operatsiya-po-udaleniyu
Papillomatous nevus - causes, symptoms and treatment
- Are intradermal nevi dangerous? Moles: questions and answers
- 29-07-2011
On the body of every person there are intradermal nevi - ordinary birthmarks that are not prone to turning into malignant ones. Although such moles are generally considered harmless, according to histological data they are the background to the development of primary melanoma in 16% of cases.
Since ancient times, attempts have been made to unravel the secret meaning of moles and birthmarks. They tried to identify it by studying the location of moles on certain parts of the body.
Since then, little has changed: people continue to wonder how the presence of a nevus on the cheek or neck will affect their fate. In addition to ordinary curiosity, spurred by belief in the supernatural and mysterious, moles also arouse purely scientific interest.
An intradermal nevus is a common benign mole that poses no danger.
Doctors are wary because dysplastic nevi (atypical birthmarks) are usually precursors to melanoma. They have an unusual appearance, are inherited and can appear in adulthood. In general, nevi are usually divided into melanoma-hazardous and melanoma-non-hazardous.
Almost every person has an intradermal nevus, or an ordinary birthmark that is not prone to malignancy (malignancy). Such a nevus is melanomonic, although according to histology it is the background for the development of primary skin melanoma in 16% of cases.
Intradermal noncellular nevus
Intradermal noncellular nevus, which most often occurs on the face and neck, should not cause concern. It is not congenital and usually appears after puberty. It is noteworthy that by the age of 60, most non-cellular nevi lose pigmentation (lighten).
Papillomatous nevus has uneven outlines, a voluminous shape and a lumpy surface
Meanwhile, intradermal papillomatous nevus can be either single or multiple. Often located on the scalp. External interventions (for example, holding a comb through the hair) cause constant inflammation, therefore, when treating papillomatous nevus, dermato-oncologists have difficulties in choosing rational treatment tactics.
Intradermal pigmented nevus
Melano-mono-dangerous ones include intradermal pigmented nevus, fibroepithelial, verrucous and papillomatous nevi, “Mongolian spot” and Setton’s nevus. After surgery and removal of such moles, the development of melanoma is not observed.
Although the risk of developing melanoma from a pigmented nevus is low, this mole can still become malignant if:
- single serious injury;
- frequent repeated damage (therefore you should not rub, scratch or scratch the pigmented nevus, or treat it with any chemical solutions);
- ultraviolet radiation (as a result of prolonged exposure to direct sunlight or visiting a solarium).
Pigmented nevus is not that uncommon: about 2% of children are born with it
If you find signs of degeneration of a mole, do not delay and consult a doctor. Most likely, it will have to be removed.
Against the backdrop of all this data, a study conducted by scientists from King's College London was encouraging. The results of the work showed that people who have a large number of moles on their bodies have much fewer wrinkles. It also became known that the presence of more than 100 nevi reduces the susceptibility to osteoporosis (thinning of bones) by 50%.
British scientists confirm that moles are directly related to the risk of developing skin cancer. However, they find more benefits for our health in birthmarks.
Other articles on MegaTexts.ru
- How to identify melanoma: causes and symptoms of skin cancer
- Are “red dots” on the body also moles?
- In contact with
Source: https://healthage.ru/poleznye-sovety/lechenie-boleznej/papillomatoznyj-nevus-prichiny-simptomy-i-lechenie/