A cough that lasts more than 2-3 weeks is considered persistent. It can be dry or wet, frequent or rare, but it always causes a lot of trouble and anxiety. A cough can interfere with sleeping, eating, and even breathing. If the cough does not go away for a long time, it is necessary to deal with the original source of the disease.
Causes
A cough of any kind is a symptom of the disease. A persistent cough may be due to a cold, serious infection, or other illness. The main causes of persistent cough:
A persistent cough in a child may indicate a number of diseases.
- ARVI;
- bacterial infection;
- allergic reaction;
- presence of helminths;
- severe runny nose and irritation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx;
- exposure to smoke or smog;
- foreign object in the respiratory tract;
- nervous shocks.
Most often, a cough is caused by the action of microbes or viruses and occurs due to infection of the respiratory system by pathogens. The cause of the cough may be worms; they cause a dry cough.
With heart pathology and the presence of diseases of the stomach or intestines, coughing occurs.
With adenoiditis and other inflammations of the nasopharynx, a cough appears, which worsens at night due to mucus flowing down the back wall of the nasopharynx and impaired nasal breathing.
If your child coughs constantly, this may indicate an allergy.
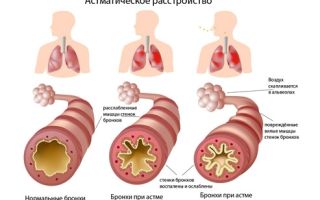
The causes of allergic cough vary from person to person. They depend on the type of allergen that causes an enhanced immune response in the child’s body. This cough occurs during bronchial asthma or hay fever.
A child may cough or cough frequently due to severe stress or emotional tension. A neurological cough occurs before important events in a child’s life, in a tense environment at home or in an educational institution, or after a strong fright.
A prolonged cough can bother you either every day or from time to time. To better understand its cause and determine subsequent treatment, it is necessary to pay attention to the accompanying symptoms.
Additional symptoms
A child who coughs constantly may have other symptoms associated with the illness. One of the important symptoms is the nature of the cough. A dry cough without fever can be caused by whooping cough or allergies. A wet cough is usually found with ARVI. Cough with fever occurs with bronchitis, flu, inflammation of the ENT organs, pneumonia and scarlet fever.
The cause of a wet cough can be determined by the color of the sputum.
A wet cough is considered productive and is characterized by coughing up sputum. Based on the color of the coughed up mucus, the doctor can make a more accurate diagnosis.
If the mucus has a green tint, this is a sign of pneumonia and sinusitis; yellow color indicates the presence of a purulent process. With tuberculosis, brown sputum appears.
Thick, whitish sputum is characteristic of ARVI; with allergies it is transparent.
The most dangerous is a paroxysmal cough with suffocation, especially in infants and preschoolers. This cough occurs when a foreign body enters the child’s respiratory tract.
The baby may choke on food during feeding or put a small toy into his mouth.
If parents are familiar with first aid techniques, they will be able to rid the child of a foreign object in the respiratory tract on their own; if not, then they must urgently call an ambulance.
A cough that occurs at night or in the morning and is accompanied by whistling and severe wheezing is also dangerous. It may be accompanied by high fever, shortness of breath, impaired consciousness, and respiratory arrest. Common additional cough symptoms include:
A runny nose is one of the most common accompanying symptoms
- runny nose and colds;
- wheezing in the lungs;
- intoxication and fever;
- inflammatory process.
Acute cough lasts up to three weeks. In the absence of proper treatment, it may be replaced by a lingering cough lasting 1-2 months. A chronic cough may not go away for a very long time, up to a year or more. It is usually a sign of serious illness.
Diagnostics
There is a physiological cough, which is a reflex aimed at removing phlegm, dust and foreign particles from the respiratory system. A healthy child can cough more than 15 times a day.
If the cough becomes constant, interferes with sleep, is accompanied by fever or vomiting, sore or sore throat, or if the child sneezes frequently, you must take the child to a pediatrician to diagnose the disease.
If you have a prolonged cough, the doctor must first rule out serious illnesses - whooping cough, laryngitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis. To diagnose the causes of cough, laboratory tests are prescribed:
To identify the causes of frequent coughing, a general blood test is taken from the child.
- general blood analysis;
- sputum analysis;
- allergy tests;
- stool examination for helminths.
A blood test shows the general condition of the child and the presence of inflammation in the body. Sputum is used to identify pathogenic flora that could cause the disease. An allergy test is carried out if there is a suspicion that the cough is allergic. It will help identify the allergen that is causing the problem.
Additional examination methods:
- radiography and fluorography;
- bronchography;
- fibrobronchoscopy;
- spirometry.
X-rays and fluorography help identify obstructive bronchitis, pneumonia, and tuberculosis. Bronchography is an X-ray examination of the bronchial tree using contrast. It is used if it is not possible to diagnose the disease using gentle methods, as well as if there is a suspicion of the presence of a foreign object in the respiratory organs.
The fiberoptic bronchoscopy method allows one to examine the mucous membranes of the patient’s trachea and bronchi under anesthesia. One of the indications for the procedure is a cough of unknown origin that lasts for over a month. Spirometry measures the patient's respiratory parameters, such as lung volume. The method is popular for bronchial asthma, obstructive pulmonary disease and allergies.
Treatment options
If any illness occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor. Depending on the cause of the disease, the doctor will prescribe medications that will help relieve the symptoms. There are two types of antitussives:
Different groups of medications are used to treat dry and wet cough in children
- drugs that prevent the cough reflex;
- drugs that thin sputum and accelerate its elimination.
Drugs from the first group are used to treat dry cough. The drugs are prescribed by a doctor when the cough becomes painful for the child, leading to vomiting and chest pain. After taking the medicine, the cough stops within 20-30 minutes.
A productive cough is treated with expectorants that help thin and remove mucus. For children, medications from both groups are available in the form of syrups and suspensions.
If the cough is caused by a bacterial infection, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. To choose the right medicine, the causative agent of the infection is determined using diagnostics. For allergies, antihistamines are prescribed and contact with the allergen is avoided.
To liquefy and remove mucus from the bronchi, inhalation is carried out with a nebulizer
Inhalations are also used to treat cough. The medicine in this procedure works directly in the respiratory tract, acting on the cause of the cough.
Inhalation reduces bronchospasm and helps thin mucus. Treatments can be done at home using steam or a nebulizer.
Steam inhalation is effective only for diseases of the upper respiratory tract and is contraindicated at elevated temperatures.
There are no such restrictions for a nebulizer. It generates an aerosol cloud of small particles, which allows the medicine to enter not only the upper but also the lower respiratory tract.
Inhalation with a nebulizer is allowed even for infants; it stops painful coughing well. For the procedure, either regular saline solution or special medications prescribed by a doctor can be used.
For effective treatment, inhalations should be repeated 2-3 times a day.
If you have a persistent cough, you can treat it with traditional medicine. Children brew herbs, such as chamomile and sage, and give them to drink several times a day. If a child coughs frequently, his throat may feel sore; in this case, warm milk with propolis or honey helps. Before using folk remedies, you must make sure that the child is not allergic to herbs and bee products.
Prevention
It is almost impossible to completely avoid childhood diseases, but if proper prevention is carried out, the child will get sick less. Ways to prevent persistent cough include:
Hardening is one of the most famous ways to strengthen children's immunity.
- hardening;
- humidification and air purification;
- proper nutrition;
- maintaining hygiene.
Prevention does not guarantee that the child will not cough at all, but the course of the disease will be easier. Children with chronic and recurrent respiratory diseases are recommended to visit a sanatorium and enjoy sea air.
If it is not possible to change the climate, then daily walks in the fresh air and a course of vitamins during the season of viral activity are mandatory. Prevention of allergic cough is also the absence of contact with allergens.
When dealing with cough prevention, you need to understand what the possible causes of its occurrence are. At the first symptoms of the disease, you should go to the hospital to immediately take control of the situation and prevent the development of a lingering or persistent cough.
Source: https://pulmohealth.com/bolezni/kashel/postoyannyj-kashel-u-rebenka/
Persistent cough in children and adults: medicine and treatment, causes
Coughing is a very useful reflex, which is necessary to clear the airways of harmful substances and foreign objects, as well as to warn of the presence of any disturbances in the patency of the airway. A persistent cough that does not go away over time can be a symptom of many serious diseases.
- Rare diseases accompanied by persistent cough
- Treatment options for adults
- Treatment in children
Possible causes of persistent cough
Chronic cough can be caused by completely different reasons. The most basic of them are:
- Smoking. Smokers, even those who do not have any diseases of the respiratory system, quite often have complaints of coughing. This is due to the fact that nicotine and tar irritate the receptors and thereby provoke coughing attacks.
- Colds. If a person’s immune system is weakened and the cold is not cured in time, the disease can affect the bronchi and cause an acute form of bronchitis, which is the cause of a prolonged cough.
- Chronic pharyngitis. With this disease, the cough is accompanied by a feeling of severe sore throat.
- Whooping cough and bronchial asthma. The persistent cough caused by these diseases most often occurs at night and does not stop until the morning.
- Allergic diseases. In this case, coughing attacks intensify with direct contact with allergens.
Rare diseases accompanied by persistent cough
In addition to the causes of this disease described above, there are other diseases. These include:
- connective tissue diseases of a systemic nature that affect the lungs (lupus erythematosus, scleroderma),
- pneumonia,
- tuberculosis,
- sarcoidosis,
- thyroid disease,
- heart failure,
- idiopathic cough,
- pathology in the nervous system (psychogenic cough),
- lung cancer (cough accompanied by hemoptysis).
There are cases when one patient has several diseases at once, the symptom of which is an incessant cough. This situation makes it very difficult to diagnose and choose appropriate treatment.
Types and diagnostic procedures
This symptom can manifest itself in many different ways. Sometimes coughing attacks can be systematic and cause quite severe pain. It also causes vomiting, insomnia and eye hemorrhages.
Chronic cough with sputum is a clear sign of infectious diseases of the respiratory tract. A persistent, hacking cough may indicate asthma, while a barking cough (which has a loud sound) indicates that there are viruses in the respiratory tract.
The process of treating persistent cough in both adults and children depends on the causes of this symptom. But the drugs that are prescribed to eliminate this problem differ quite greatly.
Establishing the true nature of a chronic cough is much more difficult than that of an acute one. But this must be done, since without the right reason it is impossible to formulate a competent and effective treatment.
If the cough is wet, then clinical examination of sputum is considered a very effective diagnostic method. She also needs to be examined for microflora and sensitivity to antibiotics.
How to treat?
After doctors have carried out all diagnostic procedures and studies and identified the nature of the disease, treatment can begin.
If the disease is caused by viruses, then antiviral drugs such as Arbidol or Acyclovir are prescribed.
Fungal diseases are treated with medications such as Thermikon and Nystatin, and for the treatment of diseases caused by bacteria, Summed, Zatrolide or Azithromycin are prescribed.
Treatment options for adults
In order to alleviate the patient's condition, doctors also prescribe mucolytic drugs such as Bromhexine or Lazolvan, as well as Mucaltin or ACC to improve expectoration. Thanks to these medications, the cough turns from unproductive to productive and, along with sputum, the causative agents of the disease are eliminated from the body.
Most often, patients are prescribed Loratadine, Suprastin or Zyrtec. When a patient has severe inflammation of the larynx, you can also use special sprays that have an analgesic, disinfectant and decongestant effect.
If the patient is at serious risk of laryngeal spasm or if the disease is advanced, the patient may be prescribed corticosteroids such as Dexamethasone, Betamethasone or Prednisolone.
Cough tablets can be an effective way to temporarily suppress this symptom. The most effective of them are Sinekod or Libexin. But these medications must be used with extreme caution.
Treatment in children
Most often, children suffer from a nonproductive cough much more severely than adults and experience more discomfort. When treating this symptom, doctors try to prescribe medications to young patients that are gentle on the body. Strong drugs are used only in the most serious cases.
If a child experiences pain during attacks, you can take Panadol for children suspension and Nurofen syrup to relieve them. It is very important to maintain the correct dosage.
Antibiotics should only be given to children if prescribed by a doctor. Typically, young patients are prescribed Sumamed or Cefodox, adapted for the child’s body.
If a child’s persistent cough requires treatment with antibiotics, then probiotics must be taken along with them.
They are necessary to restore the intestinal microflora. Effective probiotic preparations are Linex and Bifidumbacterin.
Also, to alleviate the child’s condition with a constant cough, parents should take some additional measures, namely:
- carry out wet cleaning of the house daily,
- do not use perfumes or any household products containing chlorine at home,
- ventilate the children's room at least twice a day,
- give the child to drink warm milk, fruit drinks and tea with honey,
- remove spicy dishes from the children's menu that can irritate the throat,
- be sure to consult a doctor.
Manifestations with sputum
If a chronic wet cough has replaced a dry one, then this can be called a positive sign, since the bronchi have begun to independently clear themselves of harmful substances. Pathogenic microorganisms leave the body along with sputum.
It is very important in this case to exclude antitussive drugs, as they suppress this useful reflex.
All other treatment should be continued according to the course that the doctor compiled for the treatment of dry cough.
With a constant wet cough, it is very important to clear the bronchi of the mucus that forms in them. For this you can use Ambroxol, Lazolvan or Pectusin.
Any type of chronic cough requires consultation with a doctor, as it can be caused by serious diseases that require proper treatment. If the process is not started, then you can get rid of the cough in a fairly short time, thereby preventing various complications.
Loading…
Source: https://prof-medstail.ru/bolezni-legkih/simptomy-i-lechenie/vse-o-postoyannom-kashle-prichiny-diagnostika-i-sposoby-lecheniya-u-detej-i-vzroslyh
A child has a constant cough: what causes it and how to treat it
In children, as in adults, there can be many reasons that cause coughing. This may be a reflex movement in response to the accumulation of sputum, which in children is more viscous, thick and often accumulates in the respiratory tract.
Most often, coughing occurs in the morning, when changing position. The appearance of such a symptom should not be ignored and consult a doctor without delay, as it may be a manifestation of dangerous diseases.
Infectious nature of coughing
- There are several common infectious diseases that cause cough.
- These include:
- ARVI;
- whooping cough;
- tuberculosis;
- helminthic infestation.
Of course, these are just the main reasons.
The full list will be much broader.
ARVI
Cough in this case usually appears later than other symptoms. Occurs against a background of increased body temperature, chills and runny nose.
Its character may be different.
Initially, a dry cough most often appears, paroxysmal, hacking, and does not bring relief. Later it can turn into wet, sputum separation is noted, and the child feels relief.
Whooping cough
This is an infectious disease that manifests itself as a hacking cough that does not bring relief. It has a paroxysmal nature and occurs mainly in the morning or night hours.
There may be a thick mucous discharge from the nose. During an attack, lacrimation and chest pain also appear. Symptoms often occur in increasing increments, then gradually decreasing. The cough has a bubbling character, is usually quite characteristic and is diagnosed in the early stages.
Tuberculosis
This is also one of the reasons for prolonged coughing in children. It can occur in a child of any age. The character changes depending on the form.
Worm infestation
Coughing during helminthic infestation is due to the fact that one of the stages of parasite development affects the lungs. In this case, there is a periodic cough in the child, without separation of obvious sputum and expectoration of noticeable particles. It usually goes away on its own.
Non-infectious factors
They can be no less dangerous in comparison with the previous ones. Therefore, the main reasons should be highlighted:
- enlarged adenoids;
- enlarged cervical lymph nodes;
- allergy;
- heart and vascular defects;
- GERD;
- reflex cough.
Enlarged adenoids
The child experiences constant discomfort and reflexively tries to cope with it by coughing. Usually the cough is not annoying. Occurs periodically. The child is breathing heavily, which is due to a mechanical obstruction; frequent nasal breathing is almost always absent. Sleep is disturbed.
Enlarged cervical lymph nodes
The child experiences constant discomfort, which he tries to relieve with coughing shocks. There is no coughing.
Allergy
One of the reasons for coughing in a child may be an allergic reaction to some irritant. Subsequently, the allergy can lead to the development of bronchial asthma.
Often a cough occurs suddenly, against the background of absolute health. The cough may be paroxysmal in nature. Usually a dry cough, rarely with a small amount of sputum.
It has a viscous consistency, transparent color, rarely with cloudy white veins. It becomes easier after the end of contact with the allergen, as well as when taking medications.
Defects of the cardiovascular system
Heart or vascular defects that lead to decompensation and the development of organ failure. A child's cough is usually caused by stagnation of phlegm, the leakage of plasma through the lung tissue.
The pose is almost always forced. The child sits leaning forward, leaning on his hands. The cough is wet and does not bring relief. The sputum is light in color and scanty. Sometimes, in severe somatic conditions, pneumonia occurs. The complexion is bluish, which is associated with hypoxia.
GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease can also cause coughing. Bitterness and soreness in the throat appear, which is associated with the reflux of gastric contents. The character is episodic. Occurs more often after sleep.
This cough can occur in children prone to anxiety and stress. Coughing often occurs after nervous strain. The cough does not bring relief without sputum production. In a calm state it almost does not occur. This coughing in children is a kind of protective reaction of the body in response to stress.
One of the most dangerous causes of coughing is a foreign body in the respiratory tract. This cough is usually paroxysmal and goes away quickly when the object is removed. Accompanied by lacrimation.
Treatment
- Therapy involves the use of certain groups of drugs.
- Namely:
- Antibacterial, antiviral, antiparasitic.
- Expectorants, mucolytics, mucus thinners.
- Antihistamines.
- Vasoconstrictors.
- Glucocorticoids.
At the first signs of cough, you should contact a specialist for qualified help.
In case of coughing associated with acute respiratory viral infections or acute respiratory infections, pathogenetic therapy is used. Antiviral or antibacterial agents of complex action are used, as well as local drugs that prevent profuse rhinorrhea.
Currently, saline solutions are widely used to rinse the nose and mouth. Warming up the nasal area will be effective. Antipyretics or expectorants may be used separately, depending on the prevailing symptoms.
Treatment of whooping cough is usually carried out on an outpatient basis, only in some cases hospitalization in the infectious diseases department is required. When diagnosing whooping cough, it is necessary to isolate the child to prevent possible infection of other people. The main means of treating whooping cough are antibiotics: macrolides, aminoglycosides, ampicillins and chloramphenicol.
The average course of treatment is 7-10 days. Symptomatic therapy (antihistamines, sedatives) is also used. Drugs with mucolytic and expectorant effects are ineffective.
At the first suspicion of tuberculosis, you should consult a phthisiatrician. Children are very susceptible to this pathology. Treatment, depending on the form, can be carried out either on an outpatient basis or in a hospital. But due to the high toxicity of the drugs, preference is given to treating children in specialized hospitals. Macrolides and rifampicin are used.
Anthelmintic treatment usually does not cause any problems. Specialized means are used, selected for a specific type of pathogen. There are age restrictions for the use of drugs. Many of them are contraindicated for use in young children. This is due to a high toxic effect on the liver.
The problem of treating enlarged adenoids is still quite painful. There are no precisely formed tactics. Many doctors adhere to a wait-and-see approach, some insist on surgery.
When using medication, preference is given to vasoconstrictors, antihistamines and systemic anti-inflammatory drugs. Homeopathic remedies and physiotherapeutic procedures are effective.
Treatment of allergies and bronchial asthma is extremely important, since without treatment the disease causes serious complications. Therapy is selected taking into account the prevailing symptoms, the patient’s age, and the degree of development of the disease. The basis of treatment is antihistamines.
If more severe symptoms develop or the selected therapy is ineffective, the use of systemic or local bronchodilators is required. In severe cases, they resort to the use of systemic hormonal agents of the glucocorticoid group. It is necessary to eliminate contact with the allergen.
Treatment of coughing in cardiovascular pathology comes down to correcting the functioning of the heart. Most often there is a need for surgical treatment. Medicines most often belong to the diuretic group. Preference is given to potassium-sparing diuretics.
The main direction in the treatment of cough with GERD is to reduce the acidity of gastric contents. It is necessary to carefully monitor nutrition, prevent overeating, and do not put the child to bed immediately after dinner. Antacids, histamine receptor blockers, and proton pump inhibitors are effective.
Folk remedies
Breastfeeding is often used to treat children. These are mixtures of herbs that are specially selected in the required proportions. They are easy to use: you need to take the amount of herb required by the recipe, pour boiling water, let it brew and drink in small portions throughout the day.
Licorice and coltsfoot have an excellent effect. It is necessary to ensure that the dosage is not exceeded.
Before using any folk remedy, you should consult a specialist.
Source: https://DeteyLechenie.ru/organy-dyhaniya/kashel-u-rebenka-postoyannyj.html
Symptoms and treatment of persistent cough
Many diseases can be accompanied by coughing. Often a cough can be dealt with quickly, literally in 4-6 days. In this case, the cough is called acute. As a rule, with an acute dry cough, a diagnosis is made quickly, a specific treatment is prescribed, and it goes away without leaving any traces behind. Dry thumping turns into coughing, sputum is removed from the bronchi and recovery occurs. However, if the cough is constant and lasts for several months, then it is called persistent or chronic.
Is coughing possible with whooping cough in adults and children?
What are the causes of persistent cough
In fact, there are many reasons that cause constant coughing. It is necessary to consider the most common ones.
The first reason that doctors identify may be “postnasal drip syndrome.” This is when nasal secretions flow down the back wall of the nasopharynx into the trachea and bronchi and irritate the sensitive receptors.
A common cold can also be the cause of a persistent cough. Since the body and immunity are weakened during illness, the infection can easily spread to the lower respiratory tract and cause bronchitis or another disease.
In this case, if the patient does not see a doctor or the treatment is incorrect, the acute form of bronchitis can become chronic. Chronic bronchitis can either be dry or occur without any symptoms.
The danger of the disease lies in the fact that due to chronic bronchitis with a constant dry cough, the appearance of pneumonia, lung abscess, and bronchial asthma cannot be ruled out.
A persistent cough may be a symptom of pharyngitis. With this disease, cough appears due to frequent soreness or tingling in the throat. Only an ENT specialist can make such a diagnosis, and this disease is treated in an inpatient clinic.
A constant cough that causes pain, fever, chest pain - all these are signs of a disease such as pleurisy. This disease is very dangerous. Also, a constant dry cough may be the only symptom of a tumor in the middle chest.
Also, chronic cough is the main symptom of tuberculosis. In addition to cough, this disease also has the following symptoms:
- elevated temperature;
- sudden weight loss;
- chills or excessive sweating.
If a person experiences these symptoms, they should definitely contact a phthisiatrician. Ignoring such symptoms for a long time can lead to death.
The most well-known causes of persistent cough lie in incorrect treatment and incorrect diagnosis. Often the first follows from the second, because patients prefer to make their own diagnosis and self-medicate. As you know, if a cough is not treated correctly, then this is the first step to bronchitis.
A persistent cough is a very dangerous sign of the presence of some disease. You cannot self-medicate or use folk remedies; this can seriously harm your health.
What to do if a cough does not go away for a month and how to treat it
Diagnosis of chronic cough
To identify the true causes of a lingering cough, you should undergo a lot of tests and examinations. If a doctor has difficulty making a diagnosis, he prescribes a number of diagnostic tests for the patient, including the main ones:
- Blood and sputum tests.
- Fluorography or x-ray.
- Spirography.
- Tussography, etc.
X-rays can reveal the true causes of a cough, such as:
- Tumor in the chest.
- Blackouts.
- Mesh rearrangement.
Doctors also resort to spirography and spirometry to establish the correct diagnosis if test results and fluorography are insufficient. Such diagnostic methods make it possible to recognize the disease in its early stages; with their help, it is possible to recognize functional disorders in those that are clinically expressed, as well as those that progress.
In special hospitals that treat and diagnose diseases accompanied by chronic cough, tousography is used as a modern examination method. Based on the data provided by tussography, we can draw conclusions about the frequency, strength of cough, its nature and periodicity.
To determine the causes of persistent boozing, doctors also use more common diagnostic methods such as bronchoscopy and bronchography.
Bronchoscopes are a special device that has a small video camera at the end that transmits an image to a screen. Using this device, you can not only make an accurate diagnosis, but also perform a lung biopsy.
Treating a persistent cough
When starting to discuss the issue of treating a persistent cough, it is necessary to immediately emphasize that symptoms such as fever, weight loss, and profuse sweating are signs of a serious illness. It is necessary to urgently contact a specialist, since the disease can pose a threat not only to your life, but also to the lives of others.
The first step in treating a disease is to identify the causative agent that irritates the receptors. They can be microorganisms that are fungal, viral or bacterial in nature. Once the pathogen is identified, special treatment is prescribed depending on its origin. Antifungal, antibacterial or antiviral drugs are prescribed.
Doctors prescribe medications that eliminate the root causes of cough, and also prescribe mucolytics and expectorants. Mucolytics promote active discharge of sputum, and the second drug removes it from the bronchi and respiratory tract.
If the cause of a persistent dry cough is an allergic reaction, the first step is to eliminate the allergen, and antihistamines are also prescribed.
When a cough accompanies severe inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, it would be advisable to prescribe special topical sprays. Such remedies relieve sore throat, disinfect and relieve swelling of the larynx and throat.
A persistent, acute cough can be effectively suppressed by antitussive medications. They are especially relevant for whooping cough or uncontrollable coughing attacks. However, they should be used with great caution. If the sputum begins to leave, then the use must be stopped immediately, since blocking the sputum waste can provoke serious infectious diseases in the lungs.
It is very important, if you have a persistent cough, to consult a specialist for diagnosis and receive quality treatment. When the doctor makes the correct diagnosis, determines the nature of the cough and its features, the treatment regimen will be prescribed correctly, and the patient will be able to get rid of the annoying symptom.
Source: https://KashelSovet.ru/vidy/simptomy-i-lechenie-postoyannogo-kashlya.html
What to do if your child’s cough won’t stop
Coughing in children may signal the onset of a serious illness or be a normal physiological response to an irritant. It is important to recognize the symptoms that appear early and understand the source of this phenomenon.
A constant cough in a child should alert parents, as it sometimes occurs against the background of severe pathologies. If the doctor reassures that there is no problem, then the child’s body will quickly cope with the obstacle without additional measures.
Why does a child cough?
The causes of cough in children are different: viral infections, foreign body entry, allergies, mucus accumulated in the throat after a night's rest. A dry cough often indicates the initial stage of ARVI. After 2-3 days, the cough becomes wet and sputum begins to be discharged.
But symptoms can also be caused by dangerous conditions, such as bronchial asthma or pulmonary obstruction. If a child constantly coughs, you should definitely consult a doctor who will help you figure out whether this condition is normal or whether the little patient is in serious danger.
Physiological reasons
Constant coughing in a child, caused by natural processes in the body, manifests itself without signs of a cold. It is caused by the following reasons:
- the flow of mucus down the back wall of the throat from the nasal cavity, when the patient cannot, due to age, or does not want (he is in class during lessons, for example) to blow his nose;
- foreign body entering the throat (usually a food particle);
- being in an area where gas, smoke, harmful chemicals are distributed - they penetrate the respiratory tract through the air;
- sore nose (pollen, pepper, poplar fluff).
After eliminating the obstacle, the cough stops, and the baby immediately feels better. There are no painful attacks, no shortness of breath, no fever. After the threat has passed, the body no longer needs protection to protect against a possible threat to life.
Allergic bronchitis
An allergic cough is a manifestation of individual intolerance to a certain substance. Irritation of the cough center can lead to constant coughing, in which watery and transparent discharge appears from the nasal cavity, and tearing is noted. The eyes turn red, the nose itches - and this is just the beginning.
If allergens are not eliminated, the patient's condition continues to worsen. Adults should know what substance the child is allergic to, and a physician will help them with this. He will determine the irritant through special tests and prescribe antihistamines that eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
Inflammation of the respiratory system
Against the background of lung diseases, a constant cough appears, which may be accompanied by difficulty breathing. Very dangerous symptoms are the appearance of blood or pus in the sputum, hissing and wheezing, fever, shortness of breath.
If it is a viral infection, then complete recovery occurs in 1-2 weeks, but with complications, the cough may not stop for up to 3 months or more.
It is necessary to accurately establish the causes of cough in children in order to differentiate the symptoms.
Possible inflammatory diseases:
- diseases of the bronchial tree - bronchitis, obstructive pulmonary disease, bronchial asthma, pneumonia;
- chronic diseases of viral etiology - lung tissue is affected by herpetic, retroviral, adenoviral infections;
- upper respiratory tract diseases – sinusitis, streptococcal tonsillitis, pharyngitis.
With ARVI, the patient suffers from attacks of dry cough in the first few days. After 2-3 days, exudate forms in the lungs, and coughing speeds up the healing process. In this way, the body cleanses the lungs of sputum, which contains a huge amount of non-viable pathogens and leukocytes.
A sore throat after an acute respiratory viral infection with a wet cough goes away in about 1 week. This is provided that the treatment was organized correctly and the parents strictly followed the doctor’s recommendations. Otherwise, the infectious agents remain in the body and, when the immune system is weakened, appear with renewed vigor.
Nervous cough
In children with an unstable psyche, whose life is full of stress, constant coughing manifests itself as a defensive reaction against a background of fear and anxiety. A child coughs when he tries to “disguise” the feeling of a trick, the fear of physical pain, or distrust of people.
It’s as if he creates a curtain that prevents a stranger from penetrating his soul, recognizing his weaknesses, feeling his cowardice. On the other hand, this gives him the opportunity to postpone the terrible moment, retreat and “hide” for a while.
Young children do not yet realize all this, but if they are constantly punished, then, like older children, they “hide” behind a cough from their fears.
Gastrointestinal diseases
A child may cough due to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract:
- gastritis;
- reflux esophagitis.
The muscle that closes the esophagus near the stomach (sphincter) prevents the contents of the stomach sac from flowing back into the esophagus.
If this happens (the stomach is full, the sphincter is weakened, gas formation begins), the food bolus along with hydrochloric acid is thrown out in portions into the esophagus, causing a strong burning sensation.
Heartburn can last for a few minutes or for hours. If the acid reaches the throat, a tickling sensation appears, and then coughing begins.
Heart problems
A periodic cough in a child may occur against the background of heart disease. When the heart malfunctions, the ventricles do not function properly. The right one fills the lungs with blood, but the left one pumps it out poorly.
The lung tissue swells - oxygen starvation begins. Against the background of hypoxia, the child feels a lack of air. He coughs to clear the obstacle. These attempts lead to nothing.
If parents do not realize it in time and consult a doctor, something irreparable can happen.
Other reasons
As when a foreign body enters the respiratory tract, a child coughs continuously with measles and whooping cough. If you have not been vaccinated against these diseases, a person can become infected with a serious illness at any time.
In the case when parents notice a cough in a child that does not stop for several days and appears more than 10-15 times a day, it is necessary to take a close look at the baby.
Infections are accompanied by skin rashes, fever, and difficulty swallowing. The diseases are insidious because at the initial stage they are disguised as ARVI, and they are difficult to recognize. At the final stage, if not treated in a timely manner, these infections can lead to disability and even death.
Diagnostics
At the first appointment, the doctor will carefully examine the child and listen to the chest with a stethoscope. To accurately establish the causes of a child’s persistent cough, additional types of examination are prescribed:
- examination of nasopharyngeal cultures;
- tuberculin test;
- blood analysis;
- radiography, CT, MRI.
The work of a specialist is complicated by the fact that coughing is possible due to various diseases. The procedures sometimes take several days, and the pathology continues to worsen during this time.
What to do if your child is constantly coughing
Cough treatment is carried out in a complex, so several procedures are carried out on one day. If a child begins to cough, he is prescribed medications for oral administration and external rubbing or compresses.
Drug therapy
To remove a dry cough during a cold and turn it into a wet one, the doctor prescribes expectorants:
- Bronchicum;
- Codelac Broncho.
Bronchicum reduces the viscosity of sputum and accelerates the process of its elimination. Doctors prescribe lozenges or syrup depending on age. Children under 2 years of age are prescribed 0.5 tsp. syrup three times a day, up to 12 years - 1 tsp. 2-3 times during the day. Lozenges are taken in the age period of 6-12 years, 1 piece 3 times a day, from 12 years old you can give 2 lozenges 3 times a day.
Codelac Broncho, in addition to chemical components, contains natural herbal extracts: thyme, licorice root. The drug is effective for a prolonged cough in a child. It speeds up recovery and promotes rapid removal of sputum. Has antibacterial and antiviral effects. For children, the release form used is syrup. It is given to children starting from 2 years old, 100 ml 3 times a day.
A dry cough can be treated with antitussive medications (Sinekod, Codelac), but only as prescribed by a doctor. Self-administration of these drugs, especially by young patients, is prohibited.
Inhalations
Inhalations are used to moisturize the mucous membranes and relieve a sore throat. Children really do not like such procedures, but even a few minutes of such treatment are enough to stop continuous coughing. Solutions and decoctions are used for inhalation:
- water with soda;
- aqueous infusions of expectorant and anti-inflammatory herbs;
- mineral water.
Solutions can be prepared on the basis of medications containing natural ingredients (for example, Doctor Mom), but these points must be discussed with your doctor.
Folk remedies
Not all traditional methods of treatment are readily tolerated by children. But there are effective recipes that do not cause rejection in the child.
Before using home remedies, you should consult your pediatrician. Then the child is likely to tolerate such treatment well.
For example:
- Wash the black radish, cut a hole in it and pour a little honey into the “bowl”. After a few minutes, juice will appear in the cavity. Together with honey, it forms a medicinal and very tasty syrup. Children drink it with great pleasure.
- Foot baths are no less effective. You need to pour water into the basin (halfway) and stir 1 tbsp in it. dry mustard. As the water cools, it should be added from a kettle with a spout. 10-15 minutes is enough. Then wipe your feet dry and put on warm socks.
Among the traditional methods of treatment, you need to choose those that involve taking the medicine internally, and external methods, such as warming compresses, applications, and rubbing. These are only auxiliary methods, and parental decisions must be approved by a specialist.
Other methods
If the child is healthy in all respects, and doctors suspect he has a nervous cough, then it is necessary to find out what is the source of negative emotions.
A psychologist is involved in the work, clarifying the cause of the pathology and using special exercises to liberate the child and reduce his level of anxiety and fear.
Drugs are prescribed that improve the functioning of the central nervous system. In some cases, antidepressants may be required.
Why is a prolonged cough dangerous?
A huge number of diseases that are accompanied by cough are diagnosed every day. The condition is dangerous because adults who think that a child is developing an acute respiratory viral infection ignore contacting a doctor. But such confidence can lead to dire consequences. If your child begins to cough, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Source: https://kashelproch.ru/rebenok/postoyannyy-kashel