Human papillomavirus (abbreviated as “HPV”) in gynecology is a disease that causes a severe weakening of the protective functions of the body of women and provokes the development of serious pathologies.
The main danger for women that the papillomavirus poses is the possibility of developing cervical cancer.
If a woman’s immune system is working at full strength and her body is healthy, then it will be able to independently get rid of the manifestations of the virus in 90% of cases. But due to a number of reasons, the body’s immunity can reduce the degree of protection, which allows the virus to develop inside the body.
Improper functioning of the immune system is the main reason why HPV begins to develop. “Trigger” factors are causes that provoke immune disorders.
HPV infection can be provoked by:
- promiscuity;
- refusal of barrier contraceptives;
- acute infectious diseases, including chronic ones;
- lack of regular genital hygiene;
- frequent hypothermia of the body;
- constant state of stress;
- hereditary predisposition.
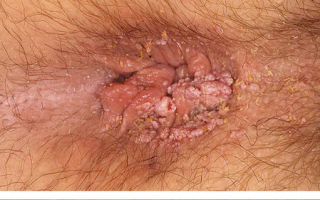
Most often, the papillomavirus does not manifest itself in any way. But there are cases when a rash on the skin and mucous membranes, similar to warts, or bloody discharge appears on the body of a woman with HPV. During a gynecological examination, the doctor should pay attention to such manifestations of infection as:
- signs resembling cervical erosion;
- neoplasms on the cervix;
- The patient complains of pain, a burning sensation in the genital area;
- unpleasant discharge from the genitals.
The duration of the incubation period of the papilloma virus depends on what type it is and how it manifests itself on the outside and inside of the body.
The most dangerous types of HPV - indirect and direct signs of the virus
Virus types can be of high, medium or low oncogenicity. The most dangerous type is the first of those listed (with a high degree of oncogenicity), combined into group “A-9”, which can lead to the development of cancer.
HPV type 16
Type 16 of the virus is the most dangerous in terms of cancer development. Once entering the body through the mucous membrane, the virus may not manifest itself for a long time. After some time, a new formation appears in this place in the form of a flat papilloma or condyloma.
Changes in the cervix lead to a high risk of developing atypical cells, which can lead to cancer.
Papillomas can manifest themselves in completely different areas of the body:
- on the mucous membrane of the genital organs;
- in the mouth and nose;
- in areas with thin skin;
- on the neck, face or armpits;
- occurs most rarely on the back.
The color is most often similar to skin color, only the shade may be slightly lighter or darker. Papillomas that appear on the mucous surface of the genital organs often have a pointed shape. At the initial stage, it may be only a slight roughness that is difficult to distinguish. Later, a capillary network is formed on it.
HPV type 18
Type 18 is the manifestation of neoplasms on the skin or mucous membranes (most often on the genitals). They can be divided into 3 types according to their shape:
- a round wart, slightly above the skin. The color is most often reddish;
- papilloma, close to the skin tone, often appears in the armpits and genitals;
- condylomas - growths on the genitals - are the most terrible manifestations, as they can transform into cancer.
At the first detection of HPV symptoms in women, you should contact a gynecologist and undergo an examination.
HPV type 31
Papillomavirus type 31 is a benign formation, but it can develop into cancer. Its main symptoms:
- various growths on the mucous membrane of the genital organs;
- discomfort in the intimate area, bloody discharge;
- discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse.
If growths appear on the body, then you should not engage in self-diagnosis, but should trust the specialists. They will be able to accurately determine whether it is a human papillomavirus or a simple mole.
HPV type 51
The 51st type of papillomavirus is its most insidious variety, since it is difficult to diagnose. There are no obvious symptoms that indicate infection with this virus.
The virus is transmitted mainly through sexual contact, but there is also a possibility of infection through household means. It affects only the mucous membranes, but the person does not feel any itching or irritation, or an unpleasant odor or discharge. Only a medical examination can diagnose infection with HPV type 51.
HPV type 56
A virus of this type can reside in a woman’s body for many years and manifest itself with the onset of menopause. During this period, type 56 virus can cause the development of cervical cancer. It is possible to understand that an infection has occurred by the large number of warts and other growths on the body. The sooner a woman turns to a specialist and begins treatment, the faster and more successful the recovery will be.
Vaccination against human papillomavirus. How is HPV transmitted?
HPV in women - what it means and how you can protect yourself from this virus can be found out during a consultation with a doctor. Transmission of the virus from one person to another can occur through close bodily contact, as well as during unprotected sexual intercourse. A mother can pass the virus to her baby while he is still in her womb.
Common routes of infection:
- touching the skin and mucous surface of an infected person;
- using personal hygiene items of an infected person;
- while visiting a sauna, bathhouse or shared shower with infected people.
In most cases, infection occurs during sexual intercourse or kissing. The causative agent of the virus instantly penetrates the mucous tissues of a healthy person.
The main risk group is women who are promiscuous and do not use barrier methods of contraception.
A woman who is pregnant at the time of infection passes the virus to her child. As a result, he may develop warts or other growths on the throat and larynx, causing difficulty breathing. It is also possible that the baby can become infected from the mother and during breastfeeding.
Vaccination against the virus is carried out among girls and adolescent girls. Age limits are from 9 to 14-15 years; in extreme cases, it is allowed to get vaccinated before reaching 26 years of age.
The vaccine contains an artificial virus, thanks to which the girl’s body will begin to develop immunity against it. After vaccination, there is no fear of infection for several decades.
It is important to remember that if the body is already infected, vaccination is prohibited, as this will only worsen the situation.
In this regard, it is advisable to give the injection before the girl begins to be sexually active.
Studies have shown that the effect of the vaccine exceeds all expectations: the risk of developing cervical cancer is reduced by more than 90%. The vaccination is absolutely safe; it does not contribute to the development of infection after its administration.
How to test for HPV in women - prevention of the virus. What is the price
It is imperative to undergo an examination if growths are found on the genitals, in the throat and mouth, or in the anus area. This will allow you to begin the necessary treatment in a timely manner and eliminate the possibility of developing cancer.
It is recommended that every woman who has reached the age of 30 undergo such an analysis every 4-5 years.
To determine the presence or absence of HPV in a woman’s body, a blood test is taken from her, a scraping and a smear are made from the cervical canal and cervix. On the eve of the test, a woman is prohibited from douching.
The costs of tests will depend on what kind of examination is ordered. Conventional diagnostics will cost about 300 rubles. If the same method is aimed at studying the type of virus and its quantity, then the price will rise to 1000 rubles or more.
Pregnancy and human papillomavirus
According to statistics, about 80% of pregnant women notice the formation of papillomas on their bodies.
Their appearance is the same as that of other infected people: skin-colored or slightly darker, round in shape, sometimes with a stalk. But during pregnancy, growths appear at high speed and on a larger scale.
After identifying the type of virus and its degree of oncogenicity, treatment is prescribed. But it should be borne in mind that therapy can be prescribed only from the 28th week of gestation; in other cases (lowered immunity, poor health, etc.) it can be postponed until the birth of the child.
If a woman’s papillomas occur in places where the skin folds and they rub until they bleed, a procedure should be performed to remove the growths.
To remove papillomas, surgical excision is used, and freezing of the skin area is used as anesthesia. But these are extreme measures, since in most cases, after pregnancy, papillomas disappear on their own.
To avoid such problems during pregnancy, a woman should undergo an examination of her body before conception and undergo treatment, if necessary. This will relieve you from unnecessary worries and discomfort during such a crucial period of life.
Treatment of papillomavirus of high oncogenic risk - drugs, tablets (“Isoprinosine”)
- The drug is available in tablets, has antiviral and anti-inflammatory effects on the body, and also stimulates increased immunity.
- Such properties allow the drug to fight oncogenic types of HPV.
- “Isoprinosine” has an effect not only on the affected cells, but also on the virus itself.
- The medicine has the ability to be quickly absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract, and its highest concentration is observed within 2 hours after taking the tablet.
- The dosage is prescribed to each patient individually, depending on age, weight and complexity of the disease:
- Adolescents over 12 years of age and adult women with HPV should take this medicine as prescribed by the doctor three times a day at the prescribed dosage. The tablets should not be crushed or chewed, but should be swallowed whole with clean, still water.
- For children from 3 to 12 years old, the dose of the medicine is calculated depending on body weight. The dose should be divided into 3-4 times a day.
A medicine has not yet been invented that could completely remove papillomavirus from the human body, but there are highly effective methods of therapy. They are determined and prescribed only by a specialist after a thorough examination of the body.
How to treat cervical HPV with folk remedies
It is allowed to independently use traditional methods of treatment that enhance the body’s protective properties. And removal of tumors can only be carried out by a qualified specialist after a full examination.
Effective recipes that can increase immunity, which will help in the fight against infection:
- Drink made from pine needles . To prepare it you need 2 tbsp. l. Finely chop the pine needles and pour a glass of boiling water. Keep on the stove over low heat for about 15-20 minutes. After this, leave the drink for half an hour to let it brew. After this, strain and take 1 tbsp daily. l. a couple of times a day. To improve the taste, it is recommended to add sugar or honey;
- Potato juice . Take a medium-sized potato, preferably with red skin. Thoroughly clear the soil, rinse and cut off the darkened areas. Pass through a meat grinder and squeeze out the juice. It should be taken half a glass every day half an hour before meals. Duration of use: at least 2 months. Please note that this drink is prohibited for people with diabetes or low stomach acidity.
HPV in women is a pathological disease, and to prevent this disease from bringing serious consequences, to reduce the risk of the virus occurring in the body, you should follow simple hygiene rules and visit a gynecologist on time.
Despite the fact that some types of virus do not pose a serious danger, it is impossible to determine this on your own.
Therefore, if timely treatment is not started, infection with papillovirus can lead to cancer and death.
Videos about papillovirus
HPV 16 in women - what it is and how to treat:
Remedy for HPV 16 18 in women:
Source: https://healthperfect.ru/hpv-in-women-what-is-it.html
10 symptoms of human papillomavirus
People have been familiar with viruses for many millennia. Already at the beginning of our era, doctors became acquainted with genital warts and discovered that they were sexually transmitted. This is a virus belonging to the genus of human papillomaviruses, transmitted from one living organism to another. The main location is the basal layer of the skin. The upper part of the dermis is used for reproduction. Its long-term presence in cells provokes their division, which negatively affects the human immune system.
Human papillomavirus, symptoms and signs
Human papillomavirus can be diagnosed through laboratory tests. If a virus is detected in the blood, we can definitely say that the person is sick and needs help. The incubation period can be 2 months or more. A person can be sick for many years and look healthy. The first manifestations of the disease make themselves felt when the immune system is weakened.
Patients learn how the virus manifests itself by multiple accumulations on the upper layer of the tumor epithelium. From a medical point of view, the resulting growths are benign. But this does not mean that there is no risk of papillomas degenerating into malignant neoplasms. The virus manifests itself in the form of warts, papillomas, condylomas and calluses.
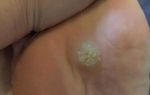
Initially, the virus appears in the form of warts with a small diameter, round shape and dense consistency. Their maximum size in diameter is 1 cm. The color of the growth is close to the color of the dermis. The location of warts is the most traumatic part of the body (fingers, knees, elbows).
Following the warts, growths appear on the stalk - papillomas. The main places of localization are the more delicate parts of the body: face, neck, chest, genitals.
Doctors' opinions on the most effective methods of treating warts and papillomas
The chief physician of Moscow City Hospital No. 62 describes his vision on this matter. Anatoly Nakhimovich Makhson
Medical practice: more than 40 years.
“I have been treating people’s papillomas and warts for many years. I’m telling you as a doctor, papillomas along with HPV and warts can really lead to serious consequences if they are not dealt with.
The human papillomavirus is present in everyone on whose body there are papillomas, moles, warts and other pigmented formations. According to rough estimates, 80-85% of the planet's population has it. By themselves they are not dangerous. The problem is that an ordinary papilloma can become melanoma at any time.
These are incurable malignant tumors that kill a person in just a few months and from which there is no salvation.
Unfortunately, in Russia and the CIS countries, pharmaceutical corporations sell expensive medications that only relieve symptoms, thereby hooking people on one drug or another. That is why in these countries there is such a high percentage of cancer diseases and so many people suffer from “non-working” drugs.
The only drug that I want to recommend, and it is also officially recommended by WHO for the treatment of papillomas and warts, is Papinol.
This drug is the only remedy that has an effect not only on external factors (that is, it removes papillomas), but also acts on the virus itself.
At the moment, the manufacturer has managed not only to create a highly effective product, but also to make it accessible to everyone. In addition, within the framework of the federal program, every resident of the Russian Federation and the CIS can receive it for 149 rubles.”
To find out more, read this article.
Transmission routes, where HPV comes from
To date, there are 3 known ways of transmitting the disease:
- Sexual contact with an HPV carrier.
Most often, the human papillomavirus appears in a healthy patient through sex with an infected partner. Papillomavirus is transmitted through anal, oral and classic sex.
Medical observations show that the initiator of infection in most cases is the male sex, but does not exclude women. The explanation for this fact is simple.
HPV is asymptomatic and can remain latent for a long time.
Using a condom does not minimize the likelihood of infection, since microparticles of the virus penetrate even through latex. HPV is found in all biological fluids of the vagina and penis, including saliva. Therefore, a healthy person can become infected even during oral sex with a sick person.
The probability of contracting HPV during sexual intercourse is 80%.
- Transmission of HPV through the birth canal.
In this case, the first signs of papillomavirus can be diagnosed both in a fragile infant and in school-aged individuals. The cause of infection should be sought in the birth procedure. Passing through the infected cervix and birth canal, the fetus is automatically infected with papillomavirus.
This type of infection in medicine is called the intrapartum method. It is with this method that papillomatosis of the larynx area is very often diagnosed in children. Doctors have not identified any inheritance of warts.
Despite the fact that the main method of transmission of HPV is sexual, there is also the possibility of infection through household contact. Let's take a look at where HPV can come from in this case:
- any handshake with an infected person can result in infection if there is a wound, abrasion or other skin damage on the surface or inside of the palm
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, including using the same underwear and accessories, increases the risk of infection
- visiting public places: gyms, saunas, baths can be a source of infection with papillomavirus
Observations show that indirect causes of HPV transmission are in second place after transmission through sexual contact. Many patients are interested in the question: if there are papillomas, then there is the HPV virus. Only specialists can answer it after conducting a diagnostic study.
Papilloma on the neck, symptoms of its danger to the body
The favorite place of papillomavirus is the delicate skin of the neck. The growth is a bodily formation in the form of a wart. The size can vary from 2 mm to 2 cm. Neoplasms spoil the aesthetic appearance and bring discomfort to a person’s life.
The main symptoms of HPV in the neck include:
- the appearance of a small elevation on the flat surface of the skin;
- the presence of a rough surface at the top of the neoplasm;
- painlessness when touching them;
- the presence of multiple growths not far from a single wart.
The danger of papillomavirus on the neck lies in the risk of frequent neck injury from jewelry. Such injuries increase the risk of the neoplasm degenerating into a malignant tumor.
The causes of unpleasant growths in the neck area can be: disorders of the thyroid gland and other hormonal imbalances, problems with body weight, trauma to the dermis.
The main reason given is a surge in hormones.
be careful
The presence of papillomas and warts on the body is the first sign of malignant melanoma!
We hasten to warn you that most drugs that “treat” warts and papillomas are a complete deception of marketers who make hundreds of percentage points on drugs whose effectiveness is zero. They do not cure the disease, but only mask the symptoms.
The pharmacy mafia makes huge money by deceiving sick people.
But what to do?
How to treat if there is deception everywhere? Doctor of Medical Sciences Anatoly Makhson conducted his own investigation and found a way out of this situation. In this article, the Doctor also told how to 100% protect yourself from melanoma, for only 149 rubles! Read the article in the official source via the link.
Warts and other neoplasms on the neck become dangerous if there is a sharp multiple spread of the virus. As a rule, this process is accompanied by itching and burning.
The beginning of scratching brown papillomas in the neck area may indicate their malignancy. At this time, you need to be especially careful about your body and not injure the tumors.
Otherwise, papillomas and warts can spread to nearby parts of the body.
Despite the benign nature of the process, papillomatosis can cause cancer. Multiple formations of growths on the neck, uncontrolled growth should alert a person and become a reason to visit a doctor. When a tumor on the neck degenerates into a malignant tumor, the following symptoms are observed:
- painful and itchy sensations appear;
- the color of the growth changes;
- the neoplasm begins to peel off and dry out into the surface layer;
- an inflammatory process appears at the apex of the neoplasm and near it;
- bleeding is noted.
These symptoms require urgent diagnosis to determine the strain of the virus and the development of subsequent treatment.
Papillomas in the throat, symptoms and types
Laryngeal papillomavirus is caused by HPV strains 6, 7, 11, 73. The first and last types are oncogenic. Their danger lies in the multiple growth of growth into the trachea and other airways. Depending on the location of the disease, the following types of growths are distinguished:
- limited – characterized by the spread of warts in the area of the larynx and tonsils;
- common - neoplasms develop into papillomatosis, which is characterized by multiple growths;
- closing – HPV causes blockage of the airways.
The main symptoms include the following manifestations from the body:
- sore throat sensation;
- sensation of a foreign body in the throat;
- constant lump in throat;
- constant coughing;
- problematic speech due to massive growth of condylomas in groups;
- difficulty breathing and swallowing saliva;
- feeling of heaviness in the throat;
- signs of suffocation.
When visually examining a patient, the human papillomavirus is very difficult to determine, since the symptoms are mild. Conducting timely diagnosis allows you to identify the disease at an early stage. If the doctor doubts the diagnosis, he refers the patient to an oncologist for further confirmation or refutation of the fact.
Human papillomavirus is an infection, a slow benign disease that can make itself felt on the head, neck, face, armpits and intimate parts of the body.
Its development can be stopped by undergoing an annual medical examination, observing personal hygiene rules and strengthening the immune system.
If it happens that a healthy person does become infected with the virus, qualified specialists and innovative medicines in combination with traditional methods will speed up the recovery process.
We invite you to watch a video about the symptoms and treatment of papillomas.
Source: https://propapilloma.ru/papilloma/chto-takoe-virus-cheloveka-ego-opasnost-dlya-organizma/
Features of the symptoms of human papillomavirus
HPV is a viral disease that affects the human body to varying degrees. It infects about 80% of the entire population of the planet. But not everyone has the disease. To detect and seek help in time, you should know the symptoms of human papillomavirus.
Symptoms of papillomavirus infection
Human papillomavirus infection is a common occurrence in gynecology. This is a common infection that is sexually transmitted, along with herpes. The disease affects men, but the destructive effect of the virus on their body is less.
There are more than 170 types of HPV, with varying degrees of oncogenic risk. Common strains include those that cause the appearance of warts vulgaris (type 2), genital warts (6,11).
Symptoms of HPV can be direct or indirect.
Direct
The human papillomavirus causes symptoms noticeable to the eye: warts, genital warts - benign formations of the skin and mucous membrane.
The following types of warts are distinguished:
- vulgar;
- youthful;
- plantar.
Vulgar warts are clinically manifested by symptoms:
- multiple growths;
- localized on the hands (fingers, periungual area), but can appear on the red border of the lips, in the mouth, and other parts of the body;
- type of papules of dense consistency up to 1 cm in size;
- the surface is rough, it is covered with plates of keratinized epithelium and cracks;
- the main wart, around it there are daughter warts, differing in smaller sizes;
- the color does not differ from healthy skin, or is grayish.
Youth:
- type of flat papules of various shapes;
- The color ranges from pale pink to brownish;
- size up to 3 mm;
- affects arms, legs, face.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Plantar lesions look like flat, hard-to-the-touch formations in places where shoes are worn out. Clearly visible boundaries, rough surface with numerous horny layers. A distinctive feature of the symptoms are black spots on the surface, a feeling of pain when pressing or walking.
Exophytic condylomas are a common variant of HPV in the intimate area.
They have the appearance of lobular formations on a stalk, protruding above the surface of the mucous membrane, with numerous vegetations. Usually the skin around them does not change, but with inflammation, swelling and hyperemia develop.
Condylomas are prone to the formation of macerations on the surface and non-healing erosions. When infection penetrates, suppuration develops.
Growths from HPV appear in places where one type of epithelium transitions to another, in particular, from the genital mucosa to the skin.
The development of condylomatous (the appearance of many condylomas) cervicitis and vaginitis is likely.
Papillomatosis of the larynx, throat, and upper respiratory tract is a consequence of infection of the child from the mother during aspiration of vaginal contents during childbirth.
Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma is distinguished by the symptoms of the formation of a large growth that affects symmetrical areas of the skin (labia majora, inguinal folds on both legs). It often occurs when women are infected with HPV during pregnancy.
Indirect
Indirect signs and symptoms when HPV enters the body directly are not specific and can be observed during the development of other diseases.
These include:
- feeling of discomfort during sexual intercourse, as well as pain;
- bleeding, mucous discharge;
- low-grade fever;
- itching, constant irritation, maceration, burning.
Such symptoms may indicate inflammation associated with infection and a decrease in local immunity. They occur in varying degrees of manifestations when:
- vulvovaginitis;
- endocervicitis;
- endometritis;
- bacterial vaginosis, when the vaginal flora and local immunity are disrupted;
- other sexually transmitted infections.
You cannot start treatment on your own. It is necessary to seek help from a specialist to identify the disease.
It is difficult to distinguish between diseases when several infections are present at the same time.
The presence of growths as the first sign of infection
The human papillomavirus remains latent for a long time. When the immune system weakens, it actively multiplies, causing papillomatosis or condylomatosis.
In men, HPV affects the foreskin, head of the penis, urethra, and scrotum. In women - the inner or outer surface of the labia, vestibule of the vagina, perineum, clitoral area, anus, pubis. Inflammation causes pain, burning, and itching.
The appearance of growths is the first noticeable symptom of infection or relapse.
Which strains of HPV have different symptoms?
Human papillomavirus has varying degrees of oncogenicity. They are classified as low, medium, and high risk. Many people are afraid of the appearance of papillomas, warts or condylomas, citing the rapid development of cancer; this statement is erroneous.
Malignancy of HPV growths is rare; a disease that does not manifest itself with similar symptoms is dangerous when the papilloma virus is integrated into the genetic apparatus of the target cells.
In this case, active production of viral oncoproteins begins, affecting the regulatory proteins of the affected cell. As a result, the cell is not able to go through the stages of differentiation. There is a high risk of mutations leading to malignancy of epithelial cells.
For this reason, highly oncogenic types of human papillomavirus (most often genotypes 16 and 18) increase cervical epithelial dysplasia, which is especially dangerous during menopause.
Oncogenic strains lead to the development of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), which is characterized by the following symptoms, determined colposcopically:
- the appearance of areas of keratinization;
- ulcerations or growths;
- the appearance of punctuation;
- mosaic;
- iodine-negative areas.
CIN is asymptomatic and is often detected in the last stages (carcinomas).
HPV infection develops against the background of cervical erosion. During colposcopy, a defect in the epithelium (red) is detected with exposure of the subepithelial layer. For cancerous erosion, the peculiarity is that the edges are stepped; necrotic masses are located at the bottom.
Methods for diagnosing the presence of HPV in the body
Diagnosis in women is carried out by a gynecologist and dermatologist.
Its methods include:
- colposcopy;
- DNA methods;
- serological studies;
- histological, cytological diagnostics.
Colposcopy allows you to examine the vagina, cervix, and identify pathological areas. You can see changes in the epithelium, foci of hyperkeratosis, vascular pattern, symptoms of cervical neoplasia. Creates conditions for accurate biopsy sampling, which is important for histological examination.
Methods for detecting the genetic material of the human papillomavirus include PCR (polymerase chain reaction), the double gene trap method (Digene tests).
The polymerase chain reaction is the most widely used. It allows you to determine the presence of HPV with high accuracy, by repeatedly copying DNA fragments of the human papillomavirus and their subsequent identification. PCR provides information about infection and strain, but does not provide information about concentration. A smear is enough to carry out the procedure.
The situation is different with Digene tests, which establish carrier status, strain, and clinically significant concentration. For the method, the material obtained by scraping is sufficient.
These tests are used as a diagnostic tool during preventive examinations in conjunction with cytological analysis.
Cytology (cytogram) allows one to judge the structure of cells and their organelles. HPV infection is characterized by a cytopathic effect, which is manifested by the appearance of koilocytes and dyskerocytes. Koilocytes have a hyperchromic nucleus and a rim of clearing around it. Diskeratocytes contain eosinophilic cytoplasm, are small in size, and have a pyknotic nucleus.
Histology gives an idea of the structure of the tissue. Histological manifestations and symptoms of HPV include CIN of varying severity, exophytic, typical flat condylomas, koilocytes, foci of dyskeratosis, acanthosis, papillomatosis. The research drug is used for biopsy.
Serological analysis involves the detection of antibodies to the human papillomavirus.
There are alternative methods, electropuncture diagnostics, which includes homeopathy, the achievement of 20th century technologies.
The method involves measuring deviations of electrical potentials from the norm at acupuncture points.
According to ancient Chinese philosophy, each energy point is associated with different elements of our body, and disruption of the functioning of these elements leads to a change in the flow of energy.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Source: https://VashaDerma.ru/hpv/simptomy
Human papillomavirus - signs
The infection that causes the appearance of warts (condylomas) is called “human papillomavirus” (HPV), the symptoms of which can be obvious or hidden.
It stays in the body for a long period without appearing externally, so diagnosing the disease is considered difficult. The general symptom is the appearance and self-propagation of papillomatous neoplasms on the skin and mucous membranes, which tend to remission and relapse.
In the chronic course of the disease, they disappear and reappear, causing discomfort to the patient.
The ways of infection with the virus are sexual and household. The carrier may not be aware of its presence in the body - this makes the spread of infection uncontrollable.
A person who follows hygiene standards and does not lead a promiscuous sex life avoids becoming infected with HPV. Those who are ill should know that this can be treated, so when the first symptoms of the disease appear, they should consult a doctor.
The danger of the disease is that neoplasms can degenerate into malignant ones, the prognosis of which is disappointing.
In women, the disease is manifested by the formation of genital warts in various parts of the body and damage to the mucous membranes. If neoplasms appear on the skin, this is a clear sign of infection. It is detected on mucous membranes only during a gynecological examination. The localization sites for condylomas are:
- labia minora;
- entrance to the vagina;
- body of the uterus;
- around the anus;
- oral cavity;
- neck, armpit area, under the mammary glands.
Condylomas can grow outward, be noticeable, or be internal, which are difficult to notice upon examination. HPV in women is considered as one of the conditions for the development of cervical erosion, which subsequently develops into oncology. This is the danger of papillomavirus damaging the mucous membranes of the reproductive system.
Indirect signs of HPV
Since diagnosing the disease is difficult, everyone should be attentive to their well-being. Based on your feelings and analysis of the unpleasant phenomena that occur during and after sexual intercourse, you can suspect that you have HPV. This conclusion can be drawn if:
- Pain is felt during sexual intercourse;
- after sexual intercourse, discharge mixed with blood is observed;
- you experience periods when a repulsive odor comes from your genitals.
But making a diagnosis for yourself, much less starting self-medication, is unacceptable, since only a detailed diagnosis can give a complete picture of the disease. It includes a gynecological examination using speculum, extended colposcopy, cytology, histology, and studies for concomitant STIs (sexually transmitted infections).
Signs of HPV in men
Male manifestations of HPV differ from female ones, but this is only because there is a difference in the anatomy of the reproductive system. Signs of human papillomavirus in men and women have common features - they mainly affect the genitals.
The localization sites for HPV are the frenulum and glans penis, and the urethra. HPV rarely spreads in the canal, but if this happens, the infected person has to endure pain when urinating, and there are other problems when emptying the bladder.
For example, urine may splash or flow intermittently.
The danger of male HPV is that it is highly oncogenic. Cancers develop in the anal area, on the genitals. For sexual partners, the presence of papillomavirus in a man is a huge risk of getting infected through contact.
Indirect signs of human papillomavirus in cytology
If in the conclusion of a study of biomaterial there is a phrase that indicates the presence of indirect signs in cytology, then this is unpleasant news.
It means that the patient has disturbances in the nuclear-cytoplasmic balance and nuclear dyskaryosis has been detected. This is the degree of precancerous disease - dysplasia (CIN I or CIN).
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) is considered a borderline cell condition. When atypia passes to the cytoplasm, cancer develops.
That is, when such signs of cell degeneration appear, it is necessary to take urgent measures to prevent malignant oncology. But there is no need to panic, because this is an early stage of change that can be cured. Remember, complications can be avoided if HPV is treated promptly.
Source: http://papillomy-lechenie.ru/po-kakim-priznakam-opredelyaetsya-virus-papillomy-cheloveka/
Human papillomavirus infection - is it so scary and how to recognize it?
To date, about 100 types of human papillomavirus (HPV) have been identified.
Living on the skin and mucous membranes, human papillomavirus infection (PVI) can cause benign neoplasms and transform epithelial cells into malignant forms.
It is recognized as one of the most common infections that can be sexually transmitted, and was detected in 30.3% of the population of the European zone of Russia.
How is human papillomavirus infection transmitted and what are the risk factors?
The maximum frequency of infection occurs at the most sexually active age (15-30 years) and is 17.6-20.8% among women, and its increase is directly proportional to the number of sexual partners they have. Particular attention to the results of research on human papillomavirus in gynecology is explained by the fact that:
- 70% of women after 3 years, counting from the beginning of sexual life, are infected with PVI;
- possible infection of the child from the mother during childbirth;
- Among all cancers in women, 12% are associated with HPV;
- although after 30 years the incidence rate of this PVI decreases (8.5-10%), the frequency of dysplasia and cervical cancer increases;
- in almost all cases of squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix, the DNA of this virus is detected in the test material; In terms of prevalence among women under 45 years of age, cervical cancer is in second place among malignant tumors (after breast cancer);
In this regard, vaccination against HPV is of particular importance.
Even minor mechanical damage and inflammatory processes of the mucous membranes or skin, diaper rash, maceration of the skin during discharge from the vagina, urethra, and accumulation of smegma in the preputial sac are the “entry gates” for the causative agent of the disease. The source of infection is sick people or virus carriers without clinical manifestations.
In most cases, infection occurs through sexual contact, but it is also possible through direct contact with a patient or virus carrier (handshake, etc.).
), less often - through the general use of hygiene items, through air or water in the gym, bathhouse, swimming pool.
It is also possible that medical workers can become infected from smoke generated during treatment with laser destruction or diathermocoagulation of condylomas, and self-infection often occurs during hair removal, shaving, “biting” nails, and scratching the skin.
The main risk factors contributing to the manifestation and/or exacerbation of the disease are:
- Reduced immunological reactivity of the body with concomitant diseases of internal organs, hypovitaminosis, smoking and alcoholism, treatment with cytostatic drugs, and immune diseases.
- Associated, mainly infectious diseases, especially those transmitted through sexual contact (gonorrhea, chlamydia, cytomegalovirus and mycoplasma, trichomoniasis, bacterial vaginosis, etc.).
- Early onset of sexual intercourse and a large number of partners; sexual contact with women suffering from genital or perianal condylomatosis, cervical cancer.
- Hormonal imbalance, especially with diabetes, taking glucocorticoids, as well as dysbiosis.
- Medical procedures and manipulations, especially insertion and removal of intrauterine devices, instrumental abortion and diagnostic curettage.
Symptoms of papillomavirus infection
Brief information about HPV
From the moment the pathogen enters the body until the first manifestations of the disease (incubation period), an average of 3 months passes (from 3 weeks to one year).
At the initial stage, in the absence of favorable conditions for the development of the virus in the body, it is possible to carry PVI without disease.
Otherwise, it is integrated into the gene structures of cells, which leads to the appearance of symptoms.
All clinical manifestations are combined into 3 groups:
- Skin lesions - common, flat, plantar, some other types of warts and non-warty lesions.
- Lesions of the mucous membranes of the genital organs - various types of condylomas, carcinoma and non-condylomatous lesions.
- Lesions of other mucous membranes - larynx, tongue, esophagus, rectum, bronchi, conjunctiva, etc.
On average, 99.5% of all cases of squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix contain human papilloma DNA. Manifestations and treatment of human papillomavirus infection largely depend on the type of virus. The most common and dangerous in terms of association with oncological forms of damage to the integumentary epithelium of the genital mucosa are about 35 types.
All types of pathogens are classified according to the degree of risk of malignant cell transformation they cause. The main ones:
- low degree of oncogenicity - types 6 and 11 of the virus, causing the development of multiple condylomas in the genitourinary organs and on the skin around the anus or anus (perianal condylomas), as well as mild dysplasia of epithelial cells of the cervix; they account for an average of 90% of cases of condylomatosis;
- medium degree of oncogenic risk - 31, 33 and 35;
- high degree of oncogenic risk - 16 and 18, which are found in 50-80% of tissue samples from the cervix with moderate dysplasia of squamous epithelium and in 90% of cancer located in the superficial layers of tissue (non-invasive cancer that does not grow deep into the tissue).
Clinical picture
In accordance with the clinical and morphological picture, infection in the anus and genital area is manifested by condylomas of various types - genital, papillary with external growth, intraepithelial (growth inside the epithelial layer), giant Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma, which is a type of genital condyloma, but with external and intraepithelial growing at the same time, and similar to a cancerous tumor.
Depending on the manifestations and nature of the course, three forms of PVI are distinguished:
- Latent, or hidden (asymptomatic) in which intensive reproduction of affected epithelial cells with mutant (altered) DNA occurs, invisible during normal examination and morphological examination. More often it is detected as a result of laboratory examination of the cervix, less often - of the vagina.
- Subclinical, characterized by the absence or minimal number of clinical symptoms and histological changes in the infected tissue in the presence of viral DNA elements in it.
- Clinical, or manifest.
Human papillomavirus infection in most cases exists in the form of latent and subclinical forms. The manifestation of the disease occurs under the influence of provoking factors or risk factors.
The subclinical form is manifested by small flat elements, often visually invisible.
After a test with 3% acetic acid (the “suspicious” area is treated), flat small warts appear on the skin.
They usually do not show any symptoms, but sometimes they can be accompanied by itching, and when localized in the vagina and cervical area, they provoke bleeding during and after sexual intercourse and vaginal discharge.
The clinical form is represented mainly by rashes of various types in the genital area, the symptoms of which depend on the location, type and size of the elements. Conventionally, the following types of warts are distinguished:
- Pointed, which are finger-shaped protrusions, on the surface of which there is a vascular “pattern” in the form of loops or dotted spots. They are localized mainly in areas of friction during sexual intercourse - in the area of the frenulum of the labia minora, at the entrance and in the vagina itself, on the labia majora and minora, clitoris, hymen, on the cervix, in the perineal area, on the pubis, around the anus and in the lowest parts of the rectum, on the mucous membrane of the urethra in the form of a ring around the external opening (in 4-8%). With deeper damage to the urethra, persistent urethritis occurs with corresponding symptoms, which is difficult to treat.
- Papillary - smooth, non-pigmented or pigmented elements without a rounded stem, slightly rising above the surface. They are located on the skin of the external genitalia.
- Papular. They are characterized by pigmentation, the absence of “finger” protrusions characteristic of genital warts, and an excess stratum corneum of the epithelium (hyprekeratosis). Localization - the scrotum, the skin of the body of the penis and the outer surface of the foreskin, the coronal groove of the penis, the lateral surface of the female external genitalia, the skin around the anus and the perineum.
- Keratotic - thickened elements that rise above the surface of the excessively dry skin of the labia majora. These formations cause easy infection of the sexual partner.
- Spot-type warts are located on the mucous membranes in the form of spots of low-intensity pinkish-red, reddish-brown or grayish-white color.
Genital warts
Dynamics and symptoms of genital warts
Genital condylomas with an exophytic type of growth (not inside the tissues, but outside) are the classic form. At the beginning of their development, they are limited papillae in the form of small nodules.
Their color does not differ from the color of the mucous membrane or skin on which they are located.
Gradually increasing, the papillae take on the appearance of thread-like growths of considerable size and look like cauliflower or a cockscomb.
An effusion of intercellular fluid appears between the papillae. The surface of the growths becomes moist and shiny, tissue swelling, maceration occurs, pain and an unpleasant odor occur.
During the period of progression, blood vessels are visible in the center of each papilloma, in contrast to elements with reverse development. Ulceration of the growths often occurs with the addition of a secondary infection.
At the regression stage, the papillae become smoothed, even velvety, due to the thickening of the layer of horny epithelium.
In pregnant women, genital warts grow very quickly as a result of a physiological decrease in immunity and their spontaneous regression occurs just as quickly after childbirth. As condylomas grow, they can even close the birth canal.
Diagnostic methods
For diagnostic purposes, in addition to the usual examination of the patient, extended colposcopy, histological and cytological examination of material taken through biopsy are carried out. Tests for the presence of other sexually transmitted infectious agents are required.
Of great importance for differential diagnosis are tests for human papillomavirus infection, carried out using PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and PCR methods with the identification of individual types of HPV.
In addition, analyzes are carried out to determine the oncoproteins E6 and E7 in material taken from the cervical canal using the immunofluorescent method, which makes it possible to differentiate carriage and the beginning transformation of affected tissue cells into malignant ones.
How to treat human papillomavirus infection
The main principles of treatment are:
- Elimination of risk factors that reduce the body's immune defense.
- Suppression of the causative agent of the disease and elimination of the conditions necessary for its existence.
- Correction of local and general immunity, including vaccination.
The most promising method is vaccination against human papillomavirus infection, which allows not only prevention, but also treatment of its manifestations that have already arisen.
Vaccination is carried out with recombinant vaccines, the effect of which is directed against pathogens with a high oncogenic risk by suppressing the activity of oncoproteins E6 and E7 and increasing the activity of cellular proteins p53 and Rb-105.
Vaccines are used for this purpose:
- "Gardasil" - in the form of a suspension for intramuscular injection. Its effect is aimed at producing specific antibodies in the body against proteins of HPV types 6, 11, 16 and 18;
- "Cervarix" is a suspension for intramuscular administration against HPV proteins types 16 and 18.
Combined therapeutic effects combine destructive and chemical methods, as well as the use of immunomodulators and nonspecific antiviral agents.
Destructive hardware methods include cryodestruction and electrodestruction, radio wave removal of condylomas, plasma coagulation and laser therapy.
Chemical destructive drugs for the treatment of papillomavirus infection are Trichloroacetate (80-90%), Podophyllotoxin (alcohol solution or cream 5%), 5-fluorouracil 5% cream, Vartek (solution), Kolkhamin (ointment), Solcoderm "(solution), etc.
Nonspecific antiviral agents: leukocyte and fibroblast interferons, Cycloferon, Intron-A, Leukinferon, Neovir, Allomedin (gel), etc. Immunomodulatory drugs: Immunomax, Panavir, Likopid , “Isonoprinosine”, “Derinat”, “Glutoxim”, “Gepon”, “Amiksin”, “Epigen-intim”, etc.
Human papillomavirus infection is an urgent medical, social and economic problem due to a significant increase in incidence, high contagiousness, decreased reproductive health and the danger of an increase in the number of cancer diseases caused by this infection.
Source: https://ginekolog-i-ya.ru/papillomavirusnaya-infekciya.html
Indirect signs of HPV in cytology: main symptoms in women and men
Human papillomavirus infection (or human papillomavirus), which most doctors briefly call HPV, is one of the most common infections transmitted to humans through household contact and sexual contact.
Today, scientists know about several dozen varieties of this disease. Some of these species belong to the category of high cancer risk, and the rest have low cancer risk.
This infectious disease can manifest itself in two forms:
- Active reproduction in cells that die as a result of exposure, and the person begins to suffer from symptoms of papillomatosis; Asymptomatic course of the disease. Often a person learns about the presence of the virus by chance while undergoing some examinations related to another case.
Getting infected with papillomavirus does not mean getting sick. According to statistics, only three carriers of the virus have the disease activated and begin to suffer with its unpleasant symptoms.
Is HPV dangerous?
It’s worth starting a conversation about the danger of the HPV virus in gynecology with the knowledge we already have about types of the disease with a high cancer risk. On average, more than 15 years pass from infection to the appearance of a malignant tumor. It is worth noting that about 100% of the entire population are carriers of this disease.
Factors that can trigger the development of cancer include:
- Women's use of birth control pills; Having several partners or changing them frequently; Weight loss through artificial dietary restriction; Early onset of sexual activity; Insufficient cellular immunity, which can manifest itself in diseases of sinusitis, tonsillitis, caries, as well as in pathologies of the thyroid gland; Sexually transmitted infections; Inflammatory processes of the cervix in women after abortion or childbirth; Smoking; Pregnancy.
Obesity, diseases associated with changes in hormonal levels, and diabetes can also reduce anticancer protection.
How do you get infected with HPV?
Of course, after such a spectacle you will want to protect yourself as much as possible from all dangerous factors. Unfortunately, this is difficult to do.
The virus can be caught even through indirect contact in the pool, hairdresser or during a manicure or pedicure.
If an HPV test in gynecology or urology reveals an infection, but there are no complaints, then the disease is not dangerous and the sexual partner can be calm about his health.
The presence of condylomas is also not a sign of an oncogenic virus. To obtain an accurate diagnosis, the doctor must take a sample for cancer cells and identify the HPV strain.
HPV in women
Since What is HPV in gynecology. Scientists have long proven that the presence of papillomavirus in a woman’s body is dangerous and can trigger the development of cervical cancer. According to numerous studies, in almost 100% of cases of cervical cancer detection, this virus is definitely detected.
Every fifth woman is a carrier of this disease. In most cases there are no symptoms. Most often, a woman begins to suspect the presence of the virus if growths appear on the skin and mucous membranes. However, growths on the external genitalia are not as dangerous as changes in the epithelium of the cervix.
To identify HPV in women, gynecology offers the following examination options:
- PCR diagnostics is one of the most accurate methods for detecting the disease; General examination by a gynecologist - the doctor can visually detect condylomas on the genitals; Cytology - a smear is taken from the cervix, which is carefully studied; Digene-test is one of the most popular diagnostic methods.
As soon as the diagnosis is made, it is necessary to begin treatment, which should be carried out jointly by a gynecologist and an immunologist.
When the HPV virus multiplies in women, gynecology without immunology is simply powerless, since this disease is a direct consequence of poor functioning of the immune system.
If there are condylomas, the doctor should suggest removing them with special preparations, for example radio wave “Surgitron”.
Against the background of papillomavirus, many women develop cervical erosion, which can be cauterized only after a course of antiviral drugs. After treatment, the woman should come for follow-up every three months so that the doctor can rule out recurrence of the disease.
HPV during pregnancy
Source: https://iklareol.ru/drugoe/kosvennye-priznaki-vpch-v-citologii-osnovnye-simptomy-u-zhenshhin-iu-muzhchin.html